The Biomedical Limitations of Magnetic Nanoparticles and a Biocompatible Alternative in the Form of Magnetotactic Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
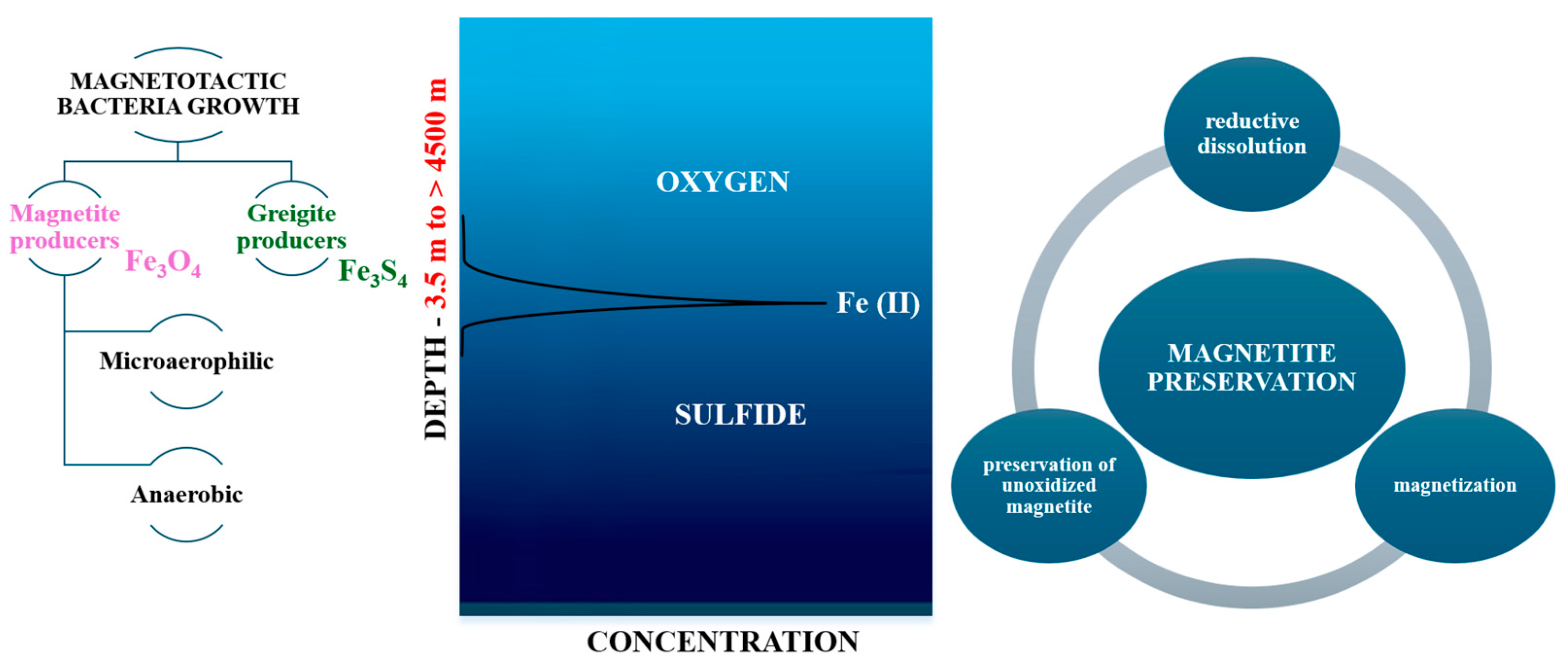
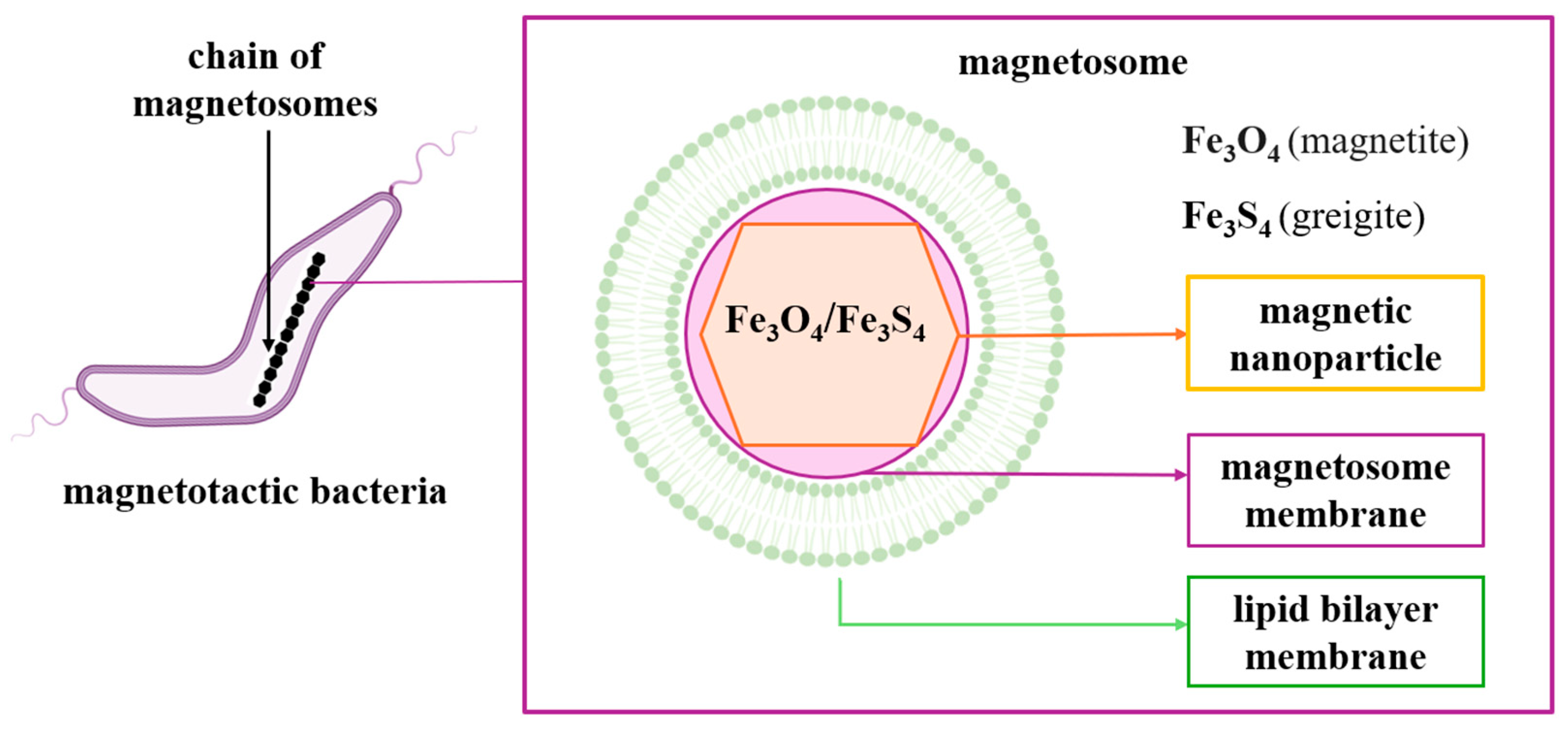
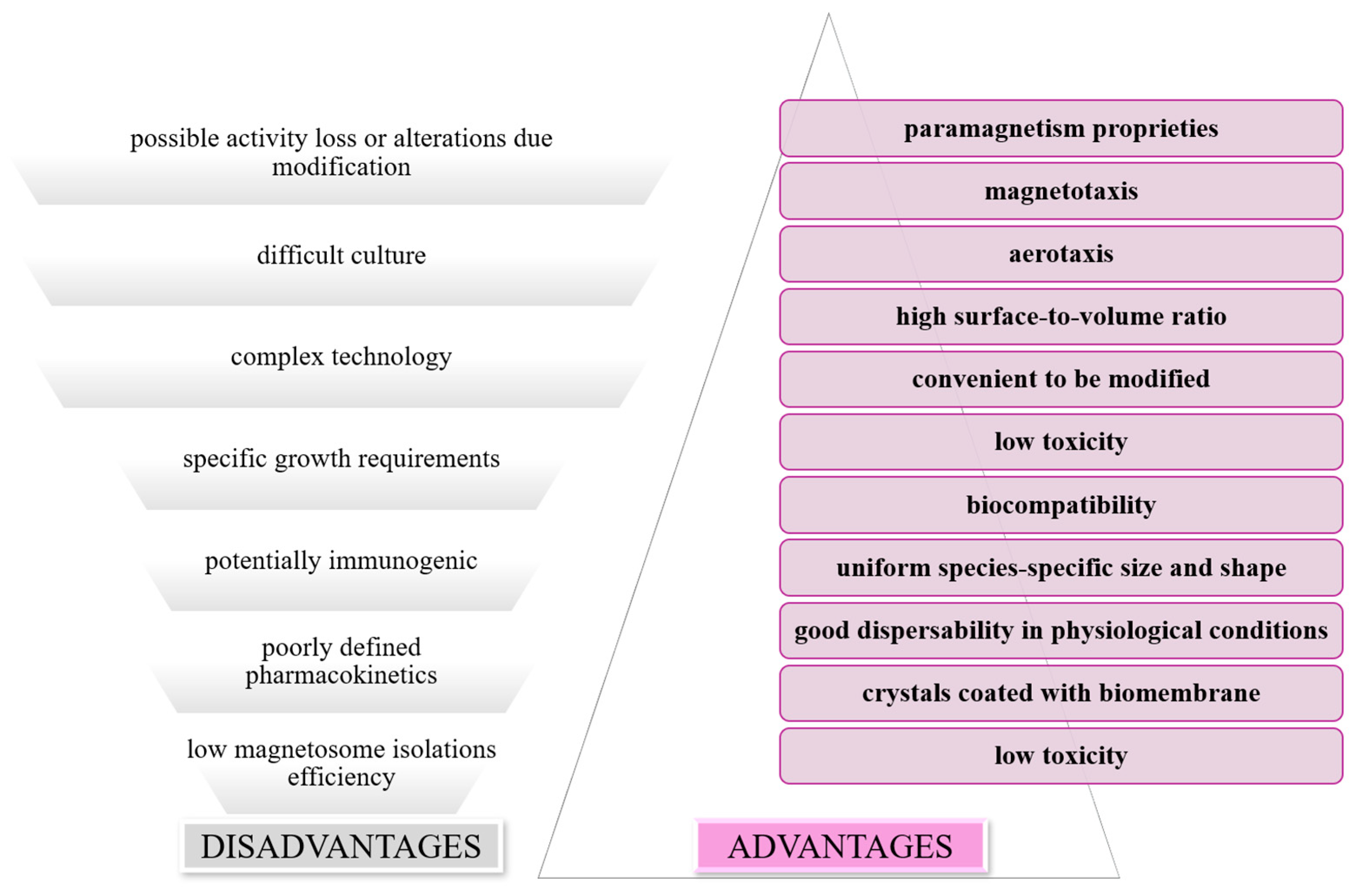
2. Magnetotactic Bacteria
2.1. General Considerations
2.2. The Presence in Nature and the Behavior of MTB
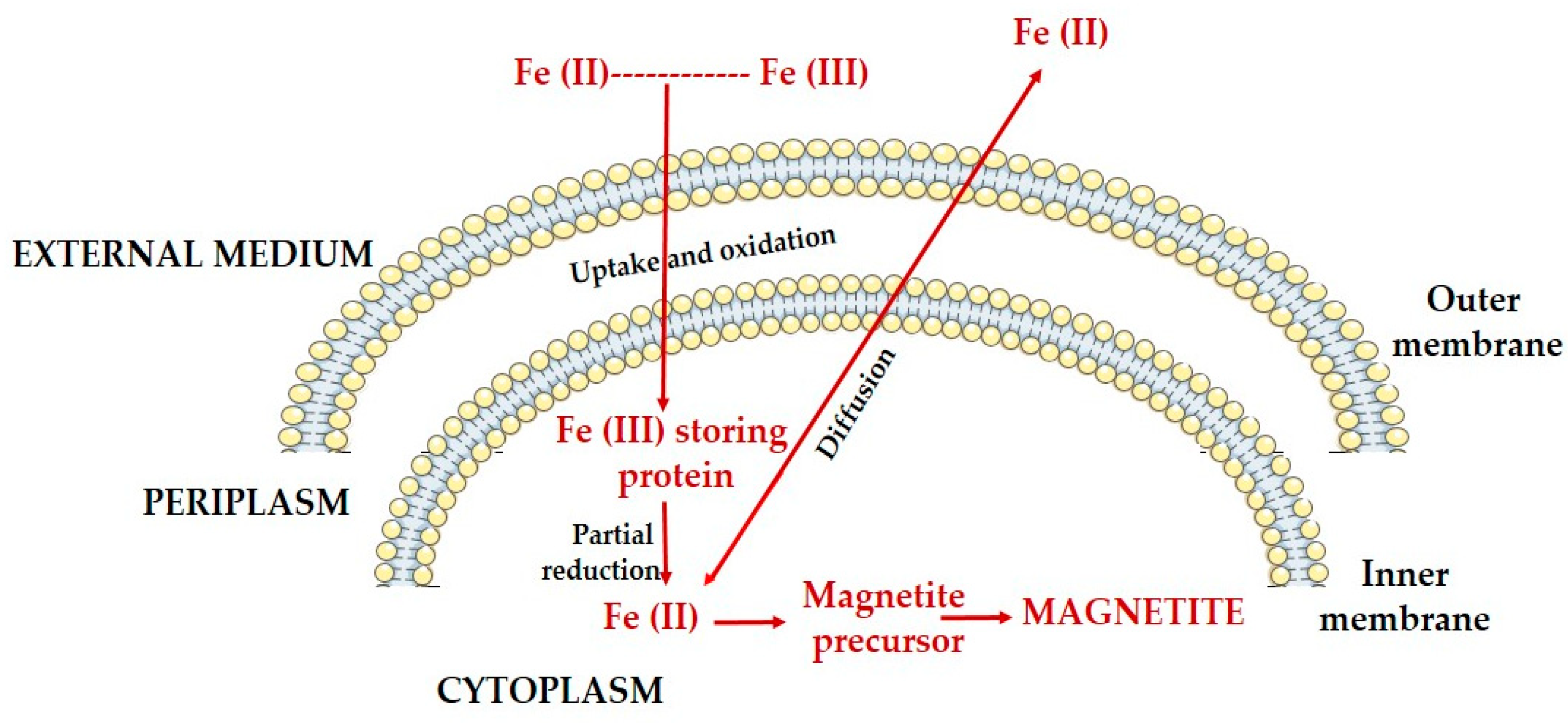
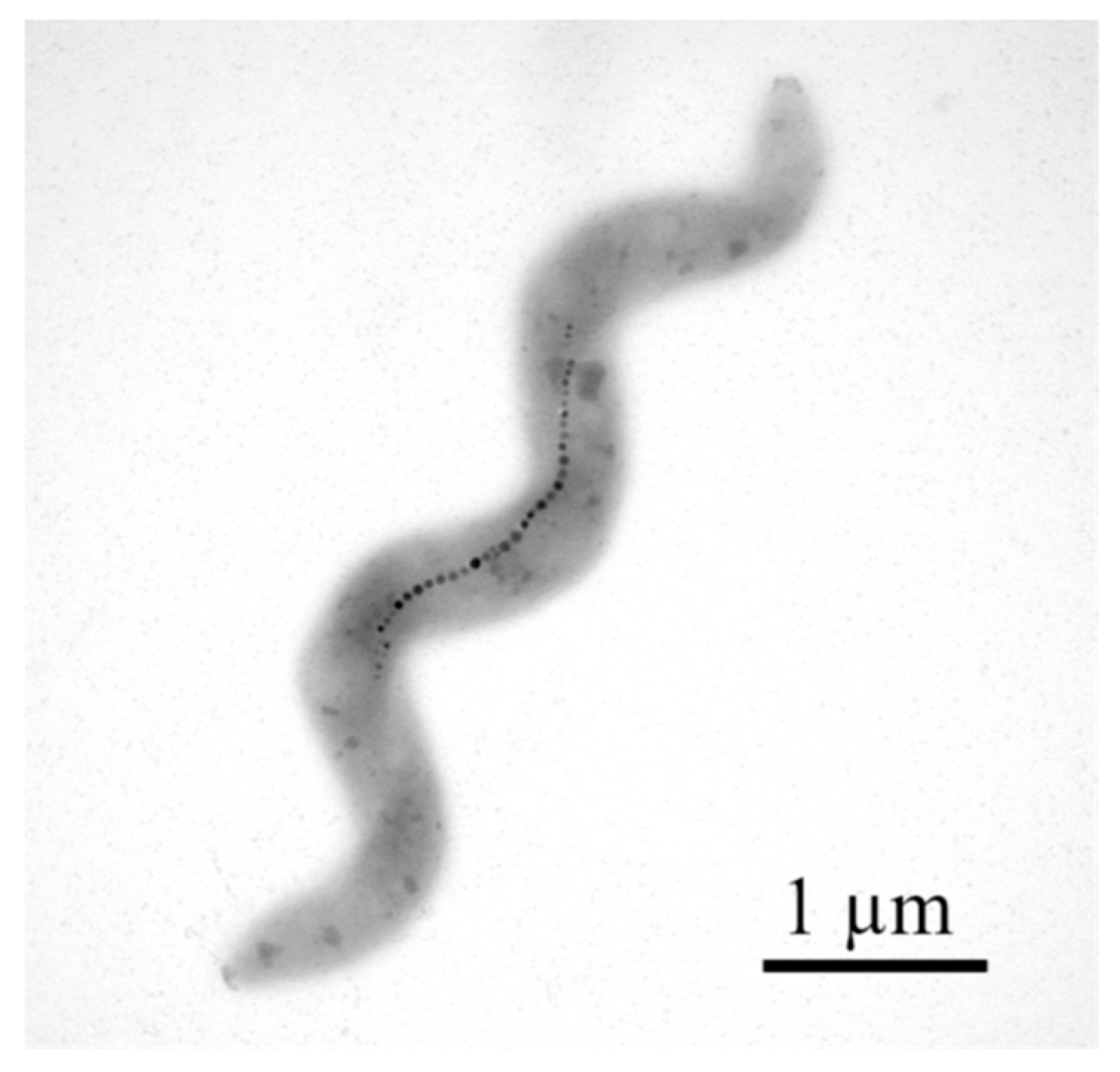
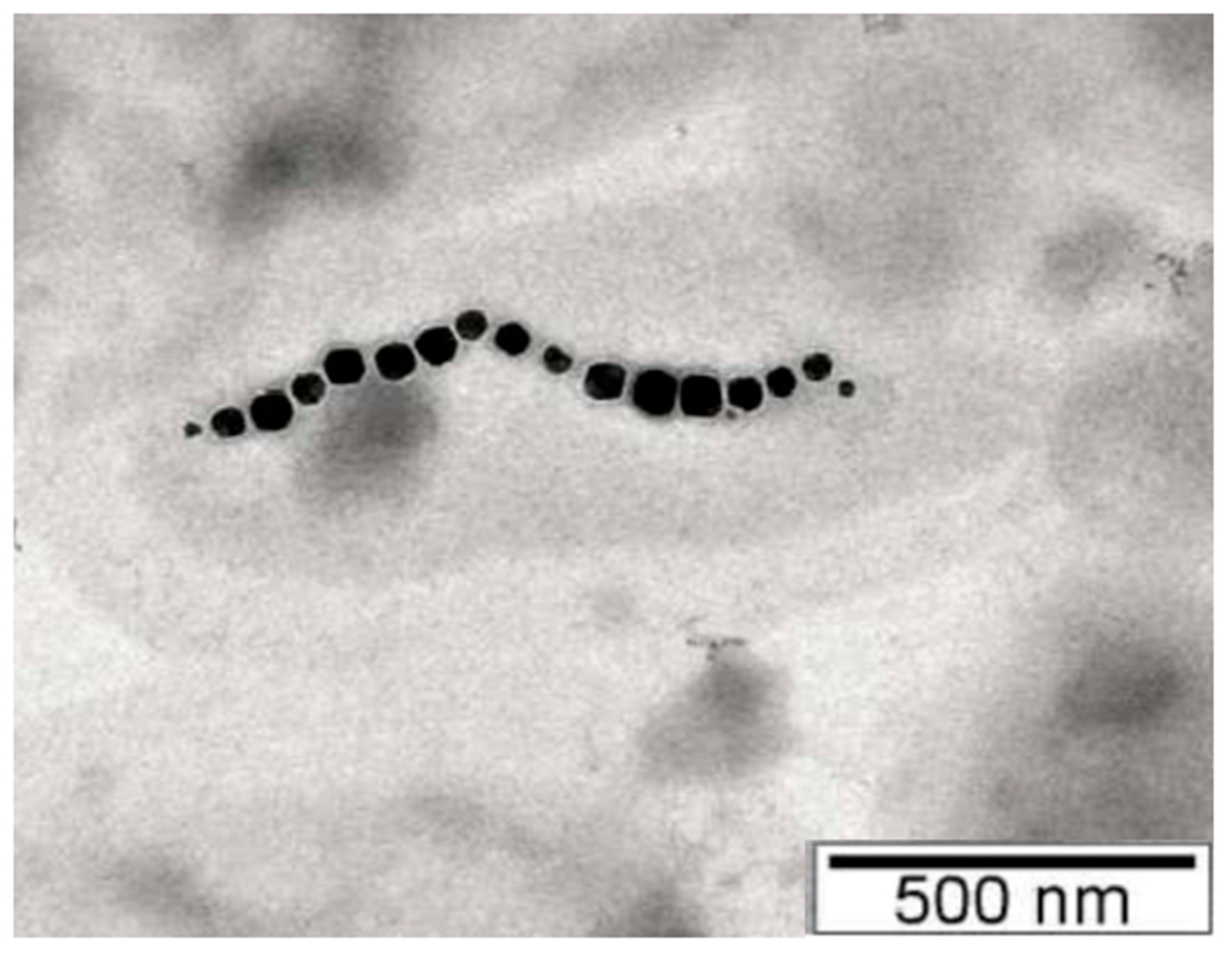
2.3. Magnetosomes: Structure, Formation, Biomineralization
2.4. Cultivation of Magnetotactic Bacteria
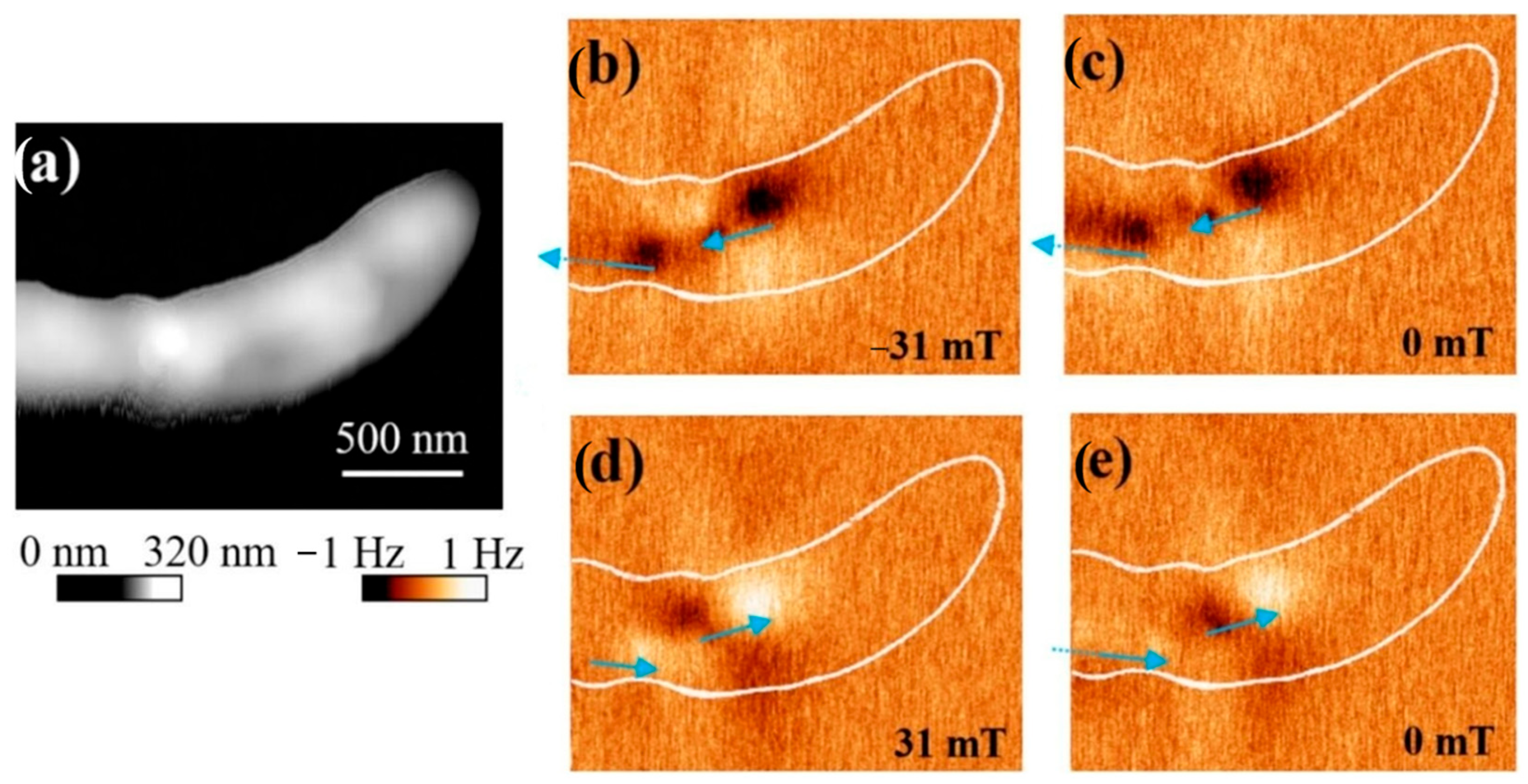
2.5. Characterization of Magnetotactic Bacteria
3. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Biofunctionalization and Medical Applications
3.1. Biofunctionalization of MNPs
3.2. Applications of MNPs in the Medical Field
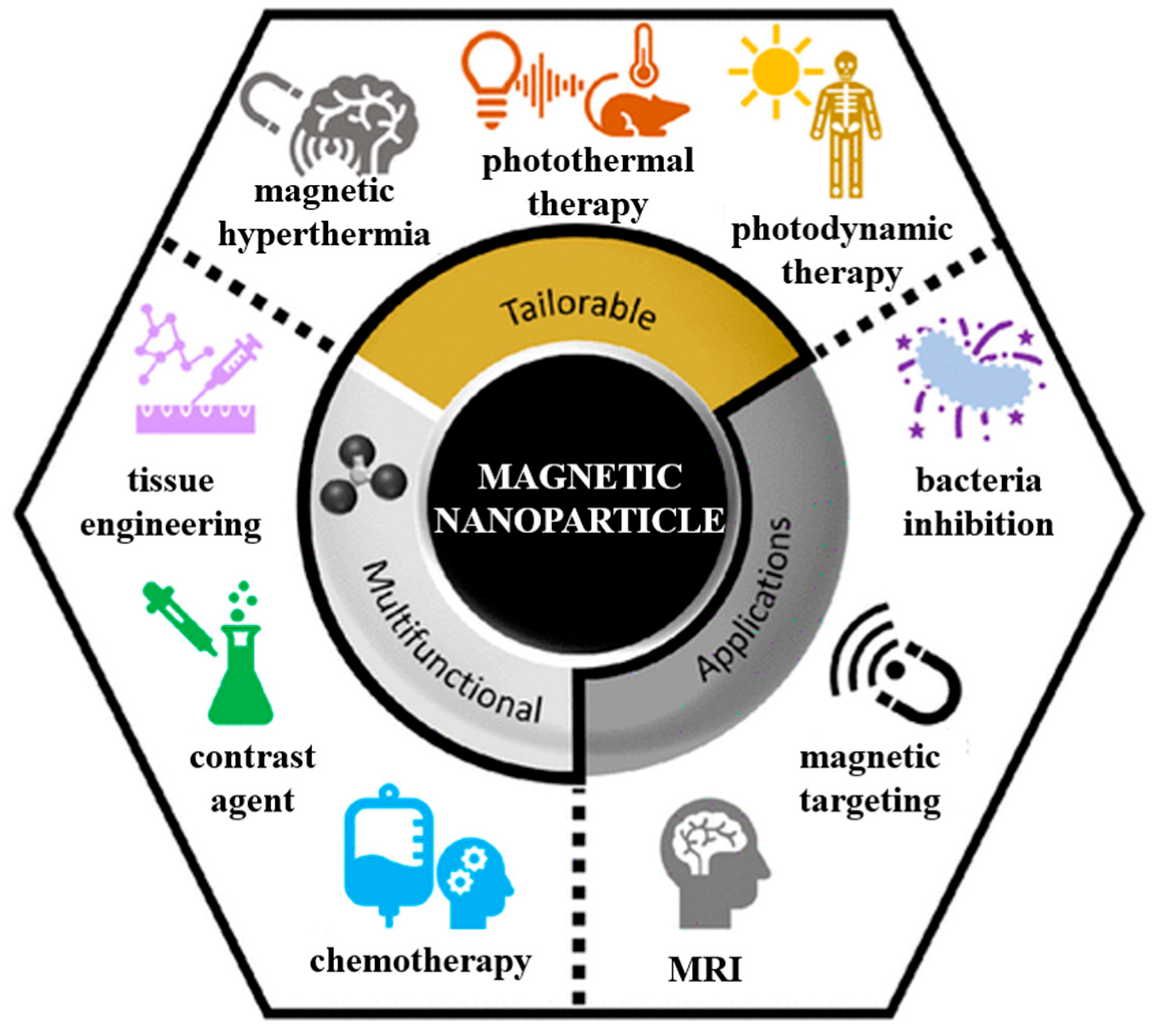
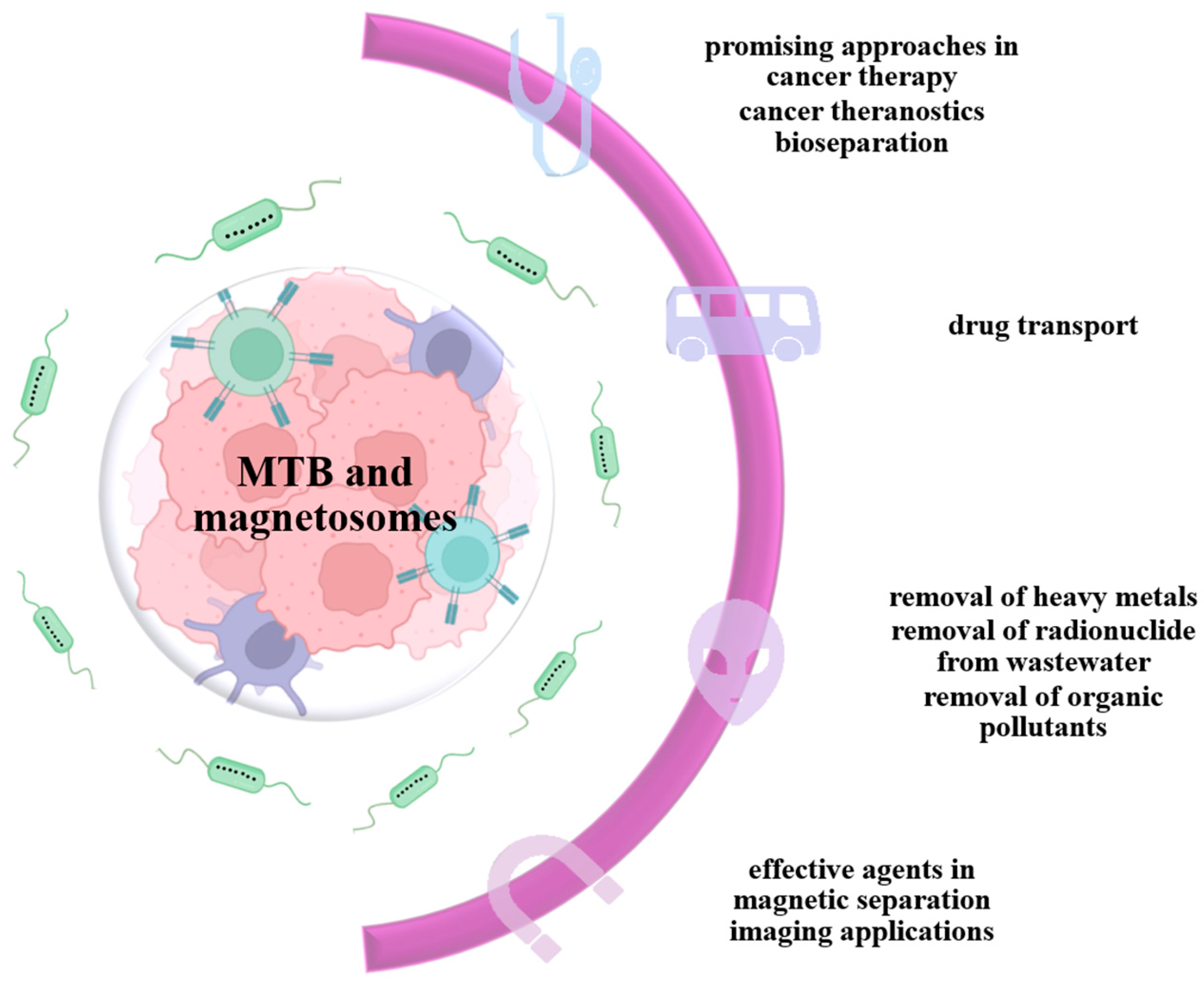
4. Medical Applications of Magnetotactic Bacteria
4.1. MTB and Magnetosomes in Drug Delivery and Anticancer Therapy
4.2. Magnetosomes in Hyperthermia
4.3. MTB and Magnetosomes as Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents
4.4. MTB and Magnetosomes in Cell Separation
4.5. MTB and Magnetosomes in the Control of Pathogens
4.6. MTB and Magnetosomes in DNA/Antigen Detection Assays and Enzyme Immobilization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szczesna-Antczak, M.; Kazimierczak, J.; Antczak, T. Nanotechnology-Methods of Manufacturing Cellulose Nanofibres. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2012, 20, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, S. A review on role of nanostructures in drug delivery system. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2014, 36, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed Hamouda, I. Current perspectives of nanoparticles in medical and dental biomaterials. J. Biomed. Res. 2012, 26, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Chen, K.; Chen, X. Production, Modification and Bio-Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles Gestated by Magnetotactic Bacteria. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakemore, R.P. Magnetotactic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1982, 36, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylinski, D.A.; Frankel, R.B. Magnetosome formation in prokaryotes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Nagard, L.; Morillo-López, V.; Fradin, C.; Bazylinski, D.A. Growing Magnetotactic Bacteria of the Genus Magnetospirillum: Strains MSR-1, AMB-1 and MS-1. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, e58536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Cabral, A.; Verdan, M.; Presciliano, R.; Silveira, F.; Correa, T.; Abreu, F. Large-Scale Cultivation of Magnetotactic Bacteria and the Optimism for Sustainable and Cheap Approaches in Nanotechnology. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeili, A. Molecular mechanisms of magnetosome formation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lefèvre, C.T.; Bazylinski, D.A. Ecology, Diversity, and Evolution of Magnetotactic Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, S.; Bazylinski, D.A. Magnetotactic Bacteria. In The Prokaryotes: Volume 2: Ecophysiology and Biochemistry; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 842–862. ISBN 978-0-387-30742-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wacker, R.; Ceyhan, B.; Alhorn, P.; Schueler, D.; Lang, C.; Niemeyer, C.M. Magneto immuno-PCR: A novel immunoassay based on biogenic magnetosome nanoparticles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Shimon, S.; Stein, D.; Zarivach, R. Current view of iron biomineralization in magnetotactic bacteria. J. Struct. Biol. X 2021, 5, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebe, R.; Schüler, D. Magnetosome biogenesis in magnetotactic bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, J.J.; Suthindhiran, K. Magnetotactic bacteria and magnetosomes–Scope and challenges. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschdorf, O.; Forstner, Y.; Kolinko, I.; Uebe, R.; Plitzko, J.M.; Schüler, D. Genetic and Ultrastructural Analysis Reveals the Key Players and Initial Steps of Bacterial Magnetosome Membrane Biogenesis. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Schüler, D. Biogenic nanoparticles: Production, characterization, and application of bacterial magnetosomes. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, S2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shah, T.; Ullah, R.; Zhou, P.; Guo, M.; Ovais, M.; Tan, Z.; Rui, Y. Review on Recent Progress in Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Diverse Applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 629054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüler, D. Genetics and cell biology of magnetosome formation in magnetotactic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 654–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strbak, O.; Hnilicova, P.; Gombos, J.; Lokajova, A.; Kopcansky, P. Magnetotactic Bacteria: From Evolution to Biomineralization and Biomedical Applications. Minerals 2022, 12, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, M.; Mathon, F.P.; Monteil, C.L.; Busigny, V.; Lefevre, C.T. Iron-biomineralizing organelle in magnetotactic bacteria: Function, synthesis and preservation in ancient rock samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3611–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calugay, R.J.; Takeyama, H.; Mukoyama, D.; Fukuda, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kanoh, K.; Matsunaga, T. Catechol siderophore excretion by magnetotactic bacterium Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Okamura, Y.; Calugay, R.J.; Takeyama, H.; Matsunaga, T. Global gene expression analysis of iron-inducible genes in Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, M.; Busigny, V.; Louvat, P.; Tharaud, M.; Gélabert, A.; Cartigny, P.; Carlut, J.; Isambert, A.; Durand-Dubief, M.; Ona-Nguema, G.; et al. Iron uptake and magnetite biomineralization in the magnetotactic bacterium Magnetospirillum magneticum strain AMB-1: An iron isotope study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 232, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josts, I.; Veith, K.; Normant, V.; Schalk, I.J.; Tidow, H. Structural insights into a novel family of integral membrane siderophore reductases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101952118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareev, K.G.; Grouzdev, D.S.; Kharitonskii, P.V.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Kosterov, A.; Koziaeva, V.V.; Levitskii, V.S.; Multhoff, G.; Nepomnyashchaya, E.K.; Nikitin, A.V.; et al. Magnetic Properties of Bacterial Magnetosomes Produced by Magnetospirillum caucaseum SO-1. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, J.; Morin, G.; Menguy, N.; Perez Gonzalez, T.; Widdrat, M.; Cosmidis, J.; Faivre, D. Magnetotactic bacteria form magnetite from a phosphate-rich ferric hydroxide via nanometric ferric (oxyhydr)oxide intermediates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14883–14888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrier, D.M.; Cerdá-Doñate, E.; Park, Y.; Cacho-Nerin, F.; Gomez-Gonzalez, M.; Uebe, R.; Faivre, D. Synchrotron-Based Nano-X-Ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Revealing Intracellular Heterogeneity of Iron Species in Magnetotactic Bacteria. Small Sci. 2022, 2, 2100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, M.; Su, Q.; Jensen, M.M.; Zhang, Y. Electroactivity of the magnetotactic bacteria Magnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1 and Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 18, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, N.; Aliofkhazraei, M. Advances in the determination of trace amounts of iron cations through electrochemical methods: A comprehensive review of principles and their limits of detection. Talanta 2024, 277, 126365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakaki, A.; Nakazawa, H.; Nemoto, M.; Mori, T.; Matsunaga, T. Formation of magnetite by bacteria and its application. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 977–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yao, H.; Chu, S.; Song, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, W. Magnetotactic bacteria: Characteristics and environmental applications. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.C.V.; Abreu, F.; Silva, K.T.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Lins, U. Magnetotactic Bacteria as Potential Sources of Bioproducts. Marine Drugs 2015, 13, 389–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareev, K.G.; Grouzdev, D.S.; Kharitonskii, P.V.; Kosterov, A.; Koziaeva, V.V.; Sergienko, E.S.; Shevtsov, M.A. Magnetotactic Bacteria and Magnetosomes: Basic Properties and Applications. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zablotskii, V.; Yurchenko, V.; Kamysa, Y.; Chelombetskaya, M. Calculations of magnetic susceptibility of magnetotactic bacteria culture. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 234, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, S.; Lefèvre, C.T.; Bennet, M.; Faivre, D. Swimming with magnets: From biological organisms to synthetic devices. Phys. Rep. 2019, 789, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, S.; Faivre, D. Magnetotactic bacteria. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2016, 225, 2173–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, M.; Guyodo, Y.; Guyot, F.; Gatel, C.; Menguy, N.; Chebbi, I.; Haye, B.; Durand-Dubief, M.; Alphandery, E.; Brayner, R.; et al. Magnetic-field induced rotation of magnetosome chains in silicified magnetotactic bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Xu, S.; Tao, T.; Qian, J.; Cui, Q.; Rehman, S.U.; Zhu, X.; Chen, R.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; et al. Magnetosome-inspired synthesis of soft ferrimagnetic nanoparticles for magnetic tumor targeting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2211228119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, C.; Keller, S.; Toro-Nahuelpan, M.; Dorscht, P.; Gross, W.; Laumann, M.; Gekle, S.; Zimmermann, W.; Schüler, D.; Kress, H. Measurement of the magnetic moment of single Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense cells by magnetic tweezers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C.; Chambel, L.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Ferreira, L.P.; Cruz, M.M. Magnetotactic Bacteria: Magnetism Beyond Magnetosomes. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience 2018, 17, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcano, L.; Orue, I.; Gandia, D.; Gandarias, L.; Weigand, M.; Abrudan, R.M.; García-Prieto, A.; García-Arribas, A.; Muela, A.; Fdez-Gubieda, M.L.; et al. Magnetic Anisotropy of Individual Nanomagnets Embedded in Biological Systems Determined by Axi-asymmetric X-ray Transmission Microscopy. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 7398–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M.; Janke, V.; Sievers, S.; Siegner, U.; Schüler, D.; Heyen, U. Scanning force microspy study of biogenic nanoparticles for medical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 290–291, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakova, O.; Puttock, R.; Barton, C.; Corte-León, H.; Jaafar, M.; Neu, V.; Asenjo, A. Frontiers of magnetic force microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 060901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués-Marchán, J.; Jaafar, M.; Ares, P.; Gubieda, A.G.; Berganza, E.; Abad, A.; Fdez-Gubieda, M.L.; Asenjo, A. Magnetic imaging of individual magnetosome chains in magnetotactic bacteria. Biomater. Adv. 2024, 163, 213969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyen, U.; Schüler, D. Growth and magnetosome formation by microaerophilic Magnetospirillum strains in an oxygen-controlled fermentor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreicher, Z.; Valverde-Tercedor, C.; Chen, L.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Casillas-Ituarte, N.N.; Lower, S.K.; Lower, B.H. Magnetosomes and magnetite crystals produced by magnetotactic bacteria as resolved by atomic force microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Micron 2012, 43, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Panda, P.K.; Kumari, P.; Patel, P.; Arunima, A.; Jha, E.; Husain, S.; Prakash, R.; Hergenröder, R.; Mishra, Y.K.; et al. Determining factors for the nano-biocompatibility of cobalt oxide nanoparticles: Proximal discrepancy in intrinsic atomic interactions at differential vicinage. Green. Chem. 2021, 23, 3439–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Das, T.; Patel, P.; Panda, P.K.; Suar, M.; Verma, S.K. Emerging trends in the nanomedicine applications of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as novel therapies for acute and chronic diseases. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, J.-P.; Natekar, N.A.; Ciannella, S.; González-Fernández, C.; Gomez-Pastora, J.; Bao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, S.; Wu, X.; et al. Roadmap on magnetic nanoparticles in nanomedicine. Nanotechnology 2025, 36, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanità, G.; Carrese, B.; Lamberti, A. Nanoparticle Surface Functionalization: How to Improve Biocompatibility and Cellular Internalization. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 587012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritika, R.I. Therapeutic applications of magnetic nanoparticles: Recent advances. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 7425–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, M.; Shamsuddin, S.; Razak, K.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Devaux, C.; Borghi, E.; Levy, L.; Sadun, C. Overview of the main methods used to combine proteins with nanosystems: Absorption, bioconjugation, and encapsulation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Haponiuk, J.T.; Thomas, S.; Gopi, S. Biopolymer based nanomaterials in drug delivery systems: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 9, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.; Hall, J.B.; McLeland, C.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle interaction with plasma proteins as it relates to particle biodistribution, biocompatibility and therapeutic efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, C.M. Semi-synthetic DNA-protein conjugates: Novel tools in analytics and nanobiotechnology. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubin-Tam, M.-E.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Structure and function of nanoparticle-protein conjugates. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, X.; Qian, Y.; Chen, W.; Shen, J. Multifunctional magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: An advanced platform for cancer theranostics. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6278–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Revia, A.R.; Zhang, M. Iron oxide nanoparticles for immune cell labeling and cancer immunotherapy. Nanoscale Horiz. 2021, 6, 696–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckmann, F.d.S.; Nunes, F.B.; Salles, T.d.R.; Franco, C.; Cadoná, F.C.; Bohn Rhoden, C.R. Biological Applications of Silica-Based Nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalegül-Ülker, Ö.; Elçin, Y.M. Magnetic and electrically conductive silica-coated iron oxide/polyaniline nanocomposites for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Chatterjee, S.; Thomas, S.; Roy, P. A Detailed Review on Synthesis, Functionalization, Application, Challenges, and Current Status of Magnetic Nanoparticles in the Field of Drug Delivery and Gene Delivery System. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 24, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetia, T.; Suleman, A.; Chetia, B. A comprehensive review on magnetic NiFe2O4 nanoparticles: Synthesis approaches and catalytic proficiency in various coupling reactions. Tetrahedron 2024, 164, 134172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, Y.A.; Hasani, I.W.; Mahmoud Ragab, W. Promising biomedical applications using superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathakoti, K.; Manubolu, M.; Hwang, H.-M. Nanostructures: Current uses and future applications in food science. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.M.; Lima, A.C.; Ribeiro, S.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Martins, P. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: From the Soul of the Earth to the Deep History of Ourselves. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5839–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Borm, P.J. Drug delivery and nanoparticles: Applications and hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.X.; Barhoum, A.; Pan, S.; Danquah, M.K. Chapter 5-Risks and toxicity of nanoparticles and nanostructured materials. In Emerging Applications of Nanoparticles and Architecture Nanostructures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G. A Review of Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates for Bioanalysis: Morphology, Function and Detection Application. Biosensors 2023, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carinelli, S.; Luis-Sunga, M.; González-Mora, J.L.; Salazar-Carballo, P.A. Synthesis and Modification of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biosensing and Bioassay Applications: A Review. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H. Recent advances in nanotechnology-enhanced biosensors for α-fetoprotein detection. Microchim. Acta 2022, 190, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia de Olazarra, A.; Chen, F.-E.; Wang, T.-H.; Wang, S.X. Rapid, Point-of-Care Host-Based Gene Expression Diagnostics Using Giant Magnetoresistive Biosensors. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 2780–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlorf, T.; Meincke, M.; Kossel, E.; Glüer, C.-C.; Jansen, O.; Mentlein, R. Biological Properties of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Cellular and Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepel, M. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Nanomedicine. Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.; Halbert, M.V.; Stephen, Z.R.; Zhang, M. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as T1 Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Fundamentals, Challenges, Applications, and Prospectives. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 1906539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Barahona, I.; Muñoz-Hernando, M.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Herranz, F.; Pellico, J. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: An Alternative for Positive Contrast in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Inorganics 2020, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Iron-oxide Nanoparticles in the era of Personalized Medicine. Nanotheranostics 2023, 7, 424–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Jenkins, G.J.S.; Asadi, R.; Doak, S.H. Potential toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION). Nano Rev. 2010, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwelt, A.; Sidhu, N.; Hu, C.-A.A.; Mlady, G.; Eberhardt, S.C.; Sillerud, L.O. Iron-Based Superparamagnetic Nanoparticle Contrast Agents for MRI of Infection and Inflammation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W302–W313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapusan, R.; Borlan, R.; Focsan, M. Advancing MRI with magnetic nanoparticles: A comprehensive review of translational research and clinical trials. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 2234–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, G.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tiwari, S.; Shi, K.; et al. Comprehensive understanding of magnetic hyperthermia for improving antitumor therapeutic efficacy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3793–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Fernandez, G.; Whear, O.; Roca, A.G.; Hussain, S.; Timmis, J.; Patel, V.; O’Grady, K. Mechanisms of hyperthermia in magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 312001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, D.; Kaczyńska, A.; Wirecka, R.; Kmita, A.; Szczerba, W.; Bodzoń-Kułakowska, A.; Sikora, M.; Karewicz, A.; Zapotoczny, S. A Hybrid System for Magnetic Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery: SPION Functionalized by Curcumin Conjugate. Materials 2018, 11, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hu, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, T.; Xiao, S.; Li, P.; Ma, X. Nanoparticles and Antiviral Vaccines. Vaccines 2024, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.S.R.; Mohammad, F. Magnetic nanomaterials for hyperthermia-based therapy and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozhdehbakhsh Mofrad, Y.; Asiaei, S.; Shaygani, H.; Salehi, S.S. Investigating the effect of magnetic field and nanoparticles characteristics in the treatment of glioblastoma by magnetic hyperthermia method: An in silico study. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles and possible synergies with cold atmospheric plasma for cancer treatment. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 29039–29051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, K.D.; Chubarov, A.S. Magnetite Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Encyclopedia 2022, 2, 1811–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Roy, I.; Gandhi, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles: An Overview for Biomedical Applications. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianfar, E. Magnetic Nanoparticles in Targeted Drug Delivery: A Review. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2021, 34, 1709–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabatina, T.I.; Vernaya, O.I.; Shabatin, V.P.; Melnikov, M.Y. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Purposes: Modern Trends and Prospects. Magnetochemistry 2020, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Okamura, Y.; Arakaki, A.; Tanaka, T.; Takeyama, H.; Matsunaga, T. Origin of magnetosome membrane: Proteomic analysis of magnetosome membrane and comparison with cytoplasmic membrane. Proteomics 2006, 6, 5234–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyhan, B.; Alhorn, P.; Lang, C.; Schüler, D.; Niemeyer, C.M. Semisynthetic biogenic magnetosome nanoparticles for the detection of proteins and nucleic acids. Small 2006, 2, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.; Togo, H.; Kikuchi, T.; Tanaka, T. Production of luciferase-magnetic particle complex by recombinant Magnetospirillum sp. AMB-1. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 70, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Schüler, D.; Faivre, D. Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles for Bio- and Nanotechnology: Genetic Engineering and Biomimetics of Bacterial Magnetosomes. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandia, D.; Gandarias, L.; Rodrigo, I.; Robles-García, J.; Das, R.; Garaio, E.; García, J.Á.; Phan, M.-H.; Srikanth, H.; Orue, I.; et al. Unlocking the Potential of Magnetotactic Bacteria as Magnetic Hyperthermia Agents. Small 2019, 15, 1902626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandarias, L.; Jefremovas, E.M.; Gandia, D.; Marcano, L.; Martínez-Martínez, V.; Ramos-Cabrer, P.; Chevrier, D.M.; Valencia, S.; Fernández Barquín, L.; Fdez-Gubieda, M.L.; et al. Incorporation of Tb and Gd improves the diagnostic functionality of magnetotactic bacteria. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 20, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzajewska, D.; Wszołek, A.; Żwierełło, W.; Kirczuk, L.; Maruszewska, A. Magnetotactic Bacteria and Magnetosomes as Smart Drug Delivery Systems: A New Weapon on the Battlefield with Cancer? Biology 2020, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J.M.; Peer, D. Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotakadi, S.M.; Borelli, D.P.R.; Nannepaga, J.S. Therapeutic Applications of Magnetotactic Bacteria and Magnetosomes: A Review Emphasizing on the Cancer Treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 789016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathy, T.; Jayasri, M.A.; Suthindhiran, K. Toxicity assessment of magnetosomes in different models. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrani, N.; Felfoul, O.; Afkhami Zarreh, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Aloyz, R.; Batist, G.; Martel, S. Magnetotactic bacteria penetration into multicellular tumor spheroids for targeted therapy. In Proceedings of the 2010 32nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC 2010), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 4371–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-B.; Duan, J.-H.; Dai, S.-L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Tian, J.-S.; Li, Y. In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of doxorubicin loaded with bacterial magnetosomes (DBMs) on H22 cells: The magnetic bio-nanoparticles as drug carriers. Cancer Lett. 2007, 258, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Wang, S.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, X. A Natural Bacterium-Produced Membrane-Bound Nanocarrier for Drug Combination Therapy. Materials 2016, 9, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huang, G.; Cong, Y.; Tong, G.; Lin, Z.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, C. The preparation and characterization of micelles from poly(γ-glutamic acid)-graft-poly(L-lactide) and the cellular uptake thereof. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, G.; Cypriano, J.; Correa, T.; Leão, P.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Abreu, F. Applications of Magnetotactic Bacteria, Magnetosomes and Magnetosome Crystals in Biotechnology and Nanotechnology: Mini-Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, K.; Ke, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, L. Advances in the Techniques and Methodologies of Cancer Gene Therapy. Discov. Med. 2019, 27, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Moroz, P.; Jones, S.K.; Gray, B.N. Magnetically mediated hyperthermia: Current status and future directions. Int. J. Hyperth. 2002, 18, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphandéry, E.; Amor, M.; Guyot, F.; Chebbi, I. The effect of iron-chelating agents on Magnetospirillum magneticum strain AMB-1: Stimulated growth and magnetosome production and improved magnetosome heating properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alphandéry, E.; Idbaih, A.; Adam, C.; Delattre, J.-Y.; Schmitt, C.; Guyot, F.; Chebbi, I. Chains of magnetosomes with controlled endotoxin release and partial tumor occupation induce full destruction of intracranial U87-Luc glioma in mice under the application of an alternating magnetic field. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, H.; Seo, J.M.; Cho, D.; Koo, K. Natural magnetic nanoparticle containing droplet for smart drug delivery and heat treatment. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2015, 2015, 3541–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Shimada, T.; Ito, Y.; Honda, T.; Maeda, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Tanaka, T. Biosynthesis of Thermoresponsive Magnetic Nanoparticles by Magnetosome Display System. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, S.K.; Ezzedine, A.H.; Abdallah, A.M.; Sougrat, R.; Khashab, N.M. Magnetotactic bacterial cages as safe and smart gene delivery vehicles. OpenNano 2016, 1, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; You, X.F.; Nie, L.; Wang, H.X.; Song, T.; Yang, W.H. Comparison of the 1H NMR Relaxation Enhancement Produced by Bacterial Magnetosomes and Synthetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Potential Use as MR Molecular Probes. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2010, 20, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, A.; Lisy, M.R.; Herrmann, K.-H.; Hilger, I.; Schüler, D.; Lang, C.; Bellemann, M.E.; Kaiser, W.A.; Reichenbach, J.R. Labeling of macrophages using bacterial magnetosomes and their characterization by magnetic resonance imaging. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herborn, C.U.; Papanikolaou, N.; Reszka, R.; Grünberg, K.; Schüler, D.; Debatin, J.F. Magnetosomes as biological model for iron binding: Relaxivity determination with MRI. Rofo 2003, 175, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mériaux, S.; Boucher, M.; Marty, B.; Lalatonne, Y.; Prévéral, S.; Motte, L.; Lefèvre, C.T.; Geffroy, F.; Lethimonnier, F.; Péan, M.; et al. Magnetosomes, biogenic magnetic nanomaterials for brain molecular imaging with 17.2 T MRI scanner. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, M.; Geffroy, F.; Prévéral, S.; Bellanger, L.; Selingue, E.; Adryanczyk-Perrier, G.; Péan, M.; Lefèvre, C.T.; Pignol, D.; Ginet, N.; et al. Genetically tailored magnetosomes used as MRI probe for molecular imaging of brain tumor. Biomaterials 2017, 121, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakamura, N.; Nakamura, K.; Hashimoto, S. Phagocytosis of bacterial magnetite by leucocytes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1989, 31, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grouzdev, D.S.; Dziuba, M.V.; Kurek, D.V.; Ovchinnikov, A.I.; Zhigalova, N.A.; Kuznetsov, B.B.; Skryabin, K.G. Optimized Method for Preparation of IgG-Binding Bacterial Magnetic Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Gao, B.; Zhang, F.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. A novel electrochemical immunosensor based on magnetosomes for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B in milk. Talanta 2013, 106, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Rapid separation and immunoassay for low levels of Salmonella in foods using magnetosome–antibody complex and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3437–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Surface expression of protein A on magnetosomes and capture of pathogenic bacteria by magnetosome/antibody complexes. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yoshino, T. Stoichiometrically Controlled Immobilization of Multiple Enzymes on Magnetic Nanoparticles by the Magnetosome Display System for Efficient Cellulose Hydrolysis. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3863–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, N.L.; Carpa, R.; Ionescu, R.E.; Popa, C.O. The Biomedical Limitations of Magnetic Nanoparticles and a Biocompatible Alternative in the Form of Magnetotactic Bacteria. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16070231
Paul NL, Carpa R, Ionescu RE, Popa CO. The Biomedical Limitations of Magnetic Nanoparticles and a Biocompatible Alternative in the Form of Magnetotactic Bacteria. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(7):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16070231
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Natalia L., Rahela Carpa, Rodica Elena Ionescu, and Catalin Ovidiu Popa. 2025. "The Biomedical Limitations of Magnetic Nanoparticles and a Biocompatible Alternative in the Form of Magnetotactic Bacteria" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 7: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16070231
APA StylePaul, N. L., Carpa, R., Ionescu, R. E., & Popa, C. O. (2025). The Biomedical Limitations of Magnetic Nanoparticles and a Biocompatible Alternative in the Form of Magnetotactic Bacteria. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(7), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16070231









