Abstract
Information Technology (IT) adoption is an important field of study in a number of areas, which include small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Due to the numerous advantages of IT, SMEs are trying to adopt IT applications to support their businesses. IT adoption by SMEs differs from larger organizations because of their specific characteristics, such as resources constraints. Therefore, this research aims to provide a better and clearer understanding of IT adoption within SMEs by reviewing and analyzing current IT literature. In this research, the review of literature includes theories, perspectives, empirical research and case studies related to IT adoption, in particular within SMEs from various databases such as Business Premier, Science Direct, JStor, Emerald Insight and Springer Link. The proposed model of effective IT adoption is believed to provide managers, vendors, consultants and governments with a practical synopsis of the IT adoption process in SMEs, which will in turn assist them to be successful with IT institutionalization within these businesses.
1. Introduction
In this 21st century, a worldwide system of commerce is evolving, in much the same way as national markets evolved from local and regional networks. The modern economic environment which is dominated by globalization, hyper-competition and the knowledge and information revolution has revolutionized the way business is conducted [1]. This new technological epoch is apparent through intensified investment in computer-processing and data preparation appliances in the manufacturing and service industries and telecommunications infrastructure, and also to its widespread usage in government agencies, educational organizations, and, more recently, in the household. As a result of this technological progress, the implementation and application of IT is a significant driving force behind many socioeconomic changes [2]. As the utilization and commercialization of IT becomes more widespread throughout the world, the adoption of novel IT can generate new business opportunities and various benefits. Nowadays, both large organizations and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are seeking ways to reinforce their competitive position and improve their productivity [3]. Accordingly, there is an increasing consciousness of the necessity to derive profit through investment in IT within SMEs. IT tools can significantly assist SMEs by supplying the required infrastructure, which is necessary for providing appropriate types of information at the right time. IT can also provide SMEs with competitiveness through integration between supply chain partners and inter-organizational functions, as well as by providing critical information [4]. However, prior IT literature has shown that only a small number of studies focused on the adoption and use of IT in SMEs [5]. Moreover, it has been found that in spite of the exponential growth of IT within SMEs, the rate of IT adoption by these businesses has remained relatively low [6], and large organizations have noticeably profited more than SMEs in both IT-enabled improved sale and costs savings [7]. In looking for reasons for such differences in IT adoption in SMEs, unique characteristics of these businesses can be highlighted. SMEs generally have limited access to market information and suffer from globalization constraint [8]. In addition, management techniques such as financial analysis, forecasting and project management are rarely used by SMEs [9]. A tendency to employ generalists rather than specialists, reliance on short-term planning, informal and dynamic strategies and decision-making process, plus an unwillingness to develop and the use of standard operating procedures are other distinctive characteristics of SMEs [10,11]. However, it is the restricted resources controlled by SMEs, commonly referred to as resource poverty [12,13], that is the major differentiator between SMEs and large organizations. Compared with large organizations, SMEs are relatively weaker at various levels (i.e., organizational, managerial, technological, individual and environmental). Therefore, IT adoption and usage in SMEs is at a disadvantage [14,15].
The aim of this research is to achieve a better understanding of IT adoption in SMEs through explicitly and understandably exploring and identifying factors influencing IT adoption processes within SMEs in both developed and developing countries. This will be undertaken by reviewing existing literature with a high concentration of certain SME-related issues. The proposed conceptual framework demonstrates the determinants of the IT adoption process in SMEs through a review of prior literature, including concepts, methodologies, theories, empirical research and case studies related to IT adoption among SMEs, and by combining existing perspectives. The research investigates and reveals a number of internal and external issues pressuring and persuading SMEs to adopt IT solutions. Likewise, barriers to IT adoption in SMEs will be addressed by reviewing and classifying IT adoption factors. In addition, by using the proposed conceptual model of effective IT adoption, the authors propose a systematic IT adoption strategy for SMEs to succeed in IT institutionalization at different adoption stages.
2. IT Adoption within SMEs
In this review, IT will cover a wide range of information processing and computer applications in organizations, since various definitions of IT have been employed widely by different researchers. Therefore, IT will cover Information System (IS), Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and the Internet, as well as and their infrastructure, including computer hardware and software, and those technologies that process or transmit information to enhance the effectiveness of individuals and organizations. A variety of perspectives on factors that affect the IT adoption process is available in a huge body of literature. The review of previous research has identified a number of influencing factors. Most of these perspectives and studies have concentrated on influencing factors such as top management, organizational behavior and characteristics, firms’ resources, government, customers, supplier and external IT consultant and vendors. From a macro-perspective, and based on the review of the existing literature on IT adoption in SMEs, an integrated framework has been developed and used to classify various issues and factors related to the process of IS/IT adoption within SMEs (Figure 1). This framework merely comprises different aspects of internal and external IT adoption factors (Drivers, Influencing factors and barriers) and does not categorize adoption factors based on being drivers or barriers of IT adoption in SMEs.
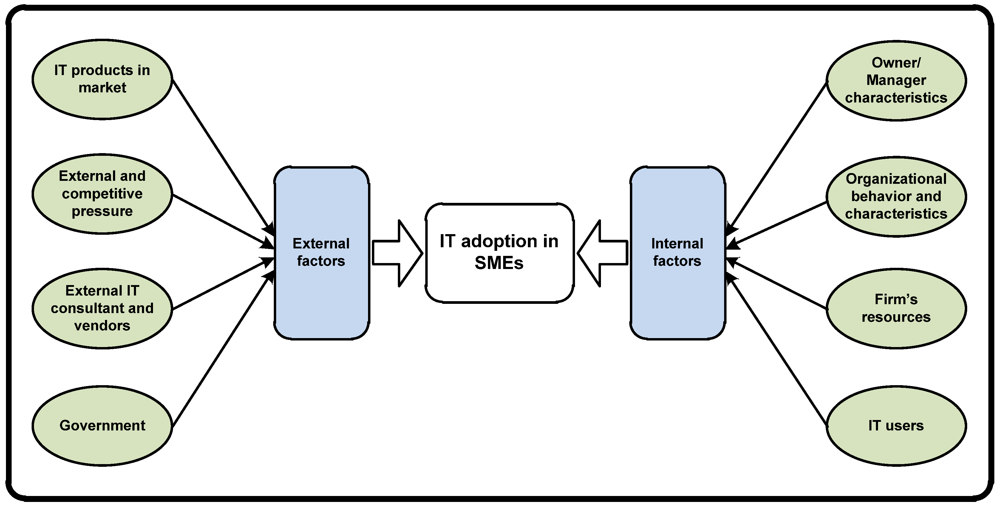
Figure 1.
Proposed framework of IT adoption influencing factors in SME context.
Likewise, the authors will address different concepts of IT adoption (also considered as different IT adoption phases) suggested by prior literature, such as decisions to accept and use innovation [16,17,18,19], the full use of innovation as intended by the designer [20], implementation success [21], extent of usage [5,22] and the effectiveness and success of adopted IT based on acceptance of, or satisfaction with, IT [23,24,25,26,27].
3. Influencing Factors
Within this study and as suggested in Figure 1, influencing factors are categorized into two major clusters of factors and their subcategories: internal and external factors. In addition, a brief review and categorizations of factors influencing IT adoption in SMEs have been offered in Table 1: factors that are merely SME-related. Internal factors are defined as factors within the technological context and organizational context of SMEs. Technological context describes the internal technologies relevant to the firm. Organizational context refers to descriptive measures regarding the organization, such as firm size and scope, managerial structure and internal resources. External factors, however, refer to the factors within the environmental context that describe the arena in which a firm conducts its business: its industry, competitors and dealings with government [28,29,30].

Table 1.
Factors affecting IT adoption in SMEs.
| Internal factors | ||
| Influencing factors | Factors | References |
| Top management (CEO) | Perception of and attitude toward IT adoption | [31,32,33] |
| CEO’s (Chief Executive Officer) support and commitment | [3,12,16,21,34,35,36] | |
| IT knowledge and experiences | [33,35,37,38,39] | |
| CEO innovativeness | [33] | |
| Perceived behavioral control over IT | [32] | |
| CEOs desire for growth | [37] | |
| Familiarity with administration | [37] | |
| Resources | Financial resources availability | [33,35,40,41] |
| Level of IT investment | [21,42] | |
| In-house IT experts | [34,39,43,44] | |
| Influencing factors | Factors | References |
| End users (staff) | Users’ IT competence (knowledge of IT) | [21,31,45] |
| Users’ training | [16,42,43] | |
| Users’ attitudes and opinions toward IT | [31,43] | |
| Users’ participation and involvement | [31,37,39,46] | |
| Organizational behavior and characteristics | Business growth and expansion | [35,46,47] |
| SME’s strategic context | [31,37,48,49] | |
| Business size (turnover and numbers of employees) | [3,16,33,38,39,40,42,50,51,52] | |
| Type of industry | [33,35,52,53,54] | |
| Information intensity | [33,38,55] | |
| Business maturity (high tech and knowledge intensive) | [35,37] | |
| Organizational structure | [31] | |
| Organizational culture | [39,46,56,57] | |
| Family intervention on management | [37,46,58] | |
| Change (technological change and business expansion) | [40,44] | |
| Integration of internal processes | [56] | |
| IS planning | [21] | |
| External factors | ||
| Influencing factors | Factors | References |
| IT products in market | Type and age of implemented IS/ITs | [31,53,59] |
| Quality of software available in market | [31] | |
| The costs of ITs | [17,39,43,60] | |
| Perceived impacts and benefits of IS/ITs in organization | [3,16,17,21,35,41,45,61] | |
| Process compatibility | [3,16,17,56] | |
| User-friendliness, complexity and popularity | [16,17,26,43,52,62,63] | |
| Security | ||
| External and competitive pressure | Competitiveness of environment (the necessity to stay competitive) | [3,33,35,40,53,54] |
| Government | Legal issues | [63,64] |
| External IT consultant and vendors | External expertise and services availability and support | [12,16,31,34,39,43,60] |
3.1. Internal Factors
3.1.1. Top Management
In SMEs, the IT adoption process is directly affected by top management where all decisions from daily functions to future investments are made by them [46,58]. SMEs mainly have simple and highly centralized structures with the CEOs in which, in most cases, the owner and chief manager are the same person [65]. A number of studies have revealed that in SMEs, the role of CEOs (top management or owner/manager) is central to the enterprise, since their decision influences all firms’ activities, both currently and in the future [66,67]. This also refers to IT adoption decision from planning stage to the implementation, maintaining, and system upgrade stages [46,58,68].
Similarly, and based on the upper echelon theory, prior literature suggests that CEO’s demographic characteristics and personality traits of openness and extraversion are the significant determinants of IT usage behavior and performance within businesses [69,70,71].
Several factors, including management’s perception of and attitude on IT, support and commitment, IT knowledge and experiences, innovativeness, perceived behavioral control over IT, desire for growth and familiarity with administration directly affect the process of IT adoption in SMEs [3,32,35,36]. Accordingly, the characteristics of CEOs should be taken into consideration in the investigation of strategic activities, such as the adoption of innovation, including IT as a new technology [72]. Small businesses that have adopted IT are more likely to have CEOs who possess better positive attitudes in IT adoption [18,33]. This view is reinforced by Caldeira and Ward [31] who found that the positive attitude of top management has resulted in relative success of IS/IT adoption in SMEs, especially in manufacturing industry. In addition, it is argued that a greater intention to adopt IT solutions is directly attributable to the more positive attitude of small and minority business owners in IT adoption [32]. Consequently, if the CEO perceives that benefits of IT adoption outweigh its risks, then the business is more likely to adopt IT [33]. Likewise, when management has been highly willing to implement IT application, SMEs do not perceive management priority on IT as a major barrier in adopting IS applications [4]. In this regard, a positive attitude by top management in using IT (as the users of IT in SMEs) will result in IT acceptance and subsequently success in SMEs [24,73,74].
On the other hand, IT adoption literature has provided evidence that top management support and commitment towards IS/IT adoption is one of the key cornerstones of higher levels of success and satisfaction with IS/IT adoption and use in SMEs [3,21,39,74]. Cragg and Zinatelli [34] identified insufficient attention by management to IS as one of the three main problem areas for computing in small firms. Since top management support and commitment are key factors contributing to IS success within small firms, these authors argued that top management directly affects IS evolution and sophistication. For success of IT in Malaysian SMEs however, it was found that the anticipated benefits of computerization in SMEs can only be achieved by the existence of five conditions, including strong top management support as the key condition [25]. In a similar context, and interpreting the successful adoption and use of IS/IT from the resource based theory, Caldeira and Ward [31], and Ghobakhloo et al. [75] demonstrated that management support towards IS/IT adoption significantly improved IS/IT adoption success within SMEs. However, some prior studies have provided evidence of an insignificant relationship between the levels of IS effectiveness and CEO support [12,36]. Thong et al. [12] defined top management support based on five elements (Table 2). They discussed that there is no difference in the level of IS effectiveness between small businesses with high levels of top management support and small businesses with low levels of top management support. However, the majority of prior studies have implied the significant role of top management support in IT adoption within SMEs, and Thong et al.'s [12,36] inconsistency in providing the support for this factor can be attributed to their unique definition of top management support and its measurement construct in their research.

Table 2.
Thong et al. [12] definition of top management support.
| Variables | CEO support elements |
|---|---|
| Top management support | Frequency of attendance at computerization project meetings |
| Level of involvement in information requirements analysis | |
| Level of involvement in decision-making relating to a computerization project | |
| Level of involvement in reviewing consultants’ recommendations | |
| Level of involvement in monitoring the project |
The literature (particularly studies using upper echelon theory) suggests that CEO’s IT knowledge and experience of IT is another trait affecting IT adoption in SMEs [35,37,65,69]. It is suggested that the greater knowledge of CEOs will reduce the degree of uncertainty entangled with IT which will result in lower risk of IT adoption [18]. Thus, small businesses with CEOs who are more knowledgeable about IT are more likely to adopt it [33]. Moreover, CEOs with higher levels of computing skills are more satisfied with the implementation of IS rather than those having inferior skills [27], given that satisfaction with IS/IT is one of the most applied measures of IT success in organizations [26,76,77]. These views are consistent with the results of other studies, which found that sufficient knowledge of IT, and its consequent influences over organization, could be provocative and supportive for IT adoption in SMEs [37,39,78].
Another influencing factor attributable to the top management characteristics is CEO innovativeness, both in general and IT-specific terms [65,75]. Personal Innovativeness in IT (PIIT) has been revealed to be a reliable predictor of users’ attitude about the simplicity of use and effectiveness of new technologies [79]. PIIT refers to “the willingness of an individual to try out any new information technology” [80]. Agarwal and Prasad [80] discuss that PIIT is a major determinant of IT acceptance by moderating in Perceived Usefulness (PU), compatibility and Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU). Here, it should be considered that in most of IT acceptance models, such as Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) [22], Decomposed Theory of Planned Behavior (DTPB) (firstly introduced by Taylor and Todd [81]), Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) [82], as well as in the majority of models of users’ satisfaction, including End User Satisfaction (EUS) model [76], Model of Small Business User IT Satisfaction [27] and Wixom and Todd [83] integrated model of user satisfaction and technology acceptance with IT, PU and PEOU, are two key constructs of user behavioral intention and subsequently IT usage behavior. Thatcher and Perrewe [84] demonstrated that highly innovative individuals with higher levels of PIIT are more likely to look for stimulating experiences, as well as having more confidence in their competence to use IT. On the other hand, individuals possessing lower levels of PIIT are more likely to present general computer anxiety, and they might have less tolerance for risk.
In general terms however and in SME context, studies by Ghobakhloo et al. [65], Thong and Yap [33], and Thong [18] revealed that movement toward IT adoption in small enterprises with innovator CEO are more probable. Innovator CEOs would prefer to apply distinctive and risky solutions such as IT that change the structure in which the problems are generated. Thus, CEOs’ desire to be more innovative will expedite the process of IT adoption [33]. Hence, it can be inferred that the above mentioned studies and researches stress the importance of innovativeness in both general terms, as well as PIIT on user perception and system acceptance, whereas Scott and Walczak [85] emphasized that individuals with higher levels of PIIT will possess greater cognitive absorption and show higher computer self-efficiency. In SMEs, where users of a new information system are both employees and owner/managers, innovative owner/managers will have a better attitude toward IT adoption.
Desire for growth is another characteristic of CEOs that deserves our attention as an important influencing factor over adoption of IT. Lybaert [37] discusses that firm’s size is positively related to the decision to accumulate additional information, and growth of a firm is coupled with the gathering of additional information. They found that an SME’s owner/manager, who makes most of the critical decisions and allows the firm to grow, uses more information when he/she possesses a greater desire for growth. Moreover, familiarity with administration is other important CEO-related determinant which influences the use of information and IS within SMEs. Lybaert [37] showed that in comparison with CEOs not possessing knowledge of administration, CEOs with high familiarity with administration will use more information and subsequently IT.
3.1.2. Resources
SMEs have generally been distinguished by and are suffering from their restricted access to particular resources compared with large organizations [86,87]. The literature on IT adoption suggest that, due to the SMEs’ unique characteristics, their financial resources, technical and managerial resources, information resources accessibility, internal and external expertise, market accessibility and in-house IT knowledge and experience can hinder or simplify the adoption of IT in SMEs, and positively or negatively affect this process as well [21,31,34,37,39,42,44,58].
Financial resources are one of the most crucial resources which are known as the key SMEs performance requirements and are the critical success factors, based on resource-based theory [88]. In general, most SMEs suffer from the lack of sufficient financial resources and most owner/managers invest their own personal assets [66]. Limited financial resources compel SMEs to be cautious about their investment and capital spending [75]. An imprecise IT investment decision can cause drastic financial consequences for SMEs and in extreme circumstances, may lead to insolvency and economical failure [78]. As implementation of a new IT system and its components requires long term investment [58] as well as the high cost of IT infrastructure [60], only SMEs that have adequate financial resources would consider adoption of IT as a feasible project to undertake [33]. Hence, SMEs’ owner/managers who have access to necessary financial resources are more able to establish the desired IS [37]. However, despite a number of studies, it has been revealed that the financial restriction of SMEs regarding IT adoption is attributable to the high cost of IT tools and infrastructure [3,43,60]. However, Dibrell et al. [10] and Wu et al. [89] suggested that IT implementation expense is not major factor hindering IT adoption process in SMEs, since the price of computer hardware and software has considerably declined in recent years. Nevertheless, it should be considered that along with the initial cost of computer hardware and software, other IS/IT implementation expenses, which include the cost of users training and development, and the post deployment costs should be undertaken by SMEs during different phases of IT adoption [58]. Consistent with this view, Ein-Dor and Segev [90] suggested that through investing sufficient financial resources, the probability of IS implementation success within organizations will be increased. This view is empirically reinforced by Thong [21] who demonstrated that after external expertise, IS investment is the second most significant determinant of IS implementation success in Singaporean small businesses. Their study demonstrated that higher levels of allocation for IS investment will amplify the possibility of IS implementation success in small businesses, while through this allocation for investment, small businesses will be able to hire more experienced external experts and/or implement better IS that meet their goals. Furthermore, due to the above mentioned restrictions, and regardless of decrease in the price of preliminary IT tools, SMEs are generally unable to meet the expense of other IT adoption costs such as taking expert professionals into service [75]. Therefore, SMEs face great difficulty hiring IT specialists to successfully implement IT with regard to financial constraints [31,78].
On the other hand, and comparing with large organization, it has been acknowledged that SMEs are suffering from a lack of in-house IT expertise which might negatively affect the process of IT adoption [34,39,43]. As a result, SMEs are facing significant risks and problems with their computerization regarding their inadequate knowledge of IS/IT implementation [86]. Cragg and Zinatelli [34] conducted a longitudinal study over an eight-year period of IS sophistication and evolution in eighteen small firms and demonstrated that evolution and sophistication of IS within small firms will be drastically inhibited when small enterprises suffer a lack of internal expertise. This view is supported through a study by Caldeira and Ward [31] who revealed that internal expertise consisting of employees, supervisors, or those from top management teams are powerful determinants of IT adoption and success. In addition, knowledge of IT is another key resource influencing IT adoption in SMEs. Development of internal IS/IT knowledge and skills is one of the most important bases required for providing superior levels of IS/IT adoption and satisfaction in SMEs [31]. In general, the lack of IT knowledge in SMEs can be regarded as a barrier to IT adoption since CEOs of SMEs might be bewildered by swift development of IT tools and a countless variety of choices [78,91].
3.1.3. End Users
In most organizations, employees are regarded as significant assets, and along with the role of owner/manager, seriously affect the firm’s survival and success [58,92]. These assets, as the users of IT within SMEs, are another precious resource for firms [31] which need to be developed to contribute to the success of business [93,94].
Characteristics of IT users, including knowledge of IT, training, attitudes and intention toward IT, and participation and involvement in adoption process could affect IS/IT acceptance, or its adoption process as well [21,31,95,96]. Lack of training and skills of IT in organizations will result in a limited use of IT and lack of success in reaping benefits from computer hardware and software in organizations. This situation will further lead to a lack of IS/IT adoption success in SMEs, given that the successful adoption of IT needs the sharing of knowledge, training, and higher levels of skills by those employees who use IT [74,93].
In order to facilitate the successful implementation of IS in SMEs, and to avoid adoption failure, these businesses should also augment the level of IS knowledge among potential IS users through providing employees with computer education and training courses [21]. Sarosa and Zowghi [78] and Ghobakhloo et al. [74] suggested that IT acceptance among users of IT who form part of a firms’ employee base will impose positive impacts on IT adoption. According to these authors, the level of IT adoption and usage by users will be affected through the provision of IT courses and training, while higher knowledge of IT among users would help them in implementing new technology.
Premkumar and Roberts [16] suggested that increasing users’ awareness of the benefits of information telecommunication technologies will also positively influence the process of adopting these technologies, while this awareness could be amplified through improved education and training. Correspondingly, a study by Kleintop and Blau [97] investigating the impact of end user training on electronic mail system implementation has demonstrated that end users practicing with new IT systems before implementation will result in higher level of IT system acceptance. In addition, their research suggested that the increment in amount of training among end users before IT implementation might lead to higher levels of perceived ease of using IT, as well as perception of IS usefulness. Moreover, it was suggested that positive change or improvement of business functionality through new systems (e.g., new IT applications) may not be believed by some employees [98]. In such circumstances, it was suggested that employing new staff instead of training current employees might be more effective [46].
A number of prior studies have demonstrated that employee acceptance and usage of, and satisfaction with, IT might be immoderately problematic regarding adoption success [73,86,94], where, according to Bull [99], more than half of the computer systems implemented in western countries are underused or not utilized at all. The acceptance of IT by users including managers, professionals and operating level personnel which is an essential condition for its success can be regarded as the adoption success measure [24]. Lack of user acceptance has long been confirmed to be an impediment to the success of new IS, so user acceptance is regarded as the key factor determining success or failure of IS/IT projects [73]. In SMEs, employee attitudes toward IT adoption might have significant impact on system acceptance and adoption success, as negative attitudes of some users toward IT could negatively affect successful implementation of IT [58]. They may not perceive that new IT can change or improve business function and when it comes to adopting IT; they might be worried about consequences such as threat of losing job [100]. Nonetheless, employee attitudes toward the use of the IS will be encouraged by clear support from top management, which will bring about a more tolerable conversion in existing work practices and company operations [12]. Moreover, Davis [73], Igbaria et al. [86], Straub et al. [101] and Szajna [102] found that attitudes toward using IT along with PU and PEOU can fully affect the acceptance of IT by its users. The above mentioned view was validated in a small business context through a study by Igbaria et al. [86] who demonstrated that users’ IT acceptance in small businesses is directly affected by PU and PEOU. In addition, the contribution of PU in promoting personal computing acceptance in small businesses is mediated by PEOU.
On the other hand, employee (as the users of IT) satisfaction with IT is another dimension of IT adoption success in SMEs [24,27,62,76,103]. Contrary to technological acceptance literature focusing on individual behavior and beliefs, system and information characteristics have been regarded as core concepts in user satisfaction literature [74]. Adam Mahmood et al. [103] argue that end-user information satisfaction is strongly affected by perceived benefit and expectations characteristics, user background and involvement, and organizational support and encouragement, as well as by subcomponents of these three factors. On the other hand, Palvia [26], and Palvia and Palvia [27] found that the unique characteristics of SMEs such as specific computing environment, mandatory environment, resource constraints, and generalist employees (employees and managers of SMEs as the users of IT are inclined to act as specialists in various aspects of IS, while not being very well qualified or expert in different IT roles) are specific attributes of user satisfaction with IT in SMEs. In this regard, Palvia [26] formulated the SBUSIT model to evaluate IT impact over SMEs, based on IT user satisfaction measures. Subsequently, this model was developed by Palvia and Palvia [27] through adding business related factors and owner/manager characteristics as two other determinants of users’ satisfaction with IT in SMEs.
Despite SBUSIT and its developed version addressing user satisfaction in small businesses in connection with their particular characteristics, this model has excluded user involvement as a determinant of user satisfaction in small business. User involvement in IS/IT development has been largely considered as a significant mechanism leading to successful implementation of a new system [104,105,106], specifically in SMEs [21,25,39,75]. In general, a firm initiating a change to a new information and computer system may causes concern over job security, causing employees to worry about the adoption outcomes, such as the threat of losing jobs [99,100]. As previously mentioned, some employees may not believe that IT will result in positive progress or improvement of organization functionality [98]. Thus, there should be assurance by owner/managers that employees are aware and have an understanding of the effects of changes to a new computer system on the organization [58,99]. Moreover, managers should keep employees aware that new IS/IT will enable them to make the best use of resources that can help them be more productive [16]. In such circumstances, involving employees as a part of new projects and systems will make them believe that as members of a family, team or organization, they are very important to and responsible for the new projects’ success in the organization. Hence, involving employees in the adoption process will result in higher levels of success [104,105]. Stewart et al. [107] suggest that this user involvement should be initiated from the commencement of IT project feasibility studies, continue throughout the design phase and must be maintained during the deployment and testing stages.
In term of IS success, Thong [21] demonstrated that user involvement in IS implementation is one of the most important factors for successful IS implementation and user information satisfaction. If end users could be encouraged to become involved with IS/IT implementation through having time off from routine responsibilities, several advantages would be achieved. These advantages include a better fit of IT to users’ expectations, ease in using IT applications due to achieved IT knowledge and learning experience during the design phase, a strong sensation of ownership and decreased resistance to change [18,39]. Accordingly, these factors could increase the probability of successful IT implementation as well [21].
In summary, it could be inferred that CEOs of SMEs are not the only users of IT who contribute to the success of the implemented IT. As the valuable assets of firms, employees also have a drastic influence over adoption and successful implementation of new IT. Therefore, development of these resources seems to be necessary for the success of the business [75,93].
3.1.4. Organizational Characteristics
Prior research on IS/IT within SMEs have revealed a number of organizational characteristics as potential determinants of the adoption process which include SME strategies, business size, type of industry, information intensity, organizational culture and technological maturity [31,35,40,49,50,52,56]. Strategically, IT tools are employed within SMEs in order to achieve pre-determined business strategy. Therefore, SMEs’ investments in IT are strongly affected by their strategic context, such as cost reduction versus value added strategies [49]. According to Nguyen [58], many businesses adopt new IT merely to keep up with other SMEs which have implemented these technologies. Under such circumstances, lack of definition or strategy of the purposes of IT adoption will lead to project failure.
Business size definable by turnover and/or number of employees is one of the most important determinants of IT adoption [16,33]. The importance of firm size is partly due to its role as the source of the firm’s capabilities [40]. Another rationale, however, is the fact that firm’s resources, including financial and human capital, might be an approximation of firm size [18]. Thong and Yap's [33] survey points out that business size is the most important discriminator between adopters and non-adopters of IT within Singaporean small businesses. Likewise, an investigation by Premkumar and Roberts [16] of rural small businesses revealed that even within the small business category, firm size is the most important determinant to the adoption of IT. This finding is reinforced by a study of Premkumar [3] on IT adoption within 207 SMEs who indicated that larger firms in the small business group have a higher inclination to adopt communication technologies than smaller ones.
Another organizational characteristic that affects the adoption of IT in SMEs is specification of industry sectors to which they belong. Prior literature provides support for type of business and information intensity as determinants of IT adoption in SMEs [65]. It is suggested that, consistent with other researches on IT adoption in different countries such as US, Malaysia or Singapore, IT adoption in Bruneian SMEs is significantly affected by type of business [38]. Likewise, it has been reported that structure of IS/IT in organizations is considerably influenced by the types of business. Salmeron and Bueno [53] found that SMEs in a same industry sector tend to implement the similar IS/IT, have similar attitudes towards technological changes and have personnel with similar attitudes toward using new technology. Porter and Millar [108] suggest that the importance and the role of IT in various industry sectors are different, due to company type and information intensity. This view is reinforced by Love et al. [52] who demonstrated that the level of IT investment made by Australian SMEs from different industry sectors will be significantly different. Consistent with these views, Thong and Yap [33] discussed that companies from different industries have dissimilar information processing requirements, and those SMEs in more information‑intensive sectors might a greater propensity to adopt IT than those in a less information‑intensive environment. Similarly, Malaysian service industries make more use of IT and are more integrated with IT, in comparison with distribution and manufacturing firms as they are active in a more information intensive environment [55]. Drew [35] suggests that high-technology/knowledge intensive SMEs are considerably more influenced by internet technologies than other types of firms, besides being more sophisticated in the use of internet technologies. Thus, SMEs must assess their IT maturity to determine their IT readiness and whether the available IT tools could be satisfactorily implemented in the current organizational and environmental conditions [78].
Organizational change is another significant influencing factor over IT adoption. Business growth forces SMEs to adopt novel and more effective technological solutions [46]. The use of ICTs in small firms is the result of many internal factors such as business expansion, downsizing or relocation, and finding and capturing new markets which bring about change in organizations. Owner/managers may regard IT or ICTs as an essential tool to help managing changes [44]. This view is supported by Drew [35], suggesting that industry changes and trends and opportunities for growth are some of the major driving forces pushing SMEs toward the adoption of IT. Since in SMEs the concept of business growth requires and is associated with deployment of a total quality system and professionalization processes as well, IT adoption might be regarded as a rational response to these alterations from managers [46].
In addition, organizational culture is another significant determinant of IS/IT implementation in organizations [46,57,109,110]. A number of organizational culture definitions can be found within the body of literature. For SMEs, culture can be regarded as the way of doing and sharing things for individuals through compliance with the firm’s beliefs, values, and attributes [58], or, it can be defined as indigenous characteristics of organization including level of openness to change and characteristics of human resources [111]. Stewart et al. [107] suggested that characterizing organizational culture is necessitated since the culture and its various impacts are the key to success of IT projects (such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)) that are an integral part of significant organizational change. These authors argued that many ERP failures can be attributed to paying inadequate attention to the culture of the organization while it is imperative to notice that in most of the time, ‘desired’ and the “actual” organizational culture are different [112]. In light of organizational readiness to change, Jones et al. [113] suggested that organizational cultures having a more supportive climate and flexible structures might be more advantageous to successful deployment of new technologies in organizations than less flexible and mechanistic cultures. In addition, constructs of organizational culture, including perceived norms, values and attitudes, predominant in organizations, might affect the behavior of employees toward ICT in those organizations [114]. Regarding these findings, Jones et al. [113] asserted that employees perceiving the culture of their organization as open system are more inclined to have positive attitudes toward organizational change, and subsequently will perceive more readiness for changes before the deployment of new technology in the organization. These authors demonstrated that employees who perceive strong human relations values in their area have shown a greater readiness for change prior to the deployment of a new computing system.
In SMEs, culture is highly affected by owner/manager attitude, perceptions and characteristics [58]. Thus, it is imperative for managers to know that employees’ usage of ICT might be affected by supervisors’ (managers at different levels) behavior toward work and IT [114]. Moreover IT conflict with organizational culture can result in user resistance to IT adoption [109]. As stated previously, openness to change is an important characteristic of organizational culture [111,115]. Thus, and given that IT deployment will often bring about significant change in SMEs, some researchers suggested that SMEs possessing an adaptable and flexible organizational culture with higher levels of openness to change will be more inclined and prepared to accept IT-related changes that might result in IT project success [58,110,116]. From the other point of view, it was suggested that the examination of SME culture should also be addressed through studying organizational learning and the learning organization pattern [117], since interrelationship between SME culture and learning processes might result in the enhancement of a firm’s competitive capacity [115]. Newell et al. [118] suggested that knowledge required for the adoption of complex IT projects which is vastly distributed needs to be integrated within the organization through a process of networking and knowledge sharing, while the effectiveness of this process is rooted in the culture of SMEs. Moreover, the adoption process requires the integration of internal and external knowledge within the firm.
Furthermore, family involvement and intervention in firm management could have significant impacts upon IT adoption [37,46]. It has been largely confirmed that in family businesses, the tenure of senior managers who are family members is much higher than those in non-family organizations [73,119,120]. Family firm managers are less inclined to have higher educational levels than those in non-family firms [119]. Family firms have also been characterized by having smaller management teams while larger management team, can result in more effective business management [121]. Smith [67] provided evidence that the size of a firm is a dominant determinant of managerial differences, since these differences between micro, small and medium enterprises have been found to be more significant than those between family and non-family businesses. The above mentioned findings, together with specific characteristics of family businesses (such as lack of professionalization, more informal organizational structures, and reliance on informal internal control systems) suggest that the objective of IT adoption as well as the implementation process might be highly different in family SMEs [46,67]. In addition, the involvement and intervention of family members in day-to-day activities and management of family business may bring about organizational issues since, in most small businesses, family members are hired to fill vital positions [37,46,67,122]. Compared with the hiring of external staff that are better fitted for positions in the business, family members’ non-qualification often results in management problems such as ineffective IT usage [58]. A study by De Lema and Duréndez [122] on managerial behavior of family SMEs found that when businesses are managed by family members, lack of attention to personnel training and management qualifications and a commitment to family well-being might result in inefficiency in the decision making process. Likewise, an empirical study by Lybaert [37] found that less significant family ownership and intervention in strategic management tends to produce higher levels of information use in SMEs.
Another influencing factor attributable to the organizational characteristics is IS/IT planning. Through IS planning, the chance of successful implementation of IS within small firms might be higher [21]. IT planning means that SMEs should determine why and how IT can enhance their business processes and profitability, and then develop a strategy and objectives to obtain the anticipated results [52]. SMEs owners/managers should assign the resources and dedicate significant time and attention to manage the adoption process [78]. They must understand that IT, requiring long-term commitment and sizeable investment, as well as having high strategic importance, can have a significant influence over organizational capacity, validity and survival. Planning of IT is perceived to be even more essential with regard to the speed at which technological innovations take place, along with the continuous efforts required by the SMEs’ internal environments to absorb them [21]. Therefore, SMEs can fully benefit from adoption of IT through IT planning to evaluate the threats and opportunities created by IT [9]. In addition, IS planning in SMEs, requiring integration with business strategy, has become more crucial as IS becomes more central to the future success and growth of SMEs and business strategy and IS strategy become intertwined [123]. When IS/IT adoption is not planned strategically, for example when SMEs invest in IS with the aim of only improving production processing without integrating other systems, IT-based competitive advantages are typically accidental rather than planned [49]. According to the literature, IS planning includes five phases; financial resources planning, human resources planning, information requirements analysis, implementation (software development, installation, and conversion) and post implementation (operation, maintenance, future needs) [124]. In addition, a review of IT adoption literature by Ayman et al. [125] places emphasis on IT projects management and argues that “highly regarded IT projects can be badly delivered if they are not properly managed”. Accordingly, a short-term strategic decision making cycle and lack of planning in some SMEs may bring about particular problems in implementation of IT [9,126]. Although it is generally believed that barriers to IT adoption arise mostly out of inaccessibility to funds and technology, the major barrier to IT adoption among US small business is the lack of an information system plan [127].
3.2. External Factors
3.2.1. External and Competitive Pressure
For many firms, pressure to keep up with the competition, providing a means to enhance survival and/or growth, managing change, promoting services to customers and staying competitive and/or enhancing innovation abilities have forced them to adopt IT [3,16,35,40,41,58]. Prior literature suggests that as small businesses are susceptible to customer pressure, these firms adopted IT as a result of demand from customers to develop the efficiency of their inter-organizational dealings [128]. Hence, it has become an indispensable strategy for firms to have these technologies [16], while others suggested that the main driving forces to move toward IT tools adoption in SMEs are internal factors., including industry changes and trends, maintaining current market, finding new markets, opportunities for growth and the necessity to keep up with competition [35,44].
A more inclusive view on the innovation literature draws attention to relevance and importance of both internal and external drivers for change [129,130]. Mehrtens et al. [131] discussed that the issue of credibility has risen as a significant motivator for adopting IT tools within SMEs. These researchers argued that credibility could be achieved through fulfilling customers’ and suppliers’ pressure and, in addition, significantly meet expectations of receiving better services. A study by Dutta and Evrard [42] on European small enterprises showed that the main focus of European small enterprises is to make use of IT to deliver a superior level of customer service and better communication with distant partners/customers. Moreover, a study by Premkumar and Roberts [16] on rural small businesses suggested that external pressure and competitive pressure are important determinants to the adoption of ICTs. Likewise, it was suggested that client and supplier pressure to adopt IS/IT was an important factor influencing the levels of IS/IT adoption and success in Portuguese manufacturing SMEs [31]. These results are consistent with studies by De Burca et al. [56] and Mole et al. [40] who suggested that customers, suppliers and larger counterpart demand were significant determinants of IT tool adoption.
On the other hand, and according to prior IS literature, drivers for IT/IS adoption in SMEs are also attributable to firms’ desires and needs to stay competitive and innovative as necessities for their survival [65]. The expression “competitive advantage” is one of the most lasting topics in the business strategy and strategic management literature and its theories have been well-founded [132,133,134,135]. Porter [134] defined competitive advantage as a direct consequence of the strategies implemented by a firm intended for adding value to customers. It has been demonstrated that competitive pressure will affect the adoption of new technologies when SMEs perceive that these technologies will possibly support their competitive position, therefore, SMEs adopt IT to gain competitive advantage [75]. Porter and Millar [108] argued that the nature of competition might change through the adoption of IT. They found that IT has changed the rules of competition through changing industrial structure, creating competitive advantage by delivering businesses in new ways to outperform their competitors and spawning new businesses by making new business technologically feasible, creating demand for products and regenerating old businesses. SMEs active in industries having a high rate of innovation and intense competitive challenge are more likely to perceive IT tools as a stronger driver for strategic change than those in other types of industries [16,35,136,137,138]. The study by Pontikakis et al. [54] investigating IT adoption within Greek SMEs suggested that highly competitive industries are often technologically intensive and SMEs operating in innovation-intensive industries might face intense competition initiated by innovations than those who are generally inclined to be more risk-averse. They found that SMEs which perceived their industries as highly competitive were more than six times more likely to adopt IT solutions. IS/IT utilization could bring about more effectiveness in the internal and external aspects of SMEs, so SMEs considered IT as an essential tool with the purpose of competing for organizational adaptation as well as environmental change [65]. Furthermore, IS/IT enhances SME survival rates where they are functioning in a competitive environment with the risk of higher rates of failure [49].
3.2.2. IT Solution (Computer Application)
The process of IT adoption within SMEs also depends on characteristics of marketed IS/IT itself which consist of a cluster of factors including type, process compatibility, user friendliness and popularity of implemented IS/IT, quality of software available in market and the costs of IT [3,25,31,53,60,106]. For adoption of enterprise application software, easy-to-understand and relatively long-experienced enterprise applications are more effective in SMEs as compared to hard-to-understand and brand-new applications [59]. Given that information systems and technologies are considered as the major enablers of superior business performance, quality of IS/IT products available in the market (e.g., attribute of the selected product, its reliability and usefulness) could be an important determinant when it comes to deciding on the adoption IS/IT products among SMEs [31,139].
The technological characteristics of IT products available in the market, including their compatibility and security, are also significant determinants of IT adoption in organizations [5]. Compatibility is an important technological characteristic perceived by individuals, which was suggested by Diffusion of Innovation theory as a driver of the decision to adopt a new system [140]. IT compatibility can be defined as the extent (or ease) with which IT is integrated with the existing technological infrastructure, culture, values, and preferred work practices of an organization [141]. Several prior studies on IT adoption within SMEs found that IT adoption and usage is significantly affected by the compatibility of relative products [142,143]. It is imperative that CEOs of SMEs consider the most appropriate application in their businesses when deciding whether or not to implement new IT [58]. Deficient IT investment decisions (regarding the compatibility and security issues of IT products) can impose a significant impact on organizational profitability [65]. It can participate in enhancing SME performance. Nevertheless, with no effectual IT adoption and development strategy in the right place, the anticipated and demanded performance enhancement may not materialize. Therefore, with its counter-productiveness, IT might be considered as an asset sinkhole [75]. In this regard, it was found that the high cost of IT tools and expensive software in addition to ICT security concerns are the major risks of ICT adoption perceived by Malaysian and Australian SMEs [17,52]. With regard to the above-mentioned findings, it could be inferred that technological characteristics of marketed IT products has become one of the common concern of SMEs when it comes to adopting IT.
Another factor that affects adoption of IT within SMEs is cost of IS/IT. It is imperative that managers consider the elements of IT costs (hardware and software) closely during IT adoption process within SMEs [39]. From a similar perspective, Walczuch et al. [60] studied internet adoption barriers for small firms in the Netherlands and explained that high costs are the important reason for Dutch small firms not having internet access and their own websites. Moreover, most US businesses have significant difficulty affording the costs of ICT tools while 90% of these businesses consider lack of financial resources and skills as the main barriers to ICT adoption [144]. With regard to the financial constraints experienced by the majority of SMEs, as well as the high start-up costs of ICT or very expensive software or ready-to-use online packages, it is expected that SMEs generally cannot afford to adopt ICT or reap its benefits through the effective use of ICT, in short or medium period of time [21,75]. Premkumar [3] however argues that IT adoption cost is not a significant factor in determining adoption within SMEs. This view is empirically supported through a study by Tan et al. (2009) who discussed that despite IT costs being one of the major risks perceived by Malaysian SMEs, there are no significant associations between high ICT infrastructure costs and ICT adoption in these businesses. Love et al. [52] suggested that although the prices of hardware and software have noticeably decreased and become more affordable, the difficulty of estimating the costs of IT adoption (which leads to uncertainty about anticipated IT benefits) is still a significant barrier to IT investment in SMEs. According to Love et al. [52], although IT’s direct costs result from the implementation of new technology, however, these direct costs are usually underestimated and regarded as the cost of hardware, software and installation. It is suggested that beside initial costs of software and hardware, costs of IT implementation should include personnel training and development expenses, as well as costs of post implementation [52,58]. In addition, indirect costs of IT adoption may be more significant than direct costs [52]. Indirect costs also comprise the early cost of any temporary loss in a firm’s productivity [145], human factors costs, organizational costs for transforming from former systems to new work practices, and costs associated with any changes to systems and business procedures [146], while management time is the main, considerable indirect cost in various organizations [145]. With regard to the aforementioned perspectives, it could be inferred that cost is still regarded as an essential issue when it comes to adopting and implementing IT in SMEs [58]. The rationale behind it is that in spite of decreases in the initial and direct costs of IT adoption, such as costs of hardware, installation and configuration, software and/or licensing in recent years, SMEs, characterized by restricted financial resources typically experience difficulty in estimating and affording total and long-term expenses associated with IT adoption. It should be noted that in addition to direct costs, such as hardware, software and installation costs, IT adoption expenses also go beyond indirect costs and include costs of staff training and motivation, transformation from old to new systems in terms of procedures and organizational structure, as well as post IT implementation expenses, cost of management time and effort, productivity losses and finally expenses encompassing the costs of maintenance and development [52,145,146].
On the other hand, time-permanency is another characteristic of IT tools which might affect the IT adoption process in SMEs. Salmeron and Bueno [53] stressed the positive role of a time-permanency factor in isomorphic application of IT tools is manifested within SMEs: in particular between those belonging to the same industry. A possible explanation for this isomorphism is that most SME managers are interested in old, safe and vastly applied IT solutions which have a lower risk of failure. As the majority of SMEs have limited financial resources [58,75], deficient IT investment decisions can impose momentous impacts on organizational profitability or even survival, while investment in newly presented technology often involve high risk and might imperil an SMEs’ survival [65]. However, it is imperative for managers to know that pioneers in adopting new information technologies reap most benefits. For example, in the banking industry, pioneer banks that adopted new technology or developed new applications for existing technologies are the organizations that achieved the most benefits from their risky investment [27]. Consistent with the resource-based view of the firm suggesting the complementarities of firm resources in value creation [147], and due to wide availability of generic IT in the market, simple IT alone cannot be a source of competitive advantage [148]. The adoption of state-of-the-art IT applications ahead of competitors will make IT resources ‘firm specific’ and imperfectly mobile across firms, providing the adopting firm with additional business value not achievable by late users [89].
3.2.3. External IT Consultant and Vendors
There is a body of research that show that the assistance of external IT expertise, consultants and vendors and their respective quality is one of the most important aspects of the IT adoption process within SMEs [75]. Their professional abilities could have positive impacts on the IT adoption process while most SMEs suffer from a lack of both IT experts and the hiring of external consultants [16,21,58,60,149,150,151]. Cragg and Zinatelli [34] pointed out that a lack of internal expertise has seriously hindered IS sophistication and evolution within small firms, therefore, they must overcome this problem through either seeking help from external sources or developing their own internal end-user computing skills [152]. Shin [59] found that SMEs are moving toward the adoption of enterprise application (EA) software to survive in competitive global markets while consultants often have a greater share in providing EA than vendors (e.g., up to 60% of ERP project costs are devoted to services provided by outside consultants). According to Thong et al. [12] and Thong [18], external consultants and vendors are the main sources of external IS expertise regarding IS implementation within small businesses.
Owing to the importance of external assistance to SMEs, these business are facing difficulties as IT vendors often restrict their marketing to larger organizations and generally do not understand SMEs’ unique needs [153]. Consequently, if powerful technology suppliers develop their marketing strategies and become more aware of issues, including quality, training provision and maintenance regarding SMEs’ needs, this will encourage SMEs to implement IT to improve their performance [44]. In general, the duties undertaken by external expertise comprise IS project management, encouraging employees to accept new systems and overcome their fear of new technology, fulfilling information requirements analysis of business needs, IS user training and recommending suitable computer hardware and software [12,33]. These external consultants act as intermediaries to compensate for the absence of IT knowledge in SMEs and diminish the IS knowledge barrier to successful and effective IS/IT implementation [21].
It is crucial for management to consider the fact that external supports provided by vendors are essential for SMEs having no sufficient IT expertise to implement these new technologies [152]. A study by Soh et al. [151] of 96 Singaporean small businesses revealed that the level of IS usage within small businesses hiring consultants is higher than those of small businesses without consultants. This result is reinforced by Thong et al. [12] who demonstrated that SMEs with high levels of external IS expertise have higher levels of IS effectiveness. In the similar context, effectiveness of external expertise is also an influencing process factor of IT adoption within SMEs [21,39,150]. Thong [21] revealed that small businesses with higher levels of IS consultant effectiveness have higher levels of user satisfaction and overall IS effectiveness. In fact, the use of ICT among SMEs is also affected by the marketing strategies of ICT suppliers [44]. These views are sported by Caldeira and Ward [31] who suggested that IS/IT vendor support is an important factor influencing IT adoption success within SMEs.
Based on the above-mentioned viewpoints and studies, the authors conclude that regarding the lack of IT knowledge and internal IT/IS experience and skills, SMEs could fill this knowledge gap the through the use of external assistance, such as engaging external experts and the use of vendor assistance. The authors suggest that because of the unique characteristics of SME resources and financial poverty, SMEs should cautiously consider the available financial resources for hiring external consultants since they generally entail considerable expense. Moreover, it should be considered that external experts’ recommendations and suggestions might not be always a practical fit for SME requirements if strategies and objectives of the businesses are not sufficiently understood. As a result, a clear objective and definition of new IT implementation within SMEs seems to be necessary [58].
3.2.4. Government
According to the literature, significant positive relationships could be found between IT adoption and government support [17,44,124,154]. Because of their size and lack of resources, SMEs generally depend more on external resources and support than other companies [78]. According to Fink [39], government support for facilitating information transfers to SMEs is incrementally increasing. Government initiatives and policies could directly and/or indirectly stimulate the development of IT infrastructure and information provision to energize faster technology diffusion [65]. Nevertheless, the literature suggests that governmental assistance is generally not advantageous. A study by Dutta and Evrard [42] on small businesses in six different European countries indicates that although governments have tried to assist SMEs in adopting IT through increasing public spending on technology projects, however, there are adoption barriers built into governmental agency mechanisms designed to help these businesses. These adoption barriers are attributable to the gap between what is really required by SMEs and what is provided by the government [78]. This result is supported by Yap et al. (1994) for analyzing the computerization experience of 40 small businesses which have computerized through government incentive programs, with another 40 small businesses which have computerized without government assistance. Yap et al. [124] showed that participation in a government computerization program has not resulted in more effectual IS. However, this program has encouraged small businesses which suffer a lack of financial resources and technical expertise to computerize their operations. From a similar perspective, Fink [39] found that government grants do not appear to be a significant factor supporting IT adoption within Australian SMEs.
Despite the above-mentioned results showing that government assistance has not generally been found to be helpful, recent studies, particularly in developing countries, have revealed that IT adoption in SMEs has significantly improved through government policies and initiatives. In light of this view, Fathian et al. [64] explained that an Iranian government plan of ICT development (TAKFA) has resulted in significant improvement in IT adoption and e-readiness within Iranian SMEs. From a similar perspective, a recent study by Tan et al. [17] found that Malaysian SMEs generally disagree with the view that cost is a significant determinant of ICT adoption. Tan et al. [17] discussed that since most SMEs are aware of government financial support and incentives, ICT costs are not regarded as a major barrier by Malaysian SMEs. This view is empirically supported by Alam and Noor [45] who demonstrated that ICT adoption in Malaysian SMEs is not directly affected by perceived ICT costs. According to them, the underlying rationale is that all types of financial support to these businesses have been provided by government for ICT adoption. For example, Malaysian SMEs do not perceive the costs of training required for successful IT adoption as a barrier since government agencies have offered and provided a number of necessary training programs [17]. Thus, it could be concluded that, with regard to the supportive policies and comprehensive IT support provided by the Malaysian government, for example through the Malaysian Technology Development Corporation, Multimedia Super Corridor (MSC), newly established SME Bank, and Small and Medium scale Industries Development Corporation (SMIDEC), the IT adoption process seems to be considerably simplified for Malaysian SMEs [17,45].
4. Guidelines for IT Adoption in SMEs
Based on suggested categorization and reviewed influencing factors, and to come up with more systematic guidelines for effective IT adoption by SMEs, the authors put forward a conceptual model (Figure 2) that is believed to assist successful IT institutionalization in this context. This model has been conceptualized based on extant perspectives and theories, and uses the technological innovation literature as a reference discipline. As suggested by prior literature, initial IT adoption, IT implementation and post-implementation of IT are three different stages in the technology innovation cycle [21]. Initial IT adoption refers to a stage in which decisions are made about whether to adopt a new IS/IT. If the decision is to go ahead with adoption, the IT implementation stage involves implementing the IT infrastructures (including hardware and software) in the organization. Once the IT has been implemented successfully, the IT post-implementation stage is concerned with how much organizational learning takes place within the business so as to facilitate further IT adoption [18,21]. Accordingly, our suggested model of the IT adoption process addresses all the three different stages and definitions of IT adoption in providing guidelines for successful IT adoption in SMEs. It is believed that the presented categorization of IT adoption issues and factors through the developed conceptual framework and conceptual model of effective IT adoption process can help governments, organizations, managers and IT consultants to achieve a clearer understanding of the IT adoption process. It may also increase the knowledge and literature bases by providing a clearer understanding of the reasons and methods that SMEs adopt IT, and establish the determinants that contribute to the success of the IT adoption process in these businesses.
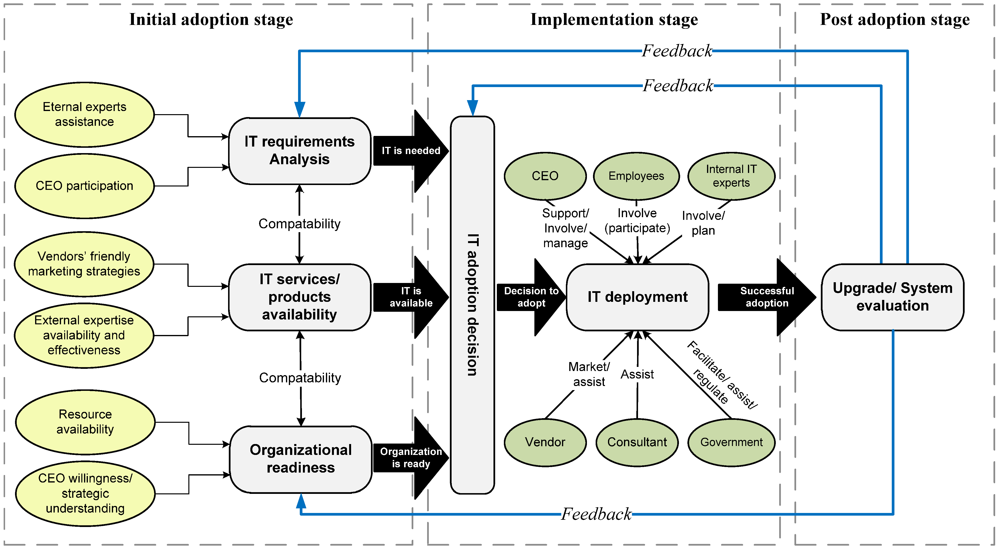
Figure 2.
Conceptual model of effective IT adoption process within SMEs.
To come up with more an organized and efficient deployment and application of IT, SMEs must precisely realize their need for it and the proportionate advantages of IT for their business. SMEs ought to judge costs and benefits associated with utilizing IT. In this regard and in addition to taking advantage of external consultants, CEOs should actively participate in the IT benefit/risk evaluation process to assess whether the benefits of IT for their business overweight its risks. In general, IS/IT is regarded as a crucial resource required for better communication and integrating business functions [4]. It is believed that IT promises many benefits for SMEs, ranging from modest advantages, such as reduced communication and administration costs, to transformative advantages such as quick response retailing [65,75]. However, the appearance of new inter-organizational systems such as electronic customer relationship management (E-CRM) and ERP has made it more sophisticated to identify and evaluate the benefits of IT adoption which necessitates more effective benefit monitoring. In particular, SMEs managers should realize that it is not only generic IT, per se, that directly affects relative firm performance, rather, higher-order process capabilities act as the mediators between IT resources and firm performance which transform the value of IT resources controlled by SMEs to business performance. In other words, a firm's IT resources can augment critical organizational capabilities (such as green management, integrated supply chain processes, and coordinated manufacturing), which can result in improved company performance.
In addition, SME managers need to assess available IT products and services that are compatible with their need and should find out existing obtainable external aid and incentives supplied by government-related agencies, advisors, vendors, and their counterparts, namely the external sources that might assist them in adopting IT. SMEs need to consider what predictable effects could be imposed by adopting IT on their business situations, customers, suppliers, competitive positions as well as their competitors. Thus, SMEs have to consider these drivers, barriers and issues that might affect the successful adoption of IT solutions. It is imperative that SMEs precisely evaluate their capability to reap benefits from IT adoption and not to underestimate them. They should know that IT is competent to act as a strategic tool to assist them in competing with their larger counterparts in the globalized market. However, it should be considered that deficient IT investment decisions and imprecise IT adoption strategies may imperil business survival. At the initial adoption stage, vendors should follow marketing strategies that enable SMEs to easily afford their products and services. Likewise, they should cooperate with SMEs to jointly improve the compatibility of IT applications with specific the characteristics of SMEs that are active in different industries.
For the implementation stage, and as suggested in literature, external assistance is imperative for successful IT implementation in SMEs, as these businesses generally suffer from a lack of IT knowledge, skills and training resources. As a result, external consultants and vendors are the main sources of external IT knowledge and skills in SMEs. Accordingly, higher levels of external consultants and vendor effectiveness and support will increase IT effectiveness in SMEs [21,43]. Nevertheless, regarding the fact that SMEs typically do not have sufficient financial resources to afford the costs associated with hiring external experts and IT training campaign expenses, as well as the fact that some SMEs do not trust in using external expertise and consultants, the role of government support and initiatives to help and encourage the adoption of IT is much more significant in the context of SMEs. Likewise, it is very important that governments precisely consider what is demanded to support IT adoption in SMEs in order to eliminate the gap between the support provided by government and the needs of SMEs. In spite of some reports of disadvantageous and ineffective assistance provided by governments, a number of studies have demonstrated that IT adoption in SMEs has been significantly improved through supportive policies and initiatives provided by both developed and developing governments, especially in recent years. Thus, governments should provide comprehensive policies and support to encourage small and medium enterprises to develop and use IT. Policies and support should be periodically re-evaluated to suit the dynamic characteristics of SMEs, IT tools, dynamism within the global economy and market conditions. On the other hand, SMEs are very susceptible to security issues, such as a sense of insecurity and vulnerability about performing transactions through the internet, as well as the risk of information loss and digital theft when putting information online. Therefore, it could be suggested that through the passing of cyber laws by governments to regulate and secure online transaction activities, and also by providing appropriate anti-virus and/or firewall/security protocols for SMEs by vendors and service providers to reduce or prevent the attacks of hackers, viruses and spyware, the perceived risk of IT adoption by these businesses, should be alleviated.
The CEOs of SMEs are required to be supportive regarding the implementation of IT in their businesses and should actively participate in the implementation process. This means that they should be willing and committed to provide the necessary resources and authority/power for IT adoption. This support can involve providing training campaigns, allocation of adequate resources such as financial resources and encouraging staff to use IS in their daily activities. Likewise, user IT knowledge is a significant facilitator of implementation success within SMEs. SMEs have to ponder the fact that due to the general lack of IS expertise in these businesses and the difficulty of recruiting IS professionals, user IS knowledge can facilitate more successful IS implementation through a decreasing degree of uncertainty entangled with IS implementation, increasing satisfaction with the implemented IS and enhancing the effectiveness of contributions to the different phases of IS adoption. Therefore, the level of IS knowledge and skills of users of IS in SMEs should be improved. Similarly, these businesses should provide themselves with potential knowledge resources from networking and also benefit from it when it comes to implementing IT, given that SMEs’ employees generally lack IT skills (e.g., IT knowledge and computing skills). In SMEs, networking can be defined as the amount of interaction between organizations, counterparts, suppliers, customers, and vendors so that they could be either personal network or business network [27]. Hence, networks are crucial ways for acquiring access to external knowledge required for successful implementation of IT [58].
5. Conclusion and Future Directions
IT has critically become an indispensable tool for the daily operations of organizations. SMEs now invest significant amounts of financial resources in IT to strengthen their competitive positions [3]. Due to the large-scale application of IT among SMEs, they have been exposed to several associated risks within the adoption and development of IT solutions [63]. Prior literature on IT adoption in SMEs shows that approximately most failures and most dissatisfaction resulted in one or more of the following reasons [31,32,33,34,49,58,78,127,155,156]:
- inappropriate connection between adopted IT and enterprise strategies,
- Inadequate realization of organizational issues,
- Inadequate realization of end user necessities,
- Lack of manager and employee involvement in different stages of IT adoption,
- Lack of required resources (knowledge, skills, finance, management),
- Inadequate teaching and preparation of end users,
- Business size and fund limitations to employ IT specialists,
- Unqualified management in highly centralized CEO structures,
- Inappropriate government assistance role and supportive regulation,
- Dissatisfaction with IT-created competitive advantages due to improper interactions with competitors, suppliers and customers, and
- The particular characteristics of organizations, their culture and family involvement in the business.
A number of prior studies have attempted to gain a clear understanding of numerous pitfalls and challenges associated with IT adoption awaiting SMEs, as well as evaluate those factors affecting the successful deployment of IT. The authors categorized influencing factors into two main groups: internal and external. Internal factors include top management, a firm’s resources, end users and organizational characteristics. External factors comprise characteristics of IT products, external and competitive pressure, external IT consultants and vendors, and government. The authors believe that the categorization of IT adoption issues and SME-related factors through a developed, integrated framework and suggested model of effective IT adoption process can help organizations, managers and IT consultants to achieve clearer understanding of IT adoption influencing factors, and also add further knowledge to the literature. Although the authors inclusively discussed various distinguished influencing factors affecting IT adoption decisions, acceptance, satisfaction and usage, the authors did not categorize the reviewed influencing factors in terms of different adoption concepts. This issue can be addressed by future research. This paper might not cover all aspects of the IT adoption process in the literature. Likewise, due to the unique characteristics of each organization and its specific conditions of technological innovation diffusion, it is not claimed that this framework is applicable for all firms or is able to deal with all of their issues. For this reason, these findings require empirical testing to determine their relevance and conformity in the practical setting. In addition, a more comprehensive study of IT adoption within SMEs for investigating SME-related influencing factors simultaneously with other aspects (drivers, enablers and inhibitors) of IT adoption seems to be necessary.
References
- Pavic, S.; Koh, S.C.L.; Simpson, M.; Padmore, J. Could e-business create a competitive advantage in UK SMEs? Benchmarking 2007, 14, 320–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckx, M.A.F.; Stroeken, J.H.M. Information technology and innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 1999, 60, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, G. A meta-analysis of research on information technology implementation in small business. J. Org. Comp. Elect. Com 2003, 13, 91–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, R.; Sharma, M.K. Information system architecture: A framework for a cluster of small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Prod. Plan. Control 2007, 18, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandon, E.E.; Pearson, J.M. Electronic commerce adoption: An empirical study of small and medium US businesses. Inf. Manag. 2004, 42, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, R.C.; Vrazalic, L. A basic model of electronic commerce adoption barriers: A study of regional small businesses in Sweden and Australia. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2005, 12, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, H. Commercial Internet adoption in China: Comparing the experience of small, medium and large businesses. Internet Res. 2002, 12, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid-Guijarro, A.; Garcia, D.; van Auken, H. Barriers to innovation among Spanish manufacturing SMEs. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2009, 47, 465–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blili, S.; Raymond, L. Information technology: Threats and opportunities for small and medium-sized enterprises. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 1993, 13, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrell, C.; Davis, P.S.; Craig, J. Fueling innovation through information technology in SMEs. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2008, 46, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, J.Y.L.; Yap, C.S.; Raman, K.S. Top management support, external expertise and information systems implementation in small businesses. Inf. Syst. Res. 1996, 7, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, J.Y.L.; Yap, C.S.; Raman, K.S. Environments for information systems implementation in small businesses. J. Org. Comput. Electron.Commer. 1997, 7, 253–278. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, J.A.; White, J.F. A small business is not a little big business. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1981, 59, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qirim, N. The adoption of eCommerce communications and applications technologies in small businesses in New Zealand. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2007, 6, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor, R.C.; Vrazalic, L. E-commerce adoption barriers in small business and the differential effects of gender. J. Electron. Commer. Org. 2006, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, G.; Roberts, M. Adoption of new information technologies in rural small businesses. Omega 1999, 27, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.S.; Chong, S.C.; Lin, B.; Eze, U.C. Internet-based ICT adoption: Evidence from Malaysian SMEs. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2009, 109, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, J.Y.L. An integrated model of information systems adoption in small businesses. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1999, 15, 187–214. [Google Scholar]
- Zaltman, G.; Duncan, R.; Holbek, J. Innovations and Organizations; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Bøving, K.B.; Bødker, K. Where is the innovation? In Networked Information Technologies; Diffusion and Adoption; Springer Boston: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004; Volume 138, pp. 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Thong, J.Y.L. Resource constraints and information systems implementation in Singaporean small businesses. Omega 2001, 29, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gahtani, S.S.; Hubona, G.S.; Wang, J. Information technology (IT) in Saudi Arabia: Culture and the acceptance and use of IT. Inf. Manag. 2007, 44, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gahtani, S.S.; King, M. Attitudes, satisfaction and usage: Factors contributing to each in the acceptance of information technology. Behav. Inf. Technol. 1999, 18, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, S.Y. Effect of end-user personal and systems attributes on computer-based information system success in Malaysian SMEs. J. Small Bus. Manag. 1999, 37, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Palvia, P.C. A model and instrument for measuring small business user satisfaction with information technology. Inf. Manag. 1996, 31, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palvia, P.C.; Palvia, S.C. An examination of the IT satisfaction of small-business users. Inf. Manag. 1999, 35, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Jang, W. Determinants of the adoption of enterprise resource planning within the technology-organization-environment framework: Taiwan’s communications. J. Comput. Inform. Syst 2008, 48, 94–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Kraemer, K.; Xu, S. Electronic business adoption by European firms: a cross-country assessment of the facilitators and inhibitors. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2003, 12, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Kraemer, K. L. Post-adoption variations in usage and value of e-business by organizations: Cross-country evidence from the retail industry. Inf. Syst. Res. 2005, 16, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, M.M.; Ward, J.M. Using resource-based theory to interpret the successful adoption and use of information systems and technology in manufacturing small and medium-sized enterprises. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2003, 12, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.; York, A.S. Information technology adoption by small businesses in minority and ethnic communities. In Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, January 2008; pp. 1530–1605.
- Thong, J.Y.L.; Yap, C.S. CEO characteristics, organizational characteristics and information technology adoption in small businesses. Omega 1995, 23, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, P.B.; Zinatelli, N. The evolution of information systems in small firms. Inf. Manag. 1995, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, S. Strategic uses of e-commerce by SMEs in the east of England. Eur. Manag. J. 2003, 21, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, J.Y.L.; Yap, C.-S.; Raman, K.S. Top management support in small business information systems implementation: How important is it? In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCPR Conference, Syracuse, NY, USA, April 1993.
- Lybaert, N. The information use in a SME: Its importance and some elements of influence. Small Bus. Econ. 1998, 10, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyal, A.H.; Rahim, M.M.; Rahman, M.N.A.; Begawan, B.S.; Darussalam, B. An empirical investigation of use of information technology among small and medium business organizations: A Bruneian scenario. Electron. J. Inf. Syst. Dev. Ctries. 2000, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, D. Guidelines for the successful adoption of information technology in small and medium enterprises. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 1998, 18, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, K.F.; Ghobadian, A.; O’Regan, N.; Liu, J. The use and deployment of soft process technologies within UK manufacturing SMEs: An empirical assessment using logit models. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2004, 42, 303–324. [Google Scholar]
- Riemenschneider, C.K.; Harrison, D.A.; Mykytyn, P.P. Understanding IT adoption decisions in small business: Integrating current theories. Inf. Manag. 2003, 40, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Evrard, P. Information technology and organisation within European small enterprises. Eur. Manag. J. 1999, 17, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, P.Y.K. Factors used in the selection of packaged software in small businesses: Views of owners and managers. Inf. Manag. 1995, 29, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, A.; Tilley, F. Small firms and information and communication technologies (ICTs): Toward a typology of ICTs usage. New Technol. Work Employ. 2000, 15, 138–154. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, S.S.; Noor, M K.M. ICT adoption in small and medium enterprises: An empirical evidence of service sectors in Malaysia. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2009, 4, 112–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bruque, S.; Moyano, J. Organisational determinants of information technology adoption and implementation in SMEs: The case of family and cooperative firms. Technovation 2007, 27, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D. A.; Mykytyn Jr, P. P.; Riemenschneider, C. K. Executive decisions about adoption of information technology in small business: Theory and empirical tests. Inform. Syst. Res. 1997, 8, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andries, P.; Debackere, K. Adaptation in new technology-based ventures: Insights at the company level. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2006, 8, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Powell, P.; Yetton, P. SMEs: Aligning IS and the strategic context. J. Inf. Technol. 2001, 16, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, E.; Koçak, I.; Sey, Y.; Arditi, D. Use of information and communication technologies by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in building construction. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2005, 23, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremillion, L.L. Organization size and information system use: An empirical study. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1984, 1, 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Love, P.E.D.; Irani, Z.; Standing, C.; Lin, C.; Burn, J.M. The enigma of evaluation: Benefits, costs and risks of IT in Australian small–medium-sized enterprises. Inf. Manag. 2005, 42, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeron, J.L.; Bueno, S. An information technologies and information systems industry-based classification in small and medium-sized enterprises: An institutional view. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 173, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontikakis, D.; Lin, Y.; Demirbas, D. History matters in Greece: The adoption of Internet-enabled computers by small and medium sized enterprises. Inf. Econ. Policy 2006, 18, 332–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valida, A.C.; Leng, A.C.; Kasiran, M.K.; Hashim, S.; Suradi, Z. A Survey of Information Technology Utilization among Business Organizations in Malaysia. In Proceedings of International Conference on IT, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1994.
- De Burca, S.; Fynes, B.; Marshall, D. Strategic technology adoption: Extending ERP across the supply chain. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2005, 18, 427–440. [Google Scholar]
- Kanungo, S. An empirical study of organizational culture and network-based computer use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 1998, 14, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.U.H. Information technology adoption in SMEs: An integrated framework. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2009, 15, 162–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, I. Adoption of enterprise application software and firm performance. Small Bus. Econ. 2006, 26, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczuch, R.; Van Braven, G.; Lundgren, H. Internet adoption barriers for small firms in the Netherlands. Eur. Manag. J. 2000, 18, 561–572. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, S.; Swatman, P.M.C. An exploratory study of small business Internet commerce issues. Inf. Manag. 1999, 35, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yingwu, C.; Changfeng, Z. Determinants affecting end-user satisfaction of information technology service. In Proceedings of ICSSSM’06: 2006 International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management, Troyes, France, 1 October 2007; pp. 25–27.
- Kazi, A.U. Small and medium business enterprises and the use and adoption of information and communication technology: A study of legal issues and legal perspectives. Int. J. Organ. Behav. 2007, 12, 144–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fathian, M.; Akhavan, P.; Hoorali, M. E-readiness assessment of non-profit ICT SMEs in a developing country: The case of Iran. Technovation 2008, 28, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Benitez-Amado, J.; Arias-Aranda, D. Reasons for Information Technology Adoption and Sophistication within Manufacturing SMEs. In the POMS 22nd Annual Conference: Operations Management: The Enabling Link, Reno, NV, USA, 29 April–2 May 2011.
- Fuller-Love, N. Management development in small firms. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2006, 8, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M. “Real” managerial differences between family and non-family firms. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2007, 13, 278–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, T.; Lewis, J. Relationships mean everything’; A typology of small-business relationship strategies in a reflexive context. Br. J. Manag. 2002, 13, 317–336. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, T.T.; Nakatani, K.; Zhou, D. An exploratory study of the extent of information technology adoption in SMEs: An application of upper echelon theory. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2009, 22, 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Karake, Z.A. Information technology performance: Agency and upper echelon theories. Manag. Decis. 1995, 33, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, C.H.; Teo, H.H.; Tan, B.C.Y. Innovative usage of information technology in Singapore organizations: Do CIO characteristics make a difference? IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2006, 53, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, E.; Lefebvre, L.A. Firm innovativeness and CEO characteristics in small manufacturing firms. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 1992, 9, 243–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: System characteristics, user perceptions and behavioral impacts. Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 1993, 38, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Zulkifli, N.B.; Aziz, F.A. The interactive model of User information technology acceptance and satisfaction in small and medium-sized enterprises. Eur. J. Econ Financ. Adm. Sci. 2010, 19, 7–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Arias-Aranda, D.; Benitez-Amado, J. Information technology implementation success within SMEs in developing countries: An interactive model. In the POMS 22nd Annual Conference: Operations Management: The Enabling link, Reno, NV, USA, 29 April to 2 May 2011.
- Adamson, I.; Shine, J. Extending the new technology acceptance model to measure the end user information systems satisfaction in a mandatory environment: A Bank’s Treasury. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2003, 15, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasuriya, R. Determinants of microcomputer technology use: Implications for education and training of health staff. Int. J. Med. Inf. 1998, 50, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosa, S.; Zowghi, D. Strategy for adopting information technology for SMEs: Experience in adopting email within an Indonesian furniture company. Electron. J. Inf. Syst. Eval. 2003, 6, 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Nov, O.; Ye, C. Personality and technology acceptance: personal innovativeness in IT, openness and resistance to change. In Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, USA, 1 January 2008.
- Agarwal, R.; Prasad, J. A conceptual and operational definition of personal innovativeness in the domain of information technology. Inf. Syst. Res. 1998, 9, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Todd, P.A. Understanding information technology usage: A test of competing models. Inf. Syst. Res. 1995, 6, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar]
- Wixom, B.H.; Todd, P.A. A theoretical integration of user satisfaction and technology acceptance. Inf. Syst. Res. 2005, 16, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, J.B.; Perrewe, P.L. An empirical examination of individual traits as antecedents to computer anxiety and computer self-efficacy. MIS Q. 2002, 26, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.E.; Walczak, S. Cognitive engagement with a multimedia ERP training tool: Assessing computer self-efficacy and technology acceptance. Inf. Manag. 2009, 46, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igbaria, M.; Tan, M. The consequences of information technology acceptance on subsequent individual performance. Inf. Manag. 1997, 32, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.J.; Fernández, Z. The role of information technology in corporate strategy of small and medium enterprises. J. Int. Entrep. 2005, 3, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangone, A. A resource-based approach to strategy analysis in small-medium sized enterprises. Small Bus. Econ. 1999, 12, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yeniyurt, S.; Kim, D.; Cavusgil, S.T. The impact of information technology on supply chain capabilities and firm performance: A resource-based view. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2006, 35, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ein-Dor, P.; Segev, E. Organizational context and the success of management information systems. Manag. Sci. 1978, 24, 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, V.; Brown, S. A. A longitudinal investigation of personal computers in homes: adoption determinants and emerging challenges. MIS Q. 2004, 25, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, N.; Kraemer, K.; Gurbaxani, V. Review: Information technology and organizational performance: An integrative model of IT business value. MIS Q. 2004, 28, 283–322. [Google Scholar]
- Egbu, C.O.; Hari, S.; Renukappa, S.H. Knowledge management for sustainable competitiveness in small and medium surveying practices. Struct. Survey 2005, 23, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, G.; Lam, T. The role of task-fit in employees’ adoption of IT in Chinese hotels. J. Hum. Resour. Hosp. Tour. 2009, 8, 96–105. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, S.L.; Howell, A.W. Beyond user acceptance: An examination of employee reactions to information technology systems. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2004, 43, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robey, D.; Zeller, R.L. Factors affecting the success and failure of an information system for product quality. Interfaces 1978, 8, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleintop, W.A.; Blau, G. Practice Makes Use: Using Information Technologies before Implementation and the Effect on Acceptance by end Users. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCPR Conference, Alexandria, VA, USA, March 1994; pp. 24–26.
- Anderson, R.E.; Huang, W.Y. Empowering salespeople: Personal, managerial, and organizational perspectives. Psychol. Mark. 2006, 23, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, C. Strategic issues in customer relationship management (CRM) implementation. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2003, 9, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, Z.; Love, P.E.D.; Li, H.; Cheng, E.Q.L.; Tse, R.Y.C. An empirical analysis of the barriers to implementing e-commerce in small-medium sized construction contractors in the state of Victoria, Australia. J. Constr. Innov. 2001, 1, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, D.; Limayem, M.; Karahanna-Evaristo, E. Measuring system usage: Implications for IS theory testing. Manag. Sci. 1995, 41, 1328–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szajna, B. Empirical evaluation of the revised technology acceptance model. Manag. Sci. 1996, 42, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam Mahmood, M.; Burn, J.M.; Gemoets, L.A.; Jacquez, C. Variables affecting information technology end-user satisfaction: A meta-analysis of the empirical literature. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2000, 52, 751–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoako-Gyampah, K. Perceived usefulness, user involvement and behavioral intention: An empirical study of ERP implementation. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2007, 23, 1232–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroudi, J.J.; Olson, M.H.; Ives, B. An empirical study of the impact of user involvement on system usage and information satisfaction. Commun. ACM 1986, 39, 212–238. [Google Scholar]
- Cynthia, M.J.; Simeon, C.; Robert, A.L. Toward an understanding of the behavioral intention to use an information system. Decis. Sci. 1997, 28, 357–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.; Milford, M.; Jewels, T.; Hunter, T.; Hunter, B. Organisational readiness for ERP implementation. In Americas Conference on Information Systems AMCIS, Long Beach, CA, USA, 1 January 2000.
- Porter, M.E.; Millar, V. How information gives you competitive advantage. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1985, 63, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.B. The inertial impact of culture on IT implementation. Inf. Manag. 1994, 27, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riolli, L.; Savicki, V. Information system organizational resilience. Omega 2003, 31, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.; Melin, L.; Nordqvist, M. Entrepreneurship as radical change in the family business: Exploring the role of cultural patterns. Fam. Bus. Rev. 2001, 14, 193–208. [Google Scholar]
- Bliss, W.G. Why is corporate culture important. Workforce 1999, 78, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.A.; Jimmieson, N.L.; Griffiths, A. The impact of organizational culture and reshaping capabilities on change implementation success: The mediating role of readiness for change. J. Manag. Stud. 2005, 42, 361–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeli, A.; Sternberg, A.; Elizur, D. Organizational culture, creative behavior, and information and communication technology (ICT) usage: A facet analysis. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2008, 11, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguzzi, A.; Passaro, R. The network of relationships between the economic environment and the entrepreneurial culture in small firms. J. Bus. Ventur. 2001, 16, 181–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, P. E.; Ramirez, J. A.; Erosa, V. E. The elaboration of a model to explain the adoption of information technologies for supply chain. In Portland International Conference on Management of Engineering and Technology, Portland, OR, USA, 1 August 2007; pp. 2379–2390.
- Graham, C.M.; Nafukho, F.M. Culture, organizational learning and selected employee background variables in small-size business enterprises. J. Eur. Ind. Train. 2007, 31, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, S.; Swan, J.A.; Galliers, R.D. A knowledge-focused perspective on the diffusion and adoption of complex information technologies: The BPR example. Inf. Syst. J. 2000, 10, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorissen, A.; Laveren, E.; Martens, R.; Reheul, A.M. Real versus sample-based differences in comparative family business research. Fam. Bus. Rev. 2005, 18, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moores, K.; Mula, J. The salience of market, bureaucratic, and clan controls in the management of family firm transitions: Some tentative Australian evidence. Fam. Bus. Rev. 2000, 13, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berghe, L.A.A.; Carchon, S. Corporate governance practices in Flemish family businesses. Corp. Gov.: Int. Rev. 2002, 10, 225–245. [Google Scholar]
- De Lema, D.G.P.; Duréndez, A. Managerial behaviour of small and medium-sized family businesses: An empirical study. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2007, 13, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Powell, P. Information systems strategy for small and medium sized enterprises: An organisational perspective. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2000, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.S.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Raman, K.S. Effect of government incentives on computerization in small business. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 1994, 3, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayman, A.T.; Mohamed, Z.; Mumtaz, K. Factors Influencing the Adoption of IT Projects: A Proposed Model. In Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Symposium on IT in Medicine and Education, ITME 2008, Xiamen, China, 1 December 2008.
- Rice, G.H.; Hamilton, R.E. Decision theory and the small businessman. Am. J. Small Bus. 1979, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Arendt, L. Barriers to ICT adoption in SMEs: How to bridge the digital divide? J. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2008, 10, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Powell, P.; Yetton, P. The dynamics of SME information systems. Small Bus. Econ. 2002, 19, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, B.; Ramanujam, R. Through the looking glass of complexity: The dynamics of organizations as adaptive and evolving systems. Org. Sci. 1999, 10, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siggelkow, N.; Levinthal, D.A. Escaping real (non-benign) competency traps: Linking the dynamics of organizational structure to the dynamics of search. Strateg. Org. 2005, 3, 85–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrtens, J.; Cragg, P.B.; Mills, A.M. A model of Internet adoption by SMEs. Inf. Manag. 2001, 39, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J.B. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. Adv. Strateg. Manag. 2000, 17, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierickx, I.; Cool, K. Asset stock accumulation and sustainability of competitive advantage. Manag. Sci. 1989, 35, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Competition in global industries: A conceptual framework. In Competition in Global Industries; Porter, M.E., Ed.; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E. Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance: With A New Introduction, 1st ed; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Marri, H.B.; Lee, B. Design and implementation of computer integrated manufacturing in small and medium-sized enterprises: A case study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2000, 16, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migiro, S.O.; Ocholla, D.N. Information and communication technologies in small and medium scale tourism enterprises in Durban, South Africa. Inf. Dev. 2005, 21, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tye, E.M.W.N.; Chau, P.Y.K. A study of information technology adoption in Hong Kong. J. Inf. Sci. 1995, 21, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardana, G.D. Measuring business performance: A conceptual framework with focus on improvement. Perform. Improv. 2008, 47, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E. M. Diffusion of Innovations; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Beatty, R. C.; Shim, J. P.; Jones, M. C. Factors influencing corporate web site adoption: A time-based assessment. Inf. Manag. 2001, 38, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Zhu, K. Migrating to internet-based e-commerce: Factors affecting e-commerce adoption and migration at the firm level. Inf. Manag. 2006, 43, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffu, K.; Walker, J. H.; Hinson, R. Strategic value and electronic commerce adoption among small and medium-sized enterprises in a transitional economy. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2008, 23, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Duncombe, R.; Heeks, R. Information and communication technologies (ICTs) and small enterprise in Africa: Lessons from Botswana. 2001. Available online: http://www.man.ac.uk/idpm (accessed on 1 September 2011).
- Love, P.E.D.; Irani, Z. An exploratory study of information technology evaluation and benefits management practices of SMEs in the construction industry. Inf. Manag. 2004, 42, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstrasser, B.; Griffiths, C. Controlling IT Investment: Strategy and Management; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Tippins, M.J.; Sohi, R.S. IT competency and firm performance: Is organizational learning a missing link? Strateg. Manag. J. 2003, 24, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Cavusgil, S.T.; Calantone, R.J. Information system innovations and supply chain management: Channel relationships and firm performance. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2006, 34, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gable, G.G. Consultant engagement for computer system selection: A pro-active client role in small businesses. Inf. Manag. 1991, 20, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.; Colebourne, D.; Thomas, B. The development of ICT advisors for SME businesses: An innovative approach. Technovation 2006, 26, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, C.P.P.; Yap, C.S.; Raman, K.S. Impact of consultants on computerization success in small businesses. Inf. Manag. 1992, 22, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, W.H. Firm size and the characteristics of computer use. MIS Q. 1981, 5, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdale, R.; Standing, C. Other papers Benefits and barriers of electronic marketplace participation: An SME perspective. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2004, 17, 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, V.; Yang, J.; Shankar, R. Study of ICT adoption for building project management in the Indian construction industry. Autom. Constr. 2009, 18, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, P.B.; King, M. Small-firm computing: Motivators and inhibitors. MIS Q. 1993, 17, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, M.; Vaidya, S.D. Adoption and implementation of IT in developing nations: Experiences from two public sector enterprises in India. J. Cases Inf. Technol. 2005, 7, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).