Natural Polymers, Their Modifications and Composites with Synthetic Polymers for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Natural Polymers Used for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration
2.1. Silk Fibroin
2.2. Chitosan and Chitin
2.3. Hyaluronic Acid
2.4. Collagen
2.5. Bacterial Cellulose
3. Other Polymers
3.1. Poly(l-lactic acid) and Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
3.2. Latex
3.3. Gelatin
3.4. Polycaprolactone
3.5. Alginates
4. Composites Based on Several Polymers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, W.; Gregory, D.A.; Tomeh, M.A.; Zhao, X. Silk Fibroin as a Functional Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novozhilov, A.A.; Shilyagin, P.A.; Novozhilova, V.A.; Smirnova, D.D.; Slepanov, A.A.; Dilenjan, A.L.; Klimycheva, M.B.; Gelikonov, G.G.; Gelikonov, V.M.; Shakhov, A.V. Measuring the tympanic membrane thickness using optical coherence tomography. Opera Med. Physiol. 2023, 10, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monasta, L.; Ronfani, L.; Marchetti, F.; Montico, M.; Vecchi Brumatti, L.; Bavcar, A.; Grasso, D.; Barbiero, C.; Tamburlini, G. Burden of Disease Caused by Otitis Media: Systematic Review and Global Estimates. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Danti, S.; Moroni, L.; Mota, C. Regenerative Therapies for Tympanic Membrane. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 127, 100942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Y.; Shen, Y.; Liew, L.J.; Wang, J.T.; von Unge, M.; Atlas, M.D.; Dilley, R.J. Rat Model of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforation: Ventilation Tube with Mitomycin C and Dexamethasone. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 80, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, M.; Yazıcı, D.; San, T.; Muluk, N.B.; Cingi, C. Fat-Plug Myringoplasty of Ear Lobule vs Abdominal Donor Sites. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2014, 272, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgursoy, O.B.; Yorulmaz, I. Fat Graft Myringoplasty: A Cost-Effective but Underused Procedure. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2005, 119, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharajan, N.; Cho, G.W.; Jang, C.H. Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration by Tissue Engineering Approach. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 133, 109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Fernandez, M.A.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Outlook for Tissue Engineering of the Tympanic Membrane. Audiol. Res. 2015, 5, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Tian, P.; Cui, X. The Latest Progress of Tympanic Membrane Repair Materials. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Bance, M.; Gratzer, P.F. Repair of Tympanic Membrane Perforation Using Novel Adjuvant Therapies: A Contemporary Review of Experimental and Tissue Engineering Studies. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 77, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira Lana, G.; Sorg, K.; Wenzel, G.I.; Hecker, D.; Hensel, R.; Schick, B.; Kruttwig, K.; Arzt, E. Self-Adhesive Silicone Microstructures for the Treatment of Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2021, 1, 2100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, N.; Zhou, L.; Quan, X.; Tang, Y.; Luo, X.; Huang, S.; Ma, R. Decellularized Tympanic Membrane Scaffold with Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Repairing Tympanic Membrane Perforation. Artif. Organs 2023, 47, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, R.; Harkut, R.; Mhashal, S.; Kadao, Y. Advancement in Tympanic Membrane Repair: Exploring the Potential of Platelet Rich Fibrin. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 76, 2962–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gür, Ö.E.; Ensari, N.; Öztürk, M.T.; Boztepe, O.F.; Gün, T.; Selçuk, Ö.T.; Renda, L. Use of a Platelet-Rich Fibrin Membrane to Repair Traumatic Tympanic Membrane Perforations: A Comparative Study. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2016, 136, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkilet, E.; Koyuncu, M.; Atmaca, S.; Yarim, M. Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Healing of Tympanic Membrane Perforations: Experimental Study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2008, 123, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Unge, M.; Dirckx, J.J.J.; Olivius, N.P. Embryonic Stem Cells Enhance the Healing of Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2003, 67, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranglani, D.; Agiwal, S.; More, N.; Parkale, R.; Shitole, V.; Hiray, A.R.; Kapusetti, G. Review on Tympanic Membrane and Auditory Canal Regeneration by Biomaterial Intervention. Mater. Highlights 2021, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, C.H.; Park, C.H.; Seo, J.-N.; Kweon, H.; Kang, S.W.; Lee, K.G. Comparison of Methods for the Repair of Acute Tympanic Membrane Perforations: Silk Patch vs. Paper Patch. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kweon, H.; Jo, Y.Y.; Park, C.H. Biodegradation Behavior of Silk Fibroin Membranes in Repairing Tympanic Membrane Perforations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100A, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Redmond, S.L.; Teh, B.M.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Budgeon, C.A.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Atlas, M.D.; Dilley, R.J.; et al. Scaffolds for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration in Rats. Tissue Eng. Part A 2013, 19, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Redmond, S.L.; Teh, B.M.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Atlas, M.D.; Dilley, R.J.; Zheng, M.; Marano, R.J. Tympanic Membrane Repair Using Silk Fibroin and Acellular Collagen Scaffolds. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.; Park, H.S.; Jeong, J.Y.; Yeon, Y.K.; Kumar, V.; Bae, S.H.; Lee, J.M.; Moon, B.M.; Park, C.H. A Prospective Cohort Study of the Silk Fibroin Patch in Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforation. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 2798–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemifar, R.; Redmond, S.; Zainuddin; Chirila, T.V. Advancing Towards a Tissue-Engineered Tympanic Membrane: Silk Fibroin as a Substratum for Growing Human Eardrum Keratinocytes. J. Biomater. Appl. 2010, 24, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harugade, A.; Sherje, A.P.; Pethe, A. Chitosan: A Review on Properties, Biological Activities and Recent Progress in Biomedical Applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2023, 191, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.W.; Choi, S.J.; Lim, K.T.; Lee, J.B.; Seonwoo, H.; Choung, P.-H.; Park, K.; Cho, C.-S.; Choung, Y.-H.; et al. A Healing Method of Tympanic Membrane Perforations Using Three-Dimensional Porous Chitosan Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 2763–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Azimi, B.; Lucena, M.; Ricci, C.; Candito, M.; Zavagna, L.; Astolfi, L.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Lazzeri, A.; Berrettini, S.; et al. Chitin Nanofibrils Modulate Mechanical Response in Tympanic Membrane Replacements. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 310, 120732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seonwoo, H.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, B.; Jang, K.-J.; Lee, M.; Choo, O.-S.; Choi, M.-J.; Kim, J.; Lim, K.-T.; Jang, J.H.; et al. Latent Stem Cell-Stimulating Therapy for Regeneration of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations Using IGFBP2-Releasing Chitosan Patch Scaffolds. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 34, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, S.; Laurent, C. Hyaluronan and Healing of Tympanic Membrane Perforations. An experimental study. Acta Otolaryngol. 1987, 442, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneri, E.A.; Tekin, S.; Yilmaz, O.; Özkara, E.; Erdağ, T.K.; Ikiz, A.Ö.; Sarioğlu, S.; Güneri, A. The Effects of Hyaluronic Acid, Epidermal Growth Factor, and Mitomycin in an Experimental Model of Acute Traumatic Tympanic Membrane Perforation. Otol. Neurotol. 2003, 24, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, I. Hyaluronic Acid Fat Graft Myringoplasty: An Office-Based Technique Adapted to Children. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 137, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.S.; Sahin, E.; Kaymaz, R.; Altunkaynak, B.Z.; Akidil, A.O.; Yanar, S.; Demir, D.; Guven, M. Histological Study of The Healing of Traumatic Tympanic Membrane Perforation After Vivosorb and Epifilm Application. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, M.; Gibbins, N.; John, G.; Rhys-Williams, S.; Scott, P. Hyaluronic Acid Ester in Myringoplasty. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2008, 122, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, K.; Yaman, H.; Cihat Avunduk, M.; Arbag, H.; Keles, B.; Uyar, Y. Effectiveness of MeroGel Hyaluronic Acid on Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006, 126, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konakçi, E.; Koyuncu, M.; Ünal, R.; Tekat, A.; Uyar, M. Repair of Subtotal Tympanic Membrane Perforations with Seprafilm®. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2004, 118, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.H.; Cho, Y.B.; Yeo, M.; Lee, H.; Min, E.J.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, G.H. Regeneration of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforation Using 3D Collagen with Topical Umbilical Cord Serum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svistushkin, M.; Kotova, S.; Zolotova, A.; Fayzullin, A.; Antoshin, A.; Serejnikova, N.; Shekhter, A.; Voloshin, S.; Giliazova, A.; Istranova, E.; et al. Collagen Matrix to Restore the Tympanic Membrane: Developing a Novel Platform to Treat Perforations. Polymers 2024, 16, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, M.; He, J. Preparation of Gelatin/Genipin Nanofibrous Membrane for Tympanic Member Repair. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 2154–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.W.; Park, S.; Lim, K.T.; Seonwoo, H.; Kim, Y.; Hong, B.H.; Choung, Y.; Chung, J.H. Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibrillar Patch as a Wound Healing Platform of Tympanic Membrane Perforation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandour, Y.M.H.; Mohammed, S.; Menem, M.o.A. Bacterial Cellulose Graft versus Fat Graft in Closure of Tympanic Membrane Perforation. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.M.d.M.R.; Kencis, C.C.S.; Miranda, D.R.P.; Sousa Neto, O.M.d. Traumatic Perforations of the Tympanic Membrane: Immediate Clinical Recovery with the Use of Bacterial Cellulose Film. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 86, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, F.C.A.; Pinto, F.C.M.; Caldas Neto, S.d.S.; Leal, M.d.C.; Cesário, J.; Aguiar, J.L.d.A. Treatment of Tympanic Membrane Perforation Using Bacterial Cellulose: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immich, A.P.S.; Pennacchi, P.C.; Naves, A.F.; Felisbino, S.L.; Boemo, R.L.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; Catalani, L.H. Improved Tympanic Membrane Regeneration after Myringoplastic Surgery Using an Artificial Biograft. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.M.; Massuda, E.T.; Hyppolito, M.A. Anatomical and Functional Evaluation of Tympanoplasty Using a Transitory Natural Latex Biomembrane Implant from the Rubber Tree Hevea Brasiliensis. Acta Cir. Bras. 2012, 27, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.-C.; He, J.-G. A Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Spontaneous Healing, Gelfoam Patching and Edge-approximation plus Gelfoam Patching in Traumatic Tympanic Membrane Perforation with Inverted or Everted Edges. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2011, 36, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakuba, N.; Tabata, Y.; Hato, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Gyo, K. Gelatin Hydrogel With Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; He, Z.; He, Z.; Li, L. Preparation of Antibacterial Gelatin/Genipin Nanofibrous Membrane for Tympanic Membrane Repair. Molecules 2022, 27, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seonwoo, H.; Shin, B.; Jang, K.; Lee, M.; Choo, O.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Garg, P.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor–Releasing Radially Aligned Electrospun Nanofibrous Patches for the Regeneration of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, S.; Shin, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Jang, K.-J.; Choo, O.-S.; Kim, J.; Seonwoo, H.; et al. Latent Stem Cell-Stimulating Radially Aligned Electrospun Nanofibrous Patches for Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforation Therapy. Acta Biomater. 2024, 188, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.E.; Semaan, M.T.; Wasman, J.K.; Beane, R.; Bonassar, L.J.; Megerian, C.A. Tissue-Engineered Calcium Alginate Patches in the Repair of Chronic Chinchilla Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, R.; Yazdian, F.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Aleemardani, M.; Chahsetareh, H.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Farhadi, M.; Bagher, Z. Fabrication and Optimization of Multilayered Composite Scaffold Made of Sulfated Alginate-Based Nanofiber/Decellularized Wharton’s Jelly ECM for Tympanic Membrane Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleemardani, M.; Akbarnejad, Z.; Jalessi, M.; Chahsetareh, H.; Hajmohammadi, Z.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Najafi, R.; Alizadeh, R.; Farhadi, M.; Bagher, Z. Silk Fibroin-Gelatin Films Crosslinked by Genipin for Regenerating Tympanic Membrane Perforations. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, B.J.; Ranney, J.D.; Khoshakhlagh, P.; Strasnick, B.; Horn-Ranney, E.L. A Novel Gel Patch for Minimally Invasive Repair of Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 115, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourheydari-Barsari, Z.; Mirzadeh, H.; Farhadi, M.; Solouk, A.; Jalessi, M. Antibacterial Aligned Nanofibrous Chitosan/PVA Patch for Repairing Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahsetareh, H.; Yazdian, F.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Aleemardani, M.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Najafi, R.; Simorgh, S.; Taghdiri Nooshabadi, V.; Bagher, Z.; Davachi, S.M. Alginate Hydrogel-PCL/Gelatin Nanofibers Composite Scaffold Containing Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Sustain Release for Regeneration of Tympanic Membrane Perforation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 130141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, C.; Danti, S.; D’Alessandro, D.; Trombi, L.; Ricci, C.; Puppi, D.; Dinucci, D.; Milazzo, M.; Stefanini, C.; Chiellini, F.; et al. Multiscale Fabrication of Biomimetic Scaffolds for Tympanic Membrane Tissue Engineering. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-Y.; Wilson, E.; Fuson, A.; Gandhi, N.; Monfaredi, R.; Jenkins, A.; Romero, M.; Santoro, M.; Fisher, J.P.; Cleary, K.; et al. Repair of Tympanic Membrane Perforations with Customized Bioprinted Ear Grafts Using Chinchilla Models. Tissue Eng. Part A 2018, 24, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xia, K.; Jian, M.; Liang, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Mechanically Reinforced Silkworm Silk Fiber by Hot Stretching. Research 2022, 2022, 9854063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, B.; Redmond, S.L.; Rajkhowa, R.; Eikelboom, R.H.; Atlas, M.D.; Marano, R.J. Utilising Silk Fibroin Membranes as Scaffolds for the Growth of Tympanic Membrane Keratinocytes, and Application to Myringoplasty Surgery. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2012, 127, S13–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allardyce, B.J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Dilley, R.J.; Xie, Z.; Campbell, L.; Keating, A.; Atlas, M.D.; von Unge, M.; Wang, X. Comparative Acoustic Performance and Mechanical Properties of Silk Membranes for the Repair of Chronic Tympanic Membrane Perforations. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 64, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Park, J.-S.; Lim, K.T.; Choung, P.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.B.; Chung, J.H.; Choung, Y.-H. Tympanic Membrane Regeneration Using a Water-Soluble Chitosan Patch. Tissue Eng. Part A 2010, 16, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopf-Marques, H.; Pravda, M.; Wolfova, L.; Velebny, V.; Schaaf, P.; Vrana, N.E.; Lavalle, P. Hyaluronic Acid and Its Derivatives in Coating and Delivery Systems: Applications in Tissue Engineering, Regenerative Medicine and Immunomodulation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2841–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, I.; Woods, O. Hyaluronic Acid Fat Graft Myringoplasty: A Minimally Invasive Technique. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhter, A.B.; Fayzullin, A.L.; Vukolova, M.N.; Rudenko, T.G.; Osipycheva, V.D.; Litvitsky, P.F. Medical Applications of Collagen and Collagen-Based Materials. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jeong, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Moon, B.M.; Park, Y.R.; Lee, O.J.; Sultan, M.T.; Kim, D.-K.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Application of a Collagen Patch Derived from Duck Feet in Acute Tympanic Membrane Perforation. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 14, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picheth, G.F.; Pirich, C.L.; Sierakowski, M.R.; Woehl, M.A.; Sakakibara, C.N.; de Souza, C.F.; Martin, A.A.; da Silva, R.; de Freitas, R.A. Bacterial Cellulose in Biomedical Applications: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, M.; Danti, S.; Livens, P.; Dirckx, J.; Scaffaro, R.; Gammino, M. Electrospun Graphene Oxide/Polymeric Nanocomposites for Eardrum Replacements. Compos. Commun. 2024, 51, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, P.A.C.; Guerra, N.B.; dos Santos, L.S.; Mussagy, C.U.; Pegorin Brasil, G.S.; Burd, B.S.; Su, Y.; da Silva Sasaki, J.C.; Scontri, M.; de Lima Lopes Filho, P.E.; et al. Natural Rubber Latex-Based Biomaterials for Drug Delivery and Regenerative Medicine: Trends and Directions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegorin Brasil, G.S.; de Barros, P.P.; Miranda, M.C.R.; de Barros, N.R.; Junqueira, J.C.; Gomez, A.; Herculano, R.D.; de Mendonça, R.J. Natural Latex Serum: Characterization and Biocompatibility Assessment Using Galleria Mellonella as an Alternative in Vivo Model. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2022, 33, 705–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.C.R.; Borges, F.A.; Barros, N.R.; Marques, M.P.; Galeane, M.C.; de Lacorte Singulani, J.; Guerra, N.B.; Brasil, G.S.P.; Mussagy, C.U.; Almeida, A.M.F.; et al. In Vitro and Alternative Animal Models to Evaluate the Biocompatibility of Natural Latex-Calcium Phosphate-Based Polymer. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3368–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.B.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.; Park, H.; Lee, S.-H. Engineering and Functionalization of Gelatin Biomaterials: From Cell Culture to Medical Applications. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2020, 26, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xin, T.; Shen, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Cui, W.; Shu, Y. Acoustic Transmitted Electrospun Fibrous Membranes for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmohammadi, M.; Nourbakhsh, M.S. Electrospun Polycaprolactone Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019, 68, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Mishra, V.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Alginate: Enhancement Strategies for Advanced Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widiyanti, P.; Angtika, R.S.; Githanadi, B.; Kharisma, D.H.; Asyraf, T.O.; Wardani, A. Collagen-Chitosan-Glycerol Bio-Composite as Artificial Tympanic Membrane for Ruptured Inner Ear Organ. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 853, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Ramesh, P.; Sayooj, K.; Unnikrishnan, M.; Unnikrishnan, G. Functionalized Polyvinyl Alcohol–Gelatin Graft for the Treatment of Tympanic Membrane Perforations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2025, 113, e37818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jang, C.H.; Kim, G.H. A Polycaprolactone/Silk-Fibroin Nanofibrous Composite Combined with Human Umbilical Cord Serum for Subacute Tympanic Membrane Perforation; an in Vitro and in Vivo Study. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2703–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscato, S.; Rocca, A.; D’Alessandro, D.; Puppi, D.; Gramigna, V.; Milazzo, M.; Stefanini, C.; Chiellini, F.; Petrini, M.; Berrettini, S.; et al. Tympanic Membrane Collagen Expression by Dynamically Cultured Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cell/Star-Branched Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Nonwoven Constructs. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Fusco, A.; Günday, C.; Günday-Türeli, N.; Donnarumma, G.; Danti, S.; Moroni, L.; Mota, C. Tunable Ciprofloxacin Delivery through Personalized Electrospun Patches for Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 38, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z. The Effect of Epidermal Growth Factor on the Pseudo-Healing of Traumatic Tympanic Membrane Perforations. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 87, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostam-Alilou, A.A.; Jafari, H.; Zolfagharian, A.; Serjouei, A.; Bodaghi, M. Using Fibrincollagen Composite Hydrogel and Silk for Bio-Inspired Design of Tympanic Membrane Grafts: A Vibro-Acoustic Analysis. Compos. Part C 2021, 6, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozin, E.D.; Black, N.L.; Cheng, J.T.; Cotler, M.J.; McKenna, M.J.; Lee, D.J.; Lewis, J.A.; Rosowski, J.J.; Remenschneider, A.K. Design, Fabrication, and In Vitro Testing of Novel Three-Dimensionally Printed Tympanic Membrane Grafts. Hear. Res. 2016, 340, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Seonwoo, H.; Garg, P.; Jang, K.J.; Pandey, S.; Park, S.B.; Kim, H.B.; Lim, J.; Choung, Y.H.; Chung, J.H. Chitosan/PEI Patch Releasing EGF and the EGFR Gene for the Regeneration of the Tympanic Membrane after Perforation. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 6, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danti, S.; Mota, C.; D’alessandro, D.; Trombi, L.; Ricci, C.; Redmond, S.L.; De Vito, A.; Pini, R.; Dilley, R.J.; Moroni, L.; et al. Tissue Engineering of the Tympanic Membrane Using Electrospun PEOT/PBT Copolymer Scaffolds: A Morphological in Vitro Study. Hear. Balance Commun. 2015, 13, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Jung, H.D.; Mittal, J.; Eshraghi, A.A. A Perspective on Stem Cell Therapy for Ear Disorders. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 233, 1823–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, L.J.; Chen, L.Q.; Wang, A.Y.; Von Unge, M.; Atlas, M.D.; Dilley, R.J. Tympanic Membrane Derived STEM Cell-Like Cultures for Tissue Regeneration. Stem Cells Dev. 2018, 27, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eken, M.; Ates, G.; Sanlı, A.; Evren, C.; Bozkurt, S. The Effect of Topical Insulin Application on the Healing of Acute Tympanic Membrane Perforations: A Histopathologic Study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2007, 264, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
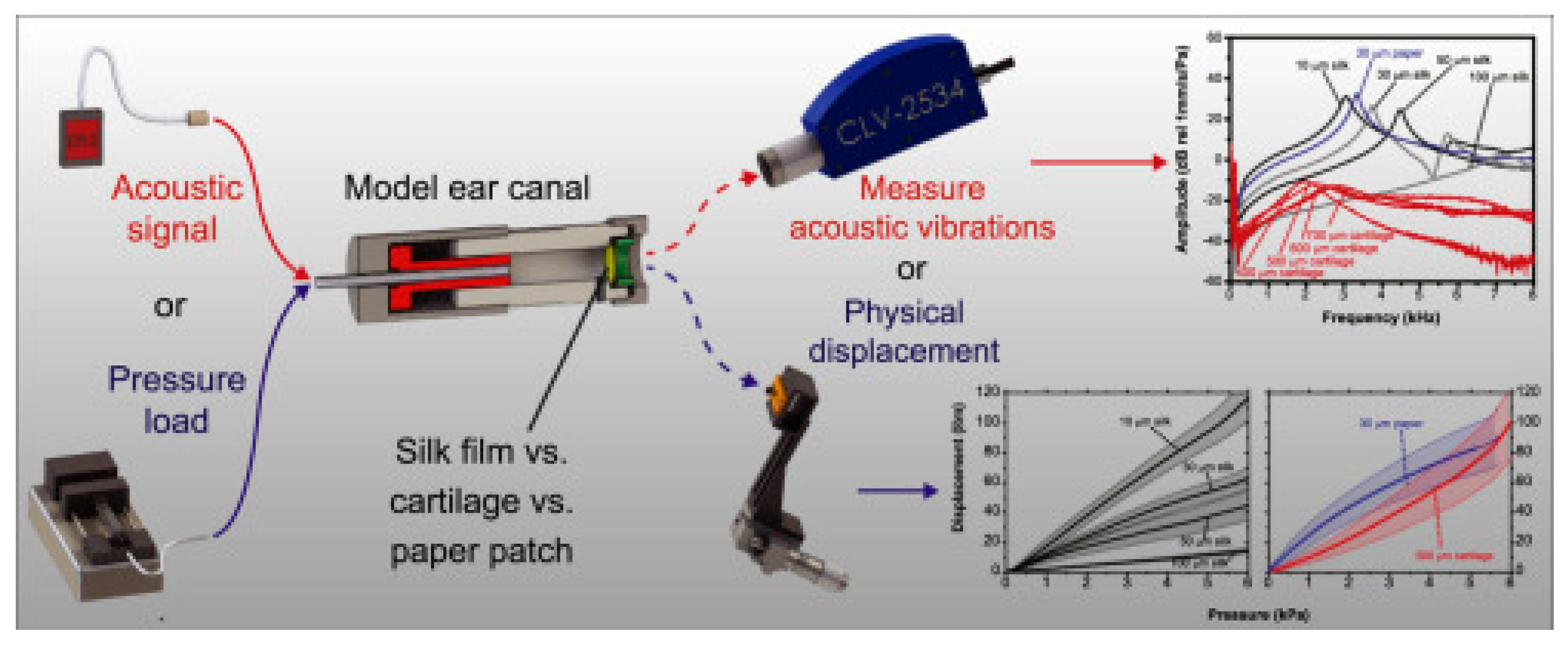


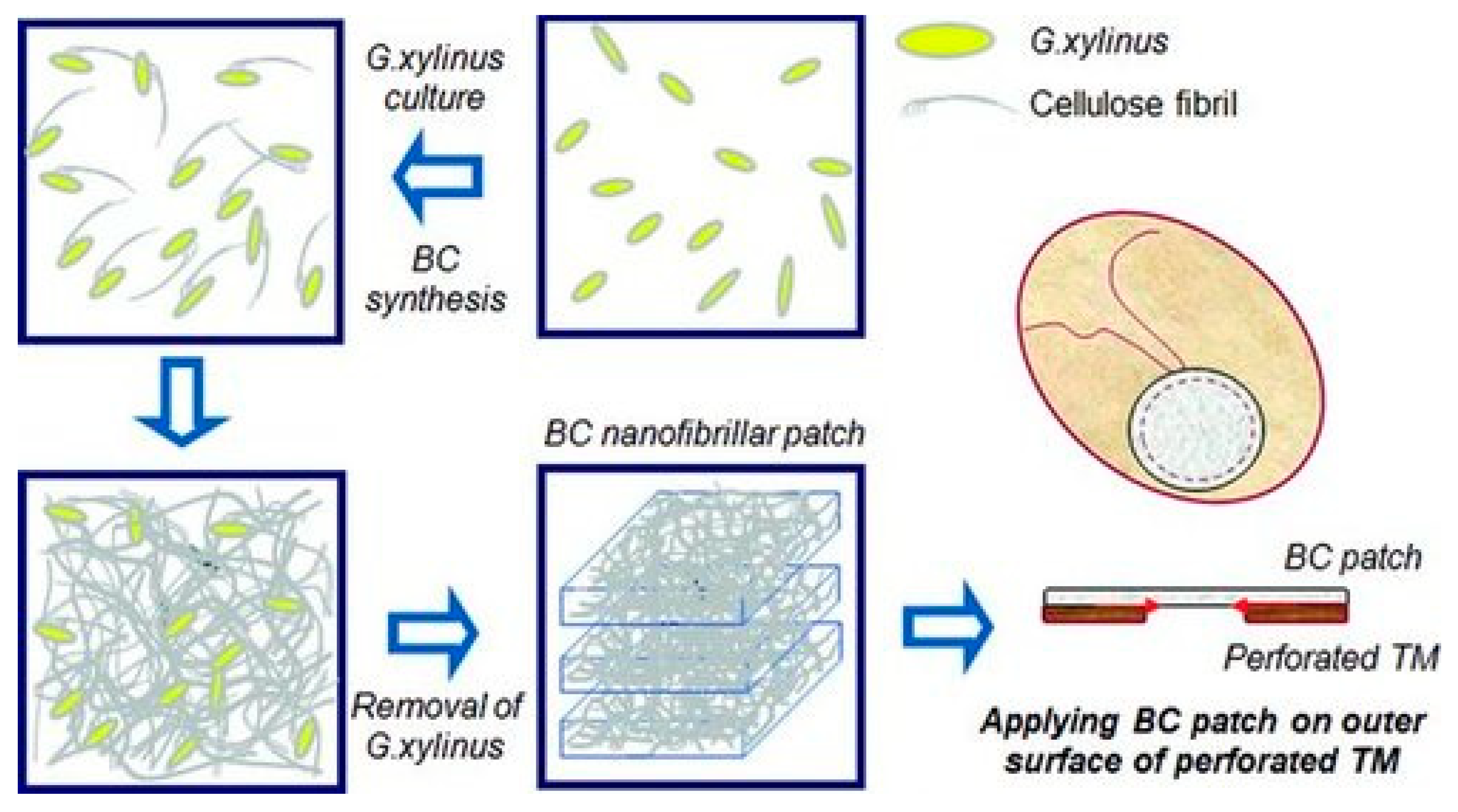
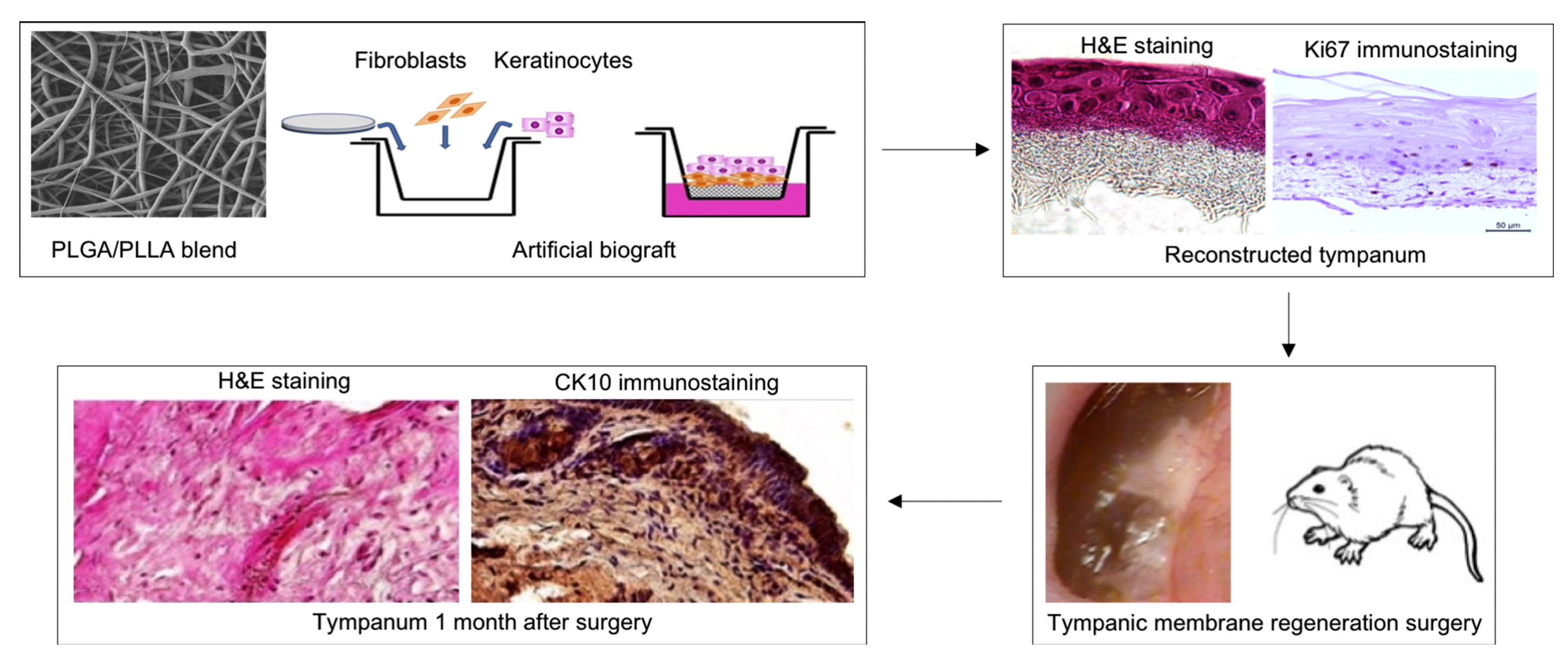


| Implant Composition | Polymer Molecular Weight | Polymer Graft form/Active Inclusions and Substances | Subject of Experiments | % of Subjects with Restored TM | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Lines | Animals and Human | ||||||
| 1 | Silk fibroin | naturally derived | casted polymer patch/- | - | rats | 93% | [19] |
| 2 | Silk fibroin | naturally derived | casted polymer patch/- | L929 cells | rats | - | [20] |
| 3 | Silk fibroin | naturally derived | casted polymer patch/- | - | rats | 100% | [21] |
| 4 | Silk fibroin | naturally derived | casted polymer patch/- | - | guinea pigs | 100% | [22] |
| 5 | Silk fibroin Tympasil® patch | - | ready film/- | - | human | 70% | [23] |
| 6 | Silk fibroin | naturally derived | casted polymer patch/- | human TM cells | - | - | [24] |
| 7 | Chitosan | 100–200 kDa | casted polymer patch/- | human TM cells | rats | 100% | [25] |
| 8 | Chitosan | 200 kDa | freezing and lyophilizing of polymer solution/- | human TM cells | rats | 100% | [26] |
| 9 | PEOT/PBT/(Chitin/PEG) | Chitin: naturally derived PEOT/PBT: 93 kDa PEG: 4000 g/mol | compression molding/- | human mesenchymal stromal cells OC-k3 HaCaT PC12 | - | - | [27] |
| 10 | Chitosan | 200 kDa | casted polymer patch/IGFBP2 | human TM cells | rats | 44% | [28] |
| 11 | HA | 4 or 6 MDa | polymer solution/- | - | rats | 100% | [29] |
| 12 | HA | - | polymer solution/- | - | rats | 100% | [30] |
| 13 | HA epidisc | - | fat graft myringoplasty | - | human | 93% | [30] |
| 14 | HA epidisc | - | fat graft myringoplasty | - | human (children) | 87% | [31] |
| 15 | HA ester Epifilm® | - | ready epidisc/- | - | rats | 100% | [32] |
| 16 | HA ester Epifilm® | - | ready epidisc/- | - | human | 0% | [33] |
| 17 | esterified HA MeroGel® | - | ready surgical tampons/- | - | rats | 92% | [34] |
| 18 | Seprafilm® | - | ready film/- | - | rats | 100% | [35] |
| 19 | Collagen | - | 3D printing/umbilical cord serum | NHDFs | guinea pigs | 100% | [36] |
| 20 | Collagen | naturally derived | electrophoretic deposition/- | - | chinchillas | 100% | [37] |
| 21 | Collagen | naturally derived | lyophilisation of polymer solution/- | - | rats | 100% | [38] |
| 22 | Bacterial cellulose | naturally derived | naturally formed/- | rat TM cells | rats | 100% | [39] |
| 23 | Bacterial cellulose | naturally derived | naturally formed/myringoplasty | - | human | 92.5% | [40] |
| 24 | Bionext® | - | ready film/- | - | human | 100% of examined patients | [41] |
| 25 | BC graft from Polisa™ | - | ready film/- | - | human | 90% | [42] |
| 26 | PLLA and PLGA | PLLA: 216,000 g/mol PLGA: 110,000 g/mol | electrospinning/fibroblasts and keratinocytes | human fibroblasts | rats | 100% | [43] |
| 27 | Latex | naturally derived | -/underlay myringoplasty | - | human | 67% | [44] |
| 28 | Gelatin gelfoam | - | -/- | - | human | 97% | [45] |
| 29 | Gelatin | - | chemically cross-linked hydrogel/basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) | - | guinea pigs | 100% | [46] |
| 30 | Gelatin and methacrylic acid | - | electrospinning/- | HEI-OC1 cells | guinea pigs | 100% | [47] |
| 31 | PCL | 80 kDa | electrospinning/epidermal growth factor (EGF) | rat TM cells | rats | 100% | [48] |
| 32 | PCL | 80 kDa | electrospinning/IGFBP2 | rat TM cells | rats | 100% | [49] |
| 33 | Calcium alginate | - | injection molding technology/- | - | chinchillas | 71% | [50] |
| 34 | Alginate sulfate and PVA | Alginate sulfate: 140 kDa PVA: 85,000–124,000 g/mol | electrospinning/Wharton’s Jelly | NIH 3T3 | rats | 100% | [51] |
| 35 | Silk fibroin and gelatin | naturally derived | casted polymer patch/- | human dermal fibroblast (HDF) | rats | 100% | [52] |
| 36 | HA and chitosan | - | photocurable gel/- | - | chinchillas | 100% | [53] |
| 37 | Chitosan and PVA | Chitosan: 600 g/mol PVA: 88–98 kDa | electrospinning/thyme essential oil | Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli and Mesenchymal stem cells | human | 100% | [54] |
| 38 | PCL, gelatin and sodium alginate | PCL: 80,000 g/mol sodium alginate: 200–300 kDa | composite structure/exosomes from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells | NIH/3 T3 | rats | 100% | [55] |
| 39 | PCL and silk fibroin | PCL: 80,000 g/mol silk fibroin: naturally derived | composite structure/umbilical cord serum | human dermal fibroblasts | guinea pigs | 100% | [56] |
| 40 | Gelatin and gelatin modified with methacrylic anhydride | - | 3D printing/EGF | NIH/3T3 | chinchillas | 100% | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaikenov, R.O.; Serbun, P.G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Snetkov, P.P.; Morozkina, S.N. Natural Polymers, Their Modifications and Composites with Synthetic Polymers for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16100384
Shaikenov RO, Serbun PG, Zhang J, Wu H, Wang Z, Snetkov PP, Morozkina SN. Natural Polymers, Their Modifications and Composites with Synthetic Polymers for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(10):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16100384
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaikenov, Roman O., Polina G. Serbun, Jingran Zhang, Hao Wu, Zuobin Wang, Petr P. Snetkov, and Svetlana N. Morozkina. 2025. "Natural Polymers, Their Modifications and Composites with Synthetic Polymers for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 10: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16100384
APA StyleShaikenov, R. O., Serbun, P. G., Zhang, J., Wu, H., Wang, Z., Snetkov, P. P., & Morozkina, S. N. (2025). Natural Polymers, Their Modifications and Composites with Synthetic Polymers for Tympanic Membrane Regeneration. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(10), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16100384








