HBiLD-IDS: An Efficient Hybrid BiLSTM-DNN Model for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoMT Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
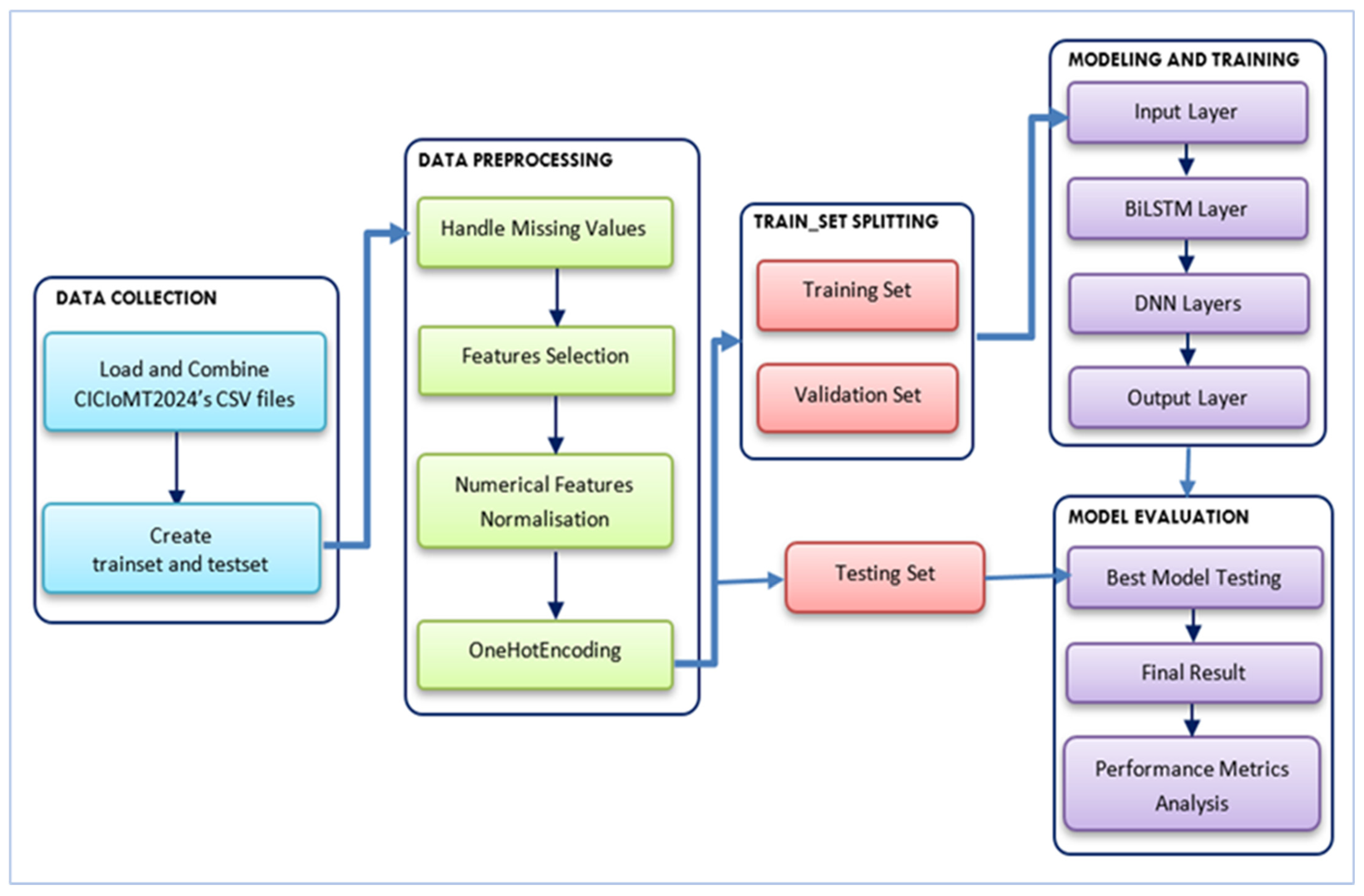
3. Methodology
3.1. Dataset
3.1.1. Dataset Description
3.1.2. Dataset Collection
3.2. Proposed Model
3.3. Data Preprocessing
3.4. Data Splitting
3.5. Model Architecture
- (a)
- Core Architecture:
- Temporal Processing: A 128-unit bidirectional LSTM layer (return sequences = True) maintains temporal resolution, with input features reshaped into 3D tensors (n_features × 1 × 1) for dimensional compatibility;
- Regularization Framework:
- -
- Immediate 40% variational dropout after BiLSTM layer;
- -
- Progressive dropout decay (40%→30%) across subsequent distillation layers;
- Feature Distillation: Two dense layers (128→64 neurons) with ReLU activation form the hierarchical feature extraction block;
- (b)
- Optimization Configuration:
- Adam optimizer (η = 5 × 10−4 initial learning rate);
- Batch training (size = 128) for a maximum of 50 epochs;
- Tri-phase callback system:
- EarlyStopping: Patience = 20 epochs; δ = 0.001 (prevents overfitting);
- ReduceLROnPlateau: Factor = 0.2 reduction; cooldown = 2 epochs (escapes local minima);
- ModelCheckpoint: Saves optimal weights based on validation performance3.6. Experimental Environnement.
3.6. Experimental Environnement
3.7. Evaluation Metrics
- True positives (TPs): Count of instances correctly predicted as positive.
- False positives (FPs): Count of instances wrongly predicted as positives.
- True positives (TNs): Count of instances correctly predicted as negatives.
- False positives (FNs): Count of instances wrongly predicted as negatives.
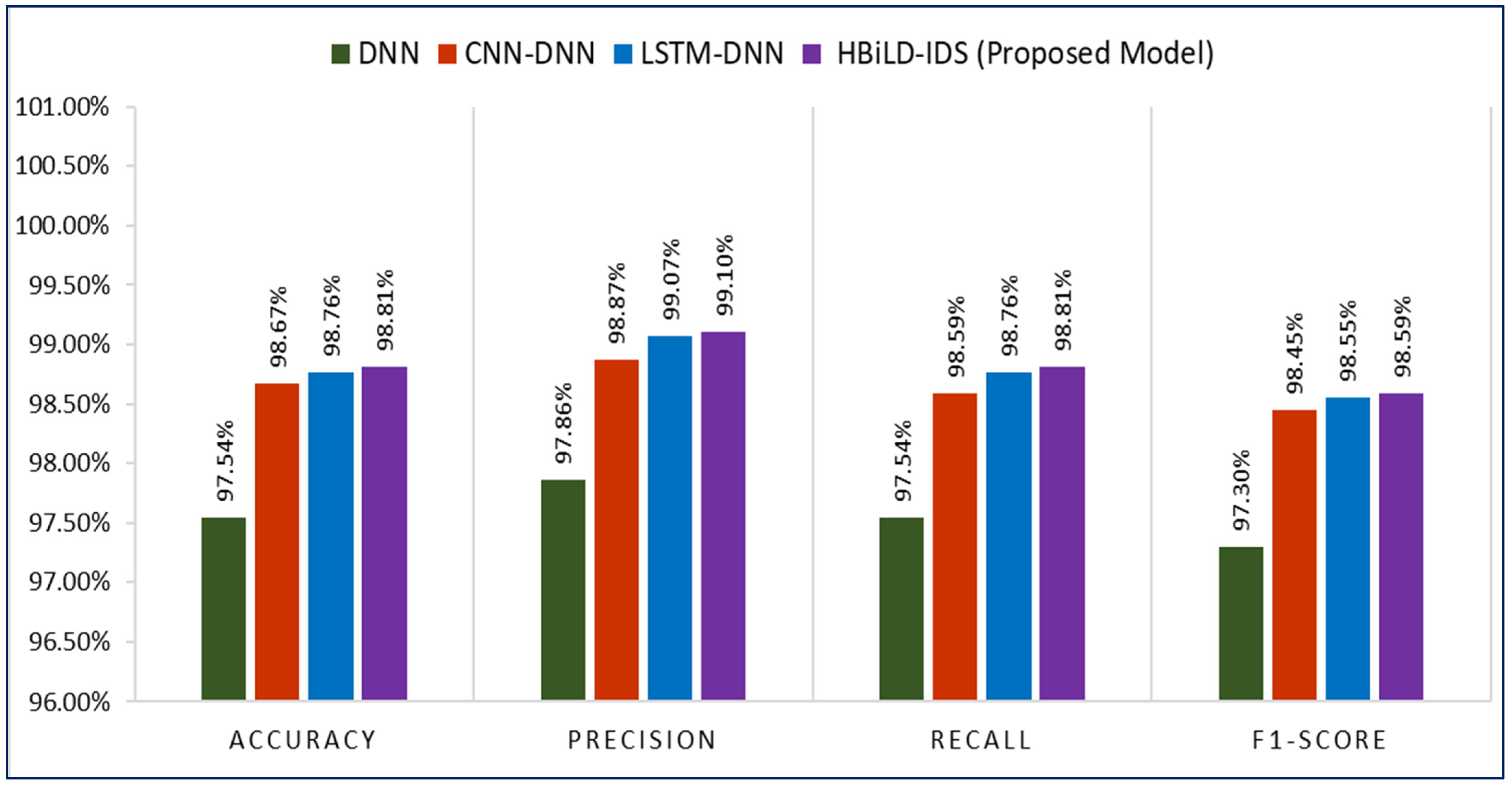
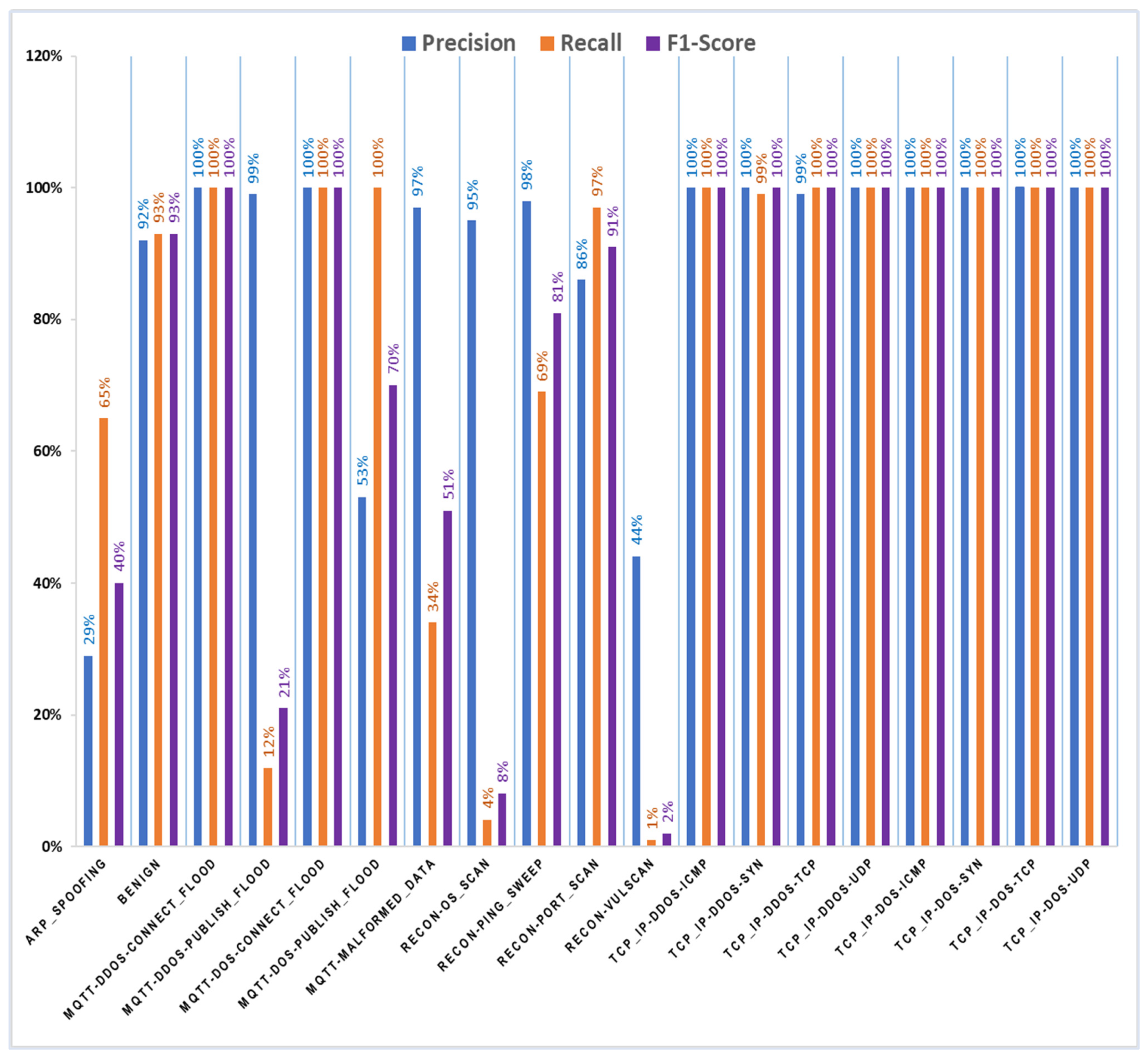
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, U.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, Y. The Internet of Things in Healthcare: An Overview. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2016, 1, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, G.; Persico, V.; Pescapé, A. The Role of Information and Communication Technologies in Healthcare: Taxonomies, Perspectives, and Challenges. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 107, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saleh, A.A.; Sheikh, A.M.; Albreem, M.A.M.; Honnurvali, M.S. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Opportunities and Challenges. Wirel. Netw. 2025, 31, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, M.; Karageorgou, M.; Mantas, G.; Sucasas, V.; Essop, I.; Rodriguez, J.; Lymberopoulos, D. A Survey on Security Threats and Countermeasures in Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Govea, J.; Jaramillo-Alcazar, A. Tamper Detection in Industrial Sensors: An Approach Based on Anomaly Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, U.; Ullah, I.; Yousuf Uddin, M.; Kwon, S.J. An Effective Self-Configurable Ransomware Prevention Technique for IoMT. Sensors 2022, 22, 8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, B.; Abu Al-Haija, Q.; Alsemmeari, R.A.; Alsulami, A.; Alqahtani, A.; Alghamdi, B.M.; Bakhsh, S.T.; Shaikh, R.A. IoMT Landscape: Navigating Current Challenges and Pioneering Future Research Trends. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Jin, K.; Chen, Z. An Intrusion Detection Method for Industrial Control System Based on Machine Learning. Information 2022, 13, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghib, A.; Gharehchopogh, F.S.; Zamanifar, A. A Comprehensive and Systematic Literature Review on Intrusion Detection Systems in the Internet of Medical Things: Current Status, Challenges, and Opportunities. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Maglaras, L.A.; Janicke, H.; Jiang, J.; Shu, L. A Systematic Review of Data Protection and Privacy Preservation Schemes for Smart Grid Communications. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 806–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wan, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D. IoT Security Techniques Based on Machine Learning: How Do IoT Devices Use AI to Enhance Security? IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, J.-P.A.; Noura, M.; Noura, H.N.; Salman, O.; Yaacoub, E.; Couturier, R.; Chehab, A. Securing Internet of Medical Things Systems: Limitations, Issues and Recommendations. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 105, 581–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimpourlas, F.; Papadopoulos, L.; Bartsokas, A.; Soudris, D. A Design Space Exploration Framework for Convolutional Neural Networks Implemented on Edge Devices. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 37, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuario, F.; Santoro, G.; Giliberti, M.; Bello, S.; Zazzera, E.; Impedovo, D. Machine Learning-Based Methodologies for Cyber-Attacks and Network Traffic Monitoring: A Review and Insights. Information 2024, 15, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, L. An Industrial Network Intrusion Detection Algorithm Based on IGWO-GRU. Cluster Comput. 2024, 27, 7199–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liang, K. A BiLSTM-Based DDoS Attack Detection Method for Edge Computing. Energies 2022, 15, 7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Tang, S.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Chen, D.; Yang, Q.; Fu, S. Characterizing Perception Deep Learning Algorithms and Applications for Vehicular Edge Computing. Algorithms 2025, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, J.A.; Wang, C.; Sima, M.W.U.; Arshad, M.; Owais, M.; Hassan, D.S.M.; Alkanhel, R.; Muthanna, M.S.A. A Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Robust Intrusion Detection System for Securing IoMT Healthcare Networks. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1524286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Shambharkar, P.G. Multi-Attention DeepCRNN: An Efficient and Explainable Intrusion Detection Framework for Internet of Medical Things Environments. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2025, 67, 5783–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, G.; Sahmoud, S.; Onat, M.; Cavusoglu, Ü.; Malondo, E. L2D2: A Novel LSTM Model for Multi-Class Intrusion Detection Systems in the Era of IoMT. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 7002–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, H.; Alsirhani, A.; Alserhani, F.M.; Ullah, F.; Krejcar, O. Augmenting Internet of Medical Things Security: Deep Ensemble Integration and Methodological Fusion. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2024, 141, 2185–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.C. Multi-Class Intrusion Detection Based on Transformer for IoT Networks Using CIC-IoT-2023 Dataset. Future Internet 2024, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharaiah, M.A.; Almaiah, M.A.; Shehab, R.; Obeidat, M.; El-Qirem, F.A.; Aldhyani, T. An Explainable AI-Driven Transformer Model for Spoofing Attack Detection in Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Networks. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruqui, N.; Abu Yousuf, M.; Whaiduzzaman; Azad, A.; Alyami, S.A.; Liò, P.; Kabir, M.A.; Moni, M.A. SafetyMed: A Novel IoMT Intrusion Detection System Using CNN-LSTM Hybridization. Electronics 2023, 12, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueriani, A.; Kheddar, H.; Mazari, A.C. Enhancing IoT Security with CNN and LSTM-Based Intrusion Detection Systems. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Pattern Analysis and Intelligent Systems (PAIS), El Oued, Algeria, 24–25 April 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, H.R.; Dong, W.; Al-Madani, A.M. Enhanced Intrusion Detection with LSTM-Based Model, Feature Selection, and SMOTE for Imbalanced Data. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jony, A.I.; Arnob, A.K.B. A Long Short-Term Memory Based Approach for Detecting Cyber Attacks in IoT Using CIC-IoT-2023 Dataset. J. Edge Comput. 2024, 3, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsa, S.; Dash, R.K.; Ivković, N. An Interpretable Dimensional Reduction Technique with an Explainable Model for Detecting Attacks in Internet of Medical Things Devices. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.A.; Islam, M.M.; Uddin, M.A.; Hasan, K.F.; Sharmin, S.; Alyami, S.A.; Moni, M.A. Machine Learning-Based Network Intrusion Detection for Big and Imbalanced Data Using Oversampling, Stacking Feature Embedding, and Feature Extraction. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Al Hejaili, A.; Sampedro, G.A.; Abisado, M.; Almadhor, A.S.; Shahzad, T.; Ouahada, K. A Novel Federated Edge Learning Approach for Detecting Cyberattacks in IoT Infrastructures. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 112189–112198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doménech, J.; León, O.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Pegueroles, J. Evaluating and Enhancing Intrusion Detection Systems in IoMT: The Importance of Domain-Specific Datasets. Internet Things 2025, 32, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanday, S.A.; Fatima, H.; Rakesh, N. A Novel Data Preprocessing Model for Lightweight Sensory IoT Intrusion Detection. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2024, 9, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, N.; Kesswani, N. Intrusion Detection System for Internet of Medical Things Using GRU with Attention Mechanism-Based Hybrid Deep Learning Technique. Jordanian J. Comput. Inf. Technol. 2024, 11, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, R.W.; Abrar, M.; Salam, A.; Ullah, F. Federated Learning with LSTM for Intrusion Detection in IoT-Based Wireless Sensor Networks: A Multi-Dataset Analysis. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2025, 11, e2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadkhah, S.; Neto, E.C.P.; Ferreira, R.; Molokwu, R.C.; Sadeghi, S.; Ghorbani, A.A. CICIoMT2024: A Benchmark Dataset for Multi-Protocol Security Assessment in IoMT. Internet Things 2024, 28, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tany, N.S.; Suresh, S.; Sinha, D.N.; Shinde, C.; Stolojescu-Crisan, C.; Khondoker, R. Cybersecurity Comparison of Brain-Based Automotive Electrical and Electronic Architectures. Information 2022, 13, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors | Year | Experimental Dataset | Techniques and Models | Classification Types | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaikh et al. [18] | 2025 | CICIoMT2024 | CNN, LSTM, and RL | Multi-class (19) | 77.73% |
| Sharma and Shambharkar [19] | 2025 | CICIoMT2024 | CNN, RNN, and Attention mechanism | Multi-class (19) | 98.56% |
| Akar et al. [20] | 2025 | CICIoMT2024 | LSTM | Multi-class (19) | 98% |
| Naeem et al. [21] | 2024 | WUSTL-EHMS-2020, CICIoMT2024 | Transformer-based DCNNs, LSTM, and Meta-learner | Binary | 98.84% |
| Tseng et al. [22] | 2024 | CICIoT2023 | Transformer Model | Binary | 99.40% |
| Alsharaiah et al. [23] | 2025 | CICIoMT2024 | Transformer-based DL and Explainable AI | Binary | 99.71%. |
| Faruqui et al. [24] | 2023 | CICIDS2017, CICIDS2018 and CICIDS2019 | CNN and LSTM | Multi-class (12) | 97.63% |
| Gueriani et al. [25] | 2024 | CICIoT2023 and CICIDS2017 | CNN and LSTM | Binary | 98.42% |
| Sayegh et al. [26] | 2023 | CICIDS2017, NSL-KDD and UNSW-NB15 | LSTM | Binary | 99.75% |
| Jony et al. [27] | 2024 | CICIoT2023 | LSTM | Multi-class (35) | 98.75% |
| Lipsa et al. [28] | 2025 | CICIDS2017 and NSL-KDD | Random Forest, XGBoost, Decision Tree, and Support Vector | Multi-class (14) | 99% |
| Abbas et al. [30] | 2023 | CICIoT2023 | Federated DNN | Binary | 99.00% |
| Doménech et al. [31] | 2025 | CICIoT2023 and CICIoMT2024 | ML models | Multi-class (6) | 99.85% |
| Doménech et al. [32] | 2025 | CICIoT2023 and CICIoMT2024 | ML models | Multi-class (6) | 99.85% |
| Saran & al. [33] | 2024 | NF-TON-IoT and ICU | Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) and Attention Mechanism | Binary | 99.99% |
| Anwar et al. [34] | 2025 | WSN-DS, CICIDS2017 and UNSW-NB15 | FL-based LSTM | Binary | 97.80% |
| Our Proposed Model (HBiLD-IDS) | 2025 | CICIoMT2024 | Hybrid BiLSTM-DNN | Multi-Class (19) | 98.81% |
| Binary | 6-Classes | 19-Classes | Count | Percentage | STRIDE Threats Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Benign | Benign (Normal Traffic) | 230,339 | 2.62% | - |
| Attack | Spoofing | ARP Spoofing | 17,791 | 0.20% | Spoofing Identity (S) |
| DoS | TCP Flood | 462,480 | 5.27% | Denial of Service (D) | |
| UDP Flood | 704,503 | 8.03% | |||
| SYN Flood | 540,498 | 6.16% | |||
| ICMP Flood | 514,724 | 5.87% | |||
| DDoS | TCP Amplification | 987,063 | 11.25% | ||
| UDP Amplification | 1,998,026 | 22.77% | |||
| SYN Flood | 974,359 | 11.10% | |||
| ICMP Flood | 1,887,175 | 21.51% | |||
| MQTT | Dos-Connect Flood | 15,904 | 0.18% | ||
| Dos-Publish Flood | 52,881 | 0.60% | |||
| DDos-Connect Flood | 214,952 | 2.45% | |||
| DDos-Publish Flood | 36,039 | 0.41% | |||
| Malformed Packets | 6877 | 0.08% | |||
| Recon | Port Scanning | 106,603 | 1.21% | Information Disclosure (I) | |
| OS Fingerprinting | 20,666 | 0.24% | |||
| Ping_Sweep | 926 | 0.01% | |||
| Vulnerability scanning | 3207 | 0.04% |
| Authors | ML/DL Technique | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaikh et al. [18] | Hybrid (CNN-LSTM-RL) | 0.7773 | 0.7602 | 0.7773 | 0.7247 |
| Akar et al. [20] | LSTM | 0.9800 | 0.9800 | 0.9800 | 0.9800 |
| Dadkhah et al. [35] | RandomForest | 0.7330 | 0.6910 | 0.5770 | 0.551 |
| HBiLD-IDS (Proposed Model) | Hybrid (BiLSTM-DNN) | 0.9881 | 0.9910 | 0.9881 | 0.9859 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benahmed, H.; M’hamedi, M.; Merzoug, M.; Hadjila, M.; Bekkouche, A.; Etchiali, A.; Mahmoudi, S. HBiLD-IDS: An Efficient Hybrid BiLSTM-DNN Model for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoMT Networks. Information 2025, 16, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080669
Benahmed H, M’hamedi M, Merzoug M, Hadjila M, Bekkouche A, Etchiali A, Mahmoudi S. HBiLD-IDS: An Efficient Hybrid BiLSTM-DNN Model for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoMT Networks. Information. 2025; 16(8):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080669
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenahmed, Hamed, Mohammed M’hamedi, Mohammed Merzoug, Mourad Hadjila, Amina Bekkouche, Abdelhak Etchiali, and Saïd Mahmoudi. 2025. "HBiLD-IDS: An Efficient Hybrid BiLSTM-DNN Model for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoMT Networks" Information 16, no. 8: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080669
APA StyleBenahmed, H., M’hamedi, M., Merzoug, M., Hadjila, M., Bekkouche, A., Etchiali, A., & Mahmoudi, S. (2025). HBiLD-IDS: An Efficient Hybrid BiLSTM-DNN Model for Real-Time Intrusion Detection in IoMT Networks. Information, 16(8), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080669







