Linear Heat Diffusion Inverse Problem Solution with Spatio-Temporal Constraints for 3D Finite Element Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Formulation of the IHCP for ceramic insulators subjected to lightning impulses, with emphasis on reconstructing the unknown initial conditions.
- Introduction of a spatio-temporal regularization framework that enhances stability and accuracy compared to spatial-only methods.
- Comprehensive numerical experiments analyzing the influence of measurement timing, mesh resolution, and measurement noise on reconstruction performance.
- Demonstration of the applicability of the proposed method to the realistic 3D complex geometries and operating conditions of high-voltage ceramic insulators.
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Three-Dimensional Heat Diffusion Equation in Ceramic Insulators
2.2. Inverse Problem with Spatio-Temporal Regularization
- is the time-evolution operator applied over time steps,
- L is the spatial regularization operator (e.g., a central difference matrix),
- is the spatial regularization parameter,
- is the temporal regularization operator,
- is the temporal regularization parameter.
3. Numerical Results
Example on a 2D Circle
4. Conclusions
- The reconstruction of the unknown initial condition is strongly dependent on the availability of early measurements. When the first measurement is delayed (e.g., s), the information loss due to thermal diffusion leads to a significant increase in reconstruction error.
- The proposed spatio-temporal regularization consistently outperforms spatial-only regularization. By enforcing both spatial and temporal smoothness, it achieves lower relative errors and better robustness against measurement noise.
- Mesh refinement improves the accuracy of reconstructions; however, its effect diminishes when measurements are taken at later times. This indicates that regularization strategies are more effective than simply refining the mesh for compensating information loss.
- Measurement noise degrades the reconstruction quality in all cases, but the spatio-temporal method exhibits improved stability compared to the spatial approach.
- The framework developed here provides a promising tool for the non-intrusive thermal characterization of ceramic insulators during transient electrical stresses, enabling condition monitoring and predictive maintenance in distribution and subtransmission networks, with potential applications to in the predictive maintenance of electrical insulators.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agüero-Barrantes, P.; Hain, A. Structural Performance of Porcelain Insulators in Overhead Railway Power Systems: Experimental Evaluations and Findings. Infrastructures 2024, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Bhatti, A.R.; Rasool, A.; Rehman, F.U.; Khan, M.A.; Ali, A.; Sherefa, A. Performance analysis of high voltage disc insulators with different profiles in clean and polluted environments using flashover, withstand voltage tests and finite element analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, J.L. Linear and non-linear thermal system identification based on the integral of non-integer order—Application to solve inverse heat conduction linear and non-linear problems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 197, 108840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, Z.; Li, E.; Wang, H. Practical uncertainty quantification for space-dependent inverse heat conduction problem via ensemble physics-informed neural networks. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 147, 106940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergagio, M.; Li, H.; Anglart, H. An iterative finite-element algorithm for solving two-dimensional nonlinear inverse heat conduction problems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 126, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, C.F.; Nieuwenhuizen, R.; van der Geld, C.W.; Kuerten, H.G.; Bsibsi, M.; van Esch, B.P. Inaccuracies in the inverse heat conduction problem solution and their effect on the estimation of heat fluxes during quenching. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 194, 122953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.; Geng, B.; Ren, J. Inverse estimation of the initial condition for the heat equation. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2013, 82, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzola, S.; Hansen, P.C.; Nagy, J.G. IR Tools: A MATLAB package of iterative regularization methods and large-scale test problems. Numer. Algorithms 2019, 81, 773–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, S.; Phirani, J.; Bahga, S.S. Fast Bayesian inference for inverse heat conduction problem using polynomial chaos and Karhunen–Loeve expansions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 219, 119616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaloul, N.; Daouas, N. An extended approach of a Kalman smoothing technique applied to a transient nonlinear two-dimensional inverse heat conduction problem. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 134, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.D.; Dhiman, S. Solutions of one-dimensional inverse heat conduction problems: A review. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2023, 47, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satmoko, A.; Kosasih, E.A.; Antariksawan, A.R.; Kılıç, M.; Zikri, A.; Al Ghafari, M.A.; Kas Yudamaulana, M.; Sholihat, S.S. Measurement of thermal conductivity using 2D inverse heat conduction problem approach by identifying simultaneously the heat dissipation phenomena. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 74, 106887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.A.; Al-Soufi, K.; Asif, M.; Alhems, L. Impact of damaged housing on the performance of field aged composite High Voltage Insulators. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 166, 108876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.A.; Alawady, A.A.; AL-Gailani, S.A.; Amer, A.A.G.; Al-Ameri, S.M.; Abd-Rahman, R.; AL-Gailani, N.A. Characterization of the impact of coating defects on ceramic insulator efficiency: Machine learning approaches. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 238, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloum, M.R.; Reddy, B.S.; Reddy, G.N. Failure analysis of field-aged polymeric outdoor insulators and performance enhancement for electric stress using nonlinear field grading composites. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Velasquez, L.F.; Giraldo, E. Nonlinear Heat Diffusion Problem Solution with Spatio-Temporal Constraints Based on Regularized Gauss–Newton and Preconditioned Krylov Subspaces. Eng 2025, 6, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Velasquez, L.F.; Giraldo, E. Nonlinear Dynamic Inverse Solution of the Diffusion Problem Based on Krylov Subspace Methods with Spatiotemporal Constraints. Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oñate, E.; Zárate, F.; Idelsohn, S.R. Finite element formulation for convective–diffusive problems with sharp gradients using finite calculus. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2006, 195, 1793–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, K.; Najafi, H.; de Monte, F.; Beck, J. Inverse Heat Conduction Problems. In Inverse Heat Conduction; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; Chapter 1; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cam, B. 12 kV Post Insulator: 3D Model of a Porcelain Post Insulator for 12 kV Distribution Systems. Published 24 May 2017. Available online: https://grabcad.com/library/12kv-post-insulator-2 (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Callister, W.D.; Rethwisch, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 9th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, P.C. Regularization Tools version 4.0 for Matlab 7.3. Numer. Algorithms 2007, 46, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belge, M.; Kilmer, M.E.; Miller, E.L. Efficient determination of multiple regularization parameters in a generalized L-curve framework. Inverse Probl. 2002, 18, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




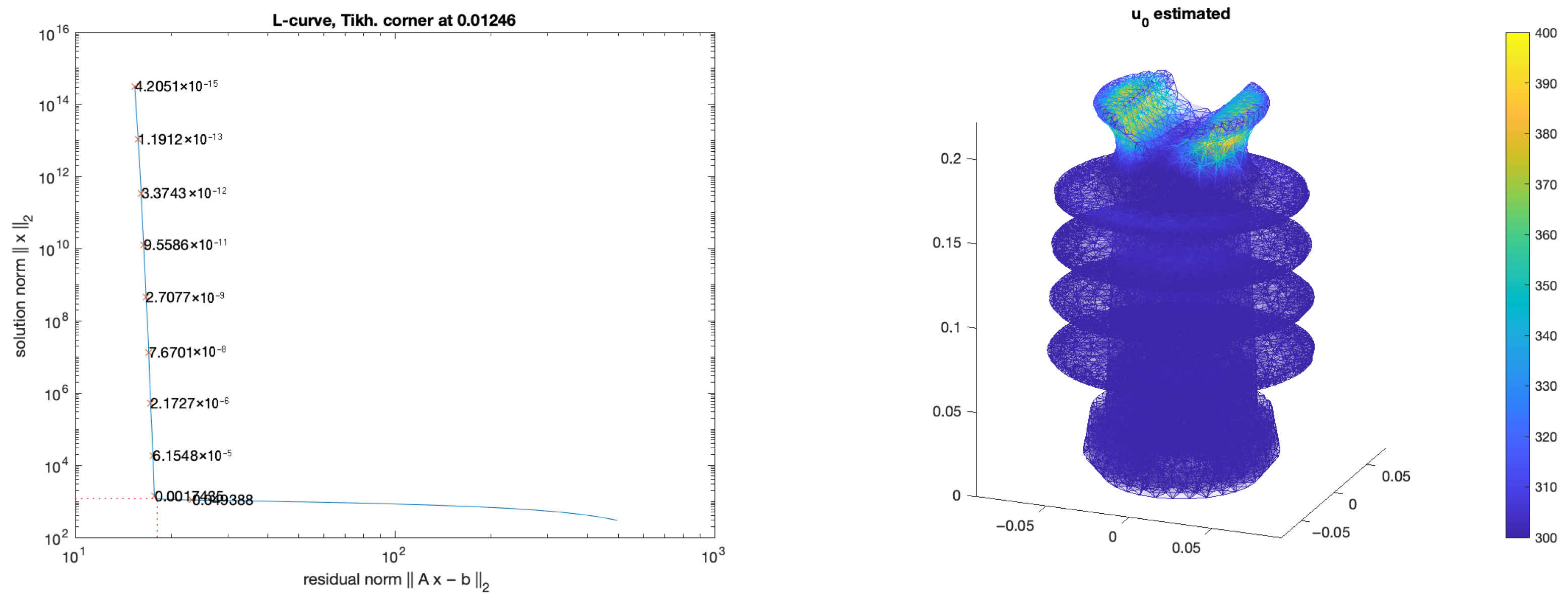
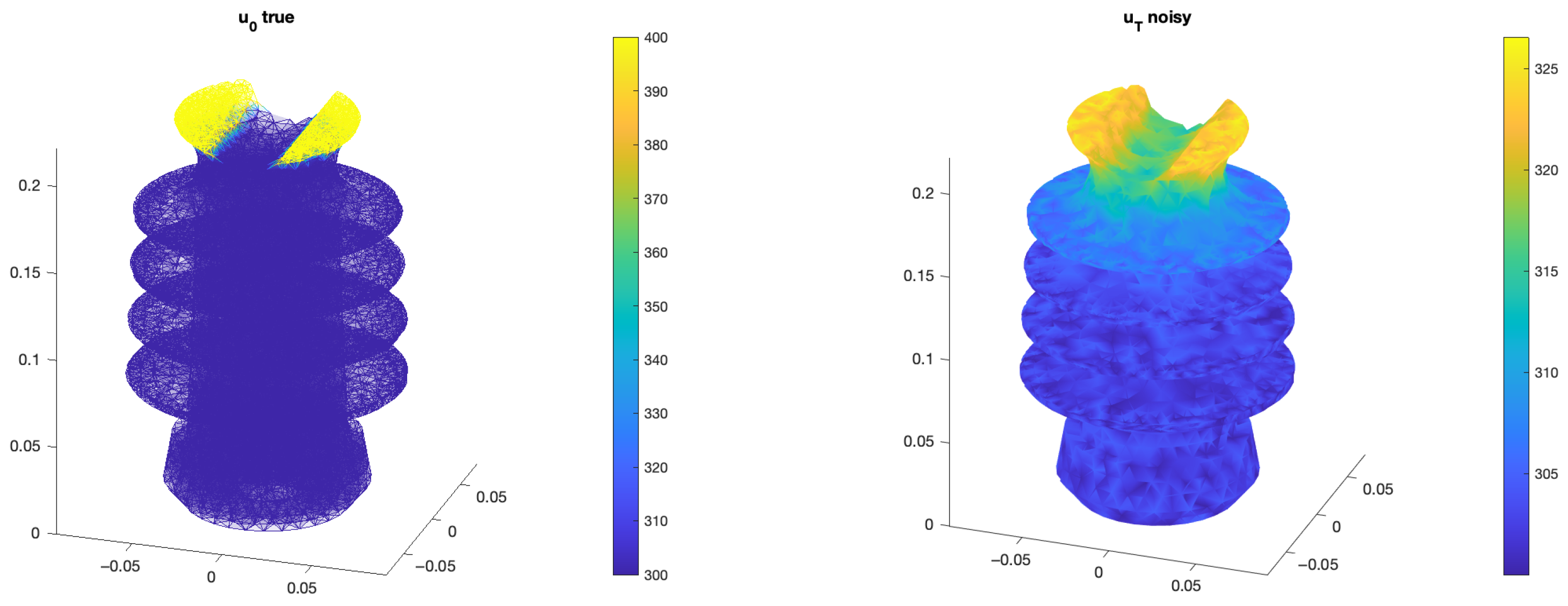
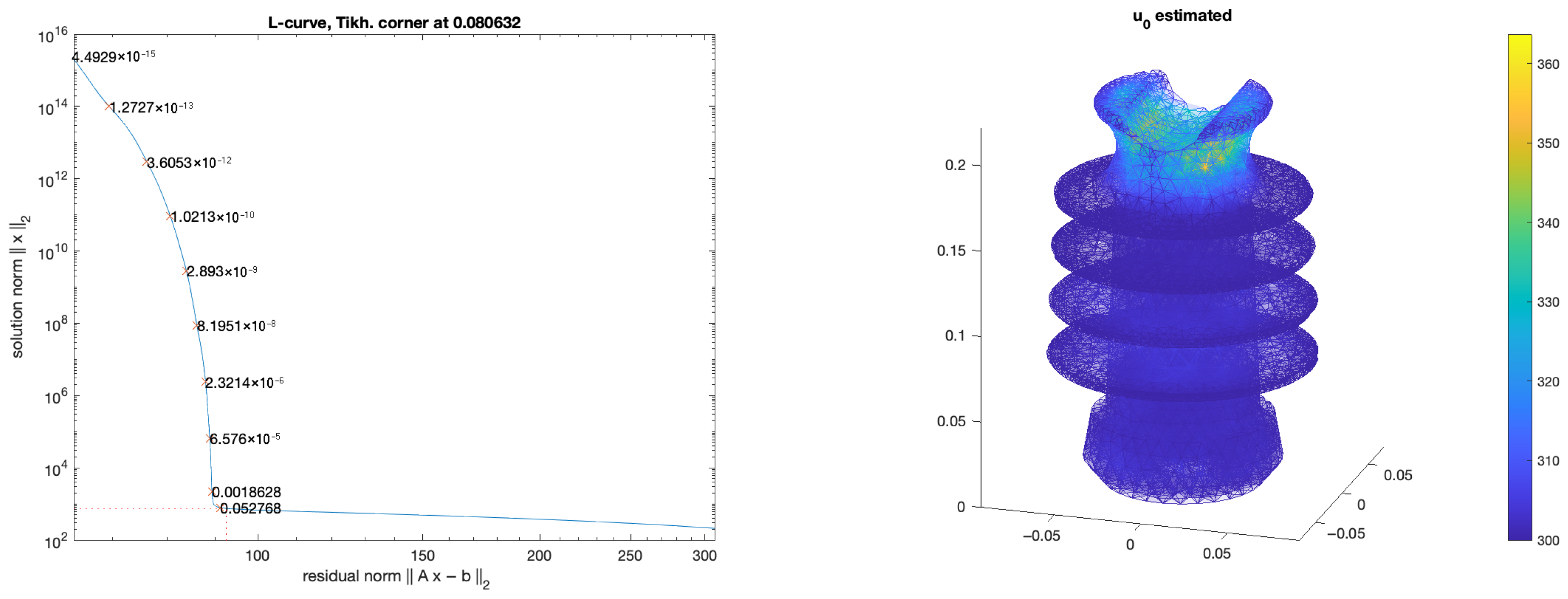

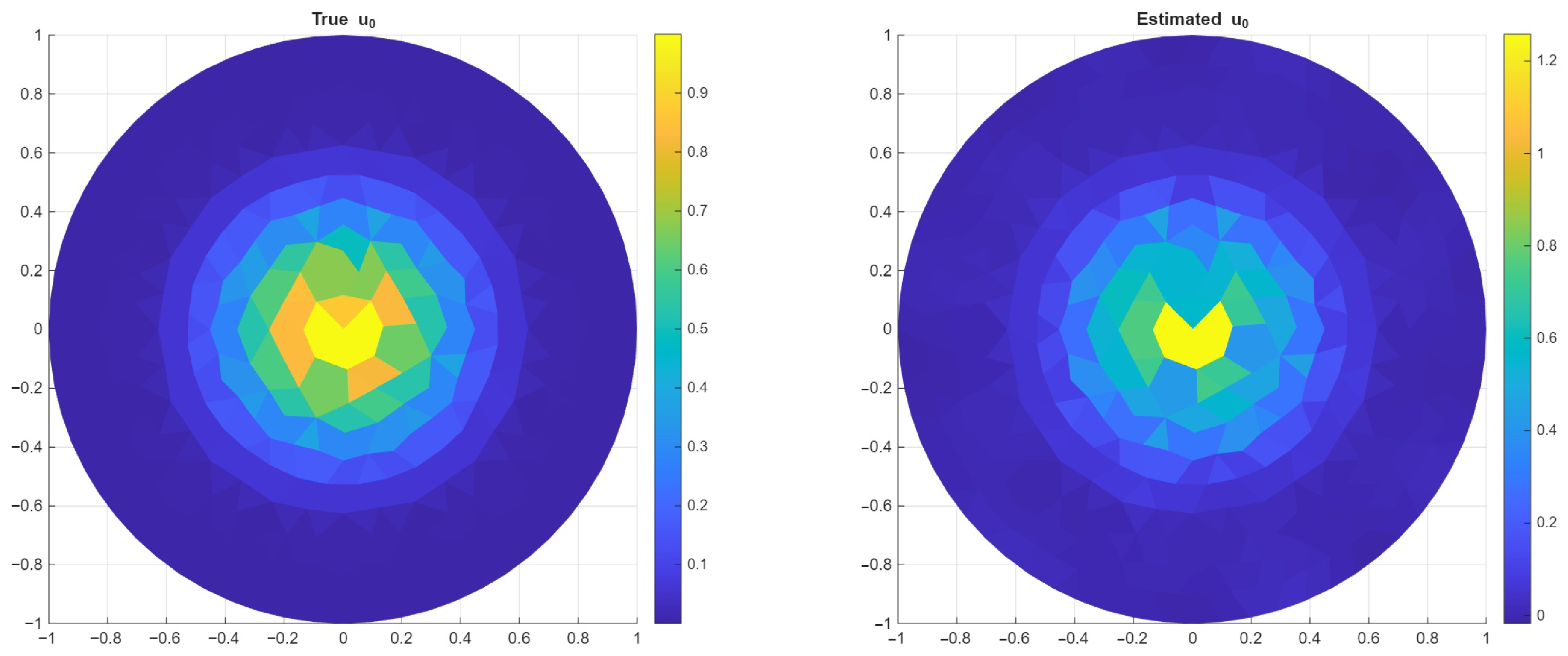


| Element Size | 20 mm | 15 mm | 10 mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of finite elements | 2334 | 3584 | 5323 |
| Surface elements for measurements | 1864 | 2849 | 3930 |
| Element Size | 20 mm | 15 mm | 10 mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial | ||||
| 0.0105 | 0.0107 | 0.0095 | ||
| 0.4915 | 0.4825 | 0.4806 | ||
| 0.0598 | 0.0584 | 0.0487 | ||
| 0.5861 | 0.5545 | 0.5262 | ||
| Spatio-temporal | ||||
| 0.0105 | 0.0107 | 0.0095 | ||
| 0.0169 | 0.0162 | 0.0162 | ||
| 0.4216 | 0.4168 | 0.4106 | ||
| 0.0598 | 0.0584 | 0.0487 | ||
| 0.0797 | 0.0635 | 0.0095 | ||
| 0.5709 | 0.5392 | 0.5041 | ||
| Element Size | 20 mm | 15 mm | 10 mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial | s | s | s |
| Spatio-temporal | s | s | s |
| s | s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element Size | 20 mm | 15 mm | 10 mm | 20 mm | 15 mm | 10 mm | |
| 0.0182 | 0.0152 | 0.0125 | 0.0356 | 0.0353 | 0.0242 | ||
| 0.8572 | 0.8319 | 0.7955 | 0.9369 | 0.9393 | 0.9170 | ||
| 0.0894 | 0.0814 | 0.0522 | 0.0968 | 0.1012 | 0.0806 | ||
| 0.8800 | 0.8641 | 0.8212 | 0.9510 | 0.9502 | 0.9309 | ||
| s | s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element Size | 20 mm | 15 mm | 10 mm | 20 mm | 15 mm | 10 mm | |
| 0.0208 | 0.0170 | 0.0147 | 0.0348 | 0.0338 | 0.0135 | ||
| 0.0072 | 0.0060 | 0.044 | 0.0041 | 0.0033 | 0.0035 | ||
| 0.8432 | 0.8134 | 0.7355 | 0.9329 | 0.9338 | 0.9039 | ||
| 0.0894 | 0.0814 | 0.0522 | 0.0968 | 0.1022 | 0.0806 | ||
| 0.0371 | 0.0235 | 0.024 | 0.0181 | 0.0158 | 0.0119 | ||
| 0.8764 | 0.8606 | 0.8076 | 0.9501 | 0.9487 | 0.9297 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez-Velasquez, L.F.; Giraldo, E. Linear Heat Diffusion Inverse Problem Solution with Spatio-Temporal Constraints for 3D Finite Element Models. Computation 2025, 13, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13110255
Alvarez-Velasquez LF, Giraldo E. Linear Heat Diffusion Inverse Problem Solution with Spatio-Temporal Constraints for 3D Finite Element Models. Computation. 2025; 13(11):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13110255
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez-Velasquez, Luis Fernando, and Eduardo Giraldo. 2025. "Linear Heat Diffusion Inverse Problem Solution with Spatio-Temporal Constraints for 3D Finite Element Models" Computation 13, no. 11: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13110255
APA StyleAlvarez-Velasquez, L. F., & Giraldo, E. (2025). Linear Heat Diffusion Inverse Problem Solution with Spatio-Temporal Constraints for 3D Finite Element Models. Computation, 13(11), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13110255







