Abstract
Much of biology-inspired computer science is based on the Central Dogma, as implemented with genetic algorithms or evolutionary computation. That 60-year-old biological principle based on the genome, transcriptome and proteasome is becoming overshadowed by a new paradigm of complex ordered associations and connections between layers of biological entities, such as interactomes, metabolomics, etc. We define a new hierarchical concept as the “Connectosome”, and propose new venues of computational data structures based on a conceptual framework called “Grand Ensemble” which contains the Central Dogma as a subset. Connectedness and communication within and between living or biology-inspired systems comprise ensembles from which a physical computing system can be conceived. In this framework the delivery of messages is filtered by size and a simple and rapid semantic analysis of their content. This work aims to initiate discussion on the Grand Ensemble in network biology as a representation of a Persistent Turing Machine. This framework adding interaction and persistency to the classic Turing-machine model uses metrics based on resilience that has application to dynamic optimization problem solving in Genetic Programming.
1. Introduction
Numerous complex real-world optimization problems have emerged in scientific fields such as biomedicine, engineering, economics, and business, that cannot be solved in reasonable amounts of time and yet precise solutions exist [1]. Such problems are often highly nonlinear and include multiple variables acting under complex constraints. Gradient based optimization methods using analytical or numerical methods can fail to solve problems with greater than one local optimum. Metaheuristic approaches produce efficient results using an iterative generation process that integrates different concepts for exploring and exploiting search spaces that guide a subordinate heuristic, with learning strategies used to find near-optimal solutions [2]. Examples of metaheuristic algorithms include: Genetic Algorithm (GA) as a popular algorithm that mimics the natural evolution process [3], Particle Swarm Optimization inspired by social behavior of birds searching for food [4], and Ant Colony Optimization inspired by the foraging behavior of ant colonies [5]. Genetic Programming (GP) is an extension of GA: using evolutionary operators on candidate programs with a tree structure to improve the adaptive fit between the population of candidate programs and an objective function. Nearly all metaheuristic algorithms are nature-inspired, do not require substantial gradient information, and can fit multiple parameters [6]. Each metaheuristic algorithm has unique advantages with respect to robustness and performance in different problem spaces [7]. Since any one metaheuristic algorithm cannot optimally solve all optimizing problems [8], new algorithms are sought to handle specific optimizing problems.
The aim of the present work is to develop a framework for optimization algorithms that is based on biological properties of RNAs interacting in a transcriptome cloud analogous to an information system [9]. The transcriptome cloud of RNAs is regulated by two opposing factors: sequence similarity and reverse complementarity to all other transcript sequences. RNA mobility and diffusion have been suggested to be influenced by simple semantic operators arising from observations of anomalous diffusion of RNA [10]. This framework supports selective transport of biological information, storage of information with rapid retrieval for dynamic problems, and prevention of run-away storage requirements. The main contribution of this paper is the presentation of a new bio-inspired framework providing guidance into solving optimization problems based on information properties of RNA.
We introduce a premise in Biology that individual RNA transcripts collectively form an information cloud of sequence words, and this cloud interacts via similarity, reverse complementarity and compartmentalism, operating on segments or words of each individual RNA in the transcriptome, which for some genes may have significant regulatory impact by decreasing or increasing their diffusion coefficient [ibid.]. In the computer science realm, transcripts are the genes in GA or the program code in GP. Certain real biology transcripts may have specific transporter proteins or translocators avoiding RNA-RNA interactions (e.g., “zipcode” motif [11]) and hence would not be significantly impacted by interaction with the surrounding transcriptome cloud. In the GA/GP realm, these would be problem-specific algorithms.
In bioinformatics, computation of scores for RNA-transcriptome word interactions would add information dimensionality to multiscale -omics data analysis, similar to the idea described as a “communicasome” by others [12]. This bioinformatic effort provides a deeper understanding of nucleotide word structure and RNA language meaning [13]. Frameworks for understanding human pathologies resulting from changes in gene expression can be applied to ideas like resilience and personalized medicine. We propose a “Connectosome”, similar to a communicasome mentioned in [12] where: (1) RNA diffuses away from point of transcription on DNA creating an information cloud of sequences; (2) all RNAs comprise the transcriptome, and each transcript is affected by local RNAs within the cloud; (3) diffusion rates of individual RNAs are modeled with a semantic analysis of similarity and reverse complementarity of RNA words at that location in the cloud of transcripts; and (4) transcriptome cloud affects anomalous RNA diffusion that can give rise to emergent and patterned behavior in the cell [14]. We consider how a systems or network biology framework translates into models of interactive computation for biology-inspired algorithms.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 provides background methods and relevant datasets. Section 3 provides a survey on evolutionary computing, then dynamic optimization strategies, in which current research has been organized so that the reader can identify open issues this new bio-inspired computing framework inspires. Emergent biology from an information cloud of RNA sequences is introduced, with connection to biology big data-omics, and description of vision of Grand Ensemble with relevance to membrane computing and Turing machines. The framework of Anomalous Diffusion for genetic programming is introduced. Finally, Section 4 is devoted to resilience with a suggested metric, and Section 5 is the conclusion and future works.
2. Materials and Methods
This work draws upon bioinformatic analyses of datasets described in [9,15] that involve spatial and temporal transcriptome measurements. As validation of this transcriptome model framework, we utilized a simple transcriptome of a few highly expressed genes. From seven published RNA studies, with data sources grouped into high and low study parameter sets, we analyzed mean enrichment values under two-sample equal variance assumption models. We assumed that appearance in exosomes or microparticles requires greater mobility and hence larger diffusion coefficients than cytoplasmic or nuclear RNAs [15]. Description of data sources are summarized here. Villarroya-Beltri [16] reports microarray datasets of exosome and cellular fractions from activated and resting human T lymphocytes. They differentially assessed whether RNAs are specifically enriched within exosomes and suggest that mRNA and miRNA loading into exosomes is not a simple passive process. Specific miRNAs were more prevalent in exosomes than in cells, and in most cases this difference is preserved under cellular resting or activated conditions. Similarly, most miRNAs preferentially found in cells than in exosomes also keep this tendency regardless of the activation state of the cell, suggesting resilience for expression patterns in the transcriptome. We calculated similarity of transcript words and reverse-complement as a count of subsequences in common with all of the subsequences in the transcriptome. Additionally, tWord and rcWord factor the expression level of that word in the transcriptome. Values of rcWord were lower than tWord for exosomes compared to cytoplasmic miRNAs. This supports the transcriptome model since exosome transcripts must diffuse further than cytoplasmic RNA, so avoiding reverse complementarity facilitates diffusion. Park [17] compared microarray analysis of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of hct116 colon cancer cells. We sorted their data into nuclear enriched, and those which were preferentially found in the cytoplasm. We found that tWord was 4.73 for nuclear and 10.58 for cytoplasmic miRNAs, with a significant t-test p-value of 0.023 between nuclear and cytoplasmic groups. We also found nuclear enriched miRNAs have higher rcWord values compared to cytoplasmic miRNA (p-value = 0.021 in Table 2 in [10]), suggesting those transcripts have greater potential to interact with other transcriptome RNAs and hence may have lower than expected diffusion coefficients. Huang [18] study utilized RNA-seq with exosomes from human plasma. We found that the top 100 abundant miRNAs in exosomes had higher similarity count measures compared to 100 with low “rcmm” reads. In support of the transcriptome model, exosome transcripts have more similarity to the simple model transcriptome. From these data, we find that exosome transcripts have less reverse complementarity to the simple transcriptome. These results are also supported by Cheng [19] study of exosomes in human blood comparing 50 most abundant miRNAs in exosome samples to low abundance transcripts.
Pseudo code for the transcriptome anomalous diffusion model can be found in Supplemental Materials section.
3. Results
3.1. Evolutionary Computing
Evolutionary Computation derives optimization algorithms inspired by biological evolution principles such as genetics and natural selection [20]. Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs) are meta-heuristics that can be applied to a variety of search and optimization problems. Existing EAs include: Genetic Algorithms (GAs), Genetic Programming (GP), Evolutionary Programming and Evolution Strategies. All of these model candidate solutions to a problem as populations of individuals with genotypes that are iteratively transformed, evaluated against some fitness criterion, then selected according to “survival of the fittest”, until an optimal solution is found. The difference among them lies in the way individuals are transformed, and on the search operators applied to obtain new solutions. Alternately, these existing iterative approaches have been referred to as Artificial Evolution, in which biology concepts are implemented [21]. A new term Computational Evolution (CE) reflects a new generation of bio-inspired computing [22] that builds upon new knowledge from biology and increased synergies between biologists and computer scientists. This present work builds a computation framework from recent biology insight, with the intent to provide new CE algorithms, and to deepen understanding of biological regulation.
3.2. Dynamic Optimization Strategies
Numerous real-world scenarios that can be modelled as dynamic optimization problems (DOPs) are characterized by the dynamic nature of the model elements, for example: the objective function or search space. Solving DOPs by metaheuristics has been productive [23,24,25] because of their capacity to deal with complex scenarios, and incorporation of specific mechanisms to face problem dynamics. Current mechanisms for DOPs can be categorized as: diversity during program run, diversity after changes, memory approaches, and multi-population approaches [26]. Nguyen [27] suggested another approach is to use the self-adaptive mechanisms of meta-heuristics to cope with changes. Self-adaptation is a commonly known parameter control technique in evolutionary computation that has been extensively studied in stationary environments [28,29,30]. Metaheuristics have certain inherent self-adaptive behavior (e.g., evolution strategy, real-coded genetic algorithms—GAs). However, such behavior can be insufficient to deal with problems in dynamic environments [28,31]. Therefore, mechanisms or extensions to metaheuristics need to be designed to deal with dynamic problems. Extensions of Cartesian Genetic Programming (CGP) [32] have significant features that correspond to the transcriptome model discussed here. In CGP, programs are represented as directed acyclic graphs using a two-dimensional grid of nodes. When the genotype is decoded, some nodes may be unconnected, and hence are non-coding which assist evolution with a ready supply of potential functions. We can model resilient properties of real biological transcriptomes that are solving multi-objectives with transport and localization of information by anomalous diffusion of individual transcripts.
3.3. Silencing and Enhancing Transcripts for Dynamic Environments
A transcript in transcriptome T could be a solution to some problem if it is not hidden or silenced. RNAs except for miRNAs typically have regions that are solvent inaccessible and/or double stranded, preventing intra-molecular interactions [33]. mRNAs have more secondary structure or intra-strand base pairing than expected by chance [34]. For each component RNA subsequence word, we determine whether it is expected in a single-stranded and solvent-accessible state (state “A”), or double-stranded or buried within the RNA molecule and is inaccessible (state “I”). Although these computations are intensive and numerous for a whole transcriptome [35], the RNA structure can be pre-calculated and supplied as a lookup table. Solvent accessibility estimates for each transcript word partition the frequency entries in the transcriptome matrix by reducing A in the amount that I increase. These shifts in A/I affect the tWord and rcWord values for most transcripts. Shifts of A → I could be caused by RNA-binding factors (RNA or protein) that cover a word in the transcript or word in the transcriptome, or indirectly by binding to some other region of the RNA causing a cis type of structural alteration leading to solvent inaccessibility. Transcriptome Cloud or nebula regulation [10] is proposed to occur as an indirect result of some factor that changes A/I for some word that then alters a different interacting transcript’s diffusion coefficient. Conversely, I → A shifts could be caused by the release of binding factors or conformational change leading to exposure of the particular word.
In a computational model, this paradigm corresponds most closely to modular CGP. As an enhancement of CGP, reusable sub-functions extend a genotype by adding more complex nodes denoted as modules [36]. The modules, which closely resemble transcripts in the biological model, are propagated through evolution by dynamically allocating and releasing them by compress and expand operators [37]. The computational operators are behaving like the transcriptome A/I shifts that expose or cover sub-functions encoded in the transcript.
3.4. Connectosome in the Grand Ensemble
We can consider the connectosome as a construct composed of three ensembles identified as the transcriptome, proteasome, and liposome (Figure 1). Instead of DNA centered, the transcriptome in the grand ensemble is an establisher or initiator of the cell state. DNA provides the raw RNA material from transcription to establish and maintain the transcriptome, but RNA flows in and out of the cell are significant from biology experiments on exosomes and microparticles. We propose self-regulatory properties of the transcriptome establish attractor states arising from the opposite tendencies of sequence similarity and reverse complementarity. The liposome is an encapsulation and compartmentalization operator formed by action of enzymes and proteins. Proteasome is composed of functions and operators that are translated from the transcriptome. Every item has a function, or provides the raw material for a possible function as in miRNA silencing. Transcriptome is composed of instructions using words to make proteasome and liposome layers, and has selection filters based on accessible (readable) words. Transfer of blocks or sets of words (RNA) is inversely proportional to relatedness to the whole transcriptome, with local interactions being stronger than remote RNA words. The extracellular pool is composed of input data sources, output solutions from sets of words as instructions, and other virtual system cells.
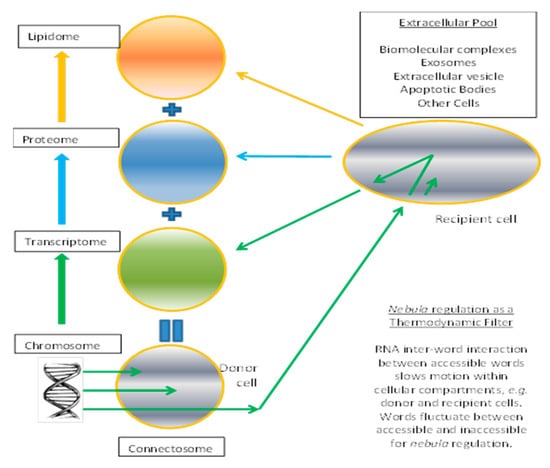
Figure 1.
Establishment of transcriptome as result of anomalous diffusion of RNA. Black represents DNA, green represents RNA, while blue and orange represent proteins and lipids respectively. Arrows denote flow of information from donor cell, to extracellular pool, to recipient cell. Biological connectosome maps to schema of enhancements in Cartesian Genetic Programming (CGP).
3.5. Relevance to Membrane Computing
Since the Grand Ensemble (Figure 1) includes the concept of lipid membranes that also get secreted and absorbed by real cells, the analogue to GA/GP could be extended to membrane computing algorithms. Membrane computing (P systems) is a class of computing model abstracted from the structure and functioning of living cells and from interactions of living cells in tissues or higher order biological structures [38]. Many variants of membrane computing models have been developed that have significant potential to be applied to various computationally hard problems in feasible time, such as the traveling salesman problem [39], maximum clique problem [40], Hamilton path problem [41], and tripartite matching problem [42]. Figure 2 shows a representation of implementation of the grand ensemble in membrane or GP algorithms. Each cell is composed of a prior transcriptome (T0), transcripts that are imported (TIN), and removal of TOUT. Import and export in each cell is subject to transcript filtering influenced by S, RC, and N. TOUT from all cells is pooled the stochastically distributed to all cells, subject to the same filtering upon importation. This scheme may help to prevent stalling in CGP [43], by allowing major shifts of transcript partitioning if the accumulation of small evolutionary changes results in shifts of compartmentalization due to rank changes in S and RC.
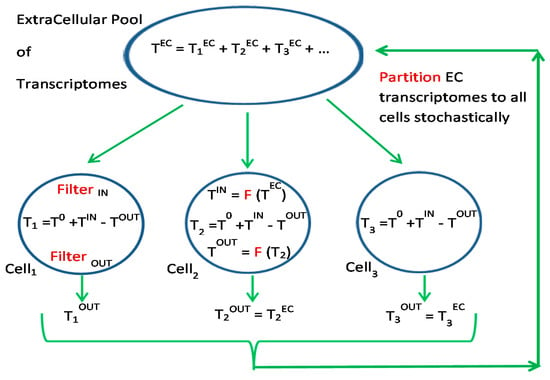
Figure 2.
Transcriptomes partitioned into cells or membrane bound computer programs. Within cells there can also be compartmentalization of transcripts leading to functional modules. Filter function F operates bidirectionally upon RNA transcripts using semantic operators.
3.6. In Silico Virtual Living System as a Persistent Turning Machine (PTM)
The Grand Ensemble biology paradigm conceptualization maps in computer science as a Persistent Turing Machine [44]. This is a Turing Machine with a read-only tape, here conceived as the genome node, a read/write tape, conceived as the transcriptome node, and a write only tape which becomes the extracellular pool. The most basic system is composed of a single entity containing the four ensemble nodes (chromosome, transcriptome, proteome, and lipidome) representing the Central Dogma. The ensemble nodes can send or receive contents to/from the extracellular pool as a flow from donor cell to extracellular pool, and adsorption by a recipient cell. This cycling in the transcriptomes would be a generation in CGP. More cells can be added in this model, which are linked by the extracellular pool.
Recurrent CGP, which is an extension to CGP, allows creation of acyclic graphs providing feedback to store internal state information [45]. The transcriptome stores its state as a distribution of diffusion coefficients for each transcript, resulting from interactions with surrounding RNA that can alter the eventual location of each transcript. Recurrent CGP connections represent controls on diffusion in the transcriptome. This extension of CGP is suited to missing data or partially observable tasks supporting a resilience feature of the system. This also is suited to implement the Anomalous Diffusion model below since the compartmentalism and module phenotype mapping is influenced by the two opposing semantic operators S and RC. The parameter values in the semantic operators are derived from the prior state of the system, and hence the transcriptome is acting recurrently. The whole is adding to the individual parts, similar to Banzhaf’s concept of emergence in CGP [46].
3.7. Anomalous Diffusion Model
RNA molecules and proteins undergo constrained diffusion, largely limited by spatial constraints of other molecules and move by a stop-and-go mechanism where free diffusion is interrupted by random association with cellular structures [47]. Most importantly, the dynamic nature of RNAs is emerging as a means to control physiological cellular responses and pathways [48]. Brownian effects are ubiquitous and play a very important role when one infers macroscopic behaviors from the mesoscopic level of description, a route utilized frequently in the study of complex systems. Dynamics at the mesoscopic level is governed by a set of Langevin processes or equivalently by the corresponding N-particle Fokker–Planck equation [49,50].
Consider a transcriptome from a cell type alpha to be represented as Tα, such that it is the sum of all RNAs, including mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA and rRNA within the cell. This set is the result of transcripts produced from the cellular DNA, Tα0, transcripts inputted from the extracellular space as microparticles and exosomes TαIN, and what remains from export to the extracellular space as TαOUT. Or, Equation (1):
with Equation (2):
where F is a filter function using Tα that increases diffusion for transcripts with greater similarity S, and decreases diffusion for larger RC and N. Thus the extracellular pool is composed of transcripts with greater similarity S, and less reverse complementarity RC to the transcriptome, and have smaller size N. If the transcripts represent subprograms in a CGP framework, then TαOUT would be the transcripts passed to the next generation in this model of anomalous diffusion of transcripts. The filter function would be easily implemented by stochastically selecting transcripts (subprograms) that share code similarity to the whole program, and have small size N. This later selection may assist with preventing program bloat [51] and is a direct consequence of diffusion’s dependence on size. The RC complementarity filter is a unique semantic selection on transcripts not found in the literature for GP. For any transcript composed of operands, a complement can be formed that reverses the order of the operands, and each replaced with its complement. Most operands can be easily identified with a complement. For instance, Input & Output, Add & Subtract or Left Shift & Right Shift would be complements (Figure 3).
Tα = Tα0 + TαIN − TαOUT
TαOUT = Tα × F[S, RC, N, Tα], TαIN = TEC × F[S, RC, N, Tα]
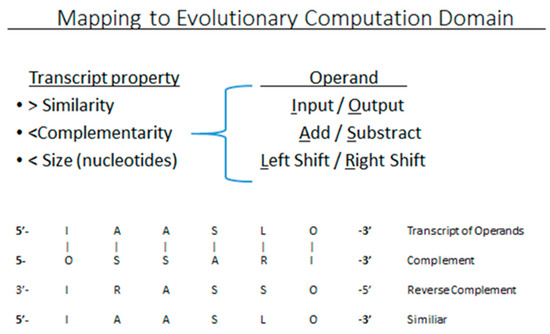
Figure 3.
Mapping Anomalous diffusion to GP domain adding a pass-thru filter that operates semantically on information encoded as either RNA or lines of code in an evolvable subroutine.
We propose that an inherent property of algorithms, whether actual biological or computational, reverse complementation generates well-formed structures that adds resilience similar to non-coding or “junk” DNA. RC structures would have similar information content or entropy to the original algorithm, and hence is very different from a random ordering of operands.
4. Discussion
4.1. Resilience as a Systems Biology Measure from Transcriptome Model
A Resilience measure from Transcriptome RNAs could provide basic knowledge of responses to system stress. Insight into structural determinants of resilience and robustness can guide the understanding of systems that go through transitions. Systems Engineering research has developed methodologies to measure the functionality and complexity of engineered systems for designing and assessing system resilience. While system functions like resilience, functionality, and complexity are widely used concepts in systems engineering, there is significant diversity in definitions and no unified approach to measurement in the Systems Biology area [52]. One method for measuring impacts to functionality in dynamic engineered systems is based on changes in kinetic energy [53]. This metric can be applied at particular levels of abstraction and system scales, consistent with the established multiscale nature of biological systems. Application of global metrics to GP could assist with prevention of stalling [43].
4.2. Measuring Complexity
A difficulty in complexity theory is the lack of clear definitions, particularly those that are measurable [54], and that there are several types of complexity. The first formal treatment of complexity focused on algorithmic complexity, which reflects the computation requirements for a mathematical process [55]. One of the most workable definitions is that of thermodynamic depth, asserting that complexity is a “measure of how hard it is to put something together” [56]. There are several variations on this approach, with the commonality that complexity disappears for both ordered and purely random systems [57]. Bar-Yam [58] defines the complexity of a physical system as the length of the shortest string that can represent its properties. In our case here, this could be the size of the transcriptome filter F composed of opposing semantic operators S and RC.
An energy-based metric proposed by Chaisson [59] measures the energy rate density, which is the energy flow through a system in a time epoch, and divided by the system mass. A practical difficulty in using this metric is determining the appropriate mass and energy. In measuring the transcriptome, we can use the mass of RNA production and the total energy processed by the system. Energy in this framework could be approximated with the sum total of all possible RNA-RNA interactions, which is just the count of all tWord and rcWord frequencies in T. A more realistic model incorporates the differing interaction energies between complement words, e.g., difference between A-U and C-G nucleotides and dinucleotides [34].
As defined by the INCOSE Resilient Systems Working Group, “Resilience is the capability of a system with specific characteristics before, during and after a disruption to absorb the disruption, recover to an acceptable level of performance, and sustain that level for an acceptable period of time” [60]. Robustness is the ability of a system to reject disturbances without altering its state. A system is robust when it can continue functioning in the presence of internal and external challenges without fundamental changes to the original system. In relation to previous section on energy availability, robustness is the ability for a system to retain reachable states in the event of falling available energy.
4.3. Measuring Resilience
From Equation (2) F is a transcriptome filter function of S, RC, and N operating on Tα. The extracellular pool is composed of transcripts with greater similarity S, and less reverse complementarity RC to the transcriptome, and have smaller size N. The filter is essentially a semantic selection on transcripts resulting from anomalous diffusion. We propose that resilience is proportional to the size of the transcriptome filter, which is composed of the opposing actions of S and RC, and to the balance between S and RC. Then the size of F, where |F| = |S| + |RC| or on a per nucleotide basis:
such that |S| is sum of all similarity matches, |RC| is sum of all reverse complement interactions, and N is the nucleotide size of the transcriptome. This work proposes Equation (3) as a measure of resilience that is proportional to the sum of similar and of reverse-complement word matches (divided by the number of nucleotides in transcriptome to normalize for size) in the whole transcriptome. For simple systems of 2 complementary letters, |S| > |RC| and scales faster than N (examined for up to N = 4), with resilience proportional to N.
Resilience = (|S| + |RC|)/N
The biology of miRNAs binding to mRNAs and regulation by lncRNAs presents a method for self-modifying CGP to be resilient to rapid changes in the problem space. mRNAs (sub-programs) could be recruited quickly in a dynamic environment by unbinding miRNA or lncRNAs (sub-program blocks or enhancers) in the realm of dynamic optimization in computer science. A more complex system or network would be consistent with being more resilient. But the difficulty is also measuring complexity, because a large sized network might contain many pathways leading from A to B, but could instead be composed of a spoke(A) & wheel(B) design, such that damage to the spoke will fail the system. So instead, as a first attempt at measuring resilience from transcriptome data, we propose that a filter mechanism acts on individual transcripts caused by opposing semantic information characteristics of the whole transcriptome. Then size of the complexity of that filter could be a simple quantifiable measure of resilience. A recent publication showed that miRNAs are filtered by sequence similarity [15] and another study shows that the same miRNAs are also filtered by reverse complementary to the same whole transcriptome model [10]. Hence the proposed measure of resilience is the sum of similarity and reverse complementary interactions possible in the whole transcriptome. Since these probability distributions are the basis of thermodynamics, taking the log of (|S| + |RC|)/N would represent the entropy of filtering in the transcriptome. We divide by the size of the transcriptome (N) to normalize on a per nucleotide basis, and realize that for a random sequence transcriptome, there will be some expected value of |S| and |RC|.
5. Conclusions
This paper illustrates recent advances in transcriptome and network biology that can lead to enhancing new frameworks in computer science. It is our intent to formalize this Grand Ensemble treatment into a language of persistent and interactive TMs that could advance the field of biology-inspired computing. Once implemented in silico, we can study these models to uncover emergent and complex behavior. Measures calculated from semantic analyses of the transcriptome relate to compartmentalization, and anomalous diffusion of transcripts, which can be utilized to structure and control self-modifying CGP. Transitions between chaos and homeostasis in these computational models may provide insight into the origins of real biological tissues, organs, and pathology states. This insight could be applied to personalized medicine to provide diagnosis and prognosis for a range of complex human disorders.
Supplementary Materials
The Pseudo Code listing are available online at www.mdpi.com/2079-3197/5/3/32/s1; also see biological background in [9,10,14].
Acknowledgments
Supported by 8U54MD007588, G12MD007602, P30 HL107238 and grants from NIH/National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities. The content is solely the responsibility of the author and does not necessarily represent official views of the respective institutions.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Talbi, E.-G. Metaheuristics: From Design to Implementation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Volume 74. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, I.H.; Laporte, G. Metaheuristics: A bibliography. Ann. Oper. Res. 1996, 63, 513–623. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Stützle, T. Ant Colony Optimization; Bradford Company: Holland, MI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Boussaïd, I.; Lepagnot, J.; Siarry, P. A survey on optimization metaheuristics. Inf. Sci. 2013, 237, 82–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibuchi, H.; Yoshida, T.; Murata, T. Balance between genetic search and local search in memetic algorithms for multiobjective permutation flowshop scheduling. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2003, 7, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Q.; Abebe, F.; Seffens, W. Dynamic System Modeling the Whole Transcriptome in a Eukaryotic Cell. In Proceedings of the Dynamic Systems and Applications, Atlanta, GA, USA, 27–30 May 2015; Volume 7, pp. 342–344. [Google Scholar]
- Seffens, W. Models of RNA Interaction from Experimental Datasets: Framework of Resilience; Marchi, F.A., Cirillo, P.D.R., Mateo, E.C.C., Eds.; InTech Publishing: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; Chapter in Transcriptome Analysis; ISBN 978-953-51-5452-5. [Google Scholar]
- Batagov, A.; Kuznetsov, V.; Kurochkin, I. Identification of nucleotide patterns enriched in secreted RNAs as putative cis-acting elements targeting them to exosome nano-vesicles. BMC Genom. 2011, 12 (Suppl. 3), S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.; Kim, O.; Gho, Y. Extracellular vesicles as emerging intercellular communicasomes. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shifrin, D.; Beckler, M.; Coffey, R.; Tyska, M. Extracellular vesicles: Communication, coercion, and conditioning. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regner, B.; Vucinic, D.; Domnisoru, C.; Bartol, T.; Hetzer, M.; Tartakovsky, D.; Sejnowski, T. Anomalous diffusion of single particles in cytoplasm. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seffens, W.; Abebe, F.; Evans, C.; Wang, X.-Q. Spatial Partitioning of miRNAs is related to Sequence Similarity in Overall Transcriptome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, D.; Vázquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.W.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Subramanian, S.; Steer, C. Mature microRNAs identified in highly purified nuclei from HCT116 colon cancer cells. RNA Biol. 2010, 7, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, T.; Tschannen, M.; Sun, Z.; Jacob, H.; Du, M.; Liang, M.; Dittmar, R.L.; Liu, Y.; Liang, M.; et al. Characterization of human plasma-derived exosomal RNAs by deep sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Sharples, R.A.; Scicluna, B.J.; Hill, A.F. Exosomes provide a protective and enriched source of miRNA for biomarker profiling compared to intracellular and cell-free blood. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 23743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiben, A.; Smith, J. Introduction to Evolutionary Computing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Banzhaf, W.; Beslon, G.; Christensen, S.; Foster, J.; Képès, F.; Lefort, V.; Miller, J.; Radman, M.; Ramsden, J. From Artificial Evolution to Computational Evolution: A Research Agenda. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmis, J.; Amos, M.; Banzhaf, W.; Tyrrell, A. Going back to our Roots: Second Generation Biocomputing. Int. J. Unconv. Comput. 2006, 2, 349–382. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, C.; González, J.R.; Pelta, D. Optimization in dynamic environments: A survey on problems, methods and measures. Soft Comput. 2011, 15, 1427–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelta, D.; Cruz, C.; Verdegay, J. Simple control rules in a cooperative system for dynamic optimization problems. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2009, 38, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa-Hernández, P.; Corona, C.; Pelta, D. Efficient multi-swarm PSO algorithms for dynamic environments. Memet. Comput. 2011, 3, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Branke, J. Evolutionary optimization in uncertain environments—A survey. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2005, 9, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Yang, S.; Branke, J. Evolutionary dynamic optimization: A survey of the state of the art. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2012, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeline, P. Adaptive and Self-Adaptive Evolutionary Computations. In Computational Intelligence: A Dynamic Systems Perspective; Palaniswami, M., Attikiouzel, Y., Eds.; IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 152–163. [Google Scholar]
- Eiben, A.; Michalewicz, Z.; Schoenauer, M.; Smith, J. Parameter Control in Evolutionary Algorithms. In Parameter Setting in Evolutionary Algorithms, Studies in Computational Intelligence; Lobo, F., Lima, C., Michalewicz, Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 54, pp. 47–75. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Nieberg, S.; Beyer, H.-G. Self-Adaptation in Evolutionary Algorithms. In Parameter Setting in Evolutionary Algorithms, Studies in Computational Intelligence; Lobo, F., Lima, C., Michalewicz, Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 54, pp. 19–46. [Google Scholar]
- Weicker, K.; Weicker, N. On Evolution Strategy Optimization in Dynamic Environments. In Proceedings of the 1999 Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 July 1999; IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA; pp. 2039–2046. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.F. Cartesian Genetic Programming (Natural Computing Series); Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, Y.H.; Andrabi, M.; Kahali, B.; Ghosh, C.; Mizuguchi, K.; Kochetov, A.; Ahmad, S. On nucleotide solvent accessibility in RNA structure. Gene 2010, 463, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seffens, W.; Digby, D. mRNAs Have Greater Calculated Folding Free Energies than Shuffled or Codon Choice Randomized Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.-K.; Digby, D.; Davis, A.; Seffens, W. Whole Transcriptome mRNA Secondary Structure Analysis Using Distributed Computation. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Granular Computing, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–12 May 2006; pp. 647–650. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, P.; Platzner, M. Multi-Objective Intrinsic Evolution of Embedded Systems. In Organic Computing—A Paradigm Shift for Complex Systems; Muller-Schloer, C., Schmeck, H., Ungerer, T., Eds.; Springer Basel AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 193–206. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, P.; Platzner, M. Advanced Techniques for the Creation and Propagation of Modules in Cartesian Genetic Programming. In Genetic and Evolutionary Computation (GECCO); ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1219–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Paun, G.H. Computing with Membranes; Technical Report; Turku Center for Computer Science: Turku, Finland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, T.Y. An approximate algorithm for NP-complete optimization problems exploiting P systems. In Proceedings of the Brainstorming Workshop on Uncertainty in Membrane Computing, Palma, Majorca, Spain, 8–10 November 2004; pp. 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Arnau, M.; Manrique, D.; Rodriguez-Paton, A.; Sosík, P. A P system and a constructive membrane-inspired DNA algorithm for solving the maximum clique problem. BioSystems 2007, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.Q.; Alhazov, A. Solving HPP and SAT by P systems with active membrane and separation rules. Acta Inform. 2006, 43, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.Y.; Pan, L.Q.; Perez-Jimenez, M.J.; Font, M.R. A Tissue P Systems Based Uniform Solution to Tripartite Matching Problem. Fundam. Inform. 2011, 109, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Haddow, P.C.; Tyrrell, A.M. Genetic Programming and Evolvable Machines; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 12, pp. 183–215. [Google Scholar]
- Goldin, D.; Smolka, S.; Wegner, P. Turing Machines, transition systems, and interaction. Electr. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci. 2001, 52, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.J.; Miller, J.F. Recurrent Cartesian Genetic Programming. In Parallel Problem Solving from Nature—PPSN XIII 2014 LNCS 8672; Bartz-Beielstein, T., Branke, J., Filipič, B., Smith, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 476–486. [Google Scholar]
- Banzhaf, W. Genetic Programming and Emergence. In Genetic Programming and Evolvable Machines; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Trovato, F.; Tozzini, V. Diffusion within the cytoplasm: A mesoscale model of interacting macromolecules. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ari, Y.; Brody, Y.; Kinor, N.; Mor, A.; Tsukamoto, T.; Spector, D.L.; Singer, R.H.; Shav-Tal, Y. The life of an mRNA in space and time. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorga, M.; Romero-Salazar, L.; Rubi, J. Stochastic model for the dynamics of interacting Brownian particles. Phys. A 2002, 307, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savel’ev, S.; Marchesoni, F.; Taloni, A.; Nori, F. Diffusion of interacting Brownian particles: Jamming and anomalous diffusion. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 021119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.J.; Miller, J.F. Cartesian Genetic Programming: Why no bloat? In European Conference on Genetic Programming—EuroGP LNCS 8599; Nicolau, M., Krawiec, K., Heywood, M.I., Castelli, M., García-Sánchez, P., Merelo, J.J., Rivas Santos, V.M., Sim, K., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 222–233. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.R.; Lenton, T.M.; Bascompte, J.; Brock, W.; Dakos, V.; van de Koppel, J.; van de Leemput, I.A.; Levin, S.A.; van Nes, E.H.; et al. Anticipating critical transitions. Science 2012, 338, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J. Functionality, Complexity, and Approaches to Assessment of Resilience under Constrained Energy and Information. Ph.D. Thesis, Air Force Institute of Technology, Wright-Patterson AFB, Greene, OH, USA, 2015. AFIT-ENV-DS-15-M-159. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, S.; Pagels, H. Complexity as thermodynamic depth. Ann. Phys. 1988, 188, 186–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corning, P.A. Complexity is just a word! Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 1998, 58, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchfield, J.P.; Shalizi, C.R. Thermodynamic depth of causal states: When paddling around in Occam’s pool shallowness is a virtue. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 59, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. On the relationship between complexity and entropy for Markov chains and regular languages. Complexity 1991, 5, 381–399. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Yam, Y. Multiscale Complexity/Entropy. Adv. Complex Syst. 2004, 7, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisson, E.J. Energy rate density as a complexity metric and evolutionary driver. Complexity 2011, 16, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INCOSE. INCOSE Resilient Systems Working Group (RSWG) Charter. 2011. Available online: http://www.incose.org/docs/default-source/wgcharters/resilient-systems.pdf?sfvrsn=6 (accessed on 2 July 2017).
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).