Log File Times as Indicators of Structured Figural Matrix Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
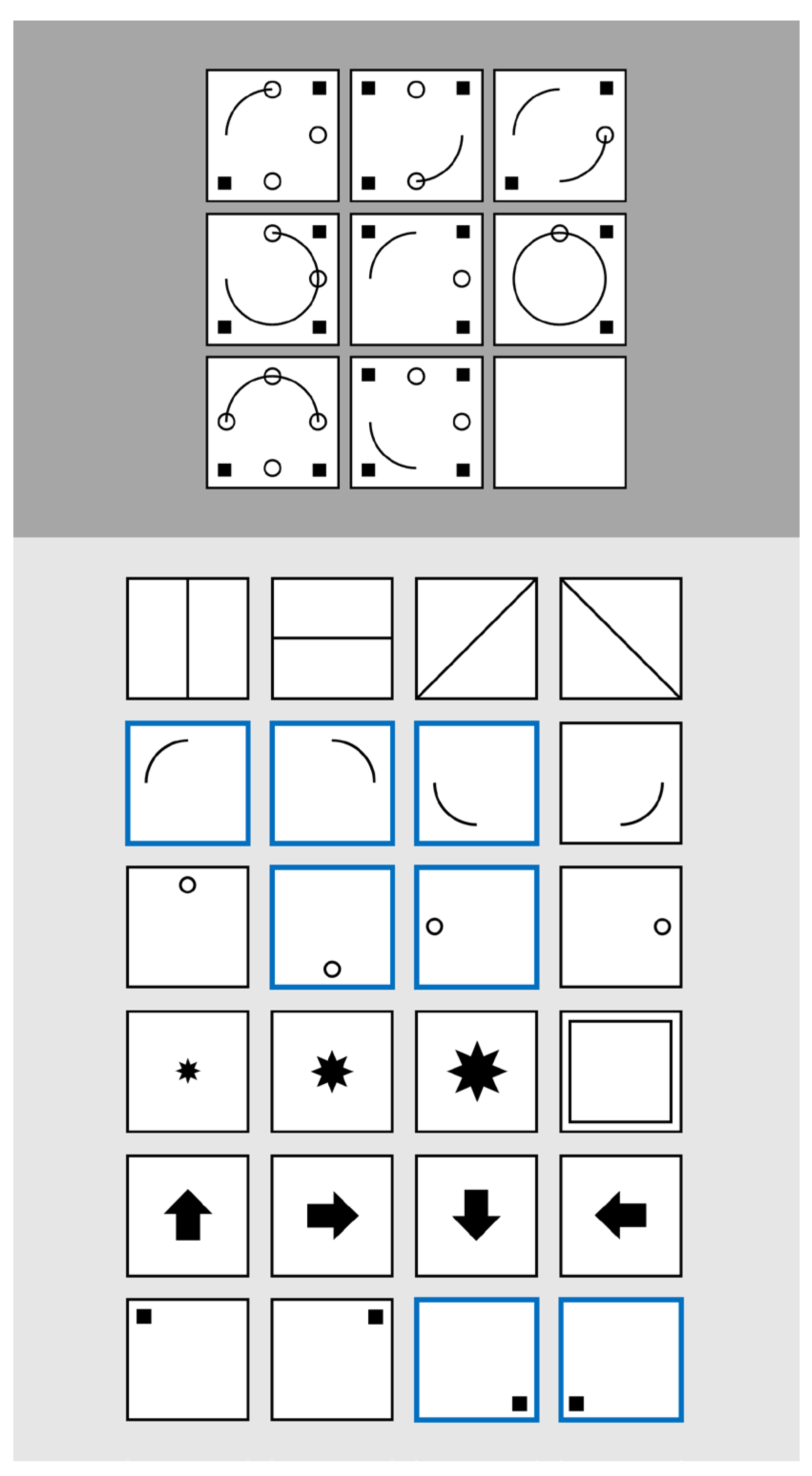
1.1. Figural Matrices in Intelligence Diagnostics
1.2. Temporal Characteristics of Matrices Processing
1.3. Structuredness in Matrix Processing
1.4. Confluence of Temporal Characteristics and Structuredness in Matrix Processing
1.5. Research Questions and Hypotheses
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample and Materials
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Replication of the ToT Effect
3.3. Clustering
3.4. Accelerating Effect of the Log File Times
3.5. Interplay of the Interrule and Intrarule Times
3.6. Importance of the Log File Times for Test Performance
3.7. External Validation of the Interrule Times
3.8. Post-Hoc Analyses of Potential Task Misunderstanding and Motivational Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary and Contextualization of the Results
4.2. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IAP | Incomplete Attempt Propensity |
| LFTs | Log File Times |
| RAPM | Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices |
| RtD | Response to Difficulty |
| ToT | Time on Task |
References
- Becker, Nicolas, and Frank M. Spinath. 2014. Design a Matrix Test. Ein Distraktorfreier Matrizentest zur Erfassung der Allgemeinen Intelligenz (DESIGMA). Göttingen: Hogrefe. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, Nicolas, Florian Schmitz, Anja S. Göritz, and Frank M. Spinath. 2016. Sometimes more is better, and sometimes less is better: Task complexity moderates the response time accuracy correlation. Journal of Intelligence 4: 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, Stefan. 2023. lm.beta: Add Standardized Regression Coefficients to Linear-Model-Objects (R Package Version 1.7-2). Vienna: Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lm.beta (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Breuer, Sonja, Thomas Scherndl, and Tuulia M. Ortner. 2020. Effects of Response Format on Psychometric Properties and Fairness of a Matrices Test: Multiple Choice vs. Free Response. Frontiers in Education 5: 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, Patricia A., Marcel A. Just, and Peter Shell. 1990. What one intelligence test measures: A theoretical account of the processing in the Raven Progressive Matrices Test. Psychological Review 97: 404–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Guanyu, Yan Liu, and Yue Mao. 2024. Understanding the log file data from educational and psychological computer-based testing: A scoping review protocol. PLoS ONE 19: e0304109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheyette, Samuel J., and Steven T. Piantadosi. 2024. Response to Difficulty Drives Variation in IQ Test Performance. Open Mind 8: 265–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formann, Anton K., Karin Waldherr, and Karl Piswanger. 2011. Wiener Matrizen-Test 2: Ein Rasch-Skaldierter Sprachfreier Kurztest zu Erfassung der Intelligenz (WMT-2). Göttingen: Beltz Test. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, John, and Sanford Weisberg. 2018. An R Companion to Applied Regression. Thousand Oaks: Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Goldhammer, Frank, Johannes Naumann, and Samuel Greiff. 2015. More is not Always Better: The Relation between Item Response and Item Response Time in Raven’s Matrices. Journal of Intelligence 3: 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhammer, Frank, Johannes Naumann, Annette Stelter, Krisztina Tóth, Heiko Rölke, and Eckhard Klieme. 2014. The time on task effect in reading and problem solving is moderated by task difficulty and skill. Insights from a computer-based large-scale assessment. The Journal of Educational Psychology 106: 608–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonthier, Corentin. 2023. Should Intelligence Tests Be Speeded or Unspeeded? A Brief Review of the Effects of Time Pressure on Response Processes and an Experimental Study with Raven’s Matrices. Journal of Intelligence 11: 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, Taylor R., Alexander A. Petrov, and Per B. Sederberg. 2011. A novel method for analyzing sequential eye movements reveals strategic influence on Raven’s Advanced Progressive Matrices. Journal of Vision 11: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassambara, Alboukadel, and Fabian Mundt. 2020. factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses (R Package Version 1.0.7). Vienna: Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Koch, Marco, Frank M. Spinath, Samuel Greiff, and Nicolas Becker. 2022. Development and Validation of the Open Matrices Item Bank. Journal of Intelligence 10: 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, Florian, Hubert D. Zimmer, Samuel Greiff, Frank M. Spinath, and Nicolas Becker. 2019. Why are difficult figural matrices hard to solve? The role of selective encoding and working memory capacity. Intelligence 72: 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, Raimund J., Marco Koch, Julie Levacher, and Florian Schmitz. 2023. Testing Replicability and Generalizability of the Time on Task Effect. Journal of Intelligence 11: 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, Alexandra, Per B. Brockhoff, and Rune H. B. Christensen. 2017. lmerTest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. Journal of Statistical Software 82: 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loesche, Patrick, Jennifer Wiley, and Marcus Hasselhorn. 2015. How knowing the rules affects solving the Raven Advanced Progressive Matrices Test. Intelligence 48: 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshalek, Brachia, David F. Lohman, and Richard E. Snow. 1983. The complexity continuum in the radex and hierarchical models of intelligence. Intelligence 7: 107–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchum, Ainsley L., and Colleen M. Kelley. 2010. Solve the problem first: Constructive solution strategies can influence the accuracy of retrospective confidence judgments. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 36: 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolay, Björn, Florian Krieger, Jörg-Tobias Kuhn, Arthur C. Graesser, Dirk Ifenthaler, Ryan Baker, and Samuel Greiff. 2023. Unsuccessful and successful complex problem solvers—A log file analysis of complex problem solving strategies across multiple tasks. Intelligence 101: 101793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørskov, Per T., Anne Norup, Erin L. Beatty, and Susanne M. Jaeggi. 2021. Exploring Individual Differences as Predictors of Performance Change During Dual-N-Back Training. Journal of Cognitive Enhancement 5: 480–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallentin, Vanessa S., Daniel Danner, and Jan Rummel. 2023. Construction and Validation of the HeiQ: An Operation-Oriented Figural Matrices Test. Journal of Intelligence 11: 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskernik, Bernhard. 2013. Free Response Matrices (FRM). Mödling: Schuhfried. [Google Scholar]
- Preuß, Julian, and Franzis Preckel. 2025. Using Cognitive Diagnostic Models to Evaluate the Two-Process Theory of Matrix Reasoning. Journal of Intelligence 13: 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, John C., J. H. Court, and Jean Raven. 1989. Standard Progressive Matrices. Camberwell: Australian Council for Educational Research Limited. [Google Scholar]
- Raven, John C., Jean Raven, and J. H. Court. 1988. Advanced Progressive Matrices, Set II. Oxford: Oxford Psychological Press. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. 2024. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Revelle, William. 2022. psych: Procedures for Personality and Psychological Research. Evanston: Northwestern University. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=psych (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Robertson, Gary J. 2010. Raven’s Progressive Matrices. In The Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology. Edited by Irving B. Weiner and W. Edward Craighead. New York: Wiley, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Rosseel, Yves. 2012. lavaan: An R Package for Structural Equation Modeling. Journal of Statistical Software 48: 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, Walter, and Richard M. Shiffrin. 1977. Controlled and Automatic Human Information Processing: I. Detection, Search, and Attention. Psychological Review 84: 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selker, Ravi, Jonathan Love, Damian Dropmann, Victor Moreno, and Maurizio Agosti. 2022. jmv: The ‘jamovi’ Analyses (R Package Version 2.3.4); Vienna: Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=jmv (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Torchiano, Marco. 2020. effsize: Efficient Effect Size Computation (R Package Version 0.8.1). Vienna: Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=effsize (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Venables, William N., and Brian D. Ripley. 2002. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed. New York: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, Dominik, Florian Krieger, Frank M. Spinath, Samuel Greiff, Johanna Hissbach, and Nicolas Becker. 2023. A Log File Analysis on the Validity of Partial Solutions in Figural Matrices Tests. Journal of Intelligence 11: 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, Hadley. 2016. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. New York: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, Hadley. 2019. stringr: Simple, Consistent Wrappers for Common String Operations (R Package Version 1.4.0). Vienna: Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=stringr (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Wickham, Hadley, Romain François, Lionel Henry, Kirill Müller, Davis Vaughan, Posit Software, and PBC. 2023. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation (R Package Version 1.1.4). Vienna: Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Wiemers, Elizabeth A., Thomas S. Redick, and Alexandra B. Morrison. 2018. The Influence of Individual Differences in Cognitive Ability on Working Memory Training Gains. Journal of Cognitive Enhancement 3: 174–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Item | Rules | P | ri(t-i) | MToT | Monset | Minter | Mintra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | .54 | .31 | 43.14 | 21.76 | 12.51 | 8.33 |
| 2 | 2 | .57 | .44 | 46.78 | 23.64 | 9.76 | 2.91 |
| 3 | 2 | .53 | .51 | 50.19 | 28.19 | 14.95 | 1.72 |
| 4 | 2 | .16 | .46 | 56.69 | 32.67 | 14.23 | 1.84 |
| 5 | 2 | .33 | .64 | 53.72 | 29.75 | 17.77 | 1.33 |
| 6 | 2 | .30 | .41 | 58.18 | 25.62 | 24.71 | 2.47 |
| 7 | 2 | .39 | .49 | 53.44 | 24.95 | 20.20 | 4.06 |
| 8 | 2 | .51 | .48 | 47.23 | 24.45 | 18.22 | 1.33 |
| 9 | 2 | .13 | .49 | 52.77 | 22.96 | 24.24 | 2.66 |
| 10 | 2 | .15 | .51 | 54.15 | 33.53 | 11.96 | 1.87 |
| 11 | 2 | .59 | .63 | 39.46 | 17.28 | 14.92 | 1.43 |
| 12 | 3 | .32 | .52 | 50.60 | 17.82 | 14.36 | 1.81 |
| 13 | 3 | .16 | .58 | 61.33 | 31.18 | 15.42 | 2.03 |
| 14 | 3 | .46 | .59 | 53.83 | 17.24 | 15.26 | 0.77 |
| 15 | 3 | .43 | .64 | 50.45 | 15.19 | 13.71 | 0.86 |
| 16 | 3 | .35 | .69 | 50.24 | 13.76 | 16.69 | 1.52 |
| 17 | 3 | .39 | .79 | 48.30 | 12.61 | 15.90 | 1.36 |
| 18 | 3 | .61 | .63 | 47.01 | 18.16 | 10.83 | 1.18 |
| 19 | 4 | .21 | .49 | 55.03 | 14.07 | 13.20 | 1.74 |
| 20 | 4 | .30 | .60 | 53.01 | 11.22 | 13.38 | 2.54 |
| 21 | 4 | .26 | .67 | 55.05 | 12.25 | 14.08 | 1.46 |
| 22 | 5 | .21 | .53 | 57.86 | 12.87 | 13.35 | 1.42 |
| Mean | 2.73 | .36 | .55 | 51.79 | 20.96 | 14.30 | 1.61 |
| Cluster | n | Mscore (SD) | Monset (SD) | Minter (SD) | Mintra (SD) | MToT (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 87 | 2.34 (1.63) | 22.82 (9.44) | 10.21 (4.38) | 1.51 (0.64) | 46.37 (15.95) |
| 2 | 111 | 12.24 (4.39) | 19.50 (6.70) | 17.50 (4.98) | 1.69 (0.76) | 56.04 (11.21) |
| Measure | ΔM | t | pΔM | d | r | pr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Cluster (n = 111) | ||||||
| ToT | −2.72 | – | – | – | −.13 | .178 |
| Onset | 13.71 | 18.87 | <.001 | 1.66 | −.14 | .138 |
| Inter | 3.06 | 3.85 | <.001 | 0.41 | .31 | <.001 |
| Intra | 0.81 | 3.73 | <.001 | 0.47 | −.01 | .934 |
| Unstructured Cluster (n = 87) | ||||||
| ToT | 2.23 | – | – | – | .04 | .682 |
| Onset | 12.44 | 11.64 | <.001 | 1.17 | .18 | .097 |
| Inter | 1.29 | 1.65 | .051 | 0.20 | .06 | .590 |
| Intra | 0.90 | 3.58 | <.001 | 0.49 | .02 | .835 |
| Statistics | ToT Only | ToT and LFT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ToT | Total | ToT | Onset | Inter | Intra | Total | |
| β | −0.22 | – | 0.35 | −0.53 | −0.63 | −0.41 | – |
| t or F | −7.11 | 50.58 | 2.29 | −5.57 | −4.95 | −5.65 | 33.73 |
| df | 109 | 1, 109 | 106 | 106 | 106 | 106 | 4, 106 |
| p | <.001 | <.001 | .024 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 | <.001 |
| R2 | 31.70% | 31.70% | 2.18% | 12.87% | 10.19% | 13.25% | 56.00% |
| ΔR2 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 24.30% |
| Predictor | ToT | Interrule Times | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | p | b | p | |
| Global IAP | 14.84 | .008 | 1.52 | .615 |
| Current IAP | −0.37 | .627 | 0.08 | .887 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weber, D.; Koch, M.; Spinath, F.M.; Krieger, F.; Becker, N. Log File Times as Indicators of Structured Figural Matrix Processing. J. Intell. 2025, 13, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13060063
Weber D, Koch M, Spinath FM, Krieger F, Becker N. Log File Times as Indicators of Structured Figural Matrix Processing. Journal of Intelligence. 2025; 13(6):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13060063
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeber, Dominik, Marco Koch, Frank M. Spinath, Florian Krieger, and Nicolas Becker. 2025. "Log File Times as Indicators of Structured Figural Matrix Processing" Journal of Intelligence 13, no. 6: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13060063
APA StyleWeber, D., Koch, M., Spinath, F. M., Krieger, F., & Becker, N. (2025). Log File Times as Indicators of Structured Figural Matrix Processing. Journal of Intelligence, 13(6), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence13060063





