Abstract
Hybrid fieldbus network integrating wireless networks with existing wired fieldbuses has become new a research direction in industrial automation systems. In comparison to wired fieldbuses, the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network has a different system architecture, data transmission mechanism, communication protocol, etc. This leads to different challenges that need to be addressed. This paper proposes a hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network which consists of a wireless industrial control network (WICN), a wired PROFIBUS-DP (Process Field Bus-Decentralized Periphery) fieldbus network, and a wired MODBUS/TCP (Mod Bus/Transmission Control Protocol) fieldbus network. They are connected by a new gateway which uses a shared data model to solve data exchange in different network protocols. In this paper, we describe the architecture of the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network and data transmission mechanisms in detail, and then evaluate the performance of hybrid fieldbus network via a set of experiments. The experiment results confirm that the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network can satisfy the performance requirement of industrial network control systems. Furthermore, in order to further investigate feasibility of the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network, it is deployed at a steam turbine power generation system, and the performance figures obtained further verify its feasibility and effectiveness.
1. Introduction
Recently, Industry 4.0 has become a hot topic that is attracting growing interest from governments, manufacturers, researchers, and developers. It is expected to offer a reduction in energy consumption, increase economic benefits, and enable smart production [1]. Therein, wireless communication technology serves as an important approach to realize Industry 4.0. During the last few years, wireless technologies have experienced a great growth in factory automation [2,3,4,5]. Applying wireless networks will be a new trend in industrial environments. For example, efforts have been made to provide wireless extension for the Fieldbus and Ethernet [6,7,8,9,10]. The benefits of wireless networks are fairly obvious: They can provide new advantages such as fully mobile operation, flexible installation, and rapid deployment, while reducing maintenance costs [11,12]. Furthermore, wireless networks can be deployed in harsh environments that are not suitable for cabling setup, such as applications involving mobile subsystems or areas with explosive chemicals. Although wireless networks play increasingly important roles in industrial fields, it is very unlikely that wireless networks will totally replace the wired fieldbus networks in industrial automation for a long time because of well-known problems such as fading, interference, multipath propagation, timeliness and so on [13]. That means that hybrid wireless/wired networks integrating with the wired fieldbus networks is worth focusing on, which may represent truly promising solutions in the context of industrial control systems [14]. The PROFIBUS-DP and MODBUS/TCP fieldbus networks are very mature and powerful solutions for wired communication networks in industrial applications. The PROFIBUS-DP network can deliver real-time services in industrial environments. It is optimized for speed, efficiency, low connection costs, and is especially designed for fast communication between automation systems and distributed I/O peripherals. The MODBUS/TCP network uses TCP/IP protocol to carry the messaging structure and attaches 10,000 or more devices in a single MODBUS/TCP network. These advantages make PROFIBUS-DP and MODBUS/TCP widely used currently in worldwide operations [15,16,17,18]. Recently, the implementation of effective Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) for Real-Time Ethernet has become a new issue which is attracting the attention of scholars [19,20].
On the other hand, wireless industrial control networks (WICN) (e.g., WirelessHART, ZigBee, and ISA SP100) have also been presented in various process control systems [21,22,23,24]. There exist many ways to connect these existing wired fieldbus networks with wireless networks. Some approaches use open database connectivity (ODBC) and object linking and embedding (OLE) for process control (OPC), which are standard database access methods in the application layer of open system interconnection (OSI) reference models. Other methods use a bridge in the data link layer of the OSI reference model. Although there are several works to address the combination of wireless communication with wired networks, it can be expected that wireless systems will be an integrated part of fieldbus networks in future standards. A natural approach is to design a new gateway as an information switching node for wired and wireless networks, while leaving the protocol stack and cable deployment of each network unchanged. This approach is attractive, since the design efforts require only an additional physical device. Furthermore, integrating wireless and wired stations is done in a single local area network.
The main work of this paper is to design a new gateway to construct a hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network. It consists of a wired PROFIBUS-DP fieldbus network, a wired MODBUS/TCP fieldbus network and a wireless industrial control network, which are connected by the gateway as an intermediate station to implement data exchange in different network protocols. The advantage of this hybrid fieldbus network is to reduce the cost of cable deployment and insure the network performance in current complex industrial environments. Meanwhile, the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network is successfully deployed at a steam turbine power generation system to verify its feasibility and effectiveness.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews related works on hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus networks and proposes a new hybrid fieldbus network. Section 3 introduces a gateway and corresponding data transmission mechanisms, and then discusses the implementation of the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network. Section 4 presents the system configuration of the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network and evaluates its network performance. Section 5 gives a real-world application to verify its feasibility and effectiveness, and conclusions and directions for future research are given in Section 6. A preliminary version of this paper was presented in reference [25].
2. Architecture of Hybrid Wired/Wireless Fieldbus Networks
This section first gives a brief introduction on several well-known wired and wireless fieldbus networks including PROFIBUS-DP, MODBUS/TCP and WICN (Section 2.1), and then reviews related works on hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus networks (Section 2.2), and finally describes the architecture of the proposed hybrid wired/wireless network (Section 2.3).
2.1. Wired Fieldbus Networks and WICN
PROFIBUS-DP is one of variations of PROFIBUS, which is one of the most popular fieldbuses, and consists of physical layer, data link layer and application layer in order to satisfy real-time requirements [17]. In industrial automation applications, PROFIBUS-DP is used to operate sensors and actuators via a centralized controller, which uses master/slave communication mechanism between different field devices and a polling method as its medium access control (MAC) protocol to achieve significantly better real-time performance. MODBUS/TCP is a MODBUS variant, which is located in application layer of the OSI model, and is now one of the most commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices [16,26]. It is designed to allow industrial input/output equipment such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), computers, operator panels, motors, sensors, and so on, to communicate via networks. MODBUS/TCP is based on the TCP/IP protocol which is embedded in the frame of MODBUS protocol, and usually uses the request/reply mechanism to connect devices on the Ethernet. WICN is a wireless network for low-rate and short distance transmission, which is based on the chirp spread spectrum (CSS) physical layer of the IEEE 802.15.4a standard [10,27]. It is designated to the 2450 MHz industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio bands, and is expected to play a key role in the deployment of WICN technologies in industrial fields. It is well known that WICN is very suitable for real-time industrial control systems because it synthesizes FSK (Frequency Shift Keying), PSK (Phase Shift Keying), and ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) modulation models. It uses master/slave communication between devices based on a single topology of a token ring, shown as Figure 1.
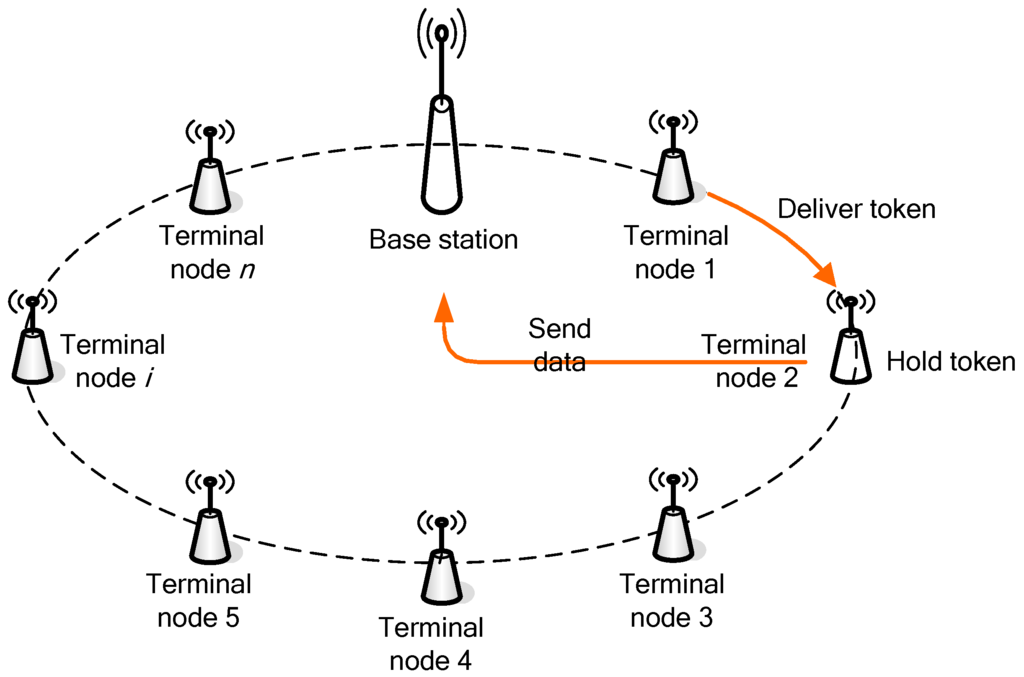
Figure 1.
Topology of token ring in wireless industrial control networks (WICN).
In the WICN depicted in Figure 1, all devices are connected as a ring. One of devices is selected to be a base station or master station, and other devices are considered as terminal nodes or slave stations. Only the base station has the authority to manage the entire wireless network and maintain the token ring. All terminal nodes are assigned exclusive addresses, and every node has its previous node and next node to deliver the token. When one of terminal nodes gets the token in a specified period of time, it has the right to transmit data to the base station. Beyond this time, the terminal node is able to receive data from any other nodes in the token ring. In this way, the transmission is collision-free in WICN, and the system’s reliability is enhanced.
2.2. Related Works on Hybrid Fieldbus Networks
There are several ways to establish hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus networks for various industrial applications. In reference [7], authors integrate a wireless I/O interface with PROFIBUS and PROFINET for factory automations, and, in reference [6], authors design and implement a wireless fieldbus for plastic machineries. A polling-based MAC protocol to improve real-time performance in a wireless PROFIBUS is presented in reference [18]. The specifications of these applications mainly cover layers 2 (data link layer and MAC) and 7 (application layer) of the OSI reference model. Table 1 shows various proposed methods and their corresponding advantages and disadvantages. It is seen from Table 1 that a gateway-based method is a favorable choice to construct a hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network due to its suitability for all seven OSI layers and its flexibly in converting data stacks between different protocols. In addition, these hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus networks mainly address the extension of the wired PROFIBUS fieldbus, and rarely relate to the wired MODBUS fieldbus. However, there usually exist more than one fieldbus network in practical industrial environments. For example, a steam turbine power generation system is presented in this paper, which includes a wired PROFIBUS-DP fieldbus network and a wired MODBUS/TCP fieldbus network. This motivates us to design a new hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network for complex industrial environments with various fieldbus networks [28].

Table 1.
Various methods proposed in references to establish hybrid fieldbus networks and their advantages and disadvantages. OSI: open system interconnection; ODBC: open database connectivity.
2.3. Hybrid Wired/Wireless Fieldbus Network Architecture
This paper proposes a hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network architecture, shown as Figure 2. It consists of a wired MODBUS/TCP network, a wired PROFIBUS-DP network, WICN, various network devices, and a gateway which connects WICN with PROFIBUS-DP and MODBUS/TCP [29]. In this architecture, the gateway is taken as a slave station of a PROFIBUS-DP network, and a client station of a MODBUS/TCP network, but as a base station in WICN. This architecture is attractive because of three main reasons. Firstly, it takes into account the increasing need for mobile devices in industrial environments, where different wired fieldbus networks simultaneously exist. Because most of the design options on previous hybrid fieldbus networks are used in one wired fieldbus network [5,15,16,18], it cannot satisfy the need for the reconstruction of more than one wired fieldbus network. One wise solution is to extend the traditional wired fieldbus networks with wireless communication techniques. Secondly, the current wired fieldbus networks have been mature and developed very well, and it is not realistic for them to be completely replaced by wireless networks, at least for a long time. Therefore, hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus networks are the best choices. Finally, this proposed architecture requires only converting one protocol into another among different sub-networks by a gateway, but the protocol stack and deployment remains unchanged within each sub-network. Namely, it does not need the high similarity for the protocols in different sub-networks, and can better connect WICN with a wired PROFIBUS-DP network and a wired MODBUS/TCP network.
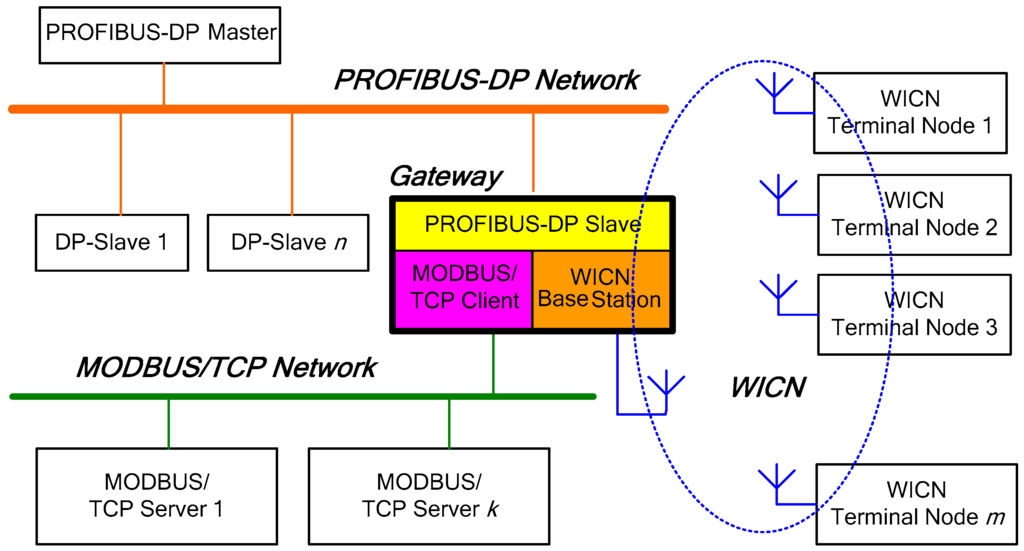
Figure 2.
Hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network architecture based on MODBUS/TCP, PROFIBUS-DP and WICN networks.
3. Implementation of a Hybrid Wired/Wireless Fieldbus Network
This section first introduces a shared data model in a gateway in the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network (Section 3.1), and then describes the data transmission mechanisms between various network protocols (Section 3.2).
3.1. Shared Data Model in the Gateway
The gateway uses a shared data model to solve communication problems in different fieldbus networks. Figure 3 shows a shared data model, where the shared data area is used as a public data buffer for information exchange. The size of the data blocks in the shared data area is 256, which are divided into two parts: the read (R) data block and the write (W) data block. The read data block saves input data, which comes from various network devices, and the write data block sends output data in the reverse direction. In addition, every data block in a MODBUS/TCP client station and a WICN base station exchanges information with the shared data area using the data mapping method because they have the highly similar network protocols, but every data block in a PROFIBUS-DP slave station exchanges information with the shared data area using the data converting method because they have different styles of data stack between two protocols. In fact, a PROFIBUS-DP slave station uses input and output stacks to switch data with the shared data area. Figure 4 presents an example of the data mapping method and the data converting method to illustrate their difference, where the data stacks in MODBUS/TCP and WICN are the same to the shared data area, but are different from those in PROFIBUS-DP.
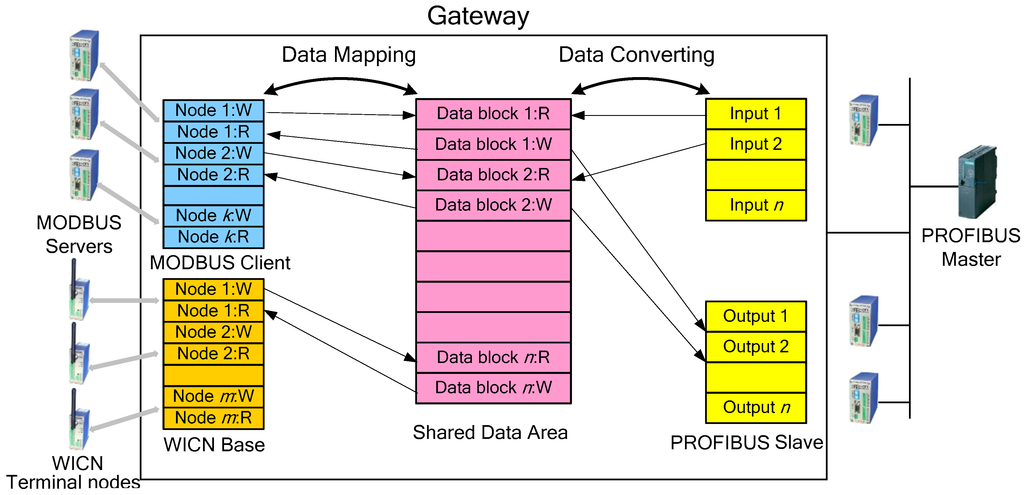
Figure 3.
Shared data model of the gateway in the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network. R: read data block; W: write data block.
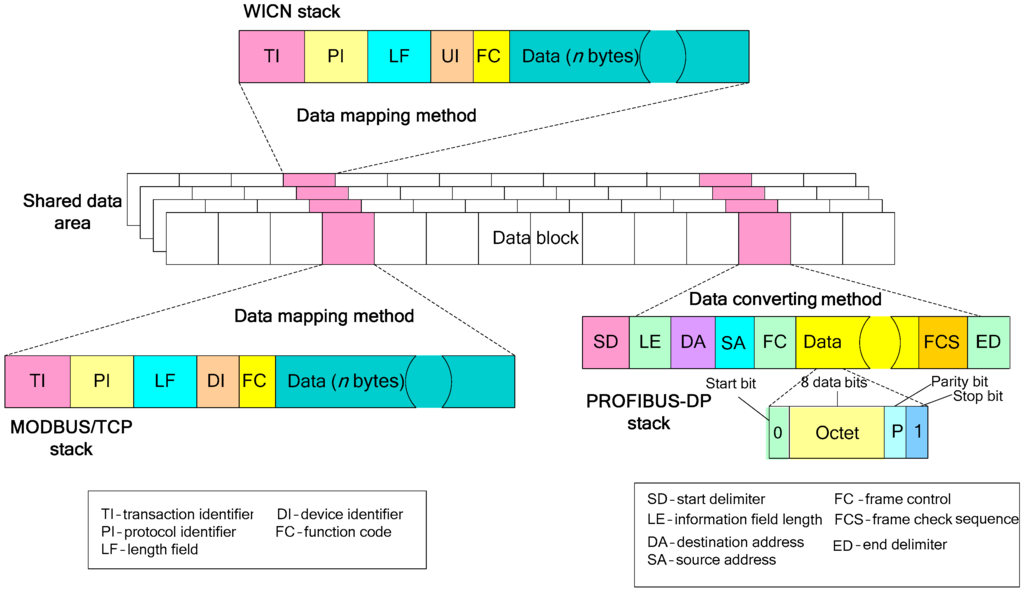
Figure 4.
An example of the data mapping method and the data converting method.
3.2. Data Transmission Mechanisms
In this subsection, data transmission mechanisms in different sub-networks are described in detail. The message sequence charts, from Figure 5 to Figure 8, are used to show the data transmission process [25]. The data transmission mechanisms consist of four parts: data transmission from WICN terminal nodes to the gateway’s WICN base station; data transmission from the gateway’s WICN base station to WICN terminal nodes; data transmission between MODBUS/TCP server stations and the gateway’s MODBUS/TCP client station, and; data transmission between the PROFIBUS-DP master station and the gateway’s PROFIBUS-DP slave station.
3.2.1. Data Transmission from WICN Terminal Nodes to the Gateway’s WICN Base Station
In a WICN sub-network, the gateway acts as a base station for all wireless terminal nodes. Figure 5 shows the data transmission from WICN terminal nodes to the gateway’s base station. Terminal nodes first wait to get a token from the WICN sub-network. Once one of terminal nodes obtains the token from the previous node, it records the token holding time and sends a data packet to the gateway’s base station. After the base station receives the data packet successfully, it sends a success message to this terminal node holding the token. The process is executed circularly until the running time terminates, and then the terminal node releases the token to the next.
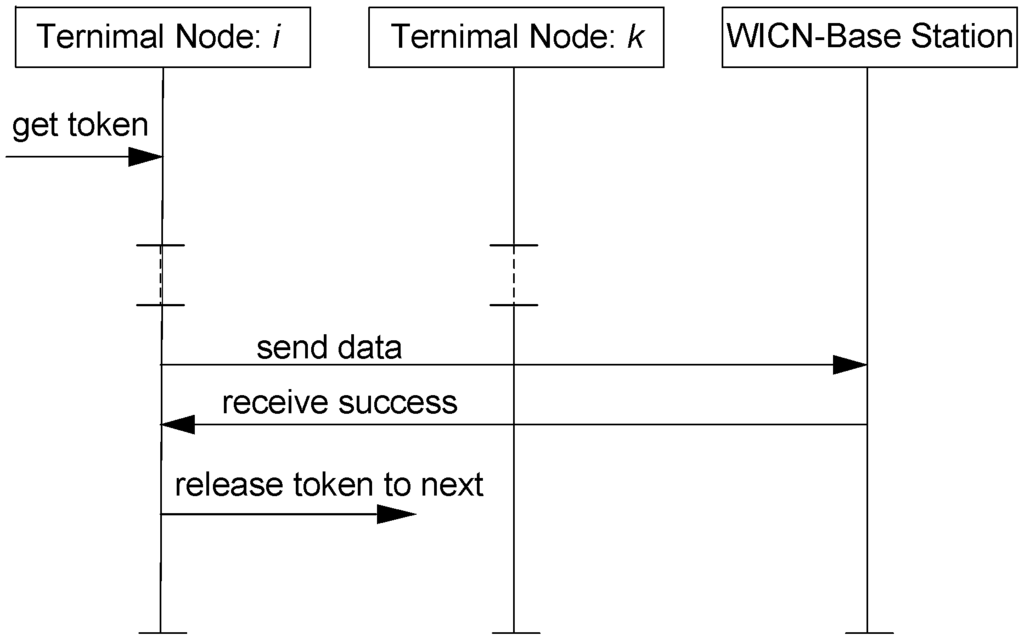
Figure 5.
Data transmission from the WICN terminal nodes to the gateway’s WICN base station.
3.2.2. Data Transmission from the Gateway’s WICN Base Station to WICN Terminal Nodes
After the gateway’s base station gets the token from the WICN sub-network, it first maps the data blocks from the WICN terminal nodes to the shared data area. Meanwhile, the data blocks from the shared data area are also mapped to the gateway’s base station upon request. Then, the WICN base station transmits data to each terminal node. When the time that the gateway’s base station holds the token runs out, it releases the token to the next terminal node. Such a round of information exchange in a WICN sub-network is shown as Figure 6.
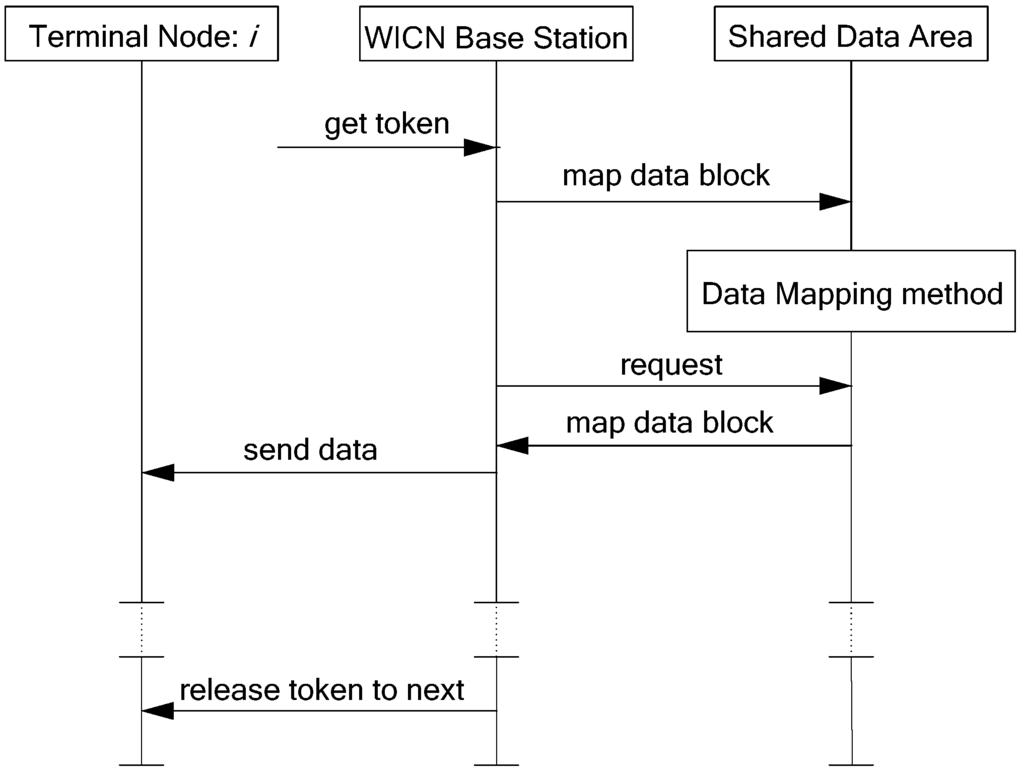
Figure 6.
Data transmission from the gateway’s WICN base station to WICN terminal nodes.
3.2.3. Data Transmission between a MODBUS/TCP Server Station and the Gateway’s MODBUS/TCP Client Station
In a MODBUS/TCP sub-network, the server station obeys a standard MODBUS/TCP protocol to poll each MODBUS/TCP client station. When the server station needs to communicate with the gateway’s client station, it emits a read/write request. If the gateway’s client station receives the server station’s read request, it responses the request and uploads data to the gateway’s client station from the shared data area using the data mapping method. Then, the gateway’s client station sends data to the server station. If the gateway’s client station receives the server station’s write request, it responds to the request and receives data from the server station, then updates data in the shared data area using the same data mapping method. Such a round of information transmission is shown as Figure 7.
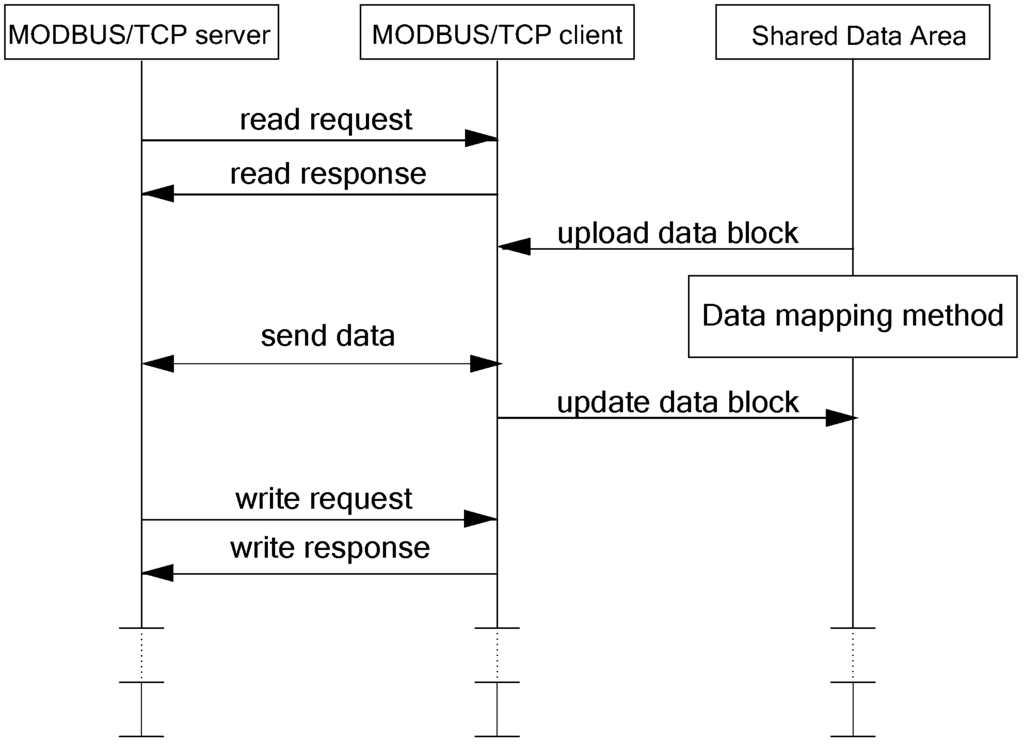
Figure 7.
Data transmission between a MODBUS/TCP server station and the gateway’s MODBUS/TCP client station.
3.2.4. Data Transmission between a PROFIBUS-DP Master Station and the Gateway’s PROFIBUS-DP Slave Station
The PROFIBUS-DP sub-network plays the role of backbone in the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network because it is widely used in industrial process control systems. The gateway is taken as a PROFIBUS-DP slave station in this sub-network. The master station obeys a standard PROFIBUS-DP protocol to poll each PROFIBUS-DP slave station distributed in the sub-network. The gateway’s slave station acknowledges received messages from the master station, and then sends response messages to the master station upon request. If the master station requests output data, the gateway’s slave station receives data from the master station and then updates data in the shared data area using the data converting method. If the master station requests input data, the gateway’s slave station uploads data from the shared data area using the same data converting method and then sends them to the master station. Such a round of information transmission is shown as Figure 8.
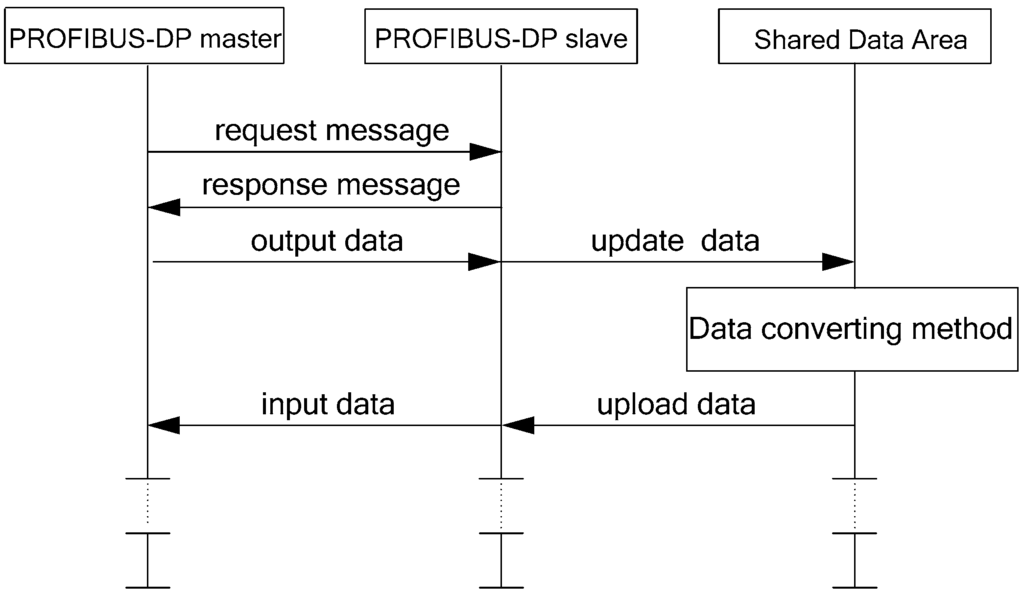
Figure 8.
Data transmission between a PROFIBUS-DP master station and the gateway’s PROFIBUS-DP slave station.
4. Experimental Performance Evaluation
This section first introduces the implementation of the gateway and system configuration of the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network (Section 4.1), and then evaluates and discusses their experimental performance (Section 4.2).
4.1. Gateway Implementation and System Configuration
The AT91RM9200 processor (Atmel Corporation, San Jose, CA, USA) is used as the hardware core of the gateway, which is an industrial-grade embedded microprocessor including abundant hardware resources and interfaces. The software running in the gateway employs VxWorks (version 6, Wind River Systems Inc., Alameda, CA, USA) which is a real-time embedded operation system. The internal wireless node uses a nanoPAN5360 RF module produced by Nanotron Technologies GmBH (Berlin, Germany), which is based on IEEE 802.15.4a-CSS (chirp spread spectrum). It has extremely low power consumption over a wide range of operating temperatures. Figure 9 shows the physical figure of the gateway.
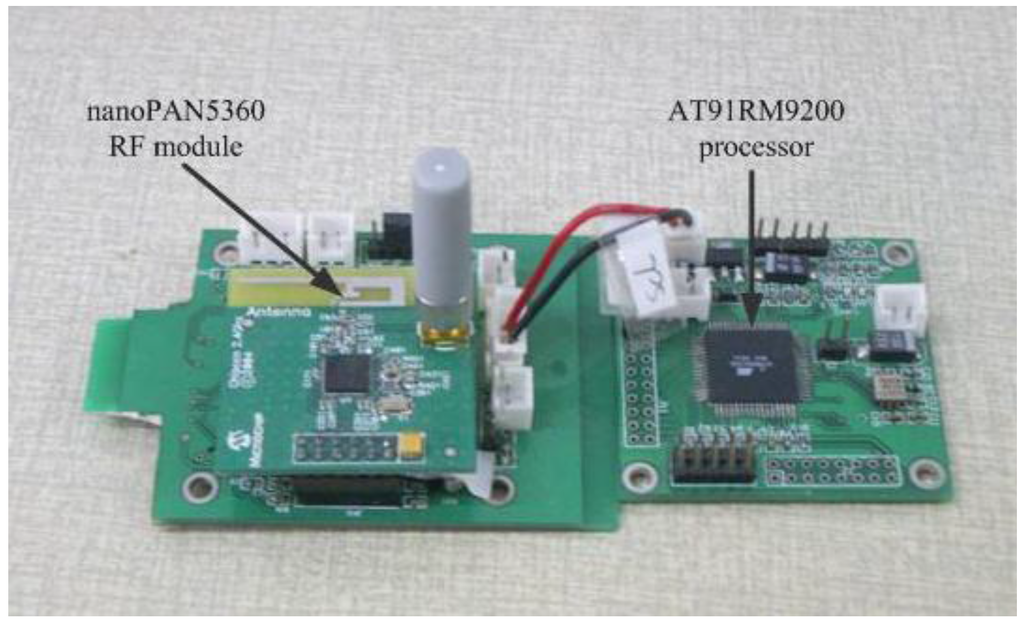
Figure 9.
Physical figure of the gateway.
The system configuration of the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network consists of WICN, a MODBUS/TCP sub-network and a PROFIBUS-DP sub-network which is the backbone network. The gateway is the key device to interconnect different sub-networks in the hybrid fieldbus network. Namely, the gateway served as a slave station of a PROFIBUS-DP sub-network, and a client station of a MODBUS/TCP sub-network, but it is taken as the base station in WICN.
Real-time performance and the packet loss rate are the most important measurement parameters in industrial network control systems. They provide methods for simultaneously capturing the timeliness and reliability capabilities of hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus networks. This paper defines a polling period (Tpp) and a control cycle time (Tctrl) to denote real-time performance. The polling period Tpp indicates the time that the gateway’s base station polls each terminal nodes in WICN, and the control cycle time Tctrl covers the whole time consumption in different sub-networks. Namely, a sensor in WICN sends a data packet, and the gateway receives this data packet and uploads to the controller in a PROFIBUS-DP sub-network. Then the controller transmits a control signal to the gateway, which continues to send it to an actuator in a MODBUS/TCP sub-network. Figure 10 shows the whole control cycle, and the control cycle time Tctrl is calculated as
where τ1 denotes the wireless transmission time that a data packet comes from the sensor in WICN to the gateway. τup denotes the part of protocol converting time which is from WICN to PROFIBUS-DP in the gateway. τ2 denotes the time that the controller in a PROFIBUS-DP master station gets a data packet from the gateway. τc denotes the process time of a data packet in the controller. τ3 denotes the time that the gateway receives a control signal from the controller. τdown denotes another part of the protocol converting time from PROFIBUS-DP to MODBUS/TCP in the gateway. τ4 denotes the transmission time for the gateway to send the control signal to the actuator in the MODBUS/TCP network. Note that τup + τdown denotes the entire protocol converting time in the gateway.
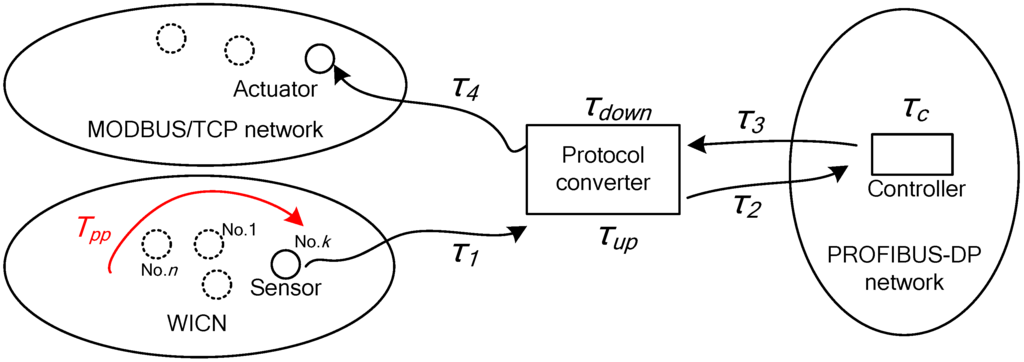
Figure 10.
Control cycle time in the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network.
Packet loss rate is another indicator of network measurement performance in this paper. It is defined as the ratio of the number of lost packets Slost to the total number of packets Ssum in the whole network control cycle. This indicator reflects data loss in the whose network, which is calculated as
4.2. Experimental Results
4.2.1. Polling Period Tpp with Different Number of Nodes and Length of Data Packets in WICN
Figure 11 shows the experimental results of 50 runs with different numbers of nodes and lengths of data packets in WICN, where the number of nodes includes five nodes, 10 nodes and 15 nodes, and the length of data packets involves 4 bytes, 12 bytes and 20 bytes. From the figure, it is seen that polling periods Tpp are almost the same in the cases of 15 nodes and different bytes, but they are different in the cases of 4 bytes and different nodes. The results illustrate that polling periods Tpp are more influenced by the number of WICN nodes than the length of data packets in the proposed hybrid fieldbus network. To further justify the experimental results, the confidence interval with a level of 95% is used based on these observed sample data. A confidence interval gives an estimated range of values which is likely to include an unknown population parameter and is calculated from a given set of sample data. Table 2 shows the mean and corresponding confidence interval of polling periods Tpp in different cases. The results verify that the length of data packets does not influence the polling period, but the number of WICN nodes is the important factor to the polling period [30].
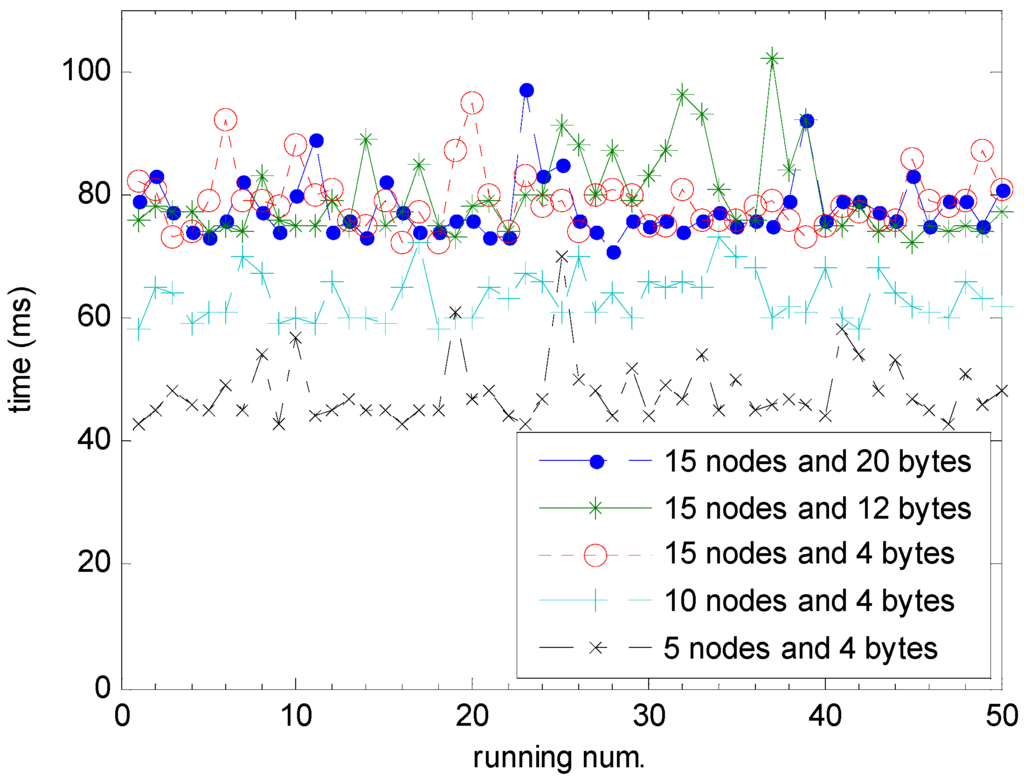
Figure 11.
Polling period Tpp with different number of nodes and length of data packets in WICN.

Table 2.
Mean and corresponding confidence interval with a level of 95% of polling periods Tpp.
4.2.2. Control Cycle Time Tctrl with Different Wireless Nodes in the Hybrid Wired/Wireless Fieldbus Network
Figure 12 shows control cycle times Tctrl with the same length of data packets and different number of wireless nodes in the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network. From the figure, it is apparently seen that the control cycle time is the largest in the case of 20 wireless nodes and the smallest is in the case of five wireless nodes, which indicates that the number of wireless nodes can affect control cycle times Tctrl. Table 3 shows the mean and corresponding confidence interval with a level of 95% of Tctrl in different wireless nodes based on these observed sample data.
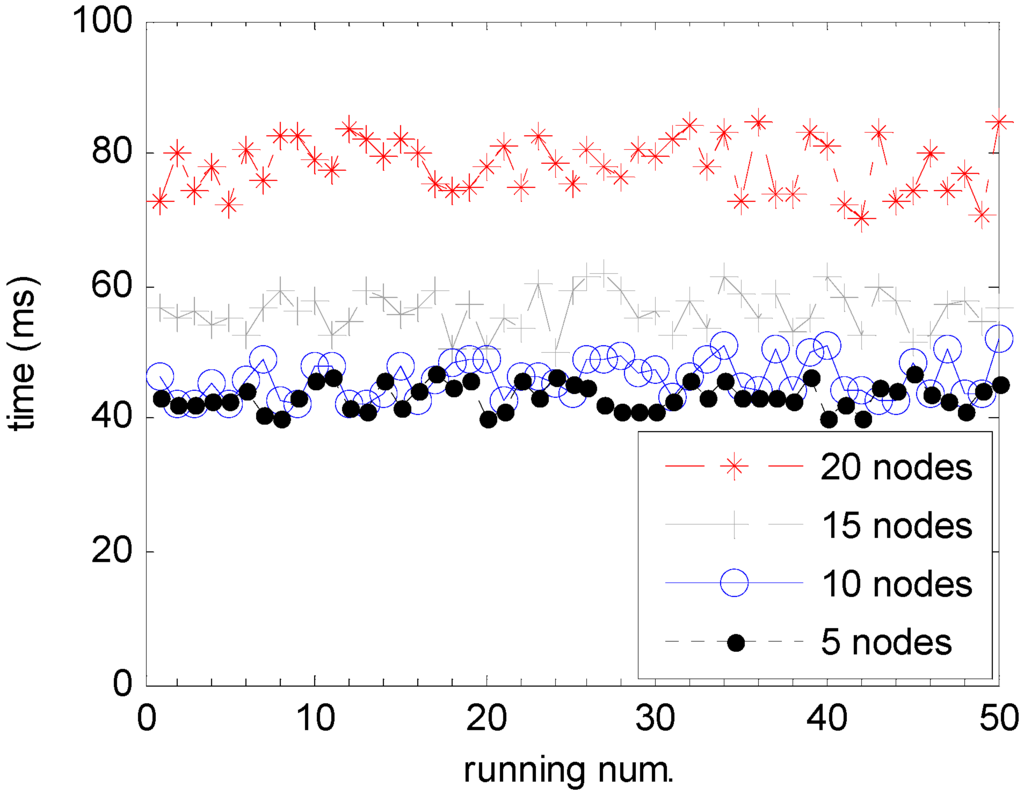
Figure 12.
Control cycle time Tctrl with different wireless nodes in the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network.

Table 3.
Mean and corresponding confidence interval with a level of 95% of control cycle times Tctrl.
4.2.3. Converting Time in the Gateway
The protocol converting time τup + τdown represents the real-time performance of the gateway. Figure 13 shows converting times of 50 runs in the gateway in the cases of 15 wireless nodes and a data packet length of 12 bytes. We can see clearly that the minimum, the maximum, and the mean values of converting times are 15 ms, 30 ms and 22.4 ms, respectively. The results illustrate that the converting time is the smaller and the real-time performance is the better for the proposed gateway.
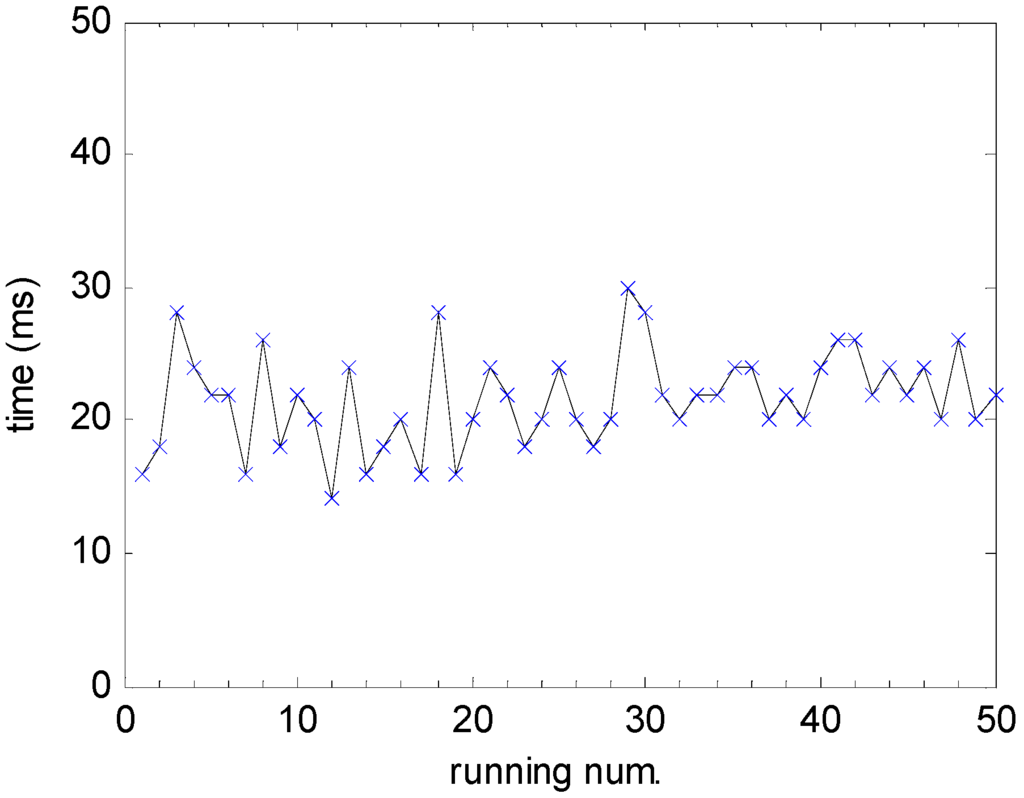
Figure 13.
Converting times τup + τdown in the gateway in the cases of 15 wireless nodes and a data packet length of 12 bytes.
4.2.4. Packet Loss Rate for the Whole Hybrid Network
Figure 14 depicts packet loss rates of 50 runs in the cases of 15 wireless nodes and a data packet length of 12 bytes in the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network. It is shown that the maximum value of packet loss rate is less than 0.1%, which is a standard reference value to measure reliability performance of network control systems [10]. It is further obtained that the mean and corresponding standard deviation values of packet loss rates are 0.044% and 0.021%, respectively. The results indicate that the packet loss rates of the proposed hybrid fieldbus network satisfy the network reliability.
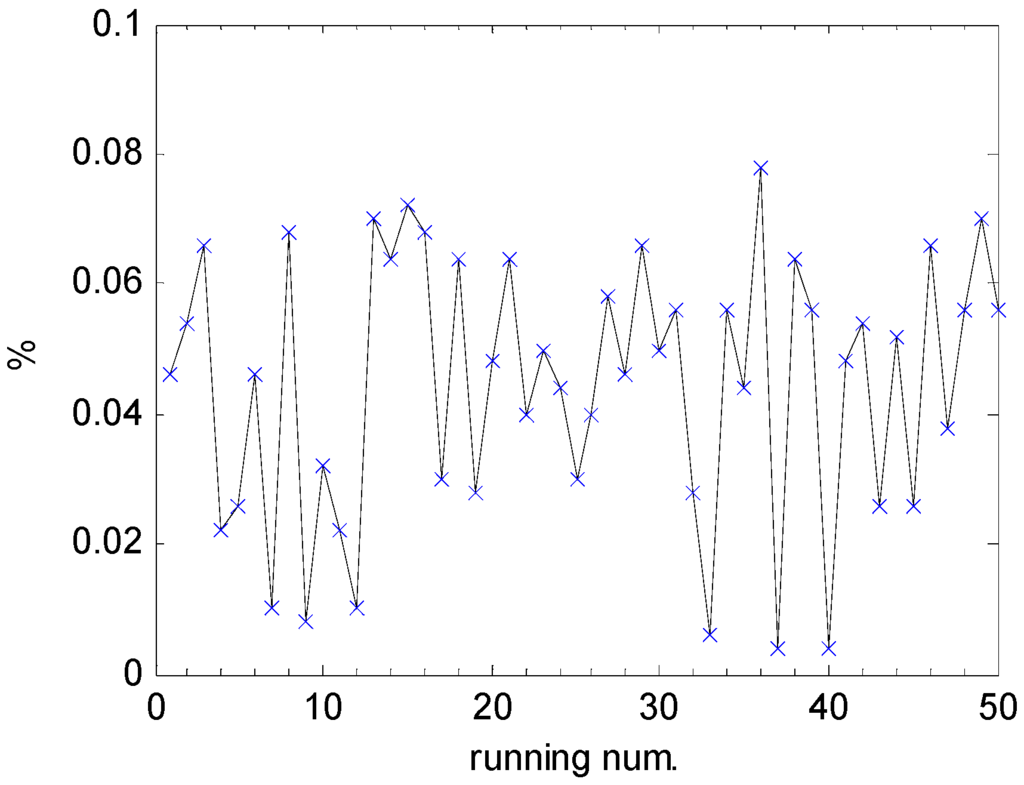
Figure 14.
Packet loss rates in the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network in the cases of 15 wireless nodes and a data packet length of 12 bytes.
Based on the real-time performance and packet loss rates obtained by the above experiments, it is confirmed that the results satisfy performance requirement of networked control systems. Namely, the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network can get better network performances, and qualify for the environment of industrial automation.
5. Application
In order to further investigate feasibility of the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network, it is applied to an experimental measurement and control platform of a steam turbine power generation system, which is composed of a gateway, a wired PROFIBUS-DP sub-network, a wired MODBUS/TCP sub-network, WICN and some power generation devices. In this system, there exist two wired fieldbuses because it is a complex distributed control plant; some devices are connected by PROFIBUS-DP fieldbuses, and other devices are connected by MODBUS/TCP fieldbuses to satisfy the cabling requirement. In fact, some interesting classes of industrial applications, such as the health monitoring of machine colonies and the Internet of things system applications, involve more than one wired fieldbus and various kinds of networked embedded devices. An important characteristic in these application areas is that technology improvement based on a wireless industry network is required. Figure 15 shows a schematic representation of the system, where electrical energy generation using a steam turbine involves three energy conversions: extracting thermal energy from the fuel in a petroleum gas tank and using it to raise steam by a steam boiler; converting the thermal energy of the steam into kinetic energy in a steam turbine, and; using a rotary generator to convert the turbine’s mechanical energy into electrical energy [31]. From Figure 15, it is known that the measured values of this system are transmitted by different wired/wireless sub-networks to the gateway, which changes the styles of data stacks and continues to transmit to the controller in a backbone PROFIBUS-DP network. Thus, the gateway becomes a bridge between wired sub-networks and wireless sub-networks. In the process of electrical energy generation, some important variables including generator voltage, generator current, generator speed, turbine inlet pressure and temperature, and turbine outlet pressure and temperature are controlled by the flow control valve. In this experiment, we use the conventional PID (proportional-integral-derivative) control to regulate the flow control valve, and the model of the plant is obtained by system identification based on data acquired during a series of experiments.
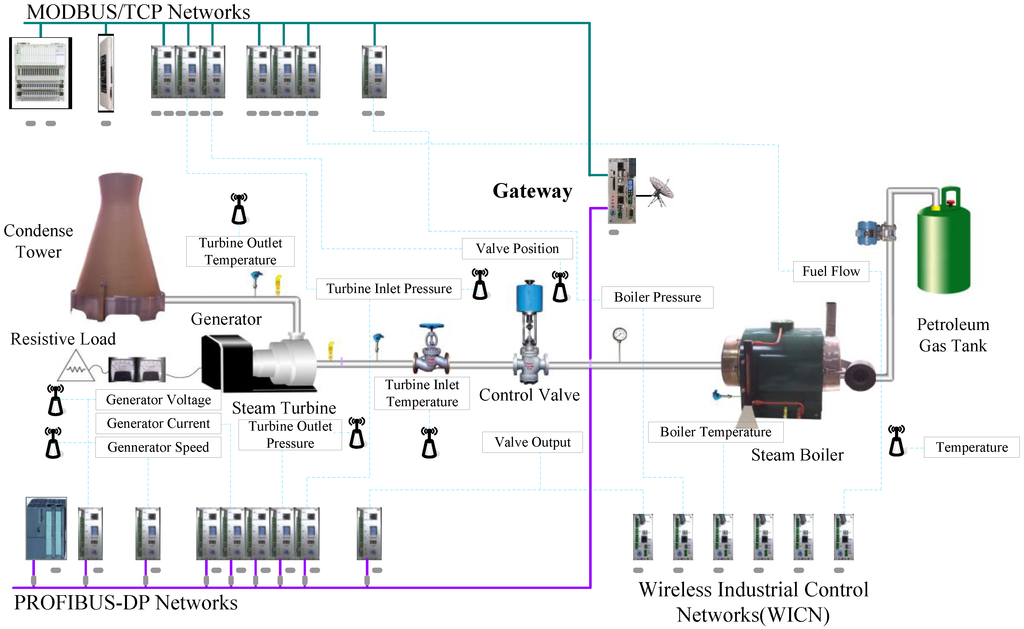
Figure 15.
Schematic representation of a steam turbine power generation system based on the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network.
Table 4 shows the performance of the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network in the steam turbine power generation system, which includes the network performance denoted by the mean transmission times from the field devices to the control panel, and the control performance denoted by the mean measurement values from different sub-networks. Note that some parts of variable values, such as indoor temperature, are only obtained by WICN, other parts, such as fuel flow, are obtained by WICN and one of the wired fieldbus sub-networks and others, such as turbine inlet pressure, are simultaneously obtained by all the three sub-networks. From this table, it is found that mean transmission times from the field devices to the control panel are very small for all sub-networks and completely satisfy the real-time requirements for industrial automation. This indicates that the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network is very feasible in the steam turbine power generation system. Furthermore, we can know that the mean transmission times of WICN are lower than those of the corresponding wired sub-networks in all cases. This illustrates that WICN can reduce transmission times and obtain better network performance. On the other hand, it is obvious that the measured values are relatively stable through different wired/wireless sub-networks. This denotes that control strategy is feasible in the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network, and such network architecture can obtain the stable control performance.

Table 4.
Network performance (mean transmission times) and control performance (mean measurement values) are obtained by a PROFIBUS-DP sub-network, a MODBUS/TCP sub-network and WICN in the steam turbine power generation system. Note that “--” denotes that there is no measurement value in the corresponding sub-network.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, a hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network is proposed to solve complex communication path problems in industrial networked control systems. The proposed hybrid fieldbus network uses a gateway to connect a wired PROFIBUS-DP fieldbus network and a wired MODBUS/TCP fieldbus network with a wireless industrial control network. Since the network protocols are different in various sub-networks, they employ a shared data model to address data exchange in different network protocols. In order to evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed hybrid fieldbus network, real-time performance and packet loss rates are adopted as performance indicators. The experiment results indicate that the hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network can satisfy the performance requirement of industrial automation systems. Meanwhile, it is deployed at a steam turbine power generation system to infer this and to further verify that it has better network performance and control performance.
There are several important directions for future work. This paper mainly focuses on designing the gateway and implementing the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network, but there is room for improvement. For example, it is of interest to optimize the architecture of the proposed hybrid fieldbus network. The second important direction for future work is to investigate the feasibility and effectiveness of this hybrid fieldbus network in other industrial real-world applications. The third important direction for future work is to develop new control strategies to improve the network control performance based on this hybrid fieldbus network.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the Funds of National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 61473182), in part by Program for the Key Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (14JC1402200, 15JC1401900), in part by Program for “Blue project” of colleges and universities in Jiangsu province, in part by Program for “Overseas Study Plan” of colleges and universities in Jiangsu province, and in part by the Funds of Natural Science Special Program of Nantong Vocational University (grant No. 1407001).
Author Contributions
Sheng Xu conceived the concept, performed the research and wrote the manuscript. Minrui Fei conceived and reviewed the manuscript. Haikuan Wang evaluated the experimental performance of the proposed hybrid wired/wireless fieldbus network. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Wan, J.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Lai, C.F.; Wang, S. A Review of Industrial Wireless Networks in the Context of Industry 4.0. Wirel. Netw. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Lee, C. A secure single sign-on mechanism for distributed computer networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cao, X.; Cheng, P.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, Y. Distributed collaborative control for industrial automation with wireless sensor and actuator networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 4219–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammini, A.; Ferrari, P.; Marioli, D.; Sisinni, E.; Taroni, A. Wired and wireless sensor networks for industrial applications. Microelectron. J. 2009, 40, 1322–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisinni, E.; Depari, A.; Flammini, A. Design and implementation of a wireless sensor network for temperature sensing in hostile environments. Sens. Actuators A. 2016, 237, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammini, A.; Marioli, D.; Sisinni, E.; Taroni, A. Design and implementation of a wireless fieldbus for plastic machineries. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellsson, J.; Vallestad, A.E.; Steigmann, R.; Dzung, D. Integration of a Wireless I/O interface for PROFIBUS and PROFINET for factory automation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4279–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, W.H.; Chapin, J.M. On the convergence of wired and wireless access network architectures. Inf. Econ. Policy. 2010, 22, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, J.A.; Reviriego, P. Energy efficiency in industrial Ethernet: The case of powerlink. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2896–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaj, P.; Jasperneite, J.; Felser, M. Computer Communication within Industrial Distributed Environment—A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, V.C.; Lu, B.; Hancke, G.P. Opportunities and challenges of wireless sensor networks in smart grid. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 3557–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.C.; Chen, O. Mobile sensor node deployment and asynchronous power management for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitturi, S.; Tramarin, F.; Seno, L. Industrial Wireless Networks: The Significance of Timeliness in Communication Systems. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2013, 7, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seno, L.; Tramarin, F.; Vitturi, S. Performance of Industrial Communication Systems: Real Application Contexts. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2012, 6, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.; Tovar, E. Real-time communications over wired/wireless PROFIBUS networks supporting inter-cell mobility. Comput. Netw. 2007, 51, 2994–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elarag, H.; Moedinger, A.; Hogg, C. TCP friendly protocols for media streams over heterogeneous wired-wireless networks. Comput. Commun. 2008, 31, 2242–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miorandi, D.; Vitturi, S. Hybrid wired/wireless implementations of PROFIBUS DP: A feasibility study based on Ethernet and Bluetooth. Comput. Commun. 2004, 27, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willig, A. Polling-based MAC protocols for improving real-time performance in a wireless PROFIBUS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2003, 50, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meike, D.; Pellicciari, M.; Berselli, G. Energy efficient use of multirobot production lines in the automotive industry: Detailed system modeling and optimization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2014, 11, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Xiao, G.; Biller, S.; Li, L. Energy saving opportunity analysis of automotive serial production systems (March 2012). IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N. ZigBee and Bluetooth strengths and weaknesses for industrial applications. J. Comput. Control Eng. 2005, 16, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, P.; Flammini, A.; Marioli, D.; Rinaldi, S.; Sisinni, E. On the implementation and performance assessment of a wirelessHART distributed packet analyzer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.; Carlsen, S. WirelessHART versus ISA100. 11a: The format war hits the factory floor. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2011, 5, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Mok, A.K.; Chen, D.; Lucas, M.; Nixon, M. WirelessHART: Applying wireless technology in real-time industrial process control. In Proceeding of IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium, St. Louis, MO, USA, 22–24 April 2008; pp. 377–386.
- Wang, H.; Hou, W.; Fei, M. Polling-based protocol gateway for the Integration of hybrid wired/wireless industrial control networks. In Proceedings of the 29th Chinese Control Conference, Beijing, China, 29–31 July 2010; pp. 5772–5777.
- Mondal, S.A.; Luqman, F.B. Improving TCP performance over wired–wireless networks. Comput. Netw. 2007, 51, 3799–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Fei, M.; Wang, H.; Li, T. Wireless network performance test in hybrid wired/wireless network system. In Proceedings of the 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Taipei, Taiwan, 21–25 June 2011; pp. 1029–1034.
- Rutagangibwa, V.; Krishnamurthy, B. A Survey on the Implementation of Real Time Systems for Industrial Automation Applications. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 174–177. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Xu, S.; Jiang, D. MFAHP: A novel method on the performance evaluation of the industrial wireless networked control system. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Electronics and Information Engineering, Dalian, China, 26–28 September 2015.
- Bertocco, M.; Narduzzi, C.; Tramarin, F. Estimation of the delay of network devices in hybrid wired/wireless real-time industrial communication systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2012.
- Ma, H.; Fei, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H. Wireless networked learning control system based on Kalman filter and biogeography-based optimization method. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).