Abstract
Here we analyze the simultaneous relationships among five variables. Two refer to childhood (episodes of various forms of maltreatment and externalizing behaviors), whereas three refer to early adulthood (intelligence, personality, and socialization difficulties). The 120 individuals considered for the present report were invited from the 650 schoolchildren participating in the Longitudinal Study of Intelligence and Personality (Minas Gerais, Brazil). The complete sample was recruited in 2002 (T1; mean age = 10.0; standard deviation (SD) = 2.2) and 120 were tested again in 2014-17 (T2; mean age = 23.5; SD = 2.2). Externalizing behaviors were registered at T1, whereas the remaining variables were obtained at T2. These were the main results: (1) externalizing behaviors predict future social effectiveness (as estimated by the general factor of personality derived from the NEO Personality Inventory-Revised (NEO-PI-R) and socialization difficulties computed from the socialization scale (SOC)) and future intelligence performance (as assessed by a set of fluid and crystallized tests); (2) episodes of self-reported childhood maltreatment predict social effectiveness, but not intelligence; (3) maltreatment and externalizing behaviors are unrelated; and (4) social effectiveness (personality) and intelligence are unrelated. Therefore, the findings support the dissociation between adult intelligence and personality with respect to maltreatment episodes and externalizing behaviors occurring in childhood. Implications of these findings for social policies aimed at preventing adult socially ineffective personalities are underscored.
1. Introduction
1.1. The Externalizing Spectrum
The effects of childhood experiences in adult behavior have been a classic topic in psychology since the early years of psychoanalysis. Despite the fact that cognitive and behavioral models have devoted less attention to childhood, current psychological explanations of abnormal behavior often rely on concepts such as dysfunctional attachment bonds, under the assumption that they extend their influence to the adult years.
An early source of negative adult outcomes is the presence of childhood disturbing behaviors. Problem behaviors such as impulsivity, aggression, violence, antisocial behavior and substance misuse have been summarized by the label “externalizing spectrum” [1]. An estimated 5% of the population (mostly men) displays these problems with noteworthy severity [2]. They seem to have developmental stability and persist from childhood to adolescence and adulthood [3,4,5]. Various forms of child psychopathology considered by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) have been included within this spectrum, in particular attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and conduct disorder (CD) [6,7].
1.2. Individual Differences and the Externalizing Spectrum
As noted, the externalizing spectrum includes several clinically recognized disorders such as ADHD, CD, and ODD. The core of these disorders refers to maladaptive behaviors, impulsivity, deficit in inhibitory control causing impairment, or interference, in everyday life functioning. Research efforts have focused on exploring the longitudinal association between early individual differences and adolescent/adult externalizing behaviors.
Thus, for instance, poor intellectual performance has been associated with externalizing behaviors in cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Analyzing a sample of 2370 secondary school students, Huepe, Roca, Salas, Canales-Johnson, Riveral-Rel, Zamorano et al. [8] found that those within the lowest 5% of the intelligence distribution (assessed with the Raven’s Progressive Matrices Test) showed higher frequency of bullying behaviors and drug use. Caspi, Houts, Belsky, Harrington, Hogan, Ramrakha, Poulton and Moffitt [9] studied a cohort from the Dunedin Longitudinal Study, finding that measures of neurological functioning, intelligence, receptive language and motor skills measured at age three predict, 35 years later, problematic adult behaviors (criminality, excess weight or dependence from social welfare) (AUC = 0.87). Childhood low IQ and low self-control did also predict adult difficulties. However, Young, Friedman, Miyake, Wilcutt, Corley, Haberstick, and Hewitt [10] supported the opposite relation: measures of conduct disorder and ADHD at age 12 predicted worse executive response inhibition at age 17 (−0.41).
Personality traits such as impulsivity, aggressiveness, empathy, honesty and irresponsibility have been related to externalizing behaviors [1,11]. The link between personality traits and externalizing behaviors has been studied within the framework of the five-factor model. Based on the correlations among the five personality traits, two higher-order traits were obtained: stability (neuroticism reversed, conscientiousness, and agreeableness) and plasticity (extraversion and openness). Considering a sample of 140 adolescents, DeYoung, Peterson, Séguin and Tremblay [12] analyzed the relation between externalizing and these higher order factors. Stability was negatively correlated (r = −0.71) while plasticity was positively correlated (r = 0.75) with externalizing behaviors. Intelligence was also negatively correlated with these behaviors (r = −0.59) as assessed by students’ teachers.
The variance shared by stability and plasticity gives rise to a single higher order dimension: the general factor of personality [13,14]. This factor is thought to reflect social effectiveness [15]. The longitudinal association between this higher-order factor and externalizing behaviors remains unexplored, but cross-sectional findings suggest that they might be related [16].
Longitudinal research has focused on the predictive power of early individual differences over the onset of later (adolescence and early adulthood) externalizing behavior, whereas less attention has been devoted to the relationship between early externalizing behaviors and individual differences in intelligence and personality in adulthood. Walton, Krueger, Elkins, D’Accordo, McGue and Iacono [17] conducted a population-based longitudinal study (N = 1252) with participants of the Minnesota Twin Family Study who completed the Multidimensional Personality Questionnaire at age 17 and were screened for diagnoses of antisocial behavior and substance misuses at ages 17, 20, 24, and 29. Aggression scores were consistently associated with diagnoses of antisocial behavior (correlations ranging between 0.26 and 0.46), and alcohol dependence (correlations between 0.2 and 0.49). Loeber, Menting, Lynam, Moffitt, Stouthamer-Loeber, Stallings et al. [18] studied a sample of boys from the Pittsburgh Youth Study (n = 422). Participants completed measures of cognitive impulsivity and intelligence at age 12. Both traits predicted the age-crime curve. Criminal behavior was more frequent in boys with high cognitive impulsivity or lower IQ.
To summarize: while the relation between externalizing disorders and individual differences in several areas seems to be supported by longitudinal studies, it is unclear how the presence of these externalizing behaviors is related to adult personality and intelligence. There are several reasons to expect that early externalizing problems will have a reflection in adult individual differences. First, there is evidence that externalizing behavior presents moderate to high stability over time, at least from childhood to adolescence [19]. Second, externalizing behavior usually relates to later antisocial behavior or delinquency [20]. Third, externalizing behavior is associated with several neuropsychological deficits such as working memory and emotional self-regulation skills [21,22]. Therefore, in the present study we assume that these neuropsychological dysfunctions may have a certain degree of developmental stability and, therefore, exert a negative influence over adult personality and intellectual level.
1.3. Child Maltreatment
Child maltreatment might predict adult negative outcomes [23,24,25,26]. Furthermore, the experience of neglect and various forms of child abuse might be associated with future cognitive impairment [27,28], and personality profiles characterized by socialization difficulties expressed by traits such as conscientiousness, agreeableness, and openness [29,30].
1.4. Present Research
The following research questions will be addressed in the present research:
- (1)
- Are individual differences in childhood externalizing behaviors associated with personality, socialization difficulties, and intelligence assessed in adulthood?
- (2)
- Is self-reported experience of childhood maltreatment related with personality, socialization difficulties, and intelligence assessed in adulthood?
Personality Traits are Considered Using Two Approaches
First, the traits tapped by the five-factor model (FFM) will be analyzed for obtaining one single dimension (GFP = general factor of personality). The conceptual relevance of this general psychological construct has been exhaustively analyzed by John Loehlin [13] who concluded: “GFPs obtained as unrotated first factors have considerable generality across personality inventories and levels of measurement (…) GFPs derived from self-reports and from others’ reports were substantially correlated (…) a GFP is a fairly generalizable and quite readily measurable phenomenon” (p. 262).
Furthermore, a large-scale meta-analysis found great overlap between the GFP and emotional intelligence [31], which might support the view of GFP as a social effectiveness factor. We note, however, that Schermer and Vernon [32] found a positive, but moderate, relation between GFP and a measure of social desirability.
As highlighted by Loehlin [13], the GFP would benefit from evidence of an association with behavioral correlates. The present research looks for evidence of associations between the GFP and nearby constructs (externalizing behaviors and socialization) along with intellectual traits.
Nevertheless, we will also report associations among the traits included in the FFM—instead of the computed GFP—and the remaining variables of interest.
Second, socialization difficulties will be assessed with the socialization scale (SOC) [33] designed from Lykken’s model of antisocial personality [34]. Greater levels of sensation seeking, fearlessness, aggressiveness, and impulsivity are expected to increase vulnerability to antisocial and disruptive behaviors. Lower intelligence levels in adulthood are also expected in the presence of childhood externalizing behaviors and maltreatment episodes. Lykken’s model is based on Gray’s [35] and Zuckerman’s [36] models of personality.
In this regard, Herrero and Colom [37] administered the SOC to prison inmates (n = 186) and controls (n = 397) finding higher scores in sensation seeking and fearlessness in the former. Moreover, SOC scores haven been related to suicidal behavior. Negredo, Melis and Herrero [38] found a positive correlation between impulsiveness and the number of suicide attempts, as well as between the latter and sensation seeking.
In the present study, intellectual functioning was measured by measures of fluid and crystalized intelligence.
For analyzing the relationships among the variables of interest (childhood maltreatment episodes, childhood externalizing behaviors, adult intelligence, adult personality, and adult socialization difficulties), we considered their longitudinal associations: maltreatment episodes (retrospective self-reports) and externalizing behaviors (observer ratings) occurring in 2002, along with intelligence and personality variables assessed in early adulthood (2014–2017).
2. Method
2.1. Participants
The dataset analyzed here is based on the Longitudinal Study of Intelligence and Personality conducted by the Laboratory of Individual Differences at the Federal University of Minas Gerais, Brazil. The study began in 2002 recruiting 650 schoolchildren and they were assessed every two years until 2010 in both intellectual and personality variables. Here, we will analyze data of 120 participants (56.7% males) assessed in 2002 (T1, mean age = 10.0; SD = 2.2) who also completed a psychological assessment in 2014–2017 (T2, mean age = 23.5; SD = 2.2); 81.7% were university graduates, 11.6% had completed high school, and 6.7% had completed compulsory school.
2.2. Measures
As described above, externalizing behaviors were assessed in childhood (T1). These behaviors were registered using the Teacher Rating Scale for ADHD [39]. This scale measures externalizing behaviors observed in school, according to DSM-IV criteria. This scale comprises 49 items organized in four sub-scales: Attention Deficit (e.g., “he/she is easily distracted by any stimuli”); Learning Problems (e.g., “he/she is reluctant to engage in tasks that require mental effort”); Hyperactivity (e.g., “he/she always seems to be connected as an engine”); and Antisocial Behavior (e.g., “he/she is always quarreling”). According to the scale’s manual, reliability values (Cronbach’s alpha) range from 0.90 (Antisocial Behavior) to 0.97 (Attention Deficit). Two teachers provided a rating (after mutual agreement) for each child. In a previous study on a sample extracted from the same longitudinal project, Andrade and Flores-Mendoza [40] found similar reliability values. The correlation between Attention Deficit and Learning Problems was 0.90, and, therefore, for the present study we considered only three subscales (Learning Problems, Hyperactivity and Antisocial Behavior; see the remaining correlations in the Supplementary Material).
Episodes of childhood maltreatment were evaluated at T2 using the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire [41,42]. This is a retrospective self-report that includes 28 items tapping emotional, physical, and sexual abuse. According to studies published in Brazil [43], reliability values (Cronbach’s alpha) are 0.90 for emotional abuse, 0.86 for sexual abuse, and 0.69 for physical abuse. In a previous study with Brazilian males [44] similar reliability values were found.
Intelligence, Personality, and Socialization Difficulties Were Assessed at T2
Intelligence was assessed by eight subtests from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—WAIS-III [45]: Vocabulary, Information, Similarities, Comprehension, Digit Span, Letter-Number Sequencing, and Arithmetic. The Raven Progressive Matrices Test was also administered [46].
Personality traits were assessed by the NEO-PI-R [47]. This questionnaire taps the personality traits considered by the FFM: extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and openness. Reliability values (Cronbach’s alpha) were: 0.875, 0.851, 0.907, 0.914, and 0.862 respectively. Test-retest reliability coefficients (four months apart) ranged from 0.869 (Openness) to 0.943 (Conscientiousness).
Finally, socialization difficulties were assessed using the SOC scale [33]. The SOC includes three subscales: Sensation Seeking, Impulsivity, and Fearlessness. Reliability values (Cronbach’s alpha) were 0.692, 0.704, and 0.764 respectively. The reliability value for the general SOC score was 0.826.
2.3. Analyses
As specified at the introduction section, the interest here focuses on the analysis of the relationships between (childhood) maltreatment episodes/externalizing behaviors (T1, 2002) and (adult) intelligence/personality/socialization difficulties (T2, 2014–2017).
The descriptive statistics and correlations among all the specific measures included in the global scores are reported in the Supplementary Material.
Because of the relatively small sample size considered in the present study, we decided to analyze global scores after computing exploratory factor analyses (EFA). Therefore, five scores were obtained for computing the analyses of interest: (1) maltreatment episodes (retrospective report); (2) externalizing behaviors (Attention Deficit, Learning Problems, Hyperactivity, and Antisocial Behavior); (3) intelligence (WAIS-III and Raven matrices); (4) general factor of personality (NEO-PI-R); and (5) socialization difficulties (SOC scale).
Factor analyses (maximum likelihood) were computed for obtaining the global scores of interest: (a) the score for externalizing behaviors is based on the variance shared by Learning Problems, Hyperactivity, and Antisocial Behavior; (b) the GFP score taps the common variance of the five personality dimensions assessed by the NEO-PI-R; (c) the socialization difficulties score reflects the variance shared by Sensation Seeking, Impulsivity, and Fearlessness; (d) the Intelligence score is based on the WAIS-III subtests and the Raven Progressive Matrices.
For each latent variable, we report the factor loadings and the percentage of explained variance in the Supplementary Material. Using FACTOR 9.2 [48] we computed the factor determinacy index (FDI). When this index is close to one, the obtained factor score properly represents the latent trait of interest. Ferrando and Lorenzo-Seva [49] showed that FDI values around 0.80 are adequate for research purposes. The Supplementary Material reports FDI indices along with the estimation of the reliability of the obtained factor scores. Additional, correlations between the three used ADHD subscales and the other general constructs (socialization difficulties, intelligence and the GFP) are also reported.
The five variables of interest were organized within one path-model distinguishing those occurring or assessed at T1 (maltreatment episodes and externalizing behaviors) and those assessed at T2 (intelligence, personality, and socialization difficulties). Path models were also computed separately for the traits included in the FFM.
3. Results
Table 1 shows the descriptive statistics for the five variables of interest. The correlation matrix is also shown.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics and correlation matrix.
Table 1 reveals that: (1) maltreatment and externalizing behaviors are unrelated (r = 0.04); (2) maltreatment is positively related to socialization difficulties (r = 0.27) and negatively related to the general factor of personality (r = −0.40); (3) maltreatment and intelligence are unrelated (r = −0.05); (4) externalizing behaviors are positively related to socialization difficulties (r = 0.22) and negatively related to the general factor of personality (r = −0.28) and to intelligence (r = −0.24); (5) socialization difficulties are negatively related to the general factor of personality (r = −0.42); and (6) socialization difficulties and the general factor of personality are unrelated to intelligence.
Results shown in Table 1 indicate that only externalizing behaviors (T1) are related to the three variables assessed in early adulthood (T2). Maltreatment episodes (T1, retrospective) are related to personality factors (T2), but not to intelligence (T2). Finally, intelligence and personality fail to show any substantial relationship at T2.
Regarding the computed factor analyses for externalizing behaviors, the GFP, socialization difficulties, and intelligence, results showed appropriate FDI values [49]. Therefore, the global scores for these latent variables capture relevant shared variance (Table S2).
In the next step, the variables of interest were submitted to a path analysis considering their longitudinal nature. Results are shown in Figure 1A. Non-significant relationships are removed from the model for simplicity but reported in the text. Fit indices for this model were excellent: chi-square = 1.533 (df = 2, p = 0.465), RMSEA = 0.000, NFI = 0.97, and CFI = 1.00.
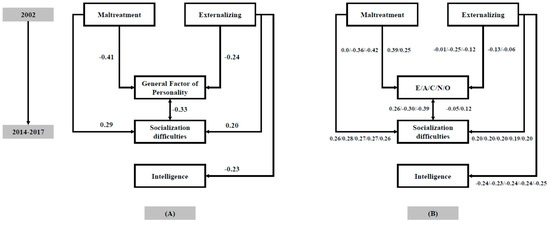
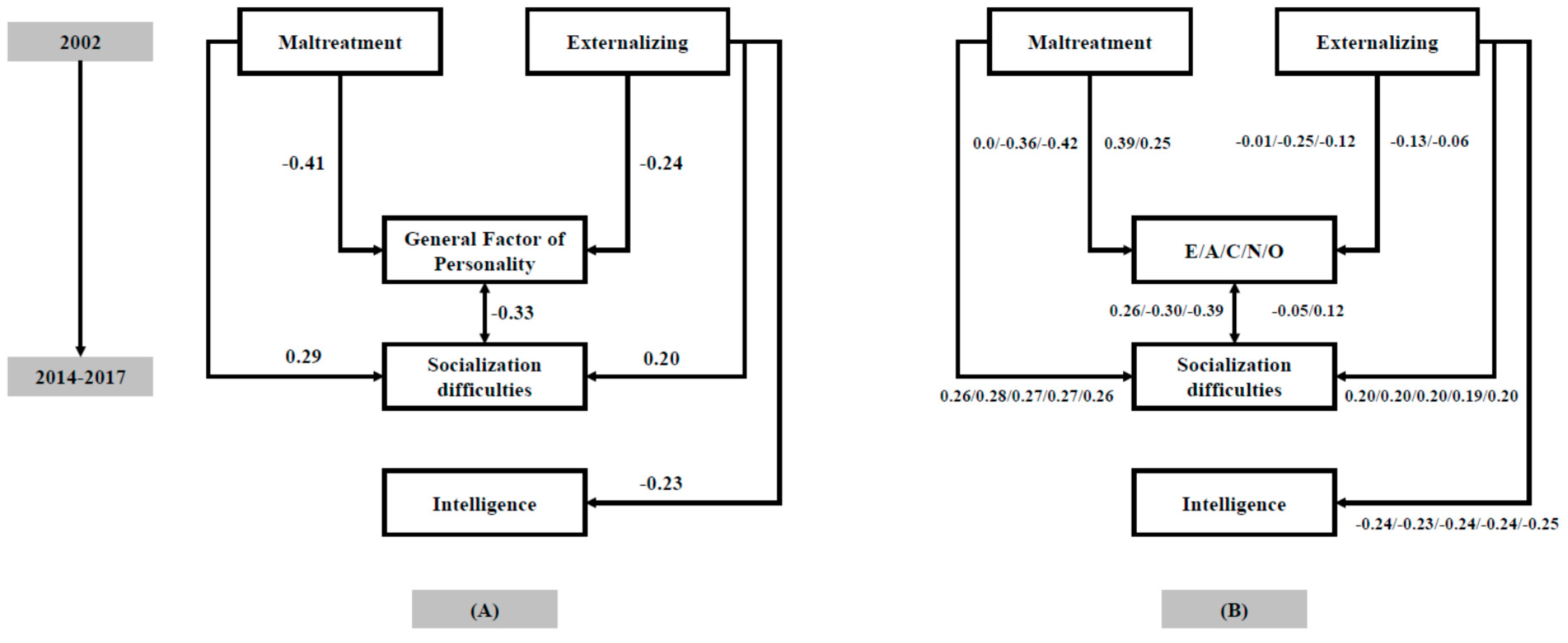
Figure 1.
(A) Path analysis relating childhood maltreatment and externalizing behaviors with adult intelligence and personality variables; (B) Path analyses computed separately for the traits included in the five-factor model (FFM).
Figure 1A shows several results of interest. First, maltreatment and externalizing behaviors occurring in childhood (T1) are unrelated (β = 0.05, p = 0.666). Second, childhood externalizing behaviors (T1, 2002) predict the three psychological variables assessed at T2 (2014–2017): personality (β = −0.24, p = 0.006), socialization difficulties (β = 0.20, p = 0.040), and intelligence (β = −0.23, p = 0.019). Third, childhood maltreatment (T1, retrospective) predicts personality (β = −0.41, p < 0.001) and socialization difficulties (β = 0.29, p = 0.002), but not intelligence (β = −0.06, p = 0.531) (T2). Fourth, personality and socialization difficulties (T2) are related (r = −0.33, p = 0.002). Finally, intelligence is unrelated to both personality and socialization difficulties (T2).
Figure 1B shows results when we replace the GFP with the personality traits included in the FFM. These are the main findings: (a) maltreatment is related to all traits except extraversion; (b) externalizing is related to agreeableness; and (c) socialization difficulties are related to extraversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness. These findings suggest that all personality traits are involved with maltreatment, externalizing behaviors, and socialization difficulties, albeit the most relevant may change depending on the variable of under consideration: (1) agreeableness is relevant regarding maltreatment, externalizing, and socialization; (2) conscientiousness is relevant for maltreatment and socialization; (3) neuroticism is relevant for maltreatment; and (4) extraversion is relevant for socialization.
4. Discussion
Here we have considered the longitudinal associations of maltreatment episodes and externalizing behaviors occurring in childhood with psychological factors (intelligence, personality, socialization difficulties) assessed in early adulthood. The observed findings are summarized and discussed next.
First, the GFP was negatively related to socialization difficulties. Therefore, this global factor might summarize “socially effective personality traits”. Figure 1B reveals that extraversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness may drive this relationship. Higher levels of extraversion, along with lower levels of agreeableness and conscientiousness, are related with socialization difficulties.
Second, maltreatment episodes and externalizing behaviors were unrelated. This suggests that children showing disruptive behaviors are not necessarily maltreated (and the other way around).
This finding is consistent with De Sanctis, Nomura, Newcom and Halperin [50], who observed that child maltreatment and conduct disorder were independent risk factors of adolescent antisocial behaviors.
Furthermore, McKee, Colletti, Rakow, Jones and Forehand [51] failed to find evidence for the specificity of parenting practices (warm, hostile, and control) regarding child disruptive behaviors.
According to the reported results, externalizing behaviors observed in childhood precede the configuration of complex personality traits, while self-reported maltreatment might be related to non-social personality variables. Teachers rated children’s externalizing behaviors and their assessments might differ from those provided by their parents. For instance, after studying 107 children from the same school, Andrade and Flores-Mendoza [40] reported high agreement between teachers and parents for Attention Deficit, but the agreement was lower for Hyperactivity and Antisocial Behavior.
Third, maltreatment and externalizing behaviors predicted socialization difficulties (as indexed by greater impulsivity, sensation seeking, and fearlessness) and one greater socially effective personality (as indexed by the general factor of personality, GFP) in early adulthood. These results might validate teachers’ assessments of externalizing behaviors made years before.
Maltreatment (adverse experiences) and externalizing behaviors were negatively related to the general factor of personality, whereas they were positively associated with socialization difficulties. Therefore, children showing disruptive behaviors and experiencing episodes of maltreatment do show a personality profile suggesting worse social adaptation. This finding is consistent with previous results (see [52] for a review). Interestingly, the general factor of personality was negatively related to socialization difficulties, which supports the view that the former might be a meaningful psychological dimension (rather than a simple statistical artifact) tapping social effectiveness [15].
Childhood maltreatment showed greater relationships than externalizing behaviors with the GFP. Nevertheless, we acknowledge that the reliability of self-reported childhood abuse may be a serious challenge in clinical research [53]. Here, the same individual did provide information regarding child maltreatment and personality traits, whereas teachers provided the assessment of the analyzed externalizing behaviors. This informant-dependency issue might increase the relationship in the first instance [53].
Fourth, only childhood externalizing behaviors predicted intelligence assessed in early adulthood. This is expected, given available research showing worse academic performance and lower cognitive functioning [54,55] in children and adults with disruptive behavior [56].
Surprisingly, we failed to find a significant relationship between episodes of childhood maltreatment and adult intelligence. Nevertheless, the type of maltreatment and time of occurrence may be relevant moderating variables. Thus, for instance, Nikulina and Widom [27] found relationships between maltreatment and cognitive functioning. However, only childhood neglect (but not physical and sexual abuse) predicted worse executive functioning and non-verbal reasoning performance. Jaffee and Maikovich-Fong [57] reported that chronic, but not temporary (situational) maltreatment, was related to externalizing behaviors and intelligence.
Finally, intelligence and personality were unrelated in the present dataset. Externalizing behaviors assessed in childhood predicted both psychological factors to the same extent (around r = 0.23), whereas self-reported episodes of childhood maltreatment predicted personality only. This suggests dissociation between adult intelligence and personality with respect to maltreatment episodes and externalizing behaviors occurring in childhood.
The interplay between intelligence and personality is highly complex [58]. Woods, Hinton, von Stumm and Bellman-Jeffreys [59] found significant correlations between a higher-order personality factor and verbal ability. However, the correlations between personality and quantitative/visuospatial abilities were non-significant. Also, null correlations between cognitive (fluid intelligence + working memory) and personality (socialization difficulties) variables were observed by Colom, Escorial, Shih, and Privado [60], although both did predict scholastic achievement to the same extent. There is also evidence from genetically informative samples indicating that g and GFP are unrelated at the genetic level. Loehlin, Bartels, Boomsma, Bratko, Martin, Nichols and Wright [61] studied a sample of monozygotic (n = 1748) and dizygotic (1329) twin pairs from different countries. The genetic correlation between GFP and g was zero. Further research found a positive relation between g and GFP. Thus, for instance, Schermen and Vernon [32] found positive correlations between GFP and a measure of g in two independent samples (r = 0.256 and 0.279, respectively).
The participants in the present study were mainly university students. However, range restriction issues can be discarded here because these students were recruited in Brazilian private universities in which there is no selection based on any academic merit.
In conclusion, here we have shown that childhood externalizing behaviors (assessed by teachers) predict (a) greater early adulthood socialization difficulties (as assessed by impulsivity, sensation seeking, and fearlessness); (b) worse social effectiveness (as indexed by the GFP) and (c) lower intelligence scores (as assessed by fluid and crystallized abilities). Lower levels of agreeableness drove the relationship between the GFP and externalizing behaviors because the remaining personality factors were unrelated to this variable (Figure 1B).
Furthermore, self-reported adverse biographical events occurring in childhood also predict greater early adulthood socialization difficulties and worse social effectiveness but are unrelated to adult intelligence. The predictive values observed for childhood externalizing behaviors and self-reported adverse biographical events were independent of each other. All the considered personality traits were related to these maltreatment episodes (except extraversion) (Figure 1B).
Finally, we acknowledge limitations in the present study. First, a lack of baseline values for personality. Second, due to attrition issues, the present report focused on variables showing small numbers of missing values in 2002. Third, the sample size in T2 was relatively small.
Despite these limitations, the reported findings support the probable utility of policies devoted to the promotion of social skills in the school setting. These policies are beginning to consider personality factors within their global framework. Here we have shown that childhood maltreatment and externalizing behaviors predict worse personality profiles and, therefore, intervention programs within the school context may help to prevent future socially ineffective and disrupting personalities.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2079-3200/6/3/31/s1. Table S1: Descriptive statistics and correlation matrix (including all the variables considered in the study); Table S2: EFA results for each general factor considered in the study; Table S3: Correlations among the three ADHD subscales and the remaining general scores.
Author Contributions
C.F.-M. conceived the study, performed the measurements and directed the project. S.E. developed the computations. C.F.-M., O.H. and R.C. wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. R.C. revised the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This article is based on data registered under support of the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq)—Grant N 472181/2013-0, and of the Foundation for Research Support of Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG)—Grant N PPM-00087-14.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Krueger, R.F.; Markon, K.E.; Patrick, C.J.; Benning, S.D.; Kramer, M.D. Linking antisocial behavior, substance use, and personality: An integrative quantitative model of the adult externalizing spectrum. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2007, 116, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, M.G.; Salas-Wright, C.P.; DeLisi, M.; Maynard, B.R. Violence and externalizing behavior among youth in the United States: Is there a severe 5%? Youth Violence Juv. Justice 2014, 12, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLisi, M.; Neppl, T.K.; Lohman, B.J.; Vaughn, M.G.; Shook, J.J. Early starters: Which type of criminal onset matters most for delinquent careers? J. Crim. Justice 2013, 41, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, T.E. Male antisocial behavior in adolescence and beyond. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2018, 2, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.I.; Hinshaw, S.P. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, trait impulsivity, and externalizing behavior in a longitudinal sample. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2017, 45, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazel, S.; Doll, H.; Långström, N. Mental disorders among adolescents in juvenile detention and correctional facilities: A systematic review and metaregression analysis of 25 surveys. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 47, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carragher, N.; Krueger, R.F.; Eaton, N.R.; Markon, K.E.; Keyes, K.M.; Blanco, C.; Saha, T.D.; Hasin, D.S. ADHD and the externalizing spectrum: Direct comparison of categorical, continuous, and hybrid models of liability in a nationally representative sample. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2014, 49, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huepe, D.; Roca, M.; Salas, N.; Canales-Johnson, A.; Rivera-Rei, Á.A.; Zamorano, L.; Concepción, A.; Manes, F.; Ibañez, A. Fluid intelligence and psychosocial outcome: From logical problem solving to social adaptation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, A.; Houts, R.M.; Belsky, D.W.; Harrington, H.; Hogan, S.; Ramrakha, S.; Poulton, R.; Moffitt, T.E. Childhood forecasting of a small segment of the population with large economic burden. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2016, 1, 0005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, S.E.; Friedman, N.P.; Miyake, A.; Willcutt, E.G.; Corley, R.P.; Haberstick, B.C.; Hewitt, J.K. Behavioral disinhibition: Liability for externalizing spectrum disorders and its genetic and environmental relation to response inhibition across adolescence. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2009, 118, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, M.M.; Levinson, C.A.; Lee, C.A.; Smith, T.E. Impulsivity symptoms as core to the developmental externalizing spectrum. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2017, 45, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeYoung, C.G.; Peterson, J.B.; Seguin, J.R.; Tremblay, R.E. Externalizing behavior and the high order factors of the Big Five. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2008, 117, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loehlin, J.C. How general across inventories is a general factor of personality? J. Res. Personal. 2012, 46, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, D.; te Nijenhuis, J.; Bakker, A.B. The general factor of personality: A meta-analysis of Big Five intercorrelations and a criterion-related validity study. J. Res. Personal. 2010, 44, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, D.; Dunkel, C.S.; Petrides, K.V. The General Factor of Personality (GFP) as social effectiveness: Review of the literature. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2016, 101, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, D.; Dunkel, C.S.; Beaver, K.M.; Louwen, M. The unusual suspect: The General Factor of Personality (GFP), life history theory, and delinquent behavior. Evolut. Behav. Sci. 2015, 9, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, K.E.; Krueger, R.F.; Elkins, I.; D’Accordo, C.; McGue, M.; Iacono, W.G. Personality traits predict the developmental course of externalizing: A four-wave longitudinal study spanning age 17 to age 29. J. Personal. 2017, 85, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeber, R.; Menting, B.; Lynam, D.R.; Moffitt, T.E.; Stouthamer-Loeber, M.; Stallings, R.; Farrington, D.P.; Pardini, D. Findings from the Pittsburgh Youth Study: Cognitive impulsivity and intelligence as predictors of the age–crime curve. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2012, 51, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemmler, M.; Losel, F. The stability of externalizing behavior in boys from preschool age to adolescence: A person-oriented analysis. Psychol. Test Assess. Model. 2012, 54, 195–207. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.B.; Beaver, K.M. The Interplay between Neuropsychological Deficits and Adverse Parenting in the Prediction of Adolescent Misconduct: A Partial Test of the Generalizability of Moffitt’s Theory. Crimin. Justice Behav. 2016, 43, 1505–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöwall, D.; Bohlin, G.; Rydell, A.M.; Thorell, L.B. Neuropsychological deficits in preschool as predictors of ADHD symptoms and academic achievement in late adolescence. Child Neuropsychol. 2017, 23, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Yagon, M.; Forte, D.; Avrahami, L. Executive Functions and Attachment Relationships in Children with ADHD: Links to Externalizing/Internalizing Problems, Social Skills, and Negative Mood Regulation. J. Atten. Disord. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D.; Rogosch, F.; Thibodeau, E.L. The effects of child maltreatment on early signs of antisocial behavior: Genetic moderation by tryptophan hydroxylase, serotonin transporter, and monoamine oxidase A genes. Dev. Psychopathol. 2012, 24, 907–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinzie, P.; van der Sluis, C.M.; de Haan, A.D.; Dekovic, M. Longitudinal relation between child personality and externalizing behavior. J. Personal. 2010, 78, 1301–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzay, M.L.; Joy, L.N.; Verona, E. Family Violence Pathways and Externalizing Behavior in Youth. J. Interpers. Violence 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widom, C.S.; Fisher, J.H.; Nagin, D.S.; Piquero, A.R. A Prospective Examination of Criminal Career Trajectories in Abused and Neglected Males and Females Followed Up into Middle Adulthood. J. Quant. Criminol. 2017, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikulina, V.W.; Widom, C.S. Child maltreatment and executive functioning in middle adulthood: A prospective examination. Neuropsychology 2013, 27, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, A.; Moffitt, T.E.; Arseneault, L.; Bleiberg, B.A.; Dinardo, P.B.; Gandelman, S.B.; Houts, R.; Ambler, A.; Fisher, H.L.; Poulton, R.; et al. The origins of cognitive deficits in victimized children: Implications for neuroscientists and clinicians. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 174, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogosch, F.; Cicchetti, D. Child maltreatment and emergent personality organization: Perspectives from the five-factor model. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2004, 32, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.J.; Tanis, T.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Nesci, C.; Halmi, W.; Galynker, I. Are there differential relationships between different types of childhood maltreatment and different types of adult personality pathology? Psychiatry Res. 2013, 215, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Linden, D.; Pekaar, K.A.; Bakker, A.B.; Schermer, J.A.; Vernon, P.A.; Dunkel, C.S.; Petrides, K.V. Overlap between the general factor of personality and emotional intelligence: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2017, 143, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schermer, J.A.; Vernon, P.A. The correlation between general intelligence (g), a general factor of personality (GFP), and social desirability. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2010, 48, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, O.; Escorial, S.; Colom, R. Escala de Dificultades de Socialización de Cantoblanco (SOC): Manual [Cantoblanco Socialization Difficulties Scale: Manual]; TEA Ediciones: Madrid, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lykken, D.T. The Antisocial Personalities; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, J.A. The Psychology of Fear and Stress; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M. Sensation Seeking: Beyond the Optimal Level of Arousal; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero, O.; Colom, R. Es verosímil la teoría de la delincuencia de David Lykken? [Is David Lykken’s theory of crime likely?]. Psicothema 2006, 18, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Negredo, L.; Melis, F.; Herrero, O. Psychopathy and suicidal behaviour in a sample of mentally disordered offenders. Revista Española de Sanidad Penitenciaria 2013, 15, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benczik, E.B.P. TDAH—Escala de Transtorno de Deficit de Atencao e Hiperatividade; Editora Casa do Psicologo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, C.A.; Flores-Mendoza, C. Transtorno do Déficit de Atenção/Hiperatividade: O que nos informa a investigação dimensional? [Attention Déficit Disorder/Hyperactivity: What dimensional research can inform?]. Estudos de Psicologia 2010, 14, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berstein, D.P.; Stein, J.A.; Newcomb, M.D.; Walker, E.; Pogge, D.; Ahkuvalia, T.; Stokes, J.; Handelsman, L.; Medrano, M.; Desmond, D.; et al. Development and validation of a brief screening version of the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire. Child Abuse Neglig. 2003, 27, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi-Oliveira, R.; Stein, L.M.; Pessi, J.C. Traducao e Validação de conteúdo da versão em português do Chilhood Trauma Questionnaire. Revista de Saude Publica 2006, 40, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodski, S.; Zanon, C.; Hutz, C.S. Adaptação e validação do Questionário sobre Traumas na Infância (QUESI) para uma amostra não clínica. Avaliação Psicológica 2010, 9, 495–497. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, B.M.C. MAOS-VNTR Externalizing Behaviors in Childhood and Personality Traits in a Male Sample. Unpublished Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. Escala de Inteligencia Weschler para Adultos; Editora Casa do Psicologo: São Paulo, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, J.; Raven, J.C.; Court, J.H. Raven Manual: Section 3, Standard Progressive Matrices, Including the Parallel and Plus Versions, 2000th ed.; Oxford Psychologists Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.; McCrae, R. Inventario de Personalidade NEO-PI-R; Vetor Editora: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Seva, U.; Ferrando, P.J. FACTOR 9.2 A Comprehensive Program for Fitting Exploratory and Semiconfirmatory Factor Analysis and IRT Models. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 2013, 37, 497–498. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrando, P.J.; Lorenzo-Seva, U. Assessing the quality and appropriateness of factor solutions and factor score estimates in exploratory item factor analysis. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, V.A.; Nomura, Y.; Newcorn, J.H.; Halperin, J.M. Childhood maltreatment and conduct disorder: Independent predictors of criminal outcomes in ADHD youth. Child Abuse Negl. 2012, 36, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, L.; Colletti, C.; Rakow, A.; Jones, D.; Forehand, R. Parenting and Child Externalizing Behaviors: Are the Associations Specific or Diffuse? Aggress. Violent Behav. 2008, 13, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luke, N.; Banerjee, R. Differentiated associations between childhood maltreatment experiences and social understanding: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Dev. Rev. 2013, 33, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.M.; Harris, T.R.; Caetano, R. Reliability of self-reported childhood physical abuse by adults and factors predictive of inconsistent reporting. Violence Vict. 2009, 24, 653–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moilanen, K.L.; Shaw, D.S.; Maxwell, K.L. Developmental cascades: Externalizing, internalizing, and academic competence from middle childhood to early adolescence. Dev. Psychopathol. 2010, 22, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogg, T.; Finn, P.R. A Self-Regulatory Model of Behavioral Disinhibition in Late Adolescence: Integrating Personality Traits, Externalizing Psychopathology, and Cognitive Capacity. J. Personal. 2010, 78, 441–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinsonneault, M.; Parent, S.; Castellanos-Ryan, N.; Séguin, J.R. Low intelligence and poor executive function as vulnerabilities to externalizing behavior. In The Oxford Handbook of Externalizing Spectrum Disorders; Beauchaine, T.P., Hinshaw, S.P., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 375–400. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffee, S.R.; Maikovich-Fong, A.K. Effects of chronic maltreatment and maltreatment timing on children’s behavior and cognitive abilities. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2011, 52, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, P.L.; Heggestad, E.D. Intelligence, Personality, and Interest: Evidence for Overlapping Traits. Psychol. Bull. 1997, 121, 219–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, S.A.; Hinton, D.P.; von Stumm, S.; Bellman-Jeffreys, J. Personality and Intelligence: Examining the Associations of Investment-Related Personality Traits with General and Specific Intelligence. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom, R.; Escorial, S.; Shih, P.C.; Privado, J. Fluid intelligence, memory span, and temperament difficulties predict academic performance of young adolescents. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2007, 42, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loehlin, J.C.; Bartels, M.; Boomsma, D.I.; Bratko, D.; Martin, N.G.; Nichols, R.C.; Wright, M.J. Is there a genetic correlation between general factors of intelligence and personality? Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2015, 18, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).