Smart Homes and Sensors for Surveillance and Preventive Education at Home: Example of Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Technologies and Methods
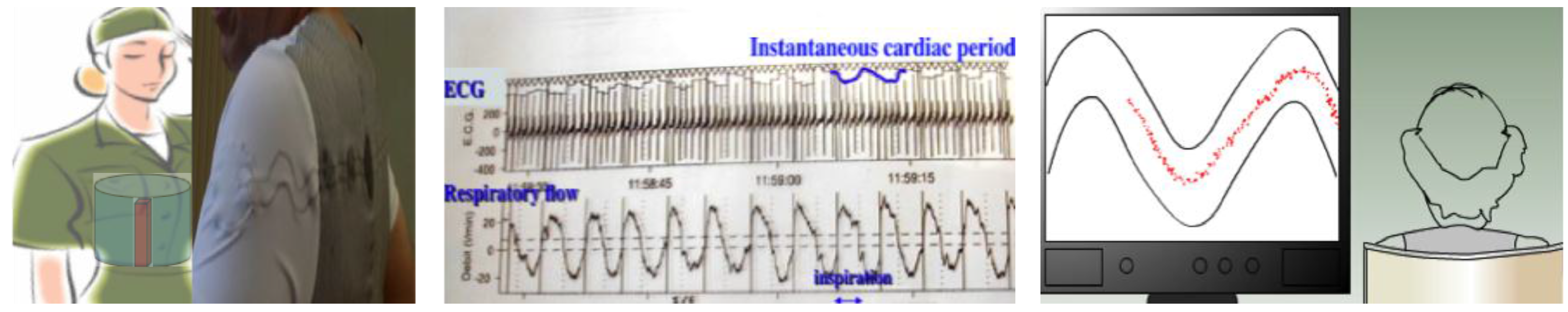
2.1. Physiological Sensors
2.2. Physical Sensors
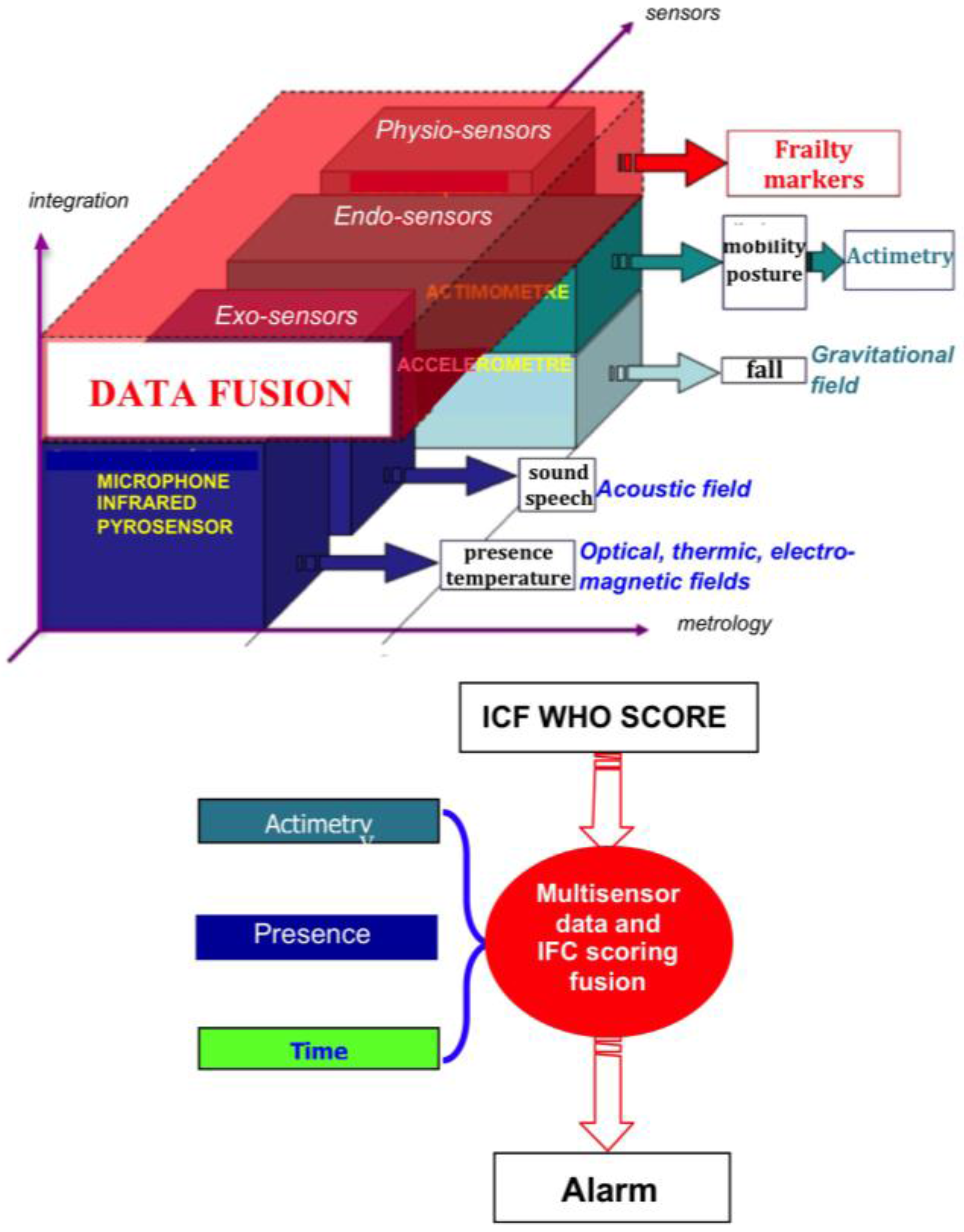
2.3. Sensor Integration
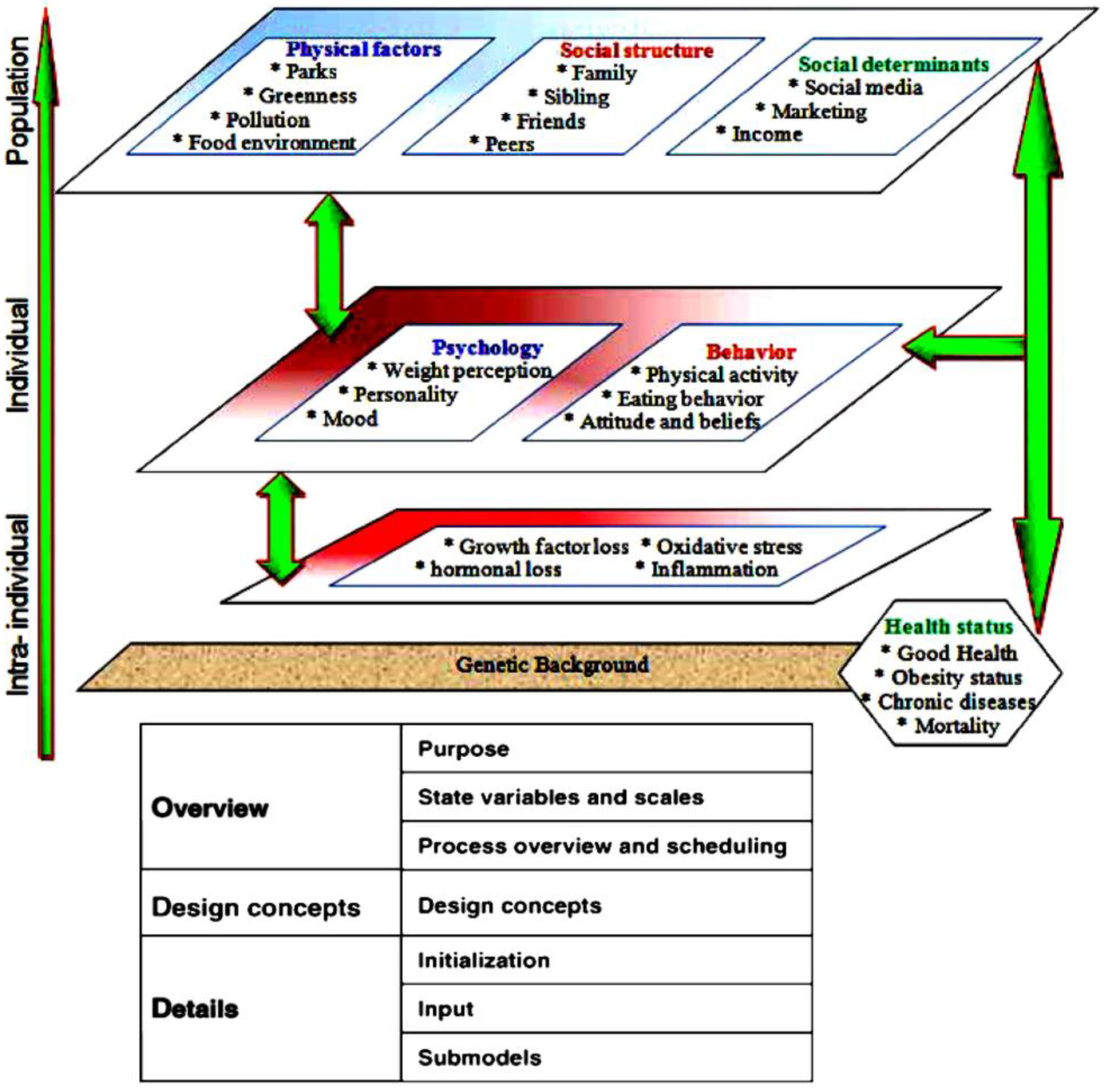
2.4. Obesity Determinants
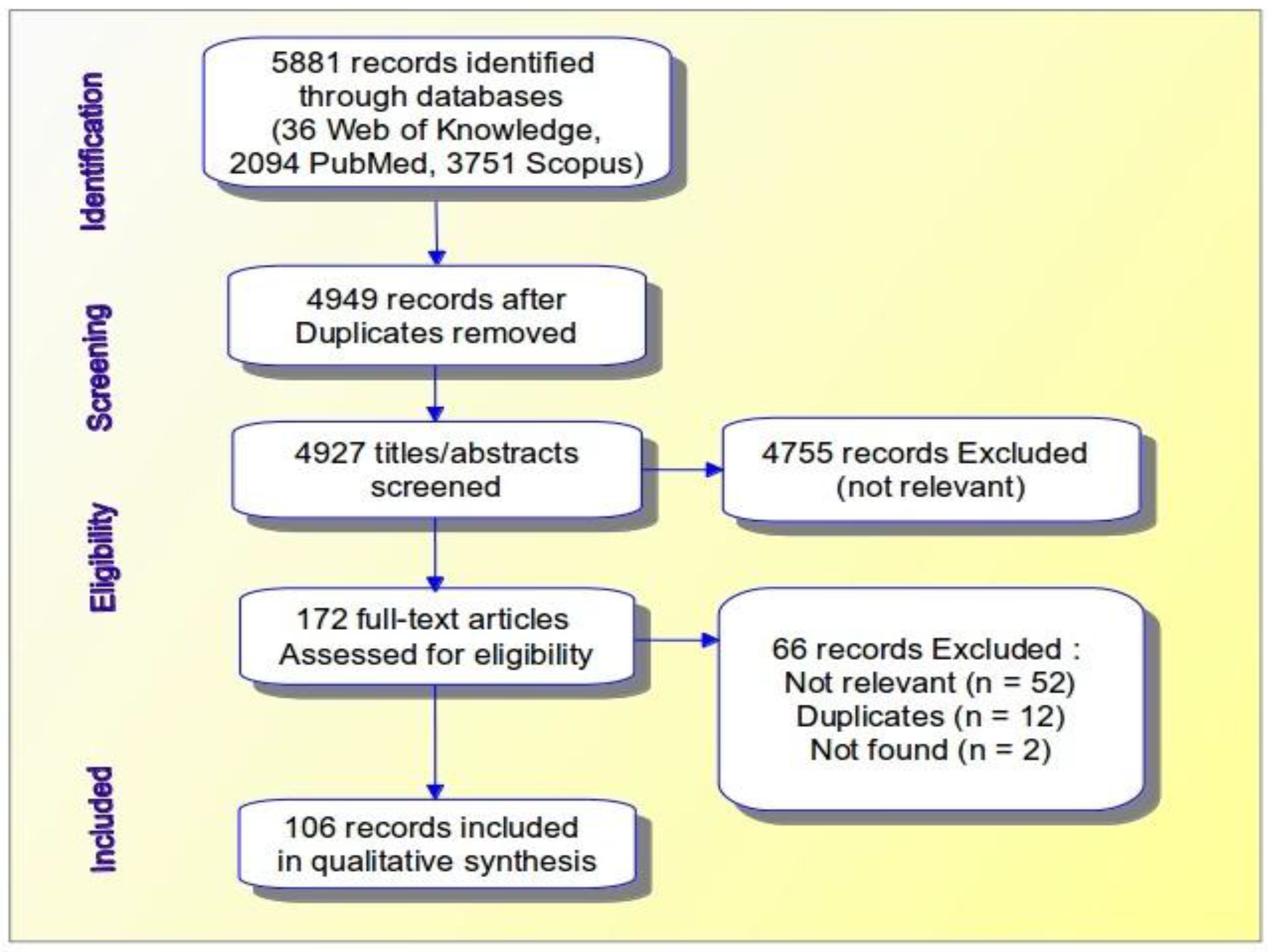
2.4.1. A Systematic Review
2.4.2. Environmental Factors
2.4.3. Physical Factors
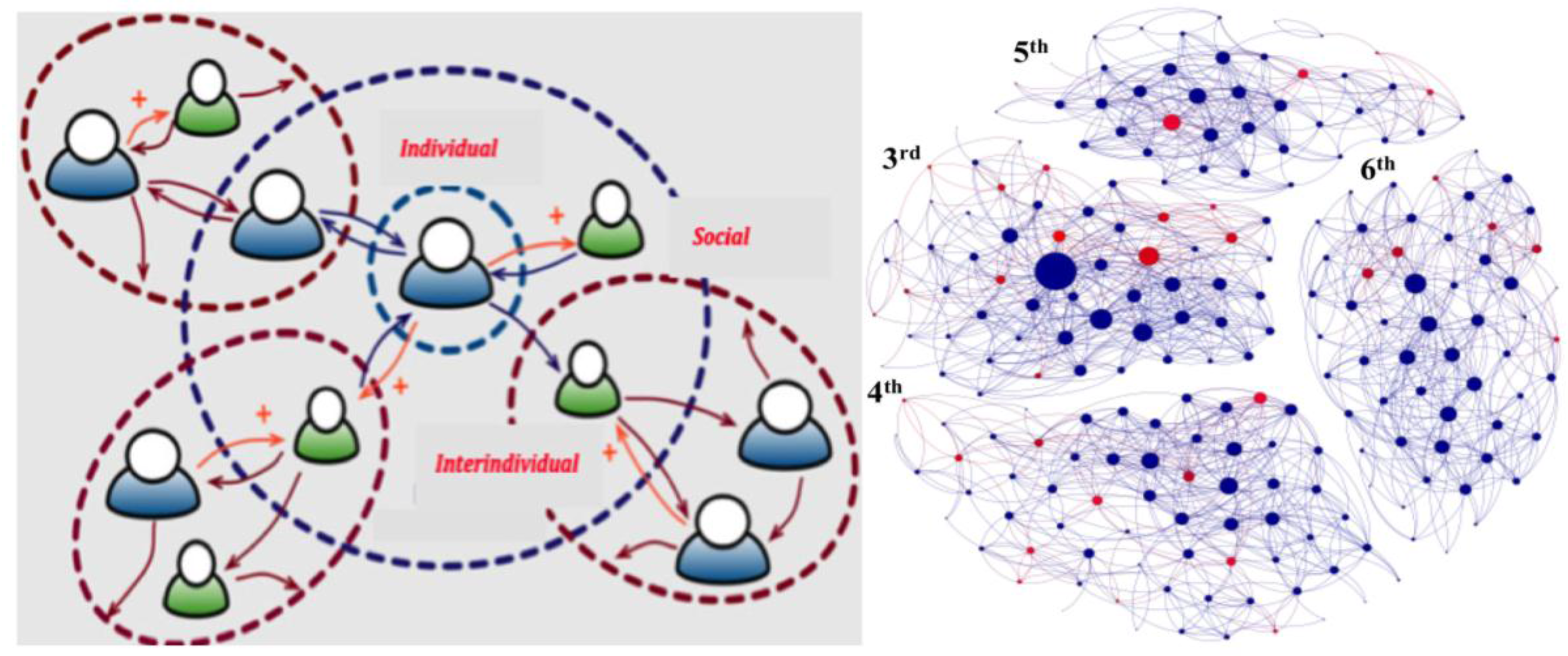
2.4.4. Social Factors
2.4.5. Psychological and Behavioral Factors
2.4.6. Biological Factors
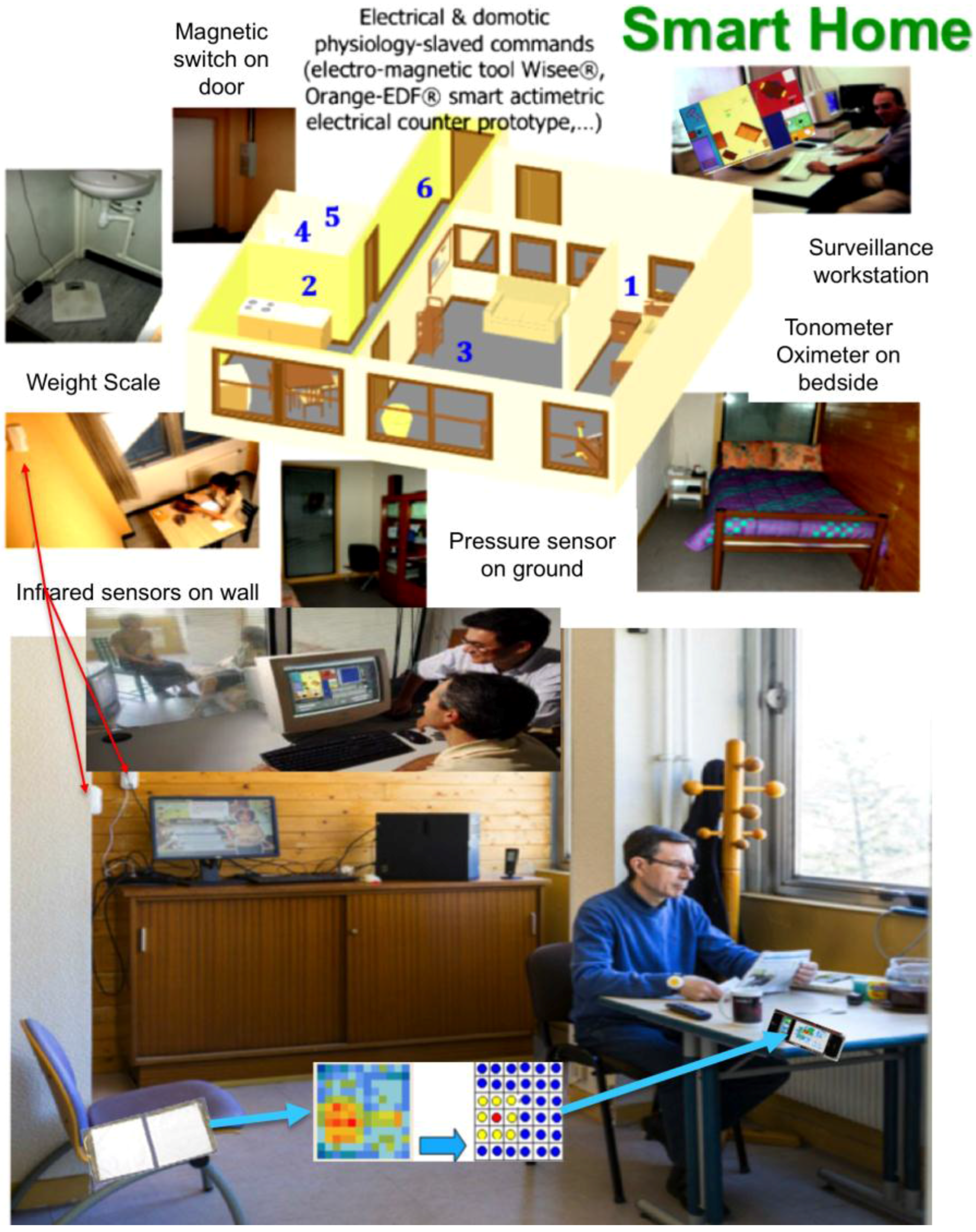
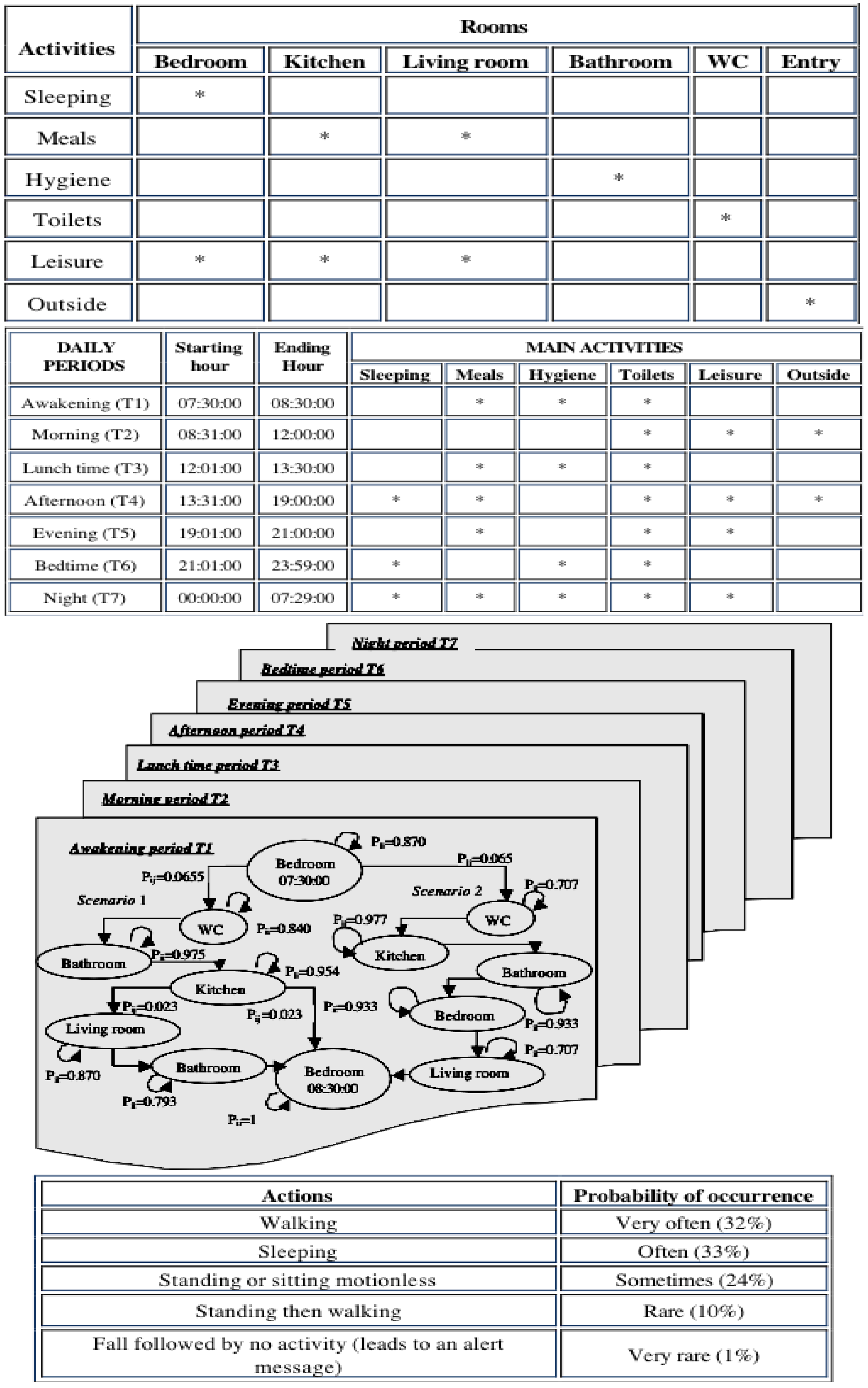
2.5. Actimetry for Chronic Patients at Home
- -
- Magnetic sensors detecting closed and open doors
- -
- Infrared sensors detecting movement
- -
- Sensors recording electric power and water consumption
- -
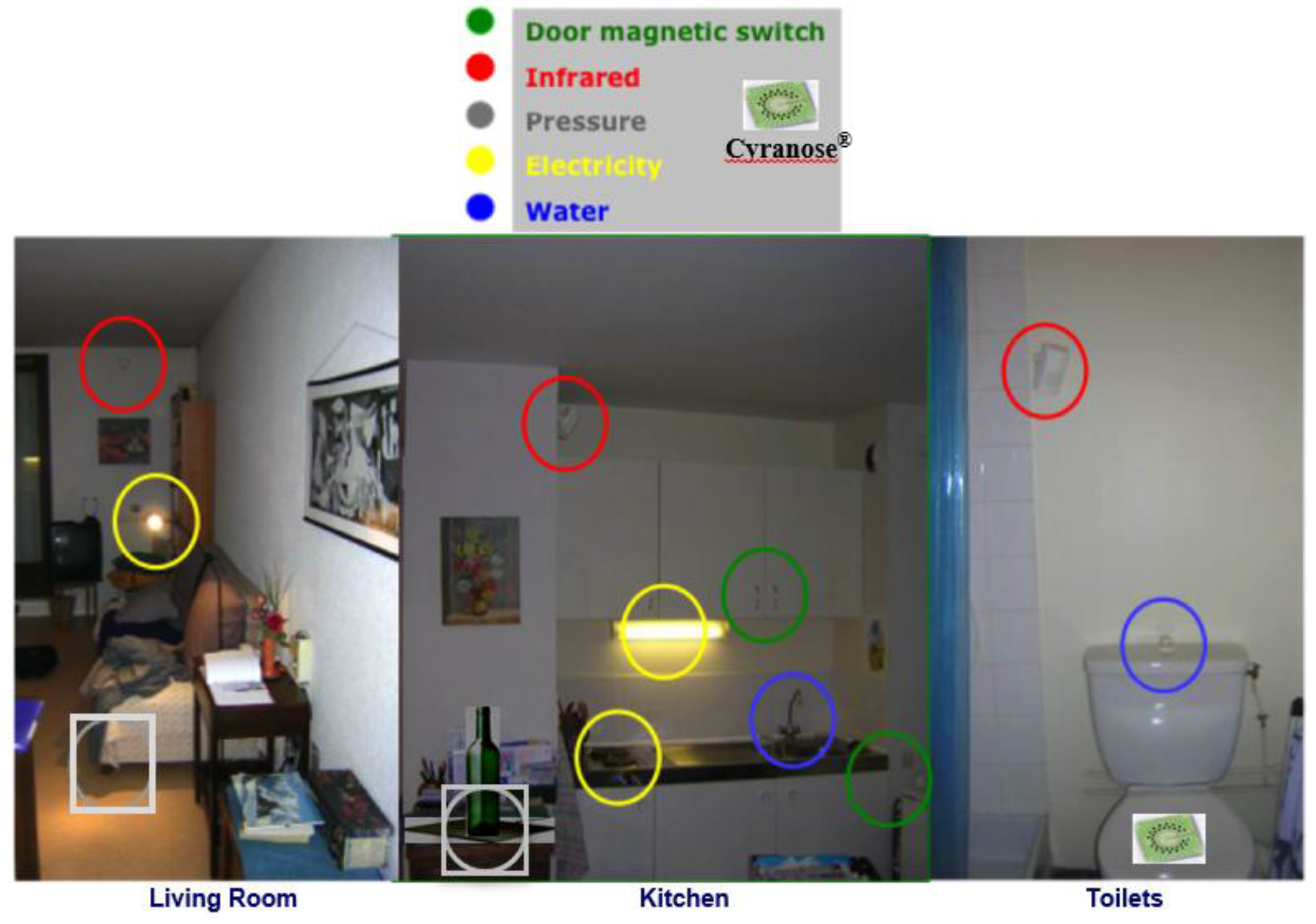
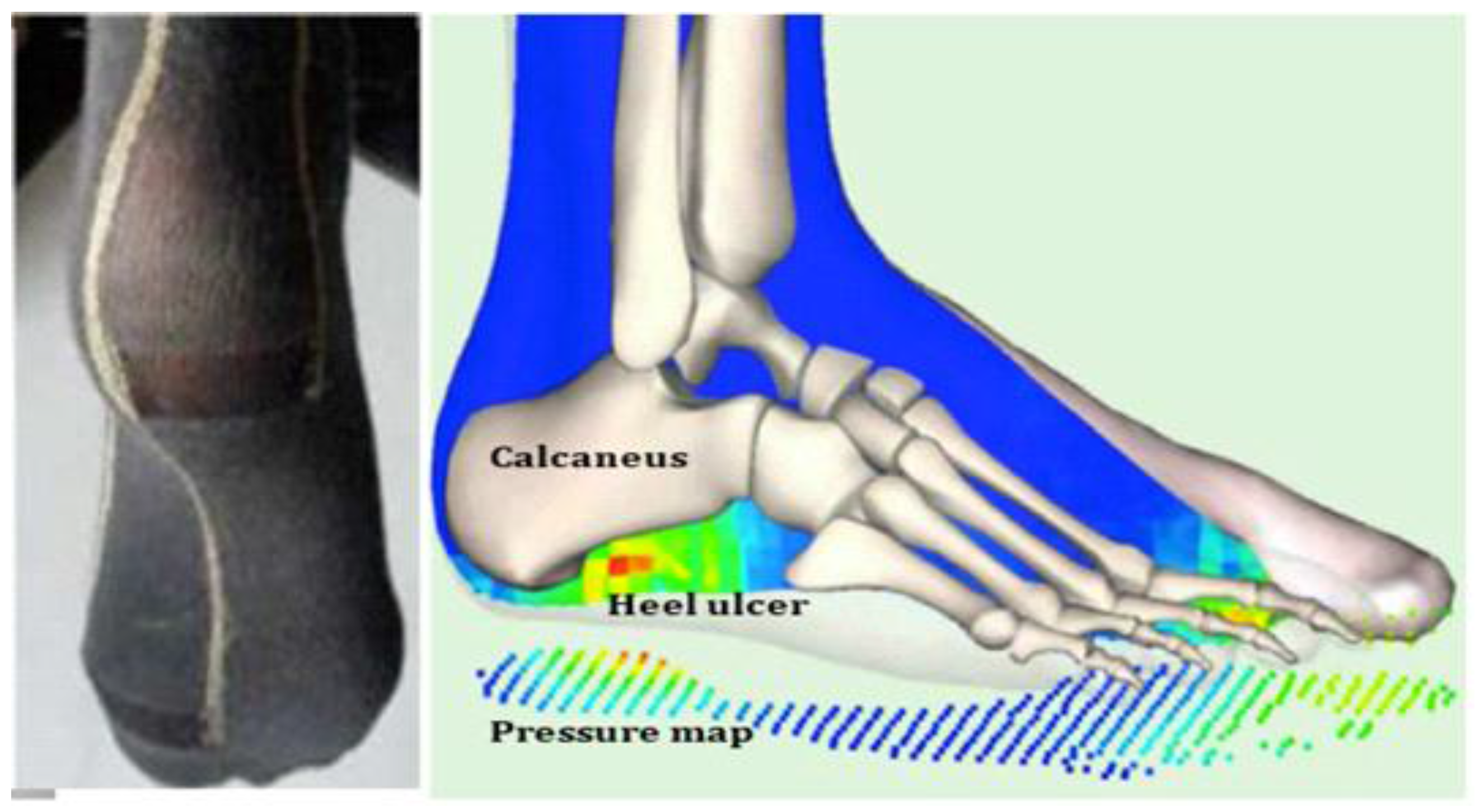
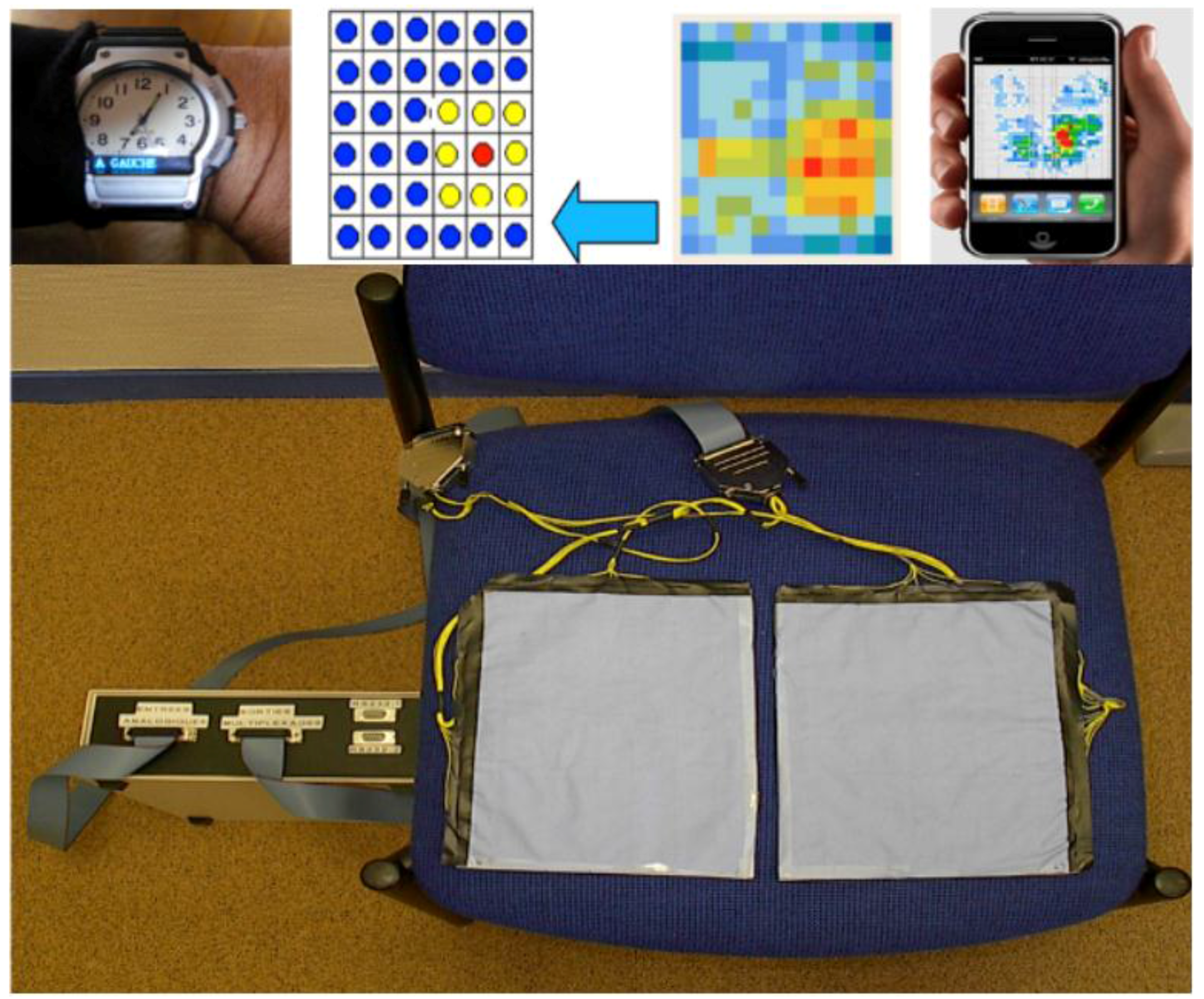
- Other dedicated sensors regarding pyro-sensing (thermal change of order of 1 °C captured by a thermocouple within a detection zone of few meters), sound-capture (microphones recording pathological and abnormal sounds and silence at home) and odor sensing (with an electronic nose, such as Cyranose®, a device sensitive to urea levels in toilets). For type II diabetics, sensors allow one to follow two kinds of complications: (i) diabetic nephropathy, which can be evaluated by considering hydric balance estimated from the water amount drawn at the tap and recorded by dedicated water sensors or from a bottle or a water dispenser, where differential pressure is recorded below the bottles or glasses, as well as before and after intake, and from skin water exchanges calculated from body and room thermo-hydration-sensors and from the volume excreted in toilets (recorded by urea sensors and level sensors in the bowl); and (ii) diabetic foot estimated by the speed and ease with which the patient moves from one room (or task in same room) to another and the way this motion is progressively reduced. Pressure sensors [120] on the ground and infrared sensors on walls allow the calculation of actigrams (Figure 7).
3. Results
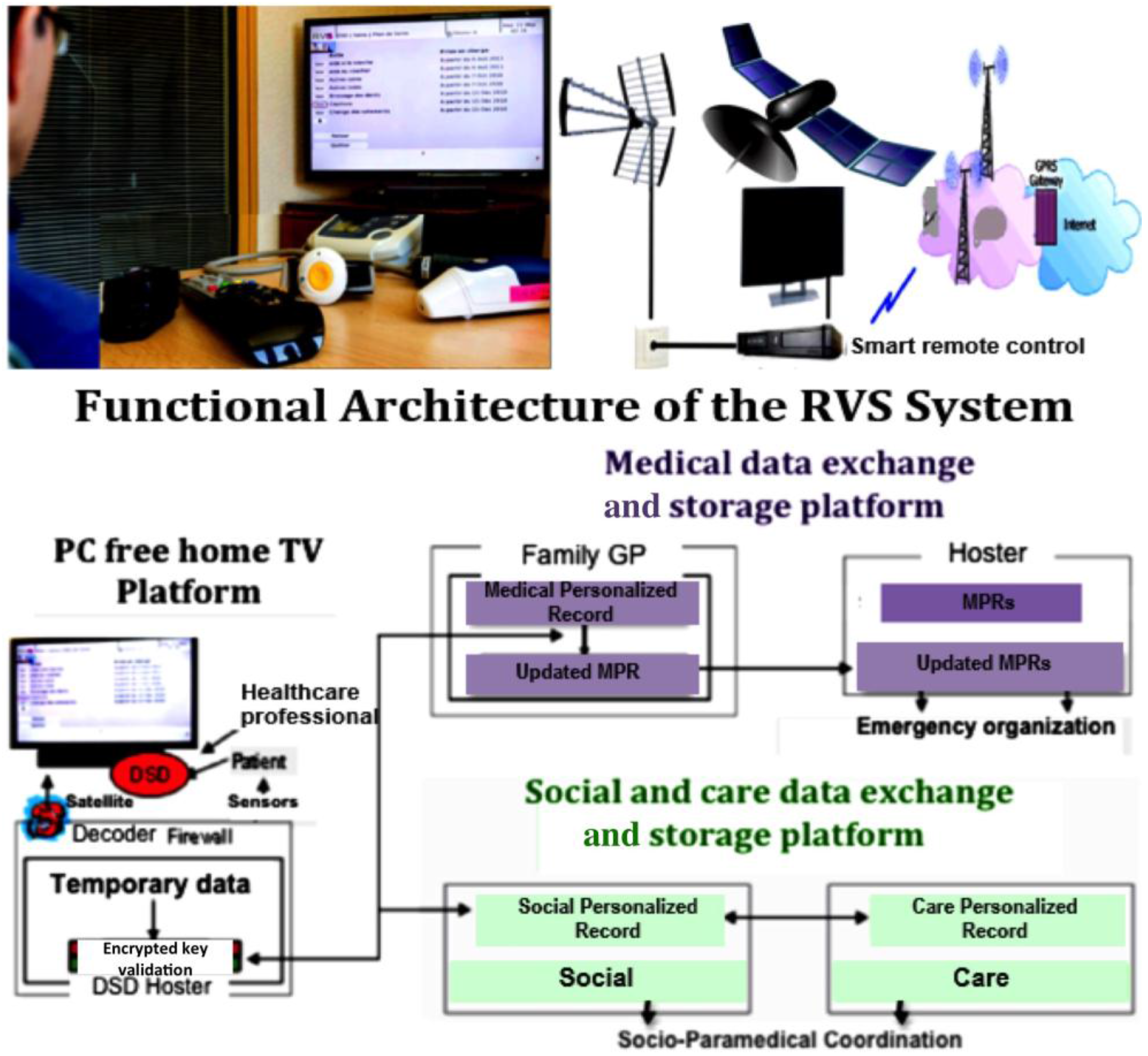
3.1. Medico-Social Information Processing for the Surveillance of Obese Elderly People in the Rural Vercors Mountains (RVS Experience)
- Contact book: contacts are sorted in two lists, personal and professional,
- Mailbox: this allows communicating with healthcare professionals of the RVS network by reading and writing some simple and pre-filled messages,
- Medical diary: professionals fill this in,
- Metrology: the patient or caregiver enters measurements, like pulse, blood pressure, glycemia, weight, etc.
3.2. Preventive and Therapeutic Education of the Obese Patient
3.3. Example of Vision and Diabetic Retinitis
3.4. Example of Locomotion and Diabetic Foot
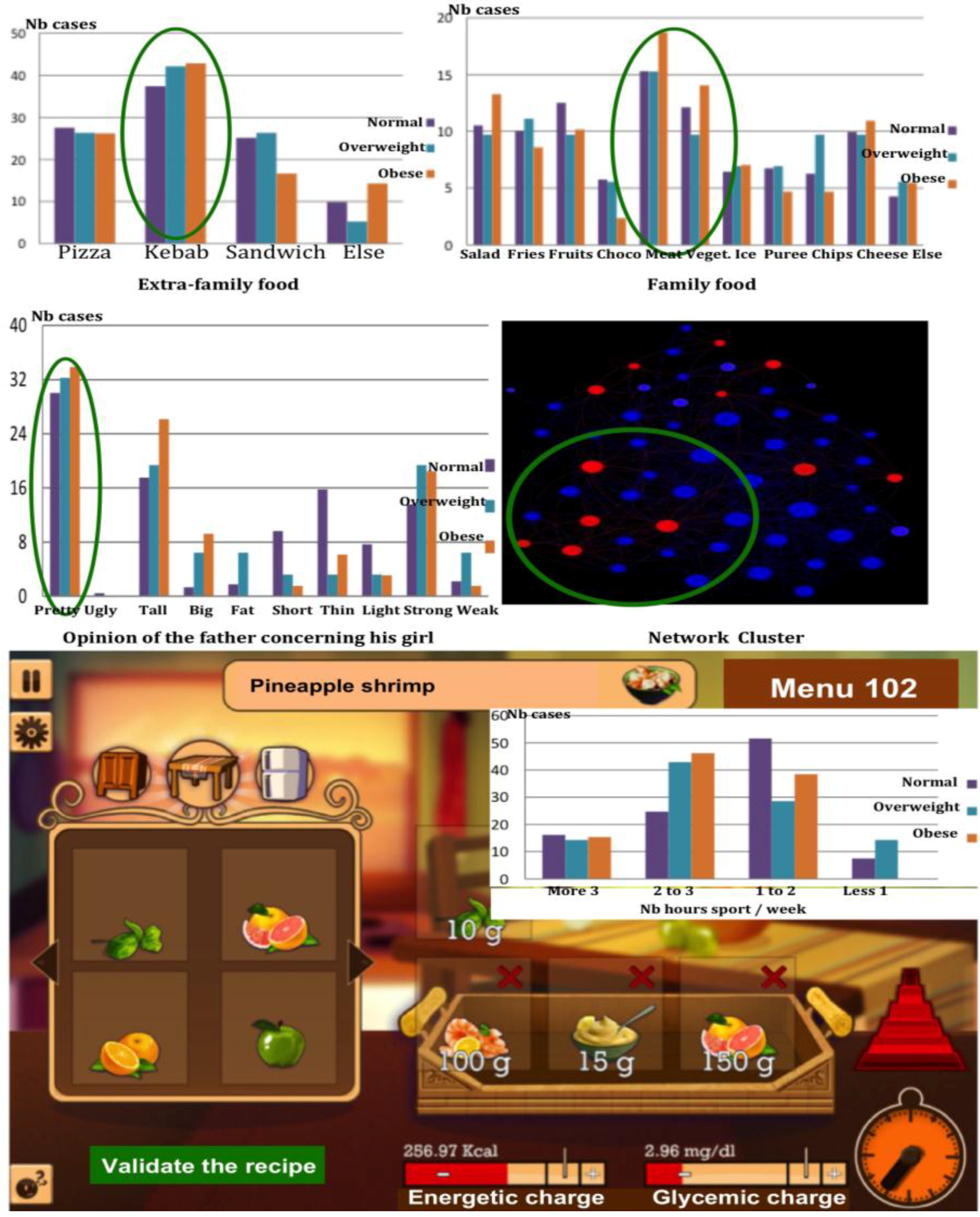
3.5. Example of Nutrition and Diabetic Disequilibrium
4. Discussion
4.1. Use of a Priori Information about Nutrition, Physical Activity and Social Individual Habits
4.2. Interest of the Actimetry Coupled to Preventive Education
4.3. Toward the Fusion of Multimodal Information
5. Perspectives and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knickman, J.R.; Snell, E.K. The 2030 Problem: Caring for Aging Baby Boomers. Health Serv. Res. 2002, 37, 849–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Economical and Social Affairs Report. World Population Ageing 2009; United Nations Publ.: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrova, R.; Petkova, V.; Dimitrov, M.; Madzharov, V.; Nikolova, I.; Petkova, E.; Andreevska, K.; Grekova, D.; Gueurguiev, S. Obesity relationship with vascular dysfunction. Adv. Obes. Weight Manag. Control 2014, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ogden, C.L. Obesity and Socioeconomic Status in Adults. United States, 2005–2008; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Suder, A. Body fatness and its social and lifestyle determinants in young working males from Cracow, Poland. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2009, 41, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; Reports 894; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Christakis, N.A.; Fowler, J.H. The spread of obesity in a large social network over 32 years. New Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles-Corti, B.; Macintyre, S.; Clarkson, J.P.; Pikora, T.; Donovan, R.J. Environmental and lifestyle factors associated with overweight and obesity in Perth, Australia. Am. J. Health Promot. 2003, 18, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, N.; Story, M. A review of environmental influences on food choices. Ann. Behav. Med. 2009, 38, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutin, A.R.; Costa, P.T.; Chan, W.; Milaneschi, Y.; Eaton, W.W.; Zonderman, A.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Terracciano, A. I know not to, but I can’t help it weight gain and changes in impulsivity-related personality traits. Psychol. Sci. 2013, 24, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, N. A glossary for social epidemiology. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2001, 55, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monasta, L.; Batty, G.; Cattaneo, A.; Lutje, V.; Ronfani, L.; Van Lenthe, F.; Brug, J. Early-life determinants of overweight and obesity: A review of systematic reviews. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobal, J.; Stunkard, A.J. Socioeconomic status and obesity: A review of the literature. Psychol. Bull. 1989, 105, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, C.A.; Moura, E.C.; Conde, W.L.; Popkin, B.M. Socioeconomic status and obesity in adult populations of developing countries: A review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2004, 82, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Der Horst, K.; Oenema, A.; Ferreira, I.; Wendel-Vos, W.; Giskes, K.; van Lenthe, K.F.; Brug, J. A systematic review of environmental correlates of obesity-related dietary behaviors in youth. Health Educ. Res. 2007, 22, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.; Crawford, D. Family food environments as determinants of preschool-aged childrens eating behaviours: implications for obesity prevention policy. Austr. J. Nutr. Diet. 2001, 58, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, I.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C. Systematic Reviews; BMJ Publishing Group: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Needleman, I.; Moles, D.R.; Worthington, H. Evidence-based periodontology, systematic reviews and research quality. Periodontology 2005, 37, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The prisma statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzuto, D.; Fratiglioni, L. Lifestyle factors related to mortality and survival: A mini-review. Gerontology 2014, 60, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, V.; Berger, U.; De Angelis, D.L.; Polhill, J.G.; Giske, J.; Railsback, S.F. The odd protocol: A review and first update. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 2760–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanetakou, I.P.; Katsilambros, N.L.; Benetos, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Perrea, D.N. Is obesity linked to aging? Adipose tissue and the role of telomeres. Ageing Res. Rev. 2012, 11, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Befort, C.A.; Thomas, J.L.; Daley, C.M.; Rhode, P.C.; Ahluwalia, J.S. Perceptions and beliefs about body size, weight, and weight loss among obese African American women: A qualitative inquiry. Health Educ. Behav. 2008, 35, 410–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.S.; Czaja, J.; Rief, W.; Hilbert, A. Personality and psychopathology in children with and without loss of control over eating. Compr. Psychiatry 2010, 51, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haworth, C.; Plomin, R.; Carnell, S.; Wardle, J. Childhood obesity: Genetic and environmental overlap with normal-range BMI. Obesity 2008, 16, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, S.; Diefenbach, M.; Streicher, S.; Jabs, E.; Smirnoff, M.; Horowitz, C.; Zinberg, R.; Clesca, C.; Richardson, L. Genetic and lifestyle causal beliefs about obesity and associated diseases among ethnically diverse patients: A structured interview study. Public Health Genom. 2012, 16, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silventoinen, K.; Sarlio-Lähteenkorva, S.; Koskenvuo, M.; Lahelma, E.; Kaprio, J. Effect of environmental and genetic factors on education-associated disparities in weight and weight gain: A study of Finnish adult twins. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gesell, S.B.; Tesdahl, E.; Ruchman, E. The distribution of physical activity in an after-school friendship network. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, G.; Christian, H.; Foster, S.; Boruff, B.J.; Bull, F.; Knuiman, M.; Giles-Corti, B. The association between neighbourhood greenness and weight status: an observational study in Perth Western Australia. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, J.H.; Neckerman, K.; Lovasi, G.S.; Quinn, J.; Weiss, C.C.; Bader, M.D.; Konty, K.; Harris, T.G.; Rundle, A. The impact of neighbourhood park access and quality on body mass index among adults in New York City. Preventive Medicine 2014, 64, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerrett, M.; McConnell, R.; Wolch, J.; Chang, R.; Lam, C.; Dunton, G.; Gilliland, F.; Lurmann, F.; Islam, T.; Berhane, K. Traffic-related air pollution and obesity formation in children: a longitudinal, multilevel analysis. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, A.; Bonell, C.; Sorhaindo, A. You are what your friends eat: systematic review of social network analyses of young people’s eating behaviours and bodyweight. J. Epidemiology and Community Health 2011, 65, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, D.R.; Simpkins, S.D. Using social network analysis to clarify the role of obesity in selection of adolescent friends. American Journal of Public Health 2014, 104, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renna, F.; Grafova, I.B.; Thakur, N. The effect of friends on adolescent body weight. Econ. & Human Biology 2008, 6, 377–387. [Google Scholar]
- Houldcroft, L.; Haycraft, E.; Farrow, C. Peer and friend influences on children’s eating. Social Development 2014, 23, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, V.; Beilin, L.; Dunbar, D. Family lifestyle and parental body mass index as predictors of body mass index in Australian children: A longitudinal study. Int. J. Obesity Rel. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timperio, A.; Salmon, J.; Ball, K.; Baur, L.A.; Telford, A.; Jackson, M.; Salmon, L.; Crawford, D. Family physical activity and sedentary environments and weight change in children. Int. J. Pediatric. Obesity 2008, 3, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, A.; Fitzgerald, N.; Aherne, C. Do peers matter? a review of peer and/or friends’ influence on physical activity among American adolescents. Journal of Adolescence 2012, 35, 941–958. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Cole, E.; Fletcher, M. Is obesity contagious? Social networks vs. environmental factors in the obesity epidemic. Journal of Health Economics 2008, 27, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J.H.; Christakis, N.A. Estimating peer effects on health in social networks: a response to Cohen-Cole and Fletcher; and trogdon, nonnemaker, and pais. Journal of Health Economics 2008, 27, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisset, S.; Gauvin, L.; Potvin, L.; Paradis, G. Association of body mass index and dietary restraint with changes in eating behaviour throughout late childhood and early adolescence: a 5-year study. Public Health Nutrition 2007, 10, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejima, K.; Aihara, K.; Nishiura, H. Modeling the obesity epidemic: social contagion and its implications for control. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2013, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, A.M.; Ortiz, A.R.; Rios-Soto, K.; Urdapilleta, A. USA the fast food nation: Obesity as an epidemic; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, 2004.
- Demongeot, J.; Hansen, O.; Hessami, H.; Jannot, A.S.; Mintsa, J.; Rachdi, M.; Taramasco, C. Random modelling of contagious diseases. Acta Biotheor. 2013, 61, 141–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, R.A.; Epstein, J.M. Exploring Price-Independent Mechanisms in the Obesity Epidemic. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, D.A.; Stamatakis, K.A. Systems science methods in public health: dynamics, networks, and agents. Annual Review of Public Health 2012, 33, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, V.T. My sibling, my weight. How gender, sibling gender, sibling weight and sibling weight level perception influence weight perception accuracy. Nutr. Diabetes 2014, 4, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, B.P.; Fiscella, K.; Duberstein, P.; Coletta, M.; Kawachi, I. Can the influence of childhood socioeconomic status on men’s and women’s adult body mass be explained by adult socioeconomic status or personality? Findings from a national sample. Health Psychol. 2009, 28, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Toyokawa, S.; Inoue, K.; Suyama, Y.; Miyano, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Miyoshi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Lifestyle, weight perception and change in body mass index of Japanese workers: My health up study. Public Health 2010, 124, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, A.A.; Elliott, M.; Glanz, K.; Haire-Joshu, D.; Lovegreen, S.L.; Saelens, B.E.; Sallis, J.F.; Brownson, R.C. Impact of the food environment and physical activity environment on behaviours and weight status in rural US communities. Prev. Med. 2008, 47, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seliske, L.; Pickett, W.; Rosu, A.; Janssen, I. The number and type of food retailers surrounding schools and their association with lunchtime eating behaviours in students. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Short, S.E.; Liu, T. Dynamic relations between fast-food restaurant and body weight status: A longitudinal and multilevel analysis of Chinese adults. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2013, 67, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, G.E.; von Korff, M.; Saunders, K.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Crane, P.K.; van Belle, G.; Kessler, R.C. Association Between Obesity and Psychiatric Disorders in the US Adult Population. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregori, D.; Foltran, F.; Ghidina, M.; Zobec, F.; Berchialla, P. Familial environment in high-and middle-low-income municipalities: A survey in Italy to understand the distribution of potentially obesogenic factors. Public Health 2012, 126, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, G.; Wabitsch, M.; Galm, C.; Berg, S.; Brandstetter, S.; Fritz, M.; Klenk, J.; Peter, R.; Prokopchuk, D.; Steiner, R.; Stroth, S.; Wartha, O.; Weiland, S.K.; Steinacker, J. Determinants of obesity in the Ulm research on metabolism, exercise and lifestyle in children (Urmel-Ice). Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 168, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Po’e, E.K.; Heerman, W.J.; Mistry, R.S.; Barkin, S.L. Growing right onto wellness (growth): A family-centered, community-based obesity prevention randomized controlled trial for preschool child-parent pairs. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2013, 36, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, S.K.; Cobiac, L.J.; Veerman, J.L. Improving diet and physical activity to reduce population prevalence of overweight and obesity: An overview of current evidence. Preventive Med. 2014, 62, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourisly, A.K. An Obesity Agent Based Model: A New Decision Support System for the Obesity Epidemic. In AsiaSim’13, Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Systems Simulation, Singapore, 6–8 November 2013; Communications in Computer and Information Science. Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 402, pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Poundstone, K.E.; Strathdee, S.A.; Celentano, D.D. The social epidemiology of human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome. Epidemiol. Rev. 2004, 26, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awada, R.; Parimisetty, A.; d’Hellencourt, C.L. Influence of obesity on neurodegenerative diseases. In Neurodegenerative Diseases; Kishore, U., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 381–401. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, D.; Cleland, V.; Timperio, A.; Salmon, J.; Andrianopoulos, N.; Roberts, R.; Giles-Corti, B.; Baur, L.; Ball, K. The longitudinal influence of home and neighborhood environments on children’s body mass index and physical activity over 5 years: The clan study. Int. J. Obesity 2010, 34, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbaghian, V.; Mago, V.K.; Wu, T.; Fritz, C.; Alimadad, A. Social interactions of eating behaviour among high school students: A cellular automata approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2012, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taramasco, C. Impact de L’obésité Sur Les Structures Sociales et Impact des Structures Sociales Sur L’obésité? Facteurs Individuels et Environnementaux. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Polytechnique, Paris, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, D.E.; Bampton, M.; Aboueissa, A.M. Two methods that dene the scale of obesogenic environments: a case study of Lewiston-Auburn, Maine. J. Hunger Environ. Nutr. 2013, 8, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, D.W.; Moffitt, T.E.; Sugden, K.; Williams, B.; Houts, R.; McCarthy, J.; Caspi, A. Development and evaluation of a genetic risk score for obesity. Biodemography Social Biol. 2013, 59, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone-Heinonen, J.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Goff, D.C.; Loria, C.M.; Kiefe, C.I.; Popkin, B.M.; Gordon-Larsen, P. The neighbourhood energy balance equation: Does neighbourhood food retail environment + physical activity environment = obesity? The CARDIA study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85141. [Google Scholar]
- Dressler, H.; Smith, C. Health and eating behaviour differs between lean/normal and overweight/obese low-income women living in food-insecure environments. Health Promot. 2013, 27, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichen, D.M.; Conner, B.T.; Daly, B.P.; Fauber, R.L. Weight perception, substance use, and disordered eating behaviors: Comparing normal weight and overweight high-school students. J. Youth Adolesc. 2012, 41, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Haye, K.; Robins, G.; Mohr, P.; Wilson, C. Homophily and contagion as explanations for weight similarities among adolescent friends. J. Adolesc. Health 2011, 49, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorm, A.F.; Korten, A.E.; Christensen, H.; Jacomb, P.A.; Rodgers, B.; Parslow, R.A. Association of obesity with anxiety, depression and emotional well-being: A community survey. Austr. N.Z. J. Public Health 2003, 27, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Marco, L.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Borys, J.; Le Bodo, Y.; Pettigrew, S.; Moreno, L. Contribution of social marketing strategies to community-based obesity prevention programs in children. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 35, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Ayers, C.R.; de Lemos, J.A.; Lakoski, G.; Vega, G.L.; Grundy, S.; Das, S.R.; Banks-Richard, K.; Albert, M.A. Relationship between perceptions about neighbor-hood environment and prevalent obesity: Data from the Dallas heart study. Obesity 2013, 21, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P.; Gupta, K.; Mishra, V.; Agrawal, S. Effects of sedentary lifestyle and dietary habits on body mass index change among adult women in India: Findings from a follow-up study. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2013, 52, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyn-Nemeth, P.; Penckofer, S.; Gulanick, M.; Velsor-Friedrich, B.; Bryant, F.B. The relationships among self-esteem, stress, coping, eating behavior, and depressive mood in adolescents. Res. Nurs. Health 2009, 32, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In-iw, S.; Manaboriboon, B.; Chomchai, C. A comparison of body-image perception, health outlook and eating behavior in mildly obese versus moderately-to-severely obese adolescents. Med. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2010, 93, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhart, C.M.; Daly, B.P.; Eichen, D.M. Is accuracy of weight perception associated with health risk behaviors in a diverse sample of obese adolescents? J. School Nurs. 2011, 27, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, S.A.; Vaquera, E.; Maturo, C.C.; Venkat Narayan, K. Is there evidence that friends influence body weight? A systematic review of empirical research. Social Sci. Med. 2012, 75, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annesi, J.J. Effects of improved self-appraisal and mood factors on weight loss in obese women initiating supported exercise. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2011, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annesi, J.J. Supported Exercise Improves Controlled Eating and Weight through Its Effects on Psychosocial Factors: Extending a Systematic Research Program Toward Treatment Development. Perm. J. 2012, 16, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.S.; Bloom, S.R. The regulation of food intake by the gut-brain axis: Implications for obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzeri, G.; Giacchi, M.V.; Spinelli, A.; Pammolli, A.; Dalmasso, P.; Nardone, P.; Lamberti, A.; Cavallo, F. Overweight among students aged 11–15 years and its relationship with breakfast, area of residence and parents’ education: Results from the Italian HBSC 2010 cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.W.; Roberts, J. Exploring the factors contributing to sibling correlations in BMI: A study using the panel study of income dynamics. Obesity 2012, 20, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandon, P. How package design and packaged-based marketing claims lead to overeating. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2013, 35, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Gupta, K.; Mishra, V.; Agrawal, S. A study on body-weight perception, future intention and weight-management behavior among normal-weight, overweight and obese women in India. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, K.J.; Edling, C.; Rydgren, J. Peer clustering of exercise and eating behaviours among young adults in Sweden: A cross-sectional study of egocentric network data. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demongeot, J.; Taramasco, C. Evolution of social networks: The example of obesity. Biogerontology 2014, 15, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.M.; Puhl, R.M.; Luedicke, J.; Peterson, J.L. Eating behaviors, victimization, and desire for supportive intervention among adolescents in weight-loss camps. Eat. Behav. 2013, 14, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroux, J.S.; Moore, S.; Richard, L.; Gauvin, L. Physical in-activity mediates the association between the perceived exercising behavior of social network members and obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provencher, V.; Pérusse, L.; Bouchard, L.; Drapeau, V.; Bouchard, C.; Rice, T.; Rao, D.; Tremblay, A.; Després, J.P.; Lemieux, S. Familial resemblance in eating behaviors in men and women from the Québec family study. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viner, R.; Haines, M.; Taylor, S.; Head, J.; Booy, R.; Stansfeld, S. Body mass, weight control behaviors, weight perception and emotional well being in a multiethnic sample of early adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, R. Increases in morbid obesity in the USA: 2000–2005. Public Health 2007, 121, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmaca, M.; Kuloglu, M.; Tezcan, E.; Ustundag, B. Serum leptin and cholesterol levels in schizophrenic patients with and without suicide attempts. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2003, 108, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Parra, G.; Villanueva, R.J.; Arenas, A.J. An age structured model for obesity prevalence dynamics in populations. Revista. MVZ Córdoba 2010, 15, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar]
- González-Parra, G.; Arenas, A.J.; Santonia, F.J. Stochastic modeling with Monte Carlo of obesity population. J. Biol. Syst. 2010, 18, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.A.; Kristjansson, E.A.; Russell, K.; Billette, J.M.; Sawada, M.C.; Ali, A.; Tremblay, M.S.; Prud’homme, D. Relationships between neighborhoods, physical activity, and obesity: A multilevel analysis of a large Canadian city. Obesity 2012, 20, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetrius, L.; Coy, J.; Tuszynski, J. Cancer proliferation and therapy: The Warburg effect and quantum metabolism. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2010, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetrius, L.; Tuszynski, J.A. Quantum metabolism explains the allometric scaling of metabolic rates. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetrius, L.; Magistretti, P.J.; Pellerin, L. Alzheimer’s disease: The amyloid hypothesis and the Inverse Warburg effect. Front. Physiol. 2015, 5, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demongeot, J.; Hansen, O.; Hamie, A.; Hazgui, H.; Virone, G.; Vuillerme, N. Actimetry@home: Actimetric tele-surveillance and tailored to the signal data compression. Lect. Notes Comp. Sci. 2015, 8456, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Demongeot, J.; Elena, A.; Taramasco, C.; Vuillerme, N. Serious games and personalization of the therapeutic education. Lect. Notes Comp. Sci. 2015, 9102, 270–281. [Google Scholar]
- Demongeot, J.; Virone, G.; Duchêne, F.; Benchetrit, G.; Hervé, T.; Noury, N.; Rialle, V. Multi-sensors acquisition, data fusion, knowledge mining and triggering in health smart homes for elderly people. C. R. Biol. 2002, 325, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virone, G.; Noury, N.; Demongeot, J. A system for automatic measurement of circadian activity deviation in telemedicine. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulrazak, B.; Mokhtari, M.; Feki, M.A.; Ghorbel, M. Integration of home networking in a smart environment dedicated to people with disabilities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies: From Theory to Applications, Damascus, Syria, 19–23 April 2004; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 125–126. [Google Scholar]
- Benneyan, J.C. An introduction to using computer simulation in healthcare: Patient wait case study. J. Soc. Health Syst. 1997, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowery, J.C. Introduction to simulation in healthcare. In Proceedings of the 28th Conference on Winter Simulation, WSC ’96, Coronado, CA, USA, 8–11 December 1996; pp. 78–84.
- O’Connor, C.M.; Smith, R.; Nott, M.T.; Lorang, C.; Matthews, R.M. Using video simulated presence to reduce resistance to care and increase participation of adults with dementia. Am. J. Alzeimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2011, 26, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowery, J.C.; Martin, J.B. Design and validation of a critical care simulation model. J. Soc. Health Syst. 1992, 3, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gibson, B.; Weir, C. Development and preliminary evaluation of a simulation-based diabetes education module. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2010, 2010, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berg, D.R.; Carlson, A.; Durfee, W.K.; Sweet, R.M.; Reihsen, T. Low-cost, take-home, beating heart simulator for health-care education. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2011, 163, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.; Graves, M.J.; Lomas, D.J. Integrated physiological flow simulator and pulse sequence monitoring system for MRI. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, S.M.; Akhlaghinia, M.J.; Lotfi, A.; Langensiepen, C. Trend Modelling of Elderly Lifestyle within an Occupancy Simulator. In Proceedings of the 2011 UkSim 13th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation (UKSim), Cambridge, UK, 30 March–1 April 2011.
- Virone, G.; Lefebvre, B.; Noury, N.; Demongeot, J. Modeling and Computer Simulation of Physiological Rhythms and Behaviors at Home for Data Fusion Programs in a Telecare System. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Enterprise Networking and Computing in Healthcare Industry, Santa Monica, CA, USA, 6–7 June 2003.
- Nabih, K.; Gomaa, M.M.; Osman, H.S.; Aly, G.M. Modeling, Simulation, and Control of Smart Homes Using Petri Nets. Int. J. Smart Home 2011, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinaux, F.; Brownsell, S.; Hawley, M.S.; Bradley, D. A home daily activity simulation model for the evaluation of lifestyle monitoring systems. Comput. Biol. Med. 2013, 43, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazovik, A.; Kaldeli, E.; Lazovik, E.; Aiello, M. Planning in a Smart Home: Visualization and Simulation. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, Thessaloniki, Greece, 19–23 September 2009.
- Poland, M.P.; Nugent, C.D.; Wang, H.; Chen, L. Development of a smart home simulator for use as a heuristic tool for management of sensor distribution. Tech. Health Care 2009, 17, 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Virone, G.; Istrate, D. Integration of an Environmental Sound Module to an Existing In-Home Activity Simulator. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International conference of the IEEE EMBS, Lyon, France, 23–26 August 2007.
- Istrate, D.; Castelli, E. Information Extraction from Sound for Medical Telemonitoring. IEEE Trans. Inform. Technol. Biomed. 2006, 10, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virone, G.; Istrate, D.; Vacher, M.; Noury, N.; Sérignat, J.F.; Demongeot, J. First Steps in Data Fusion between a Multichannel Audio Acquisition and an Information System for Home Healthcare. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003.
- Weight Sensors. Available online: www.techtry.co.jp/weight_en/#sts (accessed on 25 August 2015).
- Royans Vercors Santé. Available online: http://www.vercors.org/act-rvs.html (accessed on 25 August 2015).
- Griffin-trust. Available online: http://www.griffin-trust.com/Leaflet5.html (accessed on 14 February 2016).
- Crous-Lyon. Available online: http://www.crous-lyon.fr/html/IMG/pdf_Crous_Lyon2013_2014_web (accessed on 14 February 2016).
- VHP@interactive. Available online: http://www.grenoblecognition.fr/index.php/actualites2/9-communiques/168-vhp-interactive-inventer-le-futur-de-l-appartement-intelligent (accessed on 25 August 2015).
- Couturier, P.; Franco, A.; Piquart, J.F.; Mansotte, J.; Montani, C.; Suarez, C.; Mollier, A.; Gucher, C.; Frossard, M.; Nicolas, L.; et al. “Telegerontology”: From teleassistance to teleconsultation of elderly people. Mythe or reality. Rev. Gériatr. 1996, 21, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Istrate, D.; Binet, M.; Cheng, S. Real Time Sound Analysis for Medical Remote Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 August 2008; pp. 4640–4643.
- Noury, N.; Virone, G.; Ye, J.; Rialle, V.; Demongeot, J. Nouvelles Directions en Habitats intelligents pour la santé. ITBM 2003, 24, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noury, N.; Fleury, A.; Nocua, R.; Poujaud, J.; Gehin, C.; Dittmar, A.; Delhomme, G.; Demongeot, J.; Mcadam, E. E-Health sensors. Biomedical sensors, algorithms and sensors networks. Recent Res. Dev. Appl. Phys. 2009, 30, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, M.E.; Bentall, R.H.C.; Monahan, J.C. Emerging Electromagnetic Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Q.; Gupta, S.; Gollakota, S.; Patel, S. Whole-Home Gesture Recognition Using Wireless Signals. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing & Networking, Miami, FL, USA, 30 September–4 October 2013; pp. 27–38.
- Tamura, T.; Miyasako, S.; Fujimoto, T.; Togawa, T. Monitoring bed temperature in elderly in the home. In Proceedings of the 18th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 31 October–3 November 1996.
- Chenu, O.; Vuillerme, N.; Moreau-Gaudry, A.; Demongeot, J.; Payan, Y. A wireless lingual feedback device to reduce overpressures of the buttock in seated posture. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadgetmac. Available online: http://www.gadgetmac.com/reviews/misfit-shine-review.html (accessed on 14 February 2016).
- Best Fitness Gadgets. Available online: www.digitaltrends.com/mobile/best-fitness-trackers-devices-gadgets (accessed on 25 August 2015).
- Carbohydrate Counting, Glycemic Index, and Glycemic Load: Putting Them All Together. Available online: http://www.digitaltrends.com/mobile/best-fitness-trackers-devices-gadgets (accessed on 25 August 2015).
- Demongeot, J. Recent advances in e-health and perspectives. Stud. Inform. Universalis 2013, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hightower, J.; Borriello, G. Location Systems for Ubiquitous Computing. Computer 2001, 47, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axisa, F.; Dittmar, A.; Delhomme, G. Smart clothes for the monitoring in real time and conditions of physiological, emotional and sensorial reaction of human. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003.
- Dittmar, A.; Axisa, F.; Delhomme, G.; Gehin, C. New concepts and technologies in home care and ambulatory monitoring. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2004, 108, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alwan, M.; Dalal, S.; Kell, S.; Felder, R. Derivation of basic human gait characteristics from floor vibrations. In Proceedins of the Summer Bioengineering Conference 03, Key Biscayne, FL, USA, 25–29 June 2003; pp. 231–232.
- Vuillerme, N.; Chenu, O.; Pinsault, N.; Fleury, A.; Demongeot, J.; Payan, Y. A plantar-pressure based tongue-placed tactile biofeedback system for balance improvement. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 10, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demongeot, J.; Kulesa, P.; Murray, J.D. Compact set valued flows II: Applications in biological modelling. C.R. Acad. Sc. Série. IIb 1997, 324, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, G.; Dardanello, D.; Rosso, V.; Pizzigalli, L.; Rainoldi, A. Application of sEMG in Aging: A Mini Review. Gerontology 2015, 61, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demongeot, J.; Waku, J. Application of interval iterations to the entrainment problem in respiratory physiology. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2009, 367, 4717–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queyroy, A.; Couturier, P.; Paramelle, P.J.; Franco, A.; Buguet, A. Virtual thermography as an actimetric tool for bedridden patients. Trav. Sci. Serv. Santé Des. Armées 1996, 17, 255–256. [Google Scholar]
- Virone, G.; Vuillerme, N.; Mokhtari, M.; Demongeot, J. Persistent Behaviour in Healthcare Facilities: From actimetric telesurveillance to therapy education. Lect. Notes Comp. Sci. 2014, 8458, 297–311. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Buenos Aires, J.; Payan, Y.; Demongeot, J. Electro-stimulation of the tongue as a passive surgical guiding system. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Coimbra, Portugal, 30 June–3 July 2003.


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demongeot, J.; Elena, A.; Jelassi, M.; Ben Miled, S.; Bellamine Ben Saoud, N.; Taramasco, C. Smart Homes and Sensors for Surveillance and Preventive Education at Home: Example of Obesity. Information 2016, 7, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7030050
Demongeot J, Elena A, Jelassi M, Ben Miled S, Bellamine Ben Saoud N, Taramasco C. Smart Homes and Sensors for Surveillance and Preventive Education at Home: Example of Obesity. Information. 2016; 7(3):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7030050
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemongeot, Jacques, Adrien Elena, Mariem Jelassi, Slimane Ben Miled, Narjès Bellamine Ben Saoud, and Carla Taramasco. 2016. "Smart Homes and Sensors for Surveillance and Preventive Education at Home: Example of Obesity" Information 7, no. 3: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7030050
APA StyleDemongeot, J., Elena, A., Jelassi, M., Ben Miled, S., Bellamine Ben Saoud, N., & Taramasco, C. (2016). Smart Homes and Sensors for Surveillance and Preventive Education at Home: Example of Obesity. Information, 7(3), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/info7030050







