Abstract
The Information and Communication Technology Master Plan—ICTMP—is an important tool for the achievement of the strategic business objectives of public and private organizations. In the public sector, these objectives are closely related to the provision of benefits to society. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) actions are present in all organizational processes and involves size-able budgets. The risks inherent in the planning of ICT actions need to be considered for ICT to add value to the business and to maximize the return on investment to the population. In this context, this work intends to examine the use of risk management processes in the development of ICTMPs in the Brazilian public sector.
1. Introduction
Information Communication Technology has become more sophisticated, a willingness to share information among organizations and stakeholders may become a major factor to those actively seeking information and resources to make value-added products [1].
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) plays an increasingly important role for public and private organizations in order to achieve their goals and fulfill its institutional mission. ICT actions need to be aligned with the organization’s strategy to enhance the added value to the business concerned with risk minimization. The aggregate value of ICT to business and the risks minimization related to ICT are considered the main objectives of ICT governance [2], which, in turn, is an integral part of corporate governance [3].
ICT risk management is a subject that needs to be well communicated and understood by management. Since the adaptation of ICT into the business is continually growing, all of the inherent risks of using ICT must be very well managed in order to support the decision-making process. It is a fact that ICT is very unique in its nature of development and complexity. Thus, a strong foundation of management skills is needed [2].
The management of ICT risks should form an integral part of the Federal Public Administration (FPA) in Brazil risk management strategy and policies. Risk management involves identification of risks concerning existing applications and ICT infrastructures, and continuous management, including an annual/periodic review and update by the management of the risks and monitoring of mitigation strategies.
In recent years, the Federal Court of Accounts—FCA—has been conducting several studies in order to obtain information on the state of ICT governance and ICT risk management in the FPA, so it can act as an inducer of the ICT governance improvement process.
The first ICT governance survey in the FPA was held in 2010 and saw the participation of 255 institutions. The second survey was held in 2015 and evaluated 301 institutions. The latest study was conducted in 2017, included 350 institutions, and aimed to monitor and maintain an updated database with the ICT governance situation in FPA, deepening the panorama outlined in 2015.
According to the latest survey, with regard to institutional and ICT planning, the improvement of these instruments and a trend of continuing evolution of ICT Governance were found. However, the obtained results still cause concern, given the number of institutions that still have not given due importance to the strategic planning process, which tends to compromise its performance. Organizations need to promote a culture for strategically planning their actions and not just react to the demands and changes taking place.
In relation to ICT planning, more specifically to the ICT Master Plan (ICTMP), it was found that almost half of the organizations did not approve or published the ICTMP internally or externally. Risk management is an important control tool to be considered during the preparation of planning instruments of public institutions, especially in ICTMP, and the main ICT planning tool at the tactical level, the object of study of this work.
Institutions must anticipate and prevent risks to the organization’s set of processes that may prevent or hinder the achievement of its objectives [4]. Among the potential effects of non-application of risk management, the organization has inefficient use of resources; ignorance of the risks to which the institution critical processes are exposed; and absence of solid criteria for planning and prioritization of information security actions [5].
In front of this scenario, this paper aims to analyse the risk management process in the preparation of ICTMP in the public sector in order to obtain information about the use of risk management mechanisms for the development of the ICTMP at FPA agencies and entities. Therefore, we have defined the following research question: Is Risk Management Important for the ICTMP Development? To achieve this goal, a survey was conducted and divided in two stages. Because it is a relatively unexplored matter, the first stage, aimed to identify and understand the context of the use of risk management in ICTMP of FPA agencies and entities. At this stage, it used a method of exploratory nature. The second stage, a descriptive one, evaluated the risk management mechanisms available in ICTMPs using as a reference the procedures recommended by [6], a standard that covers the principles and guidelines of risk management.
The analysis performed in this work will allow the Federal Public Administration to value the importance of its achievement of risk management, when it elaborates its strategic planning.
The rest of this paper is is organized as follows. Section 2 presents an overview of issues related to institutional planning and ICT instruments in the public sector, and likewise explores risk management in national and international public domains. In Section 3, the search tools used are addressed. The results obtained from the research in Section 4. The conclusions and future work are presented in Section 5.
2. Literature Review
Risk Management (RM) refers to the coordinated activities to direct and control an organization with regard to risks. In this context, the risk is the effect of uncertainty in objectives, where effects can be understood as a deviation from the expected—positive or negative [7].
From the view of [7], risk is the possibility that an event will occur and adversely affect the achievement of objectives. In this work, the broader concept is adopted which is advocated for by the standard that considers that the risk may give rise to positive or negative impacts.
According to [8], there is no real risk or objective. The implication is that risk is not something that is waiting to be measured independently of our minds, cultures, policies or views of the world—it is inherently subjective. To protect oneself against all risks is impossible because any opportunity invariably entails risks [8].
2.1. Risk Management in the Public Sector
In recent years, the use of the risk management in a public sector became important in some countries. Javani and Rwelamila [9] studied the South African case. They found a significant statistical support for the conclusion that risk management is being applied in IT projects and that it is understood by project clients, although risk management status in the South African public sector is little known.
In Thailand, Kongmalai et al. [10] found empirical evidence of corporate governance in state-owned enterprises. They develop a multi-attribute pattern of the corporate governance model and provide detailed information of each corporate governance practice, including risk management.
In Indonesia, Amali et al. [11] discussed a framework of Information Technology governance in the Public Sector where there is an absence of IT resource, IT strategic alignment and risk management. The results showed the local need for that framework.
In Canada, Leung and Frances [12] studied the risk management in public sector based on the National Research Council (NRC). They map multiple sources of strategic and operational risks, which might arise from political and other stakeholder interests, intellectual property ownership and policy, funding structures, public perceptions of science and technology, occupational health and safety, management of highly qualified personnel, and others.
Risk management in the Brazilian public sector is still a relatively unexplored subject. The FCA started a survey on risk management in the federal indirect administration, in order to understand and evaluate the risk management maturity of these entities. The instrument used for the survey is based on recognized international standards, such as [6].
The only way for public organizations to manage the responsibilities and protect citizens is to implement their risk management [13].
According to [14], the government’s ability to manage risk depends on the skills of its employees. Therefore, the ability to manage risk is broader than the concern with scientific capacity.
The scientists need to know that making proper scientific analysis and the effective risk management in the context of public policy also requires the ability to make the right questions about scientific issues, risks, public perception and policy options and how these factors can be related to each other.
According to [15], the main points to be noted in order to implement risk management in the public administration are:
- To ensure that decision-making takes into account the risks, so that risk management becomes a requirement for the decision-making process;
- To ensure that risk management is effectively established and that the tools and methods selected are applied;
- To organize itself for risk management, ensuring that the responsibility for dealing with risks be of those best prepared for their management and that the flow of information supports the division of such tasks;
- To develop skills to ensure that those responsible for decision-making are prepared to understand and analyze the risks and that they are advised by experienced professionals, if necessary;
- To ensure quality by adopting standards and benchmarking practices;
- Manage risk communication to the public;
- To ensure that the government has a leading and stimulating role for cultural change.
According to [16], the risk management process in the public sector is increasingly better understood; however, the knowledge of these elements and of the associated processes does not guarantee appropriate treatment of risks in an organization. Effective risk management requires a risk assessment culture that supports a holistic approach to risk identification and management throughout the organization.
According to [17], risk assessment is inherently subjective and represents a mixture of scientific observations and individual judgments with significant psychological, social, cultural and political factors. The one who controls the definition of a risk, controls the rational solution to the problem under discussion. When a risk is defined in a particular way, a specific option will appear as the most effective in terms of costs, for being the safest or the best. When it is defined otherwise, perhaps incorporating qualitative characteristics and other contextual factors, the ordering of possible solutions tends to be different. Defining risk, therefore, is an exercise of power.
The limitations of risk science, the importance and the difficulty to maintain the trust and the complex and socio-political nature of risks point out the need to adopt a new approach—an approach focused on more public participation in the evaluation and decision-making involving risks, so that the decision-making process can be more democratic; relevance and technical analysis quality be improved and the resulting decisions have more legitimacy and greater public acceptance. Risk management has improved significantly, but project success rates have failed to improve at the same rate. Attained improvements are also seen to deteriorate remarkably quickly, and the development is topped with real dilemmas. The five specific challenges in uncertainty analysis identified indicate that even professional risk managers and their teams do not have the right competences, adequate planning data or effective procedures to properly identify risks and uncertainties, quantify and analyze them, communicate them to decision makers or incorporate the consequences into their risk management [18,19].
In [7], the principles and general guidelines on risk management for any type of organization, groups or individuals in general are provided. It can be applied to various activities, including strategies, decisions, operations, processes, projects, services and assets.
According to [7], an organization should, at all levels, meet a set of eleven principles for risk management (RM) to be effective. Among them, risk management should:
- Create and protect value—RM contributes to the demonstrable achievement of objectives and to the performance improvement of various aspects, such as security, legal compliance, environmental protection, product quality, operations efficiency, governance and reputation;
- Be an integral part of all organizational processes—the RM is not an autonomous activity separated from main activities and organizational processes. It is part of management’s responsibilities and is an integral part of all organizational processes, including strategic planning and all project management processes and change management;
- Be part of decision-making—RM helps decision makers make informed choices, prioritize actions and distinguish among alternative courses of action;
- Be systematic, structured and timely—a systematic approach, timely and structured to risk management contributes to efficiency and conscious, comparable and reliable results;
- Be transparent and inclusive—the proper and timely involvement of stakeholders and, in particular, of decision makers at all levels of the organization ensures that risk management remains relevant and updated. In addition to the principles and structure, the standard also establishes the risk management process that can be used by any type of organization. It is appropriate that the risk management process be an integral part of management, incorporated into the culture and the organization’s practices and be tailored to the organization’s business processes. Figure 1 shows the risk management process defined in [7].
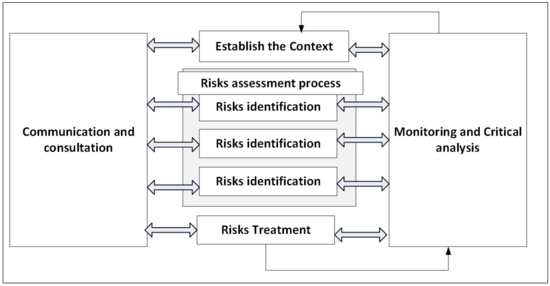 Figure 1. Risk management process [7], adapted.
Figure 1. Risk management process [7], adapted.
The process of communication and consultation aims to ensure that communication and consultation with internal and external stakeholders occur during all stages of the risk management process. The establishment of a context provides the scope and risk criteria and sets the external and internal parameters that must be considered in risk management [20].
The process of risk assessment is considered the overall process of risk identification, risk analysis and risk assessment. Treatment of risks involves the selection of the most suitable alternatives to modify the risks, together with the plans necessary to implement them. In turn, the process of monitoring and critical analysis aims to ensure that controls related to risks are effective and efficient, as well as to obtain additional information to improve the process of risk assessment [20].
2.2. Institutional Planning in the Public Sector
Huang [21] established an analytical framework for exploring the ICT-oriented urban planning experience of Taipei City. He tests the limitations and application of the framework. The study finds technological trends, physical infrastructure and ICT content.
In Jordan, Onizat et al. [22] evaluate the ICT process in the Jordanian e-Government program. They found the lack of the systematic evaluation process as the main reason for the retreating of the e-Government program in Jordan.
The institutional planning in the Brazilian public sector is governed by a set of constitutional provisions. In addition to being mandatory, the planning activity enhances the achievement of established goals and assists in the perception of predictability of results.
The Constitution of the Federal Republic of Brazil of 1988 (CF/1988—[23]) states that, as the normative and regulating agent of the economic activity, the State shall, in accordance with the law, exercise supervisory, incentive and planning functions, which are crucial for the public sector and indicative for the private sector.
In addition, it states that the direct and indirect public administration of any of the powers of the Union, the States, the Federal District and the Municipalities shall obey the principles of legality, impersonality, morality, publicity and efficiency (...). The Multi-Year Plan (MYP) is the main and most comprehensive planning tool for agencies and entities of the Federal Public Administration. It should contain the guidelines, objectives and goals of the federal government for capital expenditures and others due and for those related to continuous programs [24].
Every year’s planning (annual budget) can not contradict the MYP determinations. Thus, it becomes mandatory for the Government to plan its actions aligned to the budget. The Budget, through the Budget Guidelines and Annual Budgets, translates the plan into financial terms and goals for a financial year, adjusting the pace of implementation of the flow of funds in order to ensure the timely release of funds [24].
The Institutional Strategic Plan (ISP) is also an essential tool for organizations. Strategic planning is a process of determining the main objectives of an organization, the policies and strategies that will govern it and the use and availability of resources to achieve these objectives, consisting of assumptions, planning itself, implementation and review [25,26].
2.3. ICT Planning in the Public Sector
The ICT planning in the public sector, similar to the private area, is used to declare the strategic objectives and initiatives of ICT by aligning information technology solutions to the organization’s goals. It constitutes also an important addition to ISP, including guidelines and cross-cutting actions, i.e., that support business goals in all areas of the institution, as well as structural and regulatory objectives of the Federal Public Administration–APF agencies [27,28].
Strategic planning at public and private organizations should be complemented by the planning of information systems, knowledge and information. This planning is also known as Strategic Information Technology Planning—SITP. Both must be integrated and aligned [29]. It establishes guidelines and goals that guide the construction of the organization’s ICT planning. At the tactical level, the most commonly used instrument to represent the ICT planning is the Information Technology Master Plan—ICTMP [29]. This instrument shows tactically how an organization, with regard to information technology, can make the transition from a current situation to a future situation, from the definition of a plan of goals and actions.
The ICTMP is defined as a diagnostic, planning and management tool of resources and information technology process that aims to meet the technological needs and information of an agency or entity for a certain period [29]. In addition, it states that ICT procurement must be preceded by planning, prepared in accordance with the ICTMP, which, in turn, should be aligned with the strategic planning of the body [29].
The ICTMP must set indicators in accordance with the strategic objectives of ICT, and include the planning of necessary investments, budget proposal, quantitative and training of people and identification and treatment of related ICT risks. It is extremely important that the ICTMP provides the alignment of ICT solutions to business goals and the organization’s needs [29]. In addition, the strategic alignment and risk mitigation, value delivery, resource management and performance measurement are considered key areas of ICT Governance [30].
ICTMP Development in the Brazilian Public Sector
The Administration of Information and Computer Resources System (AICRS) aims to organize the operation, control, supervision and coordination of information resources and information of direct, independent and foundation of the Federal Executive Branch.
The Preparation Guide for the Information Technology Master Plan (ICTMP) of AICRS, which aims to provide information to assist the development of ICTMP, with content and minimum quality to improve the ICT management in APF agencies [31].
The Guide, despite not having normative character, is considered an important tool for assisting public agencies and entities to develop its ICTMPs adherents to several regulations that deal with the matter, as well as good market practices. The literature research conducted in this study found that the risk management issue in FPA is still under explored. With respect to planning, the Brazilian public sector has a wide range of legislation governing the matter, either on the institutional or ICT levels. Regarding the application of risk management in the public planning instruments, particularly in ICTMP, there were no publications that deal specifically with the matter.
3. Research Methodology
Every decision that is made by managers and policy-makers in a public sector organization requires an evaluation and a judgment of the risks involved. This vital requirement has been recognized in the growth of risk management. However, risks can never be fully prevented, which means that public managers also have to be crisis managers [32].
Today’s crises develop in unseen ways; they escalate rapidly and transform through the interdependencies of modern society, and their frequency is growing: the global financial crisis, the European volcanic ash cloud, the Japanese tsunami and subsequent Fukushima nuclear plant meltdown, the Christchurch earthquake and the Queensland floods. All highlight the extreme challenges that public sector organizations across the world have had to face in recent years [27].
Risk management in the Federal Public Administration (FPA), especially for the development of institutional arrangements is a relatively unexplored matter. In the first stage of the work, a qualitative research method of exploratory nature was used. A work is exploratory in nature when it involves literature and analysis of examples that encourage the understanding of the problem in order to provide the researcher better knowledge on the matter and enable the formulation of more precise problems and create hypotheses that can be researched by subsequent studies [17].
At this stage, seventeen ICTMPs were analyzed from major federal agencies and public entities belonging to the three powers of the Union, effective between the years 2010 to 2017. In conducting the research, the ICTMPs from federal level agencies and entities that had published their documents on the internet were considered for the selection of the sample. Additionally, via email, the availability of agencies and entities ICTMPs belonging to the Applied Information Technology to Control Community was requested. This community brings together representatives of the Legislative, Executive, Judiciary, Public Ministry and the Attorney General’s Office. Its purpose is to contribute to the increasing of efficiency, efficacy and effectiveness in the public administration. Some of these institutions have provided their plans through electronic messages.
In the second stage of the work, we used a descriptive method that aims to describe the characteristics of a given population or phenomenon [33]. In order to mark the analysis of risk management use in the ICTMP preparation, key risk management processes recommended by the Brazilian standard were used as reference [7].
Key standard processes were selected and the verification of adherence to guide [31] to those processes performed, using a qualitative scale to value the degree of adherence: low (absence of the process), medium (partial presence of the process) and high (total process presence). The aim of this step was to determine whether the risk management mechanisms present in the Guide were aligned to the main standard dealing with the matter. The result of this verification facilitated the analysis of the risk management process during the preparation of ICTMPs that used the guide [31].
The ICTMPS were grouped to facilitate the analysis and to provide a quantitative view of the presence or not of risk management in these documents, as well as to establish compliance with the risk of mechanisms suggested by the Guide. For each group, a subset of documents for a more detailed analysis was selected in order to describe the risk management mechanisms used or to analyze the reasons for its absence.
To expand the focus of the analysis, a grouping of documents was chosen in order to obtain a holistic view of the use of risk management mechanisms in the preparation of federal public organizations ICTMPs. The grouping of the sample was given into three groups:
- Own risk management and is adhering to ICTMP Drafting Guide SISP, [31,34];
- Has risk management and is not adhering to ICTMP Drafting Guide SISP, [31,34];
- Has no risk management.
Figure 2 shows the quantity and percentage distribution for each group of sample. On average, a total of 120 employees of the organization were part of each group of the sample. Two documents, representing twelve percent of the sample, had management risks adherent to the Guide (Group 1—12%). Two others, despite their risk management related mechanisms, were not adhering to the Guide (Group 2—12%). Thirteen documents, representing seventy-six percent of the sample, were classified in Group 3 (76%) due to a lack of evidence on the presence of risk management processes.
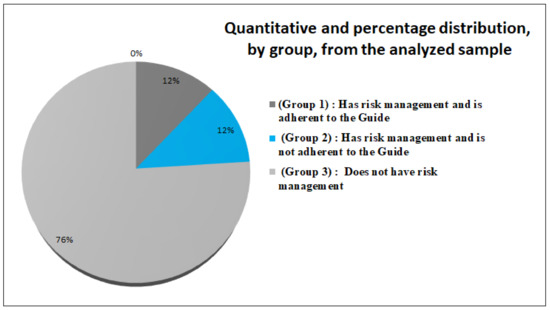
Figure 2.
Quantitative and percentage distribution, by group, from the analyzed sample.
4. Analysis of Results and Discussion
Acknowledging that there are many official standards for IT risk management that are designed to improve the organization’s decision-making and activities that address key uncertainties as: ISO 31000, BS 3100:2008, COSO:2004 and FERMA:2002, the following analysis is focused on ISO 31000 [7] as it is the basis for the Brazilian Standard [6].
4.1. Analysis of Risk Management Processes Adherence to AICRS ICTMP Planning Guide to ISO 31000
In order to verify the adherence to the management mechanisms of risks present in the Guide [34] to Brazilian standards dealing with the risk management principles and guidelines, the main processes of the Brazilian standard were used as a reference [6,7].
The Guide addresses risk management explicitly in various sections of the document: in the overview, in the preparation stage and the ICTMP planning stage. Table 1 shows the adherence analysis to mechanisms related to risk management present in the Guide [34] for the processes that were highlighted in the standard [6,7]. For each process (column 2), the most relevant sub-processes were selected (column 3) in order to perform the adherence analysis. A qualitative scale to value the degree of adherence was used: low (absence of the process), medium (partial presence of the process) and high (total process presence). In the fourth column, evidence of the presence of the ISO 31000 process [6,7] in the Guide [34] is shown.

Table 1.
Degree of adherence to the ISO 31000 Processes Guide [6,7].
During the analysis, explicit evidence of the application of mechanisms related to the communication and consultation process on the content of the analyzed Guide was not identified. Thus, the Guide was considered with low adherence to the communication and consultation process of ISO 31000 [6]. According to the standard, this process has no highlighted sub processes.
The process of context establishment consists of a set of sub-processes. The Guide adherence analysis in relation to the context establishment process restricts only to the risk criteria defining sub-process, for its relevance, because much of the information produced by the other sub-processes is used as input for the definition of risk criteria. The analysis showed the presence of a specific item in the Guide that deals with the definition and updating of prioritization criteria and risk acceptance, providing even a model for the registration of such information. It follows, therefore, that the Guide has a high degree of adherence in relation to the context establishment process to the Brazilian standard highlighted.
According to [6,7], the risk assessment process is composed of the following sub-processes: risk identification, risk analysis and risk assessment. The mentioned sub-processes are essential for the effective realization of the risk assessment process. For being relevant and complementary, the adherence analysis was performed for all of them. It was found that the item “Risk management or planning” in the Guide explicitly covers the three sub-processes related to the ISO 31000 risk assessment process [7], providing even a model for recording of information. Thus, it was observed that the Guide has a high degree of adherence to the risk assessment process stipulated in the standard.
The risks’ treatment process recommended by the Brazilian standard involves the selection of the most suitable alternatives to modify the risks, as well as the preparation of necessary plans to implement them. Those aspects are addressed in the “Risk Management Plan” contained in the Guide; however, a lack of items were found, such as the definition of those responsible for the execution and approval of plans, timeline for implementation and resource requirements. In this sense, it is considered that the Guide has a medium degree of adherence to the ISO 31000 Risk treatment process [6,7].
Regarding the monitoring and reviewing process, only the mention of responsibility for the constant risk in the risk management model plan recommended by the Guide was identified. The Brazilian standard recommends that monitoring processes and critical analysis of the organization should cover all aspects of the risk management process in order to ensure that controls are effective and efficient, as well as detection of changes in the external and internal context and identification of emerging risks among others. Thus, it was found that, in relation to these aspects, the Guide has medium adherence to the monitoring process and critical analysis of ISO 31000 [6,7], since it has partial presence of the process in the Guide.
Despite the absence of some processes recommended in the Guide by the Brazilian standard, it was found that most of the ISO 31000 [6,7] processes are treated by the AICRS Guide [34]. It is concluded, therefore, that the processes that deal with risk management in the Guide adhere to ISO 31000 [6,7].
4.2. Analysis of ICTMPs Included in Group 1—Has Risk Management and Is Adhering to the ICTMP of the AICRS Development Guide
Twelve percent of the sample, representing two ICTMPs were classified in Group 1, which comprises the documents that have risk management adherent to the Guide. Both documents belong to agencies from the indirect federal administration. These agencies legally have special authorities, typified as regulatory agencies. Later, an analysis of each document will be done. In order to preserve the identification of agencies and entities, in this work, they will be identified by a number (value corresponding to the group to which it belongs) followed by a letter.
The first agency’s ICTMP analyzed, called 1A agency, effective from 2012 to 2014. As recommended by [6,7] (part of the establishment process) and recommended by the Guide [6,7], the sub-process that deals with the definition and updating of the acceptance risks criteria is essential in order to guide the evaluation of the actions planned and the design of new actions intended to address the existing risks. This aspect was addressed in the analyzed ICTMP, through meetings of the ICT agency’s committee, as shown in the implementation schedule of the existing plan in the document.
The risk assessment processes, treatment of risks and risk monitoring and analysis were addressed according to the guidelines in the present Guide. Table 2 shows the result of the execution of these processes.

Table 2.
Risk Management Plan of 1A agency. Source: ICTMP 2012–2017 of 1A agency.
For each action proposed in the plan, the identified agency analyzed and assessed the risks as well as adopted a treatment strategy and response to them. The set of possible strategies was set in line with the Guide. They are: mitigate (develop actions to minimize the risk occurrence probability or its impact on the project in order to make the risk acceptable); avoid (change the project plan eliminating the condition to which the project was exposed to risk); transfer (pass on the risk consequences as well as response responsibility to those better prepared to deal with it) and accept (indicated in situations where the risk criticality is medium or low, or when it is not possible or there is no interest in implementing a specific action).
The risk assessment processes, risk treatment and monitoring and critical analysis present in the 1B agency’s ICTMP were addressed according to the guidelines in the present Guide. Table 3 presents a small sample of the result of the execution of these processes. It consists of seven columns: action identification, action description, risk description, probability, impact, contingency action and responsibility.

Table 3.
1B Agency Risk Management Plan. Source: ICTMP 2012–2017 of 1B Agency.
For each action in the plan, the risks were identified and assessed in regards to the probability and impact of occurrence, applying a scale with five levels of classification: very low, low, medium, high and very high. The criteria used to perform the classification in each of these levels have been established and communicated. After classification, response to risks planning was done, establishing contingency actions and responsibility for their treatment.
The analysis performed on the ICTMPs of 1A and 1B agencies comprised in group 1 showed that the risk management mechanisms present in these documents follow the guidelines in the AICRS Guide in relation to risk management. An existence of small variations in relation to risk treatment among the examined documents was found, without prejudice to the adherence to the Guide.
4.3. Analysis of the ICTMP Included in Category 2—Has Risk Management and Is Not Adhering to ICTMP of the AICRS Development Guide
Two ICTMPs, representing twelve percent of the sample, were classified in Group 2, comprising the plans that have risk management, but are not adhering to the Guide. Both documents belong to important agencies of the Federal Administration. In the following, an analysis of each document will be done. Within Group 2, an ICTMP of a major federal public foundation, an agency of indirect administration, with high ICT investment was selected. Within this study, this agency will be named 2A.
There was a lack of processes related to the context establishment, specifically the risk criteria definition, as well as the analysis and risk assessment sub-processes, recommended by the Brazilian standard and suggested by the Guide. Only evidence and its responsibilities were observed. Table 4 shows, in full, the risk management plan in ICTMP. In the table, four columns are present representing the description of the risk, preventative measures, contingency measures and the person responsible for risk. The column responsibility represents the person responsible for the information in the agency.

Table 4.
Risk Management Plan of 2A Agency Source: ICTMP 2011–2017 of 2A Agency.
There was an absence of probability analysis on the occurrence of risks as well as of impacts from identified risks, key step to support the decision-making regarding acceptance, prioritization, treatment and monitoring of risks. There was also no correlation between the identified risk and the action plan of pretended to be run, making difficult the traceability between items.
According to [6,7], the risk assessment sub-process involves comparing the level of risk found during the analysis process with the risk criteria established when the context was considered. Based on this comparison, it is confirmed if there is the need for certain risks to be treated. Since no risk criteria was established or conducted, the risk analysis regarding the likelihood and impact, risk management mechanisms present in the ICTMP are insufficient for the risk management process execution effectively. Therefore, despite the existence of risk management mechanisms, the analyzed ICTMP does not follow the guidelines recommended by the Guide with respect to risk management processes.
Furthermore, in relation to the analysis of the documents included in category 2, the ICTMP of another important agency of the federal administration was analyzed. Within this study, this agency will be called 2B. The risk management mechanisms present in this document differ from the traditional way used by another ICTMP, where, in general, the risks are identified, analyzed, evaluated, treated and monitored for each share in this plan. The analyzed document only showed the impacts of the non-implementation of ICTMP. Table 5 shows the list of possible impacts resulting from non-performance of the ICTMP of agency 2B.

Table 5.
List of the impacts of non-implementation of the ICTMP of 2B agency. Source: PDTI 2010–2017 of 2B agency.
This approach ignored the use of risk management mechanisms associated with each action in this plan. Moreover, it was not clear during the analysis if the agency considered only the total non-performance impacts of the ICTMP or if the list presented in Table 5 represents the impact on the risk of non-performance of certain actions in the plan.
The conclusion of the analysis of the two ICTMPs included in Group 2 is that the plans analyzed need more robust tools for planning and monitoring the risks inherent in the execution of the Information Technology Master Plan, an essential tool for the realization of actions responsible for conducting much of the organization’s business objectives. High ICT budgets present in ICTMPs demonstrate the need to use a formal risk management process and integrated with ICT governance mechanisms of the institutions. The Guide [31,34] is one of the instruments that can contribute to these objectives.
4.4. Analysis of ICTMPs Included in Category 3—Does Not Have Risk Management
In this group, most analyzed ICTMPs are included. Seventy-six percent of the sample did not have evidence of risk management mechanisms use in their ICTMPs. This finding led to a central question that will be discussed during the analysis: Was risk management for the preparation of these ICTMPs really unnecessary?
Here, major federal agencies and entities of the three powers of the Union were considered. Thirty-eight percent of the documents included in category 3 belong to ICT Superior Governing Agencies—OGS, responsible for regulating and supervising the use and ICT management in their respective areas of the APF [5]. Similarly, to the analysis carried out in the other groups, an ICTMP was selected from an agency belonging to Group 3 for a particular analysis. The analyzed document belongs to an important agency. The plan considers dozens of actions that deal from the development of corporate solutions, investment in hardware and software infrastructure, to ICT governance improvement. In the whole set of these actions, no evidence related to the use of risk management mechanisms was found. The other ICTMP analyzed belong to agencies and entities that have similar characteristics. They are prominent institutions, behavior-inducing within the APF and have sizable ICT budgets to achieve organizational strategies and business objectives of the institution.
According to [35], risk is the situation where the decision maker has a prior knowledge of both the consequences of different alternatives as the probability of occurrence. In this sense, the perceived risk has two main components: uncertainty (the possibility of unfavorable results) and consequences (relevance of loss). When that information is not considered in the planning of a given action, the chances of the occurrence of tangible and intangible losses increase to the extent that the risks are not identified, monitored and recorded through a formal process of risk management. Similarly, opportunities will be hardly exploited.
5. Conclusions
The study of risk management applied to planning tools, particularly to the ICTMP, has an important role for organizations in order to achieve their goals and fulfill their institutional mission since ICT actions are present in all organizational processes. The risks inherent in the planning of ICT actions in the public sector need to be considered so that ICT adds value to business and maximizes the return on investment of the population. This work examined the use of risk management processes in the development of ICTMPs in the Brazilian public sector.
Because it is a relatively unexplored matter, a qualitative method of exploratory nature for understanding it was initially used. At this stage, seventeen ICTMPs were analyzed from major federal agencies and public entities belonging to the three powers of the Union. The main criterion for choosing the sample was the ease of access to the documents. In a second stage, a descriptive method for performing detailed analysis of each document was used. To mark the analysis of the risk management use in the preparation of ICTMPs, key risk management processes were used as reference.
The vast majority of the evaluated agencies and entities did not use risk management processes in the preparation of their ICTMPs. This finding led to the analysis of the real need for the use of risk management processes in each studied/evaluated ICTMP, taking into account the relevance, scope and materiality of the actions contained in the plans. The examined documents had structural and essential actions for achieving the organizational strategies and business goals of the institutions. Therefore, risk management can contribute to the preparation of the analyzed ICTMPs, to increase efficiency in the use of resources, to facilitate the understanding of the risks to which the critical processes of the institution are exposed, to provide solid criteria for planning and prioritization of actions, to enable the exploration opportunities and to minimize adverse effects.
Another worrying fact was the finding that thirty-eight percent of the analyzed documents belong to ICT Superior Governing Agencies—OGS responsible for regulating and supervising the use and ICT management in their respective segments of the APF. These agencies, besides having legislative powers, are behavior inducers.
The absence of risk management in the preparation of the analyzed organizations’ ICTMPs can contribute negatively to the achievement of strategies and business goals of these organizations. The possible consequences are exacerbated on account of them being public organizations, which should uphold the principles of legality, efficiency and economy, providing a quality service to the main interested and affected one: the Brazilian society.
Author Contributions
The Analysis of the Risk Management Process on the Development of the Public Sector Information Technology Master Plan was made by S.A.A.F., E.D.C., R.C.S.F., and H.A.T.L. All authors contributed to Writing Original Draft Preparation and Writing Review & Editing.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Myeong, S.; Kwon, Y.; Seo, H. Sustainable e-governance: The relationship among trust, digital divide, and e-government. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6049–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Get.IT: Governance Evaluation Techniques for Information Technology: A WGITA Guide for Supreme Audit Institutions. 2016. Available online: https://portal.tcu.gov.br/biblioteca-digital-8a81881f6364d8370163bc5ce6d85b14/get-it-governance-evaluation-techniques-for-information-technology-a-wgita-guide-for-supreme-audit-institutions.htm (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- ISACA. COBIT 5: Enabling Processes; ISACA: Rolling Meadows, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Klamm, B.K.; Watson, M.W. SOX 404 reported internal control weaknesses: A test of COSO framework components and information technology. J. Inf. Syst. 2009, 23, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da União, T.d.C. Levantamento de Governança de TI 2012. Recuperado em. 2015. Available online: https://portal.tcu.gov.br/biblioteca-digital/levantamento-de-governanca-de-ti-2012.htm (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- ISO 31000:2009: Gestão de Riscos; Brazilian National Standards Organization (ABNT): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009.
- Purdy, G. ISO 31000: 2009—Setting a new standard for risk management. Risk Anal. 2010, 30, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, N.; Hu, Y.; Cui, C. Importance Degree Research of Safety Risk Management Processes of Urban Rail Transit Based on Text Mining Method. Information 2018, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javani, B.; Rwelamila, P.M.D. Risk management in IT projects—A case of the South African public sector. Int. J. Manag. Proj. Bus. 2016, 9, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongmalai, O.; Tang, J.C.; Siengthai, S. Empirical evidence of corporate governance in Thai state-owned enterprises. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2010, 10, 617–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amali, L.; Mahmuddin, M.; Ahmad, M. Information Technology Governance Framework in the Public Sector Organizations. TELKOMNIKA 2014, 12, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, F.; Isaacs, F. Risk management in public sector research: Approach and lessons learned at a national research organization. R&D Manag. 2008, 38, 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Zsidisin, G.A.; Ritchie, B. Supply chain risk management—Developments, issues and challenges. In Supply Chain Risk; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- López-Navarro, M.Á.; Llorens-Monzonís, J.; Tortosa-Edo, V. The effect of social trust on citizens’ health risk perception in the context of a petrochemical industrial complex. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, M. The Risk Management of Everything: Rethinking the Politics of Uncertainty; Demos: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- McPhee, I. Risk and Risk Management in the Public Sector; Australian National Audit Office: Canberra, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.; Lloyd-Walker, B. Understanding collaboration in integrated forms of project delivery by taking a risk-uncertainty based perspective. Adm. Sci. 2016, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slovic, P. The Perception of Risk; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Klakegg, O.J. Project Risk Management: Challenge Established Practice. Adm. Sci. 2016, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimes, Y.Y. Risk Modeling, Assessment, and Management; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.J. ICT-Oriented Urban Planning Strategies: A Case Study of Taipei City, Taiwan. J. Urban Technol. 2012, 19, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onizat, H.H.A.; Oqeili, S.; Hijazi, B. e-Government performance in Jordan. Eur. Sci. J. 2013, 9, 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Brasil, C.F. de outubro de; Publicada no Diário Oficial da União em: Brasília, Brazil, 1988; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, M.S.; Souza Neto, J. Fatores Críticos de Sucesso Para os Comitês de Governança de Tecnologia da Informação na Administração Pública Federal. 2014. Available online: http://banco.consad.org.br/handle/123456789/1095 (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Jurison, J. Toward more effective management of information technology benefits. J. Strat. Inf. Syst. 1996, 5, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.D. An organizational perspective and a team approach: Keys to successful business planning. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2016, 13, 228–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dooren, W.; Bouckaert, G.; Halligan, J. Performance Management in the Public Sector; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, D.A.; Canedo, E.D.; de Oliveira, E.C. Proposta para Análise de Riscos no Processo de Planejamento da Contratação de TI: um Estudo Exploratório para Órgãos Governamentais. iSys-Revista Brasileira de Sistemas de Informação 2016, 9, 168–186. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.E.B.; Neto, J.S. Diretrizes de Plano Estratégico de Tecnologia da Informação para Órgãos da administração Pública Federal. Gestão & Planejamento-G&P 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldentops, E.; De Haes, S.; Hardy, G.; Ormsby, J.; Singleton, J. Board Briefing on IT Governance; IT Governance Institute: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, C.S.d.; Figuereido, R.M.d.C.; Andrade, E.L.P.d. Processo de Contratação de Serviços de Tecnologia da Informação Para Organizações Públicas. 2011. Available online: http://livroaberto.ibict.br/handle/1/756 (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Drennan, L.T.; McConnell, A.; Stark, A. Risk and Crisis Management in the Public Sector; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; EBSE Technical Report EBSE-2007-01; Software Engineering Group, School of Computer Science and Mathematics, Keele University: Keele, UK; Department of Computer Science, University of Durham: Durham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, D.L.N.; Neto, J.S. Avaliação da percepção da conformidade de processos de contratação de soluções de Tecnologia da Informação com a Instrução Normativa no 4/2010 da SLTI. Revista do Serviço Público 2013, 64, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Renn, O. Risk Governance: Coping with Uncertainty in a Complex World; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).