Abstract
Background: Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is drug-induced bone destruction that is exposed for a minimum of 6 to 8 weeks in patients who have not received head and neck radiotherapy and who have not been diagnosed with facial bone metastases. MRONJ treatment outcomes are unpredictable. Therefore, alternative treatment methods are being explored, such as blood-derived platelet-rich preparations enriched with growth factors, including advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF). The presence of growth factors may enhance healing and reduce post-procedure complications. There are no studies examining the effect of A-PRF on the healing of patients with MRONJ. The aim of this study was to retrospectively evaluate treatment outcomes of patients with MRONJ surgically treated without and with the use of A-PRF. Materials and methods: This retrospective study included 28 patients who suffered from osteomyelitis due to MRONJ and underwent surgical treatment between 2019 and 2024. The patients were divided into two groups: the first group received surgical treatment without A-PRF, and the second group received surgical treatment with the application of A-PRF. This study analyzed demographic and clinical data, as well as treatment outcomes. Results: The patients were aged from 43 to 82 years. The most common cause of MRONJ was the administration of zoledronic acid for oncological reasons (22 patients, 78.6%), given intravenously. In 20 patients (71.4%), the antiresorptive treatment lasted longer than three years. The obtained healing distribution was binomial (presence or absence of healing). Estimation of the probability of healing using the maximum likelihood method provided a result of approximately 64%. The probability of ten or more healed patients in the A-PRF group was 41%. A-PRF helps with a probability of 59%, and without A-PRF, it was lower. Concomitantly, the differences between the group with A-PRF and without A-PRF were not statistically significant. Conclusions: The patients with MRONJ should have regular check-ups with radiological examinations at least every six months to detect possible recurrence. Treatment for MRONJ is long and difficult. Treatment of non-advanced lesions, without additional risk factors (such as treatment with zoledronate intravenously for oncological purposes for 3 years), showed a better prognosis. Sometimes, in addition to surgery, it is necessary to consider alternative methods. A-PRF may enhance MRONJ healing. However, there is no evidence of a significant effect of A-PRF on the healing of MRONJ.
1. Introduction
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) refers to the destruction of jawbones caused by certain drugs. It occurs in patients undergoing or following treatment with antiresorptive or antiangiogenic drugs (e.g., bisphosphonates (BPs; alendronate, etidronate, ibandronate, clodronate, medronate, oxydronate, pamidronate, risedronate, tiludronate, and zoledronate), corticosteroids, denosumab (anti-RANKL), bevacizumab and aflibercept (anti-VEGFR), sunitinib, sorafenib, cabozatinib (tyrosine kinase inhibitors), sirolimus, everolimus (anti-mTOR), and adalimumab (anti-TNF)). In the early stage, avascular necrosis may occur and can only be detected by radiological examination. MRONJ involves the destruction of exposed bone (not covered by oral mucosa), with the exposure persisting for at least 6–8 weeks [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. It develops in patients who have not undergone head and neck radiotherapy and do not have facial bone metastases (Figure 1) [1,2,3,10,11,12]. In patients receiving antiresorptive or antiangiogenic drugs, delayed wound healing in the oral cavity and osteonecrosis may occur after surgical procedures or due to other irritating factors, such as sharp edges of teeth or fillings, prosthetic restorations, tooth decay, periodontitis, bone fractures, exostoses, or a pronounced mylohyoid ridge. These complications are most often observed after teeth extractions. Drugs affecting bone turnover are used in the treatment of patients with bone metastases (most frequently for breast or prostate cancer), osteoporosis, fibrous dysplasia, osteogenesis imperfecta, otosclerosis, or multiple myeloma [2,4,7]. The risk of MRONJ is significantly higher in the cases undergoing treatment for tumor metastases when antiresorptive drugs are administered intravenously over 3 years and in those patients receiving additional therapies, such as chemotherapy, steroids, or thalidomide. Additional risk factors are comorbidities (e.g., diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, calcium deficiency, and hyperparathyroidism) and tobacco smoking [7,10,11,12].
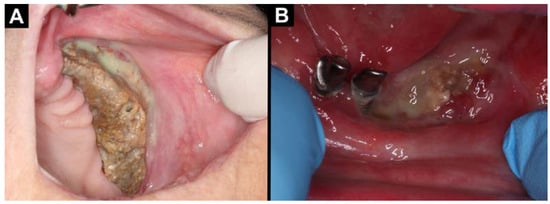
Figure 1.
Intraoral photographs (A,B): (A) MRONJ located in the maxilla on the left side; (B) MRONJ located in the central part of the mandible.
Oral irritants should be eliminated prior to initiating treatment with drugs that affect bone turnover. Dental caries must be treated, dentures adjusted, and damaged teeth removed to prevent MRONJ. Patients should undergo regular clinical and radiological examinations [10,11,12].
Osteonecrosis occurs approximately in 2/3 of cases in the mandible and in 1/3 in the maxilla. The main symptoms include exposed bone, often accompanied by purulent exudate, pain, soft tissue swelling, an active fistula (intra- or extraoral), halitosis, loosening or loss of teeth, numbness of the lip, a feeling of heaviness, and changes in tactile sensations. In advanced stages, pathological fractures of the mandible may occur. For an extended period, the affected area may remain asymptomatic [2,9,10,16,17,18,19,20,21].
The presence of osteonecrosis and other MRONJ signs can be assessed in radiological examinations, including dental X-rays, orthopantomography, cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), computed tomography (CT), scintigraphy, single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT/CT), and positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT). Non-ionizing diagnostic methods, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are also utilized. Lesions may appear as radiolucent areas with osteolysis and osteosclerotic defects (commonly referred to as sequestrum with peripheral radiolucency). Unhealed tooth sockets are frequently observed. Pathological cracks, fractures, narrowing of the marrow space, cortical and trabecular bone destruction, and, sometimes, thickening and swelling of the periosteum and soft tissues can be identified on CBCT, CT, or MRI. On T1-weighted MRI, a loss of the fat signal in the bone marrow (typically present in the mandible) may be observed. In contrast, T2-weighted sequences show hypointensity in the bone marrow. Bone scintigraphy shows increased radionuclide uptake at the periphery of the lesion. Similarly, SPECT/CT reveals abnormal radionuclide uptake, such as technetium-99m methylene diphosphonate (99Tcm-MDP) or technetium-99m dicarboxypropane diphosphonate DPD (99Tcm-DPD). However, no uptake is observed in areas of necrosis. In PET/CT imaging, the uptake of fludeoxyglucose F18 (18F-FDG) is higher in inflamed areas compared to necrotic regions. In cases of aseptic necrosis, the affected area cannot be assessed due to the lack of inflammatory processes, which are essential for an accurate analysis [20,22,23,24,25,26].
Histopathological specimens reveal fragments of necrotic bone tissue containing bacteria. Necrotic bone is most commonly infected with Actinomyces sp., which are commensal bacteria in the oral cavity. The development of infections and actinomycosis is often associated with a decrease in the host’s immunity, commonly observed during oncological treatment. Actinomycetes sp. are Gram-positive (+) anaerobes. Bone necrosis creates an anaerobic environment because of vascular degradation and the formation of clots. Actinomyces sp. receive an ideal anaerobic environment for their existence. Other bacteria that have been successfully cultured from MRONJ include Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus anginosus, and Pseudomonas mendocina [19,27,28].
Treatment is mainly based on prevention, the elimination of risk factors, and, in advanced stages, on surgical treatment. MRONJ treatment outcomes are unpredictable [1,2,5]. Therefore, alternative treatment methods are being explored, such as blood-derived platelet-rich preparations enriched with growth factors, including advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF). A-PRF is a blood-derived platelet-rich preparation enriched with growth factors. It belongs to the third generation of preparations derived from blood. A-PRF was developed to obtain advanced blood derivatives rich in growth factors. Compared to classic PRF or L-PRF (leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin), its preparation involves a reduction in the centrifugation speed and a slight increase in the centrifugation time (A-PRF: 1500 rpm/14 min vs. PRF: 3000 rpm/12 min vs. L-PRF: 2700 rpm/12 min). As a result, the biological and physical properties of A-PRF are altered. It contains a greater number of leukocytes and platelets, and the resulting fibrin matrix is more cohesive and exhibits improved adhesion. Additionally, A-PRF is enriched with higher concentrations of cytokines, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), which enhance healing and stimulate tissue regeneration. An advancement of A-PRF is A-PRF+, which is produced at even lower speeds (1300 rpm/8 min), yielding a preparation with an even higher concentration of growth factors and neutrophils. The presence of growth factors may enhance healing and reduce post-procedure complications, which has been proven in many oral surgery procedures [29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
The aim of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the treatment outcomes of patients with medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw, both without and with the use of advanced platelet-rich fibrin.
2. Materials and Methods
The retrospective study included 28 patients (43–82 years old) who suffered from osteomyelitis due to medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw and underwent surgical treatment at the Division of Oral Surgery, University Dental Center of Medical University of Gdańsk, Poland, between 2019 and 2024. The retrospective research was carried out following the Declaration of Helsinki principles. Approval from the institutional ethics committee was obtained (Independent Bioethics Commission for Research, Medical University of Gdańsk, number of approval KB/510/2024). The patients signed an informed written consent to the surgical procedures.
The analysis considered several factors, including the patients’ age, gender, primary disease, duration of antiresorptive or antiangiogenic drug use (less than 3 years or 3 years and above), and route of drug administration (intravenous or oral). Additional factors included the presence of triggers for necrosis development (e.g., tooth extraction, periapical lesion), stage of the disease as classified by the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons (AAOMS, Table 1), and the extent of the lesions in the clinical and radiological imaging (less than 3 cm and 3 cm and above). The analysis also evaluated the type of treatment applied: either surgical removal of the necrotic bone alone or combined with the local administration of growth factors derived from the patient’s blood. Treatment success and the duration of the follow-up were assessed. Additionally, several factors influencing a worse prognosis were evaluated, including the use of zoledronic acid, intravenous administration, treatment duration of at least three years, a previous episode of jawbone necrosis, and oncological treatment.

Table 1.
Classification of MRONJ by the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.
Two groups of patients were compared. The first group comprised patients who received surgical treatment involving the removal of necrotic lesions. The second group included patients who, in addition to the removal of necrotic lesions, received advanced platelet-rich fibrin.
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
The study included adult patients with MRONJ who had been treated with antiresorptive or antiangiogenic drugs. The eligibility criteria required bone exposure persisting for a minimum of 6–8 weeks, the absence of prior head and neck radiotherapy, and no diagnosis of facial bone metastases. Surgical procedures were performed only on patients in good general condition with normal results in basic diagnostic tests (e.g., blood morphology).
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
The study excluded patients with osteonecrosis of the jaw who had not been treated with antiresorptive or antiangiogenic drugs, whose bone exposure persisted for less than 6–8 weeks, who had undergone head and neck radiotherapy, or who were diagnosed with facial bone metastases. Additionally, underage patients and those who did not provide consent for treatment were excluded.
2.3. Surgical Procedure
Before the treatment, extraoral and intraoral examinations and radiological diagnostic imaging were performed. Orthopantomography or cone beam computer tomography was assessed using the CS 3D Imaging v3.5.18 software (Carestream Health Inc., Trophy, Croissy-Beaubourg, France). Each patient received 1 g of amoxicillin with cluvuate acid (0.875 g + 0.125 g; Augmentin, GlaxoSmithKline, London, UK) every 12 h one day before the procedure. In patients with allergies, 300 mg of clindamycin was administered every 8 h starting the day before the surgery (Dalacin C, Pfizer, Brooklyn, NY, USA). The antibiotic therapy protocol was implemented according to the Recommendations of the Working Group of the Polish Dental Association and the National Antibiotic Protection Program regarding the use of antibiotics in dentistry [36]. Additionally, the patients rinsed their mouths with a 0.1% chlorhexidine solution (Eludril Classic, Pierre Fabre Oral Care, Lavaur, France).
In the group of patients who received A-PRF before the surgery, 4 tubes of 10 mL venous blood were collected into sterile, anticoagulant-free, glass-coated plastic tubes. After that, the tubes were immediately centrifuged (All Centrifuge, Scilogex, LLC, Rocky Hill, CT, USA). The blood was centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 14 min. Then, the A-PRF clots were put into a PRF box (Quadrostom, Kraków, Poland), and A-PRF plugs were made.
The surgical procedure was performed under local anesthesia administered via injection (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The type of anesthesia depended on the location of the lesion. The nerves were blocked using 4% articaine hydrochloride with 1:100,000 epinephrine (Septodont, Lancaster, PA, USA). A 15c scalpel blade (Swann-Morton, Sheffield, UK) was used, and the mucoperiosteal flap was raised. The epithelialized edges of the mucosa were prepared and debrided. The necrotic bone was curetted, fixed in 10% formalin, and submitted for histopathological examination. The bottom of the lesion was cleaned down to the bleeding bone using a rose head bur (Meisinger, Hager, and Meisinger GmbH, Neuss, Germany) mounted on a surgical straight handpiece (S-11 L G, W&H Dentalwerk Bürmoos GmbH, Bürmoos, Austria) at 40,000 rpm, with abundant irrigation using 0.9% NaCl. The wound was rinsed with 20 mL of 0.5% metronidazole solution (Polpharma SA, Starogard Gdański, Poland). In the A-PRF group, four wound plugs were placed at this stage. The wound was sutured without tension, and hemostasis was achieved. A gauze pad was applied, and the patient was instructed to bite on it and hold it in place for 20 min.
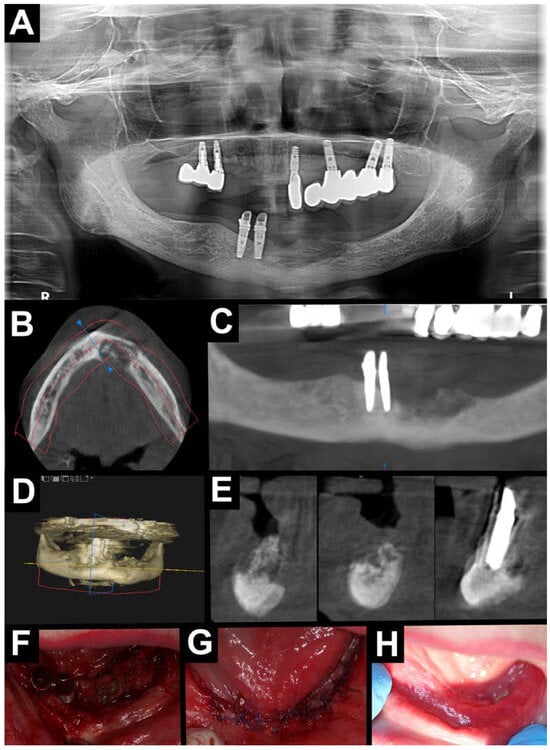
Figure 2.
Treatment without A-PRF. Radiological diagnostic imaging of MRONJ (A–E). (A) Orthopantomography—area with osteolysis and osteosclerosis located in the mandible on the anterior area; CBCT (B–E). (B) Axial view—area with osteolysis and osteosclerosis on the anterior area of the mandible. (C) Orthopantomographic reconstruction—area with osteolysis and osteosclerosis on the anterior area of the mandible. (D) Pseudo-3D reconstruction—area with osteolysis and osteosclerosis on the anterior area of the mandible. (E) Cross-sectional view—area with osteolysis and osteosclerosis on the anterior area of the mandible. Intraoral photographs (F–H). (F) Visible necrotic bone after mucoperiosteal flap elevation. (G) After suturing the wound without tension. (H) Healing after 2 weeks (red line—panoramic reconstruction site; yellow line – cross-sectional area line; blue line—cross-sectional area line).
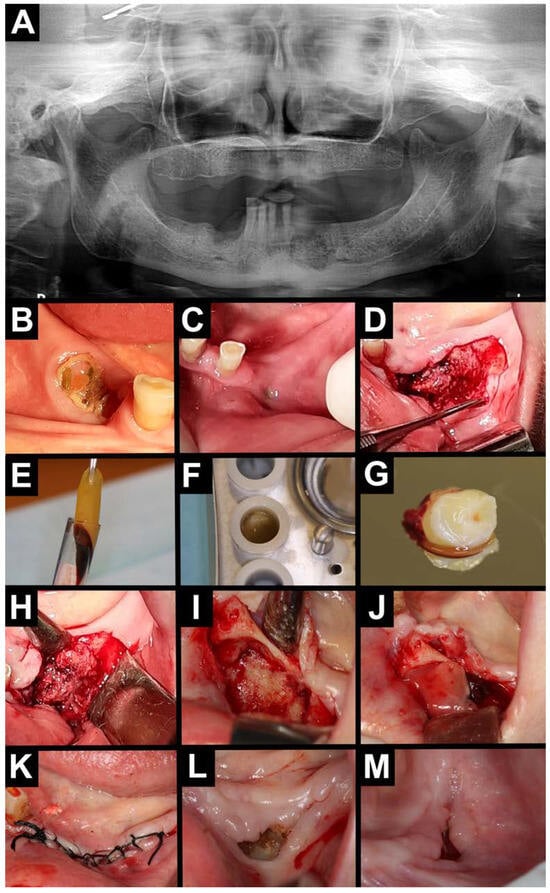
Figure 3.
Treatment with A-PRF. (A) Orthopantomography—area with osteolysis and osteosclerosis on the left and right sides of the mandible. Intraoral photography (B–D). (B) Exposed necrotic bone on the right side of the mandible. (C) Intraoral purulent fistula on the left side of the mandible. (D) Visible necrotic bone after mucoperiosteal flap elevation on the left side of the mandible. A-PRF preparation (E–G). (E) A-PRF clot. (F) A-PRF in a PRF box. (G) A-PRF plug. Intraoral photographs (H–M). (H,I) Necrotic tissue was removed, and the bone was bled. (J) A-PRF plug placed intra-wound. (K) Wound was sutured. (L) Healing after 2 weeks. (M) Healing after 6 weeks.
Patients continued antibiotic therapy for 14 days in the high-risk group (defined as receiving zoledronic acid, intravenous bisphosphonates, or the drug for at least 3 years, or those with a previous episode of jawbone inflammation or necrosis) and for 7 days in the low-risk group (not meeting these criteria) [36]. The sutures were removed after 14 days.
2.4. Post-Operative Evaluation and Follow-Up
Patients attended regular follow-up appointments: initially at 2 and 6 weeks, then every 3 months, and annually if the lesions healed properly. For non-healing lesions, the frequency of visits was adjusted on an individual basis.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
A statistical analysis was performed using the R software (version 4.4.2, the R Foundation for Statistical Computing Platform, Boston, MA, USA). Patients’ age, gender, primary disease, duration of antiresorptive or antiangiogenic drug use (less than 3 years or 3 years and above), route of drug administration (intravenous or oral), the presence of triggers for necrosis development (e.g., tooth extraction, periapical lesion), stage of the disease as classified by the AAOMS, the extent of the lesions in the clinical and radiological imaging (less than 3 cm and 3 cm and above), the type of treatment applied, treatment success, and the duration of follow-ups were quantitatively summarized. Statistical analyses were performed using the maximum likelihood method. The non-parametric ANOVA test was used for a comparative analysis. Statistically significant results were accepted for p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
A total of 28 patients with MRONJ were included in this study. At the time of the MRONJ diagnosis, the patients were aged between 43 and 82 years, with a mean age of 70.2. The female group was larger than the male group (n = 21, 75% vs. n = 7, 25%).
Eleven patients (39.3%) had multiple myeloma, seven (25%) had breast cancer, four (14.3%) had prostate cancer, four (14.3%) had osteoporosis, and two (7.1%) had other. All patients were treated exclusively with bisphosphonates—either zoledronic acid or alendronic acid. The most common cause of MRONJ was the administration of zoledronic acid for oncological indications (n = 22, 78.6%). Zoledronic acid was administered intravenously (100% of cases), and alendronic acid was given only orally. In 20 patients (71.4%), the antiresorptive treatment lasted longer than 3 years.
The factors contributing to MRONJ included surgical procedures or infection in the oral cavity. These were tooth extraction (n = 25, 89.3%), inflammatory lesions such as periapical lesions or periodontal disease (n = 2, 7.1%), or the presence of dental implants (1/3.6%).
The location in the mandible was more common than in the maxilla (n = 24, 82.1% vs. n = 5, 17.9%). All patients were diagnosed with stage 3 according to the AAOMS classification. All patients had an intraoral fistula, and two also had an extraoral fistula. In most cases, the lesion size was up to 3 cm (n = 22, 78.6%). Among the oncological patients, lesions up to 3 cm occurred in 100% of the patients in the A-PRF group, and in the group without A-PRF, they were 73%.
Among the non-oncological patients, lesions up to and above 3 cm occurred in the same number of patients in both groups (three patients each). In the A-PRF group, healing was complete in 100% of the patients, and in the non-A-PRF group, it was 66.8%. The average follow-up period was 14.79 months. The demographic and clinical characteristics, divided into groups with and without A-PRF treatment, are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Demographic and clinical features divided into two groups: surgically treated and surgically treated with A-PRF application.
3.2. Comparison of the Impact of A-PRF Use in Relation to Demographic and Clinical Features
The use of A-PRF was compared in relation to demographic and clinical features. No statistical significance was found for the healing and location of lesions (mandible vs. maxilla, p = 0.4373) or the size of the lesion (less than 3 cm vs. 3 cm and above, p = 0.8957). Statistical significance was obtained only for the presence of healing and the number of additional risk factors (1–5), including zoledronic acid use, intravenous drug administration, drug use for at least three years, a previous episode of jawbone necrosis, or oncological treatment (p = 0.006989).
The obtained healing distribution was binomial (presence or absence of healing). Estimation of the probability of healing using the maximum likelihood method provided a result of approximately 64%. The probability of ten or more healed patients in the A-PRF group was 41%. A-PRF helps with a probability of 59%. Concomitantly, the differences between the group with A-PRF and without A-PRF were not statistically significant (p = 0.449).
4. Discussion
For patients planned to receive oncological or osteoporosis treatment with drugs associated with MRONJ, prophylactic management should be pivotal. Therapy with antiresorptive and antiangiogenic drugs should be started only after eliminating the infection foci in the oral cavity. The patient should undergo a clinical and radiological evaluation or at least an orthopantomographic examination. In complex cases, such as previous endodontic treatments, periodontal disease assessments, or completely impacted teeth, additional tissue evaluation in CBCT may be necessary [10,11,12].
Due to the challenges in treating medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw, various therapy approaches are undertaken, including non-surgical and surgical treatments, as well as a combination of both. Alternative techniques are also explored. According to the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, in the initial stage (stage 0) of the disease, the primary goal is to eliminate irritating factors. Patients are advised to rinse their mouths with 0.12% chlorhexidine. Antibiotic treatments, typically amoxicillin with clavulanic acid or clindamycin, are recommended in the cases of infection. Pain and inflammation management includes analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications. For patients with mucosal damage but no symptoms of infection (stage I), treatment follows the same protocol as in stage 0. In the case of pain, low-level laser therapy (LLLT) can be introduced for biomodulation. In stage II, where bone exposure is accompanied by an active infection, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antiseptic rinses are necessary. At this stage, radiological examination often reveals bone lysis with sequestration. Surgical treatment should be considered as a last resort, as it may exacerbate the lesion progression. Alternatively, a superficial MRONJ debridement can be performed. In the advanced stage (III), surgical treatment is necessary. In stage III, intraoral and extraoral purulent fistulas and, in some cases, pathological fractures are observed. Surgical procedures include sequestrum removal, bone debridement down to healthy bone, or segmental resection [1,2,4,34,35]. In addition to LLLT, other supportive therapies include hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HOT), photobiomodulation, ozone therapy, blood-derived platelet-rich preparations enriched with growth factors, and recombinant human bone morphogenetic proteins (rhBMP). Additional pharmacological treatments involve teriparatide, pentoxifylline, and vitamins E and D. However, alternative methods should not be used as monotherapy but rather as part of a multimodal treatment approach [34,35,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44].
A-PRF is an autogenous, non-allergenic, and non-immunogenic blood-derived platelet-rich preparation enriched with growth factors. Due to the presence of growth factors, it promotes healing and helps reduce postoperative complications. Wound healing is supported by the gradual release of growth factors (for up to 4 weeks), which enhances regenerative processes, such as cell proliferation and differentiation—particularly of fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and osteoblasts—crucial for both soft and hard tissue regeneration. It also stimulates neovascularization, modulates inflammation, and accelerates the formation of epithelium and connective tissues [29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
The available studies about platelet-rich preparations are case reports [45,46,47,48,49] or were used in prophylaxis (e.g., filling the post-extraction socket) [50,51,52,53,54,55] or other blood products—PRF [46,51,53,56,57,58] and L-PRF [45,47,48,52,54,59,60,61,62,63,64]. A-PRF has been used in an animal model [65] and in one case report article [66]. Three original publications analyzed A-PRF+, not A-PRF, as it differs in the production process compared to A-PRF [49,67,68]. In the available studies, the authors reported that the addition of blood-derived agents was a valuable addition, supported healing, and even led to the complete healing of lesions. In a study using PRF, de Almeida Barros Mourão et al. [56] achieved complete treatment success, while in the case of L-PRF, Zelinka et al. [59]—85–94%, Özalp et al. [60]—69%, Aslam et al. [62]—100%, and Yalcin-Ülker [63] achieved a success rate of 80%.
To date, our study is the only one to have investigated A-PRF and its effect on healing in patients with MRONJ. More than 85% of the study participants were oncology patients treated with zoledronic acid administered intravenously. Moreover, the lesions were highly advanced, classified as stage III according to AAOMS. This could have influenced the treatment outcomes. In our study, whether the patient was an oncology patient or not had no impact on the healing process at such advanced stages, regardless of the use of A-PRF. Referring to studies analyzing A-PRF+ (not A-PRF), Giudice et al. [49] reported that 74.5% of their study group consisted of oncology patients, with a predominance of stage II cases according to AAOMS (53%) over stage III (47%). Their findings indicated that A-PRF+ improved the patients’ quality of life in the first month after the procedure, reducing both pain and the risk of post-procedure infections. This relationship was not observed in later follow-up periods. Blatt et al. [68] also primarily evaluated oncology patients (84.7%); however, the majority (78.8%) had AAOMS stage I disease, while only 1.9% had stage III disease. Their study found no statistical correlation between healing and the use of A-PRF+. Roman et al. [67] had a heterogeneous study group, including patients with MRONJ who had undergone radiotherapy and cases with a combination of MRONJ and radiotherapy. Among patients with MRONJ, 60.5% were taking oral antiresorptive drugs, which is considered a lower-risk group for MRONJ based on current knowledge. Regarding MRONJ staging, 42.5% of patients were classified as AAOMS stage II, 18.5% as stage I, and 3.7% as stage III. This study concluded that A-PRF+ may serve as an adjunctive method to support wound healing; however, no correlation was found with reductions in disease severity, pain, or oral health-related quality of life.
The early and accurate diagnosis of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw is pivotal. Our article broadens the knowledge to include the latest advances in diagnosis and treatment of MRONJ. This article presents diagnostic methods as well as a simple and cheap technique of treating MRONJ using A-PRF. Most importantly, it is non-allergenic and does not cause immunological reactions. Biocompatible healing and the pursuit of nature is called biomimetic treatment. Many patients may require this type of treatment from their doctor due to their beliefs or religion.
The study was limited by the relatively small study group, and the treatment was used only in the advanced stages (which could have resulted in worse treatment results). It would be valuable to compare two groups that are homogeneous in terms of the number of participants and the stage of disease progression but differ in the indication for antiresorptive therapy—oncologic versus non-oncologic patients. A significantly better response to A-PRF treatment was observed in the case of small lesions. Some patients experienced progression of the neoplastic disease, which resulted in a deterioration of their general condition and could have contributed to possible healing failure in the group with or without A-PRF.
Future research directions should focus on large cohort studies. It is important to remember to support the treatment with antibiotic therapy. An interesting solution would be a combined treatment with pentoxifylline and tocopherol, then performing a surgical procedure—bone debridement with additional bone ablation with a laser and the application of growth factors in an antibiotic cover, followed by laser biostimulation.
5. Conclusions
The patients with medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw should undergo regular check-ups, including radiological examinations, at least every six months to detect possible recurrence. MRONJ treatment is prolonged and challenging. Non-advanced lesions, in the absence of additional risk factors (such as zoledronate treatment administered intravenously for oncological reasons over a period of more than 3 years), tend to have a better prognosis. In some cases, alternative therapies may support surgical treatments. A-PRF may enhance MRONJ healing. However, there is no evidence of a significant effect of A-PRF on the healing of MRONJ. We believe that increasing awareness and understanding of these therapeutic approaches is essential. Further studies on the use of A-PRF in the treatment of MRONJ are needed in a homogeneous, large study group in oncological and non-oncological patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.A.; methodology, P.A.; software, P.A. and M.S. (Marcin Stasiak); validation, P.A. and M.S. (Marcin Stasiak); formal analysis, P.A.; investigation, P.A.; resources, P.A. and N.K.; data curation, P.A. and N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, P.A.; writing—review and editing, P.A., M.S. (Marcin Stasiak), M.B. and M.S. (Michał Studniarek); visualization, P.A.; supervision, P.A., A.Z. and M.S. (Michał Studniarek); project administration, P.A. and M.S. (Michał Studniarek). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Independent Bioethics Committee for Scientific Research at the Medical University of Gdańsk, Poland (protocol code KB/510/2024 and date of approval 12 December 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Paulina Adamska and Natalia Kobusińska would like to thank Antoni Jusyk for his guidance and support in helping us develop the art of surgery as our mentor.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| 99Tcm-DPD | technetium-99m dicarboxypropane diphosphonate |
| 99Tcm-MDP | technetium-99m methylene diphosphonate |
| A-PRF | advanced platelet-rich fibrin |
| A-PRF+ | advanced platelet-rich fibrin + |
| AAOMS | American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons |
| anti-mTOR | anti-mammalian target of rapamycin |
| anti-RANKL | anti-receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand antibody |
| anti-VEGFR | anti-vascular-endothelial growth factor receptor |
| BPs | bisphosphonates |
| CBCT | cone beam computed tomography |
| F18-FDG | fludeoxyglucose F18 |
| HOT | hyperbaric oxygen therapy |
| L-PRF | leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin |
| LLLT | low-level laser therapy |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRONJ | medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw |
| PET/CT | positron emission tomography/computed tomography |
| PRF | platelet-rich fibrin |
| rhBMP | recombinant human bone morphogenetic proteins |
| SPECT/CT | single-photon emission computed tomography |
References
- Marx, R.E. Oral and Intravenous Bisphosphonate-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Jaws. History, Etiology, Prevention, and Treatment; Quintessence Publishing Co., Inc.: Batavia, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 9–96. [Google Scholar]
- American Dental Association Council on Scientific Affairs. Dental management of patients receiving oral bisphosphonatetherapy: Expert panel recommendations. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2006, 137, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, J.; DeRossi, S.S.; Akintoye, S.O. Updates on bisphosphonates and potential pathobiology of bisphosphonate-induced jaw osteonecrosis. Oral Dis. 2008, 14, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Jung, Y.S.; Park, H.S.; Jung, H.D. Osteonecrosis of the jaw related to everolimus: A case report. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, e302–e304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Dodson, T.B.; Fantasia, J.; Goodday, R.; Aghaloo, T.; Mehrotra, B.; O’Ryan, F.; American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw-2014 update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, 1938–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarelis, H.; Shah, N.P.; Dhariwal, D.K.; Pazianas, M. Infection and medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosella, D.; Papi, P.; Giardino, R.; Cicalini, E.; Piccoli, L.; Pompa, G. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Clinical and practical guidelines. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, H.H.; Al-Sahafi, E.N. The role of dental care providers in the management of patients prescribed bisphosphonates: Brief clinical guidance. Gen. Dent. 2018, 66, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nancollas, G.H.; Tang, R.; Phipps, R.J.; Henneman, Z.; Gulde, S.; Wu, W.; Mangood, A.; Russell, R.G.; Ebetino, F.H. Novel insights into actions of bisphosphonates on bone: Differences in interactions with hydroxyapatite. Bone 2006, 38, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, G.; Mauceri, R.; Bertoldo, F.; Bettini, G.; Biasotto, M.; Colella, G.; Consolo, U.; Di Fede, O.; Favia, G.; Fusco, V.; et al. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of Jaws (MRONJ) Prevention and Diagnosis: Italian Consensus Update 2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, V.; Campisi, G.; Carcieri, P.; Fagioli, F.; Bertetto, O.; Mignogna, M.D.; Bedogni, A. Osteonecrosis of Jaw Related to Bisphosphonates and Other Drugs—Prevention, Diagnosis, Pharmacovigilance, Treatment: A 2021 Web Event. Oral 2022, 2, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cicco, D.; Boschetti, C.E.; Santagata, M.; Colella, G.; Staglianò, S.; Gaggl, A.; Bottini, G.B.; Vitagliano, R.; D’amato, S. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws: A Comparison of SICMF–SIPMO and AAOMS Guidelines. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovari-Biri, J.; Miskei, J.A.; Kover, Z.; Steinerbrunner-Nagy, A.; Kardos, K.; Maroti, P.; Pongracz, J.E. Advancements in Bone Replacement Techniques–Potential Uses After Maxillary and Mandibular Resections Due to Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ). Cells 2025, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laputková, G.; Talian, I.; Schwartzová, V. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Systematic Review and a Bioinformatic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, M.; Di Spirito, F.; Acerra, A.; Galdi, M.; Sisalli, L. Multiple-Drugs-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in a Patient Affected by Multiple Myeloma: A Case Report. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Jain, V. Dental complications and management of patients on bisphosphonate therapy: A review article. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2012, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarasquete, M.E.; González, M.; San Migel, J.F.; García-Sanz, R. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis: Genetic and acquired risk factors. Oral Dis. 2009, 15, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolatou-Galitis, O.; Schiødt, M.; Mendes, R.A.; Ripamonti, C.; Hope, S.; Drudge-Coates, L.; Niepel, D.; Van den Wyngaert, T. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Definition and best practice for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 127, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, D.K.; Sándor, G.K.; Holmes, H.I.; Evans, A.W.; Clokie, C.M. A review of bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaws and its management. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2007, 73, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero, S.L. Guidelines for the diagnosis of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ). Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2012, 4, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gutta, R.; Louis, P.J. Bisphosphonates and osteonecrosis of the jaws: Science and rationale. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 104, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, A.E.; Webb, J. Skeletal complications of bisphosphonate use: What the radiologist should know. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu-Arasa, V.C.; Chapman, M.N.; Kuno, H.; Fujita, A.; Sakai, O. Craniofacial manifestations of systemic disorders: CT and MR imaging findings and imaging approach. Radiographics 2018, 38, 890–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.Y.; Yang, W.-F.; Leung, Y.Y. The Role of Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) in the Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ). Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, B.-I.; Mueller, A.A.; Augello, M.; Berg, S.; Jaquiéry, C. Imaging in Patients with Bisphosphonate-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ). Dent. J. 2016, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Soutome, S.; Otsuru, M.; Hayashida, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; Sawada, S.; Umeda, M. Factors Exacerbating Clinical Symptoms and CT Findings in Patients with Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Receiving Conservative Therapy: A Multicenter Retrospective Study of 53 Cases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Apandi, N.I.M.; Shuhardi, S.A.; Ramli, R. Actinomyces sp. Presence in the Bone Specimens of Patients with Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: The Histopathological Analysis and Clinical Implication. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, G.A.; Mogoantă, L.; Camen, A.; Ionescu, M.; Vlad, D.; Staicu, I.E.; Munteanu, C.M.; Gheorghiță, M.I.; Mercuț, R.; Sin, E.C.; et al. Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of MRONJ in Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, M.; Pilloni, A.; Adamska, P. Application of Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery: A Systematic Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamska, P.; Kaczoruk-Wieremczuk, M.; Pylińska-Dąbrowska, D.; Stasiak, M.; Bartmański, M.; Zedler, A.; Studniarek, M. Treatment of Oroantral Communication and Fistulas with the Use of Blood-Derived Platelet-Rich Preparations Rich in Growth Factors: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamska, P.; Pylińska-Dąbrowska, D.; Stasiak, M.; Kaczoruk-Wieremczuk, M.; Kozłowska, E.; Zedler, A.; Studniarek, M. Treatment of Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis with the Use of Growth Factors in Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin for Immediate Closure of Oro-Antral Communication: A Case Report. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, M.; Pilloni, A.; Adamska, P. Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin Plus (A-PRF+) as an Additive to Hard Tissue Managing Protocols in Oral Surgery: A Systematic Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamska, P.; Pylińska-Dąbrowska, D.; Stasiak, M.; Sobczak-Zagalska, H.; Jusyk, A.; Zedler, A.; Studniarek, M. Tooth Autotransplantation, Autogenous Dentin Graft, and Growth Factors Application: A Method for Preserving the Alveolar Ridge in Cases of Severe Infraocclusion—A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jornet, P.; Perez, A.S.; Arturo, S.P.; Rui, A.M.; Aurelio, T. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Is autologous platelet concentrate application effective for prevention and treatment? A systematic review. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutuoso, F.; Freitas, F.; Vilares, M.; Francisco, H.; Marques, D.; Caramês, J.; Moreira, A. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. Diseases 2024, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarczyk, T.; Babiuch, K.; Bołtacz-Rzepkowska, E.; Dominiak, M.; Konopka, T.; Lipski, M.; Olczak-Kowalczyk, D.; Szeląg, A.; Szuta, M.; Hryniewicz, W. Rekomendacje Grupy Roboczej Polskiego Towarzystwa Stomatologicznego i Narodowego Programu Ochrony Antybiotyków w Zakresie Stosowania Antybiotyków w Stomatologii; Narodowy Instytut Leków: Warszawa, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Momesso, G.A.C.; Lemos, C.A.A.; Santiago-Júnior, J.F.; Faverani, L.P.; Pellizzer, E.P. Laser surgery in management of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: A meta-analysis. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 24, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberger, J.J. Utility of hyperbaric oxygen in treatment of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nica, D.F.; Riviș, M.; Roi, C.I.; Todea, C.D.; Duma, V.-F.; Sinescu, C. Complementarity of Photo-Biomodulation, Surgical Treatment, and Antibiotherapy for Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ). Medicina 2021, 57, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripamonti, C.I.; Cislaghi, E.; Mariani, L.; Maniezzo, M. Efficacy and safety of medical ozone (O(3)) delivered in oil suspension applications for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients with bone metastases treated with bisphosphonates: Preliminary results of a phase I-II study. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-D.; Kim, D.-Y. Role of Teriparatide in Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ). Dent. J. 2016, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Yoo, H.Y.; Kim, G.T.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, Y.A.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, Y.D. Short-term teriparatide and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 for regenerative approach to medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A preliminary study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colapinto, G.; Goker, F.; Nocini, R.; Albanese, M.; Nocini, P.F.; Sembronio, S.; Argenta, F.; Robiony, M.; Del Fabbro, M. Outcomes of a Pharmacological Protocol with Pentoxifylline and Tocopherol for the Management of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ): A Randomized Study on 202 Osteoporosis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, F.; Dominiak, M.; Kiryk, J.; Popecki, P.; Kubicki, D.; Matys, J.; Grzech-Leśniak, K. The Influence of Vitamin D Levels and Supplementation on the Treatment of Patients Affected by MRONJ. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Zamora, G.; Martínez, Y.; Moreno, J.A.; Ortiz-Ruíz, A.J. Treatment of Stage 2 Medication-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Case Series. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennardo, F.; Bennardo, L.; Del Duca, E.; Patruno, C.; Fortunato, L.; Giudice, A.; Nisticò, S.P. Autologous platelet-rich fibrin injections in the management of facial cutaneous sinus tracts secondary to medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Tian, Z.; Li, S.; Yan, K.; Xue, Y. Osteonecrosis of the jaw induced by bisphosphonates therapy in bone metastases patient: Case report and literature review. Oral Oncol. 2022, 128, 105852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouland, C.; Meuleman, N.; Widelec, J.; Keiani-Mothlagh, K.; Voisin, C.; Lagneaux, L.; Philippart, P. Case reports of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) treated with uncultured stromal vascular fraction and L-PRF. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 122, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.; Antonelli, A.; Muraca, D.; Fortunato, L. Usefulness of advanced-platelet rich fibrin (A-PRF) and injectable-platelet rich fibrin (i-PRF) in the management of a massive medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ): A 5-years follow-up case report. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2020, 31, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaka, T.; Ohga, N.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sato, J.; Satoh, C.; Kitagawa, Y. Platelet-rich fibrin may reduce the risk of delayed recovery in tooth-extracted patients undergoing oral bisphosphonate therapy: A trial study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Gianfreda, F.; Raffone, C.; Antonacci, D.; Pistilli, V.; Bollero, P. The Role of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) in the Prevention of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ). Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4948139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besi, E.; Pitros, P. The role of leukocyte and platelet-rich fibrin in the prevention of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw, in patients requiring dental extractions: An observational study. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 28, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrmali, A.; Saleh, M.H.A.; Kurdi, S.M.S.; Sabri, H.; Meghil, M.M.; Wang, H.L. Prevention and management of drug-induced osteonecrosis of the jaws using platelet-rich fibrin: A clinical feasibility study. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2023, 9, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parise, G.K.; Costa, B.N.; Nogueira, M.L.; Sassi, L.M.; Schussel, J.L. Efficacy of fibrin-rich platelets and leukocytes (L-PRF) in tissue repair in surgical oral procedures in patients using zoledronic acid-case-control study. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 27, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şahin, O.; Tatar, B.; Ekmekcioğlu, C.; Aliyev, T.; Odabaşı, O. Prevention of medication related osteonecrosis of the jaw after dentoalveolar surgery: An institution’s experience. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2020, 12, e771–e776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida Barros Mourão, C.F.; Calasans-Maia, M.D.; Del Fabbro, M.; Le Drapper Vieira, F.; Coutinho de Mello Machado, R.; Capella, R.; Miron, R.J.; Gomes Alves, G. The use of Platelet-rich Fibrin in the management of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A case series. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 121, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.; Barone, S.; Giudice, C.; Bennardo, F.; Fortunato, L. Can platelet-rich fibrin improve healing after surgical treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw? A pilot study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 126, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchingolo, F.; Cantore, S.; Dipalma, G.; Georgakopoulos, I.; Almasri, M.; Gheno, E.; Motta, A.; Marrelli, M.; Farronato, D.; Ballini, A.; et al. Platelet rich fibrin in the management of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A clinical and histopathological evaluation. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 811–816. [Google Scholar]
- Zelinka, J.; Blahak, J.; Perina, V.; Pacasova, R.; Treglerova, J.; Bulik, O. The use of platelet-rich fibrin in the surgical treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: 40 patients prospective study. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc. Czech Repub. 2021, 165, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özalp, Ö.; Yıldırımyan, N.; Öztürk, C.; Kocabalkan, B.; Şimşek Kaya, G.; Sindel, A.; Altay, M.A. Promising results of surgical management of advanced medication related osteonecrosis of the jaws using adjunctive leukocyte and platelet rich fibrin. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.J. Does the Addition of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 to Platelet-Rich Fibrin Improve Healing After Treatment for Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, R.D.; Pitros, P.; Liew, J.; Besi, E. The adjunctive use of Leukocyte-Platelet Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) in the management of Medication Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ): A retrospective observational study. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 28, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin-Ülker, G.M.; Duygu, G.; Tanan, G.; Cakir, M.; Meral, D.G. Use of Leukocyte-rich and Platelet-rich Fibrin (L-PRF) Adjunct to Surgical Debridement in the Treatment of Stage 2 and 3 Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2023, 34, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenore, G.; Zimbalatti, A.; Rocchetti, F.; Graniero, F.; Gaglioti, D.; Mohsen, A.; Caputo, M.; Lollobrigida, M.; Lamazza, L.; De Biase, A.; et al. Management of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ) Using Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) and Photobiomodulation: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalpour, M.R.; Shahabi, S.; Baghestani, M.; Shokri, A.; Jamshidi, S.; Khazaei, S. Complementarity of surgical therapy, photobiomodulation, A-PRF and L-PRF for management of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ): An animal study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfour, M.A.R.; Aljoujou, A.A.; Saifo, M.S.; Jabban, H.A.L. The use of advanced-platelet rich fibrin (A-PRF) in the management of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ): A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, R.C.; Moldovan, M.A.; Pop, L.S.; Megieșan, S.; Faur, C.I. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Treatment Evaluation in Patients with Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw and Osteoradionecrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, S.; Krüger, M.; Kämmerer, P.W.; Thiem, D.G.E.; Matheis, P.; Eisenbeiß, A.-K.; Wiltfang, J.; Al-Nawas, B.; Naujokat, H. Non-Interventional Prospective Observational Study of Platelet Rich Fibrin as a Therapy Adjunctive in Patients with Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).