GCM Solver (Ver. 3.0): A Mathematica Notebook for Diagonalization of the Geometric Collective Model (Bohr Hamiltonian) with Generalized Gneuss–Greiner Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Motivation
2. Physics Background
Matrix Elements
3. Program Explanation
4. BasMat Library Description
4.1. Control of “Border Effects” Due to the Truncation of the Matrices
4.2. Scaling Factor in the Radial Variable
5. Model Calculations and Examples
6. Playing Area and Fitting Subroutines
7. Installation Tips
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bohr, A. The Coupling of Nuclear Surface Oscillations to the Motion of Individual Nucleons. Dan. Mat. Fys. Medd. 1952, 26, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bohr, A.; Mottelson, B.R. Collective and Individual-Particle Aspects of Nuclear Structure. Dan. Mat. Fys. Medd. 1953, 27, 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Gneuss, G.; Greiner, W. Collective potential energy surfaces and nuclear structure. Nucl. Phys. A 1971, 171, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, W.; Maruhn, J.A. Nuclear Models; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996; ISBN 978-3-642-60970-1. [Google Scholar]
- Iachello, F. Dynamic Symmetries at the Critical Point. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iachello, F. Analytic Description of Critical Point Nuclei in a Spherical-Axially Deformed Shape Phase Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, L. Solutions of the Bohr Hamiltonian, a compendium. Eur. Phys. J. A 2005, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buganu, P.; Fortunato, L. Recent approaches to quadrupole collectivity: Models, solutions and applications based on the Bohr hamiltonian. J. Phys. G 2016, 43, 093003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolteiner, D.; Maruhn, J.A.; Hess, P.O. Numerical Application of the Geometric Collective Model. In Computational Nuclear Physics 1: Nuclear Structure; Langhanke, K., Maruhn, J.A., Koonin, S.E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991; ISBN 978-3-642-76356-4. [Google Scholar]
- Caprio, M.A. Phonon and multi-phonon excitations in rotational nuclei by exact diagonalization of the Bohr Hamiltonian. Phys. Lett. 2009, 672, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, T.A.; Rowe, D.J. A computer code for calculations in the algebraic collective model of the atomic nucleus. Comp. Phys. Commun. 2016, 200, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budaca, R.; Buganu, P.; Budaca, A.I. Bohr model description of the critical point for the first order shape phase transition. Phys. Lett. B 2018, 776, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram Research, Inc. Mathematica; Version 8.0; Wolfram Research, Inc.: Champaign, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari-Ruffino, F. Il Modello Geometrico Collettivo: Metodi di Soluzione, Transizioni di Forma e Applicazioni. Master’s Thesis, University of Padova, Padova, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bohr, A.; Mottelson, B.R. Nuclear Structure; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 1998; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Heyde, K. Basic Ideas and Concepts in Nuclear Physics, 3rd ed.; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2004; ISBN 9780750309806. [Google Scholar]
- Casten, R.F. Nuclear Structure from a Simple Perspective; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; ISBN 9780198507246. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, D.J. Nuclear Collective Motion: Models and Theory; Methuen: London, UK, 1970; ISBN 9780416449600. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, D.J.; Wood, J. Fundamentals of Nuclear Models: Foundational Models; World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2010; ISBN 9812569561. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, J.M.; Greiner, W. Nuclear Models, 3rd ed.; North-Holland Physics Pub.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Próchniak, L.; Rohoziński, S.G. Quadrupole collective states within the Bohr collective Hamiltonian. J. Phys. G 2009, 36, 123101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, L. Nuclei at the top of their shape. Europhys. News 2009, 40, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casten, R.F. Shape phase transitions and critical-point phenomena in atomic nuclei. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, J.M.; Alonso, C.E.; Vitturi, A.; Garcia-Ramos, J.E.; Dukelsky, J.; Frank, A. U(5)-O(6) transition in the interacting boson model and the E(5) critical point symmetry. Phys. Rev. C 2003, 68, 041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, E.; Moshinsky, M.; Sharp, R.T. U(5) ⊇ O(5) ⊇ O(3) and the exact solution for the problem of quadrupole vibrations of the nucleus. J. Math. Phys. 1976, 17, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, E.; Moshinsky, M. Group theory of the collective model of the nucleus. J. Math. Phys. 1977, 18, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, T.M.; Margetan, F.J.; Williams, S.A. Exact solution of the quadrupole surface vibration Hamiltonian in body-fixed coordinates. Phys. Rev. C 1976, 14, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bés, D.R. The γ-dependent part of the wave functions representing γ-unstable surface vibrations. Nucl. Phys. 1959, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, Z. On the collective model wave functions. Nuovo Cimento 1959, 14, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmer, N.; Pursey, D.L.; Williams, S.A. Irreducible Representations of the Five-Dimensional Rotation Group. I. J. Math. Phys. 1968, 9, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.A.; Pursey, D.L. Irreducible Representations of the Five-Dimensional Rotation Group. II. J. Math. Phys. 1968, 9, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habs, D.; Klewe-Nebenius, H.; Wisshak, K.; Löhken, R.; Nowicki, G.; Rebel, H. The Spherical to Asymmetric Shape Transition in the Mass Region with 50 < (N,Z) < 82. Z. Phys. 1974, 267, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margetan, F.J.; Williams, S.A. Optimization of finite expansion bases for nuclear collective-model calculations. Phys. Rev. C 1982, 25, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
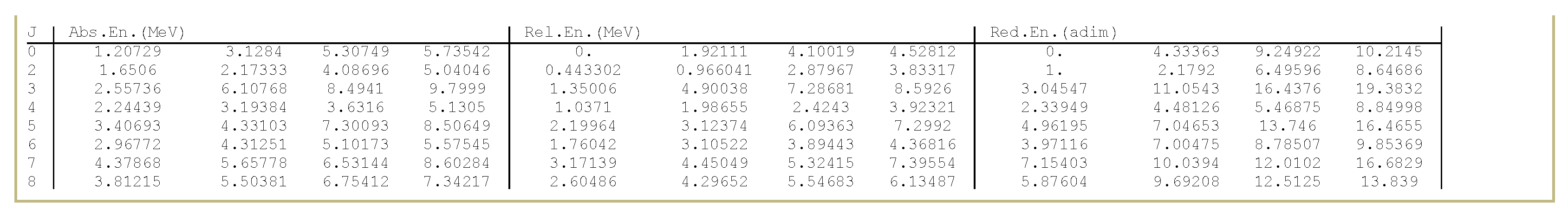
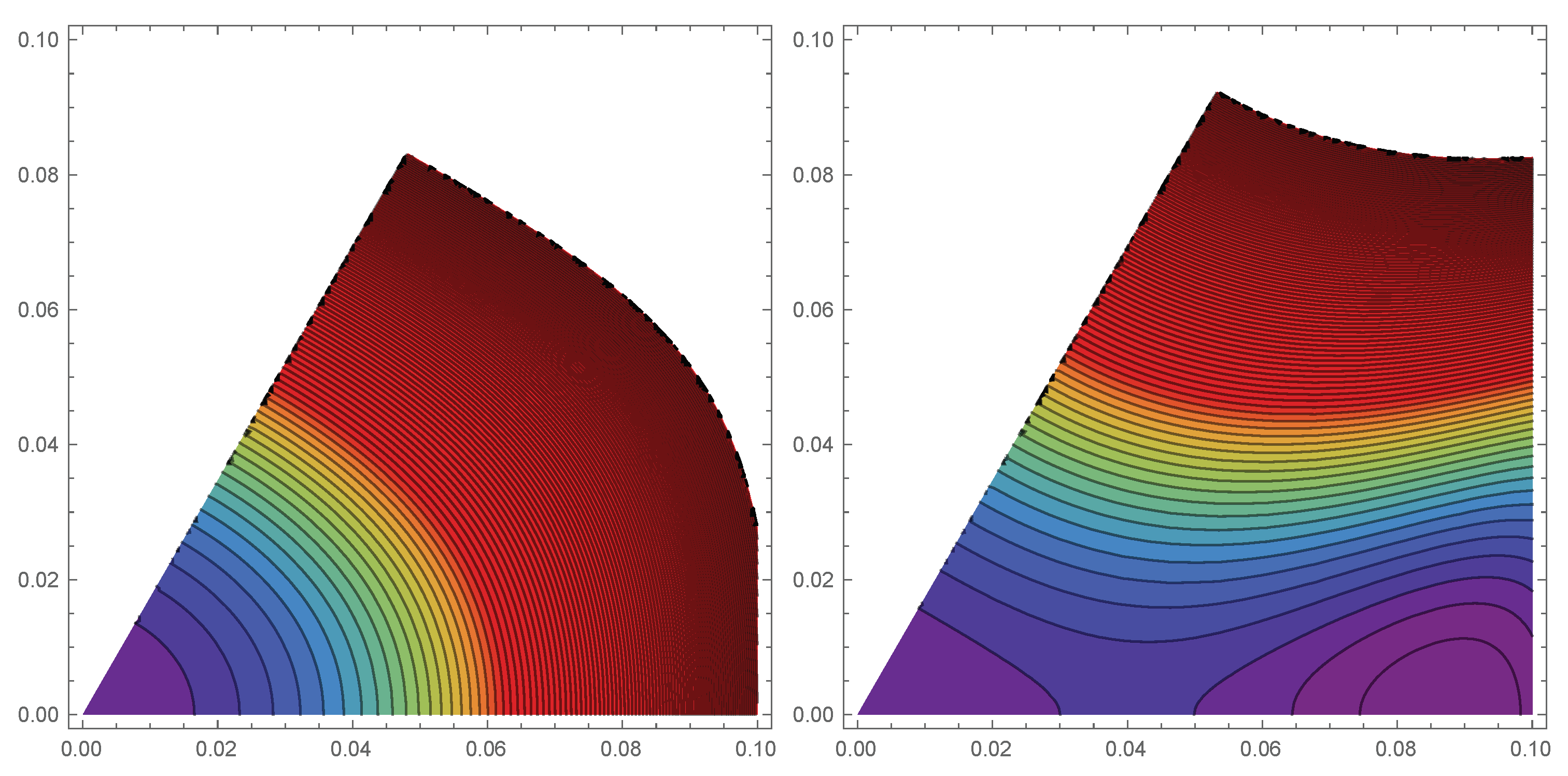
| L | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dim | 200 | 376 | 176 | 529 | 330 | 660 | 462 | 771 |
| dim (trimmed) | 147 | 273 | 127 | 380 | 234 | 469 | 324 | 540 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrari-Ruffino, F.; Fortunato, L. GCM Solver (Ver. 3.0): A Mathematica Notebook for Diagonalization of the Geometric Collective Model (Bohr Hamiltonian) with Generalized Gneuss–Greiner Potential. Computation 2018, 6, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation6030048
Ferrari-Ruffino F, Fortunato L. GCM Solver (Ver. 3.0): A Mathematica Notebook for Diagonalization of the Geometric Collective Model (Bohr Hamiltonian) with Generalized Gneuss–Greiner Potential. Computation. 2018; 6(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation6030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrari-Ruffino, Fabrizio, and Lorenzo Fortunato. 2018. "GCM Solver (Ver. 3.0): A Mathematica Notebook for Diagonalization of the Geometric Collective Model (Bohr Hamiltonian) with Generalized Gneuss–Greiner Potential" Computation 6, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation6030048
APA StyleFerrari-Ruffino, F., & Fortunato, L. (2018). GCM Solver (Ver. 3.0): A Mathematica Notebook for Diagonalization of the Geometric Collective Model (Bohr Hamiltonian) with Generalized Gneuss–Greiner Potential. Computation, 6(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation6030048





