Abstract
Electronic voting allows people to participate more easily in their country’s electoral events. Nevertheless, its adoption is still far from widespread. In this paper, we provide a detailed survey of the state of adoption worldwide and investigate which socio-economic factors may influence such an adoption. Its usage is wider in North and South America, while remaining considerably lower in Europe and Asia and practically absent in Africa. We distinguish between e-voting, which maintains the traditional polling station structure while adding technological components, and i-voting, which enables remote participation from any location using personal devices. Five factors (country’s surface and population, Gross Domestic Product, Internet Usage, and Democracy Index) are investigated to predict adoption, and an accuracy of over 79% is achieved through a machine learning random forest model. Larger, wealthier, and more democratic countries are typically associated with a larger adoption of internet voting.
1. Introduction
Although digitalization has impacted most areas of public administration, there is noticeable hesitance in embracing computerized solutions for the management of political elections. The current widely employed system of paper voting is marred by many inefficiencies, as it requires the involvement of a large number of people and the associated costs of such broad participation. Scrutineers are asked to count the ballot results manually, leading to the possibility of errors [1,2]. In a world where sustainability holds great importance, the production of large numbers of paper ballots and the need to transport voters to and from polling stations have serious environmental consequences [3]. In addition, people who live far from their polling stations have to bear the financial burden of exercising their right to vote. In addition, people with disabilities face enormous difficulties [4].
On the surface, electronic voting would seem to offer a solution to these problems. However, despite the many benefits of this technology, few countries have utilized such tools for organizing elections. One of the main concerns is that the technology required is not universally accessible. Moreover, when available, it can prove difficult to understand for certain categories of society, creating a barrier between some citizens and the voting process. The primary obstacle to its adoption, however, is a distrust of what is considered an opaque and manipulable tool. For example, a study [5] focusing on Balkan and Southeastern European countries raised concerns about voter authentication and software reliability, highlighting the challenges of citizen engagement in different international practices.
In the paper, we will distinguish two main approaches to electronic voting:
- E-voting (electronic voting): A voting system that takes place at central polling locations with the same oversight and observer procedures as traditional voting but incorporates technology into one or more of the voting processes. This can include using voting machines for ballot casting, employing machines for vote counting/tabulation, or transmitting polling station results electronically to central tallying locations via the Internet.
- I-voting (internet voting): A remote electronic voting procedure that allows people to cast their votes from any location using personal devices such as computers, smartphones, or other electronic devices, rather than requiring physical presence at a polling station.
The key distinction is that e-voting maintains the traditional polling station structure while adding technological components, whereas i-voting enables remote participation from any location using personal devices.
A worldwide analysis of the current state of voting systems that offer alternatives to paper-based ones would help to identify the barriers and draw the roadmap ahead for a significantly wider usage of more advanced voting systems. The research questions we are facing are the following:
- RQ1
- What is the state of diffusion of electronic voting worldwide?
- RQ2
- What are the determinants of electronic voting adoption?
The aim of this study is to answer these RQs by examining electronic voting around the world. Our major contributions are the following:
- To provide an in-depth examination of electronic voting technologies in various countries, describing the existing systems, their successes, challenges, and evolution globally;
- To provide insights into the current landscape of electronic voting technologies and identify obstacles to their adoption;
- To analyze the relevance of socio-economic indicators as determinants of electronic voting adoption.
While a variety of previous studies have analyzed the adoption of electronic voting systems, these contributions have predominantly focused on single-country case studies, specific regional contexts, or particular technological challenges such as security and verifiability. To date, there is a lack of comprehensive, quantitative analyses that examine how broad socio-economic and political factors correlate with the adoption of both e-voting and i-voting at a global level. This paper aims to fill this gap by leveraging a newly assembled dataset covering all recognized countries and applying machine learning techniques to uncover empirical patterns and predictive determinants of electronic voting adoption. In doing so, we contribute to the literature by providing a global, data-driven perspective on the interplay between technological infrastructure, governance quality, and voting system modernization.
2. Related Literature
We can divide the literature concerning e-voting into three streams. One stream includes those papers proposing or assessing new voting technologies. A second stream is devoted to reporting the state of voting technology adoption in one or several countries. The third stream consists of survey papers about technology adoption that take a wider view, examining, e.g., a continent or the whole world. We will examine the papers belonging to the second stream in the next section, whereas this section will focus on reviewing the survey papers about electronic voting adoption and the technology-related papers.
A number of reviews have already been conducted on the subject. Nonetheless, some of them are either outdated or focused on specific aspects or countries. We subdivide the existing literature into two groups, adopting, as convention, a time threshold spanning back ten years from the present (i.e., before and after 2014).
In 2007, Krimmer conducted a study to review remote electronic voting options in elections [6]. The study analyzed factors such as technology, election size, and providers to understand the current status and potential for widespread adoption. Similarly, in the same year, Wang reviewed electronic voting technology, with a focus on security and voter trust [7]. The study summarized security requirements, reviewed existing systems, and explored usability and cryptographic tools, serving as an introduction for e-voting researchers. Four years later, in 2011, Kumar et al. analyzed the electronic voting situation in various countries at the time, including whether a paper trail was used for auditing, how blank votes were treated, and whether the type of software used was proprietary or not [8].
In the last ten years, a book by Hao et al. was devoted to a comprehensive analysis of various voting systems in different countries [9]. Gibson et al. conducted a detailed analysis in 2016, providing a historical introduction and discussing technical issues related to online voting. The authors also analyzed the current status of electronic voting worldwide, including countries where it is being considered, on trial, implemented, or discontinued [10]. Given that both of these reviews were conducted in 2016, they may not be entirely representative of the current situation in certain countries. A more recent study has been published on the different electronic voting technologies, with evidence from Estonia, Brazil, India, Namibia, and the USA [11]. Another review by Adekunle et al. examines the literature on electronic voting systems and focuses on the experiences of the Netherlands, USA, India, Switzerland, Estonia, Namibia, Brazil, and Nigeria [12]. As can be seen, no recent review has provided a global overview, but rather a few countries at best.
We can now consider the papers describing the different technologies involved in electronic voting. Though we have thus far talked about electronic voting in general terms, at this point, we make a distinction, already mentioned in the introduction, that we will keep throughout the paper between electronic voting in a narrower way (e-voting) and internet voting (i-voting). We draw on the definitions reported by [13]. E-voting takes place at central polling locations in the same manner as for traditional voting procedures, with observers overlooking the process. Contrary to traditional paper voting, e-voting involves using technology in any of the following processes:
- Ballot casting, when technology is introduced for casting the vote through voting machines;
- Tabulation, when machines are used in the counting process;
- Transmission, when voting operations are conducted traditionally but the results of polling stations are sent via the Internet to the central tallying location.
Instead, i-voting consists of a remote electronic voting procedure, where people vote from their location, using computers, smartphones, or other devices to cast their vote.
Regarding the devices employed in e-voting, we can identify three major approaches: using ballot marking devices that produce a printout, machines that require touching a key or touchscreen to record the vote without producing a printout, or optical scanners. Examples of the first kind have been reported in the USA, Argentina, Venezuela, Albania, Belgium, Bulgaria, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Namibia, and India. Machines that do not produce a printout have been reported in Brazil, Paraguay, and Bhutan. Finally, optical scanners have been employed in Iraq, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, and the Philippines.
Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) may have buttons to press or a touch screen through which the voter can select the candidate he or she wishes to vote for. Some of these machines also produce a paper record of the vote for audit or verification purposes [14,15]. They were compared against traditional procedures in [16]. Some of their security issues were highlighted in [17,18]. Other machines are capable of scanning the content of a ballot filled in by the voter [19]. EVMs can be connected to a network (incorporating the Transmission function) or, as is most often the case, operate as standalone systems, releasing at the end of the ballot an indication of the votes received by the individual machine.
Another recent technology that offers security guarantees and impacts the transmission of votes is blockchain. Abuidris et al. reviewed blockchain-based e-voting systems and the requirements that such a system should have [20]. A similar review, which identifies challenges and suggests future research topics to enhance system reliability, has been published in [21]. In addition, a systematic literature review by [22] further explores this field, offering an in-depth mapping of blockchain components, consensus mechanisms, cryptographic algorithms, and implementation challenges, highlighting the need for real-world testing and legal compliance. This technology has the potential to enhance transparency and security in sensitive operations if used in e-government [23]. However, the transparency of the blockchain implies that all transactions are visible to all participants in the network. In an electronic voting system, this could compromise the secrecy of voting, a fundamental principle of democratic elections. It is therefore crucial to maintain voter privacy, yet blockchain, by its nature, makes it difficult to ensure that votes cannot be traced back to voters. Consequently, an implementation of blockchain that can guarantee democratic principles and voter rights should be engineered. The opportunity of applying this technology to e-voting and its adaptation to the voting context has been discussed by [24]. Furthermore, a comprehensive and updated review by [25] offers an extensive survey of both blockchain-based and traditional e-voting systems, highlighting their fundamental properties, implementation approaches, and known vulnerabilities. This text focuses on the classification of cyberattacks and the associated challenges, particularly with regard to ensuring properties such as verifiability, coercion resistance, and software independence. The latter refers to the ability of a voting system to ensure that errors or malicious modifications in the software cannot lead to undetectable alterations of the election outcome.
I-voting is typically accomplished by either using a website or a mobile application. In the case of a website, voters must log in, sometimes authenticating with an ID or special pin, and cast their vote [26]. This approach has been employed, e.g., in Panama, Ecuador, Mexico, France, Armenia, Australia, Canada, Estonia, Norway, and Switzerland. In some cases, the use of a website may be limited to uploading scanned documents and ballot papers, as reported in New Zealand, where voters are required to download voting papers before uploading scanned copies of their ballot and supporting documents to a designated website [27]. The use of a mobile application has instead been reported in the Sultanate of Oman and the United Arab Emirates. That app also includes a feature for voter face recognition [28,29].
Contribution of This paper compared with prior work: The existing literature on electronic voting can be broadly grouped into three streams: studies proposing or assessing specific technologies, analyses focused on adoption within individual countries or regions, and survey works examining adoption trends from a broader perspective. However, most prior contributions are either dated, region-specific, or limited to qualitative assessments. Notably, comprehensive, up-to-date quantitative studies at the global scale—especially those employing machine learning techniques to predict adoption—remain scarce. This paper contributes to closing this gap by (i) providing a global and recent dataset integrating socio-economic and political factors; (ii) offering a comparative analysis across all countries rather than limited case studies; and (iii) applying predictive models (decision trees and random forests) to systematically assess which features most influence e-voting and i-voting adoption. This multi-faceted contribution advances the field by combining data-driven insights with global coverage, an approach not yet fully explored in prior publications.
3. Worldwide Adoption of E-Voting and I-Voting
In this section, we provide a global view of the current state of advanced voting technologies. Based on the data on the introduction of e-voting and i-voting provided by the International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance (International IDEA), an intergovernmental organization based in Stockholm [30], we have carried out a bibliographic survey in various countries. We first show an overall view and then focus on e-voting and i-voting, respectively, using a continent-by-continent approach.
3.1. Overall View
According to the IDEA survey mentioned above, 36 nations worldwide have opted to integrate information technology into the electoral process.
The commonest approach, adopted by 20 countries, involves deploying electronic voting machines (EVMs) in polling stations in a controlled environment (i.e., e-voting). These machines permit voters to pick their desired candidates either by pushing buttons or utilizing the touch screen. The voting machine records the vote for counting purposes and, in most cases, also produces a paper ballot for verification purposes. Typically, these machines are not interconnected or connected to a central server.
Conversely, 16 countries have adopted i-voting. This system permits certain groups of citizens (or, in some cases, all those eligible to vote) to cast their ballots from their own devices without physically attending a polling station.
In Figure 1, we can observe a balance between e- and i-voting in North America, while e-voting is widely adopted in South America. The European continent is predominantly anchored to the old paper system, with some exceptions using i-voting technologies. Only two cases of e-voting implementation have been reported on the African continent, while voting is still paper-based in the rest of the world. In Asia, some countries use e-voting, while i-voting is adopted in Russia. In Oceania, we find Australia and New Zealand using i-voting.
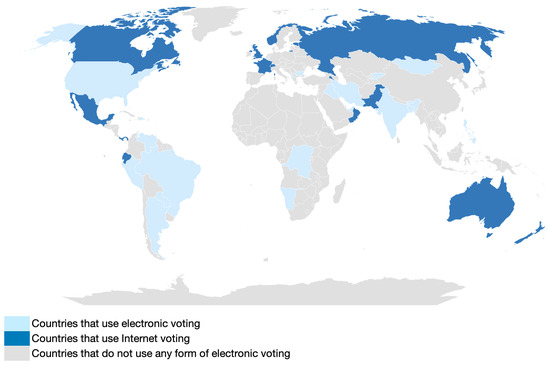
Figure 1.
Worldwide use of e-voting and i-voting.
In order to provide a comprehensive overview of the global adoption of e-voting technologies, we present below a summary of the Democracy Index 2024. The Democracy Index is a comprehensive measure of the democratic health of countries around the world. The index is predicated on five key dimensions: electoral process and pluralism, government functionality, political participation, political culture, and civil liberties.
The Democracy Index data is sourced from the Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), part of The Economist Group. Socio-economic indicators—including GDP, population, surface area, and Internet usage—are derived from the most recent available World Bank datasets at 1 July 2025. The present study utilized these indicators within a model to explore the correlations with the adoption of electronic and internet voting systems. The full dataset is available from the URL https://bit.ly/eVotingDataset2025.
The complete classification is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Global dataset on democracy, socio-economic indicators, and the adoption of electronic voting technologies.
3.2. E-Voting Adoption
E-voting is the method adopted by most countries. In this section, we report the information available for each country, arranged by continent.
3.2.1. North and Central America
Although the United States of America is a technologically advanced country, electronic voting presents a complex situation. The majority of Americans use paper ballots to cast their votes. Voters typically mark the ballots by hand. However, in some scenarios, voters use a "ballot marking device" to select their preference, which then generates a printout for submission. The reliance on digital technology for voting has varied throughout the years. Paperless electronic voting has become less popular since the mid-2000s. States have opted for paper as a more secure means of monitoring elections and detecting potential vote tampering. Even with paper ballots, machines remain essential to the electoral process, since optical scan tabulators are employed to count the results.
Concerns about paperless voting among election officials and the public had been circulating since the early 2000s. These concerns became heightened during the 2016 presidential election, which marked a turning point in the history of America’s voting machines. In that year, Russia attempted to use social media campaigns to manipulate the election, and Russian hackers also scanned the voter registration systems in search of vulnerabilities to collect information on American voters [31,32]. Government investigations revealed no evidence that election results had been tampered with, but officials are now recognizing the importance of securing election outcomes in the event that electronic machines are breached. Furthermore, a significant event took place during the 2020 elections in Georgia: the state had been using paperless voting machines for several years, but shortly before the election, it replaced them with machines that electronically record selections and print a paper ballot. Donald Trump contested the election results and alleged widespread irregularities and fraud. As paper ballots were used, election officials in Georgia were able to manually count the votes and verify that Biden had won the state [33]. This demonstrates the critical role that paper ballots play in ensuring election integrity and public confidence [34]. In the 2024 elections, minor issues have been reported with electronic voting. These include delays in Milwaukee due to misconfigured tabulation machines and thousands of mail-in ballots in Nevada that were flagged for signature mismatches or missing signatures, causing processing delays [35].
Aside from the U.S.A., a single case of e-voting use has been reported in North America. Elections were held in the Dominican Republic in February 2020 using electronic voting machines. However, major problems arose. During the polls, voting procedures were suspended for three hours because 50 percent of the polling places using electronic ballot machines reported problems [36].
3.2.2. South America
Four countries in South America have adopted e-voting: Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Venezuela.
In Argentina, electronic voting systems have been in operation since 2009. Voters are required to insert a blank paper ballot into a machine to cast their vote. They must select their preference on a touch screen, and then the preference is recorded both physically on the ballot and on an RFID chip. The voter can then remove the ballot and place it in the ballot box. The machine does not retain the votes cast, but the counting is performed later using a scanner [37]. During the recent elections in August 2023, there were some disputes due to malfunctions in some machines, estimated to be 240, which accounts for 2.4% of the total [38]. The malfunction resulted in delays and multiple complaints.
Brazil was among the leading nations in the adoption of electronic voting. The decision to adopt electronic voting was made due to numerous cases of fraud and a high illiteracy rate. Since 1994, EVMs have been implemented, with 35 million voters, i.e., 33% of the population, already utilizing them during the 1996 elections. Electronic voting in Brazil has been conducted in all polling stations since 2000, with no major issues reported [39]. With the use of EVMs, Brazilian voters need only enter their candidate’s number to cast their ballot. The electronic voting machines utilized in Brazil do not have network hardware but require a connection to a computer for the transmission of results to the national authority responsible for counting. No paper record is generated. Overall, Brazilians express satisfaction with the system, and no instances of fraud or significant issues have been reported [40]. Furthermore, a study indicated that if internet voting were to be implemented in Brazil, this would lead to an 8.9% increase in voter turnout [41].
In Paraguay, electronic ballot boxes were used for the first time in the country during the municipal elections on 18 November 2001. At first, the model seemed successful, even capable of being exported to Ecuador. In 2006, however, accusations of fraud emerged. The absence of a paper trail to recount votes in the electoral system created numerous controversies, resulting in the return to traditional paper voting methods in 2008. After the pandemic and subsequent restoration of faith in electronic tools, electronic voting machines were finally reintroduced in a political election in Paraguay in 2021 [42].
Venezuela has been holding elections since 2004 by using machines that print out ballot papers to be placed in ballot boxes. In 2012, biometric authentication using fingerprint recognition was also introduced. From the outset, electronic elections have raised doubts among politicians, academics, and the population, even though the governments of Hugo Chávez and Nicolás Maduro have called the system ’the most perfect electoral system in the world’ [43].
3.2.3. Europe
In Albania, Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) with touch screens using Android were deployed in the parliamentary elections held in April 2021 and some municipal elections held in March 2022 [44]. Following the casting of each ballot, the machines generated a paper copy for verification purposes, and at the end of the elections, the machines tallied the results at the individual polling stations. Based on the turnout figures, technology did not appear to present any significant obstacles to participation. In terms of invalid ballots, only those intentionally left blank by the voter were reduced. There were no significant technical issues noted during the process, but it is worth mentioning that the system was purposefully designed to prevent any connection to the internet.
In Belgium, an experiment with electronic voting using EVMs was initiated in 1991, with successful outcomes leading to implementation in 1994. By 2014, 44% of voters were able to cast their votes electronically, representing a significant increase from the initial 20%. Several issues arose during the past elections. In 2003, a candidate received over 4,000 additional preferences in the municipality of Schaerbeek, and in 2004, a defective floppy disk caused problems during counting. Additionally, a software malfunction in 2014 resulted in the loss of 2,240 votes. Therefore, from 2015 onward, some regions in Belgium opted to discontinue electronic voting, while others chose to upgrade their systems by incorporating the feature of producing a paper trail. Belgian concerns with electronic voting are strengthened by studies revealing lower voter turnout in cantons that adopt e-voting compared with those that use traditional paper voting methods [45].
In Bulgaria, electronic voting was recently implemented following a 2015 referendum in which 72.79% of voters opted for e-voting. A hybrid EVM model that prints a paper ballot and has no direct connection to central systems was selected [46]. Nonetheless, there is ongoing debate about introducing a remote voting system, similar to the one used in Estonia [47].
3.2.4. Africa
Namibia was the first African country to successfully implement e-voting in 2014. The introduction of electronic voting machines in Namibia began with the implementation of the Electoral Act in 2009. The purpose of this act was to facilitate the eventual use of EVMs in the country’s elections. This initiative gained momentum due to issues encountered during the counting and tabulation procedures in the 2009 elections, causing a postponement of the announcement of the outcome. In the Namibian case, a pair of devices is employed, provided by India, and tailored to meet the legal prerequisites of Namibia. The voter operates the Ballot Unit while the Presiding/Electoral Officer handles the Control Unit. The Ballot Unit has a button for each potential candidate and can hold up to fifteen candidates, although as many as four units can be networked with a cable to accommodate a total of sixty candidates. It should be noted that EVMs function independently and are not linked to any computer network. The devices neither transmit nor receive signals and operate on batteries, thus eliminating the need for electricity. To transfer the records, they should be connected to a laptop. The machine provides a paper audit trail as a verification system in case of a vote recount [48,49].
The Democratic Republic of Congo implemented EVMs in 2018 with a touch screen and paper trail. Nevertheless, the system’s implementation raised numerous cybersecurity concerns due to inadequate testing. These concerns include threats to ballot secrecy and the potential for results manipulation [50,51,52].
3.2.5. Asia
In Bhutan, electronic voting machines have been employed to conduct elections. These machines feature physical buttons and display a tally after the election. Again, there is no internet connection for the final transmission of outcomes [53,54].
India has utilized electronic voting in its political elections. Being the world’s largest democracy, India has a voting population of 814 million. The Election Commission of India implemented the EVM for vote recording, storage, and counting. Despite early trial runs commencing in 1982, electronic voting was only implemented nationwide in the year 2004. Initially, the e-voting system in India consisted of two components: the voting machine, which is positioned in the polling booth, and the control unit, which is kept under the supervision of the polling officer. Since the 2014 elections, the use of an additional machine alongside the voting machine allows for the printing of ballot papers, which can be manually counted if desired. All the electronic voting equipment operates independently of both the internet and the electricity supply [55]. The Indian development and implementation of EVMs in elections is considered a noteworthy achievement for global democracy. Indian experts argued that the process would enhance inclusion, which has traditionally been impeded by the high percentage of illiterate voters. Additionally, cost savings were a driving force. The government developed this system, comprising simple units, produced for less than $300 per unit. This price is significantly lower than the cost of other electronic voting equipment, which typically ranges from $3000 to $6000 per unit and offers more advanced features. Despite the low cost, Indian authorities take pride in their electronic voting machines, describing them as one of the most secure and tamper-proof systems available [39].
The Islamic Republic of Iran established an electronic voting system in preparation for the June 2021 elections for use in both presidential and city/village council elections. However, plans to implement the electronic voting machines in the upcoming presidential election have been suspended by Iran’s Interior Ministry and the Guardian Council. While electronic voting has been utilized for city and village council elections, the traditional paper ballot has been retained for the presidential elections. As a result, voters were obliged to use two distinct systems on the same day [56,57].
In Iraq, electronic systems have been utilized since the elections in May 2018. While voters are required to vote using a paper ballot, an electronic verification, counting, and transmission system has been implemented. To verify their identity, voters use a ’Voter Verification Device’ to provide their fingerprints, along with a QR code found on the paper ballot. To cast their ballot, a ’Polling Centre Optical Scanner’ is employed. The ballot paper issued to voters is verified by the system via QR code matching. The system then reads the ballot paper to determine if the vote has been marked correctly and is thus deemed valid or invalid. The vote is recorded and transmitted to a ’Result Transmission System’ connected to the scanner, which transmits the results via satellite link. During the May 2018 elections, disputes arose regarding the system, leading to a manual counting of the votes. The machines were provided by a South Korean company, and the Iraqi Election Commission disregarded warnings from an anti-corruption organization regarding the reliability of the digital vote tabulation devices utilized in the elections. Nonetheless, the method was also employed in subsequent elections [58,59].
Electronic voting was introduced in Kyrgyzstan in 2016 to ensure impartial elections following numerous violent political uprisings in the post-communist era, which led to fraud and vote buying. E-voting was first utilized during the 2016 local elections carried out by the Osh City Council, and the voting process was carried out through optical scanning of ballots. Although no technical problems were reported, one study found that e-voting contributed to the continuance, adaptation, and reinforcement of existing methods of electoral fraud, thus failing to solve the problems for which e-voting had been introduced [60]. After this trial, despite the suspicion of fraud, the electronic voting system was further utilized in subsequent parliamentary elections [61].
Mongolia implemented an electronic voting system for the first time in the 2012 parliamentary election to regain the public’s confidence, which was eroded by the violent demonstrations following the 2008 parliamentary election outcomes. Polling stations have electronic vote-counting equipment to scan and count ballots. Results are verified through a manual vote count conducted in up to 50% of randomly selected polling stations [62,63].
The Philippines first applied electronic voting in the 2010 elections, even though the first pilot programs date back to 1996. The system was based on optical recognition. Voters arrived at the polling station and were issued a ballot paper, on which they indicated their choice. When the polling station closed, the votes were scanned by machines, and a report was printed detailing the number of votes for each candidate. The result sheets were then sent to the tabulation office at the city or district level [55,64].
3.3. I-Voting Adoption for Special Classes of Citizens
A number of countries utilize i-voting, but only for certain categories of citizens, mainly those living abroad. Sometimes, the voting systems involved are not sophisticated enough and do not address even the most basic cybersecurity issues. It might be the case that these systems are used without particular concern, given that they are directed at a minority of citizens.
In Table 2, we report the countries adopting selective admission to i-voting and the categories admitted.

Table 2.
Categories of people with access to internet voting in some countries.
In this section, we survey the specific conditions, again by continent.
3.3.1. North America
During the 2019 elections in Panama, the Electoral Tribunal (TE) offered the 7674 Panamanians registered to vote abroad the opportunity to cast their ballots via the Internet. Subsequently, the Electoral Voting Corporation printed the votes cast via the internet and deposited them in an acrylic ballot box in a public place, then proceeded to count the votes [65].
3.3.2. South America
Ecuador allows online voting for citizens residing abroad. Notably, during the recent election on 20 August 2023, the National Electoral Council president, Diana Atamaint, disclosed that the electronic voting system employed by Ecuadorians residing abroad had been the subject of numerous cyberattacks, including some originating from China, India, and Bangladesh. Nevertheless, she stated that these events had not compromised the vote count [66].
In Mexico, the National Electoral Institute (INE) was authorized to utilize electronic voting for overseas voters, thus circumventing the cumbersome postal system. The Independent National Electoral Commission (INE) commenced the development of a secure internet-based voting framework with dual-factor verification in 2018. The system underwent verification and received approval from two independent entities as required by law in late 2020, and it was first utilized in local elections in 2021. Votes can be cast via a website, and voters should authenticate themselves using their telephone [67,68].
3.3.3. Europe
During the last legislative elections held on 27 May 2022 in France, French citizens residing outside the country were offered multiple voting options. These included casting their vote in person, through a proxy, by mail, or via the Internet. The adoption of digital voting, backed by the Ministry for Europe and Foreign Affairs in France, formed part of a significant endeavor to enhance the engagement of the 1.444 million overseas voters enlisted on the consular electoral rolls [69].
The situation in the United Kingdom is peculiar and has been considered worthy of inclusion in this section due to its impact on the democratic process. Even though experiments have been carried out in the past [70,71], electronic voting has not been employed in general elections. However, although remote voting is not possible in elections for general citizens, the House of Lords has introduced the option for Lords to participate in parliamentary proceedings through remote voting in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. This measure was taken to prevent the suspension of regular operations. The House of Lords implemented an online voting system from 15 June 2020 until September 2021. Today, members are still able to cast their votes online, but only if they are physically present on the parliamentary estate [72].
3.3.4. Asia
Armenia implemented internet voting in 2011, enabling diplomatic personnel and their families and the representatives of Armenian-registered corporations deployed overseas to vote. In 2016, under the new Electoral Code, internet voting rights were also granted to military personnel studying or serving abroad. In the 2021 election, a total of 2,595,512 registered votes were tallied, with only 500 cast via the Internet from overseas. As such, they do not hold significant weight [73,74].
In the Sultanate of Oman, all voting processes are digital, with citizens able to register as voters online but voting in person. Overseas citizens have been able to cast their votes through a mobile application since 2019 [75,76].
3.3.5. Oceania
Electronic voting has been implemented in some polling places in Australia, enabling voters to cast their ballot on locally connected computers. Since 2011, New South Wales has utilized a system known as iVote, which enables remote voting over the Internet or by telephone during state elections. In the 2015 election, individuals with disabilities, the visually impaired, and those living over 20 kilometers from their nearest polling station, including those residing overseas or in another Australian state or territory, were afforded the option of registering their vote online via a web browser. A total of 283,669 individuals successfully used the iVote system; nonetheless, some issues were identified. Specifically, two parties were not listed on the electronic ballot paper for the New South Wales Legislative Council, and a higher-than-expected number of voters chose to submit a "donkey vote" compared with the traditional paper ballot. In ranked voting electoral systems, a donkey vote refers to a cast ballot where the candidates are ranked based on the order of appearance on the ballot. Additionally, two academics claimed to have identified a security issue with the system. The New South Wales Electoral Commission has stated that iVote will continue to replace postal, interstate, and overseas voting. At present, however, there are no intentions to substitute the standard paper-based voting system [77].
New Zealand allows citizens residing abroad to vote online. They need to download and print a declaration paper along with the ballot paper. The declaration paper must be signed in the presence of a witness. After completing and signing the declaration and casting the vote, the documents must be scanned or photographed using a smartphone and then uploaded to a government website. Blind or partially sighted people, or those with physical disabilities that prevent them from marking their voting paper without assistance, are eligible to vote by telephone dictation [27].
3.4. I-Voting Adoption for All Citizens
Some countries have implemented the option for citizens to cast their votes online, eliminating the need to physically attend polling stations for all citizens. In this section, we review those countries that allow generalized i-voting, adopting the same continent-by-continent approach.
3.4.1. North America
Canada appears as the only country in North America that allows i-voting with no restrictions. In particular, online voting is possible in the provinces of Ontario and Nova Scotia. Ontario, which makes up approximately 1.51 million voters (16% of the country’s voting population), used paperless ballots cast online, either by a website or by telephone. The online voting infrastructure is provided by the Spanish company Scytl Election Technologies. Ontario implemented online voting in 2003 and has since experienced exponential growth, with each successive election cycle nearly doubling the number of online voters. More than 200 municipalities have opted to use online voting in the 2022 elections, up from more than 170 in 2018. Some have completely eliminated paper ballots [78,79].
3.4.2. Europe
Three countries allow for i-voting in Europe: Estonia, Norway, and Switzerland. Germany has also conducted a notable large-scale i-voting pilot, albeit in a non-political context; nonetheless, we consider it relevant to include and examine this case in the present analysis.
Estonia is considered the most advanced country in terms of electronic voting. Since 2005, citizens have been able to vote online, starting with local elections and later expanding to parliamentary elections in 2007. Citizen identification is achieved through an electronic identity card or a specific SIM card assigned to the citizen. Online voting is available from 10 to 4 days before the election. The remaining days are reserved for error-checking and correction. To prevent coercion, voters can change their vote freely until the end of the voting period. In 2013, a private individual applied to the Supreme Court to invalidate the outcome of the 2011 elections, claiming that it was possible to manipulate the voting process through malicious software running on the electors’ devices without their knowledge. However, the court did not find any evidence that this flaw had an impact on the election result. The source code has been released on GitHub, and no vulnerabilities compromising voting security have been found [80]. Over two decades, the Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE/ODIHR) has published final observation reports on Estonian parliamentary elections in 2007, 2011, 2015, 2019, and 2023, issuing numerous recommendations concerning vote secrecy, coercion resistance, and end-to-end verifiability. Some of these recommendations have led to improvements in the system, while others have proven difficult to implement or revealed tensions between transparency, security, and voter privacy [81]. Estonia’s approach to mitigating coercion—by allowing re-voting—has been positively noted, although OSCE/ODIHR raised concerns about timestamp logging and the potential for voters to undermine secrecy themselves by sharing verification data. Despite these challenges, Estonia’s internet voting system has gained increasing popularity and has not experienced any major security incidents to date.
Internet voting has been trialed in Norway since 2011. The first trial was conducted during municipal elections in 2011, followed by another trial in 12 municipalities during the 2013 general elections. Both trials used a system provided by the Spanish company Scytl. Despite this, due to political disagreement, the pilots for internet voting in Norway have been put on hold [82,83,84]. In 2018, Finnmark, the northernmost county in Norway, reintroduced internet voting for a referendum. The Estonian Smartmatic-Cybernetica Centre of Excellence for Internet Voting (SCCEIV) provided the online voting system used in this instance. In 2022, Innlandet, another county in Norway, held a referendum that allowed internet voting, using the SCCEIV system once again [85].
Switzerland has a long history of involvement in i-voting systems, although the relationship has been complicated. Legislative work on electronic voting began in 2000. Since then, over 300 referendums and elections have taken place, with internet voting available in more than 150 municipalities. Switzerland’s political system is highly decentralized due to its federal state structure, and the cantons are responsible for implementing elections and referendums. Geneva, Zurich, and Neuchâtel were the first cantons to experiment with i-voting. To enhance trust in the system, the source code of the voting system has been made publicly available. However, since 2015, pessimism has spread due to the threat of cybercrime, resulting in a withdrawal from the concept of online voting. As a result, online voting has not been available since July 2019 [80,86]. On 26 June 2019, the Federal Council tasked the Federal Chancellery with collaborating with the cantons to redesign the trial phase of e-voting. The aim was to improve the system by providing effective control and oversight, thus increasing transparency and trust. New legislation came into force in 2022, and electronic voting became available again in 2023 [87,88].
Germany piloted an i-voting system during the 2023 Sozialwahlen (Social Elections), one of the largest elections in the European Union, with over 50 million eligible voters. As indicated above, this case differs from the others in that it does not qualify as a political election: the Sozialwahlen are institutional elections that appoint representatives to the self-governing boards of health insurance and pension bodies, without the involvement of political parties or legislative power. Despite being a legally regulated and nationwide electoral process, its nature excludes it from the Council of Europe’s category of political elections. For this reason, while technically significant, it was not included in the charts among the countries officially adopting i-voting for political purposes. Nevertheless, the German 2023 i-voting pilot represents a relevant case study in understanding how online voting has been tested in practice, even if its implementation revealed several critical issues. The system followed an envelope-based protocol inspired by the Estonian model, with modifications including the use of homomorphic encryption and a digital signature surrogate based on a unique voter identifier (WKZ). Although designed as a “model project” and governed by the Federal Ministry of Health, the implementation raised serious concerns. According to [89], the system failed to guarantee key voting principles such as secrecy, individual verifiability, and auditability. The technical configuration allowed, in certain conditions, the reconstruction of voter–vote linkage and did not enable independent recounts or verifications. Furthermore, participation remained low, with only 2.4% to 9.9% of votes cast electronically depending on the institution. These issues have led experts to recommend against its use in any future political elections.
3.4.3. Asia
Two countries have been using i-voting in Asia: the United Arab Emirates and Russia.
The United Arab Emirates has been using e-voting since 2011. Starting with the parliamentary elections in October 2023, citizens can cast their vote at one of the voting centers or through a digital application, which can be run on any device connected to the Internet. Also, in this case, the technical infrastructure was supplied by the Spanish corporation Scytl, as in Norway. Before voters can cast their preference, the digital application conducts a facial identification procedure [90,91,92].
Internet voting was made available in Russia during the 2019 Moscow local elections. Subsequently, by the 2021 parliamentary elections, two novel voting systems were being implemented. A system was created for conducting e-voting in Moscow by the Department of Information Technologies of Moscow and Kaspersky Lab. Additionally, Rostelecom and Waves Enterprise collaborated to develop an e-voting system for six federal districts in Russia. The system’s source code underwent public scrutiny, but the documentation was inadequate. Nevertheless, serious cryptographic issues were identified in the system: researchers identified weaknesses in the password-based authentication process. Additionally, the attack surface is significant since the authentication system is utilized to authenticate users for over 1000 IT systems. Further analysis showed that an adversary could compromise the voting device, which poses a potential threat to the secrecy of the vote, as it is not individually verifiable, and manipulation could go undetected by the voter. Furthermore, the system employs an unconventional approach to generate the encryption key. The preferable approach is to utilize established cryptographic methods instead of introducing a novel key-sharing technique [93]. Online voting was available for the 2024 presidential elections, enabling voters to cast their ballots via an application. On the first day of the election, the system briefly crashed but was promptly restored [94]. Nevertheless, experts suggest that this technology could potentially enable the manipulation of election results in favor of the current President Putin [95].
3.5. E-Voting Abandonment
There are also cases of countries that have experienced e-voting and have decided to abandon it and return to ordinary paper elections. In Table 3, we have categorized the reasons for the abandonment of electronic voting.

Table 3.
Reasons for abandoning electronic voting.
3.5.1. South America
In Colombia, a pilot project was successfully conducted in 2007 and was deemed reliable. The system employed EVMs, which produce a physical paper record [96,97]. Although electronic voting is mandated in the Colombian constitution, additional regulations have been established, and the technology is not currently in use.
In Peru, electronic voting was first implemented in 2011, with 1354 voters participating. In 2018, 1,729,028 people cast their votes, marking the last time electronic voting was used. However, due to citizen perceptions of the system as a black box, mistrust from political organizations, and high maintenance and storage costs, the decision was made to discontinue its use. The ONPE (National Office of Electoral Processes) is currently investigating internet voting systems (votación electrónica no presencial in Spanish), which are already being used for elections by internal organizations such as the Medical College of Peru [98].
3.5.2. Europe
In Iceland, a pilot test was held in the municipality of Ölfus, where an online referendum was held with a 43% participation rate among the residents [99]. Although the experiment was reported as successful, there are currently no plans for electronic voting in Iceland.
In Ireland, electronic voting machines were introduced in 2002, following research that began in 1999. In 2004, plans to extend electronic voting to all polling stations were put on hold due to public opposition and political controversy. Although electoral law was amended in 2001 and 2004, and sufficient voting machines for the entire state were purchased, the plan was officially dropped in 2009 due to a lack of trust and the inability to audit the vote without a paper trail. The machines were subsequently decommissioned, and elections in Ireland continue to use paper ballots [100].
The situation in Italy is currently in a state of flux. In 2017, a pilot experiment was conducted during a referendum in the Lombardy region. The results were deemed unsatisfactory due to the approach used: the votes were transferred to pen drives, which were physically taken to the processing center. Unfortunately, some of the pen drives were found to be faulty upon arrival, leading to mishaps and the subsequent abandonment of this system [101,102,103]. Currently, electronic voting is not available in Italy. Efforts are being made to develop a system that enables remote voting for citizens living abroad: a trial was conducted in December 2023 to evaluate the performance of a dedicated portal [104].
3.5.3. Asia
In Bangladesh, electronic voting machines were used in 2011. EVMs allowed voters to press a button associated with their preferred candidate. The votes were recorded in the machine and could be counted electronically. These machines were not connected to the internet. In 2018, newer models of the machines were installed, incorporating fingerprint and National Identification Number scanners [105]. Unfortunately, serious issues with the supply of new equipment have resulted in Bangladesh abandoning e-voting for the 2023 elections [106].
Pakistan introduced e-voting through electronic voting machines in 2021, but the decision was reversed in 2022. After their 2018 election victory, Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (Pakistan Movement for Justice) pledged to tackle the longstanding issues of distrust within Pakistani politics. They drafted a contentious bill featuring a substantial range of revisions to the 2017 Election Act. Not only would the implementation of Electronic Voting Machines formalize the voting process, but it would also provide for the extension of voting rights to Pakistani citizens residing abroad via an online voting system. This has been a longstanding demand and topic of discussion. Pakistan’s own electronic voting machine was created and utilized during the 2021 elections. However, in 2022, the newly elected government swiftly passed the Election Amendments Bill, which overturned the implementation of EVMs and reinstated traditional voting methods [107].
3.6. Security Measures Overview
While several studies have addressed the technical design of electronic and internet voting systems, a consolidated view of the security mechanisms actually adopted across countries remains essential. To address this, Table 4 summarizes key security features—such as authentication methods, presence of paper trails, and internet connectivity—implemented in each country currently using e-voting or i-voting systems. The table also highlights general notes about implementation choices or known limitations, providing a practical overview of the current global security landscape in electoral technology.

Table 4.
Security measures adopted in countries using e-voting or i-voting.
4. Determinants of Electronic Voting Adoption
In the previous sections, we have surveyed the countries worldwide, pinpointing those nations that have adopted electronic voting and their degree of adoption. The RQ we now face is, "Are there some characteristics of those countries that render them more willing to adopt some form of electronic voting?" In this section, we will try to answer that question. To this end, we will first suggest some indicators that may serve as determinants of electronic voting adoption. We will then examine the value of those indicators for the countries adopting electronic voting and provide a machine-learning model to extract the most useful indicators to predict adoption.
As possible determinants of electronic voting adoption, we have chosen the following characteristics of countries:
- Surface;
- Population;
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP);
- Democracy Index;
- Internet usage.
The dataset used in this study includes all recognized countries worldwide, ensuring comprehensive coverage without the need for sampling. Each country is characterized by the five key socio-economic features mentioned above: surface area, population size, GDP per capita, Democracy Index, and Internet Usage, with data sourced from the most recent releases of the World Bank and the Economist Intelligence Unit. Additionally, the percentage of Internet users was included to capture technological readiness. The target variable categorizes countries into three classes: no adoption, e-voting adoption, and i-voting adoption, based on an established international survey. Prior to model training, the data was randomly divided into training and testing sets using an 80-20 split. Given the structured nature of the dataset and the absence of missing values, no further preprocessing steps such as normalization, standardization, or imputation were necessary. The Gini index was employed as the splitting criterion in the decision tree and random forest models applied in the analysis.
The surface of a country may play a role in introducing electronic voting, as movements to reach polling stations may be more significant for larger countries and lead to greater abstention from voting. By removing the need to reach a possibly distant polling station, electronic voting may be chosen to increase the level of participation in elections.
Instead, another indicator of a country’s size, i.e., its population, is more controversial. Could we guess that larger countries have more incentives to adopt electronic voting than smaller ones? Although larger countries can rely on larger infrastructures, creating an electronic voting infrastructure is certainly easier for smaller countries due to the scale of the enterprise. Nevertheless, we have included it as a potential candidate.
The level of wealth, as embodied by the GDP, may also be associated with voting tool choices. Electronic voting adoption relies on the widespread use of electronic devices and the internet, which are typically associated with a country’s wealth [108].
Finally, the intertwining of electronic voting and democracy has long been supported in the literature. Several positive factors of influence of ICT-aided elections on democracy have been listed by [109]. The other way round, i.e., if established democracies may be expected to be early adopters of electronic voting, has been considered by [10], who found the relationship not to be so sharp. For the purpose of measuring the level of democracy, we have considered the Democracy Index, which is published annually by the Economist Intelligence Unit, part of the Economist Group. The Democracy Index is based on five categories: electoral process and pluralism, the functioning of government, political participation, political culture, and civil liberties. Each country is then classified as one of four types of regime based on its scores on a range of indicators within those categories: full democracy, flawed democracy, hybrid regime, and authoritarian regime [110]. We used Internet usage data, also from the World Bank, that directly relates to the digital readiness of a country’s population, especially relevant for Internet voting (i-voting). These features were selected to balance economic capacity, technological readiness, and political context, as supported by prior literature and empirical analysis in the study [10,108,109].
To understand the importance of each indicator, we first plot the boxplot for each category of voting adoption, i.e., no adoption of electronic voting, adoption of e-voting, and adoption of i-voting. The boxplots have been plotted with the first and third quartiles as box boundaries and the (Inter-Quartile Range) values for the whiskers. We have used 2021 data for all the indicators, except the Democracy Index, for which we have used 2022 data.
We start by considering the impact of the country’s surface. As hinted above, a larger surface should be a positive factor for the adoption of electronic voting. Actually, in Figure 2, we see that the presence of countries with a larger surface grows as we progress from the non-adoption case to the most advanced i-voting case. This appears to confirm our hypothesis when including the surface as a determinant for electronic voting adoption.
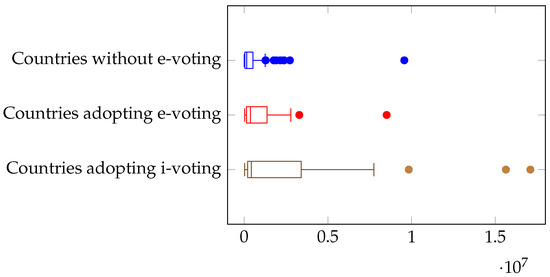
Figure 2.
Electronic voting and country surface.
We now turn to the country’s population, shown in Figure 3. We see very close medians and a slightly growing third quartile as we progress from no e-voting to e-voting and i-voting. We have, therefore, a mild confirmation of the role of population as a factor in electronic voting adoption.
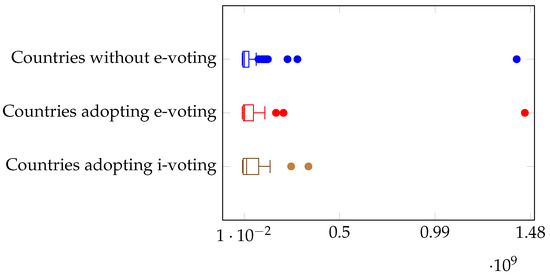
Figure 3.
Electronic voting and population.
The degree of wealth plays a different role. In Figure 4, we see that there is a significant difference in the medians between countries adopting the most advanced i-voting system and the others. Richer countries are readier to adopt i-voting. However, this is just partly confirmed for countries adopting e-voting, which belong to a lower range of GDP values. It would seem that greater wealth leads to more advanced forms of voting, skipping the intermediate step of having some form of electronic voting without taking full advantage of online procedures.
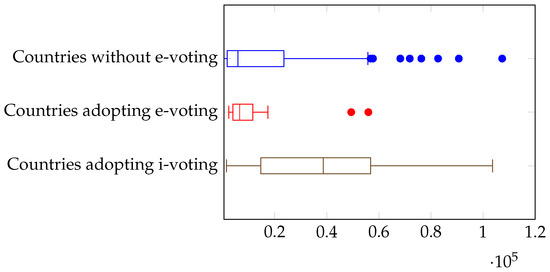
Figure 4.
Electronic voting and GDP per capita.
We finally turn to the impact of the democracy index, which is shown in Figure 5, and the Internet usage, shown in Figure 6. Here, we can observe a behavior similar to that for GDP. The boxplots for countries that do not adopt any form of electronic voting and those that adopt e-voting are largely overlapping, especially in Figure 5. Instead, countries adopting i-voting exhibit larger values of the democracy index and the Internet usage. It should be noted that there is no leakage effect, since the way the vote is collected and processed is not taken into account in the determination of the democracy index. We can conclude here that countries with higher levels of democracy are more willing to embrace advanced forms of electronic voting (namely, i-voting).
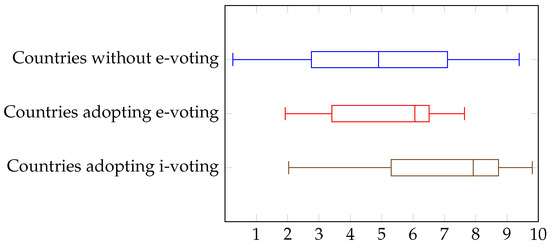
Figure 5.
Electronic voting and democracy index.
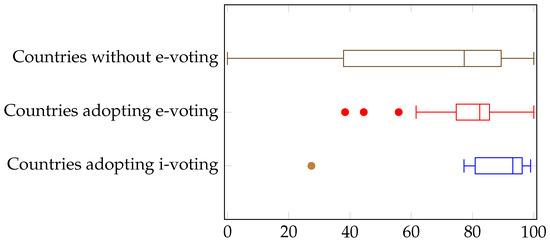
Figure 6.
Electronic voting and Internet usage.
So far, we have considered the relevance of each indicator individually. We now consider the full set of indicators and see if their joint use may help determine a country’s willingness to adopt electronic voting. For that purpose, we resort to machine learning. Following this approach, we consider the four indicators as features and the adoption of electronic voting as our target variable. The prediction of electronic voting is then a classification task. As a prediction tool, we adopt a decision tree due to its simplicity and explainability, which would allow us to understand the relative importance of the indicators in determining the electronic voting stance of a country.
Decision tree methodology [111] is a supervised machine learning technique used for both classification and regression tasks. It works by recursively splitting the dataset into subsets based on feature values, creating a tree-like structure where each internal node represents a decision rule on a feature, each branch represents an outcome of the rule, and each leaf node represents a predicted class or value. The goal is to partition the data in a way that maximizes the separation of classes (in classification) or minimizes prediction error (in regression) at each step. Decision trees are popular due to their interpretability and simplicity, as they closely mimic human decision-making processes. However, they can be prone to overfitting, which is often mitigated through techniques like pruning, limiting tree depth, or using ensemble methods such as random forests.
In addition, the low number of features does not warrant the use of a more sophisticated prediction algorithm, e.g., based on a deep learning network. When building the decision tree, the Gini index has been used to decide the sequence of features and the splitting rules [112]. The subdivision of the dataset into a training and a testing portion has been made randomly with an 80-20 split.
We follow two different mechanisms for prediction:
- A three-class classifier;
- A cascade of two-class classifiers.
In the first mechanism, the three classes to predict are, respectively, non-adoption, e-voting adoption, and i-voting adoption. Alternatively, we first use a two-class classifier that discriminates solely between adoption and non-adoption, where adoption is meant as including either form of electronic voting. The instances classified as adopting electronic voting are then further processed by another two-class classifier that discriminates between e-voting and i-voting.
We consider a dataset consisting of the full set of countries in the world (hence, there is no sampling, as the dataset represents the full population). The labels have been assigned according to the survey we have described in the first part of this paper.
We report first the results obtained with our three-class classifier. In Figure 7, we show the resulting decision tree. The classification outputs reported in that picture pertain to the training dataset. As in any decision tree, the features employed at the root of the tree are likely to be the most relevant ones. In this case, that role is taken by the democracy index, which can be deemed as the most seminal feature in determining the willingness to adopt electronic voting or not. The accuracy is 0.735, which is significantly above a random classifier (which would achieve an accuracy of 0.333, as we have three classes).
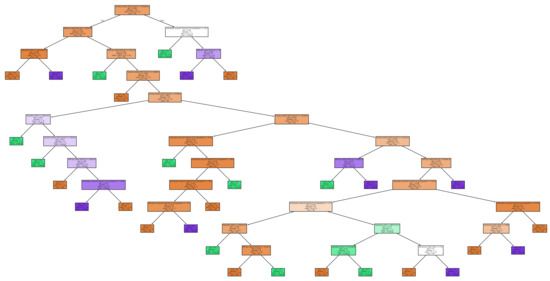
Figure 7.
The three-class decision tree.
Nonetheless, we can extend the decision tree approach and hopefully enhance the performance by turning to ensemble learning and using a random forest, i.e., a collection of trees.
Random forests [113] are an ensemble machine learning method that combines the predictions of multiple decision trees to improve accuracy and reduce overfitting. Each tree in the forest is trained on a random subset of the data (using bootstrap sampling) and, at each split, considers a random subset of features rather than all available features. This randomness introduces diversity among the individual trees, making the overall model more robust and less prone to the noise or biases present in a single decision tree. For classification tasks, the final prediction is typically made by majority voting among the trees, while for regression tasks, it is computed as the average of their outputs. Random forests are widely used because they generally provide high predictive performance with minimal parameter tuning and retain some interpretability through feature importance measures.
We have built 100 trees, adopting a majority voting rule to obtain the final classification. The passage to a random forest, although entailing that we lose some degree of explainability, is a boost for performance, as the accuracy jumps to 0.794.
In the cascade of two two-class classifiers, we can first look at the classifier discriminating between non-adoption and adoption of either e- or i-voting. In Figure 8, we see the resulting decision tree for this first stage. The accuracy of this first-stage classification is 0.705. A major difference with the three-class classifier is that now the country surface appears as the feature at the root of the tree. In the image shown, the single labels are not readable, but we display them to help illustrate the complexity of the resulting decision tree. A full-size, readable figure can be downloaded from the URL https://bit.ly/eVotingDecisionTrees2025.
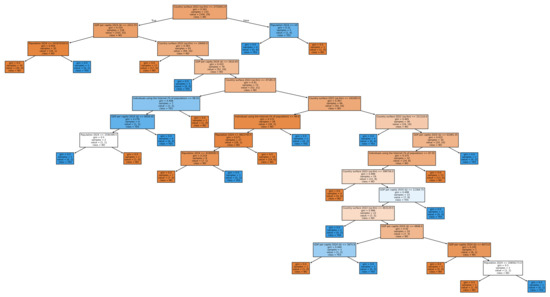
Figure 8.
Two-class decision tree for adoption vs no adoption of electronic voting.
For the second stage of the cascade, where we decide between e-voting and i-voting for those instances classified as adopting electronic voting, we get the tree depicted in Figure 9, which achieves an accuracy of 0.5, which is not better than using a coin. The root feature is now again the Democracy index.
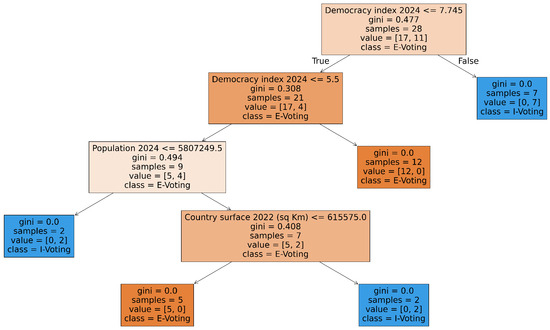
Figure 9.
Two-class decision tree for adoption of e-voting vs i-voting.
This accuracy is achieved by considering the output of the second stage just for the instances that have been classified as adopting either form of electronic voting in the first stage. If we indicate by the non-adoption of either form of electronic voting (ground truth), by that non-adoption as estimated through the first stage, by E the adoption of e-voting (ground truth), by I the adoption of i-voting (ground truth), and by and the respective estimated cases through the second stage, the compound accuracy is
By combining the outputs of the two stages, the cascade achieves a compound accuracy of 0.735, which is exactly the same as the score of the three-class classifier. (0.735).
Similarly to what we have done for the three-class classifiers, we can generate a forest of 100 trees and obtain the decision by majority voting also for the cascade of two-class classifiers. We now get an accuracy of 0.765 and 0.75 for the first and second stages, respectively. The compound accuracy is 0.937; in this case, it is definitely better than the ternary classifier (0.794).
After concluding that the four features considered allow us to predict the adoption of either form of electronic voting with very high accuracy, we can now investigate which feature is most important. We resort to a widely employed measure of feature importance for trees, which is the contribution of each feature to the reduction of Gini impurity (see Section 2.4 of [113,114]). We have evaluated the feature importance for all three decision trees. We show the results in Figure 10 for the three-class classifier and in Figure 11 and Figure 12 for the two stages of the cascade of two-class classifiers, respectively.
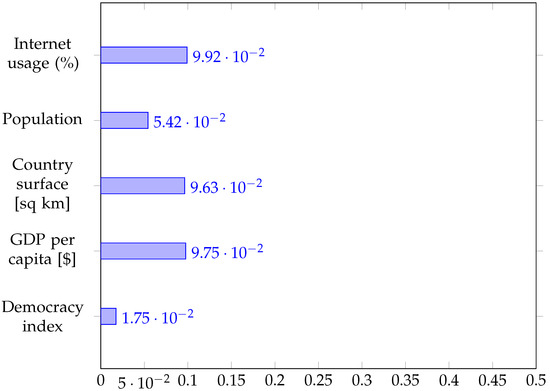
Figure 10.
Mean decrease of Gini impurity index for three-class decision tree.
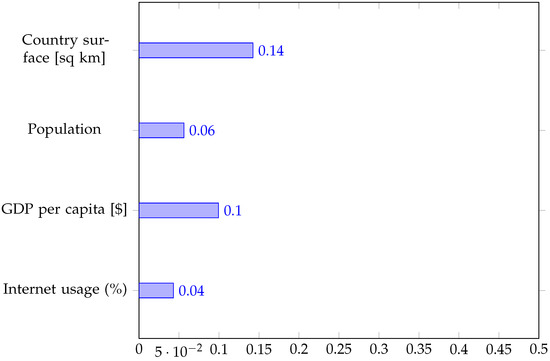
Figure 11.
Mean decrease of Gini impurity index for the first stage of the cascade of two-class decision trees (adoption vs. non-adoption).
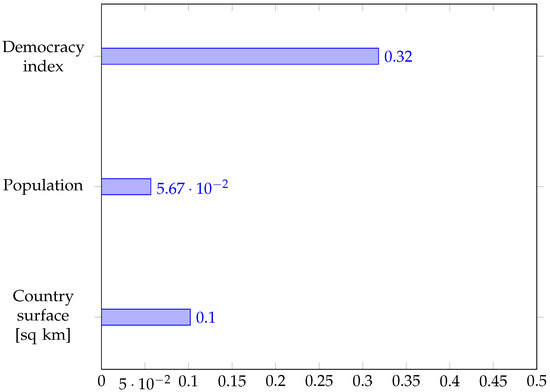
Figure 12.
Mean decrease of Gini impurity index for the second stage of the cascade of two-class decision trees (e-voting vs i-voting).
When we seek to classify by the adoption and the type of electronic voting all at once, we see that the most important features are related to the country’s size (geographical or economic) and the degree of internet usage, with all three features (surface, GDP, and internet usage) exhibiting roughly the same importance (0.096–0.099), as can be seen in Figure 10. The Democracy Index appears as the least important. When we decompose the problem into two steps, considering first the adoption vs non-adoption and then the type of electronic voting, the results are somewhat different. The size factors still appear as the most relevant, with the country’s surface area achieving 0.14 importance and the GDP lagging behind with 0.1 in Figure 11, but internet usage is definitely less relevant, which appears a bit counterintuitive. The decision between e-voting and i-voting is instead largely dictated by the level of democracy (importance of 0.32 in Figure 12), with internet usage again playing a minimal role.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have analyzed the diffusion of electronic voting around the world and the features potentially related to its adoption.
While e-voting appears to be either widely employed or undergoing trials in South America, and various forms of electronic voting are available in North America, adoption is much less widespread in other parts of the world. Africa remains largely absent from the landscape of electronic voting, and even in Europe, adoption is scattered and inconsistent. Both forms of electronic voting have been implemented in several large Asian countries. Much remains to be done to achieve widespread use of modern voting systems globally.
Expectations for adoption are higher in countries with advanced levels of technology and industrial development. However, other factors also influence adoption. A country’s surface area emerges as a significant determinant of whether any form of electronic voting is used, while the democracy index strongly predicts whether countries opt for e-voting or i-voting. Countries adopting i-voting tend to be larger both in surface area and population, wealthier (as measured by GDP per capita), and exhibit higher democracy levels (as measured by the democracy index). The random forest model we proposed achieves an accuracy exceeding 90.
The findings of this study offer important policy insights for governments and international organizations considering the adoption of electronic voting systems. The strong association between e-voting adoption and factors such as higher GDP per capita, greater Internet penetration, and higher democracy scores suggests that investments in technological infrastructure and digital literacy are foundational prerequisites for successful implementation. Moreover, the link between democracy levels and adoption rates indicates that trust in electoral institutions and transparency mechanisms should be prioritized alongside technological deployment. Policymakers in emerging democracies or developing countries should view electronic voting not only as a technological upgrade but also as part of broader governance reforms aimed at improving participation, reducing logistical barriers, and ensuring electoral integrity. Finally, tailored strategies may be needed: while highly developed countries might focus on expanding i-voting for convenience and accessibility, countries with larger populations or geographical challenges may benefit more from controlled e-voting solutions that modernize in-person voting without compromising oversight.
While this study focuses on socio-economic determinants of e-voting adoption, it is important to acknowledge that ethical and privacy concerns play a critical role in the broader debate on digital elections. The deployment of electronic voting systems, particularly i-voting solutions, raises significant challenges related to data protection, voter anonymity, system transparency, and cybersecurity. Prior literature highlights concerns about coercion resistance, vote manipulation, and digital exclusion, especially for marginalized groups. Although these aspects were not the primary focus of our quantitative model, future work should integrate qualitative analyses and country-specific governance indicators to assess how ethical safeguards and privacy standards impact adoption and public trust. Policymakers should not view technological readiness in isolation but should consider robust institutional safeguards and transparent auditing mechanisms as integral to any e-voting implementation strategy.
In a future world where all countries adopt some form of electronic voting—likely with i-voting prevailing in the long run—such differences may eventually disappear. However, based on our current findings, it is possible to identify which types of countries are most likely to be early adopters of new voting technologies.
Future research on electronic voting adoption can be expanded in several directions. First, incorporating longitudinal data would allow for the analysis of trends over time and the identification of causal relationships between socio-economic developments and voting technology adoption. Second, more granular indicators—such as digital literacy rates, cybersecurity readiness, and levels of political trust—could provide a deeper understanding of the contextual factors influencing adoption decisions. Furthermore, given the evolving landscape of digital governance, future studies could explore the impact of emerging technologies, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, on the security and accessibility of electronic voting systems. Cross-country comparative case studies, especially in countries undergoing political or technological transitions, may offer valuable qualitative insights to complement quantitative models. Overall, future work should aim to bridge the gap between technological feasibility and democratic legitimacy to inform policy decisions and foster broader, equitable adoption of electronic voting systems.
In particular, the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in electoral management is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. AI is already being explored for applications such as voter registration verification, fraud detection, logistical optimization of polling stations, and real-time election monitoring. While AI can offer considerable improvements in efficiency and accuracy, it also introduces new risks, including algorithmic bias, opaque decision-making processes, and increased cybersecurity vulnerabilities. These dimensions were beyond the scope of the present analysis but represent a critical avenue for future research, especially in assessing how AI tools interact with electoral integrity and citizen trust. Future studies should investigate the co-evolution of AI adoption and e-voting deployment, particularly in countries with advanced digital governance systems.
In addition to the factors examined in this study, future research could benefit from considering additional socio-demographic dimensions. Variables such as literacy rates, educational attainment, gender equality indicators—including women’s participation in political and electoral processes—and urbanization levels could provide further explanatory power in understanding the adoption and inclusiveness of electronic voting systems. These factors may be particularly relevant in capturing not only technological and economic readiness but also social accessibility and equity in electoral participation. Incorporating such indicators in future analyses would allow for a more comprehensive assessment of the societal conditions that favor or hinder the adoption of modern voting technologies, ensuring that progress in electoral modernization aligns with broader democratic and social development goals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.I. and L.L.; methodology, P.F., M.N. and V.R.; software, P.F. and L.L.; validation, M.N. and V.R.; formal analysis, M.N.; investigation, M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, M.I.; writing—review and editing, M.I., L.L. and M.N.; supervision, P.F. and V.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available at https://bit.ly/eVotingDataset2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Challú, C.; Seira, E.; Simpser, A. The Quality of Vote Tallies: Causes and Consequences. Am. Polit. Sci. Rev. 2020, 114, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goggin, S.N.; Byrne, M.D.; Gilbert, J.E. Post-Election Auditing: Effects of Procedure and Ballot Type on Manual Counting Accuracy, Efficiency, and Auditor Satisfaction and Confidence. Elect. Law J. Rules Politics Policy 2012, 11, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemson, J.; Krips, K. Estimating Carbon Footprint of Paper and Internet Voting. In Electronic Voting; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 140–155. [Google Scholar]
- Schur, L.; Adya, M.; Ameri, M. Accessible Democracy: Reducing Voting Obstacles for People with Disabilities. Elect. Law J. Rules Politics Policy 2015, 14, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsamidis, S.; Nerantzis, V.; Kerenidou, E.; Karakos, A. Survey on e-voting and electoral technology for Balkan and South-Eastern Europe countries. In Proceedings of the Economies of Balkan and Eastern Europe Countries in the Changed World, Kavala, Greece, 7–9 May 2010; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Krimmer, R.; Triessnig, S.; Volkamer, M. The Development of Remote E-Voting Around the World: A Review of Roads and Directions. In E-Voting and Identity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.H.K.; Mondal, S.K.; Chan, K.C.; Xie, X. A Review of Contemporary E-voting: Requirements, Technology, Systems and Usability. Data Sci. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 1, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.S.; Walia, E. Analysis of electronic voting system in various countries. Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2011, 3, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, F.; Ryan, P.Y.A. Real-World Electronic Voting: Design, Analysis and Deployment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.P.; Krimmer, R.; Teague, V.; Pomares, J. A review of e-voting: The past, present and future. Ann. Telecommun. 2016, 71, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikrissi, G.; Mazri, T. Electronic Voting: Review and Challenges. In Innovations in Smart Cities Applications; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 7, pp. 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Adekunle, S.E.; Adewale, O.S.; Boyinbode, O.K. A Review of Electronic Voting Systems: Strategy for a Novel. Int. J. Inf. Eng. Electron. Bus. 2020, 12, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lake, J. What are the Risks of Electronic Voting and Internet Voting? 2022. Available online: https://www.comparitech.com/blog/information-security/electronic-voting-risks/ (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- Kumar, D.A.; Begum, T.U.S. Electronic voting machine—A review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Informatics and Medical Engineering (PRIME-2012), Salem, India, 21–23 March 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shejavali, N. Electronic Voting Machines; No. 1; Institute for Public Policy Research (IPPR): London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, S.P.; Greene, K.K.; Byrne, M.D.; Wallach, D.S.; Derr, K.; Sandler, D.; Torous, T. Electronic voting machines versus traditional methods: Improved preference, similar performance. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Florence, Italy, 5–10 April 2008; pp. 883–892. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, S.P. The Usability of Electronic Voting Machines and How Votes Can Be Changed Without Detection. Ph.D. Thesis, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wolchok, S.; Wustrow, E.; Halderman, J.A.; Prasad, H.K.; Kankipati, A.; Sakhamuri, S.K.; Yagati, V.; Gonggrijp, R. Security analysis of India’s electronic voting machines. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Chicago IL, USA, 4–8 October 2010; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kiayias, A.; Michel, L.; Russell, A.; Shashidhar, N.; See, A.; Shvartsman, A.; Davtyan, S. Tampering with Special Purpose Trusted Computing Devices: A Case Study in Optical Scan E-Voting. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Third Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC 2007), Miami Beach, FL, USA, 10–14 December 2007; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Abuidris, Y.O.; Kumar, R.; Wenyong, W. A Survey of Blockchain Based on E-voting Systems. In Proceedings of the ICBTA 2019: 2019 2nd International Conference on Blockchain Technology and Applications, Xi’an, China, 9–11 December 2019; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Vladucu, M.V.; Dong, Z.; Medina, J.; Rojas-Cessa, R. E-Voting Meets Blockchain: A Survey. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 23293–23308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul; Gulia, P.; Gill, N.S. Articulation of blockchain enabled e-voting systems: A systematic literature review. Peer-Peer Netw. Appl. 2025, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullits, J. Deciphering blockchain’s role in Danish decision-making: Evaluating opportunities and challenges through the prism of due process. Law Innov. Technol. 2024, 16, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maaitah, S.; Qatawneh, M.; Quzmar, A. E-Voting System Based on Blockchain Technology: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT), Amman, Jordan, 14–15 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Barelli, R.; D’Onghia, M.; Longari, S. Toward secure electronic voting: A survey on E-voting systems and attacks. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 89600–89626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Blanco, D.Y.M.; Gascó, M. A Protocolized, Comparative Study of Helios Voting and Scytl/iVote. In Proceedings of the 2019 Sixth International Conference on eDemocracy & eGovernment (ICEDEG), Quito, Ecuador, 24–26 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- New Zealand Electoral Commission. How to Vote from Overseas. 2023. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20231211001803/https://www.vote.nz/voting/overseas/vote-from-overseas/ (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Ministry of Transport, Communications and Information Technology. Antakhib App. 2023. Available online: https://oman.om/en/home-top-level/eparticipation/e-voting (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Ministry of State for FNC Affairs. United Arab Emirates E-Voting App Download Page. 2023. Available online: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.uaevoting.ae (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- International IDEA. ICTs in Elections Database. 2024. Available online: https://www.idea.int/data-tools/data/icts-elections-database (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- McCombie, S.; Uhlmann, A.J.; Morrison, S. The US 2016 presidential election & Russia’s troll farms. Intell. Natl. Sec. 2020, 35, 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Burr, R.; Warner, M.; Collins, S.; Heinrich, M.; Lankford, J. Senate INTEL Committee Releases Unclassied 1st Installment in Russia Report, Updated Recommendations on Election Security. 2018. Available online: https://www.justsecurity.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/5.8.18-Statement-on-SSCI-Report.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Zdun, M. Machine Politics: How America casts and counts its votes. Reuters 2022. [Google Scholar]
- King, B.A. State online voting and registration lookup tools: Participation, confidence, and ballot disposition. J. Inf. Technol. Politics 2019, 16, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Sowell, S.; Quinlan, K. Election Day Ends with Reports of Vote Counting Tech Challenges, Text Scams in Several States. 2024. Available online: http://statescoop.com/election-day-ends-with-reports-of-vote-counting-tech-challenges-text-scams-in-several-states/ (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Alcántara, M.J.A. Dominican Government Asks OAS to Investigate e-Vote Failure. 2020. Available online: https://apnews.com/international-news-general-news-293e335b22b24fa6bd5945733b2a27a8 (accessed on 9 December 2023).
- Pomares, J.; Levin, I.; Alvarez, R.M. Do voters and poll workers differ in their attitudes toward e-voting? Evidence from the first e-election in Salta, Argentina. In Proceedings of the 2014 Electronic Voting Technology Workshop/Workshop on Trustworthy Elections (EVT/WOTE 14), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–19 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Evoting Communications. What Happened to Electronic Voting in Argentina’s Primary Elections? 2023. Available online: https://evoting.com/en/2023/08/21/voto-electronico-primarias-argentina/ (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Okuro, O. Comparative Review of E-Voting in India and Brazil: Key Lessons for Kenya. Lagos Hist. Rev. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Krimmer, R.; Volkamer, M.; Binder, N.B.; Kersting, N.; Loeber, L. TUT Press Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Electronic Voting (E-Vote-ID); TUT Press: Bregenz, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320618317_TUT_Press_Proceedings_of_the_Second_International_Conference_on_Electronic_Voting_E-Vote-ID (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Spada, P.; Mellon, J.; Peixoto, T.; Sjoberg, F.M. Effects of the internet on participation: Study of a public policy referendum in Brazil. J. Inf. Technol. Politics 2016, 13, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudio Fuentes Armadans, J.S.C. History of Electronic Voting in Paraguay; Technical Report; TEDIC (Asociación de Tecnología, Educación, Desarrollo, Investigación, Comunicación). 2022. Available online: https://www.tedic.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/HistoriaVotoElectronicoParaguay.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Machin-Mastromatteo, J.D. The most “perfect” voting system in the world. Inf. Dev. 2016, 32, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Këlliçi, E. Increasing Public Trust Through Technology, eVoting Case Albania. 2023. Available online: https://uet.edu.al/ingenious/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/ingenious-2-Increasing-public-trust-through-technology-eVoting-case-Albania.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Dandoy, R. An Analysis of Electronic Voting in Belgium: Do voters behave differently when facing a machine? In Belgian Exceptionalism; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2021; pp. 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wetherall-Grujić, G. Manufacturing Distrust: Voting Machines in Bulgaria. 2022. Available online: https://democracy-technologies.org/voting/manufacturing-distrust-voting-machines-in-bulgaria/ (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Bg, M.W.H. A System for Remote Electronic Voting Is Being Developed in Bulgaria. 2022. Available online: https://www.novinite.com/articles/214773/A+System+for+remote+Electronic+Voting+is+being+developed+in+Bulgaria (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Freyer, U. Introduction of Electronic Voting In Namibia; Technical Report; Electoral Commission of Namibia: Windhoek, Namibia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mpekoa, N.; van Greunen, D. E-voting experiences: A case of Namibia and Estonia. In Proceedings of the 2017 IST-Africa Week Conference (IST-Africa), Windhoek, Namibia, 30 May–2 June 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, C. DR Congo Elections: Why do Voters mistrust electronic voting? BBC News, 28 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Congo Research Group. The Electronic Voting Controversy in the Congo; Congo Research Group Election Brief No 1. 2018. Available online: https://s44308.pcdn.co/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/Electronic-Voting-Controversy-1.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- The Sentry Team. Electronic Voting Technology DRC. 2018. Available online: https://thesentry.org/reports/electronic-voting-technology-drc/ (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Election Commission of Bhutan. Handbook for Polling Officiers; Election Commission of Bhutan: Jangsa, Bhutan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Election Commission of Bhutan. Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) Rules and Regulations of the Kingdom of Bhutan, 2018; Election Commission of Bhutan: Jangsa, Bhutan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Risnanto, S.; Rahim, Y.B.A.; Herman, N.S. Success Implementation of E-Voting Technology In various Countries: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2nd Faculty of Industrial Technology International Congress, Bandung, Indonesia, 28–30 January 2020; pp. 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Tasnim News Agency. E-Voting In Iran Presidential Election Off The Table; Eurasia Review; Tasnim News Agency: Tehran, Iran, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- National Democratic Institute. Iran’s June 18, 2021 Elections; Technical Report; National Democratic Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq (UNAMI). Elections for Iraq’s Council of Representatives-Facts Sheet; Technical Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, A.; Jalabi, R.; Aboulenein, A. Exclusive: Iraq Election Commission Ignored Warnings over Voting Machines-Document; Reuters: Tokyo, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sheranova, A. Cheating the machine: E-voting practices in Kyrgyzstan’s local elections. Eur. Rev. 2020, 28, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umarova, A. Why Kyrgyzstan Uses Biometrics in Its Voting System. 2018. Available online: https://govinsider.asia/intl-en/article/kyrgyzstan-uses-biometrics-voting-system (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- OSCE Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights. Mongolia-Parliamentary Elections, ODIHR Needs Assessment Mission Report; Technical Report; OSCE Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights: Warsaw, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gangabaatar, D. Electoral Reform and the Electronic Voting System: Case of Mongolia. In Digital Transformation and Its Role in Progressing the Relationship Between States and Their Citizens; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 182–204. [Google Scholar]
- Elven, T.M.A.; Al-Muqorrobin, S.A. Consolidating Indonesia’s Fragile Elections Through E-Voting: Lessons Learned from India and the Philippines. Indones. Comp. Law Rev. 2020, 3, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Foundation for Electoral Systems. Elections in Panama-2019 General Elections - Frequently Asked Questions; Technical Report; IFES-International Foundation for Electoral Systems: Arlington, VA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Associated Press. Ecuadorians Vote for President, Overseas Voting System Sees Cyberattacks. 2023. Available online: https://www.voanews.com/a/ecuadorians-vote-for-president-overseas-voting-system-sees-cyberattacks/7233360.html (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Finn, V.; Besserer Rayas, A. Turning rights into ballots: Mexican external voting from the US. Territ. Politics Gov. 2022, 12, 1425–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INE. Electronic Voting System for Mexican Residing Abroad Manual; Instituto Nacional Electoral: Mexico City, Mexico, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ministère de l’Europe et des Affaires ètrangères. Legislative Elections–Opening of the Internet Voting Portal (27 May 2022). 2022. Available online: https://www.govmemo.com/northern_ireland/foreign_affairs_c50/legislative_election..._d7303id.shtml (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Xenakis, A.; Macintosh, A. Major Issues in Electronic Voting in the Context of the UK Pilots. J. Inf. Technol. Politics 2004, 1, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, T.; Duncan, I. Polsterless Remote Electronic Voting. J. Inf. Technol. Politics 2004, 1, 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Parliament staff. Online Voting in the House of Lords. 2022. Available online: https://www.parliament.uk/about/how/changes-to-lords-proceedings/online-voting-in-the-house-of-lords/ (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Manougian, H. Did You Know Armenia Allows Internet Voting? (But It’s Only For Some). 2020. Available online: https://evnreport.com/politics/did-you-know-armenia-allows-internet-voting-but-it-s-only-for-some/ (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights (ODIHR). Republic of Armenia Early Parliamentary Elections 20 June 2021; Technical Report; Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD): Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, L.; Shaikh, A.K.; Tan, H.Y.; Raahemifar, K. A Review of Contemporary Governance Challenges in Oman: Can Blockchain Technology Be Part of Sustainable Solutions? Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2022, 14, 11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Open Government Case Study—Sample Case Submission Form. 2019. Available online: https://opengov.unescwa.org/sites/default/files/inline-files/Om02-e-Voting-System-En.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Mc Keown, D. New South Wales State Election 2015. Research Paper Series (Parliamentary Library, Australia). 2016. Available online: https://parlinfo.aph.gov.au/parlInfo/download/library/prspub/4630824/upload_binary/4630824.pdf;fileType=application%2Fpdf#search=%22library/prspub/4630824%22 (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Cardillo, A.; Akinyokun, N.; Essex, A. Online Voting in Ontario Municipal Elections: A Conflict of Legal Principles and Technology? In Electronic Voting; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chughtai, W. Online voting is growing in Canada, raising calls for clear standards. CBC News, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Górny, M. I-voting–opportunities and threats. Conditions for the effective implementation of Internet voting on the example of Switzerland and Estonia. Prz. Politol. 2021, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemson, J. Recommendations to OSCE/ODIHR (on how to give better recommendations for Internet voting). arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.06385. [Google Scholar]
- Scytl. 94% Trust Rate in Norway’s Online Voting Channel. 2014. Available online: https://scytl.com/94-trust-rate-in-norways-online-voting-channel/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Cortier, V.; Wiedling, C. A Formal Analysis of the Norwegian E-voting Protocol. In Principles of Security and Trust; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.J.M. Comparison of e-voting schemes: Estonian and Norwegian solutions. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Syst. 2013, 6, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Smartmatic. Norwegian County Conducts Referendum Using Online Voting. 2022. Available online: https://www.smartmatic.com/media/norwegian-county-conducts-referendum-using-online-voting/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Reiners, M. Vote electronique in Switzerland: Comparison of relevant pilot projects. J. Commonw. Comp. Polit. 2020, 13, 58–75. [Google Scholar]
- Swiss Federal Chancellery FCh. E-Voting. 2023. Available online: https://www.bk.admin.ch/bk/en/home/politische-rechte/e-voting.html (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- Ridard, E.; Eichenberger, M. Swiss Abroad: E-Voting Doesn’t Make up for Frustrations. 2023. Available online: https://www.swissinfo.ch/eng/politics/swiss-abroad–e-voting-does-not-make-up-for-frustrations/48920054 (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- Bagnato, D.; Müller-Török, R.; Prosser, A.; Stein, R. Evoting at the German Social Elections–lessons learnt. Masaryk Univ. J. Law Technol. 2025, 19, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khouri, A.M.; Authority, E.I.; Dhabi, A. E-Voting in UAE FNC Elections: A Case Study. Inf. Knowl. Manag. 2012, 2, 25–84. [Google Scholar]
- The United Arab Emirates’ Government Portal. Elections. 2023. Available online: https://u.ae/en/about-the-uae/the-uae-government/the-federal-national-council-/elections- (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Scytl. United Arab Emirates Becomes First Country to Hold Fully Digital Elections with Scytl. 2023. Available online: https://scytl.com/united-arab-emirates-becomes-first-country-to-hold-fully-digital-elections-with-scytl/ (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Vakarjuk, J.; Snetkov, N.; Willemson, J. Russian Federal Remote E-voting Scheme of 2021–Protocol Description and Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 European Interdisciplinary Cybersecurity Conference, New York, NY, USA, 15–16 June 2022; EICC ’22; pp. 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Chingaev, Y. Russia’s Online Voting System Briefly Crashes on First Day of Election. 2024. Available online: https://www.themoscowtimes.com/2024/03/15/russias-online-voting-system-briefly-crashes-on-first-day-of-election-a84470 (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Dyxon, R. As Russian voting moves online, Putin’s foes say another path to curb Kremlin is lost. The Washington Post, 14 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, R.M.; Katz, G.; Llamosa, R.; Martinez, H.E. Assessing Voters’ Attitudes towards Electronic Voting in Latin America: Evidence from Colombia’s 2007 E-Voting Pilot. In E-Voting and Identity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 75–91. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, R.M.; Katz, G.; Pomares, J. The Impact of New Technologies on Voter Confidence in Latin America: Evidence from E-Voting Experiments in Argentina and Colombia. J. Inf. Technol. Politics 2011, 8, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvetto Salinas, P.A. Implementación del voto electrónico en Perú; Technical Report; Oficina Nacional de Procesos Electorales (ONPE)-Perú: Lima, Peru, 2022; Available online: https://www.ine.mx/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/deoe-voto-elec-pres-PCorvetto.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Scytl. Scytl Online Voting Helps Iceland Successfully Run Fully Online Referendums. 2015. Available online: https://scytl.com/news/scytl-online-voting-helps-iceland-successfully-run-fully-online-referendums/ (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- European Digital Rights. Ireland: E-Voting Machines Go to Scrap After Proving Unreliable. 2012. Available online: https://edri.org/our-work/edrigramnumber10-14evoting-machines-scrap-ireland/ (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Il Post, Il Pasticcio del Voto Elettronico in Lombardia. 2017. Available online: https://www.ilpost.it/2017/10/23/voto-elettronico-lombardia/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Regione Lombardia, Lombardia, Referendum: Il Sistema di Voto Elettronico; Lnews—Lombardia Notizie. 2017. Available online: https://www.expartibus.it/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/notiziario-del-28-luglio.pdf#page=10.12 (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Wikipedia. Referendum Consultivo in Lombardia del 2017. 2017. Available online: https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Referendum_consultivo_in_Lombardia_del_2017 (accessed on 21 August 2022).
- Dipartimento per gli Affari Interni e Territoriali. E-Vote. La Simulazione del Voto Elettronico. 2023. Available online: https://dait.interno.gov.it/elezioni/notizie/e-vote-simulazione-del-voto-elettronico (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Irani, B. EC to Buy 2,535 New EVMs at Four Times the Cost of Previous Models. 2018. Available online: https://www.dhakatribune.com/bangladesh/145403/ec-to-buy-2-535-new-evms-at-four-times-the-cost-of (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- The Wire Editorial Staff. Bangladesh Election Commission Forced to Drop EVMs. 2023. Available online: https://thewire.in/south-asia/bangladesh-election-commission-drop-evms (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Mackisack, D. There and Back Again–The Story of Pakistan’s Brief Experiment with Electronic Voting. 2022. Available online: https://democracy-technologies.org/voting/there-and-back-again-the-story-of-pakistans-brief-experiment-with-electronic-voting/ (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Billon, M.; Marco, R.; Lera-Lopez, F. Disparities in ICT adoption: A multidimensional approach to study the cross-country digital divide. Telecommun. Policy 2009, 33, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimmer, R. The Evolution of E-Voting: Why Voting Technology Is Used and How It Affects Democracy. Ph.D. Thesis, Tallinn University of Technology, Tallinn, Estland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Economist Intelligence Unit. Democracy Index 2022. 2023. Available online: https://www.eiu.com/n/campaigns/democracy-index-2022/?utm_source=economist&utm_medium=daily_chart&utm_campaign=democracy-index-2022 (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Wadsworth International Group: Belmont, CA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X. Gini-impurity index analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 3154–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampi, A. Interpretable AI: Building Explainable Machine Learning Systems; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).