In Vitro Study of the Toxicity Mechanisms of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) and Released Iron Ions Using Earthworm Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles (nZVI NPs)
2.2. Characterization of nZVI and Quantification of Soluble Iron Species
2.3. Earthworms and Coelomocytes Extrusion
2.4. Quantification of Reactive Oxygen Species and Lipid Peroxidation
2.5. Phagocytosis
2.6. Viability, Apoptosis, and Necrosis Analyses
2.7. Flow Cytometry
3. Results and Discussion
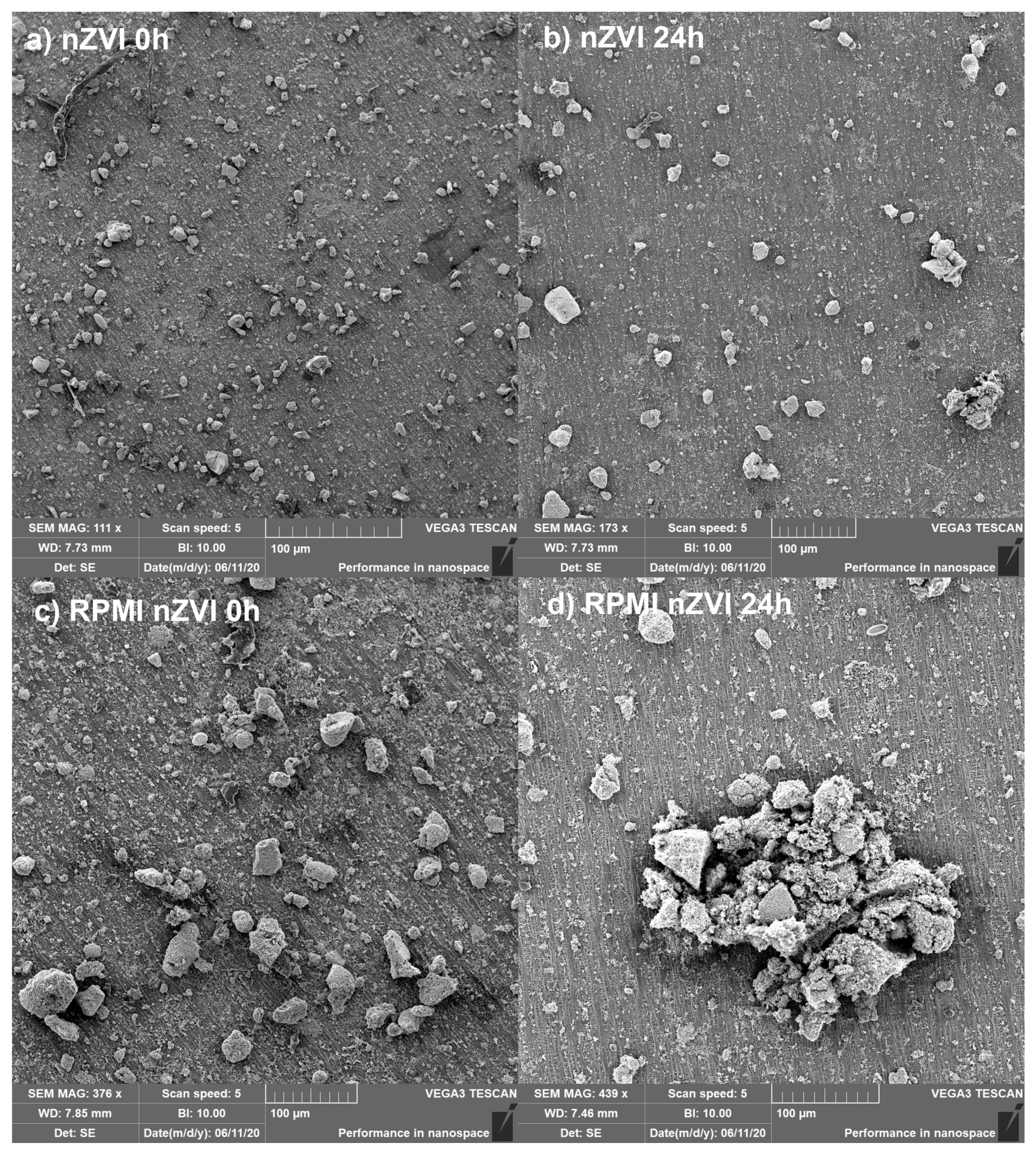
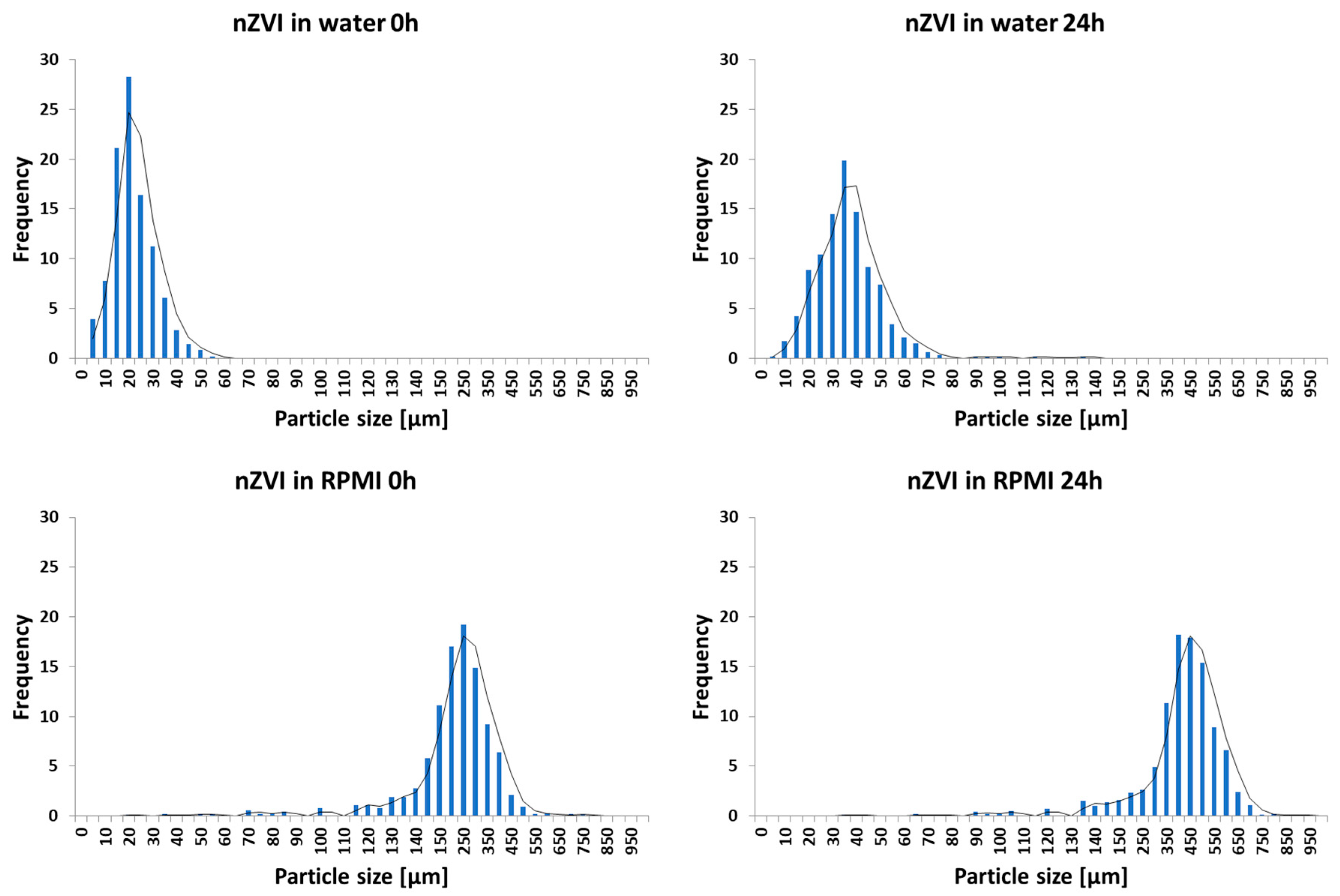
3.1. Particle Aggregation and Iron Release
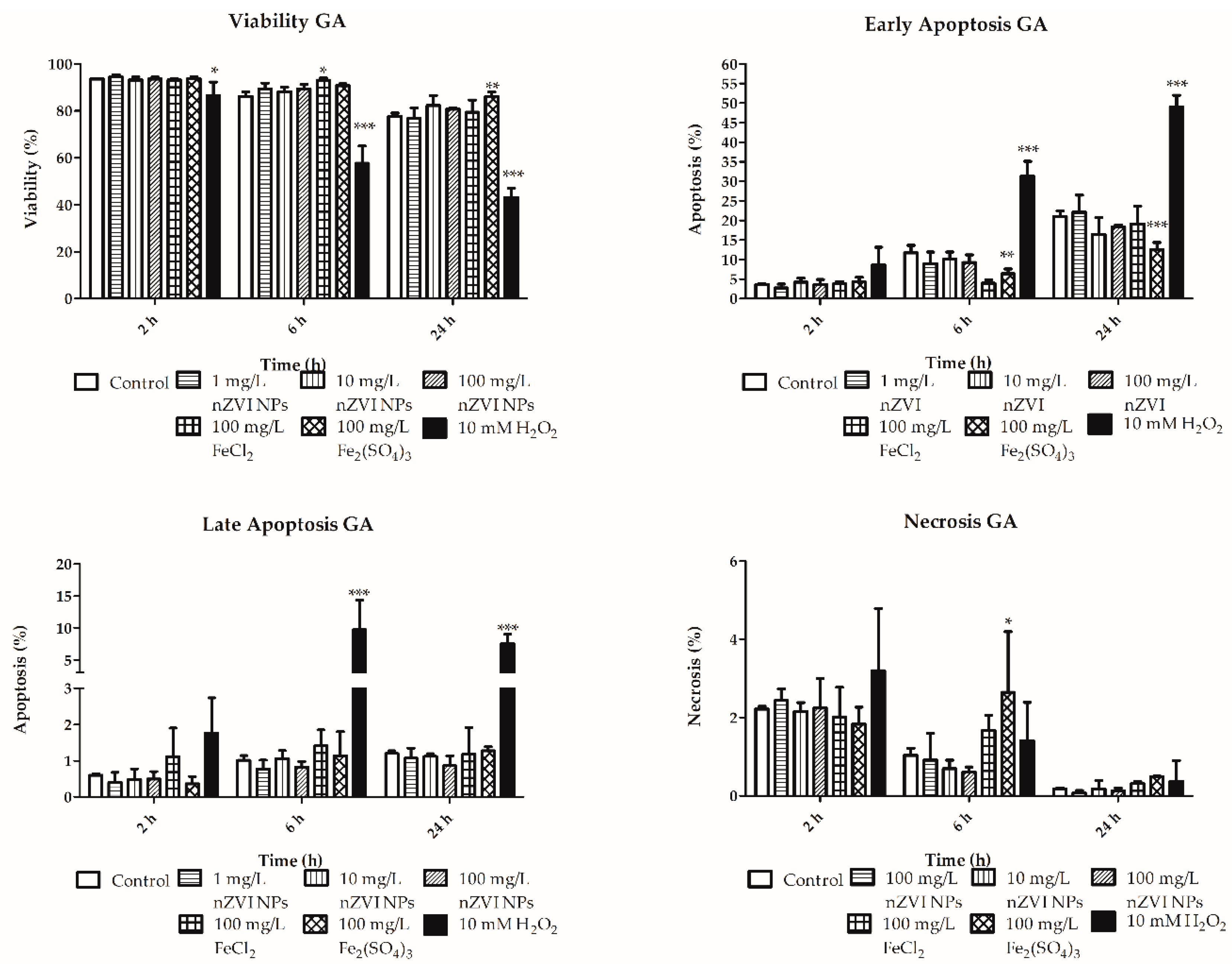
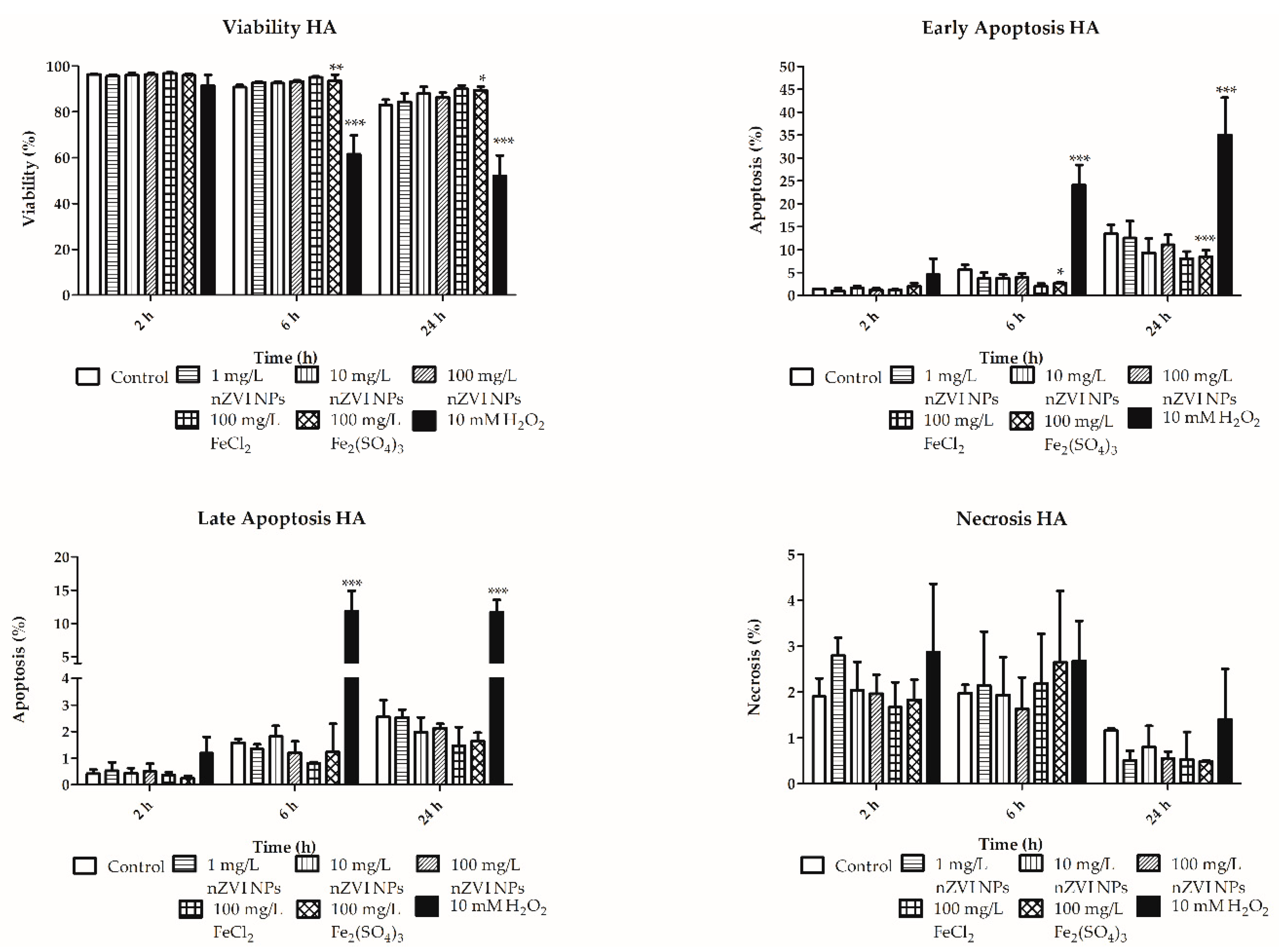
3.2. Viability, Apoptosis, and Necrosis
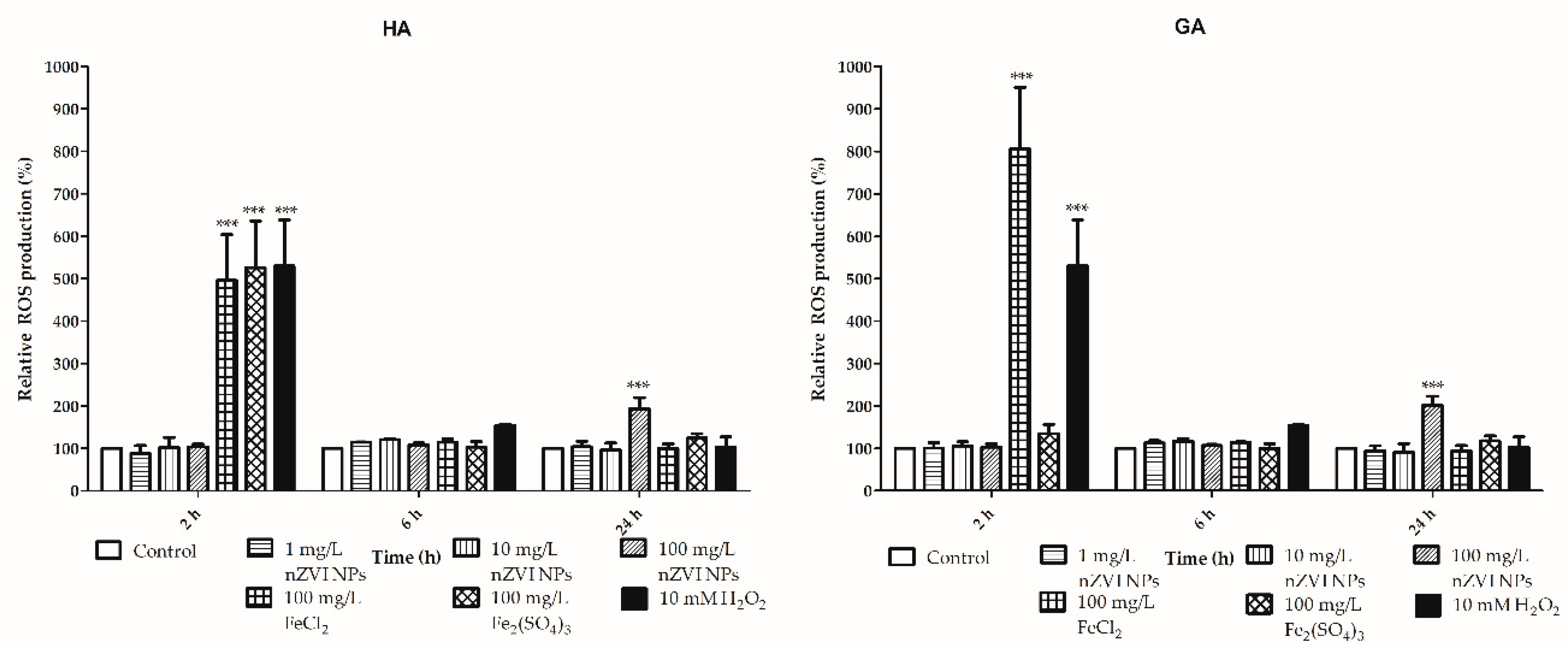
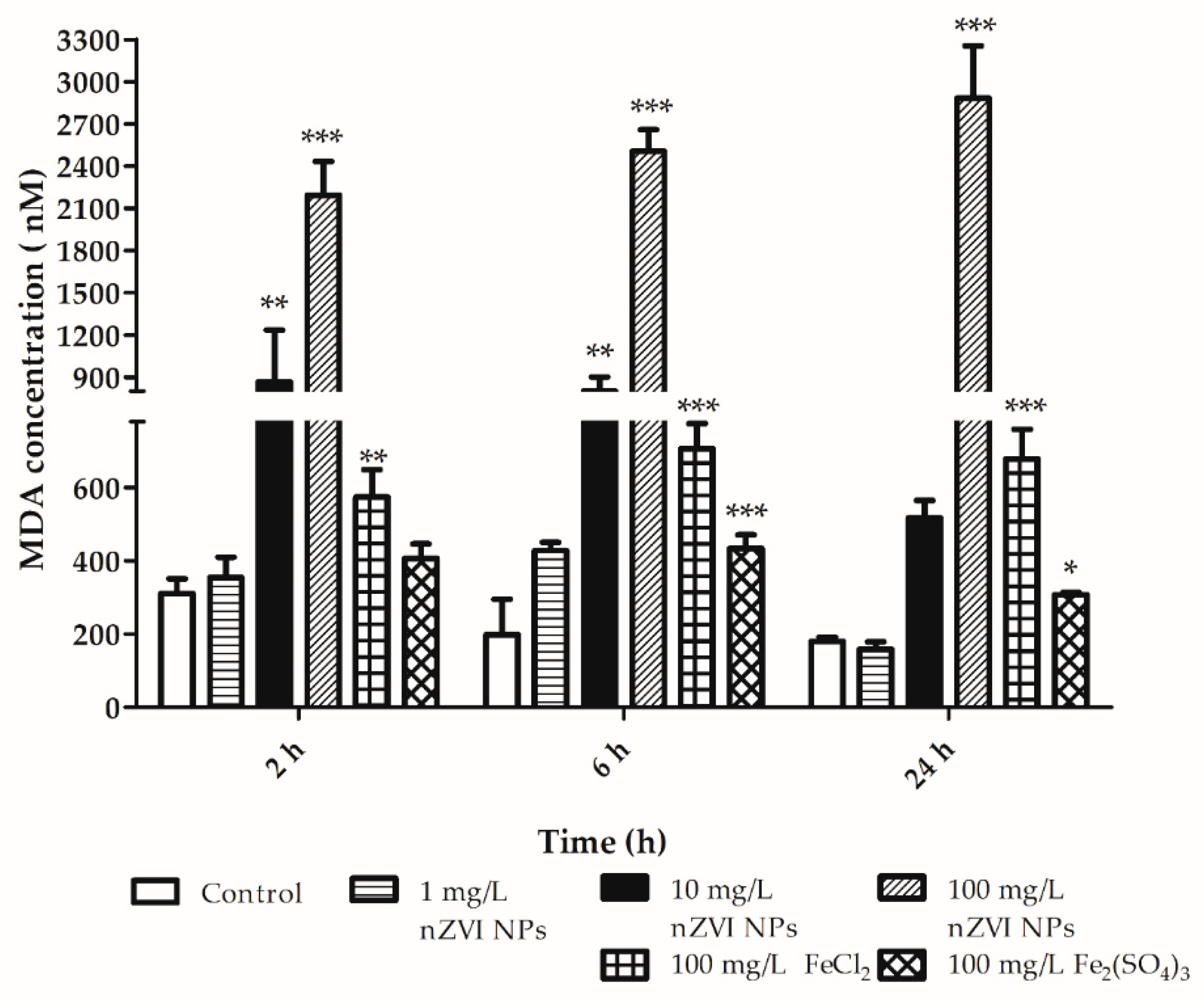
3.3. Sublethal Effects: Reactive Oxygen Species, Lipid Peroxidation, and Phagocytosis
3.4. The Effect of Dissolved Iron Species on Toxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mueller, N.C.; Braun, J.; Bruns, J.; Cernik, M.; Rissing, P.; Rickerby, D.; Nowack, B. Application of nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) for groundwater remediation in Europe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M. Synthesis and application of zero-valent iron nanoparticles in water treatment, environmental remediation, catalysis, and their biological effects. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerad, J.; Cajthaml, T. Ecotoxicity and environmental safety related to nano-scale zerovalent iron remediation applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9809–9819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocur, C.M.; Chowdhury, A.I.; Sakulchaicharoen, N.; Boparai, H.K.; Weber, K.P.; Sharma, P.; Krol, M.M.; Austrins, L.; Peace, C.; Sleep, B.E.; et al. Characterization of nZVI mobility in a field scale test. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2862–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.L.; Nurmi, J.T.; O’Brien Johnson, G.S.; Fan, D.; O’Brien Johnson, R.L.; Shi, Z.; Salter-Blanc, A.J.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Lowry, G.V. Field-Scale Transport and Transformation of Carboxymethylcellulose-Stabilized Nano Zero-Valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.-H.; Lim, M.; Hwang, Y.S. Potential environmental implications of nanoscale zero-valent iron particles for environmental remediation. Environ. Health Toxicol. 2014, 29, e2014022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, E.; Bossa, N.; Wiesner, M.R.; Gunsch, C.K. A review of the environmental implications of in situ remediation by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevcu, A.; El-Temsah, Y.S.; Filip, J.; Joner, E.J.; Bobcikova, K.; Cernik, M. Zero-valent iron particles for PCB degradation and an evaluation of their effects on bacteria, plants, and soil organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21191–21202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Temsah, Y.S.; Sevcu, A.; Bobcikova, K.; Cernik, M.; Joner, E.J. DDT degradation efficiency and ecotoxicological effects of two types of nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) in water and soil. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Temsah, Y.S.; Joner, E.J. Ecotoxicological effects on earthworms of fresh and aged nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) in soil. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xia, X.Q.; Zhang, W.; Zaman, W.Q.; Lin, K.F.; Hu, S.Q.; Lin, Z.F. The biochemical and toxicological responses of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) following exposure to nanoscale zerovalent iron in a soil system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Xia, X.Q.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, K.F.; Zhou, B.S.; Hu, S.Q. The reproductive responses of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in the presence of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.; Pangging, M.; Jang, M.H.; Hwang, Y.S.; Chang, Y.S. Impact of surface modification on the toxicity of zerovalent iron nanoparticles in aquatic and terrestrial organisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yirsaw, B.D.; Mayilswami, S.; Megharaj, M.; Chen, Z.L.; Naidu, R. Effect of zero valent iron nanoparticles to Eisenia fetida in three soil types. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9822–9831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevcu, A.; El-Temsah, Y.S.; Joner, E.J.; Cernik, M. Oxidative Stress Induced in Microorganisms by Zero-valent Iron Nanoparticles. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerad, J.; Cvancarova, M.; Filip, J.; Kaslik, J.; Zlota, J.; Soukupova, J.; Cajthaml, T. Novel assay for the toxicity evaluation of nanoscale zero-valent iron and derived nanomaterials based on lipid peroxidation in bacterial species. Chemosphere 2018, 213, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerad, J.; Moeder, M.; Filip, J.; Pivokonsky, M.; Filipova, A.; Cajthaml, T. Oxidative stress in microbes after exposure to iron nanoparticles: Analysis of aldehydes as oxidative damage products of lipids and proteins. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33670–33682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manerikar, R.S.; Apte, A.A.; Ghole, V.S. In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity assessment of Cr(VI) using comet assay in earthworm coelomocytes. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 25, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Engelmann, P. Earthworm’s immunity in the nanomaterial world: New room, future challenges. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2013, 10, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Muangphra, P.; Kwankua, W.; Gooneratne, R. Genotoxic effects of glyphosate or paraquat on earthworm coelomocytes. Environ. Toxicol. 2014, 29, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, K.E.; Thompson, H.M.; Tarrant, K.A. Effects of agrochemicals on the immune systems of earthworms. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 57, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, M.; Ji, F.; Hu, C.; Cui, Y. Evaluation of Complex Toxicity of Canbon Nanotubes and Sodium Pentachlorophenol Based on Earthworm Coelomocytes Test. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Engelmann, P.; Foldbjerg, R.; Szabo, M.; Somogyi, I.; Pollak, E.; Molnar, L.; Autrup, H.; Sutherland, D.S.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.; et al. Earthworms and Humans In Vitro: Characterizing Evolutionarily Conserved Stress and Immune Responses to Silver Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4166–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigorgne, E.; Foucaud, L.; Caillet, C.; Giamberini, L.; Nahmani, J.; Thomas, F.; Rodius, F. Cellular and molecular responses of E. fetida coelomocytes exposed to TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Cajthaml, T.; Semerad, J.; Filipova, A.; Klementova, M.; Skala, R.; Vitkova, M.; Michalkova, Z.; Teodoro, M.; Wu, Z.; et al. Nano zero-valent iron aging interacts with the soil microbial community: A microcosm study. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1189–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangayayam, M.C.; Alonso-de-Linaje, V.; Dideriksen, K.; Tobler, D.J. Effects of common groundwater ions on the transformation and reactivity of sulfidized nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerad, J.; Filip, J.; Sevcu, A.; Brumovsky, M.; Nguyen, N.H.A.; Miksicek, J.; Lederer, T.; Filipova, A.; Bohackova, J.; Cajthaml, T. Environmental fate of sulfidated nZVI particles: The interplay of nanoparticle corrosion and toxicity during aging. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 1794–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaslik, J.; Kolarik, J.; Filip, J.; Medrik, I.; Tomanec, O.; Petr, M.; Malina, O.; Zboril, R.; Tratnyek, P.G. Nanoarchitecture of advanced core-shell zero-valent iron particles with controlled reactivity for contaminant removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Miclaus, T.; Scavenius, C.; Kwiatkowska, K.; Sobota, A.; Engelmann, P.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.J.; Enghild, J.J.; Sutherland, D.S. Species Differences Take Shape at Nanoparticles: Protein Corona Made of the Native Repertoire Assists Cellular Interaction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14367–14375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; Garner, K.; Miller, R.J.; Lenihan, H.S. Toxicity of Nano-Zero Valent Iron to Freshwater and Marine Organisms. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocur, C.M.; O’Carroll, D.M.; Sleep, B.E. Impact of nZVI stability on mobility in porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 145, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Carroll, D.; Sleep, B.; Krol, M.; Boparai, H.; Kocur, C. Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidic, J.; Haque, F.; Guigner, J.M.; Vidy, A.; Chevalier, C.; Stankic, S. Effects of Water and Cell Culture Media on the Physicochemical Properties of ZnMgO Nanoparticles and Their Toxicity toward Mammalian Cells. Langmuir 2014, 30, 11366–11374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskokovic, V.; Huynh, E.; Wu, V.M. Mimicking the transit of nanoparticles through the body: When the path determines properties at the destination. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, A.; Berger, T.; Feinle, A.; Husing, N.; Himly, M.; Duschl, A.; Diwald, O. Bovine Serum Albumin Adsorption on TiO2 Colloids: The Effect of Particle Agglomeration and Surface Composition. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2551–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, J.T.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Sarathy, V.; Baer, D.R.; Amonette, J.E.; Pecher, K.; Wang, C.M.; Linehan, J.C.; Matson, D.W.; Penn, R.L.; et al. Characterization and properties of metallic iron nanoparticles: Spectroscopy, electrochemistry, and kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Ma, J.X.; Collins, R.N.; Waite, T.D. Effect of structural transformation of nanoparticulate zero-valent iron on generation of reactive oxygen species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3820–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, A.; Chan, W.C.W. Effect of Gold Nanoparticle Aggregation on Cell Uptake and Toxicity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5478–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumiti, A.; Thorley, A.J.; Arostegui, I.; Reip, P.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Tetley, T.D.; Cajaraville, M.P. Cytotoxicity and cellular mechanisms of toxicity of CuO NPs in mussel cells in vitro and comparative sensitivity with human cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 48, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, L.L.; Si, Y.B.; Shu, K.H. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles to Azotobacter vinelandii: Growth inhibition, cell injury, oxidative stress and internalization. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodo, K.; Ernszt, D.; Nemeth, P.; Engelmann, P. Distinct immune- and defense-related molecular fingerprints in sepatated coelomocyte subsets of Eisenia andrei earthworms. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2018, 15, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Mosquera, J.; Garcia, I.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Cellular Uptake of Nanoparticles versus Small Molecules: A Matter of Size. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.W.; Xu, G.H.; Yu, Y. In-vivo and in-vitro tests to assess toxic mechanisms of nano ZnO to earthworms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.; Andrews, K.J.; Jeon, B. Enhanced biofilm formation by ferrous and ferric iron through oxidative stress in Campylobacter jejuni. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Shen, F.; Yao, M. Biological responses of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria to nZVI (Fe0), Fe2+ and Fe3+. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 13835–13842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, C.R.; Goth-Goldstein, R.; Lucas, D.; Sedlak, D.L. Oxidative Stress Induced by Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles and Fe(II) in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4555–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, W.I.; Nelson, K.L.; Yoon, J.; Sedlak, D.L. Bactericidal effect of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4927–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semerad, J.; Pacheco, N.I.N.; Grasserova, A.; Prochazkova, P.; Pivokonsky, M.; Pivokonska, L.; Cajthaml, T. In Vitro Study of the Toxicity Mechanisms of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) and Released Iron Ions Using Earthworm Cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112189
Semerad J, Pacheco NIN, Grasserova A, Prochazkova P, Pivokonsky M, Pivokonska L, Cajthaml T. In Vitro Study of the Toxicity Mechanisms of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) and Released Iron Ions Using Earthworm Cells. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112189
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemerad, Jaroslav, Natividad Isabel Navarro Pacheco, Alena Grasserova, Petra Prochazkova, Martin Pivokonsky, Lenka Pivokonska, and Tomas Cajthaml. 2020. "In Vitro Study of the Toxicity Mechanisms of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) and Released Iron Ions Using Earthworm Cells" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112189
APA StyleSemerad, J., Pacheco, N. I. N., Grasserova, A., Prochazkova, P., Pivokonsky, M., Pivokonska, L., & Cajthaml, T. (2020). In Vitro Study of the Toxicity Mechanisms of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) and Released Iron Ions Using Earthworm Cells. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112189




