A Survey on Data Compression Methods for Biological Sequences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Protein Sequence Compression
3. Genomic Sequence Compression
3.1. Reference-Free Methods
3.2. Reference-Based Methods
4. File Formats
4.1. FASTA/Multi-FASTA
4.2. FASTQ
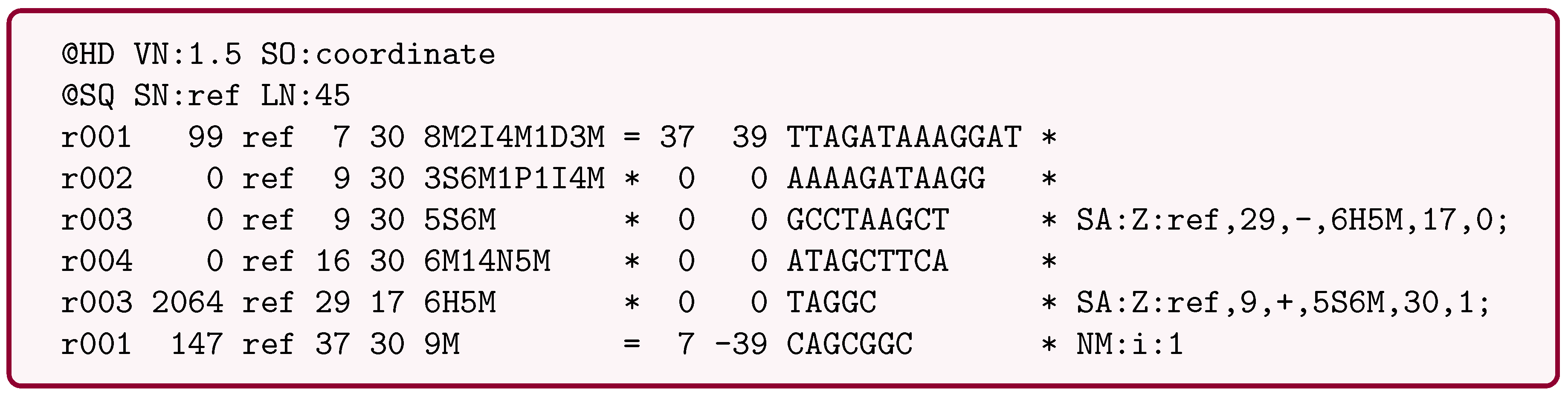
4.3. SAM/BAM
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muir, P.; Li, S.; Lou, S.; Wang, D.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Salichos, L.; Zhang, J.; Weinstock, G.M.; Isaacs, F.; Rozowsky, J.; et al. The real cost of sequencing: Scaling computation to keep pace with data generation. Genom. Biol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S. On the future of genomic data. Science 2011, 331, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, C.; Mattavelli, M.; Hernandez, A.; Chiariglione, L.; Xenarios, I.; Guex, N.; Stockinger, H.; Schuepbach, T.; Kahlem, P.; Iseli, C.; et al. Investigation on Genomic Information Compression and Storage; ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29/WG 11 N15346; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Giancarlo, R.; Rombo, S.; Utro, F. Compressive biological sequence analysis and archival in the era of high-throughput sequencing technologies. Brief. Bioinform. 2014, 15, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruijn, N. A Combinatorial Problem. Available online: https://pure.tue.nl/ws/files/4442708/597473.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Compeau, P.; Pevzner, P.; Tesler, G. How to apply de Bruijn graphs to genome assembly. Nat. Methods 2011, 29, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, T.; Bromage, A. Succinct data structures for assembling. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Dix, T.; Allison, L. A genome alignment algorithm based on compression. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Dix, T.; Allison, L.; Mears, C. A simple statistical algorithm for biological sequence compression. In Proceedings of the DCC ’07: Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 27–29 March 2007; pp. 43–52.
- Rafizul Haque, S.; Mallick, T.; Kabir, I. A new approach of protein sequence compression using repeat reduction and ASCII replacement. IOSR J. Comput. Eng. (IOSR-JCE) 2013, 10, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M. Virtual Organisms: The Startling World of Artificial Life; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wootton, J. Non-globular domains in protein sequences: Automated segmentation using complexity measures. Comput. Chem. 1994, 18, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, D.; Caglioti, E.; Chica, C. Compressing proteomes: The relevance of medium range correlations. EURASIP J. Bioinform. Syst. Biol. 2007, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Cao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Su, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Natural protein sequences are more intrinsically disordered than random sequences. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2949–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Human Proteome Project. Available online: http://www.thehpp.org (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Three sequenced Neanderthal genomes. Available online: http://cdna.eva.mpg.de/neandertal (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Nevill-Manning, C.; Witten, I. Protein is incompressible. In Proceedings of the DCC ’99: Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 29–31 March 1999; pp. 257–266.
- Matsumoto, T.; Sadakane, K.; Imai, H. Biological sequence compression algorithms. Genom. Inform. 2000, 11, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hategan, A.; Tabus, I. Protein is compressible. In Proceedings of the 6th Nordic Signal Processing Symposium, Espoo, Finland, 9–11 June 2004; pp. 192–195.
- Willems, F.; Shtarkov, Y.; Tjalkens, T. The context tree weighting method: Basic properties. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1995, 41, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hategan, A.; Tabus, I. Jointly encoding protein sequences and their secondary structure. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Genomic Signal Processing and Statistics (GENSIPS 2007), Tuusula, Finland, 10–12 June 2007.
- Daniels, N.; Gallant, A.; Peng, J.; Cowen, L.; Baym, M.; Berger, B. Compressive genomics for protein databases. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: Pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashida, M.; Ruan, P.; Akutsu, T. Proteome compression via protein domain compositions. Methods 2014, 67, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giancarlo, R.; Scaturro, D.; Utro, F. Textual data compression in computational biology: Algorithmic techniques. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2012, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Z.; He, S.; Yang, X. High-throughput DNA sequence data compression. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakr, N.; Sharawi, A. DNA lossless compression algorithms: Review. Am. J. Bioinform. Res. 2013, 3, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wandelt, S.; Bux, M.; Leser, U. Trends in genome compression. Curr. Bioinform. 2014, 9, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumbach, S.; Tahi, F. Compression of DNA sequences. In Proceedings of the DCC’93: Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 30 March–2 April 1993; pp. 340–350.
- Ziv, J.; Lempel, A. A universal algorithm for sequential data compression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1977, 23, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumbach, S.; Tahi, F. A new challenge for compression algorithms: Genetic sequences. Inf. Process. Manag. 1994, 30, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivals, E.; Delahaye, J.; Dauchet, M.; Delgrange, O. A guaranteed compression scheme for repetitive DNA sequences. In Proceedings of the DCC ’96: Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 31 March–3 April 1996; p. 453.
- Ukkonen, E. On-line construction of suffix trees. Algorithmica 1995, 14, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kwong, S.; Li, M.; Delgrange, O. A compression algorithm for DNA sequences and its applications in genome comparison. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual International Conference of Research in Computational Molecular Biology (RECOMB ’00), Tokyo, Japan, 8–11 April 2000; pp. 107–117.
- Chen, X.; Li, M.; Ma, B. DNACompress: Fast and effective DNA sequence. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 1696–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Tromp, J.; Li, M. PatternHunter: Faster and more sensitive homology search. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabus, I.; Korodi, G.; Rissanen, J. DNA sequence compression using the normalized maximum likelihood model for discrete regression. In Proceedings of the DCC ’03: Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 25–27 March 2003; pp. 253–262.
- Korodi, G.; Tabus, I. An efficient normalized maximum likelihood algorithm for DNA sequence compression. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2005, 23, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Agarwal, S. A scheme that facilitates searching and partial decompression of textual documents. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Eng. 2008, 1, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Agarwal, S. A novel approach for compressing DNA sequences using semi-statistical compressor. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 33, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.; Ferreira, P.; Neves, A.; Bastos, C. On the representability of complete genomes by multiple competing finite-context (Markov) models. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Ji, Z.; Shi, Y. DNA sequence compression using adaptive particle swarm optimization-based memetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2011, 15, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Suganthan, P.; Deb, K. Novel composition test functions for numerical global optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium (SIS 2005), Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–10 June 2005; pp. 68–75.
- Liang, J.; Qin, A.; Suganthan, P.; Baskar, S. Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2006, 10, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, S.; Kim, J.; Xiong, H.; Ohno-Machado, L.; Jiang, X. DNA-COMPACT: DNA compression based on a pattern-aware contextual modeling technique. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Xie, M. Genome compression based on Hilbert space filling curve. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Management, Education, Information and Control (MEICI 2015), Shenyang, China, 29–31 May 2015; pp. 1685–1689.
- Xie, X.; Zhou, S.; Guan, J. CoGI: Towards compressing genomes as an image. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2015, 12, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.; Fahmy, M. Binary image compression using efficient partitioning into rectangular regions. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 43, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, M. Optimized context weighting based on the least square algorithm. In Wireless Communications, Networking and Applications, Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Applications (WCNA 2014), Shenzhen, China, 27–28 December 2014; Zeng, Q.-A., Ed.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 348, pp. 1037–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Pratas, D.; Pinho, A.; Ferreira, P. Efficient compression of genomic sequences. In Proceedings of the DCC ’16: Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 30 March–1 April 2016; pp. 231–240.
- Pinho, A.J.; Pratas, D.; Ferreira, P.J. Bacteria DNA sequence compression using a mixture of finite-context models. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), Nice, France, 28–30 June 2011; pp. 125–128.
- Pratas, D.; Pinho, A.J. Exploring deep Markov models in genomic data compression using sequence pre-analysis. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Lisbon, Portugal, 1–5 September 2014; pp. 2395–2399.
- Wandelt, S.; Leser, U. Adaptive efficient compression of genomes. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deorowicz, S.; Grabowski, S. Compression of DNA sequence reads in FASTQ format. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 860–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christley, S.; Lu, Y.; Li, C.; Xie, X. Human genomes as email attachments. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruppu, S.; Puglisi, S.; Zobel, J. Relative Lempel-Ziv compression of genomes for large-scale storage and retrieval. String Process. Inf. Retr. 2010, 6393, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Kuruppu, S.; Puglisi, S.; Zobel, J. Optimized relative Lempel-Ziv compression of genomes. Conf. Res. Pract. Inf. Technol. Ser. 2011, 113, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, D. A novel compression tool for efficient storage of genome resequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffman, D. A method for the construction of minimum redundancy codes. Proc. IRE 1952, 40, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.; Pratas, D.; Garcia, S. GReEn: A tool for efficient compression of genome resequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissanen, J. Generalized Kraft inequality and arithmetic coding. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1976, 20, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deorowicz, S.; Grabowski, S. Robust relative compression of genomes with random access. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2979–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deorowicz, S.; Danek, A.; Niemiec, M. GDC 2: Compression of large collections of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storer, J.; Szymanski, T. Data compression via text substitution. J. ACM 1982, 29, 928–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, R.; Vitter, J. Compressed suffix arrays and suffix trees with applications to text indexing and string matching. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Portland, OR, USA, 21–23 May 2000; pp. 397–406.
- Kuruppu, S.; Beresford-Smith, B.; Conway, T.; Zobel, J. Iterative dictionary construction for compression of large DNA data sets. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2012, 9, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannane, A.; Williams, H. General-purpose compression for efficient retrieval. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2001, 52, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Xiong, H.; Jiang, X.; Ohno-Machado, L. An adaptive difference distribution-based coding with hierarchical tree structure for DNA sequence compression. In Proceedings of the DCC ’13: Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 20–22 March 2013; pp. 371–380.
- Cleary, J.; Witten, I. Data compression using adaptive coding and partial string matching. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1984, 32, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandelt, S.; Leser, U. FRESCO: Referential compression of highly-similar sequences. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2013, 10, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Sohn, I. Streamlined genome sequence compression using distributed source coding. Cancer Inform. 2014, 13, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, S.; Ramchandran, K. Distributed source coding using syndromes (DISCUS): Design and construction. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 626–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Rajasekaran, S. ERGC: An efficient referential genome compression algorithm. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3468–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffat, A. Implementing the PPM data compression scheme. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1990, 38, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, I.; Hernaez, M.; Weissman, T. iDoComp: A compression scheme for assembled genomes. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.; Peng, C. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, J.; Moorman, J. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar]
- Cosic, I. Macromolecular bioactivity: Is it resonant interaction between macromolecules?—Theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1994, 41, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanus, P.; Dingel, J.; Chalkidis, G.; Hagenauer, J. Compression of whole genome alignments. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2010, 56, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, L.; Pratas, D.; Pinho, A. A compression model for DNA multiple sequence alignment blocks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2013, 59, 3189–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, L.; Neves, A.; Pratas, D.; Pinho, A. MAFCO: A compression tool for MAF files. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layer, R.M.; Kindlon, N.; Karczewski, K.J.; Quinlan, A.R.; Consortium, E.A.; Exome Aggregation Consortium. Efficient genotype compression and analysis of large genetic-variation data sets. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lipman, D.; Pearson, W. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Brief. Bioinform. 1985, 227, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, T.; Mohammed, M.; Dutta, A.; Mande, S. BIND—An algorithm for loss-less compression of nucleotide sequence data. J. Biosci. 2012, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LZMA. Available online: http://www.7-zip.org/sdk.html (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Mohammed, M.; Dutta, A.; Bose, T.; Chadaram, S.; Mande, S. DELIMINATE—A fast and efficient method for loss-less compression of genomic sequences: Sequence analysis. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2527–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Lu, Y.; Lai, F.; Chien, Y.; Hwu, W. Integrating human genome database into electronic health record with sequence alignment and compression mechanism. J. Med. Syst. 2012, 36, 2587–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolico, A.; Fraenkel, A. Robust transmission of unbounded strings using Fibonacci representations. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1987, 33, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.; Pratas, D. MFCompress: A compression tool for FASTA and multi-FASTA data. Bioinformatics 2013, 30, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, G.; Lemaitre, C.; Lavenier, D.; Drezen, E.; Dayris, T.; Uricaru, R.; Rizk, G. Reference-free compression of high throughput sequencing data with a probabilistic de Bruijn graph. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, A.; Mitzenmacher, M. Less hashing, same performance: Building a better bloom filter. J. Random Struct. Algorithms 2008, 33, 187–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Zhang, X.; Ligo, J.G.; Farnoud, F.; Veeravalli, V.V.; Milenkovic, O. MetaCRAM: An integrated pipeline for metagenomic taxonomy identification and compression. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.; Salzberg, S. Kraken: Ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments. Genom. Biol. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S. Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.; Yiu, S.M.; Chin, F.Y. IDBA-UD: A de novo assembler for single-cell and metagenomic sequencing data with highly uneven depth. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golomb, S. Run-length encodings. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1966, 12, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, K.; Domnic, S. Extended golomb code for integer representation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2007, 9, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, I.; Asnani, H.; Bharadia, D.; Chowdhury, M.; Weissman, T.; Yona, G. Qualcomp: A new lossy compressor for quality scores based on rate distortion theory. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cock, P.; Fields, C.; Goto, N.; Heuer, M.; Rice, P. The Sanger FASTQ file format for sequences with quality scores, and the Solexa/Illumina FASTQ variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 38, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daily, K.; Rigor, P.; Christley, S.; Xie, X.; Baldi, P. Data structures and compression algorithms for high-throughput sequencing technologies. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, P. Universal codeword sets and representations of the integers. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1975, 21, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, P.; Benz, R.; Hirschberg, D.; Swamidass, S. Lossless compression of chemical fingerprints using integer entropy codes improves storage and retrieval. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 2098–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tembe, W.; Lowey, J.; Suh, E. G-SQZ: Compact encoding of genomic sequence and quality data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2192–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roguski, L.; Deorowicz, S. DSRC 2—Industry-oriented compression of FASTQ files. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2213–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, D.; Motta, G. Handbook of Data Compression; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bhola, V.; Bopardikar, A.; Narayanan, R.; Lee, K.; Ahn, T. No-reference compression of genomic data stored in FASTQ format. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM 2011), Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–15 November 2011; pp. 147–150.
- Jones, D.; Ruzzo, W.; Peng, X.; Katze, M. Compression of next-generation sequencing reads aided by highly efficient de novo assembly. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hach, F.; Numanagic, I.; Alkan, C.; Sahinalp, S. SCALCE: Boosting sequence compression algorithms using locally consistent encoding. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3051–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahinalp, S.; Vishkin, U. Efficient approximate and dynamic matching of patterns using a labeling paradigm. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS), Burlington, VT, USA, 14–16 October 1996; pp. 320–328.
- Cormode, G.; Paterson, M.; Sahinalp, S.; Vishkin, U. Communication complexity of document exchange. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA), San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–11 January 2000; pp. 197–206.
- Batu, T.; Ergun, F.; Sahinalp, S. Oblivious string embeddings and edit distance approximations. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithm (SODA), Miami, FL, USA, 22–24 January 2006; pp. 792–801.
- Howison, M. High-throughput compression of FASTQ data with SeqDB. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2013, 10, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alted, F. Available online: http://www.blosc.org (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Alted, F. Why modern CPUs are starving and what can be done about it. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2010, 12, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfield, J.; Mahoney, M. Compression of FASTQ and SAM format sequencing data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelwien, E. Available online: http://compressionratings.com/i_ctxf.html (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Mahoney, M. Available online: http://mattmahoney.net/dc/zpaq.html (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Mahoney, M. Adaptive Weighing of Context Models for Lossless Data Compression; Technical Report CS-2005–16; Florida Institute of Technology CS Department: Melbourne, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski, S.; Deorowicz, S.; Roguski, L. Disk-based compression of data from genome sequencing. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.; Hayes, W.; Hunt, B.; Mount, S.; Yorke, J. Reducing storage requirements for biological sequence comparison. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3363–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movahedi, N.; Forouzmand, E.; Chitsaz, H. De novo co-assembly of bacterial genomes from multiple single cells. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM 2012), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 4–7 October 2012; pp. 1–5.
- Li, Y.; Kamousi, P.; Han, F.; Yang, S.; Yan, X.; Suri, S. Memory efficient minimum substring partitioning. In Proceedings of the 39th international conference on Very Large Data Bases (VLDB 2013), Trento, Italy, 26–30 August 2013; pp. 169–180.
- Chikhi, R.; Limasset, A.; Jackman, S.; Simpson, J.; Medvedev, P. On the representation of de Bruijn graphs. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology (RECOMB 2014), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2–5 April 2014; pp. 35–55.
- Deorowicz, S.; Kokot, M.; Grabowski, S.; Debudaj-Grabysz, A. KMC 2: Fast and resource-frugal k-mer counting. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkarin, D. PPM: One step to practicality. In Proceedings of the DCC ’02: Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, UT, USA, 2–4 April 2002; pp. 202–211.
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; He, S. Light-weight reference-based compression of FASTQ data. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The SAM/BAM Format Specification Working Group. Sequence Alignment/Map Format Specification. Available online: https://samtools.github.io/hts-specs/SAMv1.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Fritz, M.; Leinonen, R.; Cochrane, G.; Birney, E. Efficient storage of high throughput DNA sequencing data using reference-based compression. Genom. Res. 2011, 21, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagne, F.; Dorff, K.; Chambwe, N.; Robinson, J.; Mesirov, J. Compression of structured high-throughput sequencing data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varda, K. PB. Available online: https://github.com/google/protobuf (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Popitsch, N.; Von Haeseler, A. NGC: Lossless and lossy compression of aligned high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hach, F.; Numanagic, I.; Sahinal, S. DeeZ: Reference-based compression by local assembly. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 1081–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- gzip. Available online: http://www.gzip.org (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Rebico. Available online: http://bioinformatics.ua.pt/software/rebico (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Human (GRC). Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Homo_sapiens/Assembled_chromosomes/seq (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Chimpanzee. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Pan_troglodytes/Assembled_chromosomes/seq (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Rice5. Available online: ftp://ftp.plantbiology.msu.edu/pub/data/Eukaryotic_Projects/o_sativa/annotation_dbs/pseudomolecules/version_5.0 (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- CAMERA Prokaryotic Nucleotide. Available online: ftp://ftp.imicrobe.us/camera/camera_reference_datasets/10572.V10.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- ERR174310_1. Available online: ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/ERR174/ERR174310/ERR174310_1.fastq.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- ERR174310_2. Available online: ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/ERR174/ERR174310/ERR174310_2.fastq.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- ERR194146_1. Available online: ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/ERR194/ERR194146/ERR194146_1.fastq.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- ERR194146_2. Available online: ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/fastq/ERR194/ERR194146/ERR194146_2.fastq.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- NA12877_S1. Available online: ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/ERA207/ERA207860/bam/NA12877_S1.bam (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- NA12878_S1. Available online: ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/ERA207/ERA207860/bam/NA12878_S1.bam (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- NA12882_S1. Available online: ftp://ftp.sra.ebi.ac.uk/vol1/ERA207/ERA207860/bam/NA12882_S1.bam (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Homo sapiens, GRC Reference Assembly—Chromosome 8. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Homo_sapiens/Assembled_chromosomes/seq/hs_ref_GRCh38.p7_chr8.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Homo sapiens, CHM Reference Assembly—Chromosome 8. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Homo_sapiens/Assembled_chromosomes/seq/hs_alt_CHM1_1.1_chr8.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Homo sapiens, GRC Reference Assembly—Chromosome 11. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Homo_sapiens/Assembled_chromosomes/seq/hs_ref_GRCh38.p7_chr11.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Homo sapiens, CHM Reference Assembly—Chromosome 11. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Homo_sapiens/Assembled_chromosomes/seq/hs_alt_CHM1_1.1_chr11.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Pan troglodytes (Chimpanze) Reference Assembly, v3.0—Chromosome 11. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Pan_troglodytes/Assembled_chromosomes/seq/ptr_ref_Pan_tro_3.0_chr11.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Pongo abelii (Orangutan) Reference Assembly—Chromosome 11. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Pongo_abelii/Assembled_chromosomes/seq/pab_ref_P_pygmaeus_2.0.2_chr11.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Homo sapiens, GRC Reference Assembly—Chromosome 16. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Homo_sapiens/Assembled_chromosomes/seq/hs_ref_GRCh38.p7_chr16.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Homo sapiens, Korean Reference—Chromosome 16. Available online: ftp://ftp.kobic.re.kr/pub/KOBIC-KoreanGenome/fasta/chromosome_16.fa.gz (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Oryza sativa (Rice), v5.0. Available online: ftp://ftp.plantbiology.msu.edu/pub/data/Eukaryotic_Projects/o_sativa/annotation_dbs/pseudomolecules/version_5.0 (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Oryza sativa (Rice), v7.0. Available online: ftp://ftp.plantbiology.msu.edu/pub/data/Eukaryotic_Projects/o_sativa/annotation_dbs/pseudomolecules/version_7.0 (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Pratas, D. Available online: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pratas/rebico/master/methods.txt (accessed on 11 October 2016).
- Li, H. BGT: Efficient and flexible genotype query across many samples. Bioinformatics 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambo, F.; Di Camillo, B.; Toffolo, G.; Cobelli, C. Compression and fast retrieval of SNP data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3078–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.D.; Dix, T.I.; Allison, L. A genome alignment algorithm based on compression. BMC bioinform. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratas, D.; Silva, R.M.; Pinho, A.J.; Ferreira, P.J. An alignment-free method to find and visualise rearrangements between pairs of DNA sequences. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beller, T.; Ohlebusch, E. Efficient construction of a compressed de Bruijn graph for pan-genome analysis. In Combinatorial Pattern Matching; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baier, U.; Beller, T.; Ohlebusch, E. Graphical pan-genome analysis with compressed suffix trees and the Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2015, 32, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, A.J.; Garcia, S.P.; Pratas, D.; Ferreira, P.J. DNA sequences at a glance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandelt, S.; Leser, U. MRCSI: Compressing and searching string collections with multiple references. Proc. VLDB Endow. 2015, 8, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| File Format | Dataset | File Size(MB) |
|---|---|---|
| FASTA/Multi-FASTA | Human (GRC) [137] | 2,987 |
| Chimpanzee [138] | 3,179 | |
| Rice5 [139] | 166 | |
| CAMERA Prokaryotic Nucleotide [140] | 43,945 | |
| FASTQ | ERR174310_1 [141] | 51,373 |
| ERR174310_2 [142] | 51,373 | |
| ERR194146_1 [143] | 209,316 | |
| ERR194146_2 [144] | 209,316 | |
| BAM | NA12877_S1 [145] | 74,455 |
| NA12878_S1 [146] | 108,290 | |
| NA12882_S1 [147] | 88,318 |
| File Format | Target Genome | File Size (MB) | Reference Genome | File Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FASTA/Multi-FASTA | HS8 [148] | 138 | HSCHM8 [149] | 136 |
| HS11 [150] | 128 | HSCHM11 [151] | 125 | |
| HS11 [150] | 128 | PT11 [152] | 126 | |
| HS11 [150] | 128 | PA11 [153] | 127 | |
| HSK16 [154] | 71 | HS16 [155] | 78 | |
| Rice5 [156] | 166 | Rice7 [157] | 164 |
| Dataset | Method | Metric | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Ratio | C-Time | D-Time | C-Mem | D-Mem | ||
| (min) | (min) | (MB) | (MB) | |||
| DELIMINATE [87] | 4.95 | 15.08 | 5.90 | 685.55 | 73.54 | |
| Human (GRC) | MFCompress [90] | 4.96 | 34.47 | 29.48 | 1,240.45 | 1,266.49 |
| (2.92 GB) | gzip [135] | 3.59 | 8.85 | 0.50 | 6.87 | 6.87 |
| LZMA [86] | 4.39 | 117.70 | 1.26 | 199.52 | 31.58 | |
| DELIMINATE | 5.36 | 16.64 | 6.62 | 683.31 | 73.55 | |
| Chimpanzee | MFCompress | 5.43 | 33.93 | 28.55 | 1,377.85 | 1,374.18 |
| (3.10 GB) | gzip | 3.85 | 8.79 | 0.52 | 6.87 | 6.87 |
| LZMA | 4.68 | 118.31 | 1.26 | 199.52 | 31.58 | |
| DELIMINATE | 5.22 | 0.59 | 0.33 | 368.11 | 43.41 | |
| Rice5 | MFCompress | 5.15 | 2.15 | 1.72 | 1,169.64 | 1,082.49 |
| (0.16 GB) | gzip | 3.28 | 0.53 | 0.03 | 6.87 | 6.87 |
| LZMA | 4.46 | 6.71 | 0.07 | 199.71 | 25.79 | |
| DELIMINATE | 5.07 | 198.24 | 85.38 | 684.66 | 687.44 | |
| CAMERA | MFCompress | 5.39 | 571.74 | 223.61 | 2,764.16 | 2,668.16 |
| (42.91 GB) | gzip | 3.52 | 141.33 | 7.66 | 6.87 | 6.87 |
| LZMA | 4.51 | 1,720.09 | 16.48 | 199.71 | 31.58 | |
| Dataset | Method | Metric | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Ratio | C-Time | D-Time | C-Mem | D-Mem | ||
| (min) | (min) | (MB) | (MB) | |||
| Fqzcomp [116] | 4.76 | 49.58 | 64.79 | 77.21 | 67.31 | |
| Quip [108] | 4.76 | 95.36 | 140.09 | 395.16 | 389.22 | |
| ERR174310_1 | DSRC [54] | 4.64 | 140.67 | 177.37 | 10,608.25 | 12,227.26 |
| (50.17 GB) | SCALCE [109] | 4.97 | 259.72 | 75.12 | 5,270.25 | 1,053.52 |
| gzip [135] | 2.90 | 119.32 | 9.48 | 6.87 | 6.87 | |
| LZMA [86] | 3.61 | 1,731.28 | 28.59 | 199.52 | 31.58 | |
| Fqzcomp | 4.93 | 51.79 | 65.47 | 77.27 | 67.24 | |
| Quip | 4.93 | 94.76 | 123.29 | 394.69 | 391.01 | |
| ERR174310_2 | DSRC | 4.82 | 150.67 | 159.58 | 11,109.85 | 11,867.62 |
| (50.17 GB) | SCALCE | 5.16 | 233.46 | 73.51 | 5,320.82 | 1,047.57 |
| gzip | 2.98 | 117.65 | 9.12 | 6.87 | 6.87 | |
| LZMA | 3.74 | 1,716.42 | 27.74 | 199.71 | 31.58 | |
| Fqzcomp | 4.87 | 186.94 | 234.54 | 79.36 | 67.21 | |
| Quip | 4.78 | 326.87 | 438.08 | 397.96 | 392.16 | |
| ERR194146_1 | DSRC | 4.72 | 490.42 | 637.80 | 11,288.26 | 11,965.20 |
| (204.41 GB) | SCALCE | 6.25 | 956.79 | 292.31 | 5,288.01 | 1,053.46 |
| gzip | 3.94 | 273.20 | 33.28 | 6.87 | 6.87 | |
| LZMA | 4.84 | 6,369.49 | 88.22 | 199.52 | 31.58 | |
| Fqzcomp | 4.85 | 166.93 | 221.19 | 61.49 | 65.18 | |
| Quip | 4.77 | 296.14 | 426.60 | 396.16 | 392.41 | |
| ERR194146_2 | DSRC | 4.70 | 600.75 | 672.58 | 11,306.27 | 14,600.30 |
| (204.41 GB) | SCALCE | 6.18 | 950.32 | 291.13 | 5,336.13 | 1,058.48 |
| gzip | 3.90 | 272.37 | 33.69 | 6.87 | 6.87 | |
| LZMA | 4.80 | 6,295.37 | 89.15 | 199.52 | 31.58 | |
| Dataset | Method | Metric | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Ratio | C-Time | D-Time | C-Mem | D-Mem | ||
| (min) | (min) | (MB) | (MB) | |||
| Deez [134] | 1.72 | 440.80 | 505.27 | 2,368.35 | 5,803.17 | |
| NA12877_S1 | Quip [108] | 1.41 | 548.97 | 584.99 | 464.84 | 459.89 |
| (72.71 GB) | gzip [135] | 1.00 | 72.85 | 12.11 | 6.87 | 6.87 |
| LZMA [86] | 0.99 | 865.02 | 133.36 | 199.45 | 31.58 | |
| Deez | 1.73 | 668.89 | 752.77 | 2,586.70 | 5,584.94 | |
| NA12878_S1 | Quip | 1.38 | 802.84 | 893.90 | 460.81 | 459.61 |
| (105.75 GB) | gzip | 1.00 | 109.88 | 17.68 | 6.87 | 6.87 |
| LZMA | 0.99 | 1,261.44 | 193.97 | 199.52 | 31.58 | |
| Deez | 1.79 | 553.17 | 641.44 | 2,699.24 | 5,773.42 | |
| NA12882_S1 | Quip | 1.38 | 665.75 | 720.99 | 463.47 | 459.09 |
| (86.25 GB) | gzip | 1.00 | 86.44 | 14.40 | 6.87 | 6.87 |
| LZMA | 0.99 | 1,024.85 | 158.24 | 199.45 | 31.58 | |
| Dataset | Method | Metric | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Ratio a | C-Time | D-Time | C-Mem | D-Mem | ||
| (min) | (min) | (MB) | (MB) | |||
| HS8 (138 MB) Ref b: HSCHM8 | iDoComp [75] | 241.77 | 9.95 | 28.48 | 787.58 | 787.58 |
| GReEn [60] | 102.98 | 242.99 | 247.32 | 1,124.38 | 1,110.83 | |
| GeCo [50] | 70.65 | 693.67 | 579.50 | 4,897.60 | 4,897.65 | |
| GDC 2 [63] | 239.72 | 2.89 | 0.07 | 1,513.25 | 166.84 | |
| GDC [73] | 4.47 | 3.44 | 0.22 | 12,256.34 | 12,256.34 | |
| HS11 (128 MB) Ref: HSCHM11 | iDoComp | 104.08 | 12.36 | 17.72 | 758.23 | 693.89 |
| GReEn | 60.74 | 200.41 | 233.40 | 1,061.21 | 1,042.00 | |
| GeCo | 67.81 | 517.44 | 509.67 | 4,897.79 | 4,897.73 | |
| GDC 2 | 110.97 | 2.78 | 0.06 | 1,415.80 | 111.89 | |
| GDC | 4.30 | 4.16 | 0.22 | 11,855.81 | 11,855.81 | |
| HS11 (128 MB) Ref: PT11 | iDoComp | 29.19 | 29.06 | 19.15 | 781.27 | 781.27 |
| GReEn | 11.99 | 252.55 | 279.45 | 1,078.43 | 1,062.30 | |
| GeCo | 24.77 | 507.39 | 520.43 | 4,897.84 | 4,897.77 | |
| GDC 2 | 27.49 | 4.65 | 0.08 | 1,434.61 | 118.70 | |
| GDC | 4.30 | 4.35 | 0.22 | 11,853.75 | 11,853.75 | |
| HS11 (128 MB) Ref: PA11 | iDoComp | 6.44 | 130.77 | 96.27 | 1,128.72 | 1,128.72 |
| GReEn | 4.21 | 323.82 | 278.12 | 1,065.21 | 1,060.59 | |
| GeCo | 12.34 | 517.65 | 524.30 | 4,897.84 | 4,897.77 | |
| GDC 2 | 6.21 | 18.45 | 0.16 | 1,459.12 | 310.48 | |
| GDC | 4.30 | 4.16 | 0.22 | 11,854.96 | 11,854.96 | |
| HSK16 (71 MB) Ref: HS16 | iDoComp | 173.93 | 5.56 | 10.66 | 461.78 | 461.78 |
| GReEn | 45.88 | 104.35 | 113.94 | 765.93 | 778.14 | |
| GeCo | 45.37 | 362.98 | 296.28 | 4,897.79 | 4,897.73 | |
| GDC 2 | 193.34 | 2.23 | 0.04 | 963.97 | 83.57 | |
| GDC | 9.16 | 1.60 | 0.06 | 11,304.26 | 11,304.26 | |
| RICE5 (166 MB) Ref: RICE7 | iDoComp | 204.38 | 28.22 | 34.50 | 950.05 | 950.05 |
| GReEn | 169.16 | 204.66 | 221.81 | 1,286.32 | 1,285.14 | |
| GeCo | 91.68 | 616.70 | 628.95 | 4,897.79 | 4,897.73 | |
| GDC 2 | 199.28 | 1.73 | 0.08 | 1,712.41 | 116.05 | |
| GDC | 4.44 | 5.36 | 0.27 | 11,789.49 | 11,789.49 | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosseini, M.; Pratas, D.; Pinho, A.J. A Survey on Data Compression Methods for Biological Sequences. Information 2016, 7, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7040056
Hosseini M, Pratas D, Pinho AJ. A Survey on Data Compression Methods for Biological Sequences. Information. 2016; 7(4):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7040056
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosseini, Morteza, Diogo Pratas, and Armando J. Pinho. 2016. "A Survey on Data Compression Methods for Biological Sequences" Information 7, no. 4: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7040056
APA StyleHosseini, M., Pratas, D., & Pinho, A. J. (2016). A Survey on Data Compression Methods for Biological Sequences. Information, 7(4), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7040056






