Kinetic Simulations of Compressible Non-Ideal Fluids: From Supercritical Flows to Phase-Change and Exotic Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
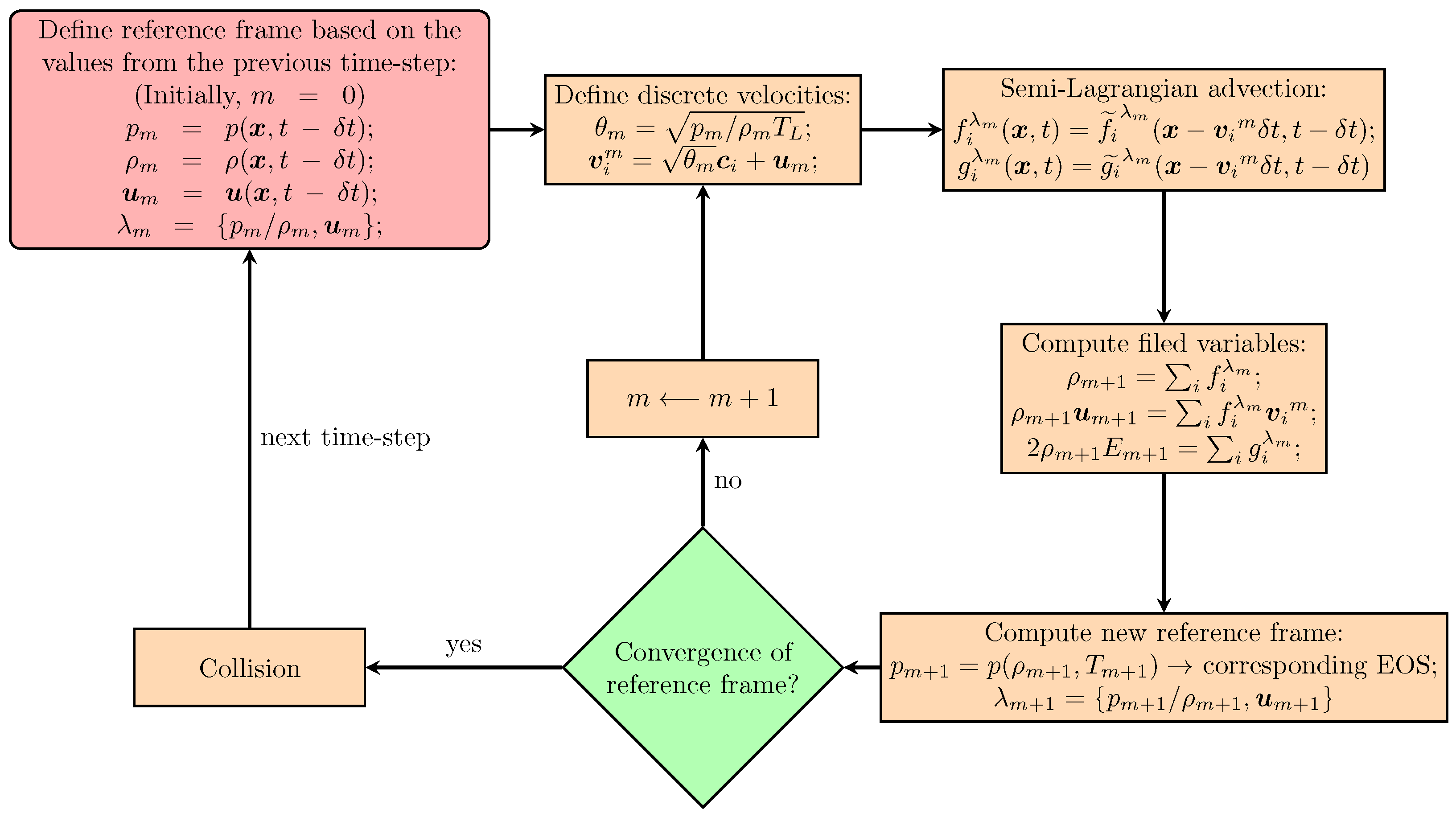
2. Methodology
2.1. Kinetic Equations
2.2. Correction of the Energy Equation
2.3. Surface Tension
3. Chapman–Enskog Analysis
3.1. Excluding the Forcing Term
3.2. Including the Forcing Term
4. Results and Discussion
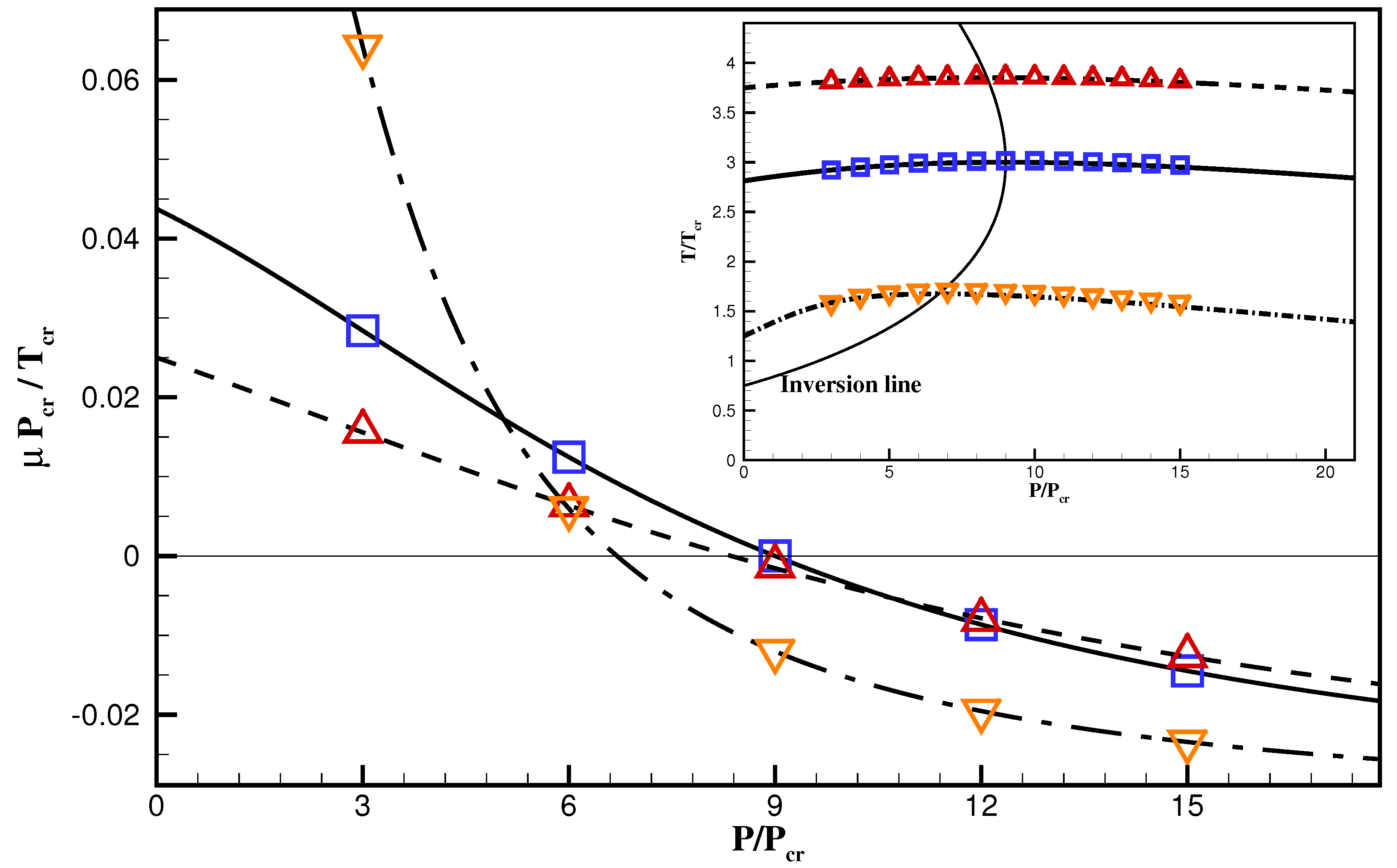
- As a first test of basic thermodynamic consistency for non-ideal fluids, we simulate the inversion line of a vdW fluid, which is one of the classic thermodynamical concepts of non-ideal fluids. To capture this phenomenon it is crucial that the model recovers the correct energy equation and can operate in a wide range of pressures and temperatures in the super-critical part of the phase diagram;
- Phase-change is the next fundamental process that is tested with our model. It is important to remind that since the full energy equation is recovered by our kinetic equations, phase-change emerges naturally in the proposed scheme and no additional ad-hoc phase-change model is required. In addition, we probe fast dynamics with temperatures near the critical point, where phase-change happens on short time scales;
- As a final test case we probe both thermodynamic consistency as well as Galilean invariance in supersonic flows. In particular, we study the behavior of a perturbed shock-front in both an ideal gas as well as a vdW fluid at Mach number Ma = 3. In agreement with theory, our model shows to capture all regimes, including the exotic behaviors of a real fluid.
4.1. Inversion Line
4.2. Phase Change: One-Dimensional Stefan Problem
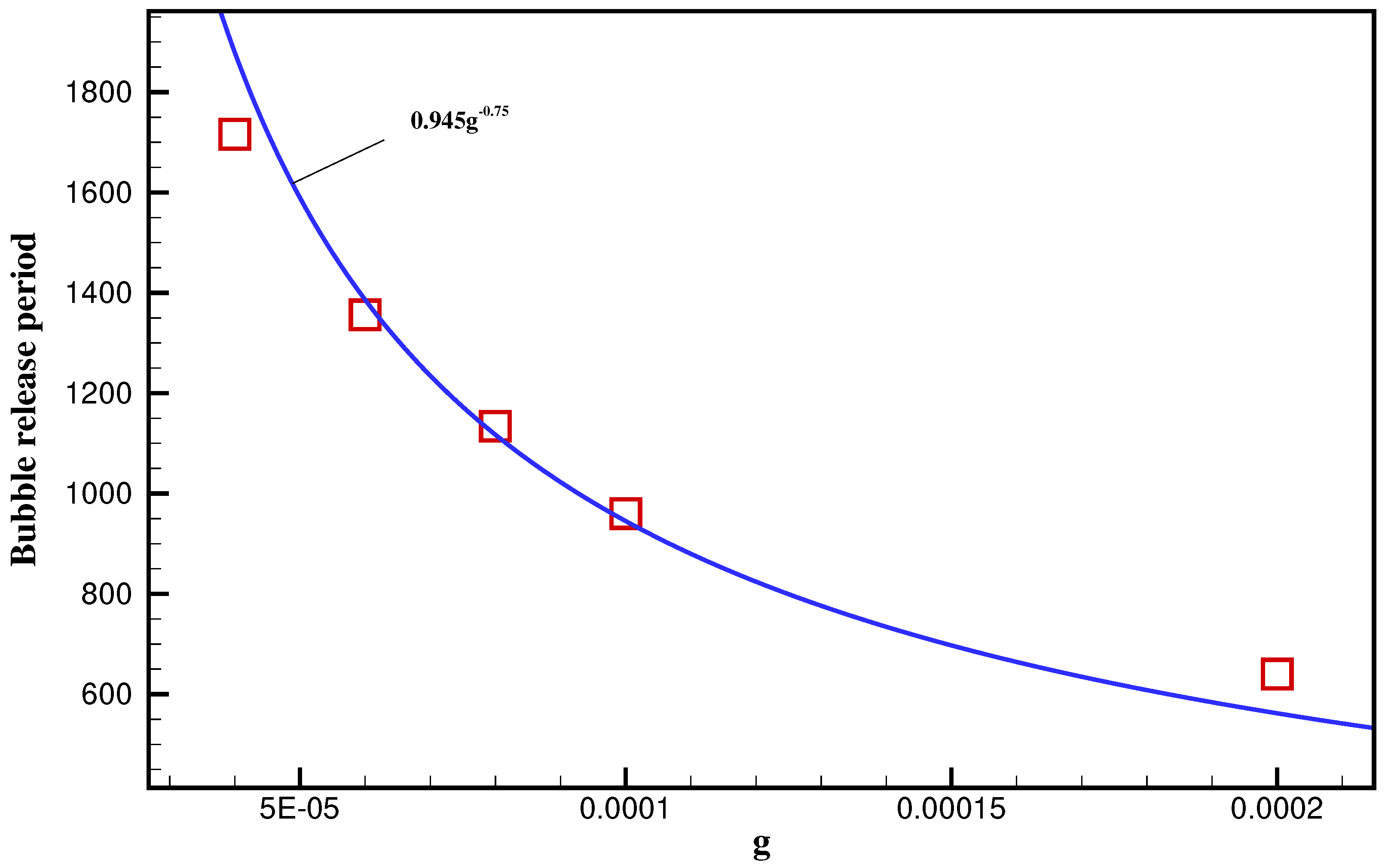
4.3. Phase Change: Nucleate Boiling
4.4. Phase Change: Single-Mode Film Boiling
4.5. On the Stability of Shock Waves
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LBM | Lattice Boltzmann method |
| EOS | Equation of state |
| PonD | Particles on Demand |
References
- Atif, M.; Kolluru, P.K.; Thantanapally, C.; Ansumali, S. Essentially Entropic Lattice Boltzmann Model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 240602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorschner, B.; Bösch, F.; Chikatamarla, S.S.; Boulouchos, K.; Karlin, I.V. Entropic multi-relaxation time lattice Boltzmann model for complex flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 801, 623–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert, C.; Harting, J. Roughness Induced Boundary Slip in Microchannel Flows. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 176001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyväluoma, J.; Harting, J. Slip Flow Over Structured Surfaces with Entrapped Microbubbles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 246001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbragaglia, M.; Benzi, R.; Biferale, L.; Succi, S.; Toschi, F. Surface Roughness-Hydrophobicity Coupling in Microchannel and Nanochannel Flows. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 204503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biferale, L.; Perlekar, P.; Sbragaglia, M.; Toschi, F. Convection in Multiphase Fluid Flows Using Lattice Boltzmann Methods. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 104502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, R.; Chibbaro, S.; Succi, S. Mesoscopic Lattice Boltzmann Modeling of Flowing Soft Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 026002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloomi, M.A.; Chikatamarla, S.S.; Karlin, I.V. Entropic Lattice Boltzmann Method for Multiphase Flows. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 174502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succi, S. The Lattice Boltzmann Equation: For Complex States of Flowing Matter; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, T.; Kusumaatmaja, H.; Kuzmin, A.; Shardt, O.; Silva, G.; Viggen, E.M. The lattice Boltzmann method. Springer Int. Publ. 2017, 10, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- Prasianakis, N.I.; Karlin, I.V. Lattice Boltzmann method for simulation of compressible flows on standard lattices. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 016704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frapolli, N.; Chikatamarla, S.S.; Karlin, I.V. Entropic lattice Boltzmann model for compressible flows. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 92, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorschner, B.; Bösch, F.; Karlin, I.V. Particles on Demand for Kinetic Theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 130602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Boivin, P.; Jacob, J.; Sagaut, P. Hybrid recursive regularized thermal lattice Boltzmann model for high subsonic compressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 394, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, D.; Krämer, A.; Reith, D.; Foysi, H. Semi-Lagrangian lattice Boltzmann method for compressible flows. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 101, 053306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.W.; Montgomery, D.C. Some numerical studies of exotic shock wave behavior. Phys. Fluids 1999, 11, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, N.; Mentrelli, A.; Ruggeri, T.; Sugiyama, M. Admissible shock waves and shock-induced phase transitions in a van der Waals fluid. Phys. Fluids 2011, 23, 086101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardone, A.; Vigevano, L. Roe linearization for the van der Waals gas. J. Comput. Phys. 2002, 175, 50–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfirescu, C.; Guardone, A.; Colonna, P. Admissibility region for rarefaction shock waves in dense gases. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 599, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.W.; Montgomery, D.C. The D’yakov-Kontorovich instability of shock waves in real gases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.W. Instability of isolated planar shock waves. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 094102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.R.; Osborn, W.; Yeomans, J. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of nonideal fluids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdych, D.; Rovas, D.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Buckius, R. An improved hydrodynamics formulation for multiphase flow lattice-Boltzmann models. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 1998, 9, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zheng, C.; Shi, B. Discrete lattice effects on the forcing term in the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 046308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Krafczyk, M.; Lu, X. Forcing term in single-phase and Shan-Chen-type multiphase lattice Boltzmann models. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 046710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lycett-Brown, D.; Luo, K.H. Improved forcing scheme in pseudopotential lattice Boltzmann methods for multiphase flow at arbitrarily high density ratios. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 023305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, A.; Li, Q. Investigation of Galilean invariance of multi-phase lattice Boltzmann methods. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2006, 362, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamuro, T.; Konishi, N.; Ogino, F. A Galilean invariant model of the lattice Boltzmann method for multiphase fluid flows using free-energy approach. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2000, 129, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Doolen, G.D. Thermodynamic foundations of kinetic theory and lattice Boltzmann models for multiphase flows. J. Stat. Phys. 2002, 107, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.R.; Orlandini, E.; Osborn, W.; Yeomans, J. Lattice Boltzmann simulations of liquid-gas and binary fluid systems. Phys. Rev. E 1996, 54, 5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moqaddam, A.M.; Chikatamarla, S.S.; Karlin, I.V. Simulation of droplets collisions using two-phase entropic lattice boltzmann method. J. Stat. Phys. 2015, 161, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösch, F.; Dorschner, B.; Karlin, I. Entropic multi-relaxation free-energy lattice Boltzmann model for two-phase flows. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2018, 122, 14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moqaddam, A.M.; Chikatamarla, S.S.; Karlin, I.V. Drops bouncing off macro-textured superhydrophobic surfaces. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 824, 866–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorschner, B.; Chikatamarla, S.S.; Karlin, I.V. Fluid-structure interaction with the entropic lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 023305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, H. Lattice Boltzmann method for simulations of liquid-vapor thermal flows. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 066711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Mo, H.; Luo, K.H. Mesoscopic simulation of three-dimensional pool boiling based on a phase-change cascaded lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Gillissen, J.; Van den Akker, H.; Sundaresan, S. Lattice-Boltzmann-based two-phase thermal model for simulating phase change. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 033302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, H.; Rahimian, M.H.; Krafczyk, M. Extended lattice Boltzmann method for numerical simulation of thermal phase change in two-phase fluid flow. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 013304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupershtokh, A.L.; Medvedev, D.A.; Gribanov, I.I. Thermal lattice Boltzmann method for multiphase flows. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 023308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyhanian, E.; Rahimian, M.H.; Chini, S.F. Investigation of 2D drop evaporation on a smooth and homogeneous surface using Lattice Boltzmann method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 89, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyhanian, E.; Dorschner, B.; Karlin, I.V. Thermokinetic lattice Boltzmann model of nonideal fluids. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 020103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, A.; Küllmer, K.; Reith, D.; Joppich, W.; Foysi, H. Semi-Lagrangian off-lattice Boltzmann method for weakly compressible flows. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 023305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ilio, G.; Dorschner, B.; Bella, G.; Succi, S.; Karlin, I.V. Simulation of turbulent flows with the entropic multirelaxation time lattice Boltzmann method on body-fitted meshes. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 849, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; He, X. Discretization of the velocity space in the solution of the Boltzmann equation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansumali, S.; Karlin, I.V. Kinetic boundary conditions in the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 026311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grad, H. On the kinetic theory of rarefied gases. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1949, 2, 331–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupershtokh, A.; Medvedev, D.; Karpov, D. On equations of state in a lattice Boltzmann method. Comput. Math. Appl. 2009, 58, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Thermal Convection in the van der Waals Fluid. In Frontiers in Computational Fluid-Structure Interaction and Flow Simulation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 377–398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, P.; Yan, H. Revised Chapman-Enskog analysis for a class of forcing schemes in the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 043313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lycett-Brown, D.; Luo, K.H. Multiphase cascaded lattice Boltzmann method. Comput. Math. Appl. 2014, 67, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A. Thermodynamic consistency of liquid-gas lattice Boltzmann simulations. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 056703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengel, Y.A.; Boles, M.A. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 6th Editon (SI Units); The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, S.W.; Wilson, J. A volume of fluid based method for fluid flows with phase change. J. Comput. Phys. 2000, 160, 662–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuki, A. Dynamic van der Waals theory of two-phase fluids in heat flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 054501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuki, A. Dynamic van der Waals theory. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 036304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, N. Nucleate boiling. The region of isolated bubbles and the similarity with natural convection. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1963, 6, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocamustafaogullari, G. Pressure dependence of bubble departure diameter for water. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1983, 10, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeeli, A.; Tryggvason, G. Computations of film boiling. Part I: Numerical method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 47, 5451–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimenko, V.; Shelepen, A. Film boiling on a horizontal plate—A supplementary communication. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1982, 25, 1611–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’yakov, S. Shock wave stability. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz 1954, 27, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Kontorovich, V.M. Concerning the stability of shock waves. Sov. Phys. JETP 1957, 6, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, J. On the theory of a shock wave driven by a corrugated piston in a non-ideal fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 691, 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Fluid Mechanics, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 61–252. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, C. Comment on“Stability of Step Shocks”. Phys. Fluids 1963, 6, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethe, H. The Theory of Shock Waves for an Arbitrary Equation of State; Report No PB-32189; Clearinghouse for Federal Scientific and Technical Information, US Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, J.W. Initial-value-problem solution for isolated rippled shock fronts in arbitrary fluid media. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 056313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

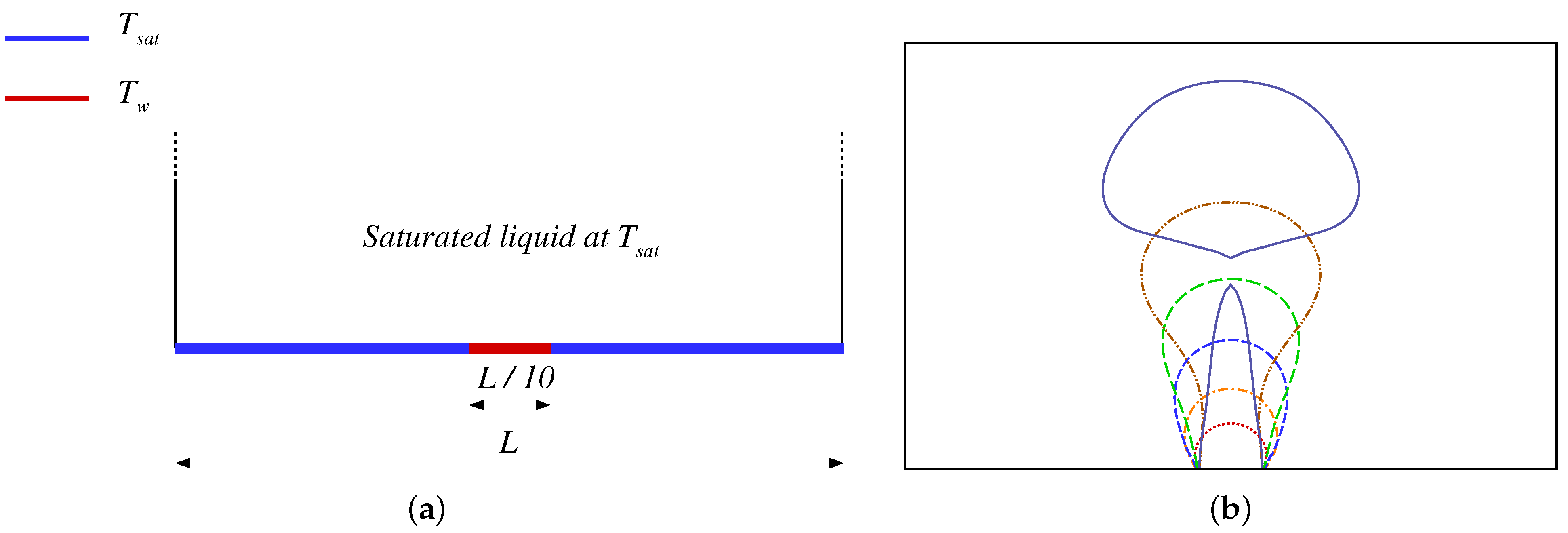
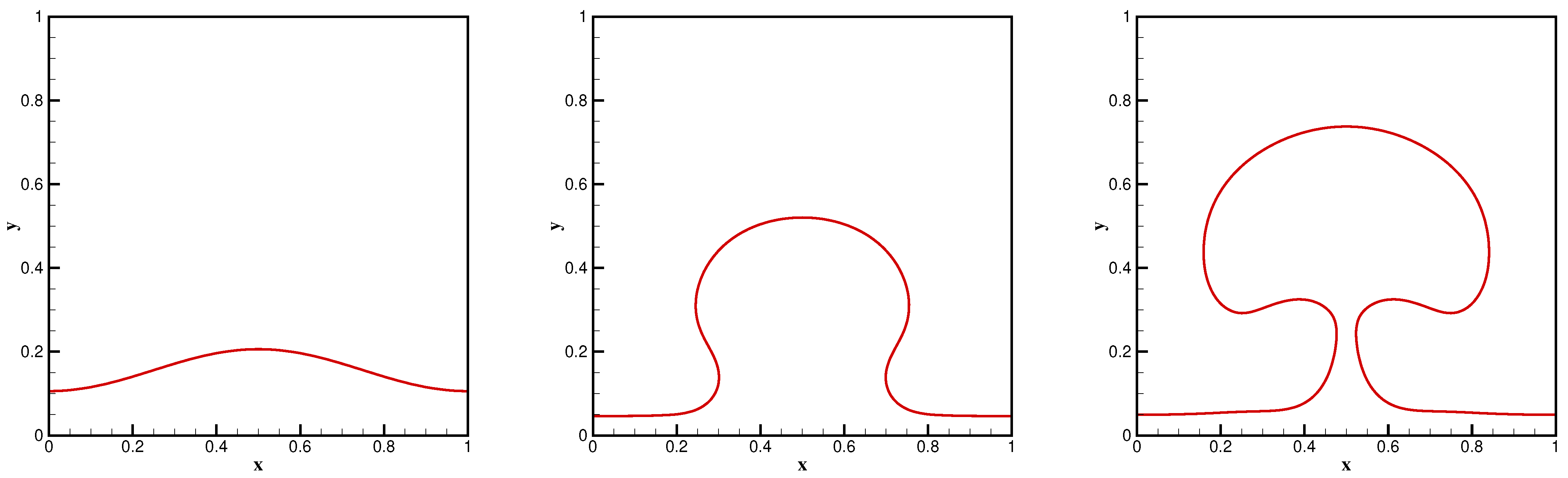
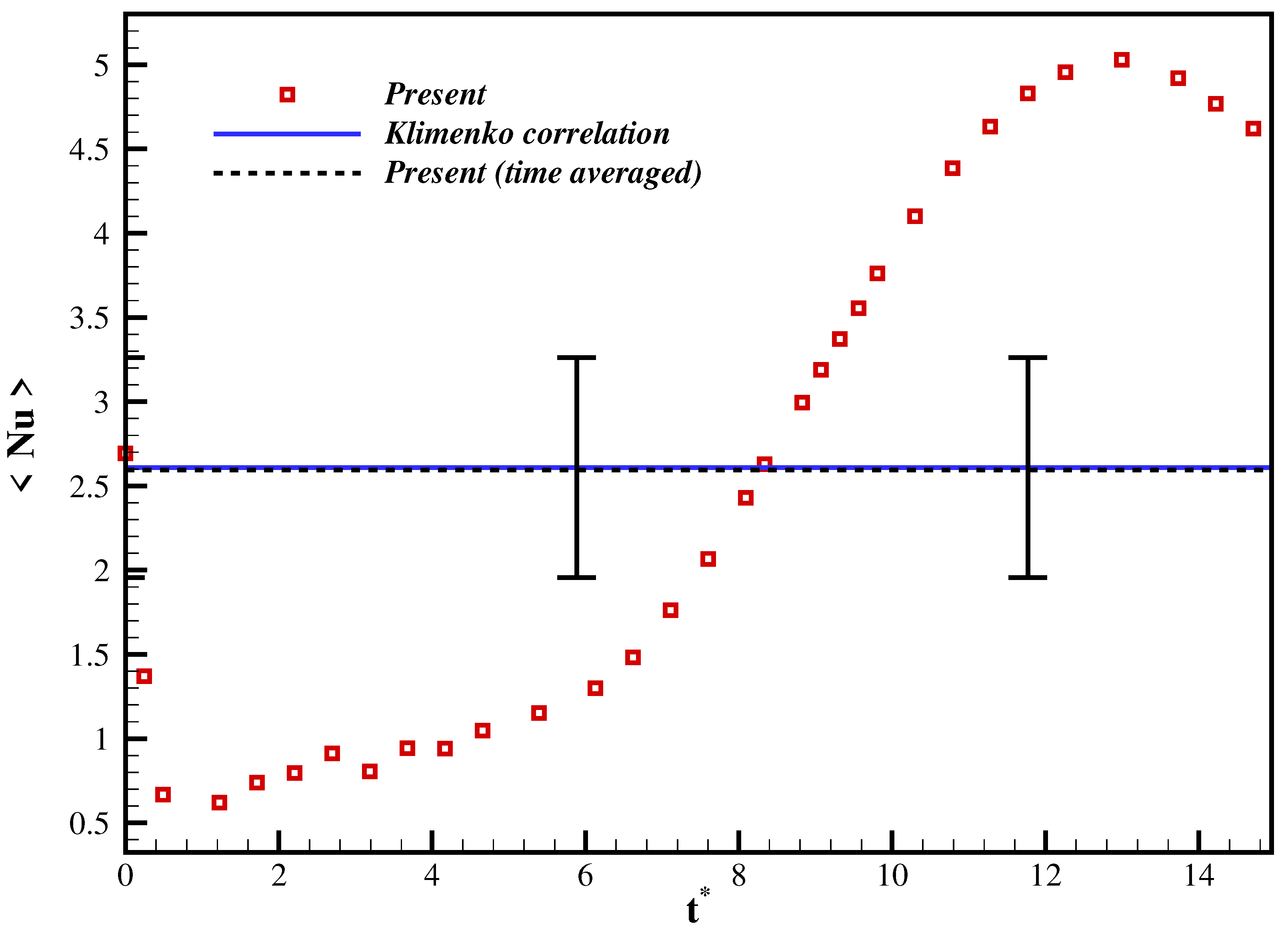
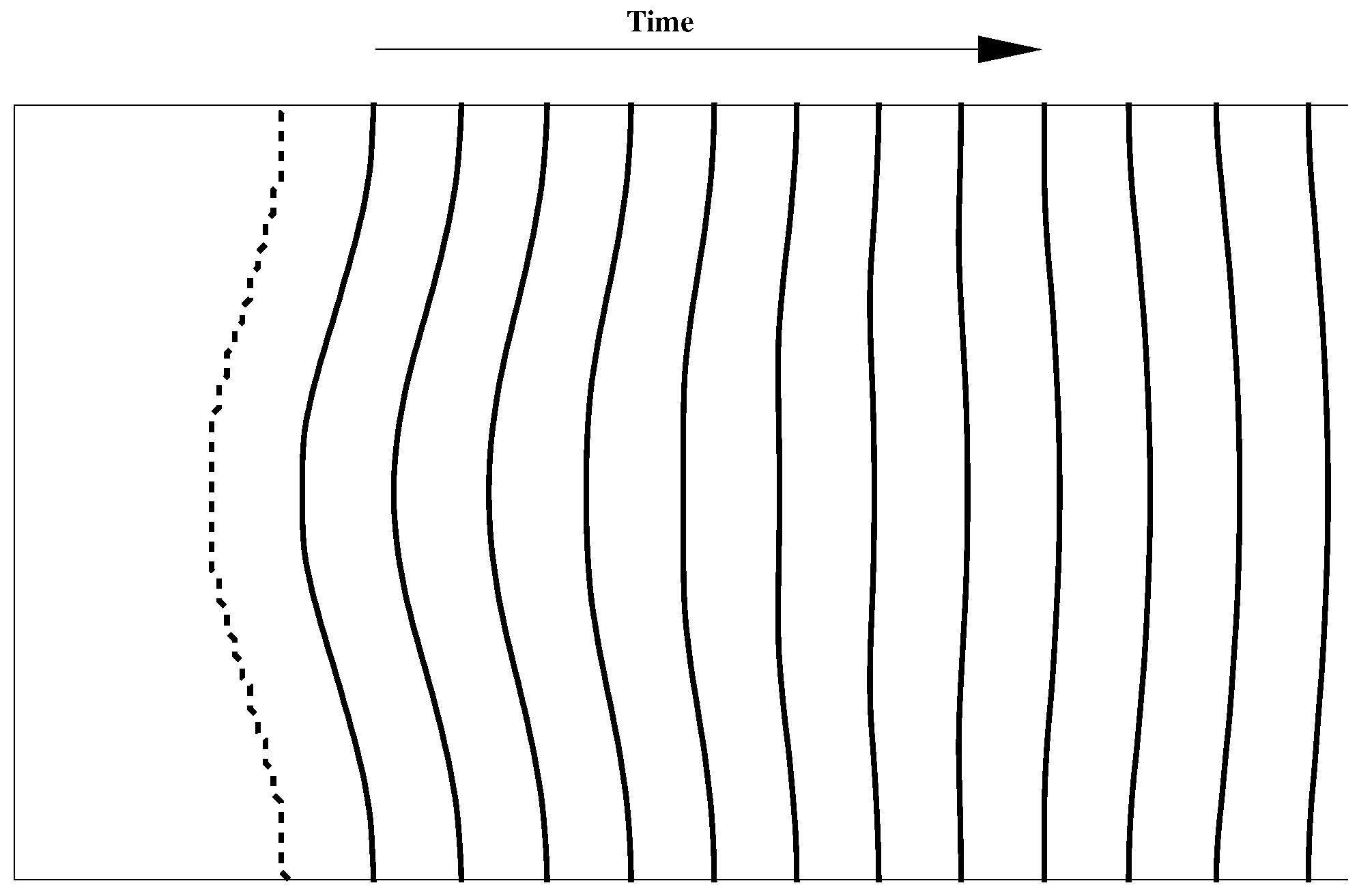
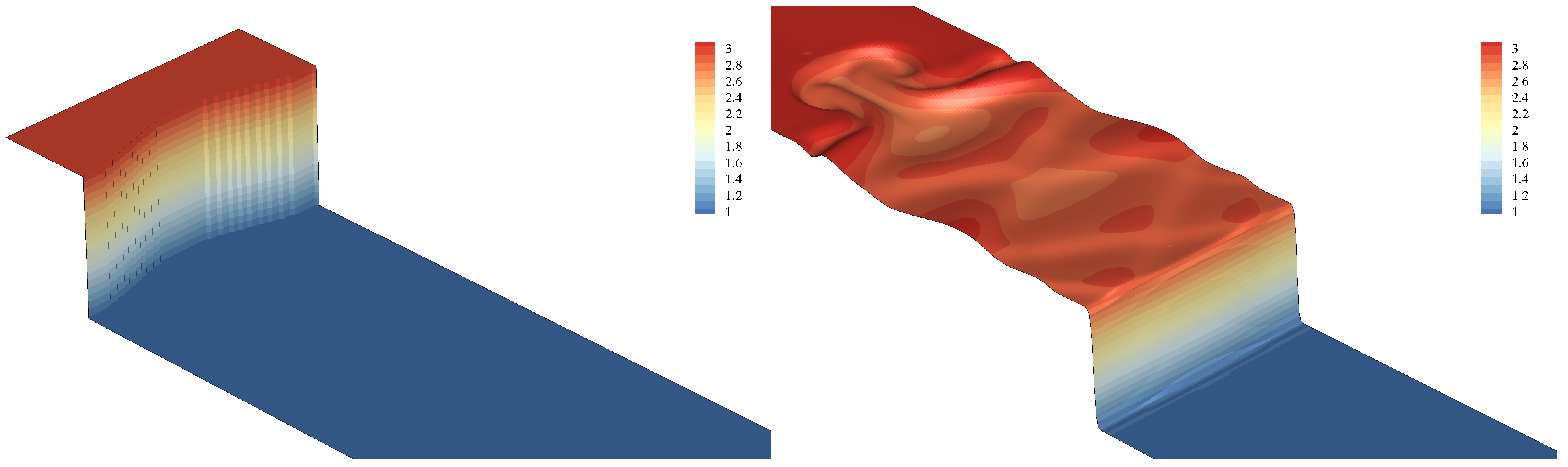
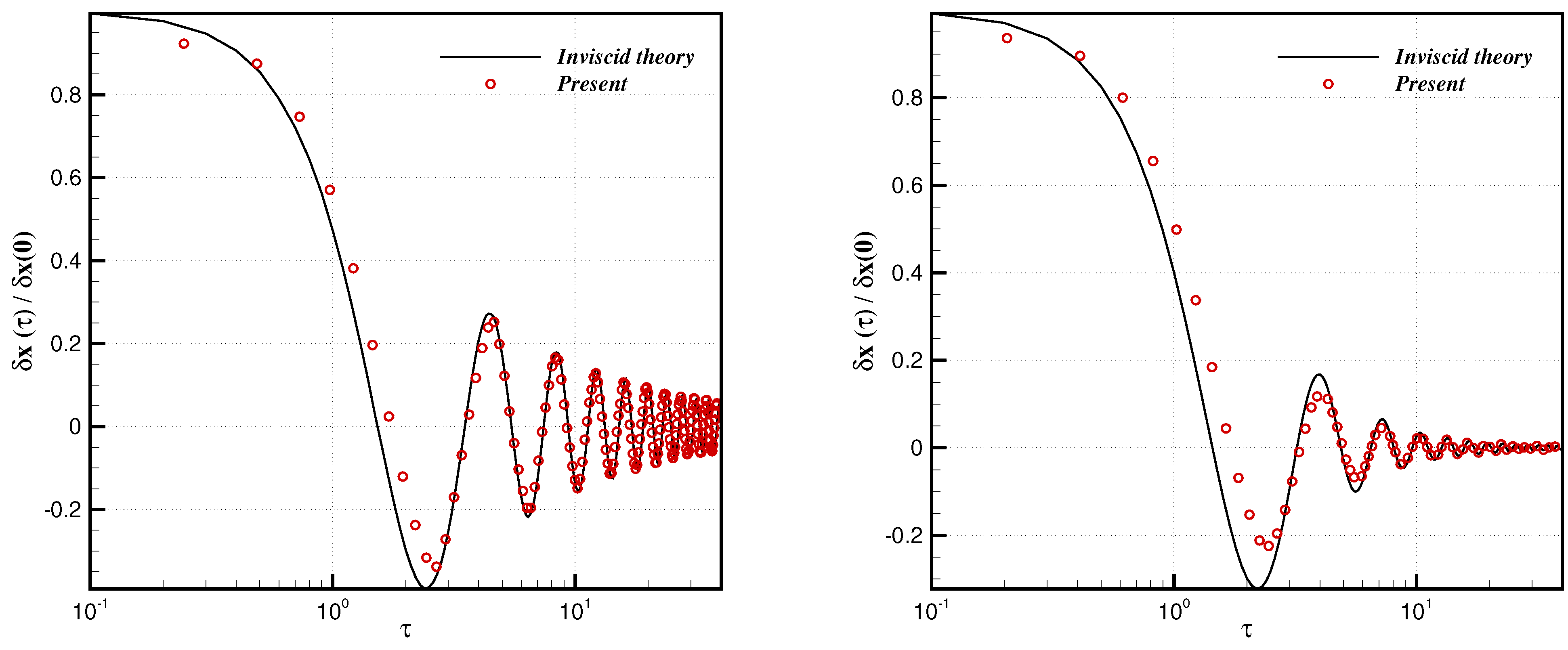

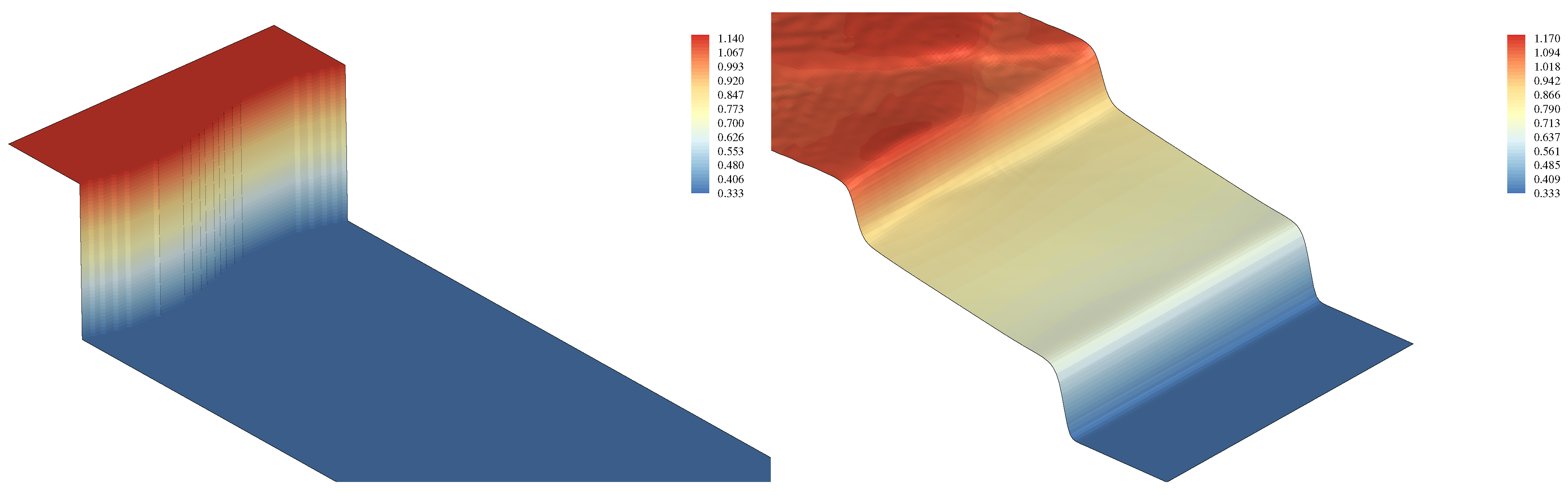
| Case | EOS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | IG | 3.0 | 1 | 1 | 0.03 | 1.5 | −1/9 | 4.214 | |
| (2) | vdW | 3.033 | 0.1 | 3.0 | −0.094 | −7.856 | |||
| (3) | vdW | 1.114 | 0.4 | 80.0 | −0.542 | 1.487 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyhanian, E.; Dorschner, B.; Karlin, I. Kinetic Simulations of Compressible Non-Ideal Fluids: From Supercritical Flows to Phase-Change and Exotic Behavior. Computation 2021, 9, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation9020013
Reyhanian E, Dorschner B, Karlin I. Kinetic Simulations of Compressible Non-Ideal Fluids: From Supercritical Flows to Phase-Change and Exotic Behavior. Computation. 2021; 9(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation9020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyhanian, Ehsan, Benedikt Dorschner, and Ilya Karlin. 2021. "Kinetic Simulations of Compressible Non-Ideal Fluids: From Supercritical Flows to Phase-Change and Exotic Behavior" Computation 9, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation9020013
APA StyleReyhanian, E., Dorschner, B., & Karlin, I. (2021). Kinetic Simulations of Compressible Non-Ideal Fluids: From Supercritical Flows to Phase-Change and Exotic Behavior. Computation, 9(2), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation9020013







