Nanofluids for Performance Improvement of Heavy Machinery Journal Bearings: A Simulation Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bearing Theory
2.3. CFD Simulation of Hydrodynamic Lubrication
2.4. Aggregation of WS2 NPs and Nanofluid Viscosity
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Case-Study: CFD Model Evaluation
3.2. Characterization of NP Aggregation and Viscosity Calculation of the Nanofluid
3.3. Simulation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruggiero, A.; D’Amato, R.; Magliano, E.; Kozak, D. Dynamical simulations of a flexible rotor in cylindrical uncavitated and cavitated lubricated journal bearings. Lubricants 2018, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratoi, M.; Niste, V.B.; Walker, J.; Zekonyte, J. Mechanism of action of WS2 lubricant nanoadditives in high-pressure contacts. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 52, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, L.; Fleischer, N.; Tenne, R. Applications of WS2 (MoS2) inorganic nanotubes and fullerene-like nanoparticles for solid lubrication and for structural nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Kao, M.J. Using TiO2 nanofluid additive for engine lubrication oil. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2011, 63, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidle, K.; Baxi, R. CFD Analysis of Fluid Film Journal Bearing: A Review. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 845–850. [Google Scholar]
- Aldana, P.U. Tungsten Disulfide Nanoparticles as Lubricant Additives for the Automotive Industry. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ide, R. Effect of Misalignment on Thrust Bearing Performance in Directional Drilling Operations. In Proceedings of the SPE Eastern Regional Meeting, Lexington, KY, USA, 3–5 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gertzos, K.; Nikolakopoulos, P.; Papadopoulos, C. CFD analysis of journal bearing hydrodynamic lubrication by Bingham lubricant. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, F.; Ochiai, M.; Hashimoto, H. CFD Analysis of Journal Bearing with Oil Supply Groove Considering Two-Phase Flow. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES, Aachen, Germany, 17–19 September 2017; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Manshoor, B.; Jaat, M.; Zaman, I.; Amir, K. CFD analysis of thin film lubricated journal bearing. Procedia Eng. 2013, 68, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, K.A.; Muthukumar, K.; Rajiev, R. CFD simulation analysis and experimental study on multilobe hydrodynamic journal bearing. In Proceedings of the International conference on Materials, Manufacturing and Machining 2019, Tamilnadu, India, 8–9 March 2019; p. 050007. [Google Scholar]
- Gangrade, A.; Phalle, V.M.; Mantha, S. CFD simulation of water lubricated conical hydrodynamic journal bearings. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshkovith, A.; Perfiliev, V.; Lapsker, I.; Fleischer, N.; Tenne, R.; Rapoport, L. Friction of fullerene-like WS2 nanoparticles: Effect of agglomeration. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 24, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhrs, C.C.; Moberg, M.; Maxson, A.; Brewer, L.; Menon, S. IF-WS2/nanostructured carbon hybrids generation and their characterization. Inorganics 2014, 2, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concli, F. Pressure distribution in small hydrodynamic journal bearings considering cavitation: A numerical approach based on the open-source CFD code OpenFOAM®. Lubr. Sci. 2016, 28, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concli, F.; Schaefer, C.T.; Bohnert, C. Innovative Meshing Strategies for Bearing Lubrication Simulations. Lubricants 2020, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandjalikhan, N.S.; Sohi, H.; Zaim, E. Study of lubricant compressibility effect on hydrodynamic characteristics of heavily loaded journal bearings. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. B Eng. 2011, 35, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Yin, Z.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X. Numerical analysis of plain journal bearing under hydrodynamic lubrication by water. Tribol. Int. 2014, 75, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Ma, L. Study on lubrication performance of journal bearing with multiple texture distributions. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Riaz, S.; Park, C.W. Hydrodynamic Conjunction of Textured Journal Surface—Bearing for Improved Frictional Response during Warm-Up of an Internal Combustion Engine. Energies 2018, 11, 3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Hu, N.; Zhou, G.; Wu, J. Tribological properties of lubricating oil with micro/nano-scale WS2 particles. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2018, 13, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sade, H.; Moshkovich, A.; Lellouche, J.-P.; Rapoport, L. Testing of WS2 Nanoparticles Functionalized by a Humin-Like Shell as Lubricant Additives. Lubricants 2018, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogovšek, J.; Kalin, M. Various MoS 2-, WS2-and C-based micro-and nanoparticles in boundary lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, L.; Leshchinsky, V.; Lvovsky, M.; Lapsker, I.; Volovik, Y.; Tenne, R. Load bearing capacity of bronze, iron and iron–nickel powder composites containing fullerene-like WS2 nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2002, 35, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, P. Tribological properties of oleylamine-modified ultrathin WS 2 nanosheets as the additive in polyalpha olefin over a wide temperature range. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 61, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Vakharia, D. Performance analysis of short journal bearing under thin film lubrication. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 281021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, M.; Dey, T. Effect of aggregation on the viscosity of copper oxide–gear oil nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ding, Y.; He, Y.; Tan, C. Rheological behaviour of ethylene glycol based titania nanofluids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 444, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, P.; Grün, F.; Summer, F.; Gódor, I. Evaluation of wear phenomena of journal bearings by close to component testing and application of a numerical wear assessment. Lubricants 2018, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binu, K.; Shenoy, B.; Rao, D.; Pai, R. A variable viscosity approach for the evaluation of load carrying capacity of oil lubricated journal bearing with TiO2 nanoparticles as lubricant additives. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1051–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirani, H.; Rao, T.; Athre, K.; Biswas, S. Rapid performance evaluation of journal bearings. Tribol. Int. 1997, 30, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasolang, S.; Ahmad, M.A.; Joyce, R.-D.; Tai, C.F.M. Preliminary study of pressure profile in hydrodynamic lubrication journal bearing. Procedia Eng. 2012, 41, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naffin, R.; Chang, L. An analytical model for the basic design calculations of journal bearings. J. Tribol. 2010, 132, 024503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckholz, R.; Hwang, B. The accuracy of short bearing theory for Newtonian lubricants. J. Tribol. 1986, 108, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, B.; Narang, I. Rapid design and performance evaluation of steady-state journal bearings—A technique amenable to programmable hand calculators. Asle Trans. 1982, 25, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budynas, R.G.; Nisbett, J.K. Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, T.-H.; Liou, W.W.; Shabbir, A.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J. A new k-ϵ eddy viscosity model for high reynolds number turbulent flows. Comput. Fluids 1995, 24, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binu, K.; Shenoy, B.; Rao, D.; Pai, R. Static characteristics of a fluid film bearing with TiO2 based nanolubricant using the modified Krieger–Dougherty viscosity model and couple stress model. Tribol. Int. 2014, 75, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, A.; Sadiki, A.; Mehdizadeh, A. A discrete model for the apparent viscosity of polydisperse suspensions including maximum packing fraction. J. Rheol. 2013, 57, 743–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SadAbadi, H.; Badilescu, S.; Packirisamy, M.; Wüthrich, R. PDMS-gold nanocomposite platforms with enhanced sensing properties. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SadAbadi, H.; Badilescu, S.; Packirisamy, M.; Wüthrich, R. Integration of gold nanoparticles in PDMS microfluidics for lab-on-a-chip plasmonic biosensing of growth hormones. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadabadi, H.; Packirisamy, M. Nano-integrated suspended polymeric microfluidics (SPMF) platform for ultra-sensitive bio-molecular recognition of bovine growth hormones. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
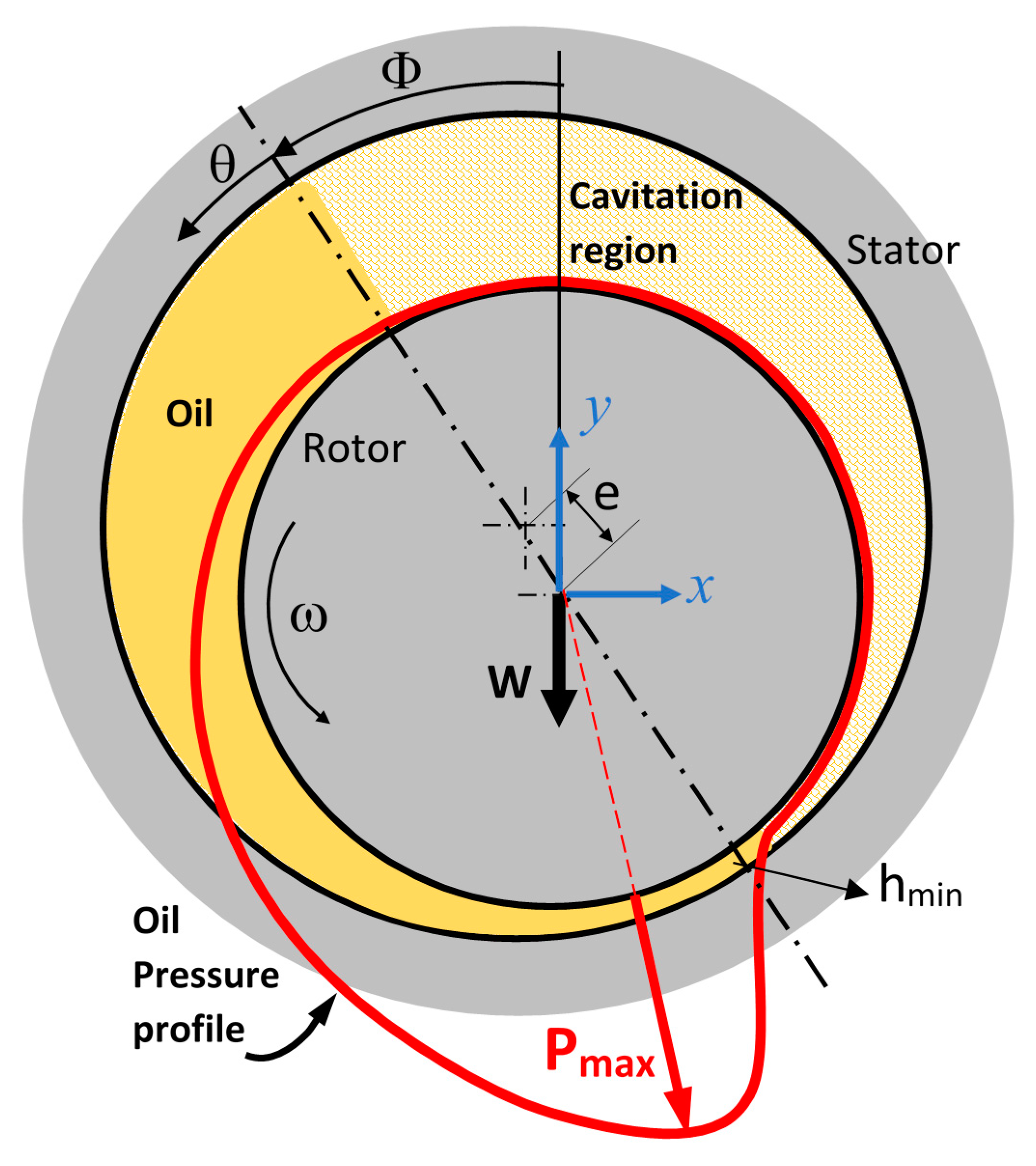




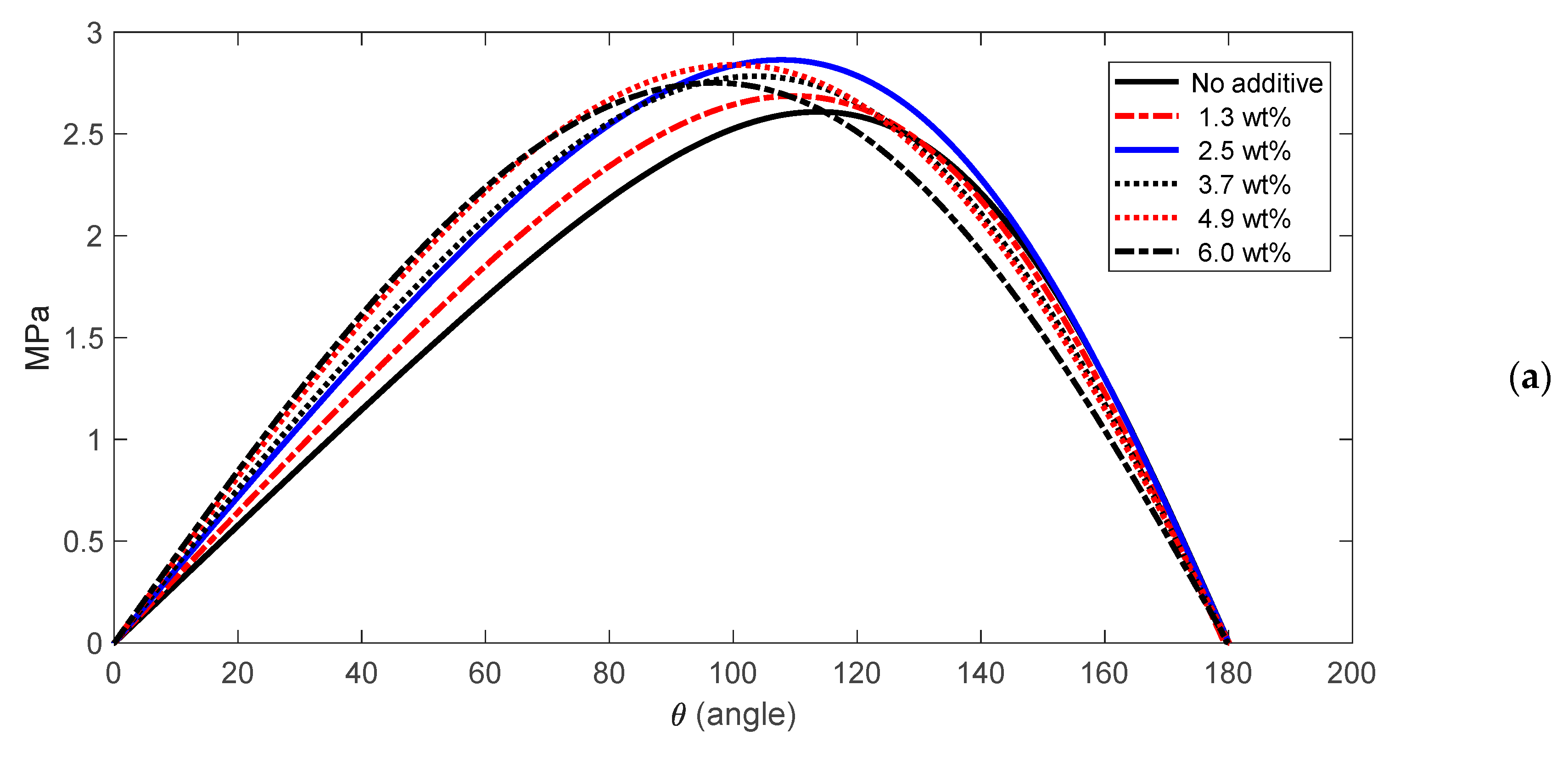
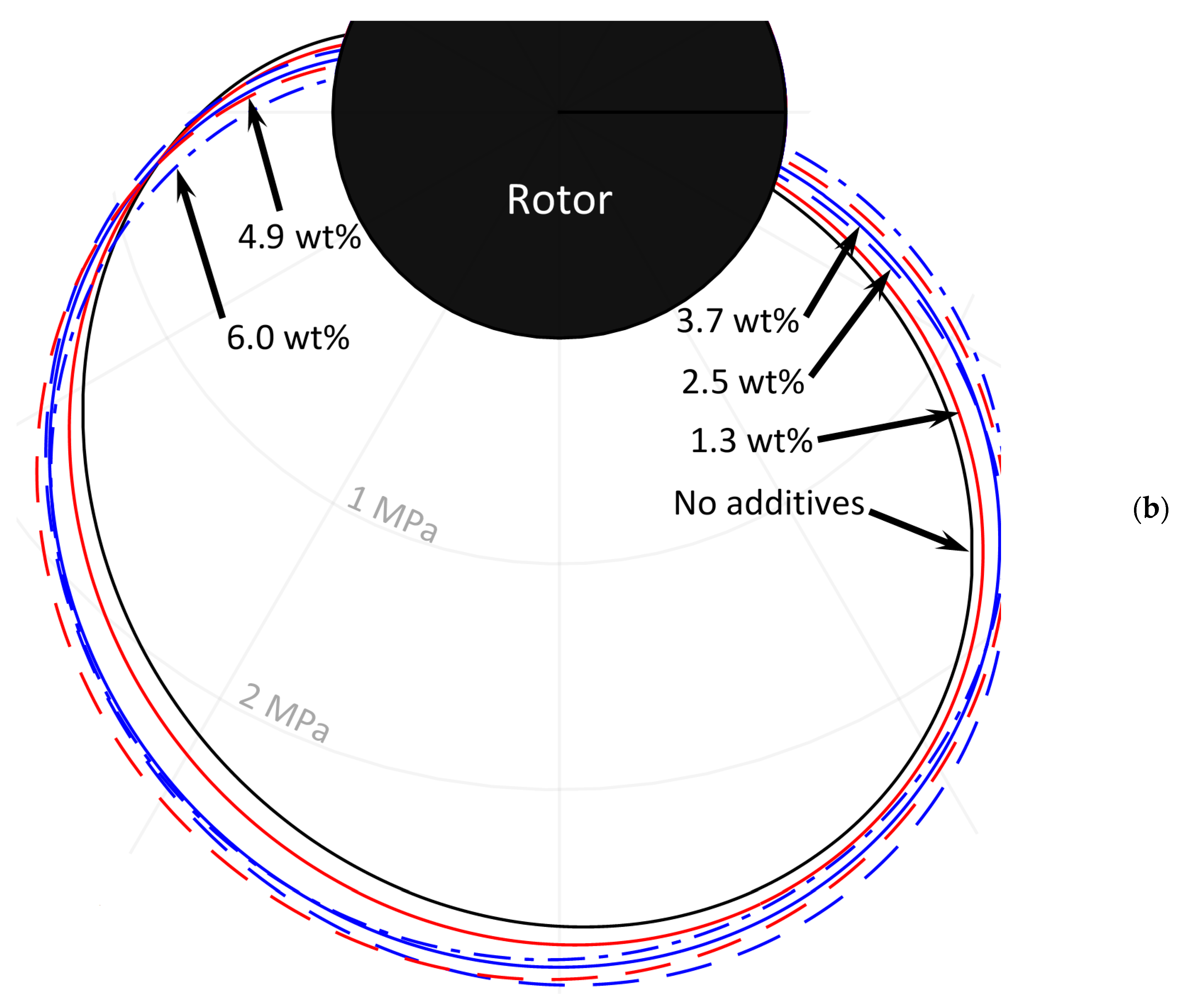
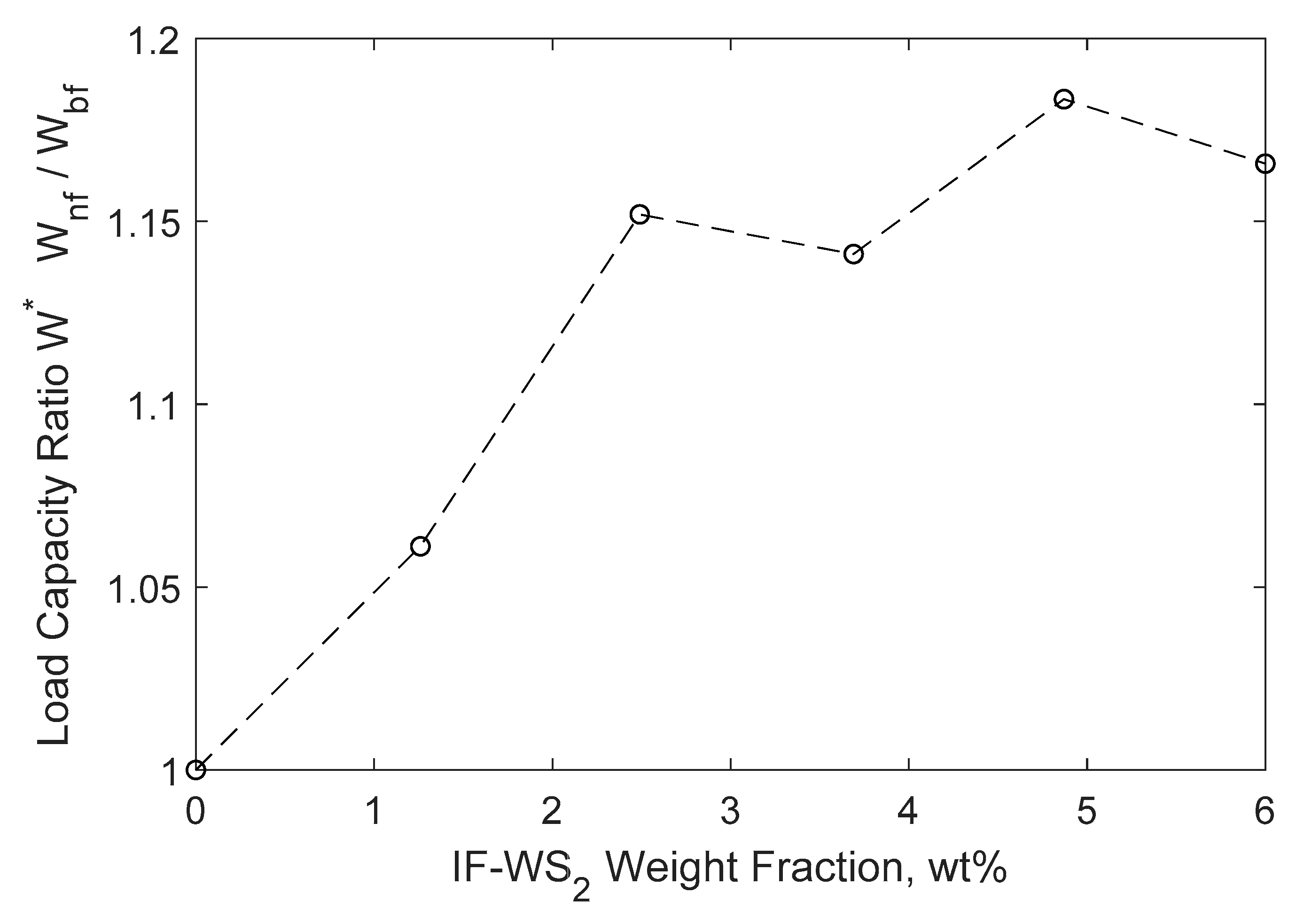
| Journal Bearing Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rotor radius | R = 19 mm |
| Rotor Length | L = 76 mm |
| Rotor angular speed | N = 200 rpm |
| Radial clearance | C = 0.038 mm |
| Base Lubricant viscosity (@100 °C) | µ = 0.02756 Pa s |
| Oil Density | ρ = 885 kg/m3 |
| Nanofluid Model | Weight Fraction (wt%) | Volume Fraction % (φ%) |
|---|---|---|
| Case 1: No additive | 0% | 0% |
| Case 2 | 1.26% | 0.15% |
| Case 3 | 2.49% | 0.30% |
| Case 4 | 3.69% | 0.45% |
| Case 5 | 4.87% | 0.60% |
| Case 6 | 6.02% | 0.75% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadabadi, H.; Sanati Nezhad, A. Nanofluids for Performance Improvement of Heavy Machinery Journal Bearings: A Simulation Study. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112120
Sadabadi H, Sanati Nezhad A. Nanofluids for Performance Improvement of Heavy Machinery Journal Bearings: A Simulation Study. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112120
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadabadi, Hamid, and Amir Sanati Nezhad. 2020. "Nanofluids for Performance Improvement of Heavy Machinery Journal Bearings: A Simulation Study" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112120
APA StyleSadabadi, H., & Sanati Nezhad, A. (2020). Nanofluids for Performance Improvement of Heavy Machinery Journal Bearings: A Simulation Study. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2120. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112120






