Application of a Deep Neural Network to Phase Retrieval in Inverse Medium Scattering Problems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
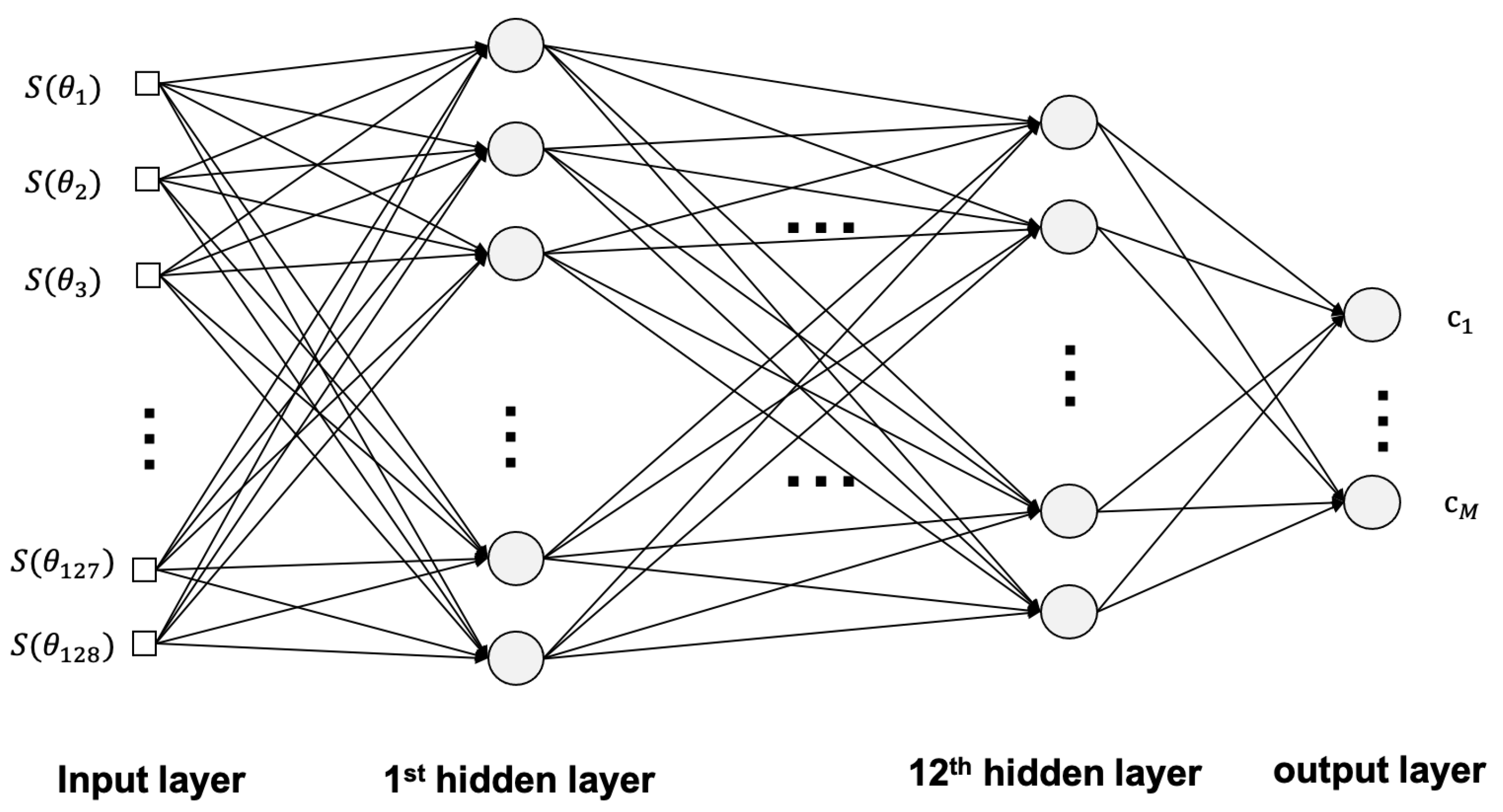
3. Deep Neural Network for the Inverse Problem
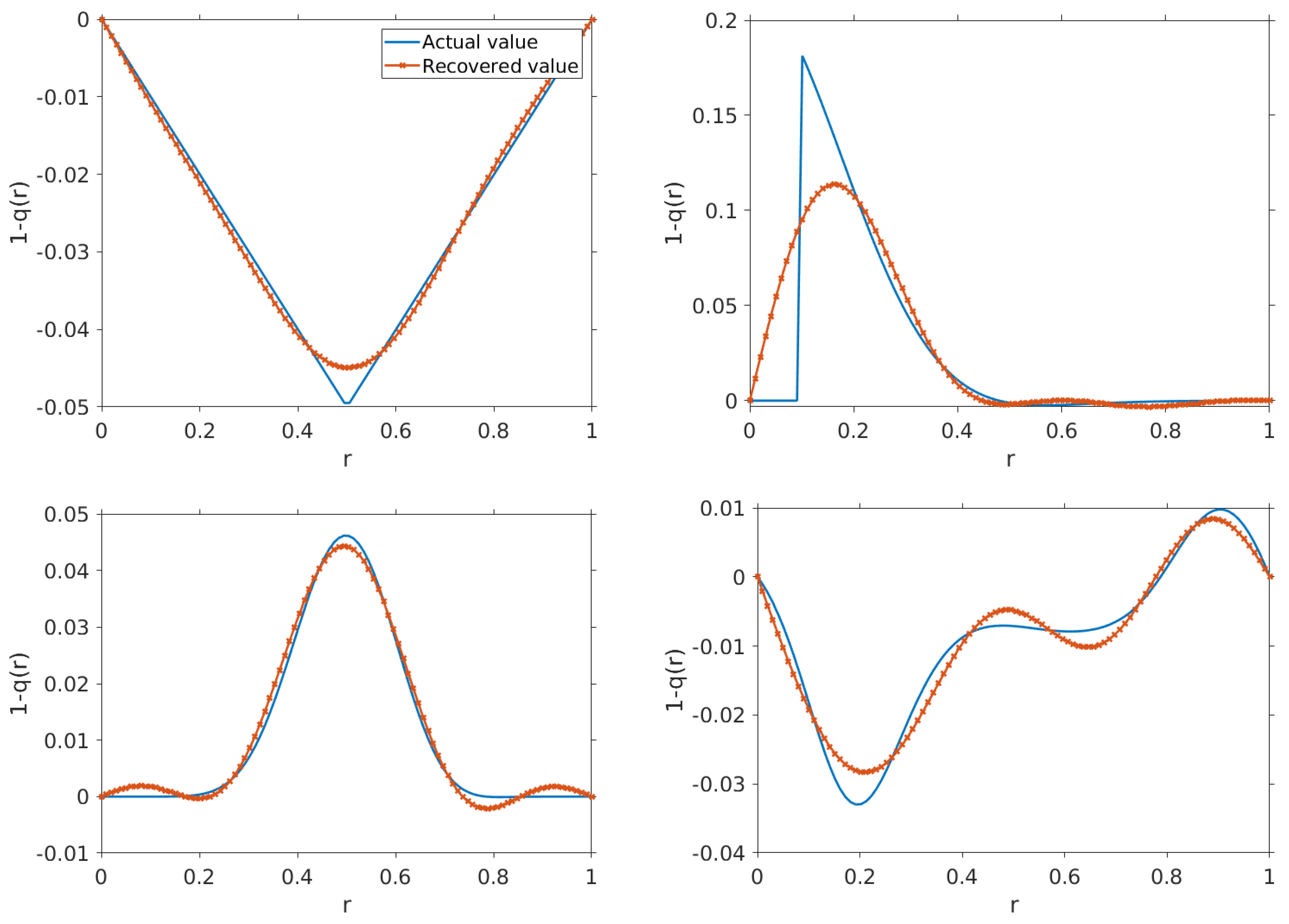
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klibanov, M.V.; Sacks, P.E.; Tikhonravov, A.V. The phase retrieval problem. Inverse Probl. 1995, 11, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, N. Phase Retrieval and Zero Crossings: Mathematical Methods in Image Reconstruction; Mathematics and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bendory, T.; Beinert, R.; Eldar, Y.C. Fourier Phase Retrieval: Uniqueness and Algorithms; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 55–91. [Google Scholar]
- Beinert, R.; Plonka, G. One-Dimensional Discrete-Time Phase Retrieval; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 603–627. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, A. An Introduction to the Mathematical Theory of Inverse Problems; Applied Mathematical Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Colton, D.; Kress, R. Inverse Acoustic and Electromagnetic Scattering Theory; Applied Mathematical Sciences; Springer: Berlin/ Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cakoni, F.; Colton, D. A Qualitative Approach to Inverse Scattering Theory; Applied Mathematical Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka, T.; Wall, D.J.N.; Harada, H.; Tanaka, M. Reconstruction algorithm of the refractive index of a cylindrical object from the intensity measurements of the total field. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 1997, 14, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanyshyn, O.; Kress, R. Inverse scattering for surface impedance from phase-less far field data. J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 3443–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Li, P.; Lv, J. Numerical solution of an inverse diffraction grating problem from phaseless data. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2013, 30, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J. Inverse obstacle backscattering problems with phaseless data. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 2016, 27, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-M. Shape reconstructions from phaseless data. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2016, 71, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammari, H.; Chow, Y.T.; Zou, J. Phased and phaseless domain reconstructions in the inverse scattering problem via scattering coefficients. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2016, 76, 1000–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klibanov, M.V. Phaseless inverse scattering problems in three dimensions. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2014, 74, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klibanov, M.V. A phaseless inverse scattering problem for the 3-d helmholtz equation. Inverse Probl. Imaging 2017, 11, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, V.G.; Yamamoto, M. Phaseless inverse problems with interference waves. J. Inverse Ill-Posed Probl. 2018, 26, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Guo, Y. Uniqueness results on phaseless inverse acoustic scattering with a reference ball. Inverse Probl. 2018, 34, 085002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H. Uniqueness in inverse acoustic and electromagnetic scattering with phaseless near-field data at a fixed frequency. Inverse Probl. Imaging 2020, 14, 489–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, M.T.; Jin, K.H.; Unser, M. Convolutional neural networks for inverse problems in imaging: A review. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.; Iliadis, M.; Molina, R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Using deep neural networks for inverse problems in imaging: Beyond analytical methods. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, A.; Marcantonio, D.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Salucci, M. Dnns as applied to electromagnetics, antennas, and propagation—A review. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, M.; Rocca, P. A Review of Deep Learning Approaches for Inverse Scattering Problems. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Pier 2020, 167, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosanio, M.; Franceschini, S.; Baselice, F.; Pascazio, V. Machine learning for microwave imaging. In Proceedings of the 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Işil, Ç.; Oktem, F.S.; Koç, A. Deep iterative reconstruction for phase retrieval. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 5422–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizaki, Y.; Horisaki, R.; Kitaguchi, K.; Saito, M.; Tanida, J. Analysis of non-iterative phase retrieval based on machine learning. Opt. Rev. 2020, 27, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wu, L.; Ye, X.; Chen, X. Deep learning-based inversion methods for solvin g inverse scattering problems with phaseless data. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 7457–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables; Ninth Dover Printing, Tenth Gpo Printing Edition; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, E.G. Fourier Acoustics—Sound Radiation and Nearfield Acoustical Holography; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Arhin, E. Determining radially symmetric potential from near-field scattering data. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 62, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K. A uniform lp estimate of bessel functions and distributions supported on sn-1. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 1997, 125, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.; Gibson, A. Deep Learning: A Practitioner’s Approach; O’Reilly: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Neural Networks and Deep Learning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, G.; Chow, S.-N.; Li, P.; Zhou, H. Numerical solution of an inverse medium scattering problem with a stochastic source. Inverse Probl. 2010, 26, 074014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Kim, K.C.; Jargal, A.; Lee, K.; Harrach, B. A learning-based method for solving ill-posed nonlinear inverse problems: A simulation study of lung eit. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2019, 12, 1275–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| M | ⋯ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2.274975 | 2.456498 | 2.500061 | 2.507212 | 2.508060 | 2.508137 | ⋯ | 2.508143 |
| 4 | 2.272488 | 2.455003 | 2.498695 | 2.505858 | 2.506708 | 2.506785 | ⋯ | 2.506790 |
| 6 | 2.270497 | 2.453404 | 2.497168 | 2.504340 | 2.505191 | 2.505267 | ⋯ | 2.505273 |
| 8 | 2.272039 | 2.454842 | 2.498589 | 2.505758 | 2.506608 | 2.506685 | ⋯ | 2.506690 |
| −0.065950 | −0.055493 | |||||||
| Recovered | −0.065947 | −0.056183 | 0.000388 | −0.000543 | 0.001080 | |||
| 0.053806 | 0.016251 | |||||||
| Recovered | 0.054025 | 0.015160 | 0.000185 | −0.001412 | −0.000185 | |||
| 0.055903 | 0.040100 | −0.042993 | 0.109659 | |||||
| Recovered | 0.056550 | 0.039870 | −0.043363 | 0.107659 | −0.000127 | |||
| −0.027582 | −0.093878 | −0.006221 | −0.001151 | |||||
| Recovered | −0.027636 | −0.094518 | −0.006339 | −0.001007 | 0.000606 | |||
| 0.026614 | −0.020468 | 0.000594 | −0.025930 | 0.103335 | −0.025599 | |||
| Recovered | 0.024475 | −0.025661 | −0.001172 | -0.027904 | 0.114871 | |||
| −0.031879 | −0.074713 | 0.012923 | 0.009334 | −0.056347 | 0.015316 | |||
| Recovered | −0.031876 | −0.075086 | 0.012429 | 0.009800 | −0.065774 | |||
| 0.001487 | −0.004899 | −0.047159 | −0.008064 | −0.056774 | 0.073704 | 0.048645 | −0.073397 | |
| Recovered | 0.000079 | −0.006535 | −0.046007 | −0.011743 | −0.058407 | |||
| −0.009015 | 0.098806 | −0.030338 | 0.008131 | 0.062194 | −0.049663 | −0.010376 | 0.021190 | |
| Recovered | −0.009203 | 0.095855 | −0.027988 | 0.006213 | 0.075342 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, S.; Shin, J. Application of a Deep Neural Network to Phase Retrieval in Inverse Medium Scattering Problems. Computation 2021, 9, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation9050056
Lim S, Shin J. Application of a Deep Neural Network to Phase Retrieval in Inverse Medium Scattering Problems. Computation. 2021; 9(5):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation9050056
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Soojong, and Jaemin Shin. 2021. "Application of a Deep Neural Network to Phase Retrieval in Inverse Medium Scattering Problems" Computation 9, no. 5: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation9050056
APA StyleLim, S., & Shin, J. (2021). Application of a Deep Neural Network to Phase Retrieval in Inverse Medium Scattering Problems. Computation, 9(5), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation9050056





