Hydrothermal Synthesis of Polyhedral Nickel Sulfide by Dual Sulfur Source for Highly-Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of NiS2 (MS) with Dual Sulfur Source
2.3. Synthesis of NiS2 with MPS
2.4. Synthesis of NiS2 with S
2.5. Materials Characterization
2.6. Electrochemical Measurements
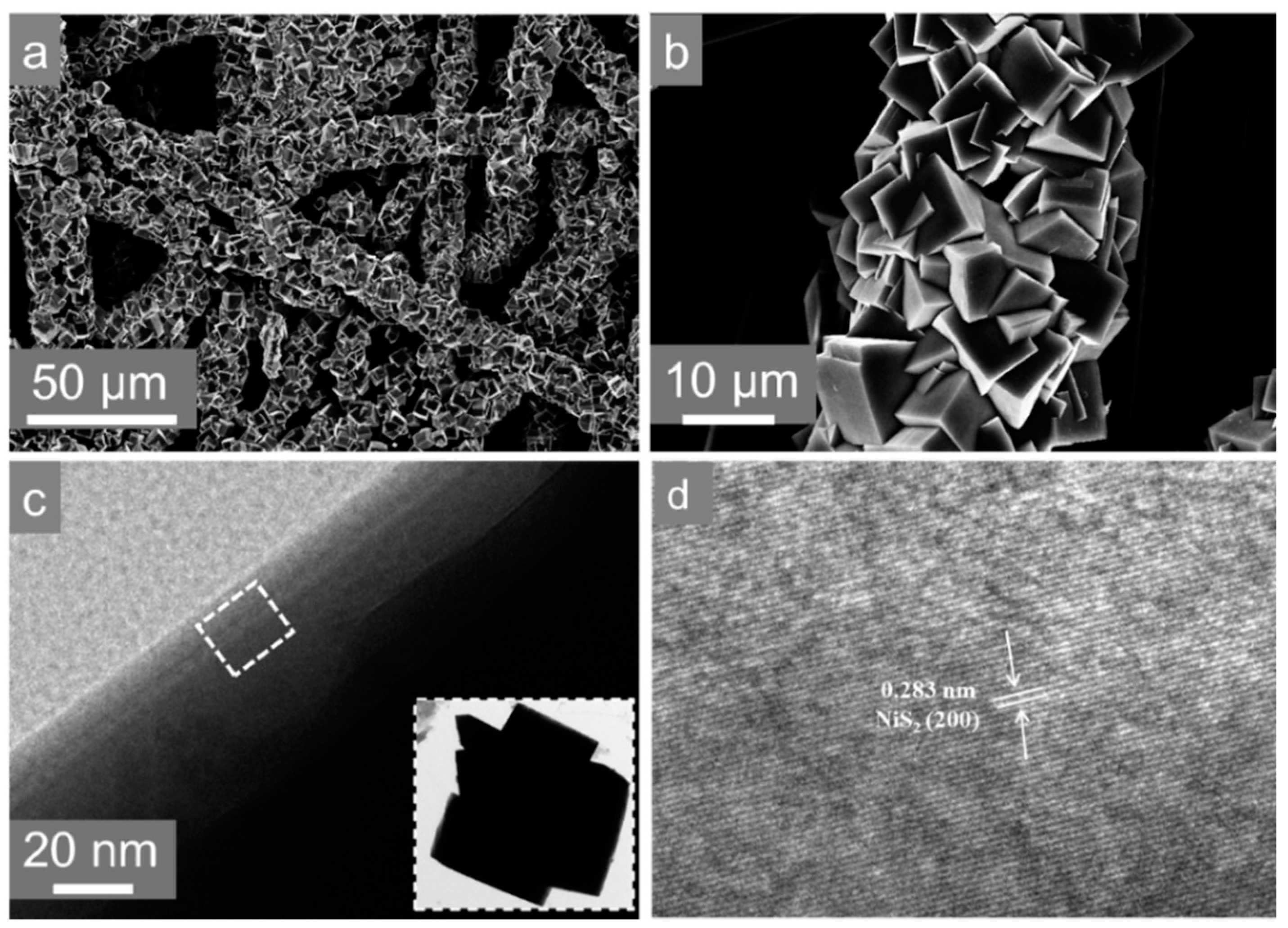
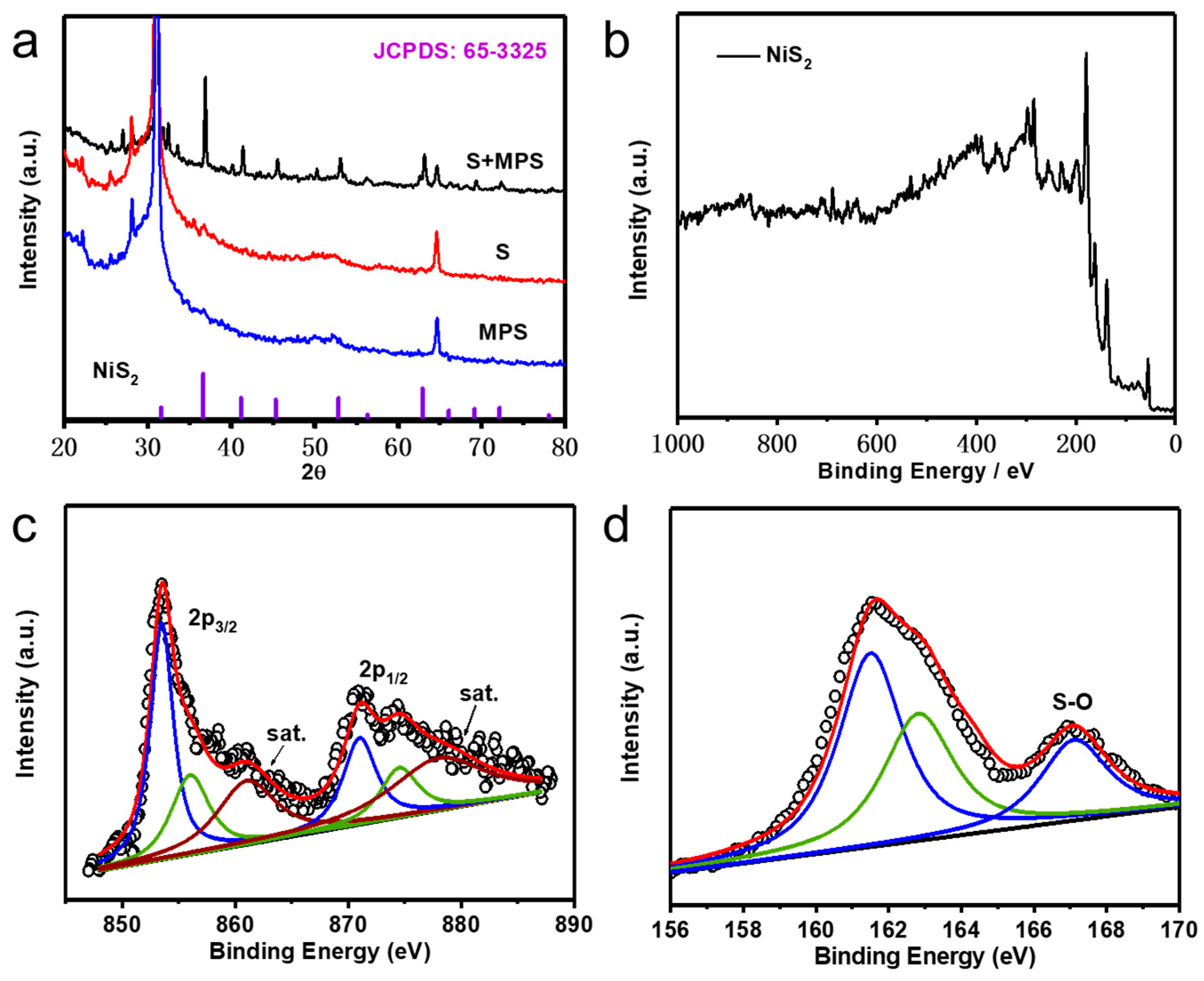
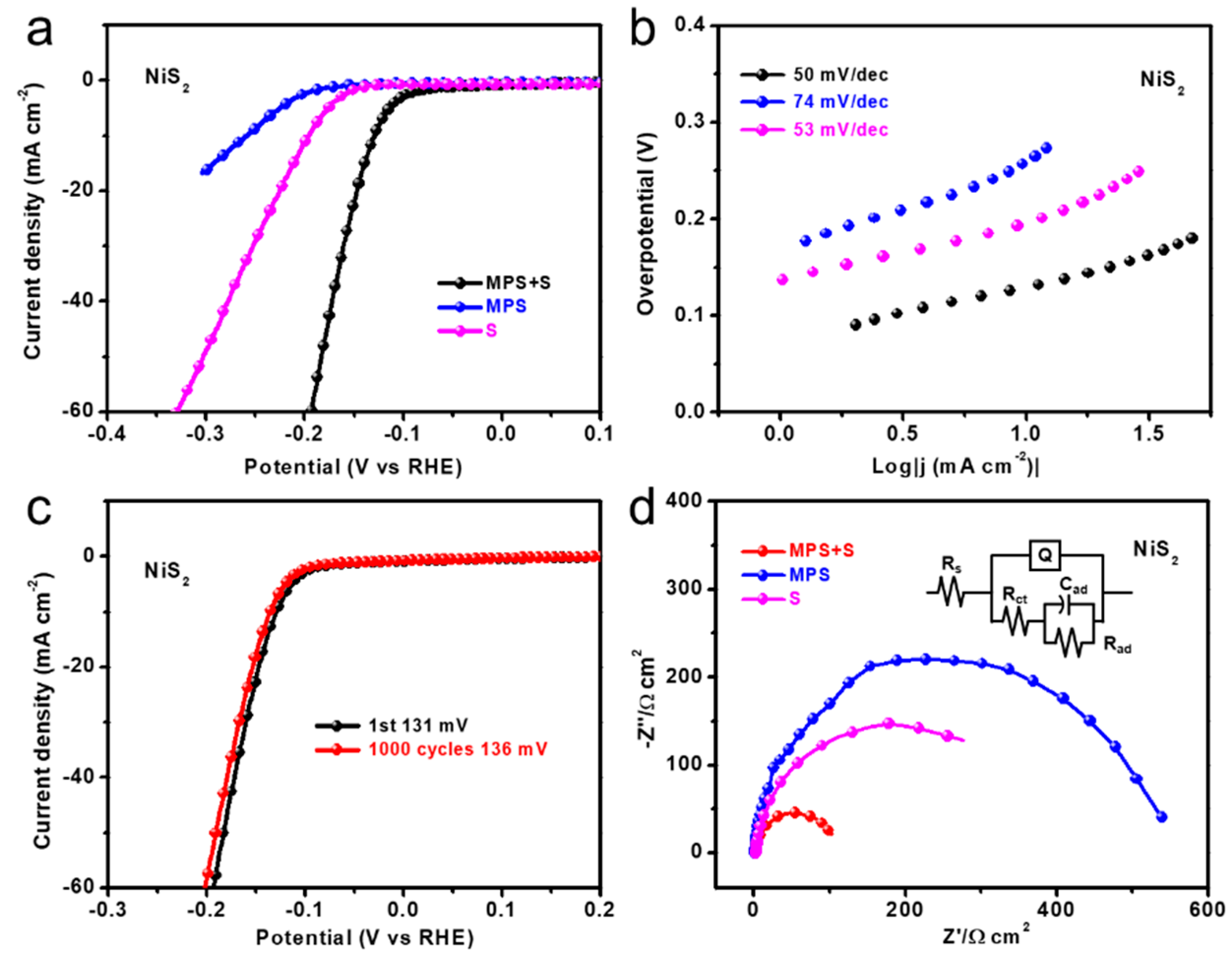
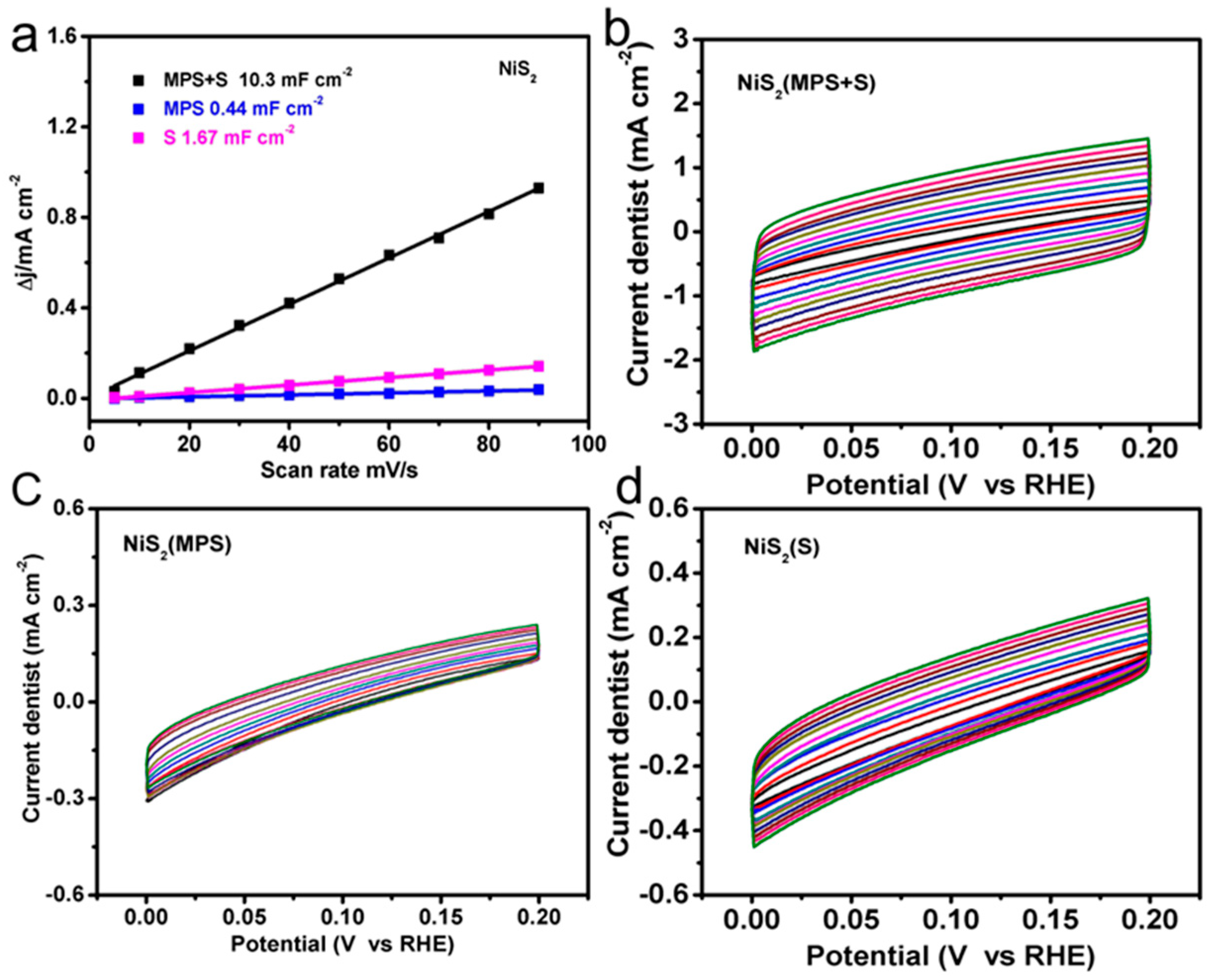
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, C.; Pu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A.M.; Jiang, P. NiS2 nanosheets array grown on carbon cloth as an efficient 3D hydrogen evolution cathode. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 153, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, H.; Sun, J.; Qin, F.; Yu, F.; Bao, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. Cu nanowires shelled with NiFe layered double hydroxide nanosheets as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seh, Z.W.; Kibsgaard, J.; Dickens, C.F.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J.K.; Jaramillo, T.F. Combining theory and experiment in electrocatalysis: Insights into materials design. Science 2017, 355, eaad4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, F.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Z.; Nielsen, R.J.; He, R.; Bao, J.; Iii, W.A.G.; Chen, S.; et al. Efficient hydrogen evolution by ternary molybdenum sulfoselenide particles on self-standing porous nickel diselenide foam. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, R.; Lu, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Hao, S.; Du, G.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. Energy-Saving Electrolytic Hydrogen Generation: Ni2P Nanoarray as a High-Performance Non-Noble-Metal Electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 56, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hao, X.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Nanostructured catalysts for electrochemical water splitting: Current state and prospects. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11973–12000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Dai, Q.; Wang, M.; Qu, L.; Dai, L. Earth-abundant carbon catalysts for renewable generation of clean energy from sunlight and water. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Zheng, X.; Cui, G. Detailed kinetic study of the electrochemical Bunsen reaction in the sulfur–iodine cycle for hydrogen production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Chen, S. Activity and stability of monometallic and bimetallic catalysts for high-temperature catalytic HI decomposition in the iodine–sulfur hydrogen production cycle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Xie, Y.; Ma, H.; Tian, C.; Gu, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Fu, H. Integrating the active OER and HER components as the heterostructures for the efficient overall water splitting. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, B.; Zhao, D.; Wang, H.; Plebanski, M. Strategies for developing transition metal phosphides as heterogeneous electrocatalysts for water splitting. Nano Today 2017, 15, 26–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, C. Ultrathin metal-organic framework array for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhattacharyya, S. Porous NiFe-Oxide Nanocubes as Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Efficient Water-Splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41906–41915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. Self-Supported Nanoporous Cobalt Phosphide Nanowire Arrays: An Efficient 3D Hydrogen-Evolving Cathode over the Wide Range of pH 0–14. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7587–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Lin, H.; Hu, C.; Long, X.; Yang, S. Hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis with binary-nonmetal transition metal compounds. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5995–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, M.S.; Lukowski, M.A.; Ding, Q.; Kaiser, N.S.; Jin, S. Earth-Abundant Metal Pyrites (FeS2, CoS2, NiS2, and Their Alloys) for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution and Polysulfide Reduction Electrocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 21347–21356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Wei, W.; Cui, X.; Alenizi, A.M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, G. Interlaced NiS2–MoS2 nanoflake-nanowires as efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts in basic solutions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13439–13443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Li, Y.X.; Lv, F.; Lu, M.; Sun, K.; Wang, W. Oxygen vacancies dominated NiS2/CoS2 interface porous nanowires for portable Zn–air batteries driven water splitting devices. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1704681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Huang, L.; Ai, L.; Jiang, J. Surface anion-rich NiS2 hollow microspheres derived from metal–organic frameworks as a robust electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 20985–20992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Lei, L.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of supported vertical NiS2 nanosheets for hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic and alkaline solution. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32976–32982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Wang, P.C.; Wang, H.H.; Li, C. Defect-Rich Heterogeneous MoS2/NiS2 Nanosheets Electrocatalysts for Efficient Overall Water Splitting. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; He, Q.; Jiang, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Habib, M.; Chen, S.; Song, L. Electronic Structure Reconfiguration toward Pyrite NiS2 via Engineered Heteroatom Defect Boosting Overall Water Splitting. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11574–11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Jiang, W.-J.; Lian, Y.; Li, H.; Hong, S.; Xu, S.; Yan, H.; Hu, J.-S. NiS2 nanodotted carnation-like CoS2 for enhanced electrocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3781–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Yang, W.; Hou, J.; Mao, B.; Huang, Z.; Shi, W. Nitrogen doped NiS2 nanoarrays with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for water oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17811–17816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Fang, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Xin, Y.; Yu, J.; Yao, S.; Zhang, Z. Electrocatalytic performance of cubic NiS2 and hexagonal NiS for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Catal. 2018, 359, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, P.Y.; He, M.; Zhu, B.C.; Yu, J.G.; Fan, K. 0D/2D NiS2/V-MXene composite for electrocatalytic H2 evolution. J. Catal. 2019, 375, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, B. Facile synthesis of NiS2 nanowires and its efficient electrocatalytic performance for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Mi, L.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, W.; Guan, X. Partial Ion-Exchange of Nickel-Sulfide-Derived Electrodes for High Performance Supercapacitors. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3418–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Qi, F.; Zheng, B.; He, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Self-Assembled Coral-like Hierarchical Architecture Constructed by NiSe2 Nanocrystals with Comparable Hydrogen-Evolution Performance of Precious Platinum Catalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7154–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Luo, S.-L.; Xu, S.-Q.; Yuan, N.-Y.; Ding, J.-N. High performance Li–S battery based on amorphous NiS2 as the host material for the S cathode. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13395–13399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, S.-W.; Wang, G.-S.; Li, Z.; Guo, A.-P.; Zhu, J.-Q.; Liu, D.-P.; Yin, P.-G. Facile synthesis of NiS2 @MoS2 core–shell nanospheres for effective enhancement in microwave absorption. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 22454–22460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, Z.; Song, H.; Duan, X.; Peng, Z.; Yan, S. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Polyhedral Nickel Sulfide by Dual Sulfur Source for Highly-Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112115
Gao Y, Wang K, Lin Z, Song H, Duan X, Peng Z, Yan S. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Polyhedral Nickel Sulfide by Dual Sulfur Source for Highly-Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112115
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yuan, Ka Wang, Zixia Lin, Haizeng Song, Xiaomeng Duan, Zehui Peng, and Shancheng Yan. 2020. "Hydrothermal Synthesis of Polyhedral Nickel Sulfide by Dual Sulfur Source for Highly-Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112115
APA StyleGao, Y., Wang, K., Lin, Z., Song, H., Duan, X., Peng, Z., & Yan, S. (2020). Hydrothermal Synthesis of Polyhedral Nickel Sulfide by Dual Sulfur Source for Highly-Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2115. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112115




