Recent Developments in Zn-Based Biodegradable Materials for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biological Functions of Zn
3. Design Criteria for Orthopedic Devices
4. In Vivo Corrosion
5. Zn-Based Biomaterials
6. Conclusions
- Zn exists in bones and muscles in the human body and performs a significant role in bone metabolism and the growth of an organism. Zn-based biodegradable materials can enhance osteoblast differentiation by promoting bone marrow genes.
- To meet the design criteria of a biodegradable device, mechanical properties such as ultimate tensile strength () > 300 MPa, tensile yield strength (> 230 MPa, and elongation () > 15–18% are required, and the elastic modulus (E) should be similar to bone (10–20 GPa). The service time of a device must be equal to 1–2 years for performing the particular function until the full absorption of the device. In vitro corrosion test degradation/penetration rate should be (DR) < 0.5 mm/year and hydrogen evolution should be less than 10 µL/cm2-day.
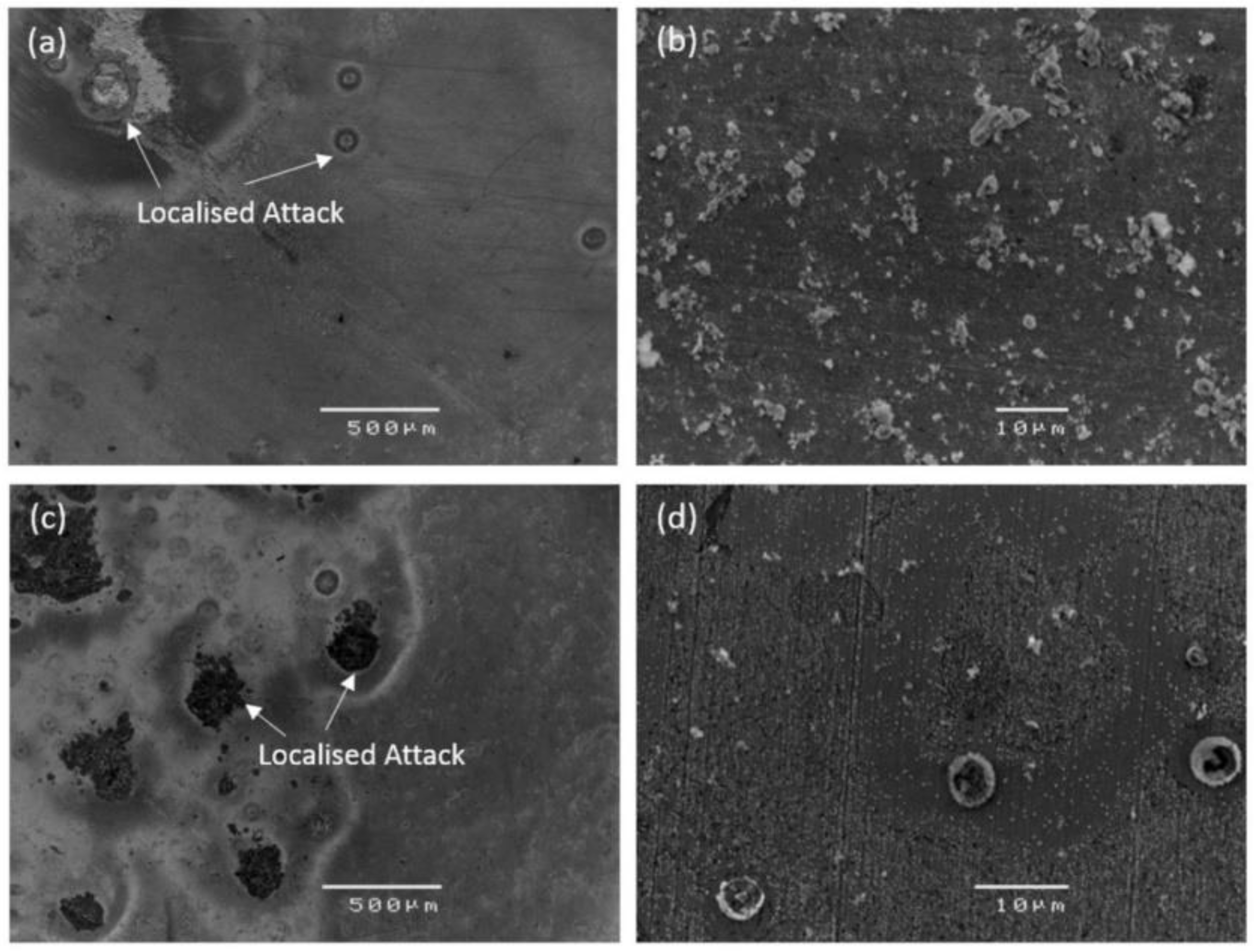
- Using in vitro corrosion, Zn-based biodegradable materials show medium degradation rates and are oxidized into hydroxides and oxides without releasing excessive hydrogen gas.
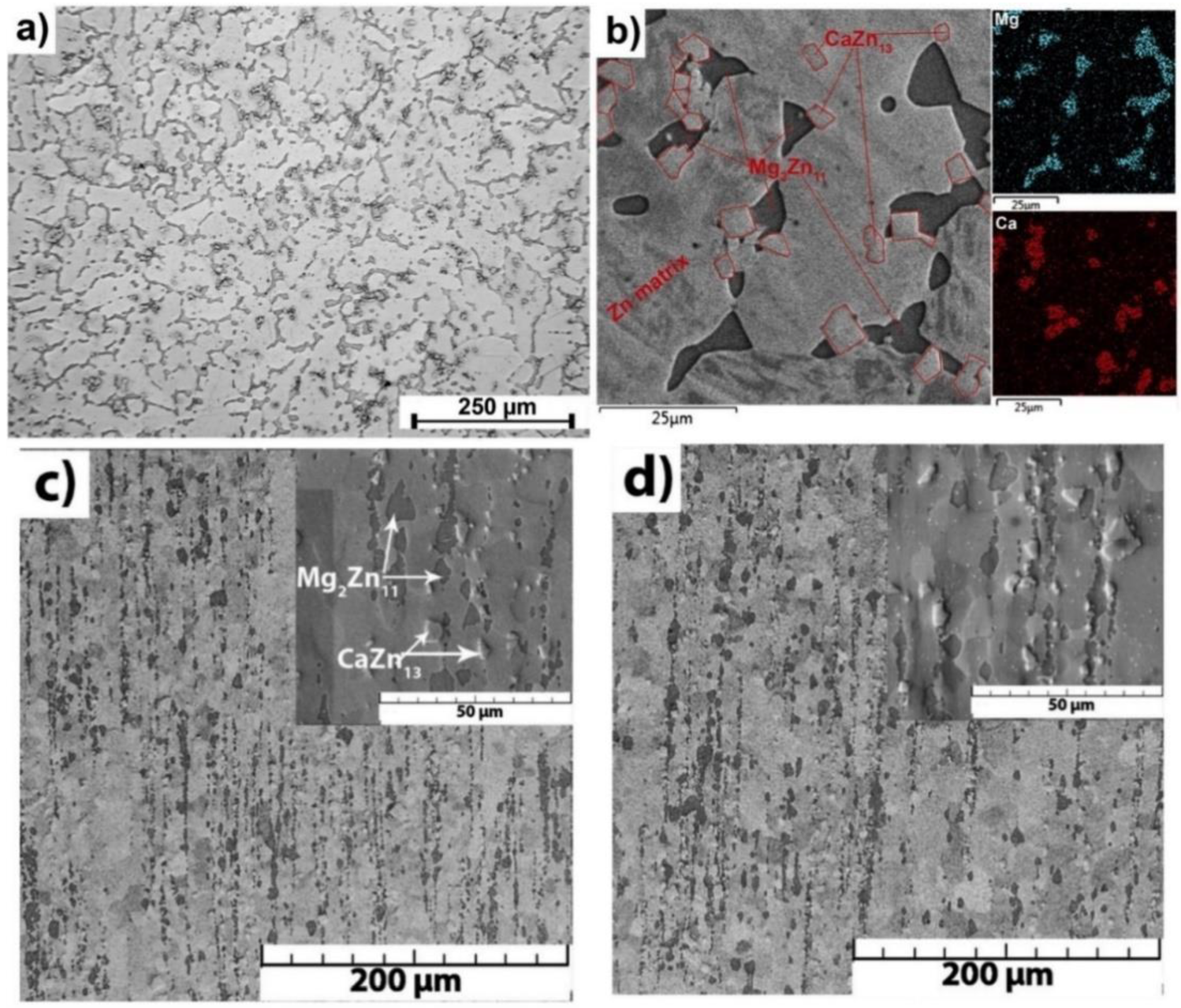
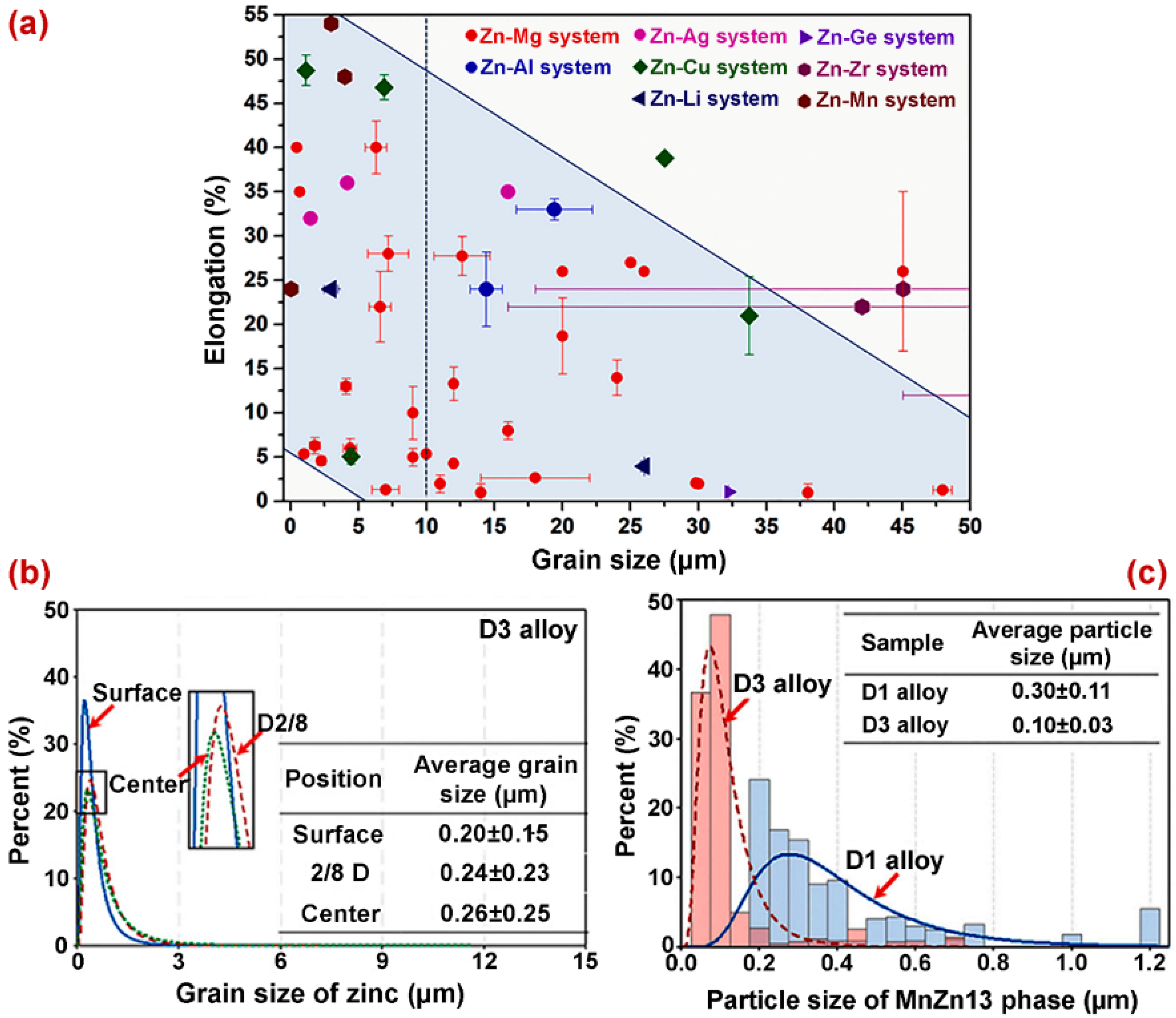
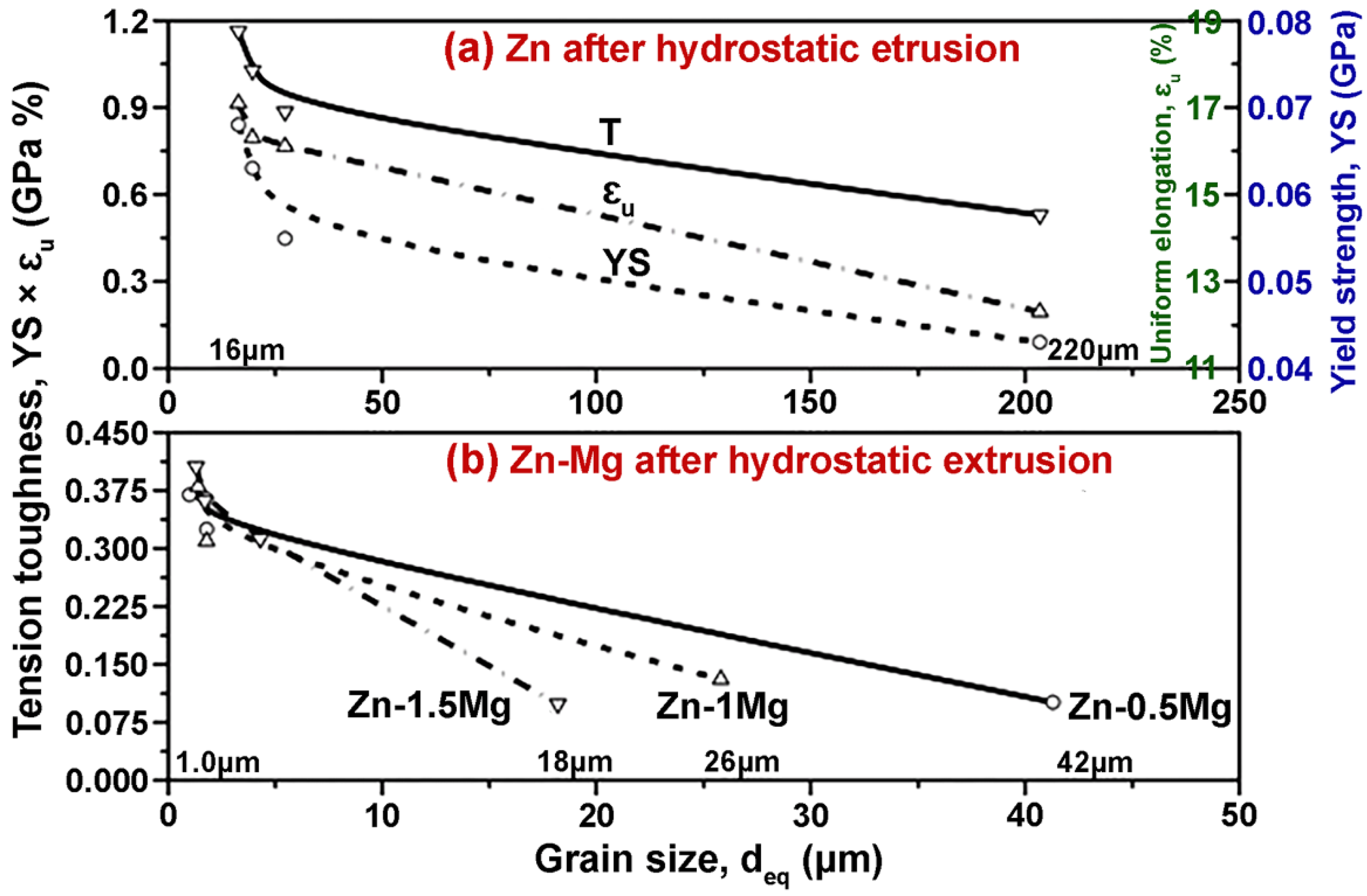
- Zn-based alloys are multiphase systems, and their mechanical and degradation properties are strongly dependent on the grain sizes and the distribution of the secondary phase in the alloy matrix. Refined microstructures and uniform distribution of the second phase throughout the alloy composition are expected to result in improved properties of biodegradable Zn alloys.
- Many post-processing methods have been used to improve the microstructure of Zn-based biodegradable materials. Among these, hot extrusion, hot rolling, and ECAP are the most effective to improve the microstructure and reducing the grain size. The grain refinement achieved in post-processing techniques improves their corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
- Zn–Mg alloys exhibit good mechanical properties and meet the required design criteria for orthopedic implants. The addition of Li into pure Zn enhances the mechanical properties of Zn-based alloys. The ternary alloy systems such as Zn–xLi–yMn (x, y = 0.1–0.8 wt.%) are the best candidates for next-generation orthopedic devices.
- There is a need to test the most suitable Zn-based biodegradable materials in all aspects before the clinical trial. The biocompatibility studies in vivo and tribological studies are limited to Zn-based biodegradable materials.
- Many suitable combinations of Zn-based biodegradable materials are listed based on the results of previous studies. Still, these materials are not used in orthopedics. There is a need to study the factors which make their use limited.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Current Advances in the Roles of Doped Bioactive Metal in Biodegradable Polymer Composite Scaffolds for Bone Repair: A Mini Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Li, S.; Yin, D.; Xie, J.; Rommens, P.M.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, M.; Ritz, U. Recent Progress in Mg-Based Alloys as a Novel Bioabsorbable Biomaterials for Orthopedic Applications. J. Magnes. Alloy 2022, 10, 1428–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unune, D.R.; Brown, G.R.; Reilly, G.C. Thermal Based Surface Modification Techniques for Enhancing the Corrosion and Wear Resistance of Metallic Implants: A Review. Vacuum 2022, 203, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dou, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, C.; Yu, H.; Chen, C. Research Progress of Biodegradable Magnesium-Based Biomedical Materials: A Review. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 923, 166377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.M.; Venkatesan, S. A Review on Application of Biomaterials for Medical and Dental Implants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2022, 14644207221121981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbogori, M.; Vaish, A.; Vaishya, R.; Haleem, A.; Javaid, M. Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone (PEEK) in Orthopaedic Practice- A Current Concept Review. J. Orthop. Rep. 2022, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, T.; Qiao, A.; Mu, Y.; Yang, H. Zinc-Based Biodegradable Materials for Orthopaedic Internal Fixation. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, J.C.C.; Oliveira, L.; Vaz, M.F.; Costa-de-Oliveira, S. Biodegradable Bone Implants as a New Hope to Reduce Device-Associated Infections—A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothupitiya, J.U.; Zheng, C.; Saltzman, W.M. Synthetic Biodegradable Polyesters for Implantable Controlled-Release Devices. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Khan, R.; Prakash, N.S.; Gupta, S.; Ghosh, D.; Nandi, S.K.; Roy, M. In Vitro Degradation and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Strontium-Doped Magnesium Phosphate-Reinforced Magnesium Composites. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 4236–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabeeh, V.P.M.; Hanas, T. Progress in Manufacturing and Processing of Degradable Fe-Based Implants: A Review. Prog. Biomater. 2022, 11, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Saijilafu; Wu, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Tan, L.; Witte, F.; Yang, H.; Mantovani, D.; Zhou, H.; et al. Biodegradable Mg-Based Alloys: Biological Implications and Restorative Opportunities. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, C.; Cai, K. Biodegradable Magnesium Phosphates in Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2097–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, A.; Das, M.; Balla, V.K. In Vitro and in Vivo Degradation Assessment and Preventive Measures of Biodegradable Mg Alloys for Biomedical Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2022, 110, 462–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, F.Z.; Ghomi, E.R.; Ramakrishna, S. Improving the Corrosion Behavior of Magnesium Alloys with a Focus on AZ91 Mg Alloy Intended for Biomedical Application by Microstructure Modification and Coating. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2022, 236, 1188–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Xie, X.; Wu, X.; Zhuang, S.; Zhang, C. Development of Degradable Magnesium-Based Metal Implants and Their Function in Promoting Bone Metabolism (A Review). J. Orthop. Transl. 2022, 36, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.R.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Chakkingal, U. A Review on Recent Advancements in Biodegradable Mg-Ca Alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy 2022, 10, 2094–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, T.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, X. Microstructure, Mechanical Performance and Anti-Bacterial Activity of Degradable Zn-Cu-Ag Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Wen, C.; Lin, J. A Biodegradable Fe/Zn–3Cu Composite with Requisite Properties for Orthopedic Applications. Acta Biomater. 2022, 146, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wątroba, M.; Bednarczyk, W.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Kawałko, J.; Mech, K.; Grünewald, A.; Unalan, I.; Taccardi, N.; Boelter, G.; Banzhaf, M.; et al. In Vitro Cytocompatibility and Antibacterial Studies on Biodegradable Zn Alloys Supplemented by a Critical Assessment of Direct Contact Cytotoxicity Assay. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Xia, D.; Wu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Guan, Z.; Rau, J.V. A Review on Current Research Status of the Surface Modification of Zn-Based Biodegradable Metals. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 7, 192–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.F.; Shi, Z.Z.; Wang, L.N. Opportunities and Challenges of Biodegradable Zn-Based Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 46, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, H.; Munir, K.; Wen, C.; Li, Y. Recent Research and Progress of Biodegradable Zinc Alloys and Composites for Biomedical Applications: Biomechanical and Biocorrosion Perspectives. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 836–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Gao, X.X.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, X.F.; Li, H.Y.; Zhou, C.; Yin, Y.X.; Wang, L.N. Design Biodegradable Zn Alloys: Second Phases and Their Significant Influences on Alloy Properties. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, G.; Jia, Q.; Bian, D.; Guan, S.; Kulyasova, O.; Valiev, R.Z.; Rau, J.V.; Zheng, Y. Recent Advances on the Mechanical Behavior of Zinc Based Biodegradable Metals Focusing on the Strain Softening Phenomenon. Acta Biomater. 2022, 152, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Venezuela, J.; Almathami, S.; Dargusch, M. Zinc-Nutrient Element Based Alloys for Absorbable Wound Closure Devices Fabrication: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, L.; Sun, J.; Gu, X.; Huang, C.; Su, H.; Fan, Y. Utilizing Biodegradable Alloys as Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) Membrane: Feasibility and Challenges. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 2627–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupo, R.; Sila, A.; Castellana, F.; Bringiotti, R.; Curlo, M.; De Pergola, G.; De Nucci, S.; Giannelli, G.; Mastronardi, M.; Sardone, R. Prevalence of Zinc Deficiency in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpellini, E.; Balsiger, L.M.; Maurizi, V.; Rinninella, E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Giostra, N.; Santori, P.; Abenavoli, L.; Rasetti, C. Zinc and Gut Microbiota in Health and Gastrointestinal Disease under the COVID-19 Suggestion. BioFactors 2022, 48, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, H.; Ahmad, R. Role of Zinc in Liver Pathology. Microb. Biofertil. Micronutr. Availab. 2022, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allai, F.M.; Gul, K.; Zahoor, I.; Ganaie, T.A.; Nasir, G.; Azad, Z.R. Malnutrition: Impact of Zinc on Child Development. Microb. Biofertil. Micronutr. Availab. 2022, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Sheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xie, X.; Liang, Y.; Wei, W.; Bao, R.; Wang, H. Conformational Remodeling Enhances Activity of Lanthipeptide Zinc-Metallopeptidases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Qian, K.; Chen, J.; Qi, Y.; E, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhao, L. A Biomimetic Zeolite-Based Nanoenzyme Contributes to Neuroprotection in the Neurovascular Unit after Ischaemic Stroke via Efficient Removal of Zinc and ROS. Acta Biomater. 2022, 144, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqib, S.; Nazeer, A.; Ali, M.; Zaman, W.; Younas, M.; Shahzad, A.; Sunera; Nisar, M. Catalytic Potential of Endophytes Facilitates Synthesis of Biometallic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Agricultural Application. BioMetals 2022, 35, 967–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.W.; Thompson, M.W. Regulation of Zinc-Dependent Enzymes by Metal Carrier Proteins. BioMetals 2022, 35, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shang, X.; Lin, G.; Li, H.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H. Effects of Zinc Glycinate on Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Indexes, and Intestinal Morphology of Yellow Feather Broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 4089–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Quintana, L.; Vázquez-Lorente, H.; Molina-López, J.; Gamarra-Morales, Y.; Martín-López, J.I.; Planells, E. Vitamin D Status in Critically Ill Patients with SIRS and Its Relationship with Circulating Zn and Related Parameters during ICU Stay. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durairaj, S.; Arumugam, G.; Kalimuthu, V.; Rajendran, R. Enhanced Anti-Biofilm and Biocompatibility of Zn and Mg Substituted β-Tricalcium Phosphate/Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composites towards A. Baumannii and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus, and MG-63 Cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 627, 122248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, X.; Pei, J.; Zhao, D.; Yan, Y. Fabrication of Magnesium Phosphate Bone Cement with Enhanced Osteogenic Properties by Employing Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 37, 2761–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazachenko, A.S.; Vasilieva, N.Y.; Malyar, Y.N.; Karacharov, A.A.; Kondrasenko, A.A.; Levdanskiy, A.V.; Borovkova, V.S.; Miroshnikova, A.V.; Issaoui, N.; Kazachenko, A.S.; et al. Sulfation of Arabinogalactan with Ammonium Sulfamate. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venezuela, J.; Dargusch, M.S. The Influence of Alloying and Fabrication Techniques on the Mechanical Properties, Biodegradability and Biocompatibility of Zinc: A Comprehensive Review. Acta Biomater. 2019, 87, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswal, T.; BadJena, S.K.; Pradhan, D. Sustainable Biomaterials and Their Applications: A Short Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, D.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, S. Drug-Loaded Biomaterials for Orthopedic Applications: A Review. J. Control Release 2022, 344, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr Azadani, M.; Zahedi, A.; Bowoto, O.K.; Oladapo, B.I. A Review of Current Challenges and Prospects of Magnesium and Its Alloy for Bone Implant Applications. Prog. Biomater. 2022, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Lin, J.; Wen, C.; Huang, S. A Biodegradable in Situ Zn–Mg2Ge Composite for Bone-Implant Applications. Acta Biomater. 2022, 146, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Khan, S.M.; Al-Khaled, K.; Ayadi, M.; Abbas, N.; Chammam, W. Performance Analysis of Biodegradable Materials for Orthopedic Applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Lin, F.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Virtanen, S. Corrosion Behavior of Biodegradable Metals in Two Different Simulated Physiological Solutions: Comparison of Mg, Zn and Fe. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, E. Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and Testing; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780471715764. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Tonna, C.; Mei, D.; Buhagiar, J.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Lamaka, S.V. Biodegradation Behaviour of Fe-Based Alloys in Hanks’ Balanced Salt Solutions: Part II. The Evolution of Local PH and Dissolved Oxygen Concentration at Metal Interface. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 7, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Yan, J.L.; Wang, P.; Jia, Z.J.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. A PH-Sensitive Self-Healing Coating for Biodegradable Magnesium Implants. Acta Biomater. 2019, 98, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnedenkov, A.S.; Mei, D.; Lamaka, S.V.; Sinebryukhov, S.L.; Mashtalyar, D.V.; Vyaliy, I.E.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Gnedenkov, S.V. Localized Currents and PH Distribution Studied during Corrosion of MA8 Mg Alloy in the Cell Culture Medium. Corros. Sci. 2020, 170, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Meng, Y.; Volinsky, A.A.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, L.N. Influences of Albumin on in Vitro Corrosion of Pure Zn in Artificial Plasma. Corros. Sci. 2019, 153, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.; Dong, C.; Yan, Y.; Volinsky, A.A.; Wang, L.N. Initial Formation of Corrosion Products on Pure Zinc in Saline Solution. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, Y.; Durán, A. Control of Degradation Rate of Mg Alloys Using Silica Sol–Gel Coatings for Biodegradable Implant Materials. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Pareek, S.; Agarwala, A.; Shrivastava, R.; Sassi, W.; Parida, S.K.; Behera, D. Effect of Exposure Time on Corrosion Behavior of Zinc-Alloy in Simulated Body Fluid Solution: Electrochemical and Surface Investigation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, L.F.; Chew, K.W.; Bokhari, A.; Mubashir, M.; Show, P.L. Biodegradation of Crude Oil in Seawater by Using a Consortium of Symbiotic Bacteria. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, F.; Farid, A.; Ullah, N.; Kiran, M.; Khan, R.U.; Aziz, T.; Mehmood, S.; Haroon, M.; Mubashir, M.; Bokhari, A.; et al. A Study on the Uptake of Methylene Blue by Biodegradable and Eco-Friendly Carboxylated Starch Grafted Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Tong, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Wei, A.; Jin, L.; Lin, J.J.; Li, Y.; et al. A Biodegradable Zn-1Cu-0.1Ti Alloy with Antibacterial Properties for Orthopedic Applications. Acta Biomater. 2020, 106, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tong, X.; Lin, J.; Wei, A.; Li, Y.; Dargusch, M.; Wen, C. Binary Zn–Ti Alloys for Orthopedic Applications: Corrosion and Degradation Behaviors, Friction and Wear Performance, and Cytotoxicity. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 74, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Voshage, M.; Jauer, L.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Y.; Poprawe, R.; Schleifenbaum, J.H. Laser Additive Manufacturing of Zn Metal Parts for Biodegradable Applications: Processing, Formation Quality and Mechanical Properties. Mater. Des. 2018, 155, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Singh, S.; Verma, K.; Sidhu, S.S.; Singh, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Mg-Zn-Mn-HA Composite by Spark Plasma Sintering Process for Orthopedic Applications. Vacuum 2018, 155, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, J.; Dai, Y.; Luan, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, Z.; Wang, K.; Gao, Y.; Lin, J.; et al. Development of Biodegradable Zn–1Mg–0.1RE (RE = Er, Dy, and Ho) Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Acta Biomater. 2020, 117, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Tong, X.; Wang, K.; Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Dargusch, M.; Wen, C. Biodegradable Zn–3Cu and Zn–3Cu–0.2Ti Alloys with Ultrahigh Ductility and Antibacterial Ability for Orthopedic Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 68, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Gong, D.; Wang, W. Microstructure, Mechanical, Corrosion Properties and Cytotoxicity of Beta-calcium Polyphosphate Reinforced ZK61 Magnesium Alloy Composite by Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Yao, G.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X. Fabrication and Characterization of In Situ Zn-TiB2 Nanocomposite. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 48, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Pan, S.; Linsley, C.; Li, X. Manufacturing and Characterization of Zn-WC as Potential Biodegradable Material. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 34, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; Linsley, C.S.; Hwang, I.; Yao, G.; Wu, B.M.; Li, X. Novel Zinc/Tungsten Carbide Nanocomposite as Bioabsorbable Implant. Mater. Lett. 2020, 263, 127282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galib, R.; Sharif, A. Development of Zn-Mg Alloys as a Degradable Biomaterial. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Qiu, K.; Yang, Y.; Pu, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y. Effects of Alloying Elements (Ca and Sr) on Microstructure, Mechanical Property and in Vitro Corrosion Behavior of Biodegradable Zn–1.5Mg Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 664, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Hamzah, E.; Low, H.T.; Kasiri-Asgarani, M.; Farahany, S.; Akbari, E.; Cho, M.H. Fabrication of Biodegradable Zn-Al-Mg Alloy: Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Behavior, Cytotoxicity and Antibacterial Activities. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vida, T.A.; Brito, C.; Lima, T.S.; Spinelli, J.E.; Cheung, N.; Garcia, A. Near-Eutectic Zn-Mg Alloys: Interrelations of Solidification Thermal Parameters, Microstructure Length Scale and Tensile/Corrosion Properties. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2019, 19, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoudeh Bagha, P.; Khaleghpanah, S.; Sheibani, S.; Khakbiz, M.; Zakeri, A. Characterization of Nanostructured Biodegradable Zn-Mn Alloy Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Xue, L.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Y. Selective Laser Melting of Zn–Ag Alloys for Bone Repair: Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Degradation Behaviour. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2018, 13, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Fang, H.; Yu, K.; Zhang, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y. Effects of the Intermetallic Phases on Microstructure and Properties of Biodegradable Magnesium Matrix and Zinc Matrix Prepared by Powder Metallurgy. Mater. Trans. 2018, 59, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Čapek, J.; Kubásek, J.; Pinc, J.; Drahokoupil, J.; Čavojský, M.; Vojtěch, D. Extrusion of the Biodegradable ZnMg0.8Ca0.2 Alloy—The Influence of Extrusion Parameters on Microstructure and Mechanical Characteristics. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 108, 103796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Zhu, X.; Yang, L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, B.Q.; Cho, K.; Sun, W.; Ren, T.; Song, Z. Ultrafine- and Uniform-Grained Biodegradable Zn-0.5Mn Alloy: Grain Refinement Mechanism, Corrosion Behavior, and Biocompatibility in Vivo. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardakani, M.S.; Mostaed, E.; Sikora-Jasinska, M.; Kampe, S.L.; Drelich, J.W. The Effects of Alloying with Cu and Mn and Thermal Treatments on the Mechanical Instability of Zn-0.05Mg Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 770, 138529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubásek, J.; Vojtěch, D.; Pospíšilová, I.; Michalcová, A.; Maixner, J. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Micrograined Hypoeutectic Zn–Mg Alloy. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vida, T.A.; Freitas, E.S.; Brito, C.; Cheung, N.; Arenas, M.A.; Conde, A.; De Damborenea, J.; Garcia, A. Thermal Parameters and Microstructural Development in Directionally Solidified Zn-Rich Zn-Mg Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 3052–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachla, W.; Przybysz, S.; Jarzębska, A.; Bieda, M.; Sztwiertnia, K.; Kulczyk, M.; Skiba, J. Structural and Mechanical Aspects of Hypoeutectic Zn–Mg Binary Alloys for Biodegradable Vascular Stent Applications. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Linsley, C.S.; Pan, S.; DeBenedetto, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, B.M.; Li, X. Highly Ductile Zn-2Fe-WC Nanocomposite as Biodegradable Material. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2020, 51, 4406–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.S.; Li, Y.H.; Agbedor, S.O.; Bai, J.; Xue, F.; Jiang, J.H. A High-Strength and Biodegradable Zn–Mg Alloy with Refined Ternary Eutectic Structure Processed by ECAP. Acta Metall. Sin. 2020, 33, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, M.B.; Moore, C.; Saptarshi, S.; Somasundaram, S.; Rahuma, M.; Lopata, A.L. Biocompatibility and Biodegradation Studies of a Commercial Zinc Alloy for Temporary Mini-Implant Applications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; Zhao, S.; Guillory, R.; Bowen, P.K.; Yin, Z.; Griebel, A.; Schaffer, J.; Earley, E.J.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Novel High-Strength, Low-Alloys Zn-Mg (< 0.1 Wt% Mg) and Their Arterial Biodegradation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 84, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jia, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, X.; Li, G.; Lin, W.; Zhu, D.; Dai, K.; Zheng, Y. Alloying Design of Biodegradable Zinc as Promising Bone Implants for Load-Bearing Applications. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubásek, J.; Vojtěch, D.; Jablonská, E.; Pospíšilová, I.; Lipov, J.; Ruml, T. Structure, Mechanical Characteristics and in Vitro Degradation, Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Mutagenicity of Novel Biodegradable Zn–Mg Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostaed, E.; Sikora-Jasinska, M.; Mostaed, A.; Loffredo, S.; Demir, A.G.; Previtali, B.; Mantovani, D.; Beanland, R.; Vedani, M. Novel Zn-Based Alloys for Biodegradable Stent Applications: Design, Development and in Vitro Degradation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 60, 581–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Cockerill, I.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.; Lee, K.-W.; Ma, J.; Okpokwasili, C.; Tang, L.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Mechanical Strength, Biodegradation, and in Vitro and in Vivo Biocompatibility of Zn Biomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6809–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Gao, C.; Feng, P.; Xue, L.; He, S.; Shuai, C. A Combined Strategy to Enhance the Properties of Zn by Laser Rapid Solidification and Laser Alloying. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 82, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarzębska, A.; Bieda, M.; Kawałko, J.; Rogal; Koprowski, P.; Sztwiertnia, K.; Pachla, W.; Kulczyk, M. A New Approach to Plastic Deformation of Biodegradable Zinc Alloy with Magnesium and Its Effect on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Mater. Lett. 2018, 211, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Ren, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, E.; Yan, C.; Liu, Q.; Sun, X.; Shou, F.; Duan, J.; et al. Indirectly Extruded Biodegradable Zn-0.05wt%Mg Alloy with Improved Strength and Ductility: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xie, H.; Li, S.; Ren, Y.; Qin, G. Effect of Cumulative Strain on the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Zn-0.02 Wt%Mg Alloy Wires during Room-Temperature Drawing Process. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 740, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambatta, M.S.; Izman, S.; Kurniawan, D.; Hermawan, H. Processing of Zn-3Mg Alloy by Equal Channel Angular Pressing for Biodegradable Metal Implants. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2017, 29, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liu, X.; Fan, B.; Lan, P.; Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Xiao, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, S.; et al. Mechanical Properties, in Vitro Degradation Behavior, Hemocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Zn–1.2Mg Alloy for Biodegradable Implants. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86410–86419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Yang, H.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Dai, K. In Vitro and in Vivo Studies of Zn-Mn Biodegradable Metals Designed for Orthopedic Applications. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Gao, X.X.; Chen, H.T.; Liu, X.F.; Li, A.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, L.N. Enhancement in Mechanical and Corrosion Resistance Properties of a Biodegradable Zn-Fe Alloy through Second Phase Refinement. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafri, A.; Ovadia, S.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.; Aghion, E. The Suitability of Zn–1.3%Fe Alloy as a Biodegradable Implant Material. Metals 2018, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Z.; Niu, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Pei, J.; Ou, J.; Yuan, G. Potential Biodegradable Zn-Cu Binary Alloys Developed for Cardiovascular Implant Applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 72, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Dai, J.; Xepapadeas, A.B.; Schweizer, E.; Alexander, D.; Scheideler, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, H.; Wan, G.; et al. Investigation of Zinc-copper Alloys as Potential Materials for Craniomaxillofacial Osteosynthesis Implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Seitz, J.M.; Eifler, R.; Maier, H.J.; Guillory, R.J.; Earley, E.J.; Drelich, A.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Zn-Li Alloy after Extrusion and Drawing: Structural, Mechanical Characterization, and Biodegradation in Abdominal Aorta of Rat. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; McNamara, C.T.; Bowen, P.K.; Verhun, N.; Braykovich, J.P.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Structural Characteristics and In Vitro Biodegradation of a Novel Zn-Li Alloy Prepared by Induction Melting and Hot Rolling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Peng, S.; Yang, W.; Qi, F. Laser Additive Manufacturing of Zn-2Al Part for Bone Repair: Formability, Microstructure and Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 798, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, P.K.; Seitz, J.-M.; Guillory, R.J.; Braykovich, J.P.; Zhao, S.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Evaluation of Wrought Zn-Al Alloys (1, 3, and 5 Wt % Al) through Mechanical and in Vivo Testing for Stent Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, K.; Lin, J.J.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.J.; Wen, C. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, Biocompatibility, and in Vitro Corrosion and Degradation Behavior of a New Zn–5Ge Alloy for Biodegradable Implant Materials. Acta Biomater. 2018, 82, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Huang, H.; Niu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Pei, J.; Tan, J.; Yuan, G. Design and Characterizations of Novel Biodegradable Zn-Cu-Mg Alloys for Potential Biodegradable Implants. Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Huang, H.; Ke, G.; Zhang, H.; Pei, J.; Xue, G.; Yuan, G. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and in Vitro Degradation Behavior of Novel Zn-Cu-Fe Alloys. Mater. Charact. 2017, 134, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guo, P.; Niu, Z.; Li, F.; Song, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, H.; Sun, W.; Ren, T. Influence of Mg on the Mechanical Properties and Degradation Performance of As-Extruded ZnMgCa Alloys: In Vitro and in Vivo Behavior. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 95, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Ran, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.G.; Hu, T.; Wang, G. Mechanical Properties, Degradation Behaviors and Biocompatibility Evaluation of a Biodegradable Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy for Cardiovascular Implants. Mater. Lett. 2019, 234, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Pu, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, in Vitro Degradation Behavior and Hemocompatibility of Novel Zn–Mg–Sr Alloys as Biodegradable Metals. Mater. Lett. 2016, 162, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Zhou, F.; Yang, Y.; Chang, R.; Qiu, K.; Pu, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y. Micro-Alloying with Mn in Zn–Mg Alloy for Future Biodegradable Metals Application. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Gao, X.; Xu, C.; Yang, L.; Guo, P.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W.; Song, Z. Evaluation of As-Extruded Ternary Zn–Mg–Zr Alloys for Biomedical Implantation Material: In Vitro and in Vivo Behavior. Mater. Corros. 2019, 70, 1056–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, H.; Zhan, W. Effects of Ti on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Biodegradation Behavior of Zn-Cu Alloy. Mater. Lett. 2019, 244, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, D.W.; Yin, Y.X.; Wang, L.N. Effects of Ag, Cu or Ca Addition on Microstructure and Comprehensive Properties of Biodegradable Zn-0.8Mn Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Dai, Y.; Kang, Y.; Yu, K. Investigation on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, in Vitro Degradation Behavior and Biocompatibility of Newly Developed Zn-0.8%Li-(Mg, Ag) Alloys for Guided Bone Regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, X.F.; Wang, L.N. Fabrication and Characterization of Novel Biodegradable Zn-Mn-Cu Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, H.T.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.F. In Vitro Evaluation of the Feasibility of Commercial Zn Alloys as Biodegradable Metals. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qu, X.; Lin, W.; Wang, C.; Zhu, D.; Dai, K.; Zheng, Y. In Vitro and in Vivo Studies on Zinc-Hydroxyapatite Composites as Novel Biodegradable Metal Matrix Composite for Orthopedic Applications. Acta Biomater. 2018, 71, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Hamzah, E.; Low, H.T.; Cho, M.H.; Kasiri-Asgarani, M.; Farahany, S.; Mostafa, A.; Medraj, M. Thermal Characteristics, Mechanical Properties, in Vitro Degradation and Cytotoxicity of Novel Biodegradable Zn-Al-Mg and Zn-Al-Mg-XBi Alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. 2017, 30, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinc, J.; Čapek, J.; Hybášek, V.; Průša, F.; Hosová, K.; Maňák, J.; Vojtěch, D. Characterization of Newly Developed Zinc Composite with the Content of 8 Wt.% of Hydroxyapatite Particles Processed by Extrusion. Materials 2020, 13, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathak, D.K.; Pandey, P.M. An Experimental Investigation of the Fabrication of Biodegradable Zinc–Hydroxyapatite Composite Material Using Microwave Sintering. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 234, 2863–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinc, J.; Čapek, J.; Kubásek, J.; Průša, F.; Hybášek, V.; Veřtát, P.; Sedlářová, I.; Vojtěch, D. Characterization of a Zn-Ca5(PO4)3(OH) Composite with a High Content of the Hydroxyapatite Particles Prepared by the Spark Plasma Sintering Process. Metals 2020, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Qu, X.; Lin, W.; Chen, D.; Zhu, D.; Dai, K.; Zheng, Y. Enhanced Osseointegration of Zn-Mg Composites by Tuning the Release of Zn Ions with Sacrificial Mg-Rich Anode Design. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubásek, J.; Dvorský, D.; Čapek, J.; Pinc, J.; Vojtěch, D. Zn-Mg Biodegradable Composite: Novel Material with Tailored Mechanical and Corrosion Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, C.; Sun, X.; Xu, G.; Su, Y.; Liu, D. The Effects of β-TCP on Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Behavior and Biocompatibility of β-TCP/Zn-Mg Composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guoliang, L.; Guangquan, X.; Bobo, H.; Li, L.; Debao, L. Fabrication and Properties of a Biodegradable β-TCP/Zn–Mg Bio-Composite. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 0865i1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Processing Method (Grain Size) | Corrosion Test Results | Mechanical Test Results | Tribological Results/Biocompatibility | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | Hot Extrusion (14) | −0.098 V 8.9 µA/cm2 DR—0.133 mm/y (14) | 55 MPa —97 MPa —7.7% | Nr | [86] |
| Zn | Hot Extrusion (151 µm) | —−0.98 V 8.98 µA/cm2 DR—0.134 mm/y (14) | 51 MPa —111 MPa —60% H—34 HV | Nr | [87] |
| Zn | Hot rolling | —−1.077 V 20.9 µA/cm2 DR—0.306 mm/y (14) | 35 MPa —49 MPa —6% H—40 HV | Nr | [88] |
| Zn | Selective laser method (104 µm) | —−0.87 V 9.24 µA/cm2 DR—0.18 mm/y (28) | 43 MPa —61 MPa E—12 GPa —1.7% H—50 HV | Nr | [89] |
| Zn-25Mg | Powder Metallurgy | DR—0.374 mm/y −1.323 V 12.2 µA/cm2 (2) | E—86 GPa —5.2% —403 MPa H—86 HV | Nr | [74] |
| Zn-1Mg | Hot Extrusion (4.4 µm) | −1.07 V 11.8 µA/cm2 DR—0.177 mm/y (14) | 180 MPa —340 MPa —6% H—75 HV | Nr | [87] |
| Zn-0.8Mg | Hot Extrusion (20 µm) | DR—0.071 mm/y (1) | 203 MPa —301 MPa —13% —186 GPa H—83 HV | Nr | [86] |
| Zn-0.5Mg | Hydrostatic Extrusion | Nr | —515 MPa 375 MPa —10.5% H—107 HV —473 MPa | Nr | [80] |
| Zn-1.6Mg | ECAP | 6.91 µA/cm2 DR—9.31 mm/y | —474 MPa —7% | Nr | [82] |
| Zn-3Mg | Selective laser method | DR—0.1 mm/y (28) | —222 MPa 152 MPa | Cytotoxic at 100% concentration of extract | [89] |
| Zn-1Mg | Hydrostatic extrusion | Nr | —435 MPa 335 MPa | Nr | [90] |
| Zn-0.008Mg | Extrusion + Drawing | Nr | —339 MPa 221 MPa | Nr | [84] |
| Zn-0.005Mg | Indirect Extrusion | DR—0.15 mm/y (14) | —225 MPa 160 MPa —26% | Cytotoxic at 100% concentration of extract | [91] |
| Zn-0.002Mg | Extrusion + Drawing | Nr | —455 MPa 388 MPa | Nr | [92] |
| Zn-0.05Mg | Hot extrusion (20 µm) | —−0.938 V 49.1 µA/cm2 DR—0.653 mm/y (14) | 160 MPa —225 MPa —26% | Nr | [91] |
| Zn-3Mg | 2 Pass ECAP (1.8 µm) | —−0.893 V 3.2 µA/cm2 DR—0.28 mm/y (14) | 205 MPa —220 MPa —6.3% E—210 GPa H—186 HV | Nr | [93] |
| Zn-1.2Mg | Hot Extrusion | —−1.18 V 7.68 µA/cm2 DR—0.12 mm/y (90) | 220 MPa —363 MPa —21% H—96 HV | Nr | [94] |
| Zn-0.5Mn | Multi-pass drawing | DR—0.5 mm/y | —127.6 MPa —245% | Good but decrease in biocompatibility | [76] |
| Zn-4Mn | Nr | 48 µA/cm2 DR—0.72 mm/y | —298 MPa —14.9% | Nr | [72] |
| Zn-0.1Mn | Extrusion | Change in volume—95% DR—0.014 mm/y | —175 MPa 125 MPa —40% —390 MPa —110 MPa H—55 HV | Nr | [85] |
| Zn-0.8Mn | Hot Extrusion | —−0.976 V 7.43 µA/cm2 DR—0.111 mm/y (30) | 162 MPa —215 MPa —44% —136 MPa H—58 HV | Nr | [95] |
| Zn-0.3Fe | Casting (7.5 µm) | −1.01 V 7.31 µA/cm2 DR—0.111 mm/y | 70.5 MPa —76.4 MPa —1.18% —117 MPa | Nr | [96] |
| Zn-1.3Fe | Casting | —−1.02 V 0.67 µA/cm2 DR—0.01 mm/y (20) | 80 MPa —134 MPa —1.8% H—56 HV | Nr | [97] |
| Zn-4Cu | Hot Extrusion (2.3 µm) | ---- | 227 MPa —271 MPa —51% | Nr | [98] |
| Zn-4Cu | Hot Rolling (40 µm) | DR—0.13 mm/y (40) | 327 MPa —393 MPa —44.6% —300 MPa H—94 HV | Nr | [99] |
| Zn-4Cu | Extrusion | DR—0.0255 mm/y (14) | —270 MPa 227 MPa —50.6% | Nr | [98] |
| Zn-0.1Li | Extrusion + Drawing | Nr | —274 MPa —17% | Nr | [100] |
| Zn-6Li | Hot rolling | 3.8 µA/cm2 DR—0.05 mm/y | —569 MPa 478 MPa —2.4% | Nr | [101] |
| Zn-0.4Li | Extrusion | DR—0.002 mm/y | —520.36 MPa 390 MPa —6% —795 MPa —415 MPa H—165 HV | Cell viability—120% (4) | [85] |
| Zn-0.4Li | Hot Rolling (10 µm) | —−1.21 V 3.80 µA/cm2 DR—0.05 mm/y (14) | 425 MPa —440 MPa —14% H—137 HV | Nr | [101] |
| Zn-0.4Li | Hot Extrusion | −1.03 V 11.26 µA/cm2 DR—0.019 mm/y (30) | 387 MPa —520 MPa —5% —434 MPa H—164 HV | Nr | [85] |
| Zn-6Ag | Selective laser method (25 µm) | −0.94 V 9.56 µA/cm2 DR—0.15 mm/y (21) | —267 MPa H—78 HV | Nr | [73] |
| Zn-2Ag | Hot extrusion | −1.06 V 17.27 µA/cm2 0.018 mm/y (30) | 186 MPa —231 MPa —36.7% —145 MPa H—55 HV | Nr | [85] |
| Zn-1Al | Hot Extrusion (14.4 µm) | −0.98 V 9.70 µA/cm2 0.145 mm/y (14) | 113 MPa —223 MPa —24% H—73 HV | Nr | [87] |
| Zn-2Al | Laser powder bed fusion (5.53 µm) | −1.059 V 8.04 µA/cm2 DR—0.142 mm/y (14) | 142 MPa —192 MPa E—65 GPa —12% | Nr | [102] |
| Zn-5Al | Hot rolling | —308 MPa —16% | Nr | [103] | |
| Zn-5Ge | Hot Extrusion | −0.1063 V 10.7 µA/cm2 DR—0.157 mm/y (14) | 175 MPa —237 MPa —22% H—60 HV | [104] | |
| Zn-3Cu-1Mg | Extrusion | 12.4 µA/cm2 DR—0.18 mm/y | —441 MPa 427 MPa —0.9% | Nr | [105] |
| Zn-0.5Al-0.5Mg | Nr | —−1.018 V 9.5 µA/cm2 DR—0.12 mm/y (30) | —102 MPa —2.1% H—94 HV | Nr | [70] |
| Zn-3Cu-1Fe | Extrusion | 8.8 µA/cm2 0.13 mm/y | —272 MPa 221 MPa —19.6% | Nr | [106] |
| Zn-0.8Li-0.8Mg | Hot Extrusion | Nr | 438 MPa —646 MPa —3.68% | Nr | [85] |
| Zn-0.8Li-0.8Mn | Hot Extrusion | Nr | 357 MPa —513 MPa —103.5% | Nr | [85] |
| Zn-1.5Mg-0.5Ca | Hot Extrusion (10–20 µm) | −1.18 V 2.08 µA/cm2 DR—0.024 mm/y | 160 MPa —442 MPa —4.9% H—111 HV | Nr | [107] |
| Zn-0.02Mg-0.02Cu | Hot Extrusion (13 µm) | DR—0.079 mm/y (15) | 216 MPa —262 MPa —28% H—74 HV | Nr | [108] |
| Zn-1Mg-0.1Sr | Hot Rolling | −1.19 V 10.2 µA/cm2 DR—0.15 mm/y | 197 MPa —300 MPa —23% H—104 HV | Nr | [109] |
| Zn-1Mg-0.1Mn | Hot Rolling | —−1.21 V 16.7 µA/cm2 DR—0.25 mm/y | 195 MPa —299 MPa —26.1% H—108 HV | Nr | [110] |
| Zn-1Mg-0.1 Zr | Hot Extrusion | −1.23 V 5.44 µA/cm2 DR—0.23 mm/y (90) | 248 MPa —314 MPa —2.5% —300 MPa H—94 HV | Nr | [111] |
| Zn-2Cu-0.1Ti | Casting | −1.164 V 2.56 µA/cm2 DR—0.022 mm/y (30) | 132 MPa —177 MPa —2.5% | Nr | [112] |
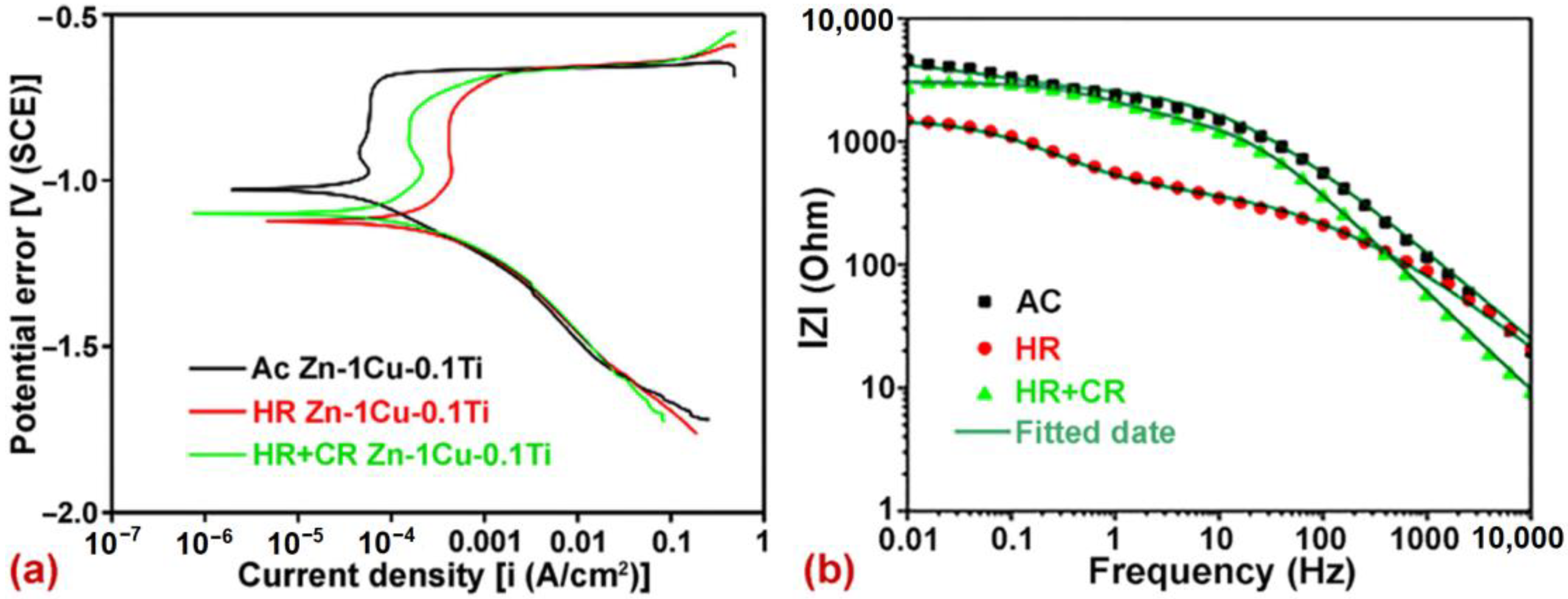
| Zn-1Cu-0.1Ti | Hot rolling + Cold rolling | DR—0.991 mm/y −1.100 V 67.7 µA/cm2 | 204.2 MPa —249.9 MPa —75.2% | Friction coefficient—0.731 Wear loss—20.2 mg Surface roughness—0.94 µm | [58] |
| Zn-0.8Mn-0.4Ag | Hot Extrusion (2 µm) | −1.19 V 11.2 µA/cm2 DR—0.160 mm/y | 156 MPa —251 MPa —63% | Nr | [113] |
| Zn-0.8Mn-0.4Cu | Hot Extrusion (1.1 µm) | −1.18 V 8.91 µA/cm2 DR—0.133 mm/y | 191 MPa —308 MPa —39% | Nr | [113] |
| Zn-0.8Mn-0.4Ca | Hot Extrusion (2.6 µm) | −1.16 V 10.7 µA/cm2 DR—0.160 mm/y | 253 MPa —343 MPa —8% | Nr | [113] |
| Zn-0.8Li-0.2Ag | Hot Rolling (2.3 µm) | −1.21 V 7.67 µA/cm2 DR—0.11 mm/y | 196 MPa —255 MPa —98% | Nr | [114] |
| Zn-0.8Li-0.2Mg | Hot Rolling | −1.32 V 11.3 µA/cm2 DR—0.17 mm/y | 254 MPa —341 MPa —31% | Nr | [114] |
| Zn-0.35Mn-0.41Cu | Hot rolling (1.1 µm) | −1.046 V 4.1 µA/cm2 DR—0.062 mm/y (14) | 198 MPa —292 MPa —30% | Nr | [115] |
| Zn-4.3Al-3.2Cu-0.06Mg | Extrusion | 7.2 µA/cm2 Corrosion rate—0.374 mm/y | —201 MPa 110 MPa —126% | Nr | [116] |
| Zn-1HA | Spark plasma sintering | 21 µA/cm2 DR—0.327 mm/y | —158 MPa 68 MPa —90% | Nr | [117] |
| Zn-2Fe-6 v.% WC | Hot rolling | DR—0.020 mm/y 5.19 µA/cm2 | —155.8 MPa —15.3% H—59.3 HV | Nr | [81] |
| Zn-0.5Al-0.5Mg-0.3Bi | Extrusion (30 µm) | −1.084 V 16.45 µA/cm2 DR—0.203 mm/y (30) | —108 MPa —2.7% H—109 HV | Nr | [118] |
| Zn-8HA | Extrusion | DR—0.40 mm/y (14) | —113 MPa —169 MPa H—44.7 HV | Nr | [119] |
| Zn-3HA | Powder Metallurgy | −1.070 V 5.16 µA/cm2 DR—0.084 mm/y | —110 MPa | Nr | [120] |
| Zn-16HA | Spark plasma sintering | CR—1.5 mm/y (14) | —46 MPa —65 MPa H—24 HV | Nr | [121] |
| Zn-5Mg | Spark plasma sintering | −1.312 V 0.43 µA/cm2 DR—0.203 mm/y (50) | —183 MPa H—80.8 HV | Nr | [122] |
| Zn-5Mg | Powder Metallurgy | −1.42 V DR—0.0016 mm/y (14) | 148 MPa —183 MPa —16% —256 MPa —209 MPa | Nr | [123] |
| Zn-1Mg-1TCP | Extrusion | DR—0.046 mm/y (14) | 294 MPa —330 MPa —11.7% | Nr | [124] |
| Zn-1Mg-1βTCP | Extrusion | −1.225 V 48.9 µA/cm2 DR—0.732 mm/y (30) | 251 MPa —331 MPa —11.7% | Nr | [125] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, M.; Ullah, S.; Raza, M.R.; Abbas, N.; Ali, A. Recent Developments in Zn-Based Biodegradable Materials for Biomedical Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010001
Hussain M, Ullah S, Raza MR, Abbas N, Ali A. Recent Developments in Zn-Based Biodegradable Materials for Biomedical Applications. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Muzamil, Sami Ullah, Muhammad Rafi Raza, Naseem Abbas, and Ahsan Ali. 2023. "Recent Developments in Zn-Based Biodegradable Materials for Biomedical Applications" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010001
APA StyleHussain, M., Ullah, S., Raza, M. R., Abbas, N., & Ali, A. (2023). Recent Developments in Zn-Based Biodegradable Materials for Biomedical Applications. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010001









