A Hybrid Model for Monthly Precipitation Time Series Forecasting Based on Variational Mode Decomposition with Extreme Learning Machine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Theory
2.1. Variational Mode Decomposition
- Step 1:
- Initialize , , , and .
- Step 2:
- Update the value of , , and according to Equations (3)–(5).
- Step 3:
- Judge whether or not the convergence condition (6) is met, then repeat the above steps to update parameters until the convergence stop condition is satisfied.
- Step 4:
- The corresponding mode subsequences are obtained according to the given model number.
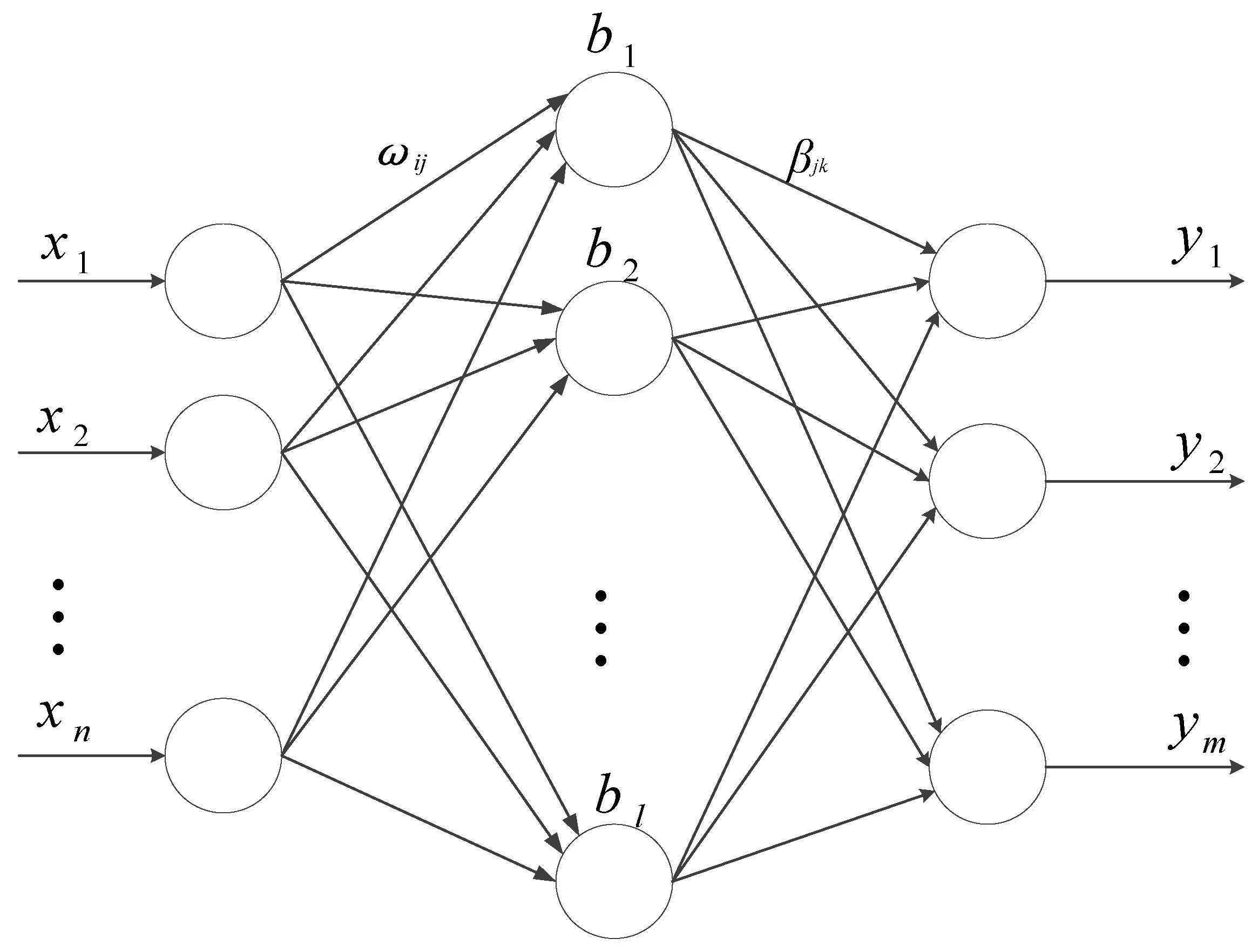
2.2. Extreme Learning Machine
- Step 1:
- Determine the number of hidden layer neurons. Randomly initialize input layer weight and hidden layer threshold .
- Step 2:
- Calculate the hidden layer output matrix H.
- Step 3:
- Calculate the output weight .
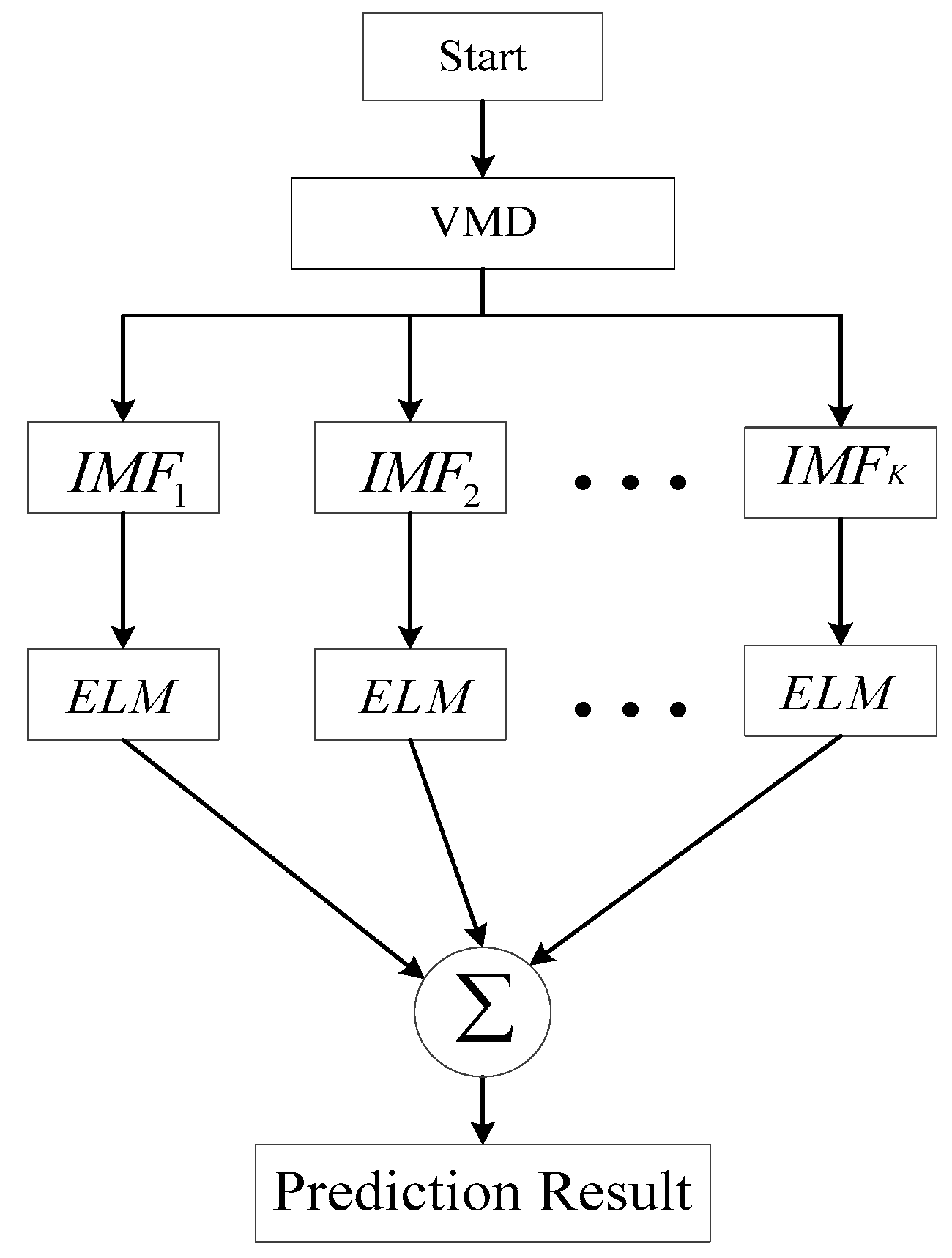
2.3. The Proposed Hybrid VMD-ELM Model
- Step 1:
- Load the original data, and the data is decomposed into a set of IMFs by using VMD method.
- Step 2:
- Set up an ELM prediction model for each IMF. Divide the data of each IMF component into training samples and test samples and all samples are normalized.
- Step 3:
- Determine the number of input layers, output layers, and hidden layers of the ELM model.
- Step 4:
- The established ELM model is used to predict each IMF. The reconstructed IMFs are the final prediction results for the monthly precipitation time series.
3. Data Simulation and Analysis
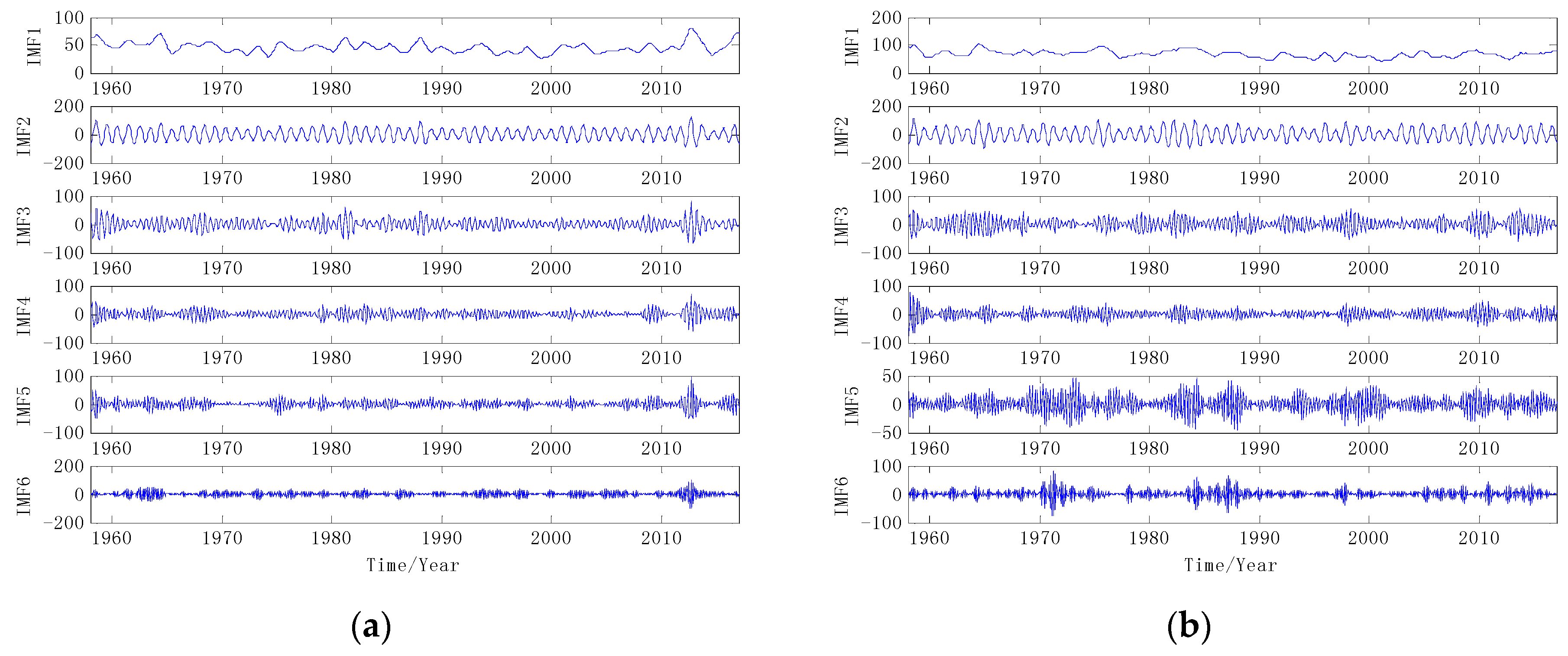
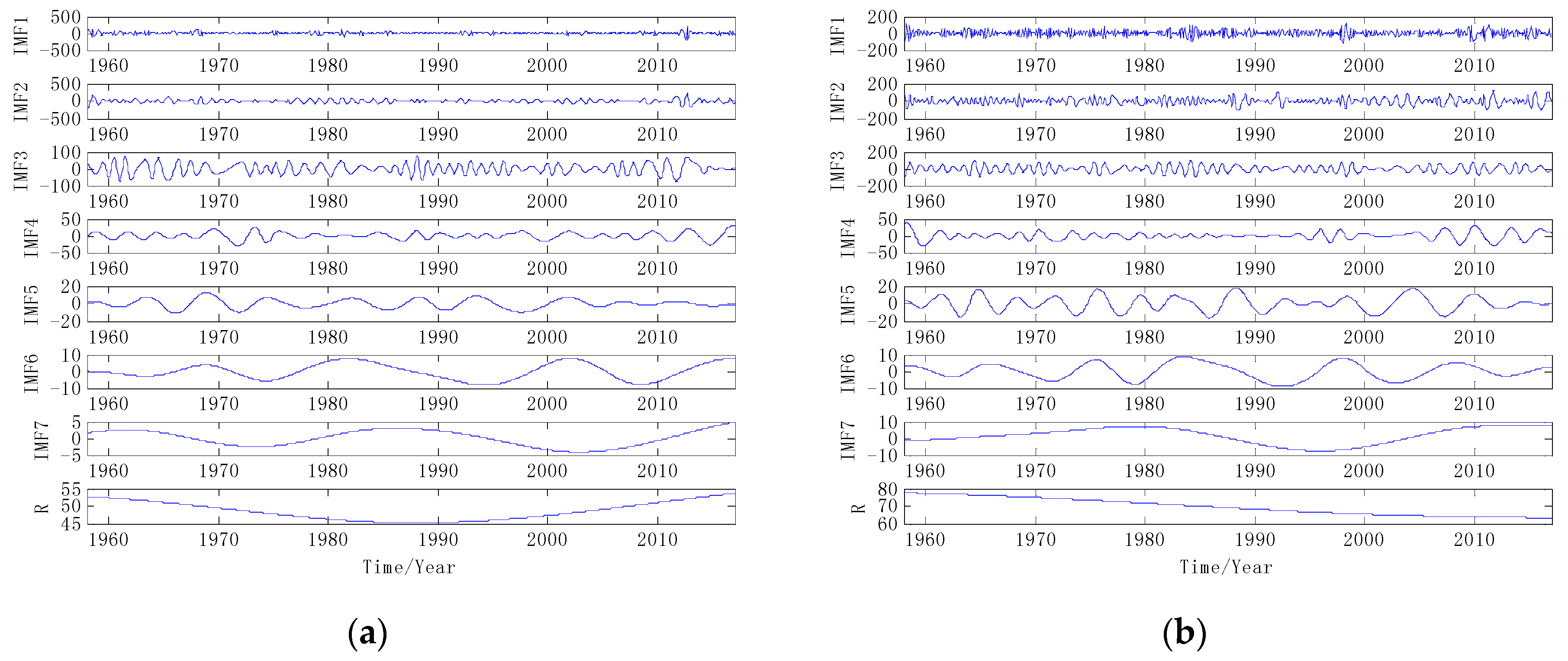
3.1. Data Decomposition Preprocessing
3.2. Performance Standards of Prediction Accuracy
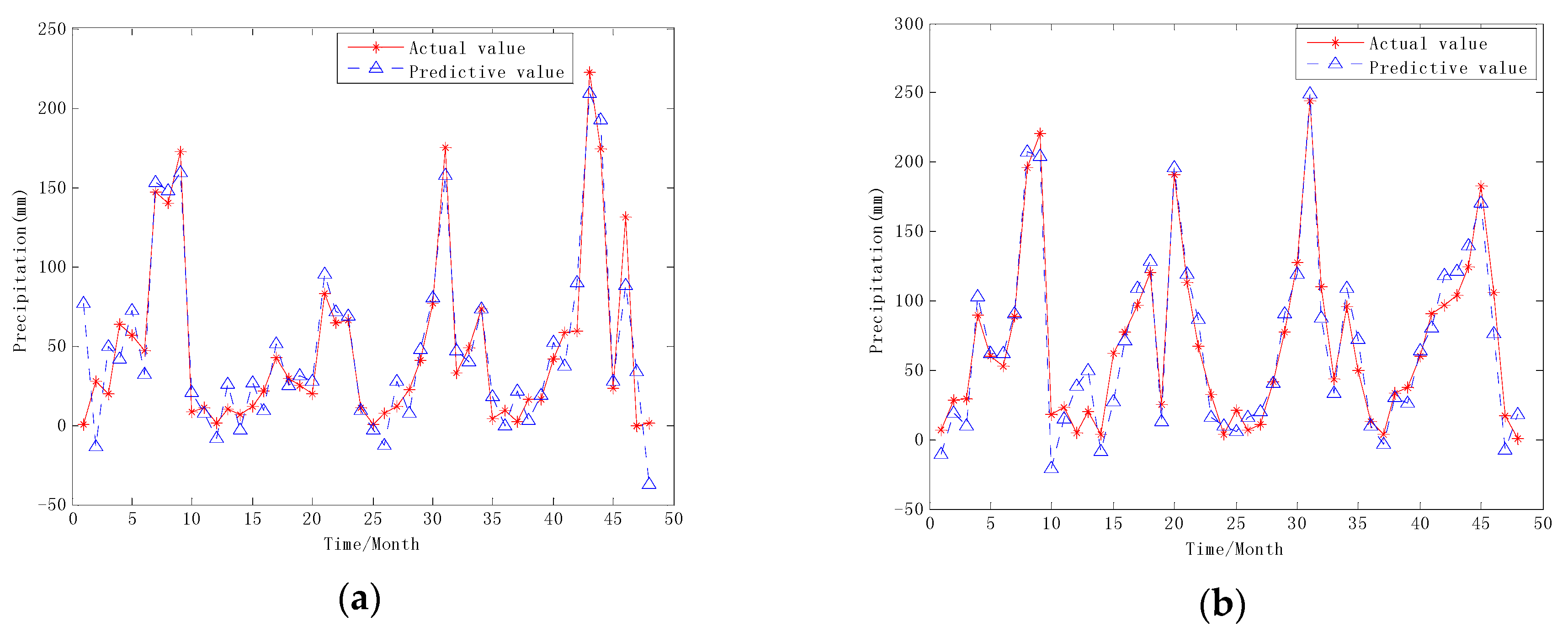
3.3. Component Prediction and Reconstruction
3.4. Results Analysis and Performance Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.C.; Zhang, X.Z.; Dai, E.F.; Song, W. Research of trend variability of precipitation intensity and their contribution to precipitation in China from 1961 to 2010. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Feng, J.Y.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, Y. Climate characteristics of precipitation and extreme drought events in northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.Y.; Fu, J.L.; Chen, F.H. Spatial differences of precipitation over northwest China during the last 44 years and its response to global warming. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2005, 25, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Chau, K.W.; Fan, C. Prediction of rainfall time series using modular artificial neural networks coupled with data-preprocessing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 146–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.M.; Guo, T.L.; Ding, Y.J. A new hybrid forecasting approach applied to hydrological data: A case study on precipitation in Northwestern China. Water 2016, 8, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Q.; Xu, M.X.; Yu, W.Y.; Wen, S.Y. Statistic Markovian model for predicting of annual precipitation. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 25, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.Z.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wu, J.F. Time Series-Markov prediction model for precipitation in the course of evaluation of groundwater resources. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2001, 21, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, Y.T.; Wang, F.L.; Fu, Q. Prediction of annual precipitation based on improved Grey Markov model. Math. Pract. Theory 2011, 41, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Gu, Y.G. Application of Grey forecasting model to area rainfall prediction in upstream of Chanjiang River. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2003, 31, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, D.C.; Zhang, T.N.; Wu, X.M.; Zhang, L.F. Application of ARMA model in the annual precipitation forecast of Taizi River. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2012, 43, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.M. Extended complex autoregressive model of low-frequency rainfalls over the lower reaches of Yangtze River valley for extended range forecast in 2013. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Cai, R.; Aili, N.; Mu, Z.X. Coupling prediction for annual precipitation in Xinjiang based on ARIMA and GA-Elman neural network. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2015, 52, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ye, W. Precipitation prediction of time series model based on BP artificial neural network. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2010, 21, 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, H.; Becker, S.; King, L. Predicting summer rainfall in the Yangtze River basin with neural networks. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 28, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, R.V. Monthly rainfall prediction using wavelet neural network analysis. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3697–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, M.M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.D. Predicting urban PM2.5 concentration in China Using support vector regression. Comput. Eng. Des. 2015, 36, 3106–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.D.; Zhang, B.H.; Yao, F.X.; He, C.X. Verification and forecasting of temperature and humidity in solar greenhouse based on improved extreme learning machine algorithm. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; You, F.; Huang, Q.; Xu, J.X. Least squares support vector machine model of multivariable prediction of stream flow. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2010, 29, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, W.J.; Feng, Z.K.; Cheng, C.T.; Zhou, J.Z. Forecasting Daily Runoff by Extreme Learning Machine Based on Quantum-Behaved Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.L.; Niu, R.Q. Displacement prediction of Baijiabao landslide based on empirical mode decomposition and long short-term memory neural network in Three Gorges area, China. Comput. Geosci. 2018, 111, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.X.; Han, D.; Wang, P.; Wu, Z.C.; Zhang, T.; Wei, Y.M. Forecasting carbon price using empirical mode decomposition and evolutionary least squares support vector regression. Appl. Energy 2017, 191, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yin, F.L. Decorrelation EMD: A new method to eliminating mode mixing. J. Vib. Shock 2015, 34, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmiri, S. Intraday stock price forecasting based on variational mode decomposition. J. Comput. Sci. 2016, 12, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Sun, G.Q.; Li, H.C.; Wei, Z.N.; Zang, H.Y.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Chen, S. Short-term load forecasting based on VMD and PSO optimized deep belief network. Power Syst. Technol. 2018, 42, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Wu, X.T.; Yuan, X.H.; Yuan, Y.B.; Xu, H.P. Prediction of solar irradiation based on improved LSSVM model. Water Resour. Power 2017, 35, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Su, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, P. A Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and an Improved Kernel Extreme Learning Machine. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Wu, Y.J.; Zhen, C.G. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on variational mode decomposition and fuzzy C means clustering. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2015, 35, 3358–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.N.; Yang, Z.J.; Wang, Z.J.; Wang, Y.L. A new compound fault feature extraction method based on multipoint kurtosis and variational mode decomposition. Entropy 2018, 7, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Li, Y.A.; Chen, X.; Yu, J. Denoising and Feature Extraction Algorithms Using NPE Combined with VMD and Their Applications in Ship-Radiated Noise. Symmetry 2017, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N. Hourly solar radiation forecasting based on EMD and ELM neural network. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2014, 34, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.F.; Gan, K.; Sun, S.L.; Li, F.Y. Application of decomposition-ensemble learning paradigm with phase space reconstruction for day-ahead PM2.5 concentration forecasting. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.K.; Zhang, Q.W.; Zhang, G.; Nie, Z.N.; Gui, Z.F. A hybrid model for annual runoff time series forecasting using Elman neural network with ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Water 2018, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wei, Z.N.; Li, H.J.; Kwork, W.C.; Sun, G.Q.; Sun, Y.H. Short-term wind speed interval prediction based on VMD and BA-RVM algorithm. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2017, 37, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, T.; Wei, Z.N.; Sun, Y.H.; Zang, H.X.; Chen, S. A carbon price forecasting model based on variational mode decomposition and spiking neural networks. Energies 2016, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Qin, Y.Z.; Chee, K.S. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Zeng, Z.G.; Yao, W.; Tang, H.M. Ensemble of extreme learning machine for landslide displacement prediction based on time series analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.W. Application of extreme learning machine to total phosphorus and total nitrogen forecast in lakes and reservoirs. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 29, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, J.; Dash, S.; Dash, P.K.; Bisos, R. Short Term Wind Power Forecasting using Hybrid Variational Mode Decomposition and Multi-Kernel Regularized Pseudo Inverse Neural Network. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 180–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

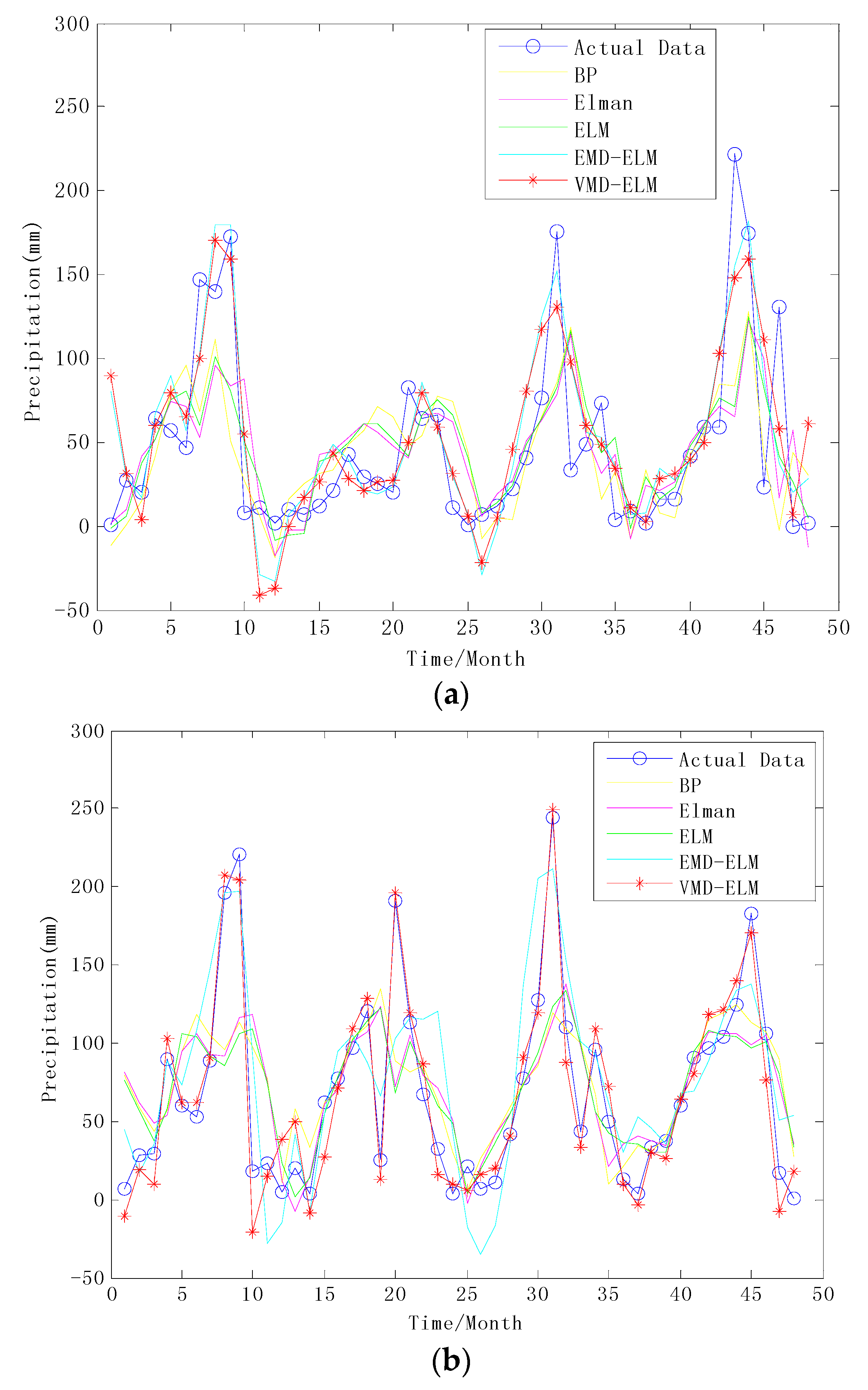
| Place | Models | Error Indicators | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MAPE | ||
| Yan’an | BP | 33.0841 | 49.7006 | 3.3536 |
| Elman | 32.7371 | 47.2576 | 2.7936 | |
| ELM | 30.5377 | 43.6451 | 2.7622 | |
| EMD-ELM | 24.4135 | 32.7755 | 2.1972 | |
| VMD-ELM | 15.2966 | 20.3605 | 1.7217 | |
| Huashan | BP | 37.4068 | 50.8760 | 4.3309 |
| Elman | 35.3464 | 49.2296 | 4.1087 | |
| ELM | 34.2236 | 48.6962 | 3.7824 | |
| EMD-ELM | 29.3452 | 38.2472 | 3.1507 | |
| VMD-ELM | 13.5179 | 16.7612 | 1.9101 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Ma, X.; Yang, H. A Hybrid Model for Monthly Precipitation Time Series Forecasting Based on Variational Mode Decomposition with Extreme Learning Machine. Information 2018, 9, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9070177
Li G, Ma X, Yang H. A Hybrid Model for Monthly Precipitation Time Series Forecasting Based on Variational Mode Decomposition with Extreme Learning Machine. Information. 2018; 9(7):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9070177
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guohui, Xiao Ma, and Hong Yang. 2018. "A Hybrid Model for Monthly Precipitation Time Series Forecasting Based on Variational Mode Decomposition with Extreme Learning Machine" Information 9, no. 7: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9070177
APA StyleLi, G., Ma, X., & Yang, H. (2018). A Hybrid Model for Monthly Precipitation Time Series Forecasting Based on Variational Mode Decomposition with Extreme Learning Machine. Information, 9(7), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/info9070177





