Abstract
Visual object tracking is a critical task in computer vision. Challenging things always exist when an object needs to be tracked. For instance, background clutter is one of the most challenging problems. The mean-shift tracker is quite popular because of its efficiency and performance in a range of conditions. However, the challenge of background clutter also disturbs its performance. In this article, we propose a novel weighted histogram based on neutrosophic similarity score to help the mean-shift tracker discriminate the target from the background. Neutrosophic set (NS) is a new branch of philosophy for dealing with incomplete, indeterminate, and inconsistent information. In this paper, we utilize the single valued neutrosophic set (SVNS), which is a subclass of NS to improve the mean-shift tracker. First, two kinds of criteria are considered as the object feature similarity and the background feature similarity, and each bin of the weight histogram is represented in the SVNS domain via three membership functions T(Truth), I(indeterminacy), and F(Falsity). Second, the neutrosophic similarity score function is introduced to fuse those two criteria and to build the final weight histogram. Finally, a novel neutrosophic weighted mean-shift tracker is proposed. The proposed tracker is compared with several mean-shift based trackers on a dataset of 61 public sequences. The results revealed that our method outperforms other trackers, especially when confronting background clutter.
1. Introduction
Currently, applications in the computer vision field such as surveillance, video indexing, traffic monitoring, and auto-driving have come into our life. However, most of the key algorithms still lack the performance of those applications. One of the most important tasks is visual object tracking, and it is still a challenging problem [1,2,3].
Challenges like illumination variation, scale variation, motion blur, background clutters, etc. may happen when dealing with the task of visual object tracking [2]. A specific classifier is always considered for tackling such kinds of challenging problems. Boosting [4] and semi-supervised boosting [5] were employed for building a robust classifier; multiple instance learning [6] was introduced into the classifier training procedure due to the interference of the inexact training instance; compressive sensing theory [7] was applied for developing effective and efficient appearance models for robust object tracking, due to factors such as pose variation, illumination change, occlusion, and motion blur.
The mean-shift procedure was first introduced into visual object tracking by Comaniciu et al. [8,9]. The color histogram was employed as the tracking feature. The location of the target in each frame was decided by minimizing the distance between two probability density functions, which are represented by a target histogram and a target candidate histogram. By utilizing the color histogram feature and the efficient seeking method, such a mean-shift tracker demonstrates high efficiency and good performance, even when confronting motion blur and deformation problems. On the other hand, the color histogram feature cannot help the tracker discriminate the target from the background effectively, especially when background clutter exists. Several new metrics or features were considered to deal with such a problem. For instance, Cross-Bin metric [10], SIFT (Scale-invariant feature transform) [11], and texture feature [12] were introduced into the mean shift based tracker, and the proposed trackers all earn a better performance than the traditional one. Besides, Tomas et al. [13] exploited the background to discriminate the target and proposed the background ratio weighting method. In addition, since estimating an adequate scale is essential for robust tracking, a more robust method for estimating the scale of the searching bounding box was proposed through the forward–backward consistency check. This mean-shift based tracker [13] outperforms several state-of-the-art algorithms. Robert et al. [14] also proposed a scale selecting scheme by utilizing the Lindeberg’s theory [15] based on the local maxima of differential scale-space filters. Although so many kinds of visual trackers have been proposed, the visual tracking is still an open problem, due to the challenging conditions in the real tracking tasks. All in all, the mean-shift tracker demonstrates high efficiency and may earn an even better performance if a more effective method can be found to discriminate the target from the background. Thus, finding a suitable way to represent the information presented by the background, as well as the target, is of high relevance.
Neutrosophic set (NS) [16] is a new branch of philosophy to deal with the origin, nature, and scope of neutralities. It has an inherent ability to handle the indeterminate information like the noise included in images [17,18,19,20,21] and video sequences. Until now, NS has been successfully applied in many areas [22]. For the computer vision research fields, the NS theory is widely utilized in image segmentation [17,18,19,20,21], skeleton extraction [23] and object tracking [24], etc. Before calculating the segmentation result for an image, a specific neutrosophic image was usually computed via several criteria in NS domain [17,18,19,20,21]. For object tracking, in order to improve the traditional color based CAMShift tracker, the single valued neutrosophic cross-entropy was employed for fusing color and depth information [24]. In addition, the NS theory is also utilized for improving the clustering algorithms, such as c-means [25]. While several criteria are always proposed to handle a specific image processing problem, an appropriate way for fusing information is needed. Decision-making [26,27,28,29,30] can be regarded as a problem-solving activity terminated by a solution deemed to be satisfactory, and it has been frequently employed for dealing with such an information fusion problem. The similarity measurement [30] using the correlation coefficient under single valued neutrosophic environment was successfully applied into the issue of image thresholding [21]. A single valued neutrosophic set (SVNS) [31] is an instance of a neutrosophic set and provides an additional possibility to represent uncertainty, imprecise, incomplete, and inconsistent information, which exists in the real world. The correlation coefficient of SVNS was proposed by the authors of [30] and was successfully applied for handling the multicriteria decision making problem. For the mean-shift tracker, the color histogram is employed for representing the tracked target. Due to the challenging conditions during the tracking procedure, indeterminate information always exists. For instance, object feature may changes due to object pose or external environment changes between frames. It is difficult to localize the object exactly during the tracking procedure. Thus, there exists indeterminate information when you try to utilize the uncertain bounding box to extract object feature. All in all, how to utilize the information of the object and the corresponding background to help the tracker discriminate the object is also an indeterminate problem.
In this work, we propose a novel mean-shift tracker based on the neutrosophic similarity score [21,30] under the SVNS environment. We build a neutrosophic weight histogram, which jointly considered the indeterminate attributes of the object and the background information. First, we propose two criteria of the object feature similarity and the background feature similarity, where each one is represented as its bin of the histogram corresponding to three membership functions for the T(Truth), I(indeterminacy), and F(Falsity) element of the neutrosophic set. Second, the neutrosophic similarity score function is introduced to fuse those two criteria and build the final weighted histogram. Finally, the weight of each bin of the histogram is applied to modify the traditional mean-shift tracker, and a novel neutrosophic weighted mean-shift tracker is proposed. To our own knowledge, it is the first time to introduce the NS theory into the mean-shift procedure. Experiments results revealed that the proposed neutrosophic weighted mean-shift tracker outperforms several kinds of mean-shift based trackers [9,13,14].
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: in Section 2, the traditional mean-shift procedure for visual object tracking and the definition of the neutrosophic similarity score are first given. Then the details of the method for calculating the neutrosophic weight histogram are presented, and the main steps of the proposed mean-shift tracker are illustrated in the following subsection. Experimental evaluations and discussions are presented in Section 3, and Section 4 has the conclusions.
2. Problem Formulation
In this section, we present the algorithmic details of this paper.
For the visual tracking problem, the initial location of the target will be given in the first frame, and the location is always represented by a rectangle bounding box [1,2,3]. Then the critical task for a visual tracker is to calculate the displacement of the bounding box in the following frame corresponding to the previous one.
2.1. Traditional Mean-Shift Tracker
The main steps of the traditional mean-shift visual tracker are summarized in this subsection.
The kernel-based histogram is employed by the traditional mean-shift tracker. At the beginning, the feature model of the target is calculated by
where is the target model, ; is the u-th bin of the target model satisfying ; is the normalized pixel location which located in the initial bounding box; and n is the number of pixels belonging to the target. In order to reduce the interference of the background clutters, the kernel k(x) is utilized. k(x) is an isotropic, convex, and monotonic decreasing kernel. The kernel assigns smaller weights to pixels farther than the center. In this work, k(x) is defined as . The function b(x): associates to the pixel at location x the index b(x) of the histogram bin corresponding to the color of that pixel. Then, C is the normalization constant, which is denoted by
The function is the Kronecker delta function. Let y be the center of the target candidate and {xi}i = 1, …, nh be the pixel locations in the bounding box of the target candidate. Here, nh is the total number of the pixels falling in the bounding box. Then when using the same kernel profile k(x), the probability of the feature in the target candidate is given by
where h is the bandwidth and Ch is the normalization constant derived by imposing the condition .
The metric based on Bhattacharyya coefficient is proposed to evaluate the similarity between the probability distributions of the target and the candidate target. Let be the similarity probability, then it can be calculated by
For the mean-shift tracker, the location in the previous frame is employed as the starting location for searching the new target location in the current frame. The estimate of a new target location is then obtained by maximizing the Bhattacharyya coefficient using a Taylor series expansion, see [8,9] for further details. To reach the maximum of the Bhattacharyya coefficient, the kernel is repeatedly moved from the current location to the new location
where g(x) is the negative derivative of the kernel k(x), i.e., . Furthermore, it is assumed that g(x) exists for all except for a finite set of points. The parameter wi in Equation (5) is denoted by
2.2. Neutrosophic Similarity Score
A neutrosophic set with multiple criteria can be expressed as follows:
Let A = {A1, A2, …, Am} be a set of alternatives and C = {C1, C2, …, Cn} be a set of criteria. Then the character of the alternative Ai (i = 1, 2, …, m) can be represented by the following information:
where . Here, denotes the degree to which the alternative Ai satisfies the criterion Cj; indicates the indeterminacy degree to which the alternative Ai satisfies or does not satisfy the criterion Cj; indicates the degree to which the alternative Ai does not satisfy the criterion Cj.
A method for multicriteria decision-making based on the correlation coefficient under single-valued neutrosophic environment is proposed in [30]. The similarity degree between two elements Ai and Aj is defined as:
Assume the ideal alternative . Then the similarity degree between any alternative Ai and the ideal alternative A* can be calculated by
Suppose wk ∈ [0,1] is the weight of each criterion Ck and , then the weighted correlation coefficient between an alternative Ai and the ideal alternative A* is defined by
The alternative with high correlation coefficient is considered to be a good choice for the current decision.
2.3. Calculate the Neutrosophic Weight Histogram
Employing the information discriminated from the background is one of the most important issues for robustly tacking a visual object. As shown in Figure 1, the smallest region GO inside the red bounding box is the object region and this region corresponds to the location of the object in the corresponding frame. Then GO is decided by the tracker and its accuracy depends on the robustness of the tracker. In this work, the surrounding area of GO is defined as the background region GB. In order to eliminate the indeterminacy of the region GO to some extent, the region far from GO is employed as GB and GB = βGO − αGO.
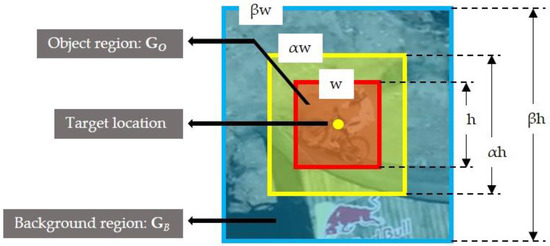
Figure 1.
Illustration of the object region.
To enhance the robustness of the traditional mean-shift tracker, a novel weight histogram wNS is defined in the neutrosophic domain. Each bin of the weighted histogram wNS is expressed in the SVNS domain via three membership functions T(Truth), I(indeterminacy), and F(Falsity).
For the proposition of object feature is a discriminative feature, TCO, ICO, and FCO represent the probabilities when a proposition is true, indeterminate and false degrees, respectively. Finding the location of the tracked object in a new frame is the main task for a tracker, and the target model (object feature histogram in the initial frame) is frequently employed as major information to discriminate the object from the background. The region which owns more similarity to the object feature is more likely to be the object region. Using the object feature similarity criterion, we can further give the definitions:
where is the u-th bin of the target model corresponding to the object region GO in the first frame of the tracking process and it is calculated by using Equation (1).
The indeterminacy degree ICO (u) is defined in Equation (12). Then, is the u-th bin of the updated object feature histogram in the previous frame. Suppose is the feature histogram corresponding to the extracted object region at time t−1, then is calculated by
where λ is the updating rate for λ ∈ (0,1).
As the tracker may drift from the object due to the similar surroundings, using the object features with high similarity to the background will bring risk to the accuracy of the tracker. The background feature similarity criterion is considered in this work. The corresponding three membership functions TCB, ICB and FCB are defined as follows:
where is the u-th bin of the object background feature histogram. This histogram is initialized in the background region GB in the first frame, as shown in Figure 1. For , Equation (1) is also employed to calculate , and , which will be updated when the surroundings of the tracked target change dramatically.
By substituting the corresponding T(Truth), I(indeterminacy), and F(Falsity) under the criteria of the object feature similarity and the background feature similarity into Equation (10), the u-th bin of the neutrosophic weight histogram can be calculated by
where wCO, wCB ∈ [0,1] are the corresponding weights of criteria and wCO + wCB = 1. The ideal alternative under two criteria is the same as .
2.4. Neutrosophic Weighted Mean-Shift Tracker
In this work, the neutrosophic weighted histogram is introduced into the traditional mean-shift procedure, and this improved mean-shift tracker is called the neutrosophic weighted mean-shift tracker. The basic flow of the proposed tracker is described below:
Initialization
- Step 1:
- Read the first frame and select an object on the image plane as the target to be tracked.
- Step 2:
- Calculate the object feature histogram and object background feature histogram by using Equation (1).
Tracking
Input: (t + 1)-th video frame
- Step 3:
- Employ the location in the previous frame as the starting location for searching the new target location in the current frame.
- Step 4:
- Based on the mean-shift algorithm and neutrosophic weight histogram, derive the new location of the object according to Equation (19) and Equation (5) as follows:
- Step 5:
- If , stop. Otherwise, set and go to Step 4.
- Step 6:
- Derive according to Equation (14) and then update object background feature histogram when the Bhattacharyya coefficient , where is the corresponding feature histogram in the current background region GB.
Output: Tracking location.
3. Experiment Results and Analysis
We tested the neutrosophic weighted mean-shift tracker on a challenging benchmark [2]. As mentioned at the outset, background clutter is one of the most challenging problems for the mean-shift tracker. Besides the 50 challenging sequences in this benchmark [2], another 10 sequences with the challenge of background clutter are also selected as testing sequences. The information of those 10 sequences is given in Table 1. The abbreviations of several kinds of challenges included in the testing sequences are shown in the footer of Table 1.

Table 1.
An overview of another 10 sequences.
To gauge the performance of the proposed tracker, we compare our results to another three mean-shift based trackers including ASMS [13], KMS [9] and SMS [14]. Some experimental results have shown that ASMS [13] outperforms several state-of-the-art algorithms. KMS is the traditional mean-shift tracker. Both SMS and ASMS are scale adaptive. All of the tested algorithms employ the color histogram as object feature.
3.1. Setting Parameters
For the proposed neutrosophic weighted mean-shift tracker, the parameter α and β relate to the background region GB are set to 1.2 and 1.48 respectively. The parameter λ in Equation (14) decides the updating rate of the object feature histogram. With the assumption that the appearance of the tracked object will not change dramatically, a low updating rate should be given. In this work, λ is set to 0.05. As seen in the Section 2.4, the accuracy of the result of the mean-shift procedure depends on the parameter ε0 to some extent, where ε0 is set to 0.1. A much greater value of ε0 may lead to failure. The parameter ε1 is a threshold for updating the object background feature histogram. During the tracking procedure, the surroundings of the object always change. Hence, it is essential to update the object background feature histogram when the similarity between the current surroundings and the object background feature falls to a specific value. If ε1 is set to 0, the updating process of the background feature will stop. If ε1 is set to 1, the updating frequency will be too high. Thus, a medium value is chosen as ε1 = 0.5. The neutrosophic weight histogram plays an essential role in this proposed mean-shift based tracker. In order to emphasize the background information when constructing the neutrosophic weight histogram, the corresponding parameter wCB should be set to a relatively high value. However, if this value is set too high, the effect of the first neutrosophic criteria will reduce, even to zero. In this work, wCB is set to 0.6, and wCO is set to 0.4. Finally, all the values of these parameters are chosen by hand-tuning, and all of them are constant for all experiments.
3.2. Evaluation Criteria
The overlap rate of the bounding box is used as the evaluation criterion, and the overlap rate is defined as
where ROITi is the target bounding box in the i-th frame and ROIGi is the corresponding ground truth bounding box. For the video datasets applied in this work, the ground truth bounding boxes of the tracked target are manually labeled for each frame. The success ratio is defined as:
where N is the number of frames and r is the overlap threshold which decides the corresponding tracking result is correct or not. The success ratio is R ∈ [0,1]. When the overlap ratio si is greater than r on each frame, R achieves the maximum, and then this means the corresponding tracker performs very well in this sequence. On the contrary, R achieves the minimum when si is smaller than r on each frame, and then this means the corresponding tracker performs the worst.
Both the one-pass evaluation (OPE) and temporal robustness evaluation (TRE) are employed as the evaluation metric. For the TRE, each testing sequence is partitioned into 20 segments, and each tracker is tested throughout all of the segments. The results for the OPE evaluation metric are derived by testing the tracker with one time initialization from the ground truth position in the first frame of each testing sequence. Finally, we use the area under curve (AUC) of each success plot to rank the tracking algorithms. For each success plot, the tracker with a greater value of AUC ranks better.
3.3. Tracking Results
Several screen captures for some of the testing sequences are given in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5. Success plots of TRE and OPE for the whole testing sequences are shown in Figure 6a and Figure 7a, and the success plots for those sequences including background clutter challenge are shown in Figure 6b and Figure 7b. In the following section, a more detailed discussion of the tracking results is documented.
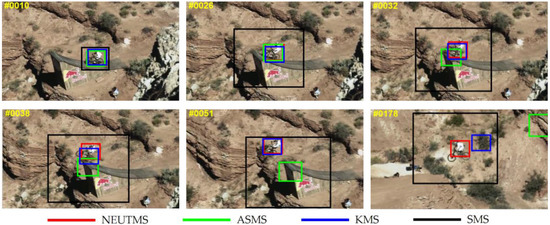
Figure 2.
Screenshots of tracking results of the video sequence used for testing (mountainBike, target is selected in frame #1).
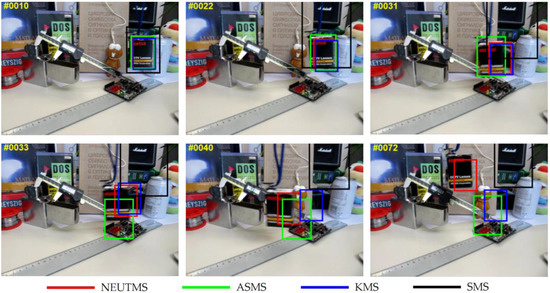
Figure 3.
Screenshots of tracking results of the video sequence used for testing (Box, target is selected in frame #1).
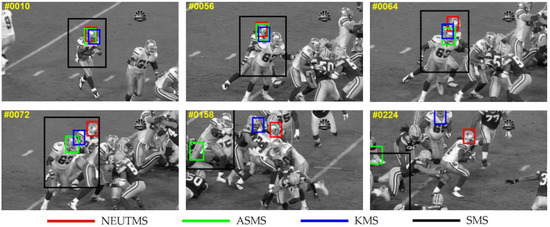
Figure 4.
Screenshots of tracking results of the video sequence used for testing (Football, target is selected in frame #1).

Figure 5.
Screenshots of tracking results of the video sequence used for testing (Bolt, target is selected in frame #1).
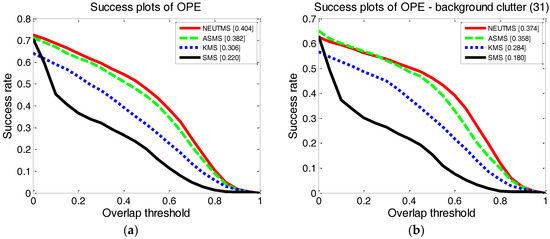
Figure 6.
Success plots of one-pass evaluation (OPE): (a) Success plots of OPE over all the testing sequences; (b) Success plots of OPE over all the 31 testing sequences included the challenge of background clutters (BC). The value shown between the brackets is the area under curve (AUC) value corresponds to the tracker.
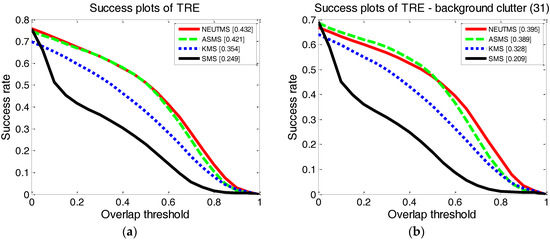
Figure 7.
Success plots of temporal robustness evaluation (TRE): (a) Success plots of TRE over all the testing sequences; (b) Success plots of TRE over all the 31 testing sequences included the challenge of BC. The value shown between the brackets is the AUC value corresponds to the tracker.
MountainBike sequence: This sequence highlights the challenges of BC, IPR and OPR. As shown in Figure 2, an improper scale of the bounding box is estimated by the SMS tracker, and the SMS tracker has failed in frame #26. The ASMS tracker, as can be seen in frame #32, has drifted from the tracking target because of the similar color of the surroundings, although an appropriate scale is given. During the first half of the tracking process, both of the KMS and our NEUTMS perform well. However, compared to the NEUTMS, the KMS tracker sometimes drifts a little farer from the biker, as seen in frame #38. When the challenge of background clutter appears, the KMS tracker may also drift from the right location of the target, as seen in frame #178. During the whole tracking process, the NEUTMS tracker performs the best result.
Box sequence: The challenges included in this sequence can be found in Table 1. This sequence is more challenging than the MountainBike sequence. As seen in frame #31 in Figure 3, all the trackers except for the SMS tracker can give a right location of the tracked box, and the ASMS performs the best result so far. Due to the black background upon the box, the SMS tracker fails soon. While the box is passing by the circuit board on the table, both the ASMS and the KMS tracker begin to lose the box. By employing the information of the background region, our NEUTMS tracker has successfully overcome the challenges like BC and MB during this sequence.
Football sequence: Challenges of BC, OCC, IPR and OPR are presented in this sequence. As shown in Figure 4, the SMS tracker has already failed in frame #10. The ASMS and KMS trackers fail when the tracked player getting close to another player on account of the factor of all the players wear the same helmet. However, the NEUTMS tracker performs well even the tracked player runs through some players with similar feature.
Bolt sequence: This sequence presents the challenges of OCC, DEF, IPR and OPR. As shown in Figure 5, all the trackers perform well till frame #117. Compared to the ASMS and SMS trackers, the KMS and NEUTMS trackers cannot calculate a proper size for the bounding box due to the fixed scale. The KMS tracker has begun to drift form the target on the account of the improper size of the bounding box since frame #117. By fusing the information of the feature of the object and background region, the NEUTMS tracker has successfully tracked the target throughout this sequence even with an inappropriate scale. Though a good scale is estimated by the ASMS tracker, it fails when Bolt passes by some other runners, as seen in frame #142 and #160.
We employ all the 61 sequences as the testing sequence dataset. Success plots of OPE and TRE over all the sequences are shown in Figure 6a and Figure 7a respectively, which show our NEUTMS tracker is superior to other trackers. Due to the fact that the focus of our work in this paper is to employ both the object and background feature to enhance the mean-shift tracker’s ability of overcoming the problem of similar surroundings, only the success plots for the challenge of BC are given, and then the BC challenge is one of the most challenging problems for the traditional mean-shift tracker [13]. The results of the corresponding success plots are shown in Figure 6b and Figure 7b, which show the robustness of the NEUTMS tracker when handling the challenge of BC.
In order to test the performance of the proposed NEUTMS tracker over other kinds of challenges, all the AUC results for each tracker are given in Table 2 and Table 3. The best result is highlighted in red italic type and the second result is highlighted in bold type. As seen in Table 2 and Table 3, the NEUTMS tracker performs the best result when tackling the challenge of BC, MB, DEF, IPR, OCC or OPR when the OPE evaluation is considered. For TRE, the NEUTMS tracker performs the best result when confronting the same kind of challenge to OPE except for the challenge of MB. The ASMS tracker wins over SV because a robust scale updating scheme is used. The NEUTMS tracker performs the second best result over FM, IV and OV mainly because some inaccurate background information may be brought into the background feature model. The NEUTMS tracker performs the second best result when confronting the challenge of LR on account of less information can be employed for enhancing the tracker.

Table 2.
AUC results of each tracker on sequences with different challenge for OPE.

Table 3.
AUC results of each tracker on sequences with different challenge for TRE.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, a neutrosophic weighted mean-shift tracker is proposed. The experimental results have revealed its robustness. While calculating the neutrosophic weighted histogram, two kinds of criteria are considered as the object feature similarity and the background feature similarity, and each bin of the weight histogram is represented in the SVNS domain via three membership functions T, I and F. Both the feature in the object and the background region are fused by introducing the weighted neutrosophic similarity score function. Finally, the neutrosophic weighted histogram is employed to decide the new location of the object. As discussed in this work, we have not considered the scale variation problem. To further improve the performance of our tracker in the future, our primary mission is to introduce a scale updating scheme into this neutrosophic weighted mean-shift tracker.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61603258, the public welfare technology application research project of Zhejiang province under Grant No. 2016C31082, and National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61703280, 61772018.
Author Contributions
Keli Hu conceived and designed the algorithm; Keli Hu, En Fan, Jun Ye and Changxing Fan performed and implemented experiments; Keli Hu and Shigen Shen analyzed the data; Keli Hu wrote the paper; Jun Ye and Yuzhang Gu have fully supervised the work and approved the paper for submission.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yilmaz, A.; Javed, O.; Shah, M. Object tracking: A survey. ACM Comp. Surv. 2006, 38, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Smeulders, A.W.M.; Chu, D.M.; Cucchiara, R.; Calderara, S.; Dehghan, A.; Shah, M. Visual tracking: An experimental survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1442–1468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grabner, H.; Bischof, H. On-line boosting and vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 260–267. [Google Scholar]
- Grabner, H.; Leistner, C.; Bischof, H. Semi-supervised on-line boosting for robust tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 234–247. [Google Scholar]
- Babenko, B.; Ming-Hsuan, Y.; Belongie, S. Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaihua, Z.; Lei, Z.; Ming-Hsuan, Y. Fast compressive tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 2002–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Comaniciu, D.; Ramesh, V.; Meer, P. Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, 15 June 2000; pp. 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Comaniciu, D.; Ramesh, V.; Meer, P. Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichter, I. Mean shift trackers with cross-bin metrics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 34, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C. Video Object Tracking Using Sift and Mean Shift. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bousetouane, F.; Dib, L.; Snoussi, H. Improved mean shift integrating texture and color features for robust real time object tracking. Vis. Comput. 2013, 29, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojir, T.; Noskova, J.; Matas, J. Robust scale-adaptive mean-shift for tracking. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 49, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.T. Mean-shift blob tracking through scale space. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Madison, WI, USA, 18–20 June 2003; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeberg, T. Scale-Space Theory in Computer Vision; Kluwer Academic: Norwell, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 349–382. [Google Scholar]
- Smarandache, F. Neutrosophy: Neutrosophic Probability, Set and Logic; American Research Press: Rehoboth, DE, USA, 1998; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Şengür, A. A novel image segmentation algorithm based on neutrosophic similarity clustering. Appl. Soft Comp. 2014, 25, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anter, A.M.; Hassanien, A.E.; ElSoud, M.A.A.; Tolba, M.F. Neutrosophic sets and fuzzy c-means clustering for improving CT liver image segmentation. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2014, 303, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Karabatak, E.; Guo, Y.; Sengur, A. Modified neutrosophic approach to color image segmentation. J. Electron. Imag. 2013, 22, 4049–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, H.D. A neutrosophic approach to image segmentation based on watershed method. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Şengür, A.; Ye, J. A novel image thresholding algorithm based on neutrosophic similarity score. Measurement 2014, 58, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hefenawy, N.; Metwally, M.A.; Ahmed, Z.M.; El-Henawy, I.M. A review on the applications of neutrosophic sets. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2016, 13, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sengur, A. A novel 3D skeleton algorithm based on neutrosophic cost function. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 36, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Ye, J.; Fan, E.; Shen, S.; Huang, L.; Pi, J. A novel object tracking algorithm by fusing color and depth information based on single valued neutrosophic cross-entropy. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 32, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sengur, A. NCM: Neutrosophic c-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 2710–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Pramanik, S.; Giri, B.C. Topsis method for multi-attribute group decision-making under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Neural Comput. Appl. 2015, 27, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharal, A. A neutrosophic multi-criteria decision making method. New Math. Nat. Comput. 2014, 10, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Single valued neutrosophic cross-entropy for multicriteria decision making problems. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, P. Neutrosophic sets and its applications to decision making. Adapt. Learn. Optim. 2015, 19, 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J. Multicriteria decision-making method using the correlation coefficient under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2013, 42, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Smarandache, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sunderraman, R. Single valued neutrosophic sets. Multisp. Multistruct. 2010, 4, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).