Cationic Serine-Based Gemini Surfactant:Monoolein Aggregates as Viable and Efficacious Agents for DNA Complexation and Compaction: A Cytotoxicity and Physicochemical Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
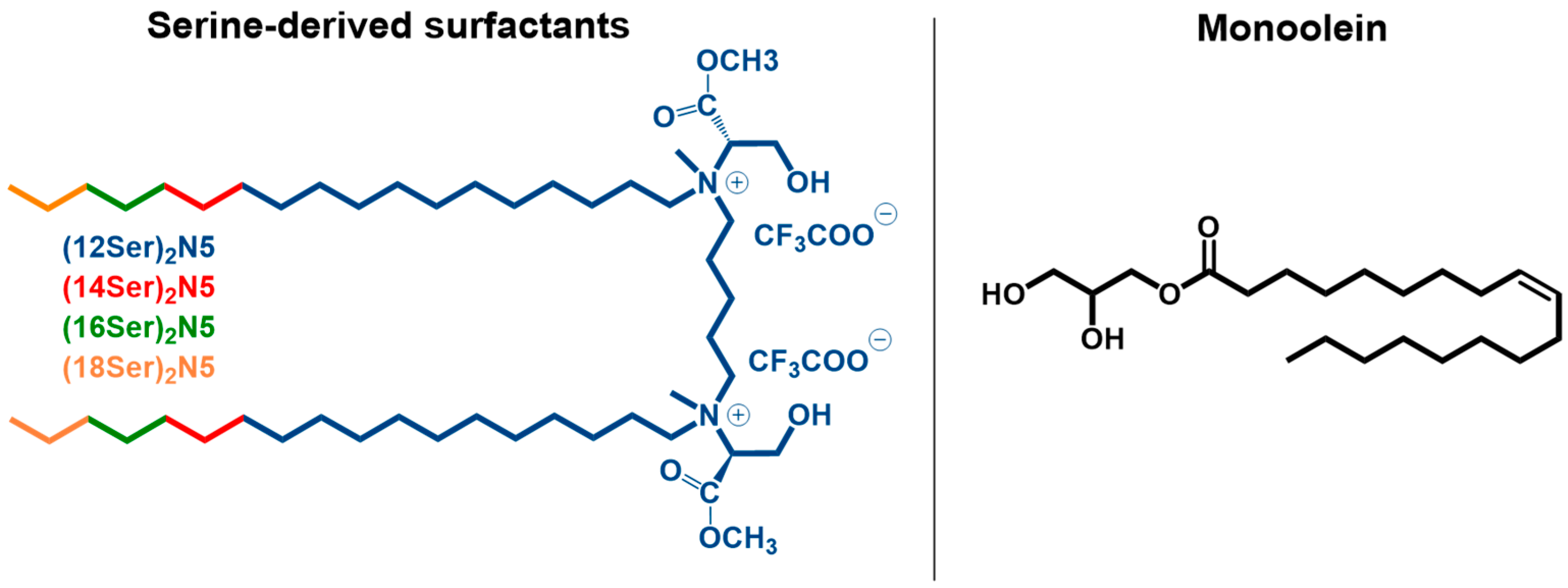
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Evaluation
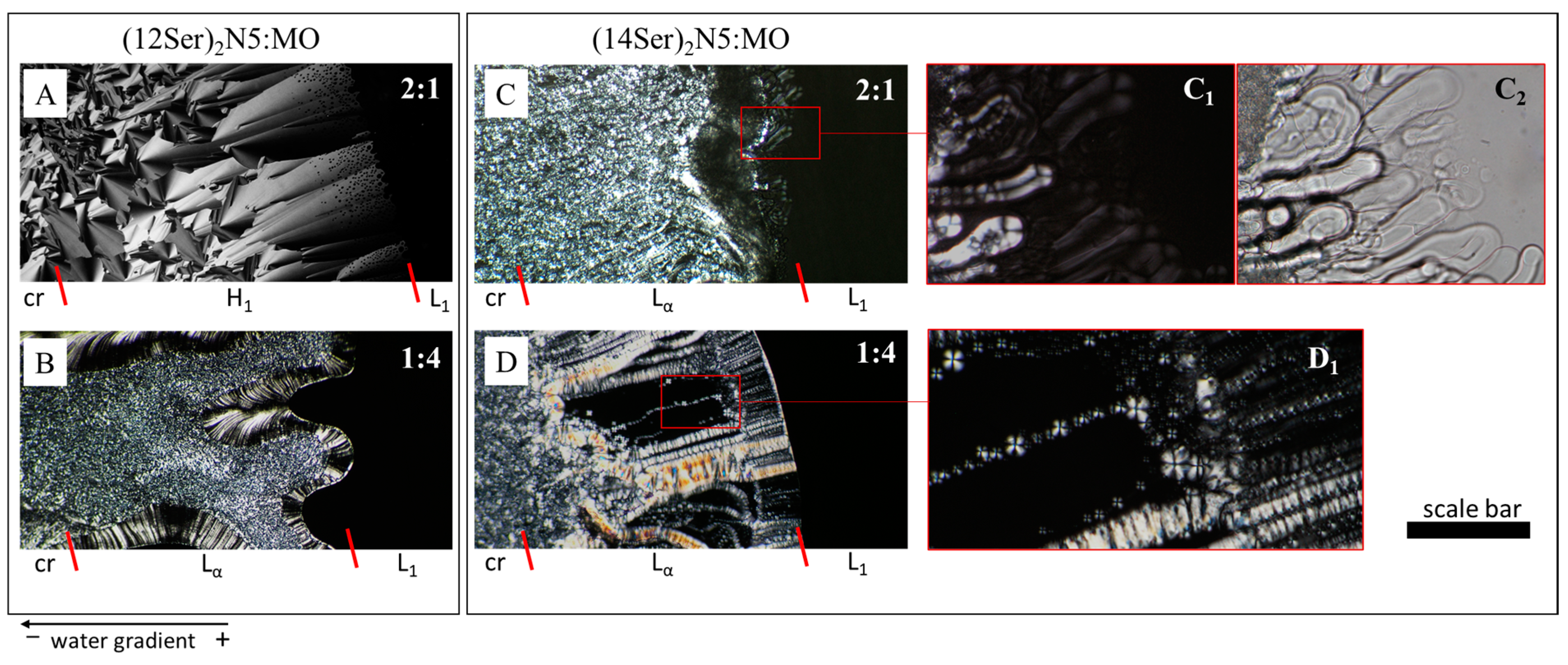
2.4. Light Microscopy
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
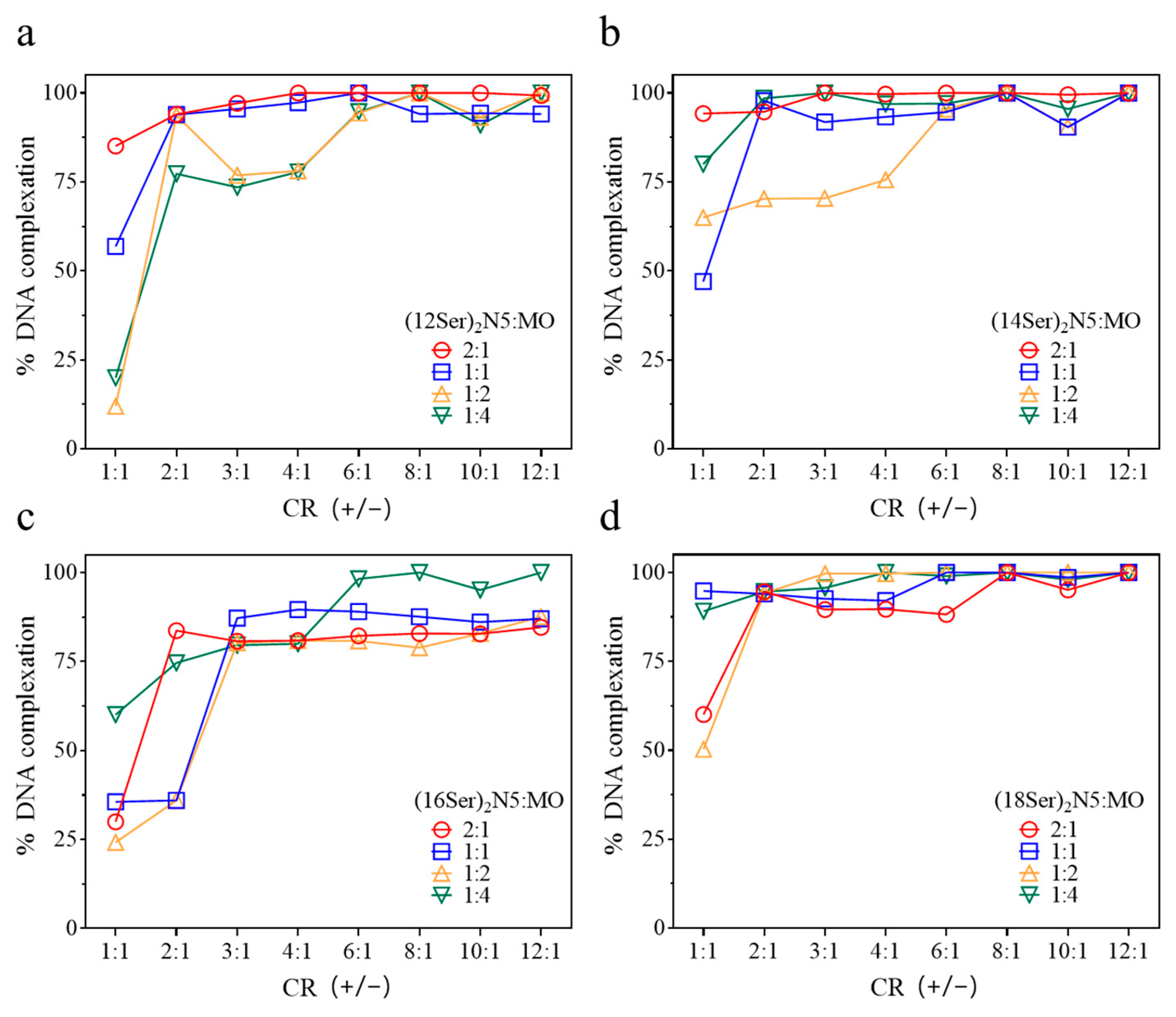
2.6. DNA Complexation: Ethidium Bromide Exclusion Assay
3. Results and Discussion
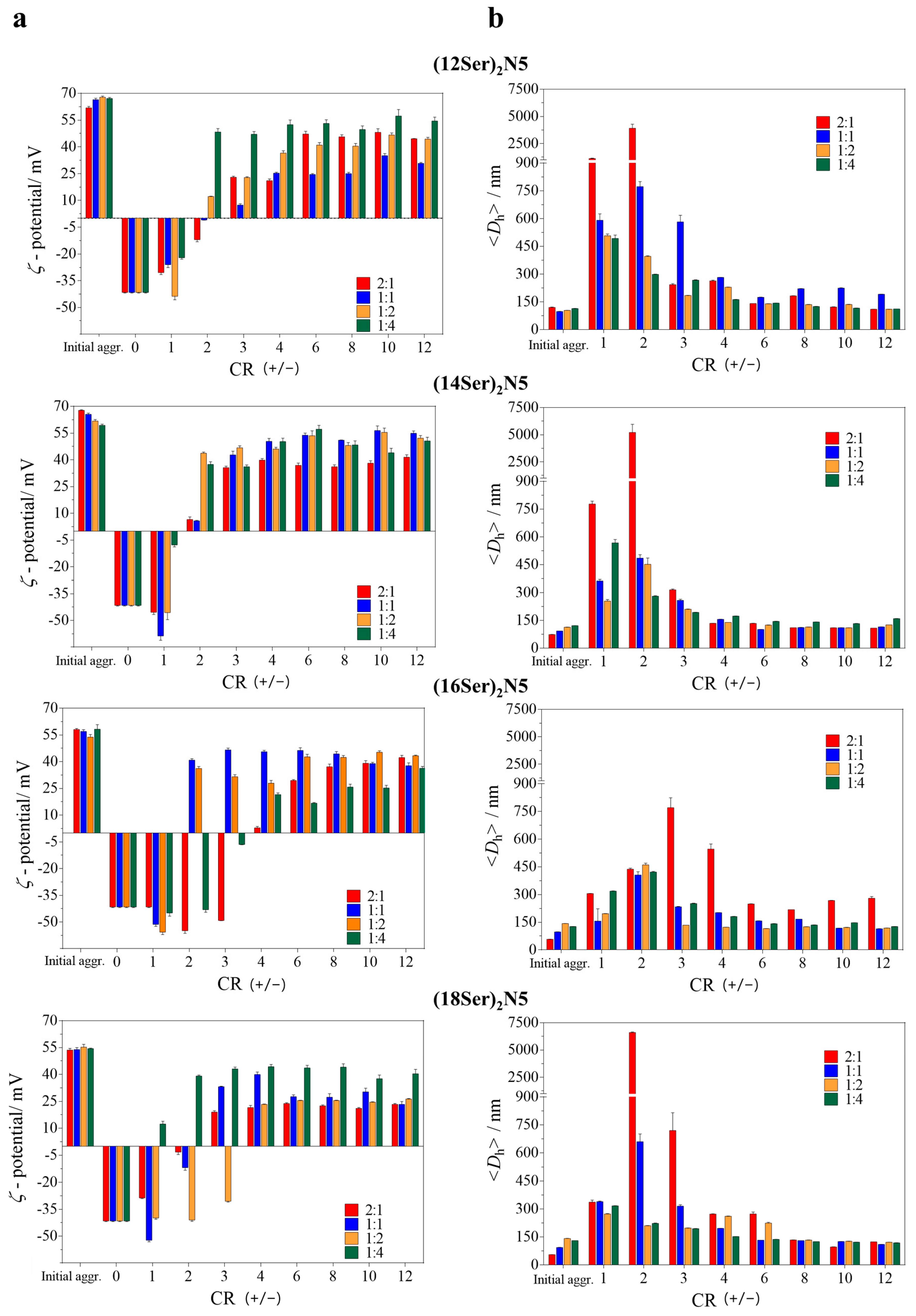
3.1. Interactions between Gemini:MO Aggregates and DNA
3.2. Characterization of the Gemini:MO Aggregation Behavior
3.3. Discussion of the Main Interaction/Aggregation Trends
3.4. Cytotoxicity of the Gemini–MO Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roberts, T.C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M.J.A. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, B.B.; Conniot, J.; Avital, A.; Yao, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, X.; Sharf-Pauker, N.; Xiao, Y.; Adir, O.; Liang, H.; et al. Nanodelivery of nucleic acids. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asami, Y.; Yoshioka, K.; Nishina, K.; Nagata, T.; Yokota, T. Drug delivery system of therapeutic oligonucleotides. Drug Discov. Today Ther. Strateg. 2016, 10, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, W.; Lin, L.; Chen, A.; Feng, J.; Qu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yue, J. Delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotides in nanoscale. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 7, 292–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Gao, Y.; He, L.; Fang, B.; Ge, W.; Yang, P.; Ju, Y.; Xie, X.; Lei, L. Biomaterial-based gene therapy. MedComm 2023, 4, e259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, C.; Xie, X.; Lin, Y. The biological applications of DNA nanomaterials: Current challenges and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Ribeiro, A.M.; Pérez-Betancourt, Y. Cationic nanostructures for vaccines design. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Göpfrich, K.; Platzman, I.; Spatz, J.P. DNA-based assembly of multi-compartment polymersome networks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, M.Y.; Nagovitsina, T.Y.; Bidanov, D.A.; Gorbachevski, O.S.; Yurtov, E.V. Nano- and microcapsules as drug-delivery systems. Resour. Effic. Technol. 2016, 2, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; You, Y. Cationic micelle: A promising nanocarrier for gene delivery with high transfection efficiency. J. Gene Med. 2019, 21, e3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid nanoparticles─from liposomes to mRNA vaccine delivery, a landscape of research diversity and advancement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16982–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Oliveira, I.S.; Silva, J.P.N.; Silva, S.G.; Botelho, C.; do Vale, M.L.C.; Real Oliveira, M.; Gomes, A.C.; Marques, E.F. Effective cytocompatible nanovectors based on serine-derived gemini surfactants and monoolein for small interfering RNA delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 584, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Al-Dulaymi, M.; Badea, I.; Leary, S.C.; Rehman, J.; El-Aneed, A. Cellular uptake and distribution of gemini surfactant nanoparticles used as gene delivery agents. AAPS J. 2019, 21, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Badea, I.; Leary, S.C.; El-Aneed, A. The determination of gemini surfactants used as gene delivery agents in cellular matrix using validated tandem mass spectrometric method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.G.; Oliveira, I.S.; do Vale, M.L.C.; Marques, E.F. Serine-based gemini surfactants with different spacer linkages: From self-assembly to DNA compaction. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 9352–9361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.K.; Kim, S.W. Recent advances in the development of gene delivery systems. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald Albertsen, C.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Lind, M.; Petersson, K.; Simonsen, J.B. The role of lipid components in lipid nanoparticles for vaccines and gene therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 188, 114416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Arribas, N.; Martínez-Negro, M.; Villar, E.M.; Pérez, L.; Aicart, E.; Taboada, P.; Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Junquera, E. Biocompatible nanovector of siRNA consisting of arginine-based cationic lipid for gene knockdown in cancer cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34536–34547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Negro, M.; Sánchez-Arribas, N.; Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Moyá, M.L.; de Ilarduya, C.T.; Mendicuti, F.; Aicart, E.; Junquera, E. A non-viral plasmid DNA delivery system consisting on a lysine-derived cationic lipid mixed with a fusogenic lipid. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Negro, M.; Blanco-Fernández, L.; Tentori, P.M.; Pérez, L.; Pinazo, A.; de Ilarduya, C.T.; Aicart, E.; Junquera, E. A gemini cationic lipid with histidine residues as a novel lipid-based gene nanocarrier: A biophysical and biochemical study. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Lee, R.J. The role of helper lipids in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) designed for oligonucleotide delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Leung, J.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Cullis, P.R. On the role of helper lipids in lipid nanoparticle formulations of siRNA. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 21733–21739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.P.N.; Oliveira, A.C.N.; Casal, M.; Gomes, A.C.; Coutinho, P.J.G.; Coutinho, O.P.; Oliveira, M. DODAB:monoolein-based lipoplexes as non-viral vectors for transfection of mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeier, G.; Dogan-Surmeier, S.; Paulus, M.; Albers, C.; Latarius, J.; Sternemann, C.; Schneider, E.; Tolan, M.; Nase, J. The interaction of viral fusion peptides with lipid membranes. Biophys. J. 2022, 121, 3811–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, R.; Coelho, F.; Silva, B.F.B. Lipid-Nucleic Acid Complexes: Physicochemical Aspects and Prospects for Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goreti Silva, S.; Fernandes, R.F.; Marques, E.F.; do Vale, M.L.C. Serine-based bis-quat gemini surfactants: Synthesis and micellization properties. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreleiro, P.C.A.; Lindman, B. The kinetics of DNA-cationic vesicle complex formation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 6208–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Murillo, R.; Cheatham, T.E., III. Ethidium bromide interactions with DNA: An exploration of a classic DNA-ligand complex with unbiased molecular dynamics simulations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 3735–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonasera, V.; Alberti, S.; Sacchetti, A. Protocol for high-sensitivity/long linear-range spectrofluorimetric DNA quantification using ethidium bromide. BioTechniques 2007, 43, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N.; Mitchell, D.J.; Ninham, B.W. Theory of self-assembly of hydrocarbon amphiphiles into micelles and bilayers. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 2 Mol. Chem. Phys. 1976, 72, 1525–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zana, R. Dimeric and oligomeric surfactants. Behavior at interfaces and in aqueous solution: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 97, 205–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-5:2009, I.S.I.; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices: Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.


| System | Gemini:MO Molar Ratio | IC50/µM |
|---|---|---|
| (12Ser)2N5:MO | 2:1 | 35 ± 5 |
| 1:1 | 50 ± 5 | |
| 1:2 | 62 ± 9 | |
| 1:4 | 64 ± 5 | |
| (14Ser)2N5:MO | 2:1 | 45 ± 6 |
| 1:1 | 51 ± 8 | |
| 1:2 | 62 ± 7 | |
| 1:4 | 55 ± 8 | |
| (16Ser)2N5:MO | 2:1 | 64 ± 3 |
| 1:1 | 72 ± 3 | |
| 1:2 | 76 ± 7 | |
| 1:4 | 90 ± 7 | |
| (18Ser)2N5:MO | 2:1 | >100 |
| 1:1 | 43 ± 7 | |
| 1:2 | 46 ± 8 | |
| 1:4 | 74 ± 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, I.S.; Silva, S.G.; Gomes, A.C.; Real Oliveira, M.E.C.D.; Vale, M.L.C.d.; Marques, E.F. Cationic Serine-Based Gemini Surfactant:Monoolein Aggregates as Viable and Efficacious Agents for DNA Complexation and Compaction: A Cytotoxicity and Physicochemical Assessment. J. Funct. Biomater. 2024, 15, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15080224
Oliveira IS, Silva SG, Gomes AC, Real Oliveira MECD, Vale MLCd, Marques EF. Cationic Serine-Based Gemini Surfactant:Monoolein Aggregates as Viable and Efficacious Agents for DNA Complexation and Compaction: A Cytotoxicity and Physicochemical Assessment. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2024; 15(8):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15080224
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Isabel S., Sandra G. Silva, Andreia C. Gomes, M. Elisabete C. D. Real Oliveira, M. Luísa C. do Vale, and Eduardo F. Marques. 2024. "Cationic Serine-Based Gemini Surfactant:Monoolein Aggregates as Viable and Efficacious Agents for DNA Complexation and Compaction: A Cytotoxicity and Physicochemical Assessment" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 15, no. 8: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15080224
APA StyleOliveira, I. S., Silva, S. G., Gomes, A. C., Real Oliveira, M. E. C. D., Vale, M. L. C. d., & Marques, E. F. (2024). Cationic Serine-Based Gemini Surfactant:Monoolein Aggregates as Viable and Efficacious Agents for DNA Complexation and Compaction: A Cytotoxicity and Physicochemical Assessment. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 15(8), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb15080224












