Abstract
Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) in furniture design is challenged by increasing product complexity and component proliferation. This study introduces a novel framework that integrates entropy reduction—achieved through dimensional standardization and modularity—as a core factor in the MCDA methodologies. The framework addresses both individual furniture evaluation and product family optimization through systematic complexity reduction. The research employed a two-phase methodology. First, a comparative analysis evaluated two furniture variants (laminated particleboard versus oak wood) using the Weighted Sum Model (WSM) and Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS). The divergent rankings produced by these methods revealed inherent evaluation ambiguities stemming from their distinct mathematical foundations, highlighting the need for additional decision criteria. Building on these findings, the study further examined ten furniture variants, identifying the potential to transform their individual components into universal components, applicable across various furniture variants (or configurations) in a furniture line. The proposed dimensional modifications enhance modularity and interoperability within product lines, simplifying design processes, production, warehousing logistics, product servicing, and liquidation at end of lifetime. The integration of entropy reduction as a quantifiable criterion within MCDA represents a significant methodological advancement. By prioritizing dimensional standardization and modularity, the framework reduces component variety while maintaining design flexibility. This approach offers furniture manufacturers a systematic method for balancing product diversity with operational efficiency, addressing a critical gap in current design evaluation practices.
1. Introduction
Furniture design involves the consideration of various—often conflicting—criteria, including manufacturability (e.g., Design for Manufacturing); functionality, with reliability as its primary aspect; aesthetics, aligned with current trends in contemporary design; mass, which affects transportation costs; and ease of assembly by the end user [1], particularly relevant for ready-to-assemble products [2,3]. Manufacturability is essential, as is the feasibility of mass production (often in mass customization mode) and the minimization of waste and energy consumption [4]. Design processes must therefore consider part simplification, modularity, and standardization, understood as the interchangeability of components, compliance with transportation and storage standards, and ease of assembly [5]. Other critical criteria include user safety, the products’ environmental impact, and recyclability [6].
Evaluating furniture design decision rationality within contexts characterized by numerous and diverse requirement categories constitutes a complex undertaking that requires methodological approaches capable of concurrent multi-criteria analysis [7,8,9,10,11,12]. For this purpose, MCDA techniques are increasingly applied [13,14,15,16,17]. The most commonly used MCDA methods include WSM (Weighted Sum Model), WPM (Weighted Product Model), AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process), ANP (Analytic Network Process), ELECTRE (ELimination and Choice-Expressing REality), PROMETHEE (Preference Ranking Organization METHod for Enrichment of Evaluations), VIKOR (in Serbian: VIseKriterijumska Optimizacija i Kompromisno Resenje, eng. Multi-Criteria Optimization and Compromise Solution), TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to an Ideal Solution), MAUT (Multi-Attribute Utility Theory), UBDA (Utility-Based Decision Analysis), Austrian Model, Decision Matrix Analysis, Simos Method, Fuzzy MCDA, GRA (Grey Relational Analysis), and DEA (Data Envelopment Analysis) [18,19,20,21,22,23]. These methods enable a comprehensive comparison of alternative design options across diverse evaluation criteria, thus supporting the decision-making process in furniture design.
Criteria such as manufacturing cost or weight are easily measurable, and thus assigning scores to them in MCDA evaluations does not pose a significant challenge. In the furniture industry, however, inherently subjective criteria—such as aesthetics and the degree of standardization—become problematic, as there is a lack of clear guidelines that would allow for an objective assessment of which design variants exhibit higher design quality or a more orderly structure.
In design decision support, artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly applied with MCDA methods, enabling automated comparisons of design variants while considering complex sets of criteria. AI is also employed in the conceptual phase of furniture design, where generative algorithms facilitate the creation of numerous alternative solutions based on predefined functional, structural, and aesthetic parameters [24]. Moreover, artificial intelligence plays a significant role in structural optimization, identifying solutions that lead to cost reduction, lower material consumption, and improved user comfort, including the simulation of structural behavior under load and stress analysis [25,26].
AI further supports the personalization of furniture designs by adapting them to individual user preferences, anthropometric characteristics, and lifestyle, which is particularly relevant in ergonomic and functional furniture design. In addition, AI assists in analyzing market and aesthetic trends by processing large datasets of visual information gathered from the internet, social media platforms, and professional design websites. This allows for identifying current tendencies in form, color, and material, providing a valuable source of inspiration for designers [25,27,28]. It is also important to emphasize the application of AI in interactive furniture configurators and AI-driven chatbots supporting customer service. These tools allow users to create personalized designs in real time and receive automated design recommendations, significantly enhancing communication efficiency between manufacturers and clients while facilitating the individualization of products within the furniture industry [29].
Despite the growing capabilities of artificial intelligence, contemporary industrial furniture design continues to rely predominantly on human-centered methodologies. Even when AI-based tools are employed, the designer remains the principal initiator and decision-maker throughout the process [30]. Consequently, the enhancement and evaluation of design processes remain relevant and necessary research areas. The article Technological Goodness Index for Furniture Design [31], highlights the absence of methods for assessing the rationality of dimensional decisions in furniture design. This study builds upon that concept by demonstrating that a limited set of cardinal dimensions can be defined for furniture components to ensure alignment with established dimensional systems. These systems may include arithmetic sequences, the Renard series, preferred number series, the Fibonacci sequence, or any dimensional scheme specified in technical standards or relevant to a particular technological field. The variety of such systems has been previously outlined in the study entitled Optimizing Dimensions in Furniture Design: A Literature Review [32].
Designing furniture components using a selected cardinal dimension system reduces the variability of component sizes—referred to as dimensional entropy—which, in turn, streamlines production planning. This approach defines a “technologically good” piece of furniture by its adherence to a coherent dimensional logic. Irrespective of the chosen system, the degree of consistency in its application is paramount. Thus, technological goodness can be understood as the extent of structural and dimensional integrity across a single piece or a family of products. Furthermore, dimensional order can enhance the objectivity of the standardization criterion in MCDA models and support the quantification of aesthetics. This is based on the assumption that more ordered structures tend to be perceived as more visually appealing [32].
This study proposes a solution to the limitations of current MCDA methods within the furniture industry. The proposed enhancement involves the integration of a proprietary Technological Goodness Index both as a new evaluation criterion and as a tool for parameterizing the standardization and aesthetics criteria. Additionally, the study assesses the practical application of the newly developed index by analyzing the furniture production process within a manufacturing enterprise.
2. Materials and Methods
Classical MCDA models, such as the WSM and the TOPSIS, are commonly applied to evaluate furniture design by comparing key technical and functional criteria. These typically include cost (lower is preferred), durability (higher is preferred), weight (lower is preferred), and ease of assembly (higher is preferred). Such models can be extended to incorporate additional criteria, such as ergonomics, aesthetics, or environmental impact, with each criterion subject to further decomposition into sub-criteria to increase the precision of the analysis.
The WSM and TOPSIS methods were selected from among numerous available MCDA approaches due to their complementary characteristics, practical applicability, and well-established use in engineering and design disciplines, particularly in contexts involving both quantitative and qualitative criteria. The choice of WSM is primarily justified by its simplicity and transparency, which enable efficient aggregation of scores across diverse criteria, including newly introduced ones such as the Technological Goodness Index. In contrast, TOPSIS provides a more nuanced evaluation by considering the relative distance of each alternative from both the ideal and anti-ideal solutions. This makes it particularly valuable for assessing criteria that are difficult to quantify directly, such as aesthetics or dimensional order. Both methods offer flexibility in incorporating new, parameterized criteria and support the comparative analysis of decision-making outcomes [33].
However, the practical application of WSM and TOPSIS reveals a significant limitation: depending on the selected MCDA method, as well as the normalization and weighting schemes used, the results regarding the optimal design variant may differ, leading to inconsistencies in decision-making outcomes. To illustrate this issue, an evaluation was conducted for two versions of a kitchen cabinet—one made of laminated particleboard and the other of solid wood—using both WSM and TOPSIS models. The comparison highlighted how methodological differences can yield divergent conclusions regarding the preferred solution.
The study investigates two design variants of a kitchen cabinet to evaluate their performance based on multiple criteria. The alternatives analyzed are as follows:
- Variant A: A kitchen cabinet made from laminated particleboard and lacquered MDF used for the front panels.
- Variant B: A kitchen cabinet manufactured from oak wood.
To support decision-making in the context of furniture design optimization, both furniture variants were evaluated using two multi-criteria decision-making methods: the WSM and TOPSIS.
In selecting evaluation criteria for the kitchen cabinet design, consideration was given to the companys profile and the characteristics of the target customer group. The manufacturing cost criterion was identified as the most critical factor for a kitchen cabinet featuring a standardized design, produced on a mass scale, and intended for customers favoring low-cost products. Accordingly, this criterion was assigned the highest decision weight, reflecting the necessity to ensure the products’ price competitiveness.
Simultaneously, in response to the expectations of a broad consumer base, significant importance was also attributed to the functionality and aesthetics of the product. These factors contribute to the kitchen cabinets overall usability and visual appeal, thereby influencing its market potential. This approach is grounded in the assumption that the primary competitive advantage of the analyzed piece of furniture should lie in its affordability while maintaining an acceptable standard of functionality and aesthetics to appeal to a wide range of consumers.
Consequently, the evaluation was based on six criteria related to technical and functional performance, as well as environmental and user-centered factors:
- Production cost;
- Reliability (as the representative factor of furnitures functionality);
- Aesthetics;
- Mass (shipping cost driver);
- Ease of assembly by end customer (RtA);
- Environmental impact.
Each criterion was assigned a weight reflecting its relative importance in the design and manufacturing context [32,34,35]. Additionally, the direction of optimization (maximization or minimization) was defined for each criterion. In the subsequent study stage, evaluative scores were assigned to design Variants A and B. The scores were assigned on a scale from 1 to 10, following the type of each criterion (disadvantage or advantage). The weights assigned to each criterion were determined using expert judgment, based on practical experience and industry-specific knowledge of the design and production context. This approach reflects real-world priorities in furniture engineering and was selected to ensure relevance to industrial decision-making scenarios. The decision matrix was normalized using the vector normalization method, as given by Equation (1), to enable objective comparison between the alternatives across criteria measured in different units and scales.
This method ensures that each criterion value is dimensionless and comparable across alternatives by dividing each performance score by the Euclidean norm of its respective criterion column. In Equation (1), the summation is performed over all alternatives for a given criterion, specifically, the values (where i denotes alternatives and j denotes the criterion) are squared and summed. The resulting square root represents the column’s Euclidean norm, which is then used to normalize each value. This vector normalization process standardizes the data while preserving the relative differences among alternatives across criteria expressed in different units and scales. Based on the adopted criteria, their corresponding weights, and the normalized performance values for Variants A and B, the ideal and anti-ideal solutions were determined following the TOPSIS methodology. The ideal solution represents the best attainable performance across all criteria (maximum or minimum, depending on the criterion type), while the anti-ideal solution represents the worst possible performance.
The ideal solution (maximization of benefit-type criteria, minimization of cost-type criteria) is as follows:
while the anti-ideal solution (minimum for benefit criteria, maximum for cost criteria) is as follows:
V+ = {0.095; 0.178; 0.045; 0.075; 0.176; 0.027};
V− = {0.285; 0.099; 0.089; 0.066; 0.098; 0.096}.
The closeness coefficient was determined by calculating the Euclidean distances of each alternative from the ideal and anti-ideal solutions. The distances from the ideal solution were calculated using Equations (2) and (3).
This coefficient reflects the relative proximity of a given alternative to the ideal solution and serves as the basis for final ranking within the TOPSIS framework. The proximity coefficient was calculated using Equation (4).
A parallel review was carried out on batches of ten cabinet models produced by a medium-scale, series-based furniture manufacturing company to enhance traditional MCDA analyses by introducing an additional criterion—namely, the rationality of dimensional decision-making in furniture design. The analysis focused on identifying components with similar but non-identical dimensions across different models. The goal was to evaluate the potential for implementing standardized or universal components, which could reduce dimensional entropy within the product family. The dimensional entropy is a quantitative indicator that reflects the degree of variation in the dimensions of structural components within a given design system. Higher entropy signifies a greater number of unique dimensions, which leads to increased technological complexity, difficulties in standardization, higher storage costs, and reduced modularity. Conversely, lower entropy indicates a more orderly system based on repetitive and standardized dimensions, which promotes production efficiency and logistical optimization [32,36]. This reduction may serve as a new, quantifiable decision criterion, supporting the rationalizing of the furniture industry’s design and manufacturing processes.
An analysis was conducted on 20 furniture variants manufactured by a furniture company (two series of 10 pieces) to demonstrate the potential for extending multi-criteria evaluation methods by incorporating additional criteria. The analysis focused on the construction parameters (specifically, the dimensions of the cut panels), aiming to identify opportunities for modifying selected dimensions to facilitate production based on the maximization of universal components shared across different furniture variants.
Each furniture variant was evaluated using a systematic methodology outlined in Figure 1. This schematic illustrates the step-by-step process employed to compare Furniture A and Furniture B.
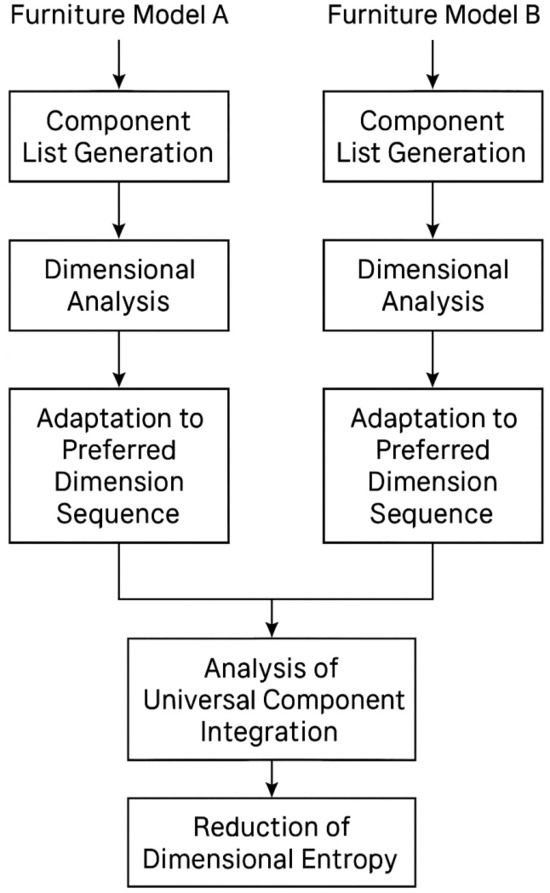
Figure 1.
A schematic of the comparative dimensional analysis of furniture aimed at maximizing the criterion of dimensional entropy reduction within a multi-criteria evaluation framework.
Initially, a component list was inferred for both furniture variants, representing each piece’s essential structural and functional components. This was followed by a dimensional analysis, where critical geometric and spatial parameters were identified and assessed. The resulting dimensions were then aligned with a predefined sequence of preferred measurements in the case of Furniture A, whereas for Furniture B, no preferential constraints were imposed during the adjustment phase. Subsequently, both variants underwent a stage of universal compromise analysis, wherein the feasibility of introducing standardized components or modularity was evaluated. This phase aimed to assess the potential for interchangeability and design unification. The process concluded with a dimensional entropy reduction, representing an optimization objective to minimize variability and enhance production efficiency and configurational coherence.
This structured approach enabled a consistent, reproducible framework for comparing furniture configurations, supporting multi-criteria decision-making in the context of design rationalization and modular optimization.
3. Results
The following presents a direct comparison of the results obtained using two MCDA methods: the WSM and TOPSIS. Both techniques were applied to evaluate two furniture design variants based on identical criteria and weights. This comparison highlights how differences in each method’s mathematical structure and evaluative logic can lead to divergent decision outcomes, even when based on the same input data.
The study also introduces a dimensional analysis based on actual Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)-derived production data to broaden the analytical scope and incorporate additional design-level considerations. This complementary evaluation identifies non-standard component dimensions and potential areas for dimensional unification, thereby illustrating the strategic value of incorporating system-level criteria in MCDA frameworks.
Table 1 presents the adopted criteria, their corresponding weights, and whether they are subject to maximization or minimization in the decision model (advantages vs. disadvantages).

Table 1.
Summary of the criteria used in the analysis, including their classification (benefit or cost type) and the respective weights used in both WSM and TOPSIS evaluations.
The evaluation scores for Variants A and B were compiled and presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The comparative assessment of design Variants A and B of the kitchen cabinet.
The normalized decision matrix, computed for both Variant A and Variant B, is presented in Table 3. This transformation facilitates subsequent aggregation steps in the TOPSIS analysis by standardizing the data while preserving the relative differences between alternatives.

Table 3.
Vector-normalized values for Variants A and B.
The normalized decision matrix was multiplied by the corresponding weights assigned to each criterion, resulting in the weighted normalized decision matrix. The results of this transformation are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Weighted matrix for Variants A and B.
To compare the results of the TOPSIS analysis with those obtained using the WSM, the cost-type criteria were transformed accordingly, as the WSM assumes that higher values indicate better performance. This transformation ensures consistency in the direction of preference across all criteria, allowing for a valid comparative assessment between the two methods. The original values were transformed using Equation (5) for each cost-type criterion [33].
The transformed data, adjusted for cost-type criteria to align with the benefit-oriented structure of the WSM, are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Decision matrix for WSM with adjusted cost criteria.
The results of the TOPSIS analysis, including the Euclidean distances (S+ and S−) and the closeness coefficient (Ci), are summarized in Table 6.

Table 6.
The Euclidean distances and the closeness coefficient for Variants A and B.
Both furniture variants obtained an identical closeness coefficient for the ideal solution. This indicates that, according to the TOPSIS analysis, the two variants are equivalent in their overall evaluation, considering all the criteria and their associated weights.
Based on the transformed data for the WSM analysis, the calculated scores for each variant are as follows:
For Variant A: WSMA = (9 × 0.3) + (5 × 0.2) + (8 × 0.1) + (8 × 0.1) + (5 × 0.2) + (2 × 0.1) = 6.6
For Variant B: WSMB = (3 × 0.3) + (9 × 0.2) + (4 × 0.1) + (7 × 0.1) + (9 × 0.2) + (7 × 0.1) = 6.5
Variant A received a slightly higher score (6.6) than Variant B (6.5), making it marginally preferred according to the WSM model.
The observed discrepancy between the outcomes of TOPSIS and WSM stems from fundamental differences in the mathematical structure and evaluative logic of the two methods:
- TOPSIS focuses on geometric distance from the hypothetical ideal (best) and anti-ideal (worst) alternatives. As such, it simultaneously accounts for both how close a variant is to the best possible option and how far it is from the worst. This leads to a more relative assessment of alternatives, where symmetrical trade-offs can neutralize each other, resulting in similar closeness scores.
- WSM, in contrast, applies a linear additive model where each criterion score is multiplied by its weight, and the results are summed. This approach inherently emphasizes the absolute contribution of each criterion to the overall performance score. Moreover, WSM requires converting cost-type criteria into benefit-type through a transformation, which may alter the balance of influence among criteria compared to TOPSIS.
In this case, the slightly higher score for Variant A under WSM can be attributed to its strong performance in transformed cost criteria (notably lower original cost and mass), which have relatively high weights in the model. Meanwhile, the equal performance under TOPSIS indicates that Variant B’s advantages (e.g., in durability and aesthetics) compensate for its higher costs in terms of distance from the ideal solution.
The different outcomes of TOPSIS and WSM do not reflect inconsistency but offer complementary perspectives. TOPSIS is suited for contexts where relative proximity to the ideal is paramount, whereas WSM provides a more absolute and additive performance measure. Therefore, decision-makers should consider the nature of trade-offs, the importance of relative vs. absolute gains, and the decision context when choosing between or combining these methods.
To introduce new directions for extending multi-criteria analyses by incorporating additional evaluation criteria, the dimensional analysis results have been compiled in Table 7. This table presents a selection of finished products extracted from the ERP system. It identifies problematic dimensions—those that do not conform to the sequence of preferred dimensions—as well as those that, with minor adjustments, could transform an individual component of a given piece of furniture into a universal component, potentially applicable in other structural configurations. This approach emphasizes the role of dimensional standardization in enhancing modularity and interoperability across product lines [37].

Table 7.
Analyzed furniture variants, identified actual dimensions deviating from dimensional unification, and proposed standardized dimensions.
The dimensions proposed in Table 7 represent the implementation of one of the dimensional unification methods presented in the article Optimizing Dimensions in Furniture Design: A Literature Review [32]. The consistent application of dimensions forming an arithmetic sequence with a common difference of 100 facilitates the organization of the design process and simplifies the technological model, warehousing logistics, and indexing in industrial ERP systems. Adjusting dimensions according to a predefined template allows for the reduction in the number of unique components and increases the use of universal components. In the presented set of 10 furniture variants, 27 components, being parts of carcasses or fronts, have been dimensionally coordinated so that a given component can be used across different furniture variants. The multiplicity of universal components occurring in the proposed furniture variants after dimensional adjustments is shown in the Table 8. Before the application of dimensional unification, no component functioned as a universal component, which posed challenges for indexing, warehousing, and production, making the process more complicated and disorganized.

Table 8.
The multiplicity of universal components occurring in the proposed furniture variants after dimensional adjustments.
The criterion of dimensional entropy may serve as a significant factor within MCDA frameworks, both for evaluating individual furniture designs and for assessing entire product families. Given the operational and logistical benefits associated with implementing a dimensional modular system—such as reduced component diversity, improved interchangeability, and streamlined inventory management—it is recommended that this criterion be assigned considerable weight in decision-making processes.
Dimensional entropy can be directly quantified using established metrics, such as Shannon’s entropy index, defined as follows:
where pi represents the probability (or relative frequency) of each unique component dimension within a given design or product family [38].
Alternatively, a domain-specific metric—the Technological Goodness Index—can also be applied. This original coefficient, introduced in our earlier study, Technological Goodness Index for Furniture Design [31], quantifies the similarity between the actual component dimensions and a reference set of preferred (standardized) dimensions. This measurement is achieved through a modified Jaccard approach for fuzzy sets [31].
As such, dimensional entropy is not a conceptual abstraction but a measurable and data-driven criterion, provided that a complete bill of materials and component structure can be extracted from an ERP database. This enables its application as an objective input in MCDA models, supporting more rationalized, repeatable, and efficiency-oriented design decisions.
The implementation of the new criterion into the presented WSM and TOPSIS analysis is shown below. The same set of criteria as previously used was applied, with the addition of the dimensional entropy criterion. The new criterion was assigned a weight equal to that of manufacturing cost, reflecting its overarching importance. Dimensional orderliness is considered a superior attribute, as it impacts aesthetics (e.g., furniture collections with coherent structural organization), ease of assembly (particularly in large-scale production, where storing standardized components and assigning universal codes simplifies production and final assembly), and environmental sustainability (standardized furniture designs are more adaptable to modernization; their lifecycle can be extended by replacing worn, universal components without requiring disposal of the entire product).
The analysis was carried out for furniture made of particleboard (Variant A) and solid wood (Variant B), extending the scope to include an assessment of the construction in terms of the dimensions applied. The example of the cabinet presented in the first row of Table 7 was used to develop the case study.
The case study thus includes the following:
Case 1: Variant A and Variant B with a dimensionally unorganized construction;
Case 2: Variant A and Variant B with a dimensionally organized construction.
In Case 1, none of the components have dimensions consistent with the adopted dimensional sequence; they are not universal from the perspective of the other furniture items in the collection presented in Table 7. As a result, the dimensional entropy is at 100% (the evaluated components include: top, bottom, left side, right side, two shelves, and two fronts).
Table 9 presents weights (adjusted to ensure the total sum remained equal to 1); types of criteria; and the scores assigned for the respective criteria, with the ratings for aesthetics, ease of assembly, and environmental impact increased or decreased by 2 points compared to the original analysis, reflecting the influence of the new criterion on the others and normalized decision matrix.

Table 9.
The comparative assessment of the kitchen cabinets design variants A and B in Case 1.
After applying the weights, the results of the WSM analysis are as follows.
Variant A
WSMA = (1.000 × 0.25) + (1.000 × 0.25) + (0.556 × 0.15) + (0.429 × 0.15) + (1.000 × 0.10) + (1.000 × 0.05) + (0.444 × 0.05) = 0.25 + 0.25 + 0.064 + 0.064 + 0.10 + 0.05 + 0.022 = 0.819
Variant B
WSMB = (0.333 × 0.25) + (1.000 × 0.25) + (1.000 × 0.15) + (1.000 × 0.15) + (0.500 × 0.10) + (0.833 × 0.05) + (1.000 × 0.05) = 0.083 + 0.25 + 0.15 + 0.15 + 0.05 + 0.042 + 0.05 = 0.775
Consistent with the previous approach, the decision matrix was normalized to conduct the TOPSIS analysis and multiplied by weights. The results are shown in Table 10.

Table 10.
Normalized decision matrix using vector normalization for TOPSIS method and multiplied by weights in Case 1.
Subsequently, the ideal and anti-ideal solutions were determined. The results are presented in Table 11.

Table 11.
The ideal and anti-ideal solutions for TOPSIS in Case 1.
The results of the TOPSIS analysis, including the Euclidean distances (S+ and S−) and the closeness coefficient (Ci) for Case 1, are summarized in Table 12.

Table 12.
The Euclidean distances and the closeness coefficient for Variants A and B in Case 1.
Following the introduction of the new criterion—dimensional entropy—and the subsequent adjustment of both the criterion weights and performance scores to reflect its influence, a consistent outcome was obtained across both multi-criteria decision analysis methods. Specifically, the evaluations conducted using WSM and TOPSIS yielded identical rankings of the design variants, thereby confirming the robustness and coherence of the assessment framework in the presence of the newly implemented criterion.
Case 2 concerns the evaluation of a dimensionally ordered design at a 50% level. The dimensional modifications proposed in Table 7 resulted in the introduction of four universal components, which are repeatable in other constructions (a universal top, bottom, and two shelves). The distinguishing components remained the sides and fronts. Accordingly, the dimensional entropy criterion was assigned a score of 5 points, and the other performance scores were proportionally adjusted—either increased or decreased—following the approach applied in Case 1. The compilation of criteria, their respective weights, and the assigned scores in Case 2 are presented in Table 13.

Table 13.
The compilation of criteria, their respective weights, and the assigned scores in Case 2.
The summary of results obtained for Case 2 using the WSM and TOPSIS methods is presented in Table 14.

Table 14.
The comparative assessment of design variants A and B of the kitchen cabinet in Case 2.
As shown in Table 14, similar to Case 1, both methods (WSM and TOPSIS) consistently identify Variant A as the more favorable option.
4. Discussion
The continuous development of MCDA methods is essential in light of the growing complexity and variability of decision-making environments across diverse sectors. The observed discrepancy between the outcomes of TOPSIS and WSM highlights a critical issue in applying the MCDA method in real-world decision-making: the sensitivity of final rankings to the underlying evaluative logic of the chosen model. While WSM aggregates weighted scores linearly, emphasizing absolute performance, TOPSIS evaluates alternatives based on their relative distance from an ideal and anti-ideal solution. As a result, two alternatives may be deemed equivalent by one method and differentiated by another. In practical settings, such inconsistencies may lead to uncertainty or disagreement among stakeholders. Consequently, this highlights the critical importance of both the judicious selection of MCDA techniques, informed by the specific decision context, and the integration of supplementary, objective criteria, such as dimensional entropy, into evaluation models. Such an approach serves to enhance the robustness of design evaluations. Recent scientific literature emphasizes the necessity of methodological improvements to enhance practical applicability, analytical robustness, and stakeholder engagement [39].
Given the many MCDA methods available, developing decision-support frameworks to guide method selection is imperative. Wątróbski and coauthors (2019) [40] proposed a generalized framework for MCDA method selection, analyzing 56 different approaches to support users in selecting the most appropriate method for their specific problem [40]. Such tools are vital for increasing the practical effectiveness of MCDA applications.
The continuous advancement of MCDA methodologies is crucial for addressing the demands of increasingly intricate decision environments. Key challenges include effective stakeholder engagement, integration of hybrid methods, uncertainty management, sector-specific considerations, and the need for methodological standardization. Addressing these challenges will contribute to greater transparency, acceptance, and practical utility of MCDA across various domains [18,20,39].
In the context of the furniture industry, one of the promising avenues for enhancing the quality of MCDA-based evaluations is the incorporation of standardization criteria, specifically, the degree of modularity within a product’s structural components. Modularization in furniture design has emerged as a significant research area within industrial design, enabling flexible, cost-effective, and sustainable furniture solutions. A comprehensive review published in the Journal of Engineering Design analyzed 163 publications related to modular product design [41]. The study found that modularity supports mass customization, reduces development costs, and facilitates end-of-life ecological strategies. However, the lack of consistent terminology and methodological frameworks hinders the standardization of practices in product development.
The criterion of dimensional entropy reduction may serve as a valuable and quantifiable factor within MCDA frameworks, applicable both to the evaluation of individual furniture designs and to the assessment of broader product families. Unlike general concepts of modularity and standardization—well established in engineering design—the proposed use of entropy provides a measurable index of dimensional convergence or disorder within a set of components. It enables decision-makers to evaluate the extent to which a design adheres to predefined dimensional grids or modules, thus offering a structured approach to assessing design rationalization and consistency [36,37,41].
Given the tangible operational and logistical advantages of implementing a dimensional modular system—such as reduced inventory complexity, better component interchangeability, lower production costs, and enhanced compatibility across product lines—it is recommended that this criterion be assigned significant weight in decision-making processes. Moreover, entropy reduction is a complementary metric supporting production efficiency and long-term planning of product families.
By incorporating dimensional entropy as a system-level criterion, MCDA models gain an additional layer of analytical depth, allowing for the integrating of the design’s structural, managerial, and informational dimensions. This approach supports more robust and scalable decision-making, especially in complex industrial environments where trade-offs between customization and standardization must be carefully managed.
The ongoing need to refine Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) evaluation criteria necessitates the parallel development of unambiguous design templates and the assessment of their implementation outcomes. Previously, our research, specifically “Optimizing Dimensions in Furniture Design: A Literature Review” [32] and “Technological Goodness Index for Furniture Design” [31], has already explored the advantages and potential directions for creating such unified design frameworks. This paper extends that research through the furniture analysis presented in Table 7. Furthermore, the developed technological index theory provides a practical application by enabling the evaluation and proposal of a unified dimensional system for furniture manufacturing enterprises.
5. Summary and Conclusions
The study advocates for “entropy reduction” in furniture design, achievable through dimensional standardization and modularity, to be incorporated as a significant criterion within MCDA frameworks. This criterion is relevant for evaluating individual furniture designs and entire product families. Given the substantial operational and logistical benefits of implementing a dimensional modular system, it is recommended that the criterion of entropy reduction be assigned a considerable weight in decision-making processes.
The two MCDA methods employed, TOPSIS and WSM, yielded different outcomes for the evaluation of Furniture Variants A and B. TOPSIS analysis indicated that Variants A and B are equivalent, with both achieving an identical closeness coefficient (Ci = 0.500) to the ideal solution. This suggests neither variant is superior when simultaneously considering proximity to the ideal and anti-ideal solutions. WSM analysis showed a marginal preference for Variant A (6.6) over Variant B (6.5).
The discrepancy in results is attributed to the fundamental differences in the mathematical structure and evaluative logic of TOPSIS and WSM. TOPSIS assesses alternatives based on their geometric distance from hypothetical ideal and anti-ideal solutions, offering a relative evaluation where trade-offs can lead to similar overall scores. WSM uses a linear additive model, emphasizing the absolute weighted contribution of each criterion. The necessary transformation of cost-type criteria in WSM can also alter the relative influence of criteria compared to TOPSIS. Variant A’s slight WSM advantage likely stems from strong performance in highly weighted transformed cost criteria, while Variant B’s countervailing strengths (e.g., durability, aesthetics) balanced this out in the TOPSIS distance-based assessment. The introduction of the dimensional entropy criterion into the analysis, along with the adjustment of weights and assigned scores based on the degree of entropy reduction, allowed for consistent results to be obtained in the WSM and TOPSIS evaluations.
- The differing outcomes are not seen as an inconsistency but as providing complementary insights. The choice of method (or the interpretation of combined results) should depend on whether relative proximity to an ideal (TOPSIS) or an absolute additive performance score (WSM) is more critical for the specific decision-making context.
- The research successfully introduces an analysis of furniture dimensions to extend the MCDA range. By analyzing existing product dimensions (Table 7) from an ERP system, the study identifies “problematic dimensions” and proposes modifications to align them with a sequence of preferred dimensions (specifically, an arithmetic sequence with a common difference of 100).
- By introducing the new criterion of dimensional entropy, it becomes possible to achieve consistent results (i.e., the same preferred alternative) in both WSM and TOPSIS analyses, provided that the remaining criteria are appropriately adjusted based on the impact of dimensional standardization and the prevalence of universal components in the construction. The assignment of scores to criteria such as aesthetics, ease of assembly, or environmental impact becomes less subjective and is grounded in the tangible benefits of dimensional unification—benefits now quantifiable through the newly introduced criterion.
The proposed dimensional modifications aim to achieve the following:
- Transform individual furniture components into universal components applicable across different structural configurations.
- Enhance modularity and interoperability within product lines.
- Simplify the design process, technological modeling, warehousing logistics, and ERP system indexing.
- Reduce the number of unique components and increase the use of universal components (though specific quantitative impacts, denoted by 27, are implied rather than explicitly stated in the excerpt).
The research demonstrates that while traditional MCDA methods provide valuable insights, their results can differ based on their underlying logic. Furthermore, it pioneers the integration of dimensional analysis and the concept of entropy reduction as crucial new criteria to enhance the comprehensiveness and practical applicability of MCDA in furniture design and manufacturing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.J. and M.S.; methodology, A.J.; software, A.J.; validation, A.J.; formal analysis, M.S.; investigation, A.J.; resources, A.J.; data curation, A.J.; writing—original draft preparation, A.J. and M.S.; writing—review and editing, A.J.; visualization, A.J.; supervision, M.S.; funding acquisition, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sydor, M.; Stańczyk, K. Analyzing Joinery for Furniture Designed for Disassembly. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wu, L. Understanding Consumer Preferences for Hedonic Furniture: A Push-Pull-Mooring Analysis. Empir. Stud. Arts 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yan, Y.; Lv, J. A Bibliometric Analysis of Current Knowledge Structure and Research Progress Related to Sustainable Furniture Design Systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingam, J. Emerging Trends in the Global Furniture Industry. In Furniture Manufacturing; Design Science and Innovation; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Smardzewski, J. Furniture Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, A. Determining and Ordering the Basic Evaluation Criteria in the Furniture Design Process. Iconarp Int. J. Arch. Plan. 2023, 11, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, K.; Burdurlu, E. Selection of wooden furniture joints with multi-criteria decision-making techniques. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 19, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Yao, L. Emotional design and evaluation of children’s furniture based on AHP-TOPSIS. BioResources 2024, 19, 7418–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogrodnik, K. Multi-Criteria Analysis of Design Solutions in Architecture and Engineering: Review of Applications and a Case Study. Buildings 2019, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshabi, P.; Nejati, E.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Chegini, A.; Makui, A.; Ghousi, R.; Pamucar, D. Developing a Multi-Criteria Decision Making approach to compare types of classroom furniture considering mismatches for anthropometric measures of university students. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, J. Smart algorithmic solutions for neutrosophic multiple-attribute decision-making and applications to chair furniture comfort design evaluation. Int. J. Knowl.-Based Intell. Eng. Syst. 2023, 27, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, M.N.; Taşdemir, Ç. Facility location selection and layout planning through AHP, PROMETHEE, and CORELAP methods in the furniture industry. BioResources 2024, 19, 6478–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siksnelyte, I.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Streimikiene, D.; Sharma, D. An Overview of Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Methods in Dealing with Sustainable Energy Development Issues. Energies 2018, 11, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkov, I.; Moberg, E. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4398-5319-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lenarczyk, A.; Jaskólski, M.; Bućko, P. The Application of a Multi-Criteria Decision-Making for Indication of Directions of the Development of Renewable Energy Sources in the Context of Energy Policy. Energies 2022, 15, 9629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferla, G.; Mura, B.; Falasco, S.; Caputo, P.; Matarazzo, A. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) for sustainability assessment in food sector. A systematic literature review on methods, indicators and tools. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.B.; Keisler, J.; Linkov, I. Multi-criteria decision analysis in environmental sciences: Ten years of applications and trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3578–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Goswami, S.S. A Comprehensive Review of Multiple Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) Methods: Advancements, Applications, and Future Directions. Decis. Mak. Adv. 2023, 1, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaube, S.; Pant, S.; Kumar, A.; Uniyal, S.; Singh, M.K.; Kotecha, K.; Kumar, A. An Overview of Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis and the Applications of AHP and TOPSIS Methods. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2024, 9, 581–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Ehrgott, M.; Figueira, J.R. Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis: State of the Art Surveys; International Series in Operations Research & Management Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 233, ISBN 978-1-4939-3093-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mardani, A.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Khalifah, Z.; Zakuan, N.; Jusoh, A.; Nor, K.M.; Khoshnoudi, M. A review of multi-criteria decision-making applications to solve energy management problems: Two decades from 1995 to 2015. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 216–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Mardani, A.; Turskis, Z.; Jusoh, A.; Nor, K.M. Development of TOPSIS Method to Solve Complicated Decision-Making Problems—An Overview on Developments from 2000 to 2015. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Decis. Mak. 2016, 15, 645–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Nilashi, M.; Zakuan, N.; Loganathan, N.; Soheilirad, S.; Saman, M.Z.M.; Ibrahim, O. A systematic review and meta-Analysis of SWARA and WASPAS methods: Theory and applications with recent fuzzy developments. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 57, 265–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribino, P.; Bonomolo, M. A multi-objective reinforcement learning approach for furniture arrangement with optimal IEQ in multi-occupant offices. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2023, 14, 16749–16770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, A.; Fabris, G.; Gasparetto, A.; Montanari, A.; Saccomanno, N.; Scalera, L. A survey on recent trends in robotics and artificial intelligence in the furniture industry. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2024, 93, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beklemysheva, K.; Vasyukov, A.; Ermakov, A.; Favorskaya, A. Numerical modeling of ultrasound beam forming in elastic medium. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 112, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y. Preliminary Research on Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Furniture Design-Take the Torii Entrance Cabinet as an Ex-ample. In Kansei Engineering and Emotion Research; Tsai, T., Chen, K., Yamanaka, T., Koyama, S., Schütte, S., Mohd Lokman, A., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2024; Volume 2314, pp. 51–63. ISBN 978-981-9799-09-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Han, S. System Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality Technology in the Interactive Design of Interior Decoration. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Le, M.; Martin, B.; Cil, I.; Fookes, C. When AI meets store layout design: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 5707–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, R.; Tang, J.; Tang, T.; Li, H.; Cui, W.; Wu, Y. Understanding Nonlinear Collaboration between Human and AI Agents: A Co-design Framework for Creative Design. In Proceedings of the CHI ‘24: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 11–16 May 2024; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Jasińska, A.; Sydor, M.; Niedziela, G.; Slebioda, L. Technological Goodness Index for Furniture Design. Acta Fac. Xylol. Zvolen 2024, 66, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasińska, A.; Sydor, M.; Hitka, M. Optimizing dimensions in furniture design: A literature review. BioResources 2024, 19, 4727–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, E. Multi-Criteria Decision Making Methods: A Comparative Study; Applied Optimization; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 44, ISBN 978-1-4419-4838-0. [Google Scholar]
- Antal, M.R.; Domljan, D.; Horváth, P.G. Functionality and Aesthetics of Furniture—Numerical Expression of Subjective Value. Drv. Ind. 2017, 67, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Kasal, A.; Erdil, Y.Z. The State of the Art of Biomechanics Applied in Ergonomic Furniture Design. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Entropy and diversity. Oikos 2006, 113, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, K. Fundamentals of Product Modularity. In Management of Design; Dasu, S., Eastman, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 219–231. ISBN 978-94-010-4609-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Więckowski, J.; Sałabun, W.; Kizielewicz, B.; Bączkiewicz, A.; Shekhovtsov, A.; Paradowski, B.; Wątróbski, J. Recent advances in multi-criteria decision analysis: A comprehensive review of applications and trends. Int. J. Knowl.-Based Intell. Eng. Syst. 2023, 27, 367–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wątróbski, J.; Jankowski, J.; Ziemba, P.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Zioło, M. Generalised framework for multi-criteria method selection. Omega 2019, 86, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvoisin, J.; Halstenberg, F.; Buchert, T.; Stark, R. A systematic literature review on modular product design. J. Eng. Des. 2016, 27, 488–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).