Buckling Assessment in the Dynamics Mechanisms, Stewart Platform Case Study: In the Context of Loads and Joints, Deflection Positions Gradient
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Evaluation and Context
1.2. Objective of This Research
2. Methodology
2.1. Theory
- The upper part exerts two different loads on the arms: a constant force due to its weight and a dynamic load that changes over time;
- Each arm has a segment with a uniform shape, without any joints or actuators;
- The deflection solution assumes that the tilt angle of the arms remains constant. (This assumption is valid because the solution is focused on a particular moment and is not dependent on time, making it reasonable to consider a fixed tilt angle.).
2.2. Slope of the End of the Arm
2.3. Critical Stress and Self-Bucking
3. Case Study via Numerical Approach
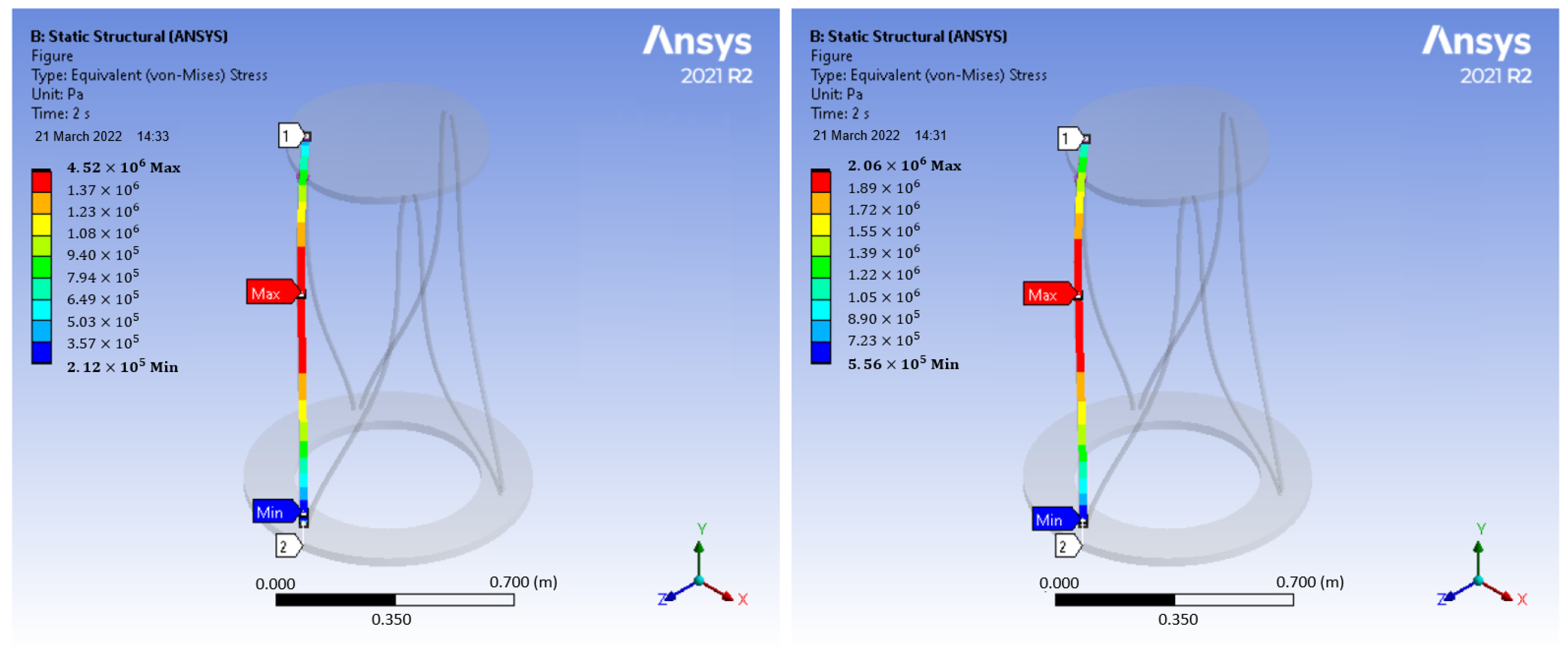
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Platform Arm Deflection
4.2. Critical Buckling Stress
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, C.C.; Ong, S.K.; Nee, A.Y.C. Design and development of 3–DOF modular micro parallel kinematic manipulator. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 31, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gough, V.E.; Whitehall, S.G. Universal Tyre Test Machine. In Proceedings of the 9th International Congress FISITA, London, UK, 30 April–5 May 1962; pp. 117–137. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, D. A Platform with Six Degrees of Freedom. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1965, 180, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlet, J.P. Parallel Robots; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, L.J. An Optimization Approach to the Determination of Manipulator Workspaces. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin, C.; Hamel, J.F. The agile eye: A high-performance three-degree-of-freedom camera-orienting device. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–13 May 1994; Volume 1, pp. 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Stoughton, R.; Homma, K.; Adachi, H.; Nakamura, T.; Nakashima, K. Development of a parallel link manipulator. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Advanced Robotics ’Robots in Unstructured Environments, Pisa, Italy, 19–22 June 1991; Volume 1, pp. 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.P.; Dunlop, G.R. Analysis of rigid-body dynamics for closed-loop mechanisms—Its application to a novel satellite tracking device. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2003, 217, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecht, D.K. A 3-DOF Stewart Platform for Trenchless Pipeline Rehabilitation. Master’s Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2015. Available online: https://ir.lib.uwo.ca/etd/3156 (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Dasgupta, B.; Mruthyunjaya, T. The Stewart platform manipulator: A review. Mech. Mach. Theory 2000, 35, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlet, J.P. Parallel manipulators: State of the art and perspectives. Adv. Robot. 1993, 8, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyman, J.A.; du Plessis, L.J.; Duffy, J. An Optimization Approach to the Determination of the Boundaries of Manipulator Workspaces. J. Mech. Des. 1998, 122, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazard, D.; Merlet, J.P. The (true) Stewart platform has 12 configurations. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–13 May 1994; Volume 3, pp. 2160–2165. [CrossRef]
- Furqan, M.; Suhaib, M.; Ahmad, N. Studies on Stewart platform manipulator: A review. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 4459–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.Q.; Wu, D.; Ding, H.; Chen, L.Q. Vibration isolation and energy harvesting integrated in a Stewart platform with high static and low dynamic stiffness. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 89, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Rui, X.; Zhu, W.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J. Modeling and control of magnetorheological 6-DOF stewart platform based on multibody systems transfer matrix method. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 035029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svinin, M.; Hosoe, S.; Uchiyama, M. On the stiffness and stability of Gough-Stewart platforms. In Proceedings of the 2001 ICRA—IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 01CH37164), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 21–26 May 2001; Volume 4, pp. 3268–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, L.P. Stiffness analysis of a Stewart platform-based parallel kinematic machine. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 02CH37292), Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 May 2002; Volume 4, pp. 3672–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adli, M.A.; Nagai, K.; Miyata, K.; Hanafusa, H. Analysis of Internal Force Effect in Parallel Manipulators. Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control Eng. 1991, 27, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Beer, F.; Johnston, E.; DeWolf, J.; Mazurek, D. Mechanics of Materials, 8th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. Determinatio onerum, quae columnae gestare valent. Acta Acad. Sci. Petropolitanae 1978, 1, 121–145. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. Examen insignis puradoxi in theoria columnarum occurentis. Acta Acad. Sci. Petropolitanae 1978, 1, 146–162. [Google Scholar]
- Euler, L. De Altitudine columnarum sub proprio pondere corruentium. Acta Acad. Sci. Petropolitanae 1978, 1, 163–193. [Google Scholar]
- Castigliano, A. The Theory of Equilibrium of Elastic Systems and Its Applications; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Ansys Workbench Teaching Version; Ansys Inc.: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2021.
- Dinnik, A.N. Buckling under Own Weight; Don Polytechnical Institute: Rostov-on-Don, Russia, 1912; Volume 1, p. 19. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Willers, F.A. Das Knicken schwerer Gestänge. ZAMM J. Appl. Math. Mech. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 1941, 21, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, H. Die Einheitliche Behandlung der Stabknickung mit Berücksichtigung des Stabeigengewichts in den Eulerfällen 1 bis 4 als Eigenwertproblem: (Exakte Lösungen, Näherungen nach Collatz und Gebrauchsformeln). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Münster, Münster, Germany, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch-Fay, R. On the stability of a strut under uniformly distributed axial forces. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1966, 2, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N. An Introduction to the Finite Element Method, 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers. 1998 ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code, 1998th ed.; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]




| Element Description | Value [Unit] |
|---|---|
| Arm Length | 1230 mm |
| Arm Diameter | 8 mm |
| Internal Height | 1200 mm |
| End-Effector Diameter | 600 mm |
| End-Effector Thickness | 25 mm |
| Base Ring External Diameter | 850 mm |
| Base Ring Internal Diameter | 550 mm |
| Base Ring Thickness | 30 mm |
| Properties | Value [Unit] |
|---|---|
| Density | 7850 Kg/m |
| Young’s Modulus | MPa |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.3 |
| Bulk Modulus | MPa |
| Shear Modulus | MPa |
| Compressive Yield Strength | 2500 MPa |
| Tensile Ultimate Strength | 4600 MPa |
| Tensile Yield Strength | 2500 MPa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassanian, R.; Riedel, M. Buckling Assessment in the Dynamics Mechanisms, Stewart Platform Case Study: In the Context of Loads and Joints, Deflection Positions Gradient. Computation 2023, 11, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11110227
Hassanian R, Riedel M. Buckling Assessment in the Dynamics Mechanisms, Stewart Platform Case Study: In the Context of Loads and Joints, Deflection Positions Gradient. Computation. 2023; 11(11):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11110227
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassanian, Reza, and Morris Riedel. 2023. "Buckling Assessment in the Dynamics Mechanisms, Stewart Platform Case Study: In the Context of Loads and Joints, Deflection Positions Gradient" Computation 11, no. 11: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11110227
APA StyleHassanian, R., & Riedel, M. (2023). Buckling Assessment in the Dynamics Mechanisms, Stewart Platform Case Study: In the Context of Loads and Joints, Deflection Positions Gradient. Computation, 11(11), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation11110227







