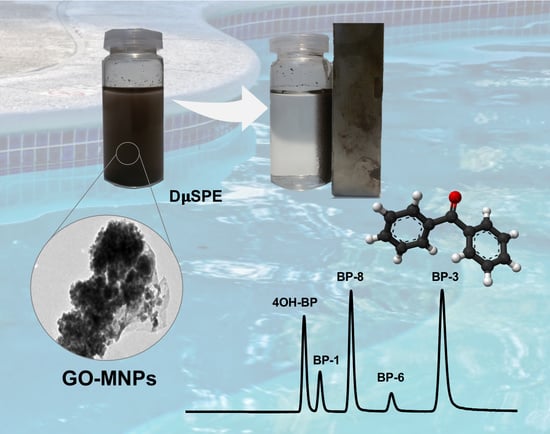
Magnetic Graphene Oxide Composite for the Microextraction and Determination of Benzophenones in Water Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
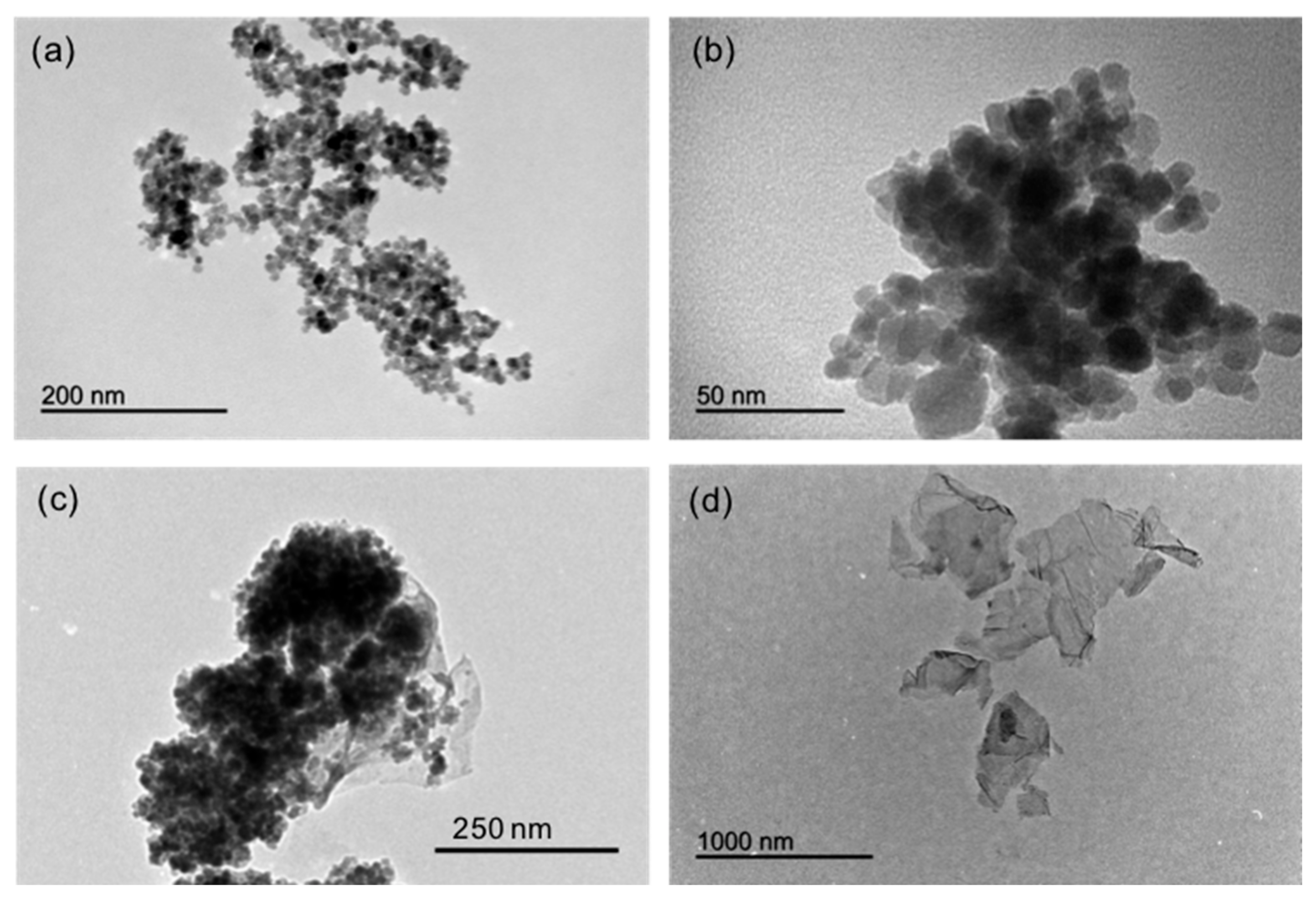
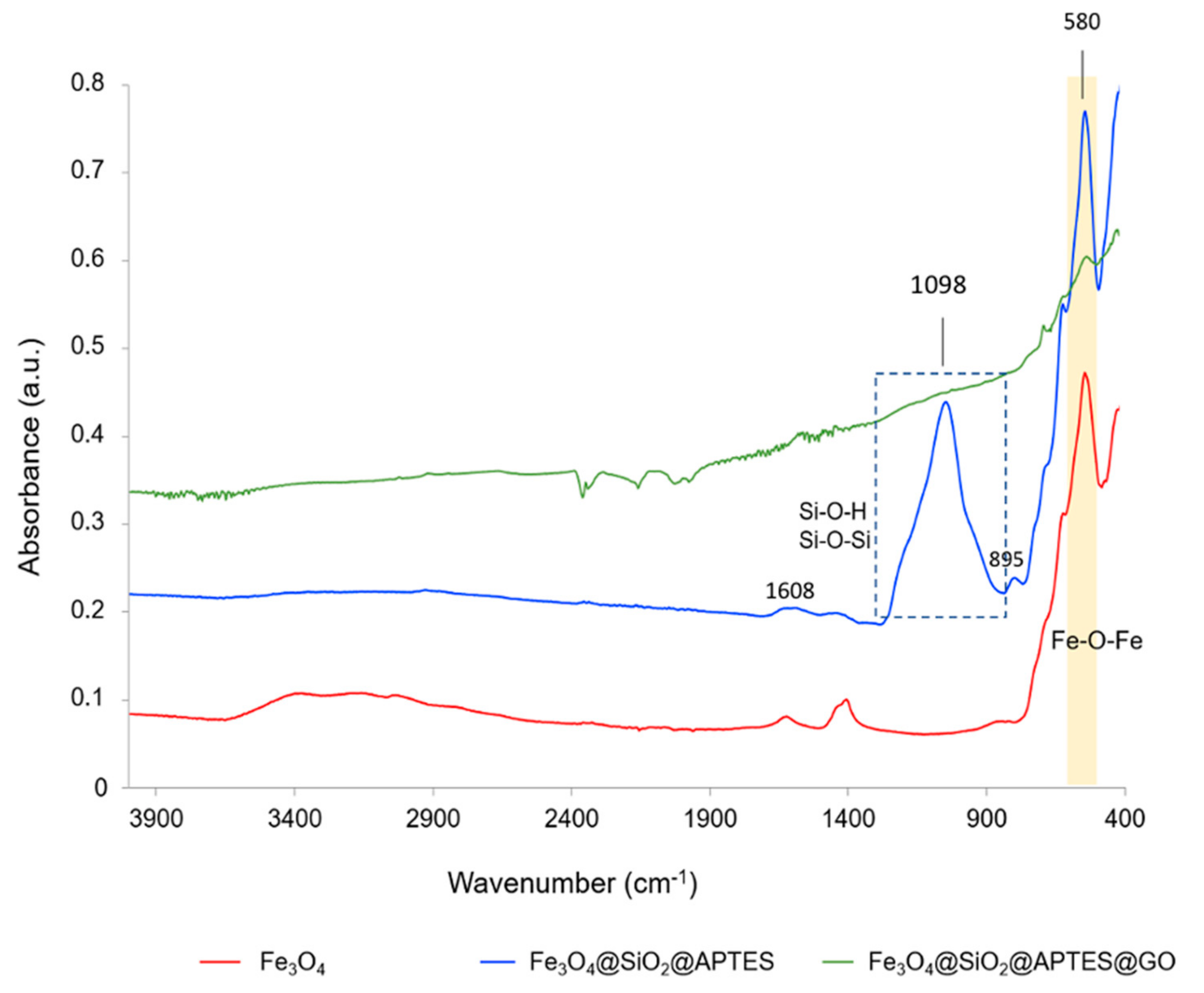
2.2. Characterization of the Nanomaterials
2.3. Chromatographic Systems
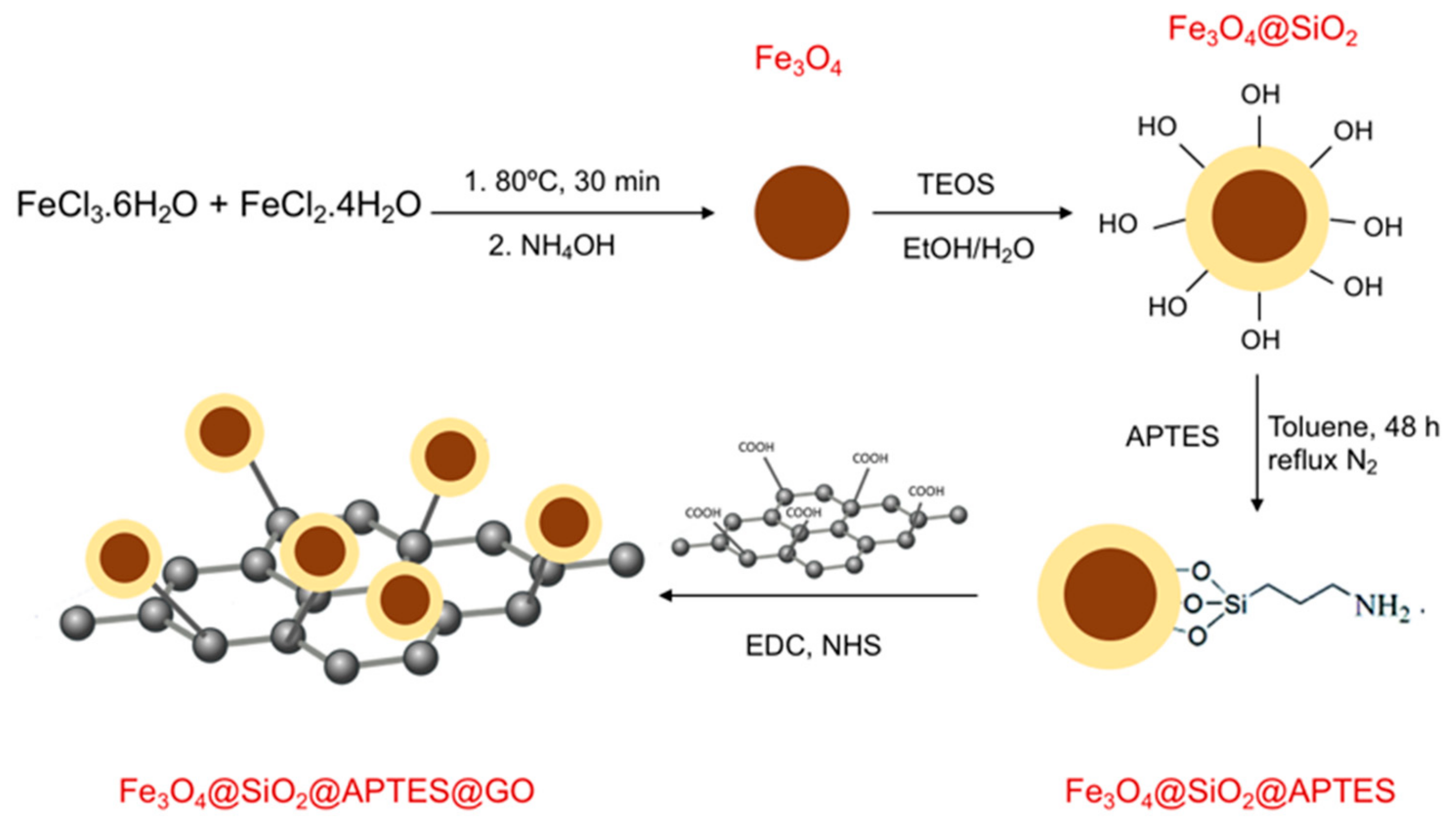
2.4. Synthesis of GO-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.5. Analytical Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Nanomaterials
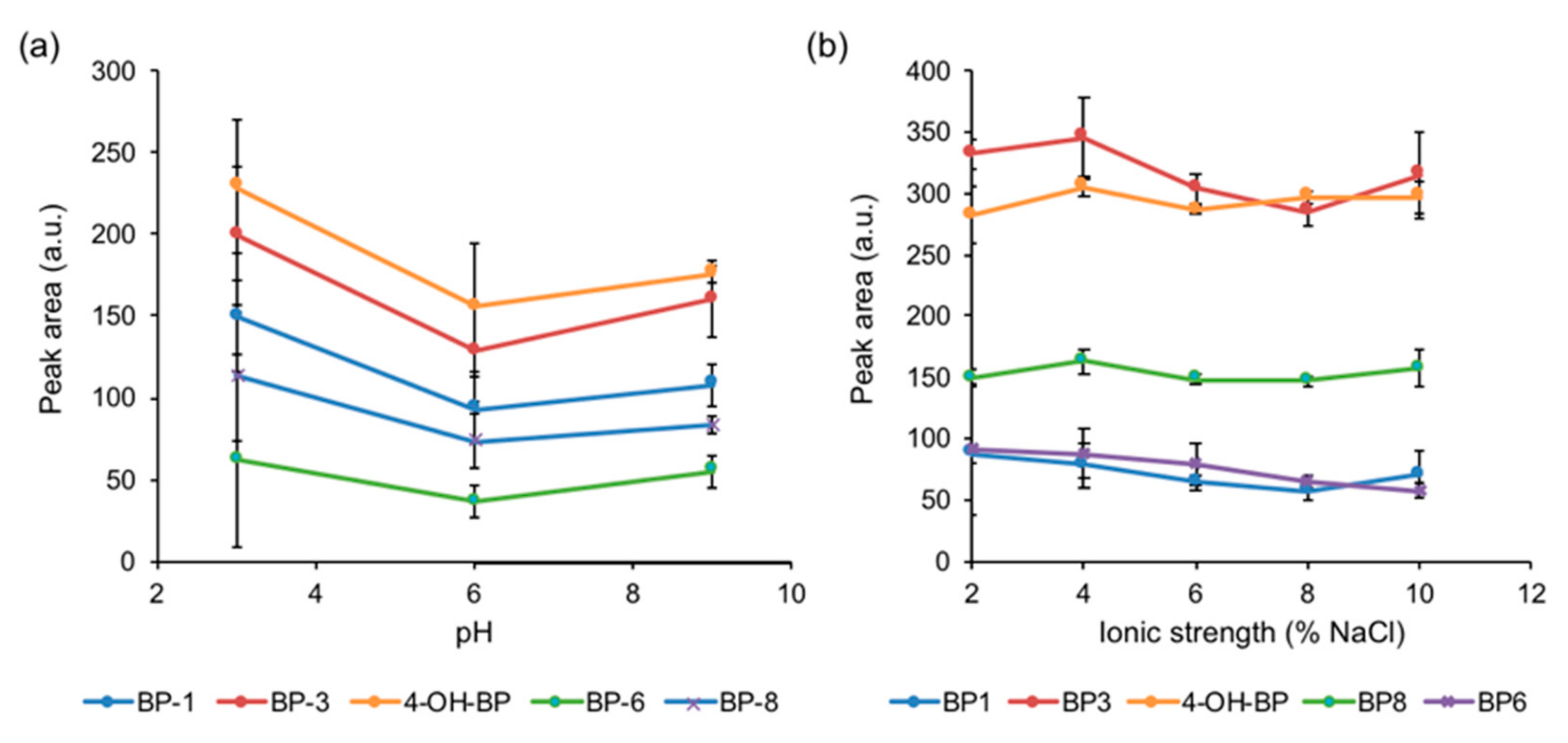
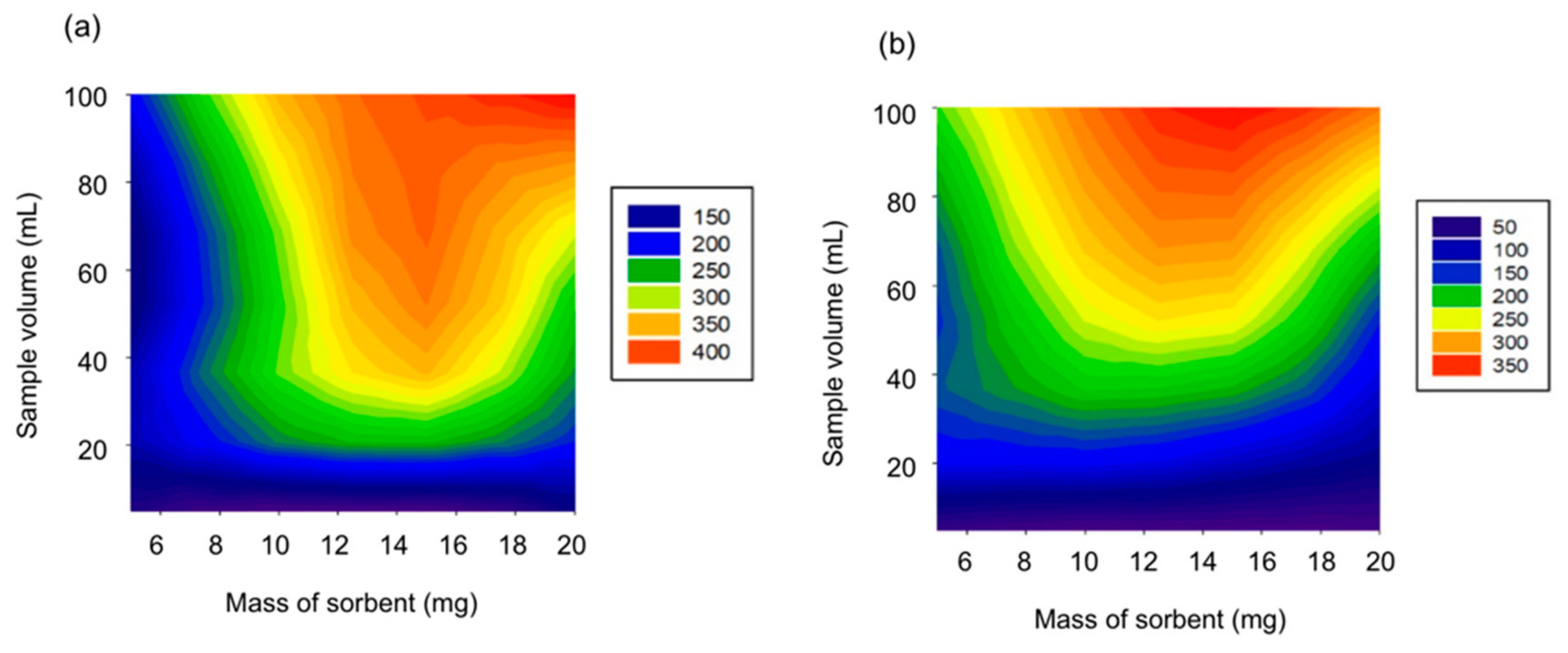
3.2. Study of the Variables Affecting the Microextraction Process
3.3. Analytical Figures of Merit
3.4. Application to Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.; Shi, J.; Jiang, G. Application of graphene in analytical sample preparation. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Lan, F.; Yu, F.; Yu, J. Applications of graphene and related nanomaterials in analytical chemistry. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 2380–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, R.; Zawisza, B.; Malicka, E. Graphene as a new sorbent in analytical chemistry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, G.; Huang, J.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Qiu, J.; Yin, L.; Ruan, W.; et al. A graphene oxide-based polymer composite coating for highly-efficient solid phase microextraction of phenols. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1015, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, J. Fabrication of graphene oxide incorporated polymer monolithic fiber as solid phase microextraction device for determination of organophosphate esters in soil samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1588, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Toffoli, A.L.; Fumes, B.H.; Lanças, F.M. Packed in-tube solid phase microextraction with graphene oxide supported on aminopropyl silica: Determination of target triazines in water samples. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2018, 53, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, X.; Chang, Q.; Liang, W.; Wu, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Micro-solid phase extraction of chlorophenols using reduced graphene oxide functionalized with magnetic nanoparticles and graphitic carbon nitride as the adsorbent. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.J.; Ripoll, L.; Hidalgo, M.; Canals, A. Dispersive micro solid-phase extraction (DµSPE) with graphene oxide as adsorbent for sensitive elemental analysis of aqueous samples by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Talanta 2019, 191, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Pan, S.; Ding, C.; He, J.; Wang, C. Dispersive solid-phase microextraction with graphene oxide based molecularly imprinted polymers for determining bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in environmental water. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1511, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; Cárdenas, S.; Lucena, R. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, I.; Marín-Hernández, J.J.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Solid-phase dispersive microextraction using reduced graphene oxide for the sensitive determination of cadmium and lead in waters. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Magnetic nanoparticles-nylon 6 composite for the dispersive micro solid phase extraction of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1345, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Gallardo, E.M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of bisphenol A from milk using magnetic nylon 6 composite and its final determination by HPLC-UV. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Carmona, F.A.; Alcudia-León, M.C.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Magnetic nanoparticles coated with ionic liquid for the extraction of endocrine disrupting compounds from waters. Microchem. J. 2016, 128, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, I.P.; Chisvert, A.; Canals, A. Dispersive solid-phase extraction based on oleic acid-coated magnetic nanoparticles followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for UV-filter determination in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovesana, S.; Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; Barbera, G.L.; Samperi, R.; Chiozzi, R.Z.; Laganà, A. A new carbon-based magnetic material for the dispersive solid- phase extraction of UV filters from water samples before liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4181–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z. Controlled assembly of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles on graphene oxide. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1446–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Qu, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, G.; Colorado, H.A.; Yu, J.; Sun, L.; et al. Magnetic Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites: Nanoparticles Growth Mechanism and Property Analysis. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 9478–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, N.; Ma, H.; Ye, M. One Step Synthesis of Graphene Oxide-Magnetic Nanoparticle Composite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Fan, J.; Ma, D.; Zhang, L.; Leung, C.; Chan, H.L. The attachment of Fe3O4 nanoparticles to graphene oxide by covalent bonding. Carbon 2010, 48, 3139–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegret, N.; Criado, A.; Prato, M. Recent advances of Graphene-based hybrids with magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, M.B.; Santos, T.R.T.; Silva, M.F.; Vieria, M.F.; Bergamasco, R.; Hamoudi, S. Graphene oxide impregnated with iron oxide nanoparticles for the removal of atrazine from the aqueous medium. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2653–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Gu, W.; Shi, X.; Xian, Y. Recyclable removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by reduced graphene oxide–magnetic nanoparticles: Adsorption and desorption. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 2014, 421, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyestani, M.R.; Shemirani, F.; Mozaffari, S.; Alvand, M. A magnetized graphene oxide modified with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole as a selective nanosorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of gold (III), palladium (II) and silver (I). Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2871–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirandish, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Pourebrahim, F. Design of a new technique based on combination of ultrasound waves via magnetite solid phase and cloud point microextraction for determination of Cr (III) ions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Xiao, C.; Chen, L.; Yang, P.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Rapid Determination of Trace Sulfonamides in Milk by Graphene Oxide-Based Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction Coupled with HPLC–MS/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feriduni, B.; Mohebbi, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Namvar, M. Magnetic graphene oxide–based solid-phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the simultaneous preconcentration of four typical pesticide residues in fruit juice and pulp. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 2742–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPS. Assessment and Analysis, EPA/630/R-36, 012; U.S. EPS: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Daston, G.P.; Cook, J.C.; Kavlock, R.J. Uncertainties for endocrine disruptors: Our view on progress. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 74, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Díaz, I.; Zafra-Gómez, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Navalón, A. Analytical methods for the determination of personal care products in human samples: An overwiew. Talanta 2014, 129, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; Benedé, J.L.; Salvador, A. Current trends on the determination of organic UV filters in environmental water samples based on microextraction techniques—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1034, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinia, A.; Dadkhah, S.; Baradaran Kayyal, T.; Jabbari, A. Design of a surface-immobilized 4-nitrophenol molecularly imprinted polymer via pre-grafting amino functional materials on magnetic nanoparticles. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1364, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Martínez, S.; López-Lorente, A.I.; Valcárcel, M. Graphene quantum dots sensor for the determination of graphene oxide in environmental water samples. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12279–12284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakapongpan, S.; Tuantranont, A.; Pooarpom, R.P. Magnetic nanoparticle-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as a novel bioelectrode for mediatorless-membraneless glucose enzymatic biofuel cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Fu, S. A novel approach for preparation of thermoresponsive microspheres with core-shell structure. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Hong, R.Y.; Wang, L.S.; Guo, L.; Li, H.Z.; Ding, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, D.G. Synthesis of Fe3O4/APTES/PEG diacid functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for MR imaging. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2008, 328, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourpa, I.; Douziech-Eyrolles, L.; Ngaboni-Okassa, L.; Fouquenet, J.F.; Cohen-Jonathan, S.; Soucé, M.; Marchais, H.; Dubois, P. Molecular composition of iron oxide nanoparticles, precursors for magnetic drug targeting, as characterized by confocal Raman microspectroscopy. Analyst 2005, 130, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavov, L.; Abrashev, M.V.; Merodiiska, T.; Gelev, C.; Vandenberghe, R.E.; Markova-Deneva, I.; Nedkov, I. Raman spectroscopy investigation of magnetite nanoparticles in ferrofluids. J. Magnet. Magn. Mat. 2010, 322, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.M.; Oh, Y.S.; Yang, Y.H.; Lim, Y.S.; Yoon, D.H.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Ruoff, R.S. Unoxidized graphene/alumina nanocomposite: Fracture- and wear-resistance effects of graphene on alumina matrix. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/238 of 10 February 2017 amending Annex VI to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on cosmetic products. Official Journal of the European Union, 11.2.2017, L36/37. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32017R0238&rid=7 (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Jiménez-Díaz, I.; Iribarne-Durán, L.M.; Ocón, O.; Salamanca, E.; Fernández, M.F.; Olea, N.; Barranco, E. Determination of personal care products -benzophenones and parabens- in human menstrual blood. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1035, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
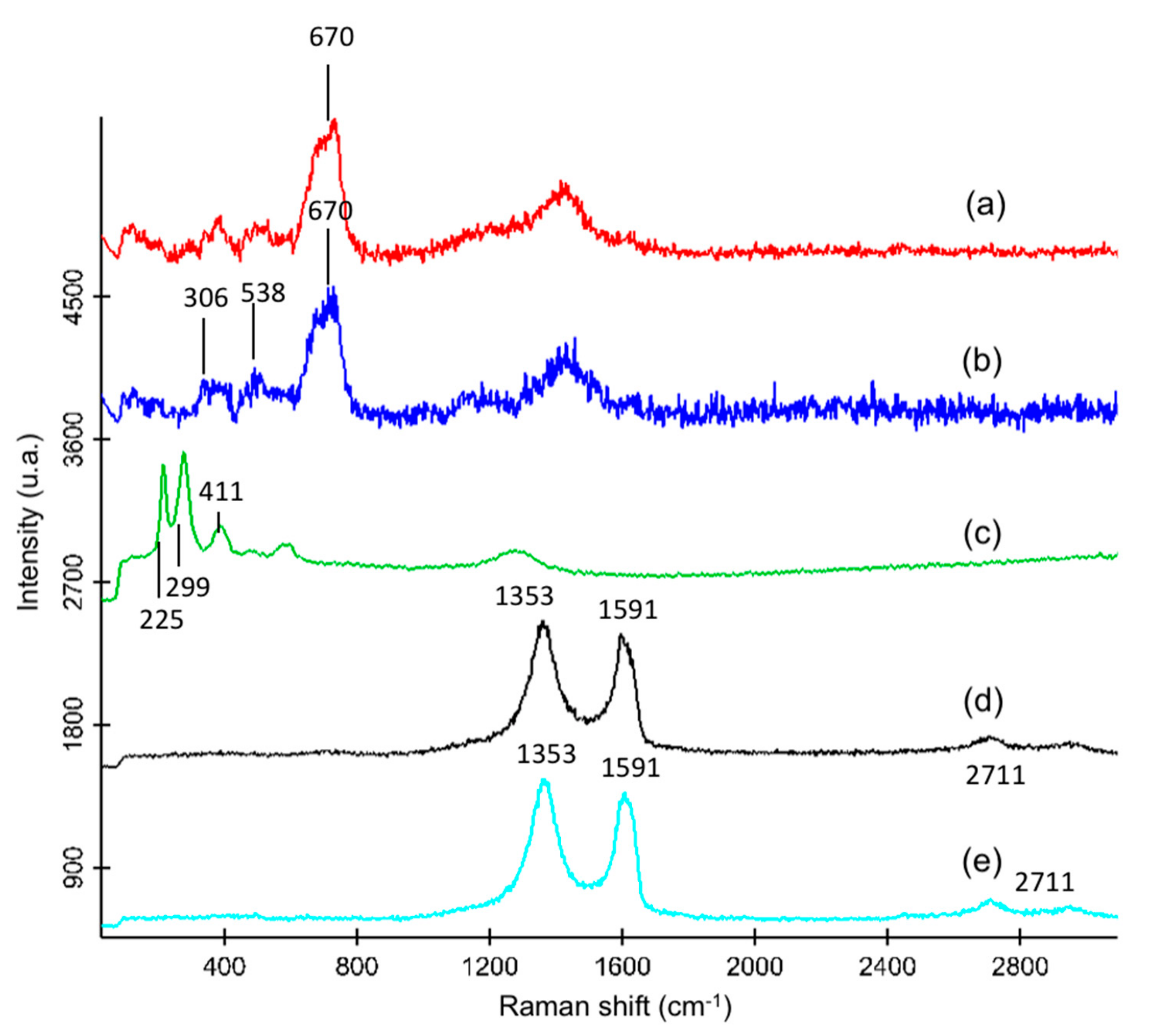
| Compound | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Fragmentor Voltage (V) | Product Ion (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | Identification Transition | Quantitation Transition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP-1 | 215 | 115 | 137 | 20 | 215 → 105 | 215 → 137 |
| 105 | 20 | |||||
| BP-3 | 229.1 | 125 | 151 | 20 | 229.1 → 105 | 229.1 → 151 |
| 105 | 20 | |||||
| BP-6 | 275 | 120 | 151 | 20 | 275 → 95.1 | 275 → 151 |
| 95.1 | 45 | |||||
| BP-8 | 244.9 | 110 | 151 | 20 | 244.9 → 151 | 244.9 → 121 |
| 121 | 20 | |||||
| 4-OH-BP | 199 | 105 | 121 | 20 | 199 → 77.2 | 199 → 121 |
| 77.2 | 45 | |||||
| BP-3-d5 | 234 | 135 | 150.9 | 20 | 234 → 110 | 234 → 150.9 |
| 110 | 25 |
| Variable | Initial Value | Interval Studied | Selected Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Not adjusted | 3–12 | 3 |
| Ionic strength (%NaCl, w/v) | 0 | 0–10 | 4 |
| Nanocomposite amount (mg) | 10 | 5–20 | 20 |
| Sample volume (mL) | 20 | 5–100 | 100 |
| Type of agitation | Mechanical | Mechanical, ultrasounds | Ultrasound + mechanical |
| Eluent | Methanol | Methanol, acetone and acetonitrile | Methanol |
| Eluent volume (µL) | 500 | 500–1000 | 500 |
| Analyte | LOD (µg·L−1) | LOQ (µg·L−1) | R2 | RSD Intra-Day, n = 5 (% RSD) | Accuracy (% RR a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP-1 | 2.5 | 8.3 | 0.996 | 2.4 | 90 ± 2 |
| BP-3 | 2.9 | 9.7 | 0.998 | 1.3 | 105 ± 2 |
| BP-6 | 7.0 | 23.3 | 0.995 | 6.4 | 102 ± 7 |
| BP-8 | 4.0 | 13.3 | 0.997 | 4.3 | 86 ± 4 |
| 4-OH-BP | 8.2 | 27.3 | 0.995 | 9.8 | 93 ± 9 |
| Sample | BP-1 | BP-3 | BP-6 | BP-8 | 4-OH-BP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swimming pool 1 | 28.7 ± 0.7 | 33.2 ± 0.4 | 39 ± 2 | 23 ± 1 | Detected |
| Swimming pool 2 | Detected | 14.3 ± 0.2 | 25 ± 2 | 16.2 ± 0.7 | Detected |
| Incorporation of GO | Extraction Technique | Analyte | Sample | Analytical Technique | LOD | RR (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO incorporated in POE 1 as fiber coating material | SPME | Phenols | River water | (HS)-SPME-CG-MS | 0.12–1.36 ng·L−1 | 81–113 | [4] |
| GO in polymer monolithic fiber | SPME | Organophosphate esters | Soil | HS-SPME-GC/FPD | 0.03–0.24 ng·g−1 | 80.1–105.6 | [5] |
| GO supported aminopropyl silica | Packed in-tube SPME | Triazines | Ground and mineral water | HPLC–MS/MS | 1.1–2.9 ng·L−1 | 90.8–111 | [6] |
| Fe3O4@rGO-g-C3N4 filled in propylene hollow tube | MSPE 2 | Chlorophenols | Toner | HPLC-UV | 0.2–0. 3 μg·Kg−1 | 80.5–104 | [7] |
| GO-MIPs 3 | DμSPE | Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | Environmental water | HPLC-UV | 0.92 μg·L−1 | 82–92 | [9] |
| Fe3O4@GO as adsorbent (coprecipitation) | MSPE | Sulfonamides | Milk | HPLC-MS/MS | 0.02–0.13 μg·L−1 | 73.4–97.4 | [26] |
| Magnetic graphene oxide (coprecipitation) | SPE + DLLME | Pesticides | Fruit juice and pulp | GC-FID | 1–6 μg·Kg−1 | 69–81 | [27] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2@APTES@GO | DμSPE | Benzophenones | Swimming pool water | HPLC-MS/MS | 2.5–8.2 μg·L−1 | 86–105 | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medina, A.; Casado-Carmona, F.A.; López-Lorente, Á.I.; Cárdenas, S. Magnetic Graphene Oxide Composite for the Microextraction and Determination of Benzophenones in Water Samples. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010168
Medina A, Casado-Carmona FA, López-Lorente ÁI, Cárdenas S. Magnetic Graphene Oxide Composite for the Microextraction and Determination of Benzophenones in Water Samples. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(1):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010168
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedina, Alejandro, Francisco Antonio Casado-Carmona, Ángela I. López-Lorente, and Soledad Cárdenas. 2020. "Magnetic Graphene Oxide Composite for the Microextraction and Determination of Benzophenones in Water Samples" Nanomaterials 10, no. 1: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010168
APA StyleMedina, A., Casado-Carmona, F. A., López-Lorente, Á. I., & Cárdenas, S. (2020). Magnetic Graphene Oxide Composite for the Microextraction and Determination of Benzophenones in Water Samples. Nanomaterials, 10(1), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010168