Abstract
Popular photoluminescent (PL) nanomaterials, such as carbon dots, have attracted substantial attention from scientists due to their photophysical properties, biocompatibility, low cost, and diverse applicability. Carbon dots have been used in sensors, cell imaging, and cancer therapy. Leek seeds with anticancer, antimicrobial, and antioxidant functions serve as traditional Chinese medicine. However, leek seeds have not been studied as a precursor of carbon dots. In this study, leek seeds underwent a supercritical fluid extraction process. Leek seed extract was obtained and then carbonized using a dry heating method, followed by hydrolysis to form carbon dot micelles (CD-micelles). CD-micelles exhibited analyte-induced PL quenching against Co2+ through the static quenching mechanism, with the formation of self-assembled Co2+-CD-micelle sphere particles. In addition, CD-micelles extracted metal ion through liquid–liquid extraction, with removal efficiencies of >90% for Pb2+, Al3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, Pd2+, and Au3+. Moreover, CD-micelles exhibited ABTS•+ radical scavenging ability and cytotoxicity for cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. CD-micelles killed cisplatin-resistant small-cell lung cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner with a cancer cell survival rate down to 12.8 ± 4.2%, with a similar treatment function to that of cisplatin. Consequently, CD-micelles functionalized as novel antioxidants show great potential as anticancer nanodrugs in cancer treatment.
1. Introduction
Carbon dots (C-dots), deemed as photoluminescent nanomaterials, have attracted considerable attention from scientists because of their unique photophysical properties, biocompatibility, environmental friendliness, easy storage, and low cost [1,2,3]. C-dots can be synthesized through hydrothermal treatment, thermal decomposition, electrochemical oxidation, or ultrasonic synthesis, with advantages of being easy to produce, photophysical stability, and eco-efficiencies [4,5].
C-dots have been applied in sensors, electronic devices, adsorbents, energy storage, catalysis, cell imaging, and cancer therapy [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. For sensors, C-dots are used for sensing Fe3+, Hg2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Au3+, Cr6+, ClO−, S2−, S2O32−, Pb2+, H2O2, cysteine, glutathione, synthetic cathinones, flunitrazepam, or nimetazepam [14,15,16,17,18] through mechanisms including the inner filter effect and dynamic or static processes [19,20,21]. For adsorbents, Zhang et al. synthesized C-dot-embedded mesoporous silica nanoparticles in 2015, which had high adsorption capacity for Cu2+, Pb2+, and Hg2+ [11]. In 2020, Issa et al. produced environmentally friendly C-dots from tapioca flour, with a removal efficiency of 80.6% for Pb2+ [12]. In 2024, Valente et al. synthesized poly(β-cyclodextrin)-modified C-dots, with removal efficiencies of almost 100% for Ni2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ [13].
In cancer therapy, C-dots have been used in photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy, and drug delivery [22,23]. Among different types of cancer, lung cancer has the fastest growing rates of morbidity and mortality [24,25]. The effectiveness of chemotherapy is frequently hampered by the low therapeutic index of drugs and the occurrence of inherent and acquired drug resistance in cancer cells [26,27]. Zhao et al. synthesized C-dots loaded with cisplatin(IV) prodrug and doxorubicin to monitor the location of nanocarriers and drug release; they exhibited anticancer effects for the effective apoptosis of A2780 and A2780cis cancer cells with cisplatin resistance [28].
C-dot precursors, such as fruits, food, beverages, vegetables, leaves, and waste materials, have been widely studied [11,29]. Leek seeds deeded as biomaterials contain oil, crude proteins, and dietary fibers; these seeds have several biological effects, including anticancer, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects, and they are used in traditional Chinese medicine [30,31,32]. However, leek seeds have not been studied as a precursor of C-dots.
Thus, leek seeds were selected in this study as starting materials because of their significant anticancer, antimicrobial, and antioxidant activities [30,31,32]. Leek seed extract was obtained through a supercritical fluid extraction process and then sequentially carbonized using a dry heating method, followed by hydrolysis to form C-dot micelles (CD-micelles). The results show that CD-micelles have multifunctional properties, including applications for Co2+ sensors and metal ion removal, as well as for anticancer nanodrugs, providing promising applications for C-dots.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Lithium chloride (LiCl), silver nitrate (AgNO3), zinc nitrate hexahydrate [Zn(NO3)2·6H2O], and potassium persulfate (K2S2O8) were purchased from Acros Organics (Geel, Antwerp, Belgium). Chromium(III) nitrate nonahydrate [Cr(NO3)3·9H2O], hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), fluorescein, ethyl acetate, and ethanol were purchased from Fisher Chemical (Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Palladium chloride (PdCl2), gold chloride trihydrate (HAuCl4·3H2O), and 2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) were purchased from Combi-Blocks (San Diego, CA, USA). Cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) (cisplatin) was obtained from AK Scientific (Union, CA, USA). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), mercuric nitrate dihydrate [Hg(NO3)2·2H2O], cupric nitrate trihydrate [Cu(NO3)2·3H2O], ferric nitrate nonahydrate [Fe(NO3)3·9H2O], aluminum nitrate nonahydrate [Al(NO3)3·9H2O], lead nitrate [Pb(NO3)2], nickel nitrate hexahydrate [Ni(NO3)2·6H2O], and cobalt nitrate hexahydrate [Co(NO3)2·6H2O] were purchased from Echo Chemical (Toufen, Miaoli, Taiwan). Deuterated oxide (D2O) was purchased from Acros Organics (Geel, Antwerp, Belgium). Carbon dioxide (purity 99.99%) was supplied by San Ying Gas Co., LTD. (New Taipei City, Taiwan). Leek seeds were obtained from a Chinese herb medicine store (Chiayi County, Taiwan). Ultrapure water (18.2 mΩ·cm) was obtained using an ultrapure water system (Direct-Q3; Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and used to prepare all of the aqueous solutions in this study.
2.2. Leek Seed Extract
The leek seeds were ground in a knife mill (CS-700; Cosuai, Jinhua, China) and then filtered through a sieve with a diameter range of 0.150–0.850 mm to yield leek seed powder, which was divided into samples of 600 g each. The leek seed powder was then extracted using supercritical carbon dioxide (scCO2) at 333 K and 5000 psi with a continuous flow rate of 6 L·min−1 for 8 h. The extraction was performed using supercritical fluid extraction equipment (OV-SCF-10000 Series; Taiwan Supercritical Technology, Changhua, Taiwan) equipped with an extractor with a volume of 1000 cm3. Light-yellow leek seed extract was obtained and then stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C until further use. The weight of the obtained seed extract was 16.6 g.
2.3. Analysis of Leek Seed Extract Through Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
The leek seed extract (50 μL) was dissolved in 500 μL of ethanol for gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) analysis (Agilent 8890/5977B, Santa Clara, CA, USA) on a fused-silica capillary column (DB-5MS; 30 m × 0.32 mm i.d.; film thickness: 0.25 µm; J&W Scientific, Koeniz, Switzerland). The parameters of the GC–MS system were as follows: electron impact mode, 70 eV; carrier gas, helium; carrier gas flow rate, 1.0 mL⋅min−1; and injection port temperature, 260 °C. The temperature was initially maintained at 135 °C for 0.5 min and then gradually increased to 300 °C at a rate of 70 °C min−1 and maintained at 300 °C for 12.5 min.
2.4. Synthesis of CD-Micelles
The leek seed extract (5 g) was added to a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and heated in a furnace at 200 °C for 3 days. After cooling to ambient temperature, a brown-yellow mixture was obtained. Subsequently, to form CD-micelles, an aliquot (1.0 g) of the obtained mixture was reacted with 5 mL of NaOH solution (0.02 N) in an ultrasonic bath at 60 °C for 120 min. To remove organic impurities, liquid–liquid extraction was performed with a solution of ethyl acetate and ultrapure water (10 mL, v/v = 1/1). The purified CD-micelles were freeze-dried. The stock aqueous solution of the purified CD-micelles was prepared at a concentration of 16 mg mL−1 and stored at 4 °C before use.
2.5. Characterization of CD-Micelles
The absorption spectra of CD-micelles were obtained using an ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometer (Evolution 220; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The photoluminescence (PL) spectra of CD-micelles were recorded using a microplate reader (SpectraMax i3x; Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA). The PL quantum yield (ΦPL) of CD-micelles was estimated by comparing their PL intensity at 460 nm (excited at 365 nm) and absorbance at 365 nm with those of quinine sulfate dissolved in 0.1 M H2SO4 (ΦPL = 0.54). The absorbance values of CD-micelles and quinine sulfate were kept under 0.1 at their excitation wavelength to minimize the re-absorption effect. The Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of CD-micelles were recorded using a spectrometer (Nicolet iS5; Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The sizes and shapes of CD-micelles with and without Co2+ were recorded using a high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) (JEM-2100F; JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) coupled with an energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer at 200 kV. Surface elements and bonding states of CD-micelles were investigated using an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) instrument from VG Scientific (East Grinstead, UK) with Al Kα X-ray radiation. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements (Nano-ZS90; Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK) were employed to measure the average sizes of CD-micelles dispersed in ultrapure water. A nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) instrument (Ultrashield-400, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) was used to perform 1H NMR and 13C NMR analyses.
Fluorescein was used to evaluate the critical micelle concentration (CMC) of CD-micelles. Briefly, 8 aliquots (125 µL) of fluorescein aqueous solution (0.32 µM) were separately mixed with 125 µL of CD-micelle solutions with concentrations from 0 to 0.06 mg mL−1 before being subjected to PL measurements. The CMC value of CD-micelles was assessed based on their PL intensity at 515 nm emitted from fluorescein under an excitation wavelength of 460 nm as concentrations of CD-micelles were increased.
2.6. Selectivity and Sensitivity of CD-Micelles for Metal Ions
To assess the selectivity of CD-micelles for metal ions, 150 μL aliquots of the CD-micelle solution (3.2 mg mL−1) were separately mixed with 150 μL of metal ion solutions (200 μM), namely Li+, Zn2+, Al3+, Pb2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Ag+, Cr3+, Pd2+, and Au3+. The PL spectra of CD-micelles with and without metal ions were separately recorded at an excitation wavelength of 365 nm. The PL intensities of CD-micelle solutions at 450 nm were separately plotted against the tested metal ions. In addition, the sensitivity of CD-micelles for Co2+ was assessed. Aliquots (150 μL) of the CD-micelle solution (3.2 mg mL−1) were separately mixed with 150 μL of Co2+ solutions of various concentrations (0–80 μM). Subsequently, the PL spectra of CD-micelles with and without Co2+ were separately recorded. The PL quenching efficiency at 450 nm of the CD-micelles against Co2+ at concentrations of 1–40 μM was thus used to evaluate the sensitivity. The PL quenching behavior between CD-micelles and Co2+ was assessed by using the Stern–Volmer equation shown in Equation (1).
where F0 and F are the PL intensities of CD-micelles in the absence and presence of the quencher, respectively. [Q] is the concentration of Co2+, and KSV is the corresponding Stern–Volmer constant. In addition, the lifetimes of CD-micelles with and without Co2+ (100 μM) were measured using a steady-state PL spectrometer with a picosecond pulsed LED (Ex 313 nm) (FS5; Edinburgh Instruments, Livingston, UK) at an emission wavelength of 450 nm. All experiments were performed under ambient pressure and temperature conditions.
F0/F = 1 + Ksv [Q]
2.7. Metal Ion Removal Using CD-Micelles Through Liquid–Liquid Extraction
Aliquots (2 mL) of the CD-micelle solution (16 mg mL−1) were separately mixed with metal ion solutions (2 mL, 500 µM) containing Li+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Ag+, Al3+, Cr3+, Pd2+, or Au3+. Subsequently, to adjust the pH to 4 and 7, 0.2 M HNO3 was separately added into the mixtures. Ethyl acetate (4 mL) was added to each mixture and stirred for 2 h. The organic and aqueous layers were separated, and the organic layer was removed. Aliquots (100 µL) of the remaining solutions were separately diluted in 1 mL of ultrapure water for analysis. Before and after liquid–liquid extraction, the metal ion concentrations of the remaining solutions were determined using inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES, PerkinElmer Optima 8300, Waltham, MA, USA). The efficiency of metal ion removal was calculated using Equation (2).
where [M]a and [M]b represent the metal ion concentrations after and before liquid–liquid extraction, respectively. For comparison, SDS and CTAB were employed with similar metal ion removal processes for CD-micelles.
Removal efficiency (%) = [M]a/[M]b × 100 (%)
2.8. Antioxidant Activity of CD-Micelles
The CD-micelle stock solution (16 mg mL−1) was separately diluted in ultrapure water for the preparation of diluted CD-micelle solutions of various concentrations (5, 25, 50, 100, 500, and 1000 μg mL−1). Subsequently, 1 mL aliquots of the as-diluted CD-micelle solutions/ultrapure water were mixed with 1 mL of ABTS (100 µM). The reaction was allowed to proceed for 2 h in the dark. Subsequently, the absorption spectra of these mixtures were recorded. The radical scavenging efficiency of CD-micelles was calculated using Equation (3) [33,34].
where Ar is the absorbance at 734 nm of ABTS•+ in ultrapure water and As is the absorbance at 734 nm for ABTS•+ with CD-micelles.
Radical scavenging efficiency (%) = (Ar − As)/Ar × 100 (%)
2.9. Cytotoxicity of CD-Micelles Against Cisplatin-Resistant Lung Cancer Cells
The potential of CD-micelles to overcome drug (cisplatin) resistance was assessed using an established cisplatin-resistant lung cancer model [35,36]. Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells and related SCLC-cisplatin-resistant (SCLC-cisplatinR) cells were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. SCLC-cisplatinR cells were cultured with 0.15 μM cisplatin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MA, USA) to maintain the resistant phenotypes that were provided from the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center [37,38]. The cytotoxicity of cisplatin and CD-micelles against SCLC-cisplatinR cells was determined using MTT assays. Briefly, SCLC-cisplatinR cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 3 × 103 cells per well. Subsequently, SCLC-cisplatinR cells in plates were separately treated with increasing doses of cisplatin (0.02–9.6 μM) and CD-micelles (1.4–72.3 μg mL−1) for 72 h, respectively [38,39]. The MTT reagent was then added at a concentration of 5 mg mL−1 for 2 h. Finally, the medium was replaced with 200 μL of DMSO to dissolve the crystal violet precipitate. The optical density of each well at 490 nm was measured using a microplate reader (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Leek Seed Extract and CD-Micelles
Scheme 1 illustrates the synthesis of CD-micelles from leek seeds. In step 1, leek seeds were ground using a knife mill and then filtered through a sieve with a diameter range of 0.150–0.850 mm to yield leek seed powders. In step 2, scCO2 extraction was employed, with the advantages of high extraction yield and environmental friendliness [40,41]. The leek seed extract (yield: 2.8%) was obtained after performing scCO2 extraction for 8 h. Figure S1 presents the total ion chromatograph of the leek seed extract, which was obtained from GC–MS analysis. The identified components are summarized in Table 1. Ten components were detected in the leek seed extract: n-hexadecanoic acid, 9(Z),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid, octadecanoic acid, (Z, E)-7,11-hexadecadien-1-yl acetate, eicosanoic acid, butyl 9,12-octadecadienoate, palmitin [hexadecanoic acid, 2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl ester], linolein [9,12-octadecadienoic acid (Z, Z)-, 2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl ester], squalene, and cholesterol. The MS spectra are shown in Supporting Information I. Of these components, n-hexadecanoic acid, octadecanoic acid, and linolein were the three major ingredients [42].

Scheme 1.
The process of the synthesis of CD-micelles from leek seeds.

Table 1.
Chemical components of leek seed extract analyzed using GC-MS.
The leek seed extract was carbonized through hydrolysis, polymerization, carbonization, and passivation using a dry heating method (step 3), followed by hydrolysis (step 4) to form CD-micelles [43,44]. The average diameter of the CD-micelles was 3.3 ± 0.4 nm (calculated from 50 counts) (Figure 1A(a)), which is similar to previous findings for C-dots [5]. Their micelles had an average diameter of 56.9 ± 14.1 nm (from 180 counts) in HRTEM images (Figure 1A(b)). In addition, the average size of the CD-micelles in ultrapure water was 178.4 nm based on the DLS analysis. Figure 1B represents the XPS spectrum of the CD-micelles; the data demonstrated three peaks obtained at 284, 532, and 1071 eV, which corresponded to C 1s, O 1s, and Na 1s, respectively [13,15,45]. Figure S2A depicts the deconvoluted C 1s peaks obtained at 284.6, 286.0, and 288.7 eV, which corresponded to C-C, C-O, and C=O, respectively [13,15]. The deconvoluted XPS spectrum of O 1s revealed two peaks at 532.5 and 531.9 eV, which were attributed to C-O and C=O, respectively (Figure S2B) [13,15]. The Na 1s signal was detected in the spectrum primarily because CD-micelles were formed through hydrolysis with NaOH. Thus, Na+ absorbed into the functional groups of CD-micelles resulted in the charge neutrality of the micelles. Figure 1C depicts the FTIR spectrum of the CD-micelles, showing a weaker and broader O–H stretching band at 3475 cm−1; moderate C–H stretching bands at 3009, 2918, and 2854 cm−1; a sharp C=O stretching band at 1737; a sharp (asymmetric) and a weak (symmetric) COO−1 stretching band at 1557 and 1378 cm−1, respectively; a moderate C–H stretching band at 1461 cm−1; and a strong C–O stretching band at 1163 cm−1 [46,47,48]. The 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz; D2O; ppm) of the CD-micelles, as shown in Figure S3, reveals that signals at around 8.37, 3.58~3.48, 2.10, 1.83, 1.51,1.23, and 0.81 are obtained, which are mainly attributed to aldehyde, ester/ether, and alkenyl groups on the surface [49]. As for weak 1H signals at around 6.76~6.44, they may correspond to aromatic groups on the surface of CD-micelles [49]. In addition, the 13C NMR spectrum of the CD-micelles was provided in Figure S4, showing aldehyde carbon atoms (171), aromatic ester/ether/alcohol carbon atoms (115, 72~68, 62), and aliphatic carbon atoms (37~21, 14, and 13 ppm) [50]. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of CD-micelles are similar to those of C-dots in the literature [51], and it is noted that 1H signals of alcohol groups on CD-micelles are not observed because of those protons undergoing fast exchanges with D2O solvent [52]. The absorption spectrum of the CD-micelles in ultrapure water (0.16 mg mL−1) revealed a broad band at 230 nm and a tail from 265 to 350 nm, corresponding to π−π* and n−π* transitions, respectively (Figure 1D) [53,54]. The excitation-wavelength-dependent PL property of the CD-micelles excited at the wavelengths of 300 to 410 nm is illustrated in Figure 1E. This property is attributed to the transitions of the nonbonding orbitals of CD-micelles into their π* orbitals [53,54,55]. Because the aggregated stacking of CD-micelles induced PL quenching, their ΦPL was estimated to be <1%, which was mainly attributed to J-type aggregation [56,57,58].
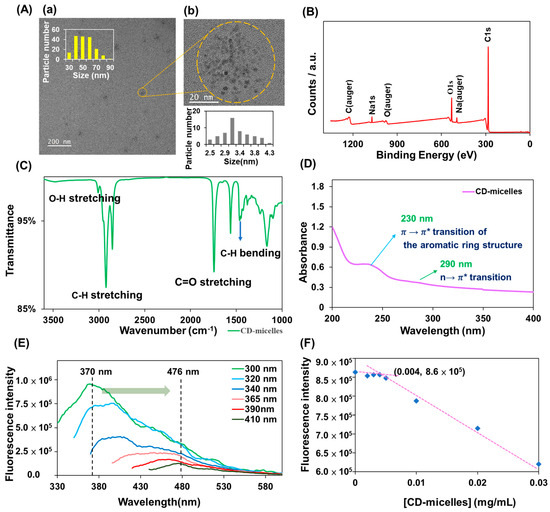
Figure 1.
(A) HRTEM images, (B) XPS spectrum, and (C) FTIR spectrum of CD-micelles. (D) Absorption spectrum of CD-micelles in ultrapure water (0.16 mg mL−1) and (E) PL spectra of CD-micelles when excited at wavelengths of 300 to 410 nm. (F) Critical micelle concentration (CMC) assessment of CD-micelles. The insets (a,b) in (A) represent an enlarged image of the CD-micelles and their size distribution, respectively.
Figure 1F shows the CMC assessment for CD-micelles by PL intensities at 515 nm of fluorescein against CD-micelle concentrations (0–0.03 mg mL−1); a cross point at the concentration of CD-micelle (0.004 mg mL−1) was obtained. As CD-micelle concentrations increased over 0.004 mg mL−1, the PL intensities of fluorescein decreased significantly. This is attributed to the fact that as the as-prepared C-dots started to form CD-micelles, PL scattering occurred [59].
3.2. Detection of Metal Ions Using CD-Micelles
Figure 2A presents the PL quenching efficiencies of CD-micelles (1.6 mg mL−1) in the presence of various metal ions (100 μM), namely Li+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, Cu2+, Co2+, Ag+, Al3+, Cr3+, Pd2+, and Au3+. The ion most effectively quenched was the Co2+, indicating that CD-micelles have high selectivity for Co2+. Figure 2B depicts the PL quenching efficiencies of CD-micelles against Co2+ (0–40 μM). A dynamic range from 2.5 to 25 μM was obtained, and the limit of detection was 1.7 μM, calculated using the equation 3σ/m, where σ is the standard deviation of the blank signal (n = 3) and m is the slope of the linear range. To examine the Co2+ quenching behavior of the CD-micelles, a Stern–Volmer plot was employed. A linear relationship between the Co2+ concentration (2.5–25 μM) and its Stern–Volmer constant of 1.3 × 10−2 μM−1 was observed (Figure 2C) [17]. A linear Stern–Volmer plot indicates that only dynamic or static quenching occurred between CD-micelles and Co2+ [17]. In this study, to confirm the quenching mechanism, fluorescence lifetime decay curves of CD-micelles with and without Co2+ were measured (Figure 2D). The two curves exhibited adequate overlap. In addition, the average lifetimes of CD-micelles with and without Co2+ were calculated to be 8.2 ns and 8.1 ns, respectively. Because no significant difference in the lifetimes of CD-micelles with and without Co2+ was observed, the dynamic quenching mechanism was ruled out [60]. Moreover, Figure 2E shows an unexpected HRTEM image of CD-micelles with Co2+, with an average diameter of 240.3 ± 66.9 nm (from 70 counts). To prove that Co2+ was present in these particles, energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry was conducted (Figure 2F). The results revealed the presence of Co2+ in the particles, with a weight percentage of 1.18%. These results confirmed that the Co2+ quenching behavior of the CD-micelles was a static process [17,60]. Additionally, CD-micelles interacted with Co2+ to form new spherical particles [61,62,63]. The detailed mechanisms of CD-micelles with high selectivity towards Co2+ and their formation of the spherical particles are unclear, but it is supposed that functional groups on the surface of CD-micelles, including O–H, C=O, and COO−1, have special interactions with Co2+ [64]. To confirm this conjecture, 1H NMR spectra of CD-micelles without and with Co2+ presented in Figure S5 show that the 1H peak of aldehyde groups on the surface of CD-micelles shifted slightly from 8.37 to 8.40 when Co2+ existed, indicating that aldehyde groups on CD-micelles have certain interactions with Co2+. On the other hand, Co2+ induced 1H peaks of CD-micelles to be broader ones due to their paramagnetic properties [65]. Unfortunately, because of fast exchanges of hydrogen in alcohol groups on CD-micelles with D2O, it is difficult to monitor their O–H chemical shifts for CD-micelles without and with Co2+ in aqueous environments using NMR measurements [52]. Lastly, carbon dots using natural biomaterials were selected for comparison. Their produced methods, precursors, and corresponding LODs are summarized in Table 2 [66,67,68]. A report involving carbon dots using straws as precursors through a hydrothermal method showed PL quenching against Co2+ with an LOD of 0.38 μM based on a static quenching mechanism and the inner filter effect [66]. In addition, limes and kelps were used to produce carbon dots through a microwave method. These two carbon dots showed PL quenching towards Co2+, with LODs of 0.39 and 1.63 μM, based on the inner filter effect and the electron transfer mechanism, respectively [67,68].

Figure 2.
(A) PL quenching efficiencies of CD-micelles (1.6 mg mL−1) in the presence of various metal ions (100 μM). (B) PL quenching efficiencies of CD-micelles against Co2+ (0–40 μM). (C) The Stern–Volmer plot of CD-micelles against Co2+. (D) Fluorescence lifetime decay curves of CD-micelles with and without Co2+. (E) The HRTEM images of CD-micelles with Co2+ and their size distribution. (F) Energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry mapping images of CD-micelles with Co2+.

Table 2.
Methods, precursors, and LODs of carbon dots produced from natural biomaterials for detection of Co2+.
3.3. CD-Micelles for Metal Ion Removal Through Liquid–Liquid Extraction
Figure 3A presents the process through which CD-micelles were functionalized as adsorbents and chelating agents to employ metal ion removal through liquid–liquid extraction. As depicted in Figure 3A(a), CD-micelle solutions were separately mixed with metal ion solution that contained Li+, Ag+, Co2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Al3+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ sequentially. After adjustment of the pH value of the above mixtures to 4 or 7 by using 0.2 M HNO3, ethyl acetate was added to each mixture (Figure 3A(b)). Liquid–liquid extraction was performed, and then we waited for solvent separation (Figure 3A(c)). The removal efficiencies of CD-micelles against various metal ions at pH 4 and 7 are provided in Figure 4B. The results indicated that through liquid–liquid extraction in acidic conditions (pH 4), CD-micelles extracted Pb2+, Al3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, Pd2+, and Au3+ with efficiencies of >90%. Moderate removal efficiencies (40–80%) were obtained for CD-micelles against Ag+, Co2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+, and low removal efficiency (7%) was obtained for Li+. This low removal efficiency indicated the poor interaction between CD-micelles and Li+, which is mainly attributed to the low positive charge (I) and small size of Li+. In neutral conditions (pH 7), CD-micelles show similar ion-extracted properties, except for Pd2+ and Au3+. For comparison, ion removal efficiencies for Pb2+ using SDS and those for Ag+, Pd2+, and Au3+ using CTAB of over 80% were obtained. The sulfate group in SDS had a strong interaction with Pb2+ to form an SDS–Pb2+ complex [69,70,71,72]. Similarly, Ag+, Pd2+, and Au3+ interacted with CTAB to form complexes [73,74,75], and those complexes were thus extracted through liquid–liquid extraction. Regarding metal ion removal using CD-micelles through liquid–liquid extraction, the illustrated mechanism is depicted in Scheme 2. Metal ions may be absorbed/bonded on the functional groups in CD-micelles. Subsequently, these metal ion absorbed/bonded CD-micelles disintegrate and are then dispersed in ethyl acetate during liquid–liquid extraction. After the separation of the organic and aqueous layers, metal ions are transferred in the ethyl acetate layer through absorption/bonding onto C-dots.
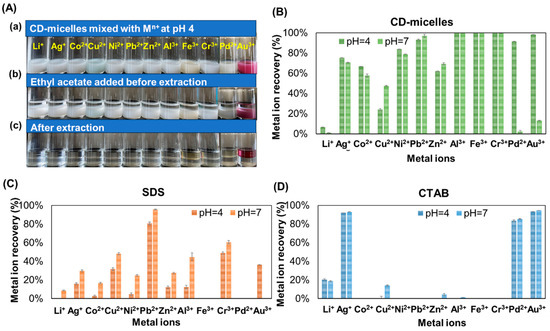
Figure 3.
(A) CD-micelles employed for metal ion removal through liquid–liquid extraction by using ethyl acetate. Removal efficiencies of (B) CD-micelles, (C) SDS, and (D) CTAB for various metal ions.
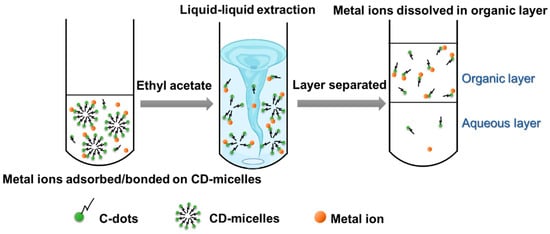
Scheme 2.
A proposed mechanism for CD-micelles to remove metal ions through liquid–liquid extraction.
3.4. Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of CD-Micelles
CD-micelles for ABTS•+ scavenging efficiency obtained from the colorimetric assay are presented in Figure 4A. The CD-micelles exhibited dose-dependent scavenging efficiencies ranging from 5.0% to 94.9% at concentrations ranging from 5 to 1000 μg mL−1 [76,77]. As depicted in Figure 4B, CD-micelles exhibited an ABTS•+ scavenging ability to form ABTS, which is mainly attributed to their π-conjugated bonds on the surfaces that stabilized the cation radical, which indicates that CD-micelles are functionalized as antioxidants [76,77]. The cytotoxicity of cisplatin and CD-micelles was evaluated using the MTT assay, as shown in Figure 4C. The results showed a small reduction in the survival rate of SCLC-cisplatinR cells from 99.2 ± 2.4% to 87.7 ± 0.5%, even at the highest concentration of cisplatin (2.88 μg mL−1 or 9.60 μM), which indicates the occurrence of cisplatin resistance. In contrast, CD-micelles were administered at concentrations ranging from 1.4 to 723 μg mL−1, resulting in a dose-dependent decrease in cell viability, with survival rates decreasing from 90.7 ± 3.2% to 12.8 ± 4.2%. Notably, the cytotoxic effects of CD-micelles at concentrations of 0.72, 1.44, and 2.88 μg mL−1 were comparable to those of cisplatin at the same concentrations. These findings suggest that CD-micelles exhibit similar therapeutic efficacy to cisplatin against SCLC-cisplatinR cells. Therefore, CD-micelles could potentially serve as a replacement for cisplatin in cases of cisplatin resistance, thereby reducing the risk of cisplatin overdose and mitigating adverse effects, such as mortality and peripheral neuropathy. Regarding the underlying mechanism, it is unclear, but it is supposed that CD-micelles were functionalized as exogenous antioxidants [78,79]. They probably quenched singlet oxygen (1O−2) anion and peroxyl (•ROO) radicals to remove free radical intermediates or to delay oxidative reactions via several modalities, including alterations in cell signaling, changes in cell cycle progression, and the modulation of enzymatic activities [80,81]. Thus, the results indicated that CD-micelles, as novel antioxidants, exhibit great potential for use in anticancer nanodrugs in cancer therapy [82,83,84].

Figure 4.
(A) CD-micelles for ABTS•+ scavenging efficiencies. (B) Illustrated mechanism for CD-micelles reacted with ABTS•+. (C) The cell survival ratios of SCLC-cisplatinR cells against cisplatin and CD-micelles.
4. Conclusions
In this study, scCO2 extraction was used to obtain leek seed extract, which was subsequently carbonized and hydrolyzed to form CD-micelles. The CD-micelles were selective for the quantitation of Co+2 through analyte-induced PL quenching, employing a static process with the formation of the self-assembly Co2+-CD-micelle sphere particles. In addition, CD-micelles can extract metal ions through liquid–liquid extraction. Removal efficiencies over 90% were obtained using CD-micelles against Pb2+, Al3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, Pd2+, and Au3+. Moreover, CD-micelles functionalized as novel antioxidants killed SCLC-cisplatinR cells in a dose-dependent manner. Thus, CD-micelles exhibit great potential as a replacement for cisplatin when cisplatin resistance occurs, thus preventing cisplatin overdoses in cancer therapy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jfb15110347/s1, Figure S1. Total ion chromatograph of the leek seed extract obtained through GC-MS analysis; Figure S2. Deconvoluted (A) C 1s and (B) O 1s XPS spectra of CD-micelles; Supporting Information I: The GC-Electron impact spectra of 10 components obtained from leek seed extract; Figure S3. 1H NMR spectrum of the CD-micelles; Figure S4. 13C NMR spectrum of the CD-micelles; Figure S5. 1H NMR spectra of the CD-micelles without (down) and with Co2+ (up).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and T.-H.T.; methodology, W.L.; validation, W.L. and T.-L.T.; formal analysis, W.L. and H.-Y.W.; investigation, W.L.; resources, T.-H.T. and T.-L.T.; data curation, W.L. and H.-Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, W.L. and T.-L.T.; writing—review and editing, T.-H.T.; visualization, W.L.; supervision, T.-H.T.; project administration, W.L.; funding acquisition, T.-H.T. and T.-L.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We are grateful to Mechema Chemicals Internation Corp., the Ministry of Education, and the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan, for providing financial support for this study (contracts NSTC-112-2314-B-006-032-MY3 and NSTC-112-2321-B-006-019).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chu, H.-W.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Anand, A.; Lin, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-C. Carbon quantum dots for the detection of antibiotics and pesticides. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S.-T. Carbon nanodots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24230–24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, P.; Negahdari, B.; Eatemadi, A. Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of carbon-based quantum dots: An updated review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciortino, A.; Cannizzo, A.; Messina, F. Carbon nanodots: A review—From the current understanding of the fundamental photophysics to the full control of the optical response. C 2018, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-C.; Lin, Y.-W.; Chang, H.-T. Carbon dots as artificial peroxidases for analytical applications. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 558–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, S.; Das, P.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.C. Advancement in science and technology of carbon dot-polymer hybrid composites: A review. Funct. Compos. Struct. 2019, 1, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, A.; Gopinath, P. Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots from coriander leaves and their potential application as antioxidants, sensors and bioimaging agents. Analyst 2015, 140, 4260–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy Padidam, S.; Kadam, B.D.; Thakkellapati, S.; Verma, M.; Raichur, A.M.; Narashimhan Ramana, L. Single-step synthesis of self-assembled carbon dots for enhanced cancer cell retention and theranostics applications. Microchem. J. 2024, 198, 110144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Giannelis, E.P.; Zboril, R.; Rogach, A.L. Carbon dots—Emerging light emitters for bioimaging, cancer therapy and optoelectronics. Nano Today 2014, 9, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, C.; Tapas, S.; Lei, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Carbon dots modified mesoporous organosilica as an adsorbent for the removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol and heavy metal ions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13357–13364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya Pudza, M.; Zainal Abidin, Z.; Abdul Rashid, S.; Md Yasin, F.; Noor, A.; Issa, M.A. Eco-friendly sustainable fluorescent carbon dots for the adsorption of heavy metal ions in aqueous environment. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.C.; Gomes, C.G.; Pina, J.; Pereira, R.F.; Murtinho, D.; Fajardo, A.R.; Valente, A.J. Carbon quantum dots-containing poly (β-cyclodextrin) for simultaneous removal and detection of metal ions from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Tiwari, P.; Mobin, S.M. Sustainable carbon-dots: Recent advances in green carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8904–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Jiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, T. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots for determination of nickel ions and morin from aqueous solution simultaneously. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chyueh, S.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Carbon dots functionalized papers for high-throughput sensing of 4-chloroethcathinone and its analogues in crime sites. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 191017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Yen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chang, H. Photoluminescent carbon nanomaterials for sensing of illicit drugs: Focus. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, T.-H.; Chyueh, S.-C.; Chang, H.-T. A carbon-dot sensing probe for screening of date rape drugs: Nitro-containing benzodiazepines. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, J.; Li, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, W. Carbon quantum dots: Comprehensively understanding of the internal quenching mechanism and application for catechol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 333, 129557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, F.; Yan, F.; Bai, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zho, X. The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: A review on mechanisms and applications. Mikrochim. Acta 2017, 184, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Lin, Q.; Chang, H.T. Recent advances and sensing applications of carbon dots. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocito, G.; Calabrese, G.; Forte, S.; Petralia, S.; Puglisi, C.; Campolo, M.; Esposito, E.; Conoci, S. Carbon dots as promising tools for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, K.; Nan, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, J.; Wang, P. Recent advances and prospects of carbon dots in cancer nanotheranostics. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Deng, Y.; Tin, M.S.; Lok, V.; Ngai, C.H.; Zhang, L.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E., III; Xu, W.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Elcarte, E. Distribution, risk factors, and temporal trends for lung cancer incidence and mortality: A global analysis. Chest 2022, 161, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bade, B.C.; Cruz, C.S.D. Lung cancer 2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.A.; Fawell, S.; Floc’h, N.; Flemington, V.; McKerrecher, D.; Smith, P.D. Challenges and opportunities in cancer drug resistance. Chem. Rev. 2020, 121, 3297–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Yu, M.; Xu, J.; Li, B.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kankala, R.K. Overcoming cancer multi-drug resistance (MDR): Reasons, mechanisms, nanotherapeutic solutions, and challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Chua, H.J.; Zhao, Y. Carbon-dot-mediated Co-administration of chemotherapeutic agents for reversing cisplatin resistance in cancer therapy. ChemNanoMat 2018, 4, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, A.; Lizundia, E. Luminescent carbon dots obtained from polymeric waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswoyo, T.A.; Mardiana, E.; Lee, K.O.; Hoshokawa, K. Isolation and characterization of antioxidant protein fractions from melinjo (Gnetum gnemon) seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5648–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognyanov, M.; Nikolova, M.; Yanakieva, I.; Kussovski, V.; Kratchanova, M. Influence of composition on the biological activity of pectic polysaccharides from leek. J. BioSci. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Chen, T.-T.; Hu, P.; Wang, S.-Y. A novel antibacterial tripeptide from Chinese leek seeds. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, C.; Yan, X.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M. Versatile carbon dots with superoxide dismutase-like nanozyme activity and red fluorescence for inflammatory bowel disease therapeutics. Carbon 2023, 204, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Chen, J.; Tu, K.; Tuo, H.; Wu, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, D. Carbon dot nanozymes as free radicals scavengers for the management of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the liver inflammatory network and inhibiting apoptosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-G.; Pan, Z.-Y.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Cao, Q.; Ji, L.-N.; Mao, Z.-W. Precisely assembled nanoparticles against cisplatin resistance via cancer-specific targeting of mitochondria and imaging-guided chemo-photothermal therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43444–43455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. Graphene quantum dots enhance anticancer activity of cisplatin via increasing its cellular and nuclear uptake. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, Y.; Furuichi, M.; Song, R.; Van, N.T.; Mulcahy, R.T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kuo, M.T. Expression of multidrug resistance protein/GS-X pump and gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase genes is regulated by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31075–31085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.S.; Savaraj, N.; Siddik, Z.H.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y.; Wu, C.J.; Kuo, M.T. Role of human copper transporter Ctr1 in the transport of platinum-based antitumor agents in cisplatin-sensitive and cisplatin-resistant cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bian, T.; Song, L.; Jiang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Salloum, R.G.; Warren, G.W.; Kaye, F.J.; Fujioka, N.; Jin, L.; et al. Reducing Chemotherapy-Induced DNA Damage via nAChR-Mediated Redox Reprograming-A New Mechanism for SCLC Chemoresistance Boosted by Nicotinem. Cancers 2022, 14, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norodin, N.; Salleh, L.; Mustafa, N.M. Supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) extraction of essential oil from swietenia mahagoni seeds. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 162, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ahmad, A. Antioxidant activity of essential oil extracted by SC-CO2 from seeds of Trachyspermum ammi. Medicines 2017, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehdi, I.A.; Sbihi, H.M.; Tan, C.P.; Al-Resayes, S.I.; Rashid, U.; Al-Misned, F.A.; El-Serehy, H.A. Chemical composition, oxidative stability, and antioxidant activity of Allium ampeloprasum L. (Wild Leek) seed oil. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Synthesis of high-quality carbon nanodots from hydrophilic compounds: Role of functional groups. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3984–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.; Chen, P.-C.; Periasamy, A.P.; Chen, Y.-N.; Chang, H.-T. Photoluminescent carbon nanodots: Synthesis, physicochemical properties and analytical applications. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XianáGuo, C. Na+-functionalized carbon quantum dots: A new draw solute in forward osmosis for seawater desalination. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7318–7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinathan, K.; Samayanan, S.; Marimuthu, K.; Yim, J.-H. Green synthesis of multicolour fluorescence carbon quantum dots from sugarcane waste: Investigation of mercury (II) ion sensing, and bio-imaging applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 601, 154266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Oktiani, R.; Ragadhita, R. How to read and interpret FTIR spectroscope of organic material. Indones. J. Sci. technol. 2019, 4, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supchocksoonthorn, P.; Hanchaina, R.; Sinoy, M.C.A.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Kangsamaksin, T.; Paoprasert, P. Novel solution-and paper-based sensors based on label-free fluorescent carbon dots for the selective detection of pyrimethanil. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 564, 150372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, B.; Karak, N. A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8286–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Su, H.; Wang, K.; Wong, W.K.; Zhu, X. Facile synthesis of N-rich carbon quantum dots from porphyrins as efficient probes for bioimaging and biosensing in living cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7375–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, I.; Bera, M.K. Microwave-Assisted Green Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Calotropis Gigantea as a Fluorescent Probe for Bioimaging. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charisiadis, P.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Tzakos, A.G.; Siskos, M.; Gerothanassis, I.P. 1H-NMR as a structural and analytical tool of intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds of phenol-containing natural products and model compounds. Molecules 2014, 19, 13643–13682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D.; Xie, H. Photoluminescent carbon dots derived from sugarcane molasses: Synthesis, properties, and applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 47840–47847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, G.N.; El-Shaheny, R.; Shabana, R.A.; Hassan, A.H. Inherent photocatalytic activity of luminescent multi-doped carbon dots manufactured from expired medicine and its application for efficient water remediation and nanosensing. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaseem, A.M.; Alhazzani, K.; Alanazi, A.Z.; Alsanad, S.M.; Alkhamees, O.A.; Alasiri, G.; El-Wekil, M.M.; Ali, A.-M.B.H. Dual-Modulation ratiometric fluorescence strategy for cobalt and topotecan detection using Red-Emissive carbon dots. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.J.; Kwak, B.E.; Kim, D.H. Self-quenching origin of carbon dots and the guideline for their solid-state luminescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 27124–27131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Lu, S. Aggregation in carbon dots. Aggregate 2022, 3, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Guan, L.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Liu, C.; Lan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, X. Effect of aggregation configuration of molecular fluorophore CZA on photoluminescence properties of carbon dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 659, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, J.K.; El-Nahhal, I.M.; Salama, S.F. Determination of the critical micelle concentration by absorbance and fluorescence techniques using fluorescein probe. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 730, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noun, F.; Jury, E.A.; Naccache, R. Elucidating the quenching mechanism in carbon dot-metal interactions–designing sensitive and selective optical probes. Sensors 2021, 21, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, J. Carbon quantum dots activated metal organic frameworks for selective detection of Cu (II) and Fe (III). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 588, 124378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Suo, T.; Xie, S.; Xia, A.; Ma, Y.-J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q. Rational design, synthesis, and applications of carbon dots@ metal–organic frameworks (CD@MOF) based sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 135, 116163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, P. Dynamic aggregation of carbon dots self-stabilizes symmetry breaking for exceptional hydrogen production with near-infrared light. Aggregate 2024, 5, e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Yan, F.; Han, Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, X.; Chen, L. Cobalt(II) ions detection using carbon dots as an sensitive and selective fluorescent probe. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 67481–67487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, E. Phase distortion-free paramagnetic NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 2021, 8–9, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Ge, L.; Li, Y.; Mukhtar, M.; Shen, B.; Yang, D.; Li, J. Carbon dots derived from flax straw for highly sensitive and selective detections of cobalt, chromium, and ascorbic acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 579, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkian, I.; Sutanto, H.; Hadiyanto, B.; Prasetio, A.; Aprimanti Utami, B. Facile synthesized carbon dots for simple and selective detection of cobalt ions in aqueous media. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2033467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Cheng, C.; Yang, Y. Green and microwave-assisted synthesis of carbon dots and application for visual detection of cobalt (II) ions and pH sensing. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, M.A.; Salam, K.A.; Evuti, A.M. Continuous removal of Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions from synthetic aqueous solutions in a fixed-bed packed column with surfactant-modified activated carbon. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhari, P.; Abdi, S.; Nasiri, M. Effect of various types of anions and anionic surfactants on the performance of micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration process in the removal of Pb (II) ions: An optimization with the response surface methodology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 187, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri Zare, S.; Raouf, F.; Miveei, L.; Roshan Zekavat, S.; Abedin Pour Farahmand, R. Investigation on the lead adsorption capacity of Iranian natural zeolite: Modifications, structural effects, adsorption isotherms, kinetics, and mechanism studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2691–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-L.; Zhang, M.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.-T.; Geng, B.-Y.; Meng, R.-B.; Yang, Y.-Z.; Zhong, Y.-S.; Liu, H.-Y. Surface modification of coconut-based activated carbon by SDS and its effects on Pb2+ adsorption. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Singh, T.; Hussain, J.I.; Hashmi, A.A. Au (III)–CTAB reduction by ascorbic acid: Preparation and characterization of gold nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 104, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shen, J.; Du, A.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, G.; Yang, H.; Wu, J. Facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles with high concentration via a CTAB-induced silver mirror reaction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 400, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagireddi, S. Effect of cetrimonium bromide (CTAB) surfactant on Pd (II) removal efficiency from electroless plating solutions. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Geng, H.; Yang, Q.; Tong, Y.; He, W. Au/N-doped carbon dot nanozymes as light-controlled anti-and pro-oxidants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 7253–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Wang, D.; Sun, B. Dual-mode colorimetric/fluorometric sensor for the detection of glutathione based on the peroxidase-like activity of carbon quantum dots. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 136, 109147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, I. Evaluation of anticancer, antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of Artemisia absinthium L. extract. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaklabi, A.; Arif, I.A.; Ahamed, A.; Kumar, R.S.; Idhayadhulla, A. Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activities of chemical constituents of the Saururus chinensis root extracts. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, B.; Nice, E.; Xu, J.; Huang, C. Antioxidant therapy in cancer: Rationale and progress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Abrahamse, H. Redox potential of antioxidants in cancer progression and prevention. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memarzia, A.; Saadat, S.; Asgharzadeh, F.; Behrouz, S.; Folkerts, G.; Boskabady, M.H. Therapeutic effects of medicinal plants and their constituents on lung cancer, in vitro, in vivo and clinical evidence. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 2841–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thara, C.R.; Mathew, S.; Chacko, A.R.; Mathew, B. Dual functional carbon nitride dots as electrochemical sensor and anticancer agent with chemotherapic and photodynamic effect. Microchem. J. 2023, 187, 108379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzycka-Ayoush, M.; Kowalik, P.; Kowalczyk, A.; Bujak, P.; Nowicka, A.M.; Wojewodzka, M.; Kruszewski, M.; Grudzinski, I.P. Quantum dots as targeted doxorubicin drug delivery nanosystems in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).