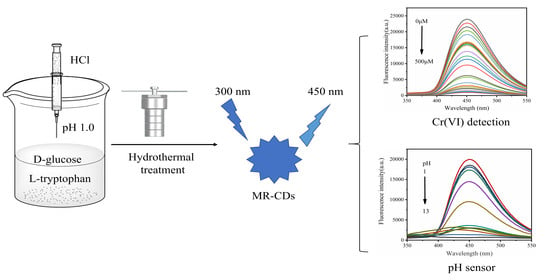
Carbon Dots Derived from the Maillard Reaction for pH Sensors and Cr (VI) Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MR-CDs
2.3. Characterization of MR-CDs
2.4. Quantum Yield Measurement of MR-CDs
2.5. pH Response of MR-CDs
2.6. Detection of Cr (VI)
2.7. Samples Pretreatment
3. Results
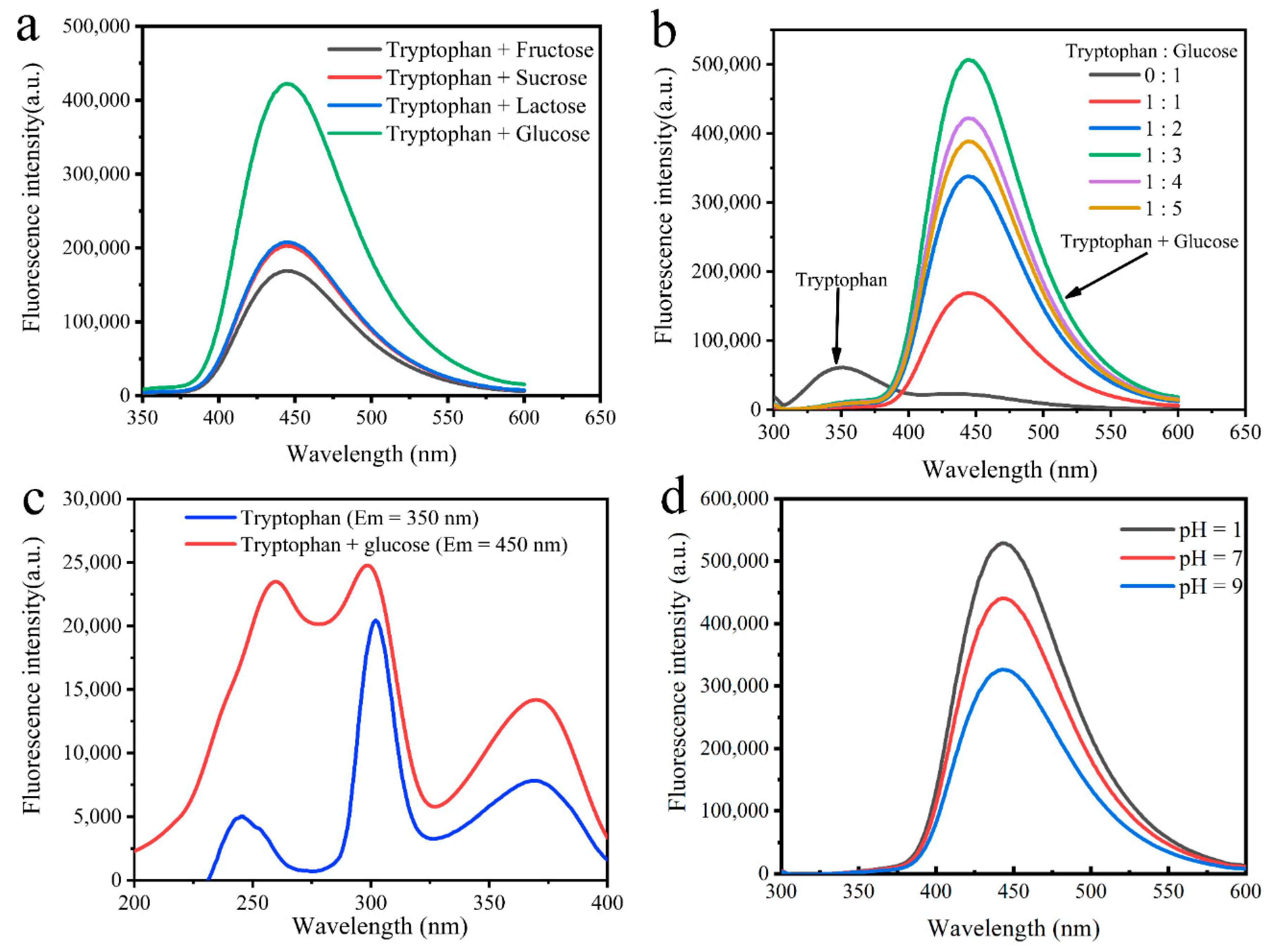
3.1. Preparation of MR-CDs
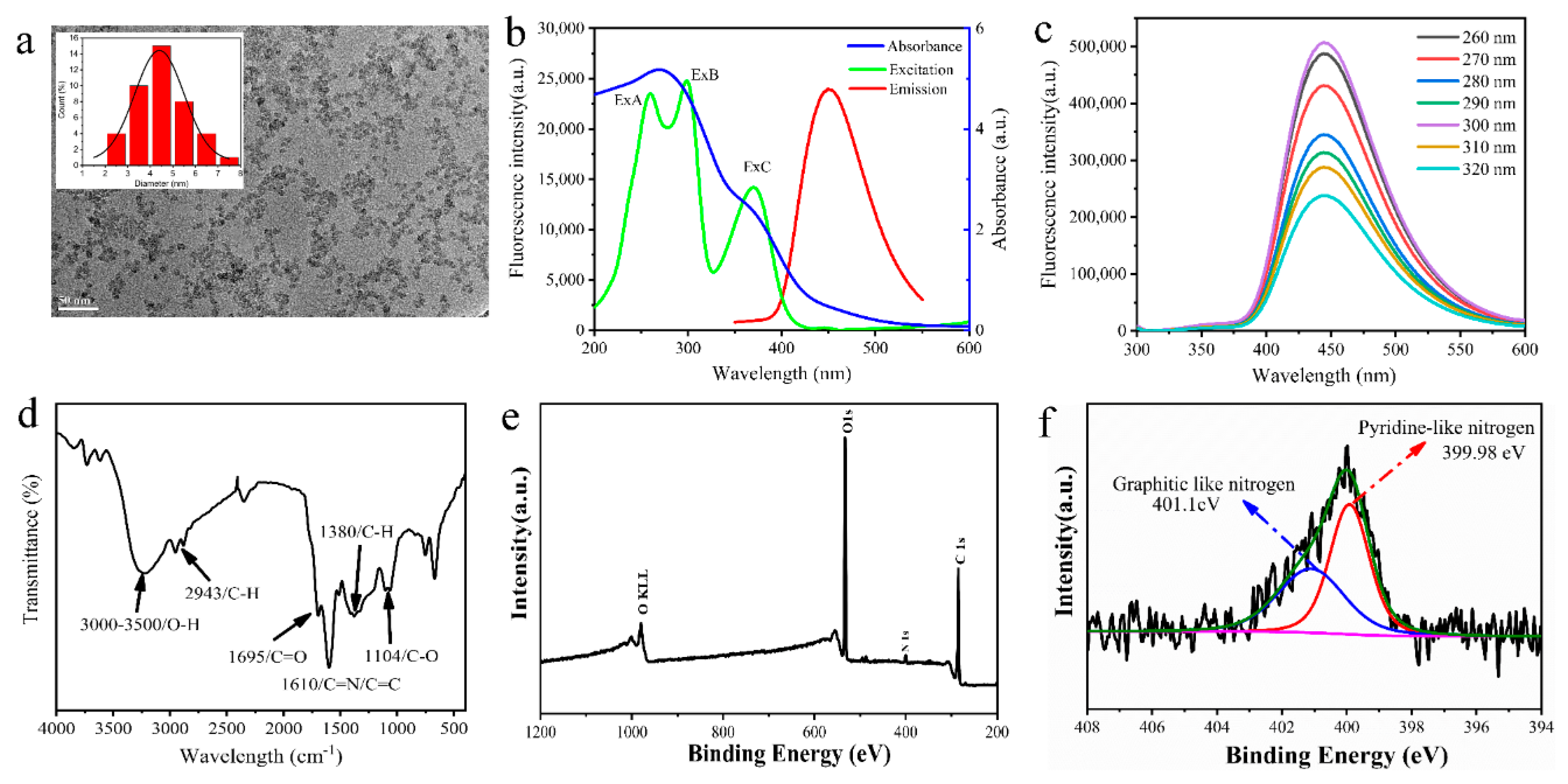
3.2. Characterization of MR-CDs
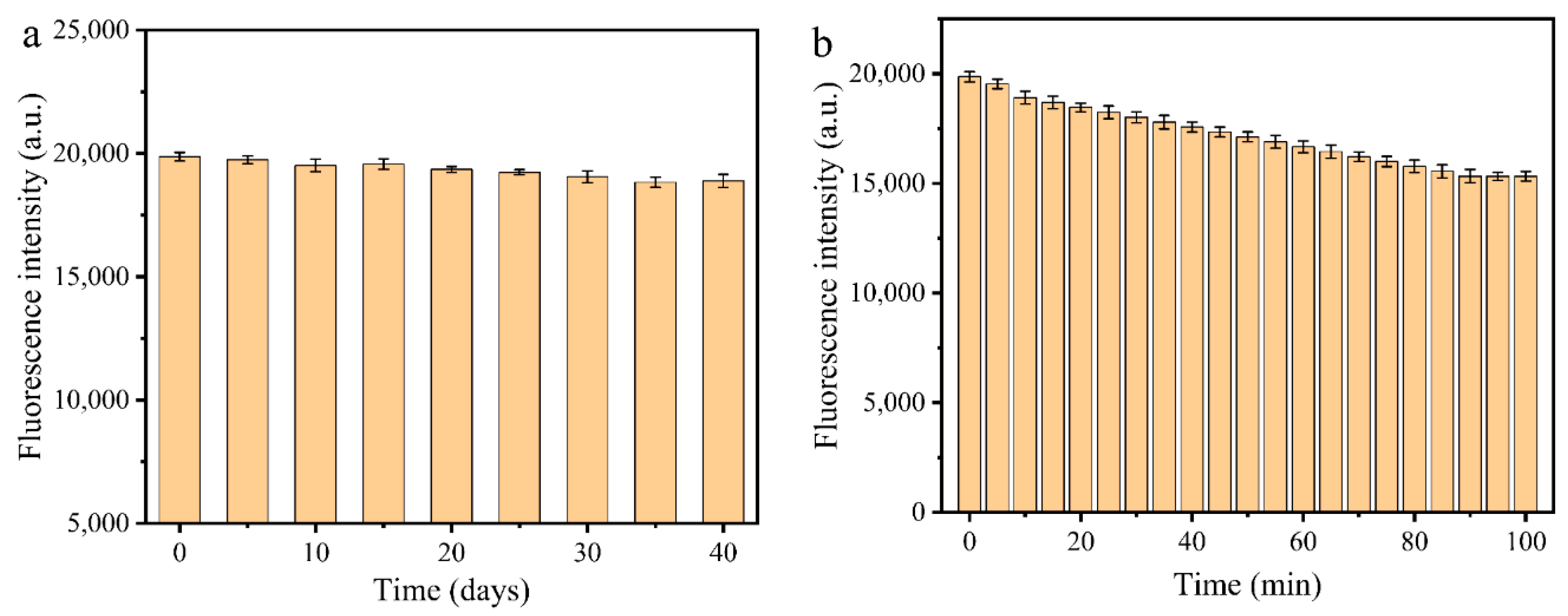
3.3. Stability of MR-CDs
3.4. pH-Dependence of MR-CDs
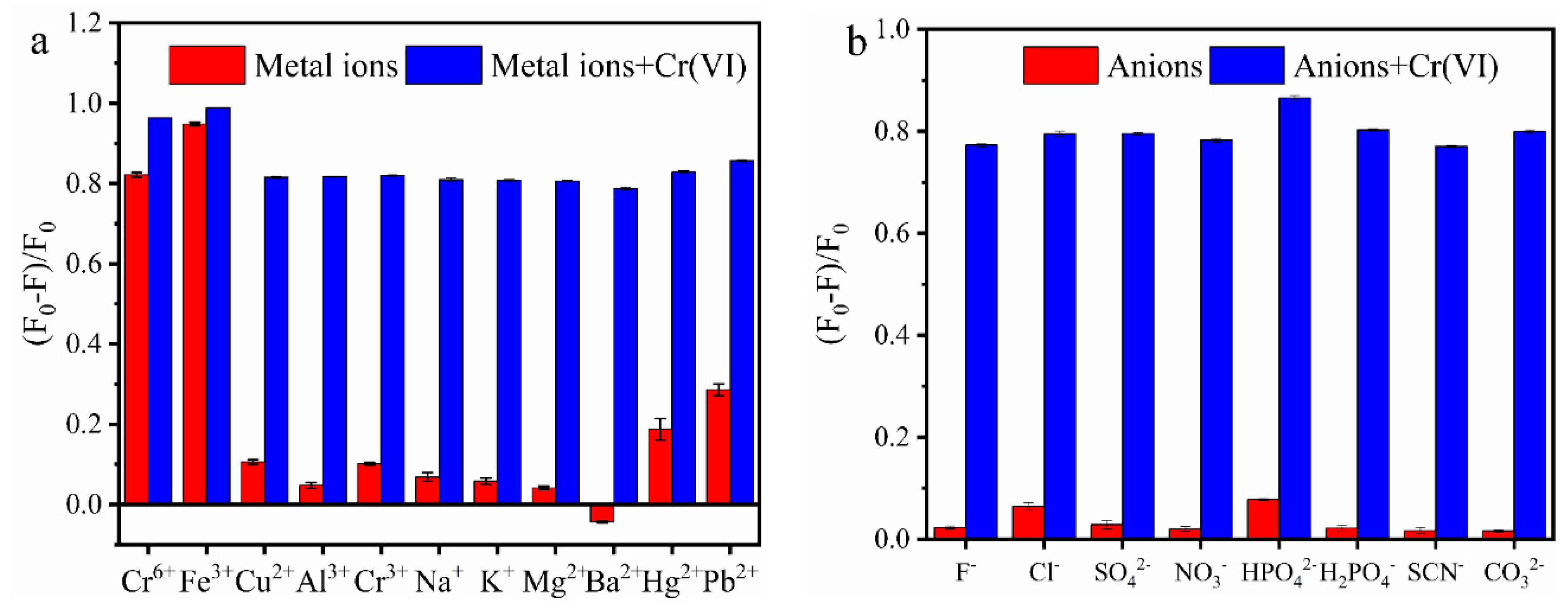
3.5. Selectivity of MR-CDs
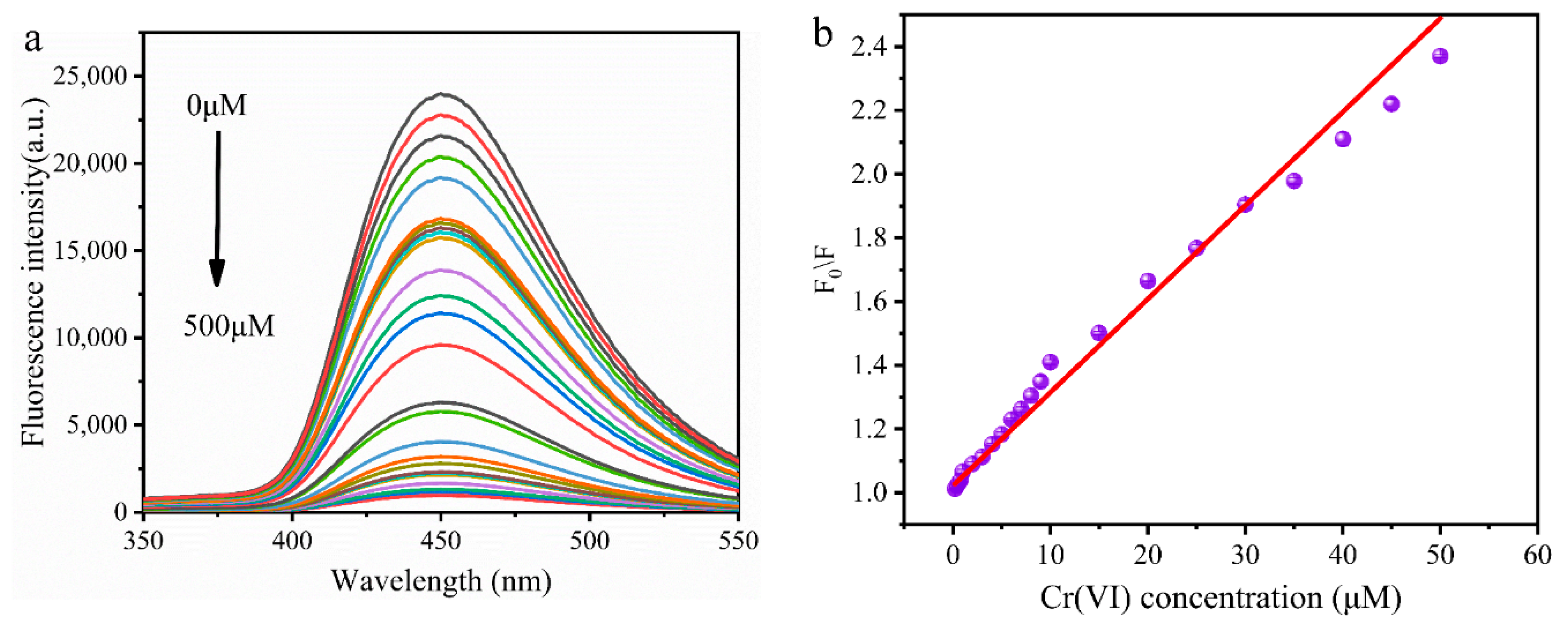
3.6. Detection of Cr (VI)
3.7. Practical Application
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Namdari, P.; Negahdari, B.; Eatemadi, A. Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of carbon-based quantum dots: An updated review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, P.; Lu, X.; Sun, Z.; Guo, Y.; He, H. A review on syntheses, properties, characterization and bioanalytical applications of fluorescent carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Al-Sibaai, A.A.; Alwael, H.; El-Shahawi, M.S. Trace determination of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) species in water samples via dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and microvolume UV–Vis spectrometry. Thermodynamics, speciation study. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 224, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerhong, M.; Xu, Y.; Yin, X.-B. Review on carbon dots and their applications. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wei, W.; Fu, Z.; Gao, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, F.; Lu, X. Review on carbon dots in food safety applications. Talanta 2019, 194, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, C.L. Action des acides aminés sur les sucres; formation des mélanoïdines par voie methodique. Comptes R. Acad. Sci. 1912, 154, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, D.; Monaro, E.R.; Siguemoto, E.; Sefora, M. Maillard Reaction Products in Processed Food: Pros and Cons. In Food Industrial Processes; InTech: London, UK, 2012; pp. 281–300. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, L.; Alegría, A.; Farré, R.; Clemente, G. Fluorescence and color as markers for the Maillard reaction in milk–cereal based infant foods during storage. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiacevich, S.B.; Buera, M.P. A critical evaluation of fluorescence as a potential marker for the Maillard reaction. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.X.; Song, X.F.; Shi, Y.; Gao, Z.F.; Li, B.L.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. A potential fluorescent probe: Maillard reaction product from glutathione and ascorbic acid for rapid and label-free dual detection of Hg2+ and biothiols. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, S. Amphiphilic egg-derived carbon dots: Rapid plasma fabrication, pyrolysis process, and multicolor printing patterns. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2012, 51, 9297–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, H.S. Green synthesis of luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots from milk and its imaging application. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8902–8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, S.; Behera, B.; Maiti, T.K.; Mohapatra, S. Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: Application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8835–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Földi, C.; Dohrmann, R.; Matern, K.; Mansfeldt, T. Characterization of chromium-containing wastes and soils affected by the production of chromium tanning agents. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GracePavithra, K.; Jaikumar, V.; Kumar, P.S.; SundarRajan, P. A review on cleaner strategies for chromium industrial wastewater: Present research and future perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthiry, G.R.; Antholine, W.E.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Myers, J.M.; Myers, C.R. Reduction of hexavalent chromium by human cytochrome b5: Generation of hydroxyl radical and superoxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 738–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; Volume 2, pp. 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Xie, Y.; Bi, J.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Cheng, S.; Li, D.; Tan, M. Facile one-step synthesis of highly luminescent N-doped carbon dots as an efficient fluorescent probe for chromium(vi) detection based on the inner filter effect. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 3729–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Tong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, S. Carbon dots codoped with nitrogen and sulfur are viable fluorescent probes for chromium(VI). Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wencel, D.; Abel, T.; McDonagh, C. Optical chemical pH sensors. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, D.; Hsieh, J.-T.; Bai, X.; Yang, J. Citrate-based fluorescent biomaterials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.Q.; Zhu, A.W.; Tian, Y. Functional surface engineering of C-dots for fluorescent biosensing and in vivo bioimaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Du, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. An intramolecular charge transfer process based fluorescent probe for monitoring subtle pH fluctuation in living cells. Talanta 2017, 162, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joniak, J.; Stankovičová, H.; Filo, J.; Gaplovská-Kyselá, K.; Garaj, V.; Cigáň, M. Small-molecule coumarin fluorescent pH probes for extremely acidic conditions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 307, 127646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.H.; Liu, W.; Sun, R.; Li, X.S.; Ge, J.F. Diaminodibenzoxanthenium based near infrared pH probes with lower pK(a). Dyes Pigment. 2016, 132, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Du, J.; Liu, H.; Lu, S.; Zhou, X.; Yang, C. A hemicyanine-based optical probe for biomembranes and intracellular pH sensing. J. Lumin. 2018, 202, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, D.S.; Pell, L.E.; Yu, Z.; Barbara, P.F.; Korgel, B.A. Size tunable visible luminescence from individual organic monolayer stabilized silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiacevich, S.B.; Santagapita, P.R.; Buera, M.P. Fluorescence from the maillard reaction and its potential applications in food science. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrens, L. Fluorescent intermediates in the Maillard reaction. Recl. des Trav. Chim. des Pays-Bas 1966, 85, 17–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, J.E. Dehydrated foods, chemistry of browning reactions in model systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1953, 1, 928–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W.R. Melanoidins produced by the Maillard reaction: Structure and biological activity. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Soladoye, O.P.; Aluko, R.E. Maillard reaction products derived from food protein-derived peptides: Insights into flavor and bioactivity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMan, J.M.; Finley, J.; Hurst, W.J.; Lee, C. Principles of Food Chemistry, 4th ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerlan, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Raghavendra, M.; Tokas, J.; Singal, H.R. Chapter 10 - Flavor addition in dairy products: Health benefits and risks. In Nutrients in Dairy and Their Implications on Health and Disease; Watson, R.R., Collier, R.J., Preedy, V.R., Eds.; Academic Press: St. Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2017; pp. 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, S.I.F.S.; Jongen, W.M.F.; Van Boekel, M.A.J.S. A review of Maillard reaction in food and implications to kinetic modelling. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Feng, Z. Nitrogen-doped carbon dot mediated fluorescence on–off assay for highly sensitive detection of I− and Br− ions. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 14332–14339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.B.; Li, Z.L.; Zhang, X.W.; Shi, Y.P.; Zhou, N. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for sensitive and selective detection of nitrite. Molecules 2017, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yuan, H.; Wei, G.; Ye, G.; Chen, J. Fluorescence sensor array based on amino acid derived carbon dots for pattern-based detection of toxic metal ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Zhang, J.; Gao, M.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, R. A facile hydrothermal approach towards photoluminescent carbon dots from amino acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 439, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga, T.; Akiu, M.; Iso, Y.; Isobe, T. Photoluminescence properties of l-cysteine-derived carbon dots prepared in non-aqueous and aqueous solvents. J. Lumin. 2020, 224, 117260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, G.; Zhou, N. Fluorescent carbon dots with two absorption bands: Luminescence mechanism and ion detection. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 6459–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.; Xie, J.; Su, W.; Sheng, J.; Xiao, Q. A carbon dots based fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of hemoglobin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.-H.; Shao, L.; Chen, J.-J.; Bao, W.-J.; Wang, F.-B.; Xia, X.-H. Catalyst-free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4350–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Zeng, J.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.; Qu, C.; Dang, D.; Liu, M. A high-performance supercapacitor electrode based on N-doped porous graphene. J. Power Sources 2018, 387, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Y.; Schneider, J.; Ushakova, E.V.; Rogach, A.L. Influence of molecular fluorophores on the research field of chemically synthesized carbon dots. Nano Today 2018, 23, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Schneider, J.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Huang, H.; Kasák, P.; Rogach, A.L. Carbonization conditions influence the emission characteristics and the stability against photobleaching of nitrogen doped carbon dots. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 11730–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Tian, B.; Liu, C.; Jia, P.; Zhu, H.; Sheng, W.; Zhu, B. A novel water-soluble fluorescent probe with ultra-sensitivity over a wider pH range and its application for differentiating cancer cells from normal cells. Analyst 2019, 144, 6975–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Ma, J.; Shan, X.; Feng, H.; Shao, L.; Chen, J. Highly luminescent N-doped carbon quantum dots as an effective multifunctional fluorescence sensing platform. Chem. (Weinh. der Bergstr. Ger.) 2014, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-J.; Xia, J.-M.; Feng, J.; He, M.-Q.; Chen, M.-L.; Wang, J.-H. Green preparation of carbon dots for intracellular pH sensing and multicolor live cell imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 7130–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, J.; Chi, Y.; Tian, B.; Li, L.; Jiang, B.; Li, D.; Feng, Z.; Liu, C. Preparation of whey protein isolate nanofibrils by microwave heating and its application as carriers of lipophilic bioactive substances. LWT 2020, 125, 109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Qin, X.; Zhu, C. Carbon quantum dots derived from pure solvent tetrahydrofuran as a fluorescent probe to detect pH and silver ion. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 382, 111981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, C.; Zheng, B.; Dai, J.; Yan, L.; Zhuang, Z.; Du, J.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, D. Green anhydrous synthesis of hydrophilic carbon dots on large-scale and their application for broad fluorescent pH sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshni, V.; Misra, S.; Santra, M.K.; Ottoor, D. One pot green synthesis of C-dots from groundnuts and its application as Cr(VI) sensor and in vitro bioimaging agent. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 373, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.; Lin, L.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yan, J.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, X.; Chen, X. Fluorescence sensing of chromium (VI) and ascorbic acid using graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as a fluorescent “switch”. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
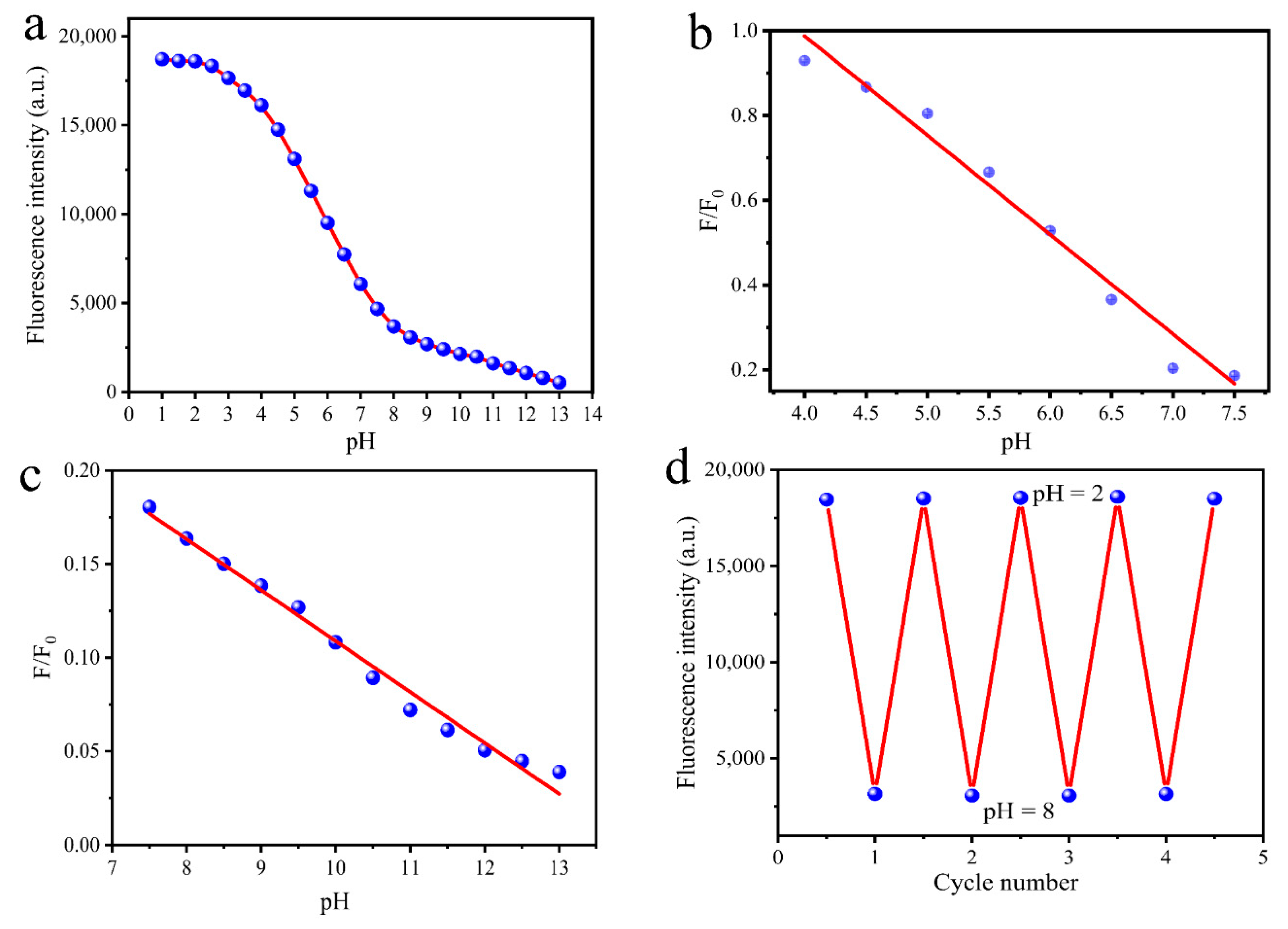
| pH Linear Range | Regression Equation | Correlation Coefficient (R2) |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0–7.5 | F/F0 = −0.2342 pH + 1.9245 | 0.984 |
| 7.5–13.0 | F/F0 = −0.0272 pH + 0.3182 | 0.985 |
| Methods | Materials | Linear Range (μM) | LOD(μM) | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N, S-CDs | Citric acid and thiourea | 1–10 | 0.20 | [19] |
| N-CDs | Citric acid and glycine | 5–200 | 4.16 | [18] |
| N, S-CDs | Thiourea and citric acid | 1–10 | 0.2 | [19] |
| Green synthesis-CDs | Peanut | 2–10 | 1.9 | [53] |
| GQDs | g-C3N4 | 0.6–300 | 0.15 | [54] |
| MR-CDs | D-glucose and L-tryptophan | 0.2–50 | 0.02 | This work |
| Samples | Added (uM) | Found (uM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | Not detected | – | – |
| 2 | 1.0 | 0.958 | 95.8 | 3.17 |
| 3 | 5.0 | 4.809 | 96.18 | 2.63 |
| 4 | 10.0 | 9.894 | 98.94 | 1.70 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Ma, Y.; Gu, M.; Huo, X.; Ma, S.; Lu, Y.; Ning, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, B.; Feng, Z. Carbon Dots Derived from the Maillard Reaction for pH Sensors and Cr (VI) Detection. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10101924
Ma Z, Ma Y, Gu M, Huo X, Ma S, Lu Y, Ning Y, Zhang X, Tian B, Feng Z. Carbon Dots Derived from the Maillard Reaction for pH Sensors and Cr (VI) Detection. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(10):1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10101924
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhi, Yun Ma, Meiyu Gu, Xiyue Huo, Sainan Ma, Yini Lu, Yao Ning, Xuan Zhang, Bo Tian, and Zhibiao Feng. 2020. "Carbon Dots Derived from the Maillard Reaction for pH Sensors and Cr (VI) Detection" Nanomaterials 10, no. 10: 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10101924
APA StyleMa, Z., Ma, Y., Gu, M., Huo, X., Ma, S., Lu, Y., Ning, Y., Zhang, X., Tian, B., & Feng, Z. (2020). Carbon Dots Derived from the Maillard Reaction for pH Sensors and Cr (VI) Detection. Nanomaterials, 10(10), 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10101924