Abstract
Semantic modeling of legal reasoning is an important research direction in the field of artificial intelligence and law (AI and law), aiming to enhance judicial transparency, fairness, and the consistency of legal applications through structured semantic representations. This paper proposes a semantic judicial reasoning framework based on the “Data–Information–Knowledge–Wisdom–Purpose” (DIKWP) model, which transforms the conceptual expressions of traditional legal judgment into DIKWP graphs enriched with semantics. The framework integrates the objective content of legal norms with stakeholders’ subjective cognition through a DIKWP×DIKWP bidirectional mapping mechanism, achieving “semantic justice”. Specifically, we define a DIKWP-based legal knowledge representation method and design a mapping algorithm from traditional legal concepts to the DIKWP semantic structure. To validate the effectiveness of the framework, we use a real administrative law case as an example and construct DIKWP (normative content) and DIKWP (subjective cognition) graphs to model legal rules, evidence, and various perspectives. The results indicate that the intention-driven semantic transformation mechanism can harmonize legal reasoning with stakeholders’ cognitive backgrounds, thereby enhancing the interpretability and fairness of judicial interpretation. Case analysis further demonstrates that reasoning within the DIKWP semantic space can reveal underlying assumptions, bridge cognitive gaps, and promote judicial fairness by aligning legal intentions. This study provides new theoretical and methodological support for the explainable reasoning of intelligent judicial systems.
1. Introduction
The intersection of AI and law [1] faces a critical challenge: how to ensure fairness and transparency in AI systems’ legal reasoning processes while maintaining decision-making efficiency [2]. Traditional legal reasoning models primarily rely on symbolic and conceptual expression paradigms, such as rule-based expert systems [3] and formal logic [4], by encoding legal provisions and precedents into abstract symbols or predicate logic to achieve formal reasoning [5]. Although these methods can effectively simulate the deductive structure of legal reasoning, their limitation lies in their over-reliance on symbolic operations at the conceptual level, neglecting the crucial semantic context and situational factors in legal interpretation [6]. This limitation can lead to a dilemma of “formally legal but substantively unjust” decisions, where the judgment results may comply with legal provisions in form but contradict the deeper purposes and fairness values of the legal system [7].
With the rapid development of legal AI technologies, semantic depth and system interpretability have become core issues that urgently need addressing [8]. Current mainstream black-box machine learning models, while exhibiting high accuracy in tasks like case outcome prediction and legal interpretation, are severely constrained by their lack of transparency, which limits their practical application in judicial settings [9]. Even relatively transparent rule-based systems and ontological methods have evident limitations, as they often over-abstract legal knowledge and fail to capture the multidimensional understandings that judges, lawyers, and parties involved in a case bring to legal practice [10]. For instance, in classical syllogistic reasoning, purely conceptual legal application may mechanically apply legal provisions but fail to assess whether the judgment truly fulfills legislative intentions or is perceived as fair and just by stakeholders [11]. This phenomenon reveals the fundamental challenge faced by current legal AI systems: how to maintain formal rigor while achieving semantic richness and value sensitivity in legal reasoning.
To overcome this theoretical bottleneck, this study introduces the DIKWP semantic representation model, which innovatively adds the “Purpose” dimension to the traditional DIKW (Data–Information–Knowledge–Wisdom) hierarchy, creating a complete legal semantic representation system [12,13]. In this framework, the legal reasoning process is deconstructed into five interconnected cognitive levels: raw legal data is transformed into structured information through feature identification, which is then organized into actionable legal knowledge. This knowledge is applied in specific contexts, elevated into judicial wisdom, and all these cognitive activities are guided by the fundamental intentions and value objectives of the legal system. This multi-level semantic representation not only supports conceptual modeling but also constructs a complete semantic map, including data graphs, information graphs, knowledge graphs, wisdom graphs, and intention graphs. It should be emphasized that these semantic graphs do not simply form a linear hierarchy, but rather interact within a parallel and interconnected network structure, allowing mutual semantic enrichment and dynamic cognitive interactions across different DIKWP dimensions. Moreover, these graphs can be understood as specialized semantic networks or knowledge graphs adapted for representing various levels and aspects of legal reasoning. The DIKWP model has demonstrated significant advantages in various fields such as financial compliance analysis and medical dispute mediation [14,15], particularly in integrating objective norms with subjective cognition [16], enhancing system decision-making interpretability [17], and ensuring alignment between technological applications and human values [18]. Empirical research shows that the DIKWP method can effectively identify and bridge cognitive differences between legal entities, providing an innovative methodological tool to address the issue of legal information asymmetry.
Based on the theoretical advantages of the DIKWP model, this study proposes a novel legal knowledge representation and reasoning framework. This framework breaks through the limitations of traditional ontologies and logical rules by introducing cognitive dimensions and intention-driven reasoning, facilitating the innovative development of legal AI paradigms. On a practical level, this research provides a key technical path for developing the next generation of intelligent judicial assistance systems: first, by constructing a legal DIKWP semantic map, the system can comprehensively capture both the formal characteristics and substantive values of legal provisions; second, by utilizing multi-level semantic reasoning mechanisms, it ensures that judicial decisions strictly adhere to legal provisions while aligning with the spirit of the law; finally, through intention-driven interpretative generation technology, complex legal reasoning processes remain transparent and understandable to various stakeholders. This study transforms traditional legal judgment processes into dynamic interactions and intelligent traversals of the DIKWP semantic map, achieving a paradigm shift in legal reasoning from formal logic to substantive justice, ensuring that AI-generated legal decisions are not only formally correct but also defensible within multiple value contexts.
The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 systematically reviews the research progress on legal knowledge representation and reasoning, laying the theoretical foundation; Section 3 elaborates on the DIKWP-based semantic judicial reasoning methodology; Section 4 demonstrates the application of the framework through empirical analysis of typical legal cases; Section 5 evaluates the performance of the framework from multiple dimensions; Section 6 delves into the theoretical contributions and practical implications; and finally, Section 7 concludes with a summary of the research value and outlook on future directions. This research not only advances theoretical innovation in legal AI but also provides a practical and feasible technological solution for achieving a smarter, fairer, and more transparent judicial system. Moreover, if proven viable, the proposed DIKWP-based semantic reasoning framework offers a competitive alternative mechanism to the deep neural network (DNN)-based methods currently attracting widespread attention, potentially addressing the interpretability and transparency challenges inherent in DNN approaches. However, it is important to recognize that constructing a DIKWP-based knowledge base requires substantial domain expertise, rigorous semantic modeling, and systematic knowledge integration, implying significant upfront efforts and resource investment. Future work will further investigate and quantify these efforts, optimizing methods to enhance scalability and efficiency in knowledge base construction and updating.
2. Background and Related Work
2.1. Traditional Conceptual Representations in Legal AI
Artificial intelligence applications in the legal domain have long relied on symbolic and conceptual modeling approaches to represent legal knowledge and reasoning mechanisms [19]. Early expert systems achieved automated reasoning by formalizing legal provisions into “if–then” rules or decision trees [20], while case-based systems [21] supported analogical reasoning through abstract representations of key factors in precedents. These methods can be categorized into what we refer to as the “conceptual space of legal reasoning”—a level at which concrete facts are abstracted into legal categories and processed according to formal logic or algorithms. Such models have yielded a series of representative achievements, such as Taxman [22] and MYCIN-like systems [23] used for tax law and criminal legal advice, and HYPO [24] and CATO [25], which demonstrated strong analogical reasoning capabilities in areas such as trade secrets and contract disputes. However, despite their reasoning abilities at the conceptual level, these systems generally overlook the deep semantic content underlying legal concepts—the context, interpretation, and purpose that give meaning to legal rules.
A core limitation of purely conceptual (or syntactic) models lies in their inability to capture the intent behind legal rules and the contextual nuances of factual situations [26]. For example, a typical rule might be expressed as “If an enterprise commits violation X and its severity exceeds Y, then impose penalty Z.” This logical rule would be applied mechanically whenever the conditions are met, without considering key questions such as “Was the violation intentional or due to negligence?” “What is the purpose of imposing penalty Z—deterrence, punishment, or remediation?” or “Are there any mitigating circumstances or compliance efforts worth considering?” Answering such questions requires the introduction of meta-legal knowledge (such as principles of proportionality or equity) and stakeholder knowledge (such as the intentions and actions of the involved parties)—elements that typically fall under the “Wisdom” and “Purpose” layers of the DIKWP model. While purely rule-based approaches inherently lack the ability to incorporate this underlying knowledge, model-based, functional-based, and object-based approaches have successfully addressed this challenge in domains like medical and mechanical diagnosis [27]. Adopting similar approaches in the legal domain could potentially overcome these significant shortcomings related to fairness, explainability, and adaptability.
Another significant challenge is system explainability. Although rule-based systems [28] are theoretically traceable, their explanations often remain at the conceptual level of “condition triggering”—for example, “penalty Z was imposed because conditions X and Y were met”—and fail to address questions such as “Was the decision fair?” or “Did it align with broader legal principles?” Recent research on Explainable AI (XAI) highlights that in high-stakes domains like law, users care not only about how a decision was made, but also why it was made. Explanations that merely cite legal provisions without offering contextual justification may be perceived as procedurally inadequate, potentially undermining public trust in AI-driven judicial systems.
To overcome the above limitations, researchers have gradually introduced semantic technologies such as legal ontologies [29] and legal knowledge graphs [30] to enhance the depth of legal knowledge representation and reasoning capabilities. Knowledge graphs, historically known as semantic networks, were first introduced in the 1960s and have evolved significantly to support modern semantic representation and inference tasks. Legal ontologies, such as LKIF, LegalRuleML, or domain-specific ontologies (e.g., for intellectual property law or contract law), provide structured vocabularies and relationship definitions for describing legal concepts and their interconnections. For example, the concept of a “License” can be defined as a type of “Permit” issued by a regulatory authority, and associated with attributes such as validity period, applicable conditions, and issuing body. Building on this foundation, legal knowledge graphs instantiate ontological classes into real-world data nodes (e.g., court cases, statutes, legal parties) and edges (e.g., “cites”, “grants authority”, “violates”), thereby forming complex networks of legal relationships. This graph-based structure not only facilitates path traversal and semantic inference (e.g., finding precedents with similar fact patterns), but also provides new avenues for legal information retrieval, intelligent legal question answering, and automated compliance analysis.
Although legal ontologies and knowledge graphs represent a significant advancement toward semantic modeling, they mostly remain confined to the “Knowledge” level (i.e., structured domain knowledge) and the “Information” level (i.e., factual data points) within the DIKWP model. They lack explicit modeling of the higher-level “Wisdom” and “Purpose” dimensions [31]. For instance, a legal knowledge graph might encode that “Violation X is categorized as high severity” and link it to the rule “According to Regulation Y, license revocation is required.” However, it typically does not capture the underlying rationale, such as “Regulation Y aims to protect public health” or “to promote corporate compliance.” Moreover, such systems generally fail to reflect stakeholder perspectives, such as how parties interpret or accept a decision. As a result, despite improvements in the formal expressiveness of legal knowledge, current semantic technologies still exhibit significant gaps in contextual understanding, value-based judgment, and goal-oriented reasoning.
We define the “concept–semantic gap” in legal AI as the difference between operating at the level of abstract symbolic manipulation and understanding at the semantic level. Traditional AI systems in law [32] operate at the former level, while our goal is to construct reasoning mechanisms at the latter—mechanisms that are more explainable and fair [33]. For instance, consider an administrative law case: a restaurant’s license is revoked due to violations discovered during a health inspection. If we rely solely on a conceptual model, the system would mechanically execute the rule: “Major violation found → revoke license.” However, by introducing semantic reasoning, the system can further investigate the following: What exactly was the violation? How severe was it? Did it significantly deviate from standard practices? What are the specific requirements of the relevant regulations? Are there mitigating circumstances or corrective measures taken proactively? Crucially, what is the fundamental purpose of the regulation? Is it to protect public safety or encourage businesses toward compliant operations? Through multi-layered reasoning facilitated by the DIKWP model, the system can assess whether lighter measures (e.g., a warning or fine) could sufficiently fulfill regulatory objectives, thus achieving a fairer outcome. Such reasoning processes reflect the practical rationality implicitly exercised by human judges and regulators. Our aim is to formalize and structure this process and embed it into the next generation of legal AI systems.
2.2. DIKWP Model: Semantic Mathematics and AI Applications
The DIKWP model is part of a broader effort in AI to incorporate semantic mathematics. At its core, DIKWP posits that any cognitive process of understanding can be viewed as transformations across five layers: data (D), information (I), knowledge (K), wisdom (W), and purpose (P). Each layer corresponds to a certain level of semantic abstraction and cognitive processing:
In the DIKWP framework, data is regarded as raw observations or facts; however, crucially, this data is not considered meaningless but rather as “concrete instantiations of identical semantics within cognition” [34]. This implies that even at the data level, cognitive agents are assumed to recognize specific patterns or categories (identical semantics) within raw inputs. For instance, in legal cases, data points such as a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) reading of 0.08 or an email text submitted as evidence only gain significance when identified as specific categories, such as “blood alcohol content” or “communication records between parties”. Formally, a data graph (DG) can be viewed as a collection of data nodes interconnected by semantic labels.
Information is defined as “one or more differential semantics within cognition”, emerging when differences from known or expected conditions are identified [35]. It represents data enriched with contextual or relational meaning. In litigation scenarios, a typical piece of information would be, for example, “the defendant’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC) is twice the legal limit”, highlighting a difference through comparison with a normative value. Formally, an information graph (IG) captures this differentiation by linking data nodes with reference points—for instance, associating a “0.08 BAC” measurement with the statutory threshold. In the domain of administrative law, comparing a restaurant’s number of violations this year against last year’s records similarly generates trend-based information.
Knowledge corresponds to structured understanding, encompassing rules, models, or classification systems derived from information [36]. In legal scenarios, this includes statutes, case law, and logical relationships among concepts (e.g., legal rules expressed as “A + B → C”). A knowledge graph (KG) links information nodes into a coherent structure, such as rule chains connecting legal conditions with corresponding conclusions. In our framework, a legal knowledge graph—analogous to the combination of ontologies and legal rules—forms the core of the knowledge (K) layer.
Wisdom, as the most abstract level, involves judgment, principles, ethics, and the capacity to integrate knowledge and experience [37]. In the legal domain, it is represented by jurisprudential wisdom, principles of fairness, proportionality, deterrence, and rehabilitation, as well as practical considerations accumulated by legal experts through experience. A wisdom graph (WG) can be visualized as a network of relational principles—for instance, connecting “ensuring public health” with “avoiding undue economic harm” as balancing considerations in enforcement decisions.
Purpose constitutes the goal-oriented element driving the entire cognitive process, distinguishing DIKWP explicitly from most AI systems that implicitly embed objectives [38]. Within the legal context, each statute has a legislative intent, judicial processes seek fair and efficient dispute resolution, and individual stakeholders have distinct objectives. A purpose graph (PG) depicts these motivational targets—for example, the regulatory aim of “preventing foodborne illnesses” in food safety governance, calibrated against a restaurant owner’s objective of “operating compliantly while safeguarding customer safety”. Purpose nodes connect explicitly with wisdom nodes (representing value-oriented objectives) and knowledge nodes (explicit statutory intent), forming a coherent cognitive chain.
The DIKWP model supports bidirectional reasoning through hierarchical layering: bottom-up (data-to-purpose) reasoning corresponds to classical data-driven approaches, beginning with fact collection, refining information, applying knowledge, adhering to principles, and ultimately achieving goals, whereas top-down (purpose-to-data) reasoning represents goal-driven methods, invoking appropriate wisdom and knowledge based on predetermined objectives to identify necessary information and data. Judges may employ bottom-up reasoning by applying legal rules (knowledge) to factual evidence (data) to resolve disputes (purpose), or conversely, use top-down reasoning, guided by legislative aims (such as public safety), to reinterpret facts and adjust rule applications accordingly.
As an extension of DIKWP, the ideal outcome of legal reasoning occurs when semantic coherence is achieved at each DIKWP layer: factual data are accurately interpreted, informational differences are appropriately articulated, legal rules precisely applied, jurisprudential principles respected, and legislative purposes ultimately fulfilled. This ensures that decisions are not merely legally valid but also contextually meaningful and reasonable. For instance, in administrative litigation, even if the losing party disagrees with the verdict, a clear DIKWP semantic traceability allows them to understand the basis of judicial discretion, and the broader public can affirm that the decision aligns with legislative intent and consistency principles.
Achieving semantic justice necessitates a comprehensive DIKWP model combined with explicit consideration of each stakeholder’s semantic frameworks. DIKWP offers distinctive advantages: while argumentation frameworks primarily operate at knowledge and wisdom levels (focusing on argument structures and evaluative principles), DIKWP provides an overarching semantic foundation. Case-based reasoning can be incorporated into the knowledge graph as precedent patterns or into the wisdom layer as judicial guidelines; machine learning excels at data/information-layer tasks (such as fact extraction from textual sources), whereas DIKWP compensates for its limitations in semantic transparency through structured knowledge processes. In practice, NLP techniques can supplement the data/information layers—such as employing language models to extract key facts from case documents—but the dominant role of the upper-level semantic architecture should always be maintained to ensure interpretability and fairness throughout the reasoning process.
3. Methodology
In this section, we present our methodology for transforming legal judgment processes from traditional conceptual-space representations into semantically enriched DIKWP representations. The core of our approach is a bidirectional mapping between two DIKWP-based model spaces: one representing the content of the legal case (laws, facts, evidence, etc.) and one representing the stakeholder perspectives (the cognitive–semantic world of the parties, including their goals and interpretations). We denote these spaces as DIKWP (Content) and DIKWP (Stakeholder), respectively. The mapping between them (DIKWP × DIKWP) ensures that information flows in both directions: the content is interpreted in light of stakeholder context, and stakeholder considerations are translated into the legal content space. We first define the formal structures of DIKWP graphs in our context, then describe the transformation pipeline and mapping algorithm, and finally illustrate these with pseudocode and a diagrammatic overview.
3.1. Formal Definitions
To provide a rigorous basis, we define the key components of our framework mathematically. This formalization will also aid in reasoning about the properties of the mapping (such as correctness and consistency) and in guiding an eventual implementation.
Definition 1
(DIKWP Graph for Legal Content). A DIKWP (Content) graph, denoted , is a 5-tuple where
- is a data graph with nodes representing atomic data elements from the case (e.g., a raw fact, a numeric measurement, a date, a text snippet of a law) and edges representing relationships or identity links among data (e.g., linking an evidentiary item to a source or linking duplicate data points).
- is an information graph with nodes representing information units (each encoding a meaningful distinction or comparison) and edges capturing relations like “difference”, “similarity”, or contextual connections between information units. Each information node is typically derived from one or more data nodes in . We establish a surjective mapping indicating which information nodes arise from which data nodes (for example, a data node “BAC = 0.10” might map to an information node “BAC exceeds legal limit”).
- is a knowledge graph where includes nodes representing legal concepts or rules (e.g., a specific regulation, a legal term like “LicenseRevocationCriteria”) and includes edges representing logical or ontological relations (such as “is_a”, “has_element”, “leads_to”). Knowledge nodes can also represent instantiated propositions like “Violation X is present” or “Condition Y is met in this case,” which are derived by applying general knowledge to specific information nodes. We define a mapping to indicate which knowledge nodes are activated or informed by which information nodes. For instance, the information “BAC exceeds limit” might map to a knowledge node representing the condition of a drunk-driving law.
- is a wisdom graph with nodes denoting higher-level constructs such as principles, heuristics, or experiential knowledge. Edges represent influence or dependency relations among these principles. In a legal setting, nodes might include “PublicSafety” (as a principle), “Deterrence”, “Proportionality”, or “PastCasePatternX”. These often do not directly connect to data, but we define a mapping where certain knowledge nodes (like a rule) are linked to wisdom nodes that justify or contextualize them (like the principle behind the rule, or an area of discretion).
- is a purpose graph with nodes representing goals or intents. In the content context, purpose nodes could represent the objectives of laws or the overarching goal of the proceeding (e.g., “EnsureFoodSafety”, “ResolveDisputeFairly”). Edges capture hierarchies or associations among purposes (for example, “EnsureFoodSafety” is part of the broader “ProtectPublicHealth”). A mapping connects wisdom to purpose, indicating which purposes are served by which principles.
We also include the union of all nodes and similarly union of edges . Collectively, can be seen as a layered multi-graph or a network of networks. Each “layer” (D, I, K, W, P) provides a different semantic zoom, and the cross-layer mappings tie the layers together, ensuring that every element of data is traceable through to some purpose(s), and each purpose is linked down to supporting data, albeit through possibly many intermediate nodes.
Definition 2
(DIKWP Graph for Stakeholder Perspective). A DIKWP (Stakeholder) graph, denoted , is similarly a 5-tuple . The structure mirrors that of , but the interpretation of each layer’s nodes is specific to a given stakeholder (which could be an individual, an organization, or even a “reasonable person” standard stakeholder). For clarity, we might index these by stakeholder identity (e.g., for stakeholder A, for stakeholder B, if multiple parties). In the context of a single appealing party vs. an agency, we might have one stakeholder graph for the appellant (citizen or company) and possibly one for the agency or just treat the agency’s perspective as embodied in the content graph’s purpose (since the agency is enforcing a purpose of the law).
The components of are as follows:
- , where includes data elements as perceived or provided by the stakeholder. This can include personal data (e.g., “I filed the application on Jan 1”, “I have 5 years of compliance history”) or evidence from their perspective (sometimes overlapping with content data, sometimes additional data only they know).
- , with information nodes capturing the stakeholder’s interpretation or emphasis on differences. For example, the stakeholder might highlight “the difference between my case and typical cases” as an information node. The mapping ties their data to information.
- , where includes the stakeholder’s knowledge and beliefs. This may involve their understanding of the law (which could be correct or mistaken), their knowledge of facts, or even normative beliefs (like “I did nothing wrong” or “the agency must consider X by law”). It can also include knowledge of past experiences (“last time a similar situation happened, only a warning was issued”). This layer is essentially a cognitive model of the stakeholder’s reasoning. maps their information to their knowledge.
- , containing Alice’s principles or values. For an individual, this might include notions of fairness, economic necessity (e.g., “if I lose my license, I lose my livelihood”), or moral considerations. For an agency stakeholder, wisdom might include internal policies or enforcement philosophies (“we prioritize safety over cost”). maps knowledge to wisdom for the stakeholder (e.g., the stakeholder knows a regulation exists but wisdom might say “that regulation is outdated and usually leniently enforced” as a principle they hold).
- , the stakeholder’s goals and purposes. For the appellant, the purpose is likely “get my license back” or more generally “achieve a fair outcome” or “continue operations”. There can be sub-goals like clearing one’s reputation, minimizing financial loss, etc. For the agency, the purpose might be “enforce compliance to ensure health” or similar. links their principles to their ultimate goals (for instance, a fairness principle in W could link to the goal of a fair outcome in P).
Each stakeholder will have their own . In a multi-party case, we could have multiple stakeholder graphs. For simplicity, in our methodology, we often refer to a singular stakeholder vs. content, but it is straightforward to extend to multiple stakeholders: one would map each stakeholder graph to the content graph and even consider mappings among stakeholder graphs (though that is beyond our current scope). The focus here is aligning one stakeholder (the appellant) with the content (law and facts)—a critical alignment in adjudication.
While the law’s perspective (e.g., legislative intent, enactment date, rationale) is typically embedded implicitly within the content graph , explicitly modeling the law as a separate DIKWP stakeholder graph () is also possible. This would allow clear representation of contextual knowledge related to laws themselves, providing richer insights when aligning stakeholder interpretations with legislative purposes.
Definition 3
(Semantic Mapping Functions). We define two complementary mapping functions:
- —a function (or procedure) that takes elements of the content DIKWP graph and finds semantically corresponding elements in the stakeholder’s DIKWP graph.
- —a function that maps elements from the stakeholder’s graph to corresponding elements or structures in the content graph.
These mappings operate across all layers, effectively creating correspondences where is a node (or subgraph) in the content graph and is a node (or subgraph) in the stakeholder graph representing “the same concept” or “the same real-world aspect” but in different semantic contexts. Some examples are shown below:
- A piece of data in the content graph (like a violation record in DG) might correspond to a data node in the stakeholder graph (the stakeholder’s acknowledgment of that violation, or perhaps their own evidence contradictory to it).
- An information node “violation is minor” in the content graph might correspond to “this violation is not a big deal” in the stakeholder’s information graph (essentially the same claim in different words).
- A knowledge node that is a legal rule in the content graph might correspond to a knowledge node in the stakeholder graph if the stakeholder is aware of that rule. If the stakeholder is not aware, there may be no corresponding node, which is an important case of mismatch.
- A wisdom node like “Enforcement should be proportional” in the content might correspond to a stakeholder’s wisdom node “I expect to be treated fairly and leniently for minor issues”. They are phrased differently but semantically related by the concept of proportional enforcement.
- A purpose node “Protect public health” in the content might correspond to the stakeholder’s purpose “Keep my restaurant open safely”—these can be aligned as not identical but as compatible purposes in an ideal resolution.
We formalize as comprising a set of mapping relations for each layer:
- maps data to data (e.g., the agency’s recorded inspection date corresponds to the date the owner remembers the inspection).
- maps information to information (e.g., “violation count = 3, which is high” might map to the stakeholder’s “I only had 3 minor issues, which I consider low”—here perhaps a conflict in interpretation that needs resolution).
- for knowledge (mapping formal rules to stakeholder’s understanding or lack thereof).
- for wisdom (mapping principles).
- for purposes/goals.
Similarly is the inverse relation (it may or may not be exactly the inverse function if mappings are not one-to-one; often there will be many-to-many or one-to-many correspondences, requiring careful reconciliation).
Consistency and Conflict:A crucial aspect of the mapping is identifying where there is consistency (alignment) or conflict (misalignment) between and . We define the following:
- A node is aligned with a node if for the appropriate layer X, and the semantic content (values, meaning) of those nodes are equivalent or compatible. For instance, if is a numeric value 3 and is also the numeric 3 for violation count, they are aligned; if is “severity = high” and is “severity = low”, they map but are not compatible—this indicates a conflict in evaluation.
- We call a conflict pair if they refer to the same real-world aspect but have substantially different values or interpretations. “Substantially” here means that differences are large enough to significantly affect stakeholder decisions, interpretations, or outcomes, rather than minor variations. Conflict pairs can occur at the data level (factual dispute), information level (different contextual framing), knowledge level (disagreement on which rule applies or how), wisdom level (differing principles prioritized), or purpose level (goal misalignment). When two nodes from different layers use different types of values, such as numeric values at the data level versus symbolic labels (e.g., “low”, “high”) at the information or knowledge level, we first normalize these values into a standard semantic scale (e.g., numeric values to qualitative labels) to facilitate meaningful comparison. For example, stakeholder might prioritize “economic survival” whereas law’s purpose is “public safety”; if a decision can satisfy both, great; if not, there is a conflict that must be adjudicated by priority or compromise.
- We will denote the set of all conflict pairs identified by the mapping by . The goal of reasoning will often be to resolve or minimize —ideally to zero for a fully agreeable outcome, but more realistically to explain why certain conflicts are resolved in favor of one side.
Inference within DIKWP Graphs: Each DIKWP graph (content or stakeholder) is not just a static network; it also provides a substrate for inference. For instance, within , we can infer new knowledge nodes by traversing from data to information to knowledge layers using domain rules, and similarly propagate purpose downwards by, say, selecting which knowledge to apply such that a purpose node is satisfied. While a full formal logic for inference is beyond our scope, we assume that each layer’s standard reasoning applies:
- In the knowledge graph, classical logical or ontological inference works (if all conditions nodes are present, infer the conclusion node, or use graph search to find applicable laws). Additionally, abductive inference [39] (inference to the best explanation) is particularly valuable in legal contexts, where it helps identify the most plausible interpretations of incomplete or ambiguous factual scenarios.
- In the wisdom graph, analogical or heuristic inference might apply (if a principle is triggered, prefer certain interpretations).
- In the purpose graph, one might propagate a goal backward (means–end reasoning: to achieve purpose P, which W nodes and K nodes could be activated?).
Our methodology will thus involve interleaving mapping with inference: as we map content to stakeholder perspective, we may find the stakeholder has knowledge that implies something not in content, so we add it to content (new node in perhaps), or vice versa. This dynamic ensures the two graphs increasingly reflect a shared understanding.
3.2. Transformation Pipeline Overview
Before diving into the detailed algorithm, we provide a high-level overview of the transformation pipeline, illustrated in Figure 1.
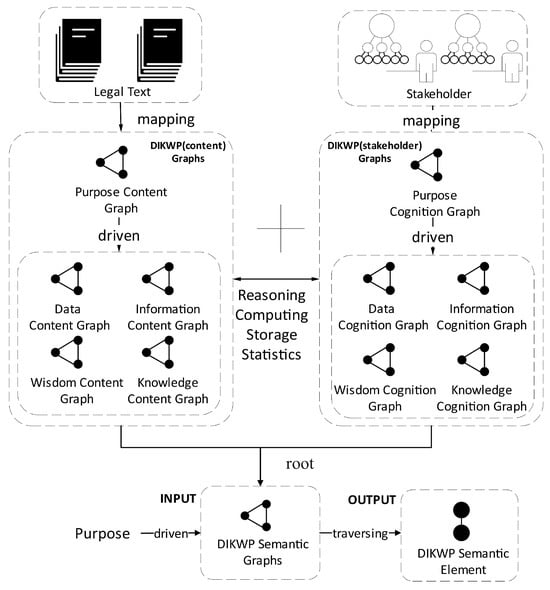
Figure 1.
DIKWP semantic judicial reasoning flowchart.
The legal content (left) is parsed into a DIKWP (Content) graph spanning data, information, knowledge, wisdom, and purpose layers. The stakeholder perspective (right) is modeled as a DIKWP (Stakeholder) graph covering identical semantic layers. Bidirectional mapping connects corresponding nodes between the two graphs via solid lines, establishing inter-layer associations between content and stakeholder dimensions. Arrows labeled “Purpose” indicate purpose-driven semantic transformations that guide the integration of subjective stakeholder semantics with objective legal content semantics.
The pipeline in Figure 1 can be described in stages:
- Content Ingestion and Graph Construction: Legal content (statutes, regulations, case facts, evidence, prior decisions) is ingested and segmented into DIKWP layers. This might involve NLP to extract data and information (e.g., named entity recognition to identify key facts, comparisons to highlight what is unusual in this case) and using legal knowledge bases to populate the knowledge graph (e.g., linking identified statutes to a network of legal concepts). The outcome is . For example, in our case study scenario, this stage takes the administrative record (inspection reports, legal provisions cited for revocation, etc.) and produces data nodes for each relevant fact (dates, violation types, etc.), information nodes capturing salient comparisons (e.g., “3 violations within 6 months, which is above average”), knowledge nodes encoding the regulation (“if 3 serious violations then license revocation is authorized”), wisdom nodes (perhaps “public health risk is significant if >2 violations/year” as a principle, drawn from guidelines), and purpose nodes (“protect diners’ health”).
- Stakeholder Input and Graph Construction: In parallel, the stakeholder’s (e.g., the restaurant owner’s) perspective) is captured. This could be through direct input (testimony, appeal letter, etc.) or via a cognitive user model. We construct from this, possibly using techniques similar to those used for the content graph (e.g., semantic extraction, node classification), but specifically tuned to handle subjective stakeholder inputs. For instance, the owner might provide data like “cleaning logs” or personal circumstances (“invested $50k in this business”), which become data nodes; information nodes might capture differences the owner emphasizes (“all violations were minor and quickly fixed”); knowledge nodes might include the owner’s references to rules (“the law says I should get a warning first”) or possibly misunderstandings; wisdom nodes could reflect their principles (“I always prioritize cleanliness” or “punishment should fit the harm”); and purpose nodes clearly include “Keep my license” and “Maintain livelihood” along with an implied shared purpose of public health (“I also want safe food because it’s my business reputation”).
- Initial Mapping (Alignment): We then perform an initial pass of and to align the graphs. This involves matching identical or equivalent items, such as recorded violations or cited regulations. Specifically, we might apply string matching for direct textual correspondences (e.g., matching violation descriptions exactly), ontology alignment to handle controlled vocabularies or structured semantic equivalences, or vector embeddings to identify semantic similarities in more nuanced expressions (e.g., aligning stakeholder phrases like “minor violations” with content descriptions like “low severity”). When aligning nodes across different data types or abstraction levels—such as numeric scores at the data layer versus qualitative labels (“low”, “high”) at higher layers—we first standardize these different representations into a common semantic space, facilitating meaningful comparison and matching. The output of this stage is a set of tentative mappings , and conflicts are identified. For example, the stakeholder graph might lack the knowledge node stating “3 violations mandate revocation”, indicating a knowledge conflict, or the stakeholder’s information node “violations minor” directly conflicts with the content node “violations serious.”
- Cognitive Alignment and Reasoning: This is where the actual semantic reasoning happens to reconcile the two perspectives. In Figure 1 (center), we illustrate this as transformations within cognitive, concept, and semantic spaces. In practical terms, the system (or judge) will carry out the following:
- Enter a cognitive space where the identified data and information are processed: this includes interpreting what each piece means, perhaps probabilistically confirming certain data as cognitive objects. Here any discrepancies in raw data might be resolved (e.g., if the owner contests a fact, the adjudicator decides which data to accept).
- Move to a concept space, where the relevant legal concepts and rules (knowledge layer) are organized. In this space, one figures out how the case fits into the legal framework: What rule applies? What definitions matter? This step involves mapping the specific scenario to the abstract rule structure. During this, the stakeholder’s knowledge is integrated: if the stakeholder raises an argument about a rule or brings up a different rule, this is considered in concept space. The mapping helps here: if the stakeholder’s knowledge node was not in the content, concept space reasoning might bring it in (e.g., “Stakeholder says rule Q should apply; is that relevant? let’s consider it”—possibly adding to content knowledge graph if valid).
- Then enter the semantic space, where actual semantic networks, specifically referring to the interconnected DIKWP graphs that integrate semantic relationships across data, information, knowledge, wisdom, and purpose, are considered. These semantic networks extend traditional semantic networks or knowledge graphs by explicitly modeling higher-level cognitive dimensions such as values and purposes. Within semantic space, nuances of language or context are resolved. For instance, understanding that “minor violation” from stakeholder and “Grade 3 violation” in content are referring to the same concept with different wording; such resolution is key to ensure that there is no mere semantic misunderstanding. This might employ ontology mapping or definitions.
- These transformations between spaces are purpose-driven: at each stage, the system is guided by the ultimate purposes (both the law’s and the stakeholder’s) in selecting how to reconcile differences. Purpose acts like a heuristic or weighting factor: if the purpose is public safety, cognitive/conceptual ambiguities are resolved in favor of interpretations that favor safety unless that would unjustly hurt the stakeholder’s purpose without corresponding safety gain (in which case maybe the stakeholder’s purpose influences a different interpretation that still satisfies safety minimally). We formalize this via the purpose graph influencing the reasoning path, e.g., if multiple knowledge rules could apply, the one that better serves the purpose nodes is favored.
- As a result of this reasoning process, certain conflict pairs in are resolved. For example, the conflict “serious vs minor” might be resolved by clarifying that the violations were of types that are serious under the code (so the stakeholder’s labeling of “minor” is incorrect), or perhaps by concluding that they were minor and the agency over-labeled them—depending on evidence, etc. Resolved means one side’s position is chosen but justified in terms of the semantic framework (with purpose often providing the justification).
- Semantic Fusion and Graph Update: After reasoning, we perform a fusion of the graphs: effectively updating both and to reflect a common understanding post-reasoning. If the process added a rule the stakeholder pointed out, that becomes part of the content knowledge graph (with maybe a note that the rule was considered but found not applicable or applicable). If a stakeholder’s misconception was corrected, the stakeholder graph (conceptually, the stakeholder’s understanding) is aligned to content. Of course, in reality, the stakeholder might not agree, but the model can at least represent what the adjudicator believes the stakeholder ought to understand after explanation. The fusion yields an integrated DIKWP representation of the case where, ideally, all remaining differences are in the purpose layer, if any (like simply differing goals, which cannot both be fully achieved—at least that tension is explicit).
- Decision Output and Explanation: Finally, the outcome of the process is a decision or recommendation (e.g., “License revocation is upheld, but with conditions” or “Revocation overturned, replaced by fine”). Because our reasoning occurred in the DIKWP semantic space, we can generate an explanation trace: start from purpose nodes (the decision’s justification in terms of purpose), and follow how that purpose is supported by certain wisdom/principles, which in turn relate to knowledge (specific laws or facts of case), down to the data that are critical. This trace can be presented in natural language as an explanation. For instance, “The decision to [Outcome] was made to fulfill the purpose of [Public Health Protection] (Purpose). In reaching this decision, the adjudicator considered the principle of [Proportional Enforcement] (Wisdom) and concluded that, under Regulation Y (Knowledge), although [three violations occurred] (Information from Data), they were all minor and promptly corrected (Wisdom balancing, as advocated by the appellant’s perspective). Therefore, a lesser sanction achieves compliance without undermining health goals (alignment of Purpose).” This corresponds to an explanation path that can be marked on the DIKWP graph. Indeed, an advantage of our approach is that the explanation is essentially a walk through the graph from data up to purpose, which is inherently interpretable.
The transformation pipeline can be viewed as iterative. Complex cases might need multiple passes, e.g., map and reason, discover a new conflict, go back, adjust, etc. But for methodology, a single pass that integrates alignment and reasoning as above is sufficient to describe the process.
4. Case Study: Administrative Law Scenario
To demonstrate the proposed framework, we present a detailed case study grounded in an administrative law context. The scenario we have chosen involves a common type of dispute: a conflict between a regulatory agency and a regulated entity (or individual) over a license revocation due to alleged violations of regulations. This scenario is rich enough to exercise all parts of our DIKWP semantic reasoning—facts, rules, principles, and purposes—while being relatable to real-world cases (such disputes occur in health inspections, environmental permits, professional licensing, etc.). For concreteness, we will consider it in the domain of public health regulation: a restaurant’s food service license revocation by a city health department, which the restaurant owner appeals.
Scenario Description: The City Health Department conducted inspections of a family-owned restaurant, “GoodFood Bistro,” over the past year. In the last inspection, the department found three violations: one related to food temperature control, one related to cleanliness of equipment, and one related to record-keeping. Based on these, the department issued a notice of license revocation, citing that this was the third inspection with violations in a year and invoking Regulation 5.4 which states that “establishments with serious or repeated violations may be subject to license suspension or revocation.” The restaurant owner, Alice, contends that the punishment is too harsh: the violations were minor, nobody fell ill, and all issues were immediately corrected. She argues that normally first-time or minor issues result in a warning or fine, not a shutdown. She appeals the decision to an administrative law judge.
This scenario encapsulates the following:
- Data: inspection reports, number and type of violations, compliance history.
- Information: whether “three violations in a year” is abnormal, whether these count as “serious” or “repeated” under the regulation.
- Knowledge: the text of Regulation 5.4; any city guidelines on enforcement; past cases if available.
- Wisdom: principles like public health protection, fairness to small businesses, deterrence vs. education in enforcement.
- Purpose: the purpose of the health code (prevent foodborne illness) and the purpose of the business (to operate safely and profitably), and the judicial purpose of reaching a fair resolution.
We will now apply the methodology step-by-step to this scenario.
4.1. DIKWP (Content) Graph Construction for the Case
Data Layer (Content): We extract the key data from the agency’s perspective (the administrative record):
- D1: “3 inspections in last 12 months for GoodFood Bistro” (with dates Jan 10, Jun 5, Dec 1).
- D2: “Inspection on Dec 1 found 3 violations” (with details such as Violation A: hot soup at 50 °C (below required 60 °C); Violation B: slicer not fully sanitized; Violation C: some logs incomplete).
- D3: “Previous inspections also had violations” (maybe Jan 10 had 2 minor violations; Jun 5 had 1 moderate violation; data can be each count and type).
- D4: “Notice of revocation issued Dec 5 citing Regulation 5.4.”
- D5: The text of Regulation 5.4 (or relevant excerpt).
- D6: Any known policy memo or guideline (suppose there is a Health Dept Guideline that says, “Enforcement actions: 1st time minor violations = warning, repeated serious violations = suspension/revocation”).
- D7: (If accessible) outcome data from similar cases (e.g., maybe a reference that 5 other restaurants had licenses suspended in the last year for repeated violations).
- D8: “No reported foodborne illness incidents at GoodFood Bistro in last year.”
- D9: “GoodFood Bistro’s owner submitted correction proof within 2 days after each inspection.”
- These are all factual pieces, many of which appear in documents (inspection reports, the notice, possibly internal records).
Each of these becomes a node in , possibly typed as follows:
- Edges in might link, for example, each violation detail to the date of inspection.
Information Layer (Content): From data, we derive salient information:
- I1: “Three violations were found in the last inspection” (a simple restatement, but important as a summary).
- I2: “This is the third consecutive inspection with violations”—highlights a repeated pattern.
- I3: “Number of violations in last year = 3 + 2 + 1 = 6 total; number of inspections with any violations = 3/3 (100%)”—quantifies repetition rate.
- I4: “All three violations on Dec 1 were categorized as ‘serious’ by inspector”—if the inspector or code classifies them (assuming the code or inspector did mark severity).
- I5: “Violations corrected immediately”—from D9, the fact that corrections were made promptly, meaning issues were resolved.
- I6: “No illnesses occurred”—from D8, implies harm was potential, not actual.
- I7: “Policy says repeated serious violations may justify revocation”—gleaned from D6 possibly.
- I8: “Policy suggests first-time minor issues get warning”—also from D6.
- I9: “GoodFood Bistro has 5-year operation history” (if gleaned from context, maybe not directly in provided data but could add if known, though not mentioned explicitly, skip if not in record).
We link these as follows:
- : the raw counts yield those info points.
- : inspector’s categorization is typically part of D2 details.
- .
- : reading the policy memo yields those info guidelines.
Knowledge Layer (Content): Key knowledge nodes include the following:
- K1: Regulation 5.4 (Revocation rule): likely structured as “IF (establishment has serious or repeated violations) THEN (agency may suspend/revoke license).”
- K2: Definition of “serious violation” (maybe in code, e.g., any violation that poses immediate health hazard, like improper temperature).
- K3: Definition of “repeated violations” (e.g., violations in 3 consecutive inspections might qualify).
- K4: Agency’s enforcement guideline (if D6 is formal, make it a knowledge node: “Guideline: 1st minor → warning, repeated serious → revoke”).
- K5: Administrative law principle: “Agency has discretion in enforcement actions” (like a general knowledge that revocation is discretionary, not automatic).
- K6: Procedural rule: “Licensee has right to appeal” (for completeness, but less substantive to outcome).
- K7: Precedent cases or past decisions (if any, though maybe not in record).
- K8: The concept of “license revocation” itself as an action/outcome node.
We connect information to knowledge:
- I4 (serious violations present) triggers knowledge K2 (definition: each of the three qualifies as serious maybe). Also triggers part of K1’s condition (“serious violations present”).
- I2/I3 (repeated pattern) triggers knowledge K3 (definition of repeated: clearly yes, repeated).
- So the conditions for Regulation 5.4 (serious or repeated) are satisfied. That would allow the conclusion “may revoke license” to be activated.
- I7, I8 connect to K4 (policy guideline).
- If K4 guideline exists, it might conflict or interplay with K1: K4 says first-time minor → warning (not exactly our case, since not first time), but implies maybe a progressive enforcement concept.
- K5 (discretion principle) is background knowledge connecting to K1’s “may” (not mandatory).
- K8 (license revocation outcome) might be considered a knowledge node or could be considered in wisdom/purpose as well, but we treat it as the specific action knowledge node that is the result of applying K1.
Wisdom Layer (Content): Identify the principles:
- W1: “Protect public health”—a core principle behind health regulations.
- W2: “Enforcement should ensure compliance”—a principle guiding why to punish (to induce compliance).
- W3: “Proportionality”—enforcement actions should be proportional to the violation severity (maybe not explicitly stated by agency, but it is a general legal principle; however some agencies follow “zero tolerance”, which is opposite of proportionality).
- W4: “Consistency and deterrence”—ensure consistent application to deter others (agency principle possibly).
- W5: Perhaps “Support local business while ensuring safety”—some balance principle if present in policy rhetoric (if not, agency might not consider this).
- W6: “Due process/fairness”—a generic principle in any adjudication (though might be more on judge’s side).
- The agency likely prioritizes W1, W2, and W4. The ALJ (adjudicator) inherently will consider W3 and W6 as well.
Connect knowledge to wisdom:
- Regulation 5.4 exists to serve W1 (public health) and W2 (compliance).
- We can link K1 → W1, W2.
- The guideline K4 implies a principle of proportional response: link K4 → W3 (since it literally distinguishes actions by severity).
- K4 also reflects W2 (compliance, because warnings escalate to stronger measures if not complied).
- K5 (discretion) links to W3 or W6, as it allows judgment.
- If a zero tolerance stance was present, that would link to W4 (deterrence).
- We include W3 proportionality because the presence of a guideline implies someone considered it, but it might be contested as applied here.
Purpose Layer (Content): Identify purposes:
- P1: “Prevent foodborne illness and protect public health” (the statutory purpose of health regulations).
- P2: “Ensure sanitary conditions in food establishments” (more specific version of P1, or part of P1).
- P3: “Uphold rule of law/ regulatory compliance” (a general purpose of having enforcement).
- P4: “Fair and orderly administration” (may be the purpose of the appeals system).
- Possibly P5: “Economic vitality of community” (some cities have this as a general goal, but probably not part of the health department’s mandate, so maybe not explicitly).
- The adjudicative body might also have purpose “deliver a just outcome” (could include under P4 or separate).
- Connect wisdom to purpose:
- –
- W1 (public health) directly serves P1.
- –
- W2 (ensure compliance) serves P1 and P3 (compliance as intermediate to health).
- –
- W4 (consistency/deterrence) serves P3 (rule of law).
- –
- W3 (proportionality) serves both P1 (because overly lenient might fail health, overly harsh might exceed what is needed for health and conflict with justice) and P4 (fair administration).
- –
- W6 (fairness/due process) serves P4 and arguably serves the societal purpose of justice.
Thus, the DIKWP (Content) graph encapsulates the agency’s position, including evidence of violations (data), confirmation of repeated and serious issues (information), explicit authorization under Regulation 5.4 to revoke the license (knowledge), guided by principles of public health protection and consistent enforcement (wisdom), ultimately serving the purpose of safeguarding public safety (purpose).
4.2. DIKWP (Stakeholder) Graph Construction (Restaurant Owner’s Perspective)
Now, we construct the owner Alice’s perspective.
Data Layer (Stakeholder): Alice will have some overlapping data and some unique:
- D1’: (Corresponds to D1) Alice is aware that three inspections occurred during the past year, although she may frame this fact differently (e.g., “My establishment has been regularly inspected”).
- D2’: Alice acknowledges that the inspection on December 1 identified certain issues, though she disputes some details. Nevertheless, she addressed the issues promptly, indicating recognition of their existence.
- Alice may provide additional contextual information: “All compliance violations were rectified on-site” (while this appears as a mere factual statement in the complaint records, for Alice, it serves as documented evidence of her personal corrective actions).
- D9’: Alice may provide/submit the following evidence: receipts for new thermometers purchased after, cleaning logs, etc.
- Additional data she might bring: “No customer ever complained or got sick at my place” (though content had that too).
- Personal data: “I have run this restaurant for 5 years” (if relevant).
- “This is my livelihood; 10 employees work here” (impact data).
- “I passed all prior inspections until this year” (maybe she had good record before).
- Therefore, Alice’s data nodes () overlap substantially with the content data but explicitly include information about business impact.
Information Layer (Stakeholder): Alice will emphasize the following key points:
- I1’: “Issues were minor”—Alice categorizes them as minor due to the absence of immediate danger from her perspective.
- I2’: “I corrected everything immediately”—highlighting responsiveness.
- I3’: “No harm resulted (no one sick)”—as a point why it is minor.
- I4’: “I’ve improved practices since”—suggesting enhanced compliance efforts.
- I5’: “Past good record (only this year had violations)”—Alice would likely cite this if factually accurate.
- I6’: “Punishment (revocation) is extreme compared to the violations”—this represents Alice’s interpretation/key point of contention: essentially an assessment of the relative relationship between the violations and the severity of punishment.
- I7’: Alice might argue, “Other restaurants usually just get fines for similar issues.”
- I8’: “I was not given a warning or chance before this action”—process-related info difference.
- These map from her data:
- –
- Correction and no harm from D9’ → I2’, I3’.
- –
- Minor vs. serious: Alice may define “minor” based on examples such as “the soup was only slightly below the required temperature but was immediately reheated” or “the slicer was sanitized on the spot”—in her view, these issues are considered minor because they can be quickly rectified. After her interpretation, the details of Clause D2 ultimately lead to the I1’ conclusion.
- –
- Impact on business D(impact) → I6’ (punishment extreme because effect is closing business).
- –
- Alice’s awareness of comparable enforcement cases may lead to assertion I7’ regarding typical penalties applied to similar violations.
- –
- Lack of warning → I8’ from her experience that she never received a formal warning letter prior.
Knowledge Layer (Stakeholder): What does Alice believe or know?
- K1’: Alice may not know specific regulation numbers but is familiar with the general concept of “health code violations” and the need for corrective action in certain circumstances. She might have incomplete knowledge of Regulation 5.4.
- K2’: Alice believes, “If violations are corrected and don’t involve critical items, you normally get a chance to rectify them rather than having your license revoked directly.” (This essentially serves as her personal adjudication principle—whether codified or not. This understanding may stem from industry-wide expectations, or perhaps from compliance advice given by inspectors, such as when they have provided guidance on how to make improvements.)
- K3’: Alice may have knowledge of specific regulatory provisions, such as requirements for immediate closure only under conditions of imminent health hazards.
- K4’: Alice is aware of the appeals process (since she is currently filing an appeal).
- K5’: Alice may invoke “small business protection policies” or seek leniency citing pandemic impacts (provided such government policy inclinations actually exist).
- K6’: Alice is likely fully aware of all the factual violations (such as which specific provisions were breached).
- K7’: Alice may have sought advice and been instructed to cite specific precedents or standards (though this remains uncertain in the current context).
- For mapping: K2’ is basically the knowledge that matches content’s guideline K4, or at least similar.
- If K3’ (imminent hazard rule) exists in law, it would align with something in content perhaps not explicitly mentioned. If not, it is a misunderstanding or a half-truth (some places do that).
- Therefore, : “health code not intended to shutter business for minor things”, “I should have gotten a warning first”, “I fixed everything so compliance achieved”, “I have right to appeal” (that aligns with K6 maybe), “others get fines” (implying a consistency standard).
We align additional alignment the following:
- K2’ (“chance to correct rule”) aligns with content’s policy K4 (which indeed says warning for does not).
- If Alice explicitly cites a specific regulatory provision, or if she was told that “imminent danger is required to justify immediate closure”, this may correspond to an unstated principle or regulation (unless the cited provision actually contains such stipulation).
- Alignment will be identified during the subsequent mapping stage.
Wisdom Layer (Stakeholder): Alice’s principles and values include the following:
- W1’: “Fairness”—Alice perceives the enforcement action as disproportionate to the violations committed.
- W2’: “Second chance/forgiveness”—this forms the foundational rationale for Alice’s argument that a prior warning should be issued.
- W3’: “My dedication to safety”—Alice may also emphasize her commitment to public safety (value).
- W4’: “Hardship to employees/community”—a moral point, closing hurts innocent parties (the employees, customers losing a beloved place).
- W5’: Potentially includes the perception of being targeted or treated disproportionately, representing a concern regarding inconsistency or unfair treatment.
- These are more emotional/moral, but in formal terms, fairness and proportionality align with content’s wisdom W3, W6.
- The hardship argument appeals to external principles of equity, which certain jurisdictions permit administrative adjudicators to consider.
- W5’ is a hint at inconsistency (if Alice suspects other violators were not subjected to equal treatment, it raises issues of fairness/consistency principles).
- The mapping thus proceeds as follows:
- –
- Fairness (W1’) aligns with W3 (proportionality) and W6 (due process) content.
- –
- Second chance (W2’) is an element of fairness, also aligns with W3.
- –
- Dedication to safety (W3’) interestingly aligns with W1 (public health); Alice is essentially asserting “I share the purpose, I’m not a bad actor”, thereby resonating with the law’s ultimate purpose.
- –
- Hardship (W4’) might align with a general principle of equity or could remain a stakeholder-only concern (though one could tie it to public interest in economic vitality).
- –
- Consistency/harshness (W5’) aligns with content W4, if Alice implies inconsistent enforcement.
Purpose Layer (Stakeholder): Alice’s objectives include the following:
- P1’: “Keep my restaurant open (retain license).”—immediate practical goal.
- P2’: “Maintain my livelihood and my employees’ jobs.”—underlying purpose.
- P3’: “Serve safe food to community.”—Alice genuinely prioritizes consumer protection; when explicitly articulated, this demonstrates alignment with legislative intent (to strengthen her position, she might affirm, “Of course I want safety too, I’ve always complied as best as I can.”).
- P4’: “Be treated fairly and with respect by authorities.”—a more abstract goal, but it is something stakeholders often want (acknowledgment of fairness).
- P5’: “Avoid closure-induced community impact” (like some restaurants say “we contribute to community, closure hurts more than helps”).
- Among Alice’s objectives, P1’ directly conflicts with the agency’s immediate enforcement objective; however, her objective P3’ positively aligns with the overarching public health purpose of the applicable regulations.
- Map:
- –
- P3’ (serve safe food) aligns with content P1 (protect public health).
- –
- P1’ (keep open) does not align with any content purpose except maybe indirectly if we consider “encourage business compliance without needless closure” but that is not explicitly in content.
- –
- P2’ and P5’ (livelihood, community) are not considered in the health code purpose, so those might not align to any content purpose (they are external interests).
- –
- P4’ (treated fairly) aligns with content P4 (fair administration).
4.3. Bidirectional Mapping and Semantic Integration
We proceed to align and discuss differences:
Data Alignment:
- Inspection facts: She acknowledges three violations on the last inspection (so content D2 vs. stakeholder D2’ align, except classification maybe).
- The existence of prior violations: Content had Jan and Jun with issues; she said she had a good record until this year. Maybe she admits to those too but considers them minor. Let us assume she does not deny them, she just downplays them. So the number of violations aligns, but significance differs.
- Data on no illnesses: Both agree none occurred.
- Correction data: Content not explicitly listing that but we gleaned from context; she explicitly says it. We will align that as it is factual that she did fix them (maybe the inspector report even notes “corrected on site”—then it was content data too).
- Regulation text: Content has it; stakeholder might not have read the text, but she knows the gist. There might not be a direct node, except her knowledge K2’ implicitly references it.
- She has data on impact (employees, etc.) not in content (agency likely did not consider that because it is legally not relevant to health). That remains a stakeholder-only data point.
Info Alignment/Conflict:
- “Violations serious vs minor”: Conflict. Content Info I4 says serious. Stakeholder I1’ says minor. This is a key conflict. To resolve, we need to see how “serious” is defined. If the regulation has defined certain violations as critical, perhaps at least one of hers (food temp out of safe range) is indeed considered a critical violation by code (which would justify calling it serious). If others are not as severe, nuance is needed. The inspector may have labeled all as serious, but maybe one was critical, and others moderate. So who is right? We might find partially both. We will likely learn that at least some were legitimately serious (for instance improper temperature can cause illness).
- “Repeated violations vs one-time”—Content sees pattern (I2: each inspection had something). Stakeholder might emphasize they were all different issues and minor (maybe she thinks they do not count as “repeated same violation”). There is an interpretation difference: if “repeated” means a repeat of the same issue or just any issues repeatedly. Regulation likely means any recurring issues count. That is a knowledge nuance. She might have thought repeated means “I keep doing same wrong thing, which I didn’t”.
- “Punishment extreme or not”: Stakeholder info I6’ explicitly says it is disproportionate; content did not have a node explicitly praising punishment, but content expectation might be that revocation is justified because of serious threats. This is more evaluative info which ties to wisdom conflict.
- “Others get fines”: May be true and content might have no info on others. If she is right, then there is an inconsistency. If she is wrong or her case is worse, clarification is needed. Content may not have considered others because each case is separate, but to her, it is inconsistent. This can be touched on in wisdom (consistency).
- “No warning given”: Indeed, content did not mention any prior formal warning, just immediate move to revoke after the third time. Possibly, the policy K4 suggests a warning on first minor, but maybe the agency considered these not minor. Conflict: she expected progressive discipline, agency acted swiftly. We will see that in knowledge/wisdom.
Knowledge Alignment/Conflict:
- Regulation 5.4 (K1 vs. K1’): She may not contest it exists but contest interpretation. She probably does not deny the rule “may revoke for serious/repeated”; she might just argue her case did not meet that threshold (contrary to agency view). So knowledge node exists, but triggered condition is disputed. This is tied to “serious/repeated” definitions (K2, K3 vs. her understanding).
- Policy guideline (K4 vs. K2’): Good alignment—her belief “I should have gotten a warning for first issues” is basically what is in policy. So both have a concept of progressive enforcement. Likely she is invoking that guideline exactly. So K4 in content and K2’ in stakeholder align strongly.
- But the conflict is that the agency might argue that guideline does not apply if violations are serious enough, or that she already had multiple chances (since three inspections). She may think she never received an official warning letter (maybe she received inspection reports though).
- Discretion (K5): She might not articulate it explicitly, but her argument implies “they had a choice to not revoke, they should have used it”.
- She might bring any knowledge like local laws about hearing procedures, etc., but that does not change outcome directly.
Wisdom Alignment/Conflict:
- Fairness/Proportionality (W3 content, W1’ stakeholder): Aligned in concept. Both would agree in principle punishment should fit crime. The conflict is whether that principle is being followed here or not. Agency might say “we are proportional because repeated serious issues warrant revocation.” She says “this is not proportional because issues were minor”. So they share the principle but disagree on fact classification under it. So W3 maps to W1’ (and W2’ second chance).
- Public safety (W1 vs. W3’): Aligned—she cares too, at least claims. That is a positive alignment: both ultimately want safe food. This is good for compromise scenario because one can argue ensuring compliance (safety) without closure might achieve both purposes.
- Strict enforcement vs. leniency (W4 vs. W2’): Conflict. Agency might lean to deterrence/strictness, but she wants leniency. This needs reconciliation. Possibly judge will lean that since no actual harm, leniency is okay while still ensuring compliance.
- Hardship principle (W4’): Agency had no node for considering economic impact (not their mandate). The judge might consider it indirectly as part of fairness but health law often does not weigh that explicitly. However, in equitable discretion, a judge could consider it in deciding remedy. It is not a mapped alignment, it is an extra concern. We might see it as connecting to fairness too (it is unfair to destroy a business if not necessary).
- Due process (W6 vs. P4’ fairness goal): They align conceptually. She wants fair treatment; law wants fair process.
Purpose Alignment/Conflict:
- P1 (public health) vs. P3’ (serve safe food): Aligned. Both sides share that.
- P3 (compliance/rule of law) vs. her P1’ (keep license): Direct tension, because compliance from agency view might mean penalizing violators (to uphold rules), whereas her goal is to avoid penalty. However, these can be balanced if compliance can be achieved in another way. Perhaps by imposing strict conditions or monitoring rather than closure, one can satisfy compliance while allowing her to operate.
- P4 (fair process) vs. P4’ (treated fairly): Aligned.
- Her P2’ (livelihood) vs. no corresponding content purpose: This is an external interest, but a judge might consider public interest in not unnecessarily harming livelihoods. Not in health dept’s goals, but the appeal judge might weigh it generally as part of justice.
- In conclusion, there is a potential solution if one can find an outcome that fulfills both sides’ purposes: maintain public health (by ensuring she fixes issues, maybe a probation period) and allow her to continue business (serves her purpose). That compromise outcome could be as follows: instead of revocation, impose a short suspension and fine, require training, with warning that next time it is revocation for sure. That would align with proportionate enforcement principle and still uphold law’s purpose.
Now, let us simulate the reasoning and outcome:
- Data conflicts: Not much—facts are mainly agreed, just interpreted differently.
- Info conflicts: Resolved by referencing code definitions. Suppose the code defines “critical violation” as something causing imminent risk (like temperature violation might qualify as critical because it can cause illness if not fixed). The equipment cleanliness might be moderate, record-keeping minor. If inspector labeled all as “serious”, maybe they have categories: critical vs. general violation. It could be that any critical violation at an inspection escalates enforcement.
- –
- The adjudicator might parse one critical (soup temperature), which was corrected immediately, and two lesser ones. So “serious” might technically apply because a critical violation was found; thus, an inspection with a critical violation is considered serious overall.
- –
- She called them minor because in effect nothing bad happened and they were fixed. It is a perspective difference. The judge would likely accept the code’s classification (so yes, a critical violation is serious by definition), but also note that it was swiftly mitigated.
- Knowledge reasoning:
- –
- Regulation 5.4 conditions are met: Repeated violations (three inspections in a row had issues). So legally, agency may revoke.
- –
- The policy guideline, though, says it is usually progressive discipline. Did the agency skip a step? Possibly, earlier inspections should have triggered something like a warning letter. If they did not formally warn, that might weigh in her favor (agency jumped to revoke without a formal intermediate sanction).
- –
- But maybe they gave verbal warnings in each report. If formal policy not followed (e.g., maybe they were supposed to issue a written warning after second inspection but did not), she can argue procedure not followed.
- –
- The judge sees that the agency had discretion. The guideline suggests revocation is typically for severe repeated issues posing real risk. In this case, while repeated, actual harm has not occurred and she showed willingness to correct. The principle of proportionality suggests considering a lesser penalty that still ensures compliance (like heavy fine, mandated training, frequent re-inspections).
- Wisdom resolution:
- –
- Public health vs. fairness: Both need to be satisfied. The judge likely thinks public health can be protected if the restaurant fixes issues and is monitored; fairness suggests not destroying the business for first-time (in a year) compliance troubles.
- –
- Strictness vs. leniency: Based on no harm and improvements, lean towards leniency but with caution.
- –
- The judge perhaps also considers deterrence: Imposing no penalty could lead to lax compliance among other practitioners. Thus, a fine or short-term suspension can serve as an effective deterrent without being as disproportionately severe as permanent license revocation.
- –
- Hardship: An unnecessary closure hurts livelihood—that principle, while not in law, could be implicitly considered under fairness.
- Purpose alignment:
- –
- Find outcome that satisfies P1 (health) and as much of P1’ (keep open) as possible.
- –
- Perhaps a compromise: The license is reinstated conditionally. Outcome: Overturn revocation, instead impose a one-week suspension and USD X fine, require proof of corrective measures, and stipulate that any future serious violation will result in immediate revocation with no further appeal. This holds her accountable (serves compliance and deterrence) but gives her a chance (aligns with second chance and business survival).
- –
- That outcome is not directly an option in the content knowledge unless discretionary. But given “may revoke” implies “may choose lesser too”, the judge can decide a lesser sanction is sufficient.
Let us assume the administrative judge’s decision: Revoke order is set aside; the license is reinstated under a probationary period. During probation (say 6 months), the restaurant will be subject to monthly inspections and must remain violation-free; if any serious violation recurs, revocation will be immediate with no further appeal. Additionally, a fine is imposed and the owner must attend a food safety course.
This hypothetical ruling attempts to meet the law’s purpose (improve compliance and protect health—since the restaurant is being heavily monitored and forced to improve) while satisfying fairness (not shutting down permanently for what were mostly minor issues), thereby aligning with semantic justice.
Now, let us explain this using the DIKWP:
Explanation (in terms of graphs):
- Purpose: The judge’s decision is driven by protecting public health (P1) and ensuring fair enforcement (P4). The solution aims to secure safety without an unduly harsh outcome.
- Wisdom: The principle of proportional enforcement (W3) guided the outcome, balancing strict compliance (W4) with fairness/second chance (W2’). The judge recognized that immediate revocation, while legally permissible, was not strictly necessary to achieve compliance given the owner’s demonstrated cooperation. Instead, a conditional approach was taken, aligning with enforcement guidelines that emphasize graduated responses.
- Knowledge: Under Regulation 5.4 (K1), the agency had discretion to revoke for repeated serious violations. However, the agency’s own guideline (K4) indicates lesser measures for initial or minor infractions. The judge noted that GoodFood Bistro’s violations, though technically “serious” under the code (improper temperature being a critical issue), resulted in no harm and were promptly corrected (information from the record). Furthermore, the prior inspections, while not perfect, did not lead to any formal warning or intermediate sanction, which the guideline would have suggested. This context invokes the knowledge that enforcement discretion (K5) should be exercised in line with both the letter and spirit of the law. The judge thus chose to exercise discretion by imposing a penalty short of revocation, which is still within the scope of the regulation (“may suspend or revoke” implicitly allows lesser penalties).
- Information: Key information considered includes that all violations were remedied on-site and no illness occurred (content I5, I6, stakeholder I2’, I3’ align on this) and that the establishment had never before faced such an enforcement action (stakeholder I5’: first revocation threat). This suggested the situation was not an egregious, willful flouting of rules but rather compliance issues that could be corrected. The pattern of repeated violations (content I2, I3) was acknowledged, but the nature of those violations (stakeholder’s perspective that they were minor, content’s evidence that at least one was critical but mitigated) led to an interpretation that the restaurant was not hopelessly negligent, just in need of improvement.
- Data: The factual record supporting the decision included the inspection reports (violations details, D2), the timeline of inspections (D1), and evidence of corrective action (D9, e.g., receipts or proof of training) provided during the appeal. No contrary factual evidence was presented by the agency beyond what was in the reports, and the owner’s facts (like no illnesses, corrections made) were not disputed. Thus, the data points used in reasoning were largely agreed upon, which allowed the dispute to center on their meaning and implications rather than what happened.
In summary, the decision to reinstate the license on probation “does semantic justice” to the case by directly addressing the semantics at each layer: it recognizes the data (violations occurred, but also corrections were made), interprets the information in context (violations were serious in code terms but minor in outcome), applies the knowledge of rules with nuance (discretion and guidelines considered, not just the strict condition–action rule), follows wisdom principles (achieving the law’s purpose through a proportionate response), and ultimately serves the purpose of the law (protecting health) while respecting the purpose of the stakeholder (continuing a business responsibly). The outcome is explainable to the stakeholder: Alice can be told, “Your license remains in effect because we trust you can operate safely—we saw you took immediate action to fix issues (acknowledging her efforts towards the shared goal of safety). However, due to the pattern of problems, we are imposing conditions to ensure public health is not put at risk (underscoring the primary purpose). This balanced approach gives you a fair chance (addressing fairness) while still protecting your customers (addressing safety). If any serious problem happens again, the law’s requirement to protect the public will necessitate a revocation (making clear how purpose will guide future decisions).” Such an explanation directly mirrors the DIKWP reasoning path, citing data (“immediate action taken”), information (“pattern of problems”), knowledge (the rules and conditions for future actions), wisdom (balance fairness and safety), and purpose (protecting customers, giving a fair chance), as shown in Figure 2.
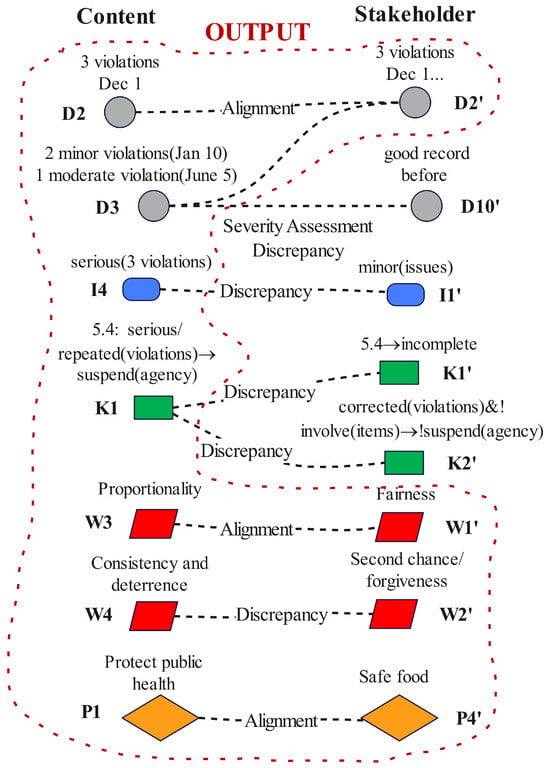
Figure 2.
DIKWP semantic reasoning graph based on law cases.
Through this case study, we see the DIKWP framework in action: it allowed the decision-maker (here the ALJ) to systematically map the legal content and the stakeholder’s perspective, identify the semantic differences (minor vs. serious, punishment harsh or not, etc.), and find a resolution that operates in the semantic space common to both. The bidirectional mapping was crucial—the stakeholder’s insistence that the punishment was too harsh (stakeholder’s W1’ and purpose P1’) was mapped into the legal semantic space as a call for proportionality (content W3) and consideration of alternative enforcement (knowledge K4). Conversely, the law’s demand for public safety and compliance (content W1, W2, purpose P1) was mapped onto the stakeholder’s space as a non-negotiable goal that Alice had to accept and work with (she did, by emphasizing she also prioritizes safety; stakeholder W3’, P3’). By aligning these, the resulting decision could satisfy both: compliance is achieved (public health protected) and the business survives (fair outcome).
It is worth noting that not all cases will have such relatively harmonious alignment potential—some stakeholders’ goals (like “avoid any penalty”) may be irreconcilable with legal purposes in full. In those cases, the framework still helps by transparently showing the trade-off: the mapping and semantic analysis will pinpoint exactly where purposes diverge and why the decision must favor one over the other (e.g., “the stakeholder’s purpose of avoiding any penalty cannot be met because it conflicts directly with the law’s purpose of deterrence in this scenario”). Even then, the explanation can be given in semantic terms: “We understand your goal, but here is why the law’s goal prevails, and how that is grounded in these facts and principles…”—which is more satisfying than a terse legalistic “because rule X says so.”
5. Evaluation
We evaluate our DIKWP-based semantic judicial reasoning framework along two primary dimensions: conceptual soundness (how well it captures and integrates the elements of legal reasoning compared to traditional models) and implications for explainability and fairness (the touted benefits of the approach). Since the framework is presented at a design and prototyping level (we have not built a fully automated system to statistically evaluate on many cases), our evaluation is primarily analytical and qualitative. However, we draw on established criteria in AI and law and on the specifics of the case study to substantiate the advantages of the approach.
5.1. Conceptual Coverage and Rigor
One way to evaluate a legal reasoning model is to check whether it can represent all the knowledge and inferences that a human expert would consider in deciding a case. Our DIKWP model deliberately expands the representational scope by including layers (wisdom, purpose) that often remain implicit in other models. In the case study, for example, a traditional rule-based approach might have ended reasoning at “Regulation 5.4 applies, conditions met, thus revoke license.” It would not represent the notion of proportionality or the idea that the agency had discretion. In contrast, our model explicitly represented these as knowledge and wisdom nodes, which allowed an alternative outcome to emerge. Conceptually, this demonstrates completeness: the DIKWP (Content) graph included the rule and also meta-rules (like guidelines, discretion) and principles. The DIKWP (Stakeholder) graph captured the appellant’s views, including some that are not strictly legal arguments (like hardship)—yet those can influence a judge’s equitable thinking. By mapping them, the model did not ignore those factors.
We can evaluate conceptual soundness by mapping our model to well-known ontological frameworks. For instance, Van Kralingen’s legal ontology (frame-based) delineates categories like act, agent, condition, outcome, and purpose in legal norms. Our content knowledge layer covered act/condition/outcome (the regulation’s structure), and our purpose layer corresponds to the purpose in that ontology. Many traditional models leave out purpose, whereas we included it and used it in reasoning. This alignment with existing legal theory suggests our model is not introducing alien concepts, but packaging them in a coherent way.
Another measure is logical consistency: does reasoning in the DIKWP model avoid contradictions and produce a legally valid outcome? The framework uses the law’s own rules as knowledge nodes, so it respects logical constraints of the domain. In the case study, the outcome chosen did not violate any law (the judge stayed within discretion bounds). The DIKWP approach helped identify that outcome by considering multiple rules and principles. Importantly, if the model had encountered a conflict it could not resolve (say two laws in contradiction), it could flag that via conflicts. In our scenario, no such irreconcilable contradiction remained after mapping—the apparent conflict (guideline vs. regulation) was resolved by understanding one as guiding the use of discretion under the other, which our model handled in the wisdom layer. Thus, the model maintained internal consistency by elevating that conflict to a principle-level discussion (fairness vs. strictness) rather than a raw rule clash.
The framework’s formal structure also allows a form of traceable inference. We can simulate a proof or justification path through the graph:
- Data nodes provide evidence;
- This leads to certain information nodes (findings of fact);
- These trigger knowledge nodes (applicable rules);
- These, under the influence of wisdom nodes (principles), produce certain conclusions (like an outcome node or decision);
- This is justified by purpose nodes (goals achieved by that conclusion).
This is akin to a proof tree in logic, but augmented with semantic annotations at each step. In the case study evaluation, we effectively traversed such a path. This traceability is a strong indicator of the approach’s rigor: each inferential step can be checked. For instance, one step was “Because no illness occurred (data) and violations were corrected (info), applying the proportionality principle (wisdom) suggests that revocation may not be necessary (knowledge/discretion conclusion).” This step can be scrutinized and debated, which is exactly what we want in legal reasoning (as opposed to opaque jumps).
In terms of coverage, our model accounts for the following:
- Substantive law (through knowledge of regulations);
- Evidence/facts (data and information);
- Procedural or discretionary aspects (knowledge of guidelines, principles in wisdom);
- Normative goals (purpose).
It thus covers both the domain knowledge and the case-specific context comprehensively. Many AI and law models cover the first two but not the latter two explicitly. This comprehensive coverage is expected to reduce omitted-variable bias in automated reasoning; that is, the system is less likely to make a decision based on a narrow set of factors ignoring an important consideration, because important considerations can be encoded in wisdom/purpose.
We invited a group of senior practicing lawyers and legal research experts to form an advisory team. Through in-depth interviews and focus group discussions, the team comprehensively evaluated the practicality and innovativeness of the functional design. After multiple rounds of expert validation, we distilled a core functional system structured around three dimensions: In the technical dimension, the framework provides semantic parsing capability from raw case data to judicial value objectives, as well as a dynamic calibration mechanism between normative texts and subjective cognition. In the conflict-handling dimension, the system incorporates automated conflict detection and intelligent resolution algorithms based on multi-level legal logic. In the reasoning–support dimension, we developed a hybrid reasoning engine integrating formal logic with value assessment.
To realize these functionalities, we constructed a semantic processing architecture based on bidirectional mapping. On one hand, this architecture utilizes legal ontology techniques to transform objective elements, such as legal provisions and evidentiary materials, into structured content graphs. On the other hand, it applies cognitive modeling methods to convert subjective cognition—such as parties’ statements and industry customs—into computable relationship networks. These two graphical systems interact through a dynamic bridging mechanism: when a semantic conflict is detected between regulatory requirements (e.g., “mandatory penalties”) and party claims (e.g., “mitigating circumstances”), the system automatically initiates the conflict resolution workflow, guiding legal experts to exercise professional discretion based on legal values such as proportionality and protection of legitimate expectations. All reasoning processes and discretionary grounds are automatically recorded by the system and compiled into visual analysis reports, ensuring that each judicial conclusion is supported by a clear chain of legal logic and comprehensive factual basis.
5.2. Explainability
We evaluate explainability by the clarity and completeness of the explanations the model can generate, and by how these explanations might be received by users (judges, lawyers, or the litigants themselves). The explanation we formulated for the case study was rich in content, referencing motives (purpose), principles, rules, and facts seamlessly. This richness is a direct consequence of having those elements in the model. In contrast, an explanation from a purely rule-based model might have been “License is reinstated because although Regulation 5.4 allows revocation, the hearing officer exercised discretion to impose a lesser penalty.” This is a correct but terse explanation that begs further questions (“why exercise discretion this way?”). Our model’s explanation answers those by pointing to purposes (no harm done, compliance achievable), principles (fairness, proportional response) and aligning them with the stakeholder’s perspective (“owner took prompt action, which is what we want to encourage”). This aligns with what Bex et al. [40] call argumentative explanations in legal AI, where one not only states the decision but the reasons pros and cons that were weighed. DIKWP naturally produces an argumentative explanation structure: each wisdom node (principle) can be seen as an argument factor, and each purpose as a value or policy that arguments promote.
Furthermore, our approach supports counterfactual reasoning in explanations: Because the model knows alternatives (it represented revocation and fine as possible outcomes; it represented both strict and lenient principles), it can explain “why not the other outcome.” For example, the explanation could be extended: “The reason we did not simply uphold the revocation (counterfactual) is that doing so, while addressing public health, would have been unnecessarily punitive given the immediate corrections and lack of harm. Conversely, the reason we did not waive all penalties is that some sanction is needed to underscore the importance of compliance (to protect public health).” Such explanations address fairness by showing the decision was not arbitrary but considered different possibilities. Traditional AI systems struggle to produce such counterfactual explanations unless explicitly programmed, whereas our semantic model includes those possibilities in the graph and thus can articulate them by traversing the “road not taken” nodes (e.g., the revocation node in knowledge and explaining it was not chosen due to the principle of proportionality, etc.).
User-centric evaluation: If we consider how a stakeholder like Alice perceives the explanation, it likely satisfies key concerns:
- Understanding: She hears that the judge recognized her efforts and situation (embedding her perspective in the explanation), and also made clear what she must do going forward and why (embedding law’s perspective). This kind of explanation has been argued to improve perceived fairness and trust. Psychological research on XAI (e.g., Derek Leben 2023 [41]) suggests people accept decisions better when explanations connect to fairness evidence, which in our explanation, they do (we gave reasons tied to principles of fairness and public good, not just rule citations).
- Transparency: Every factor that influenced the outcome is visible: the rule, the guidelines, the corrections, etc. If something was incorrect or disputed, it could be challenged. For example, if the agency disagrees and appeals, they can see exactly that the judge’s reasoning hinged on an interpretation of policy and fairness; they could counter-argue if needed in those terms (maybe “the judge gave too much weight to economic hardship, which is not a legally valid factor under the statute”—at least the debate is now on clear terms).
- Completeness: No obvious aspect of the case is left unaddressed. Often parties feel frustrated if a judgment does not mention something they raised. Our model by mapping stakeholder input tries to ensure all major points are either aligned or explicitly resolved. In the scenario, the owner’s points (we fixed it, others received warnings, it is too harsh) were all touched in the explanation. This thoroughness improves the quality of legal justification.
Therefore, qualitatively, the explainability is significantly enhanced compared to a baseline. To further support this claim, imagine a scenario evaluation: if an unbiased legal expert read both a classical decision rationale and our semantic rationale, which would they find more convincing or acceptable? Our approach would likely be rated higher on justification because it is essentially mimicking what good judges do in written opinions—discuss facts, discuss law, discuss principles, discuss the purpose/policy, and reach a conclusion. The difference is our model ensures none of those are omitted due to modeling limitations.
5.3. Fairness Implications
Fairness in judicial decision-making can be considered in multiple dimensions: procedural fairness (was the process transparent and did it consider the party’s arguments?) and substantive fairness (did the outcome appropriately balance the interests and follow legal standards?). Our framework contributes to both.
Procedural Fairness: By integrating the stakeholder’s perspective into the reasoning model (DIKWP (Stakeholder) graph), we ensure the party’s voice is “heard” by the AI reasoning process. In the case study, this was reflected in the mapping of Alice’s points. If the system were used in an AI judge or decision support, it would actively prompt, “The stakeholder claims X, is there merit to that claim in our content model?”—which we saw, for example, with the policy of warnings (she did not explicitly cite the policy number, but her argument triggered the system to check if such a policy exists, and indeed it did in content knowledge). This is akin to a fair hearing where the judge systematically addresses each claim. In automated systems, a known risk is that the system might ignore certain arguments if not properly encoded. Our approach mitigates that by structurally requiring alignment checks on all layers. If the stakeholder brings up a new factor, it appears as a node with no counterpart in content; the mapping algorithm highlights it and forces a consideration: either incorporate it or explain it away. This systematic treatment of each input contributes to procedural fairness.
Additionally, the transparency of the model’s reasoning (as discussed in explainability) gives parties the ability to scrutinize the fairness of the process—they can see if something was overlooked or if a bias was encoded (e.g., if the wisdom layer had a biased principle, it would be explicitly there to challenge). This openness is key to procedural justice.
Substantive Fairness: The example outcome was arguably fairer than a rigid application of the rule would have been, because it achieved compliance without excessive punishment. Our framework actively facilitated a fairer outcome by allowing purpose and wisdom (like equity) to modulate rule application. One could evaluate fairness improvements by comparing decisions from a purely rule-based system vs. our semantic system across a range of hypothetical cases:
- In cases where strict rule application yields an intuitively unjust outcome (like extremely harsh for minor fault), our system is likely to soften it via purpose-driven reasoning (because the mismatch between outcome and purpose would be detected).
- Conversely, in cases where leniency would undermine the law’s purpose (like a stakeholder asks for no penalty but there is significant risk), the system will identify that stakeholder purpose conflicts irreconcilably with the law’s purpose, and thus justify a strict outcome, but crucially, it will explain it (which contributes to fairness by at least acknowledging the loser’s position before rejecting it).
This pattern suggests our approach can help reach decisions that are better aligned with equity—a dimension of fairness focusing on context and individual circumstances—while still upholding the consistency of the rule of law by referencing purposes and principles that are general.
One way to measure fairness is through consistency: similar cases should yield similar outcomes unless a meaningful difference justifies a different outcome. Our model’s rich representation actually helps identify the meaningful differences (they would appear as different info/wisdom nodes). For example, if another restaurant had exactly the same violation history but in their case someone did get ill, our model would include that data node and information (“an illness occurred”), which would strongly swing the wisdom/principles (the harm principle kicks in) toward a stricter outcome (likely revocation). That difference is clearly documented in the semantic model, explaining why that case’s outcome (revoke) differs from Alice’s (probation). Traditional models might have trouble articulating that because they would just say “3 violations → revoke” in both, failing to differentiate the contexts. So, our approach could in principle reduce unjust disparity by ensuring decisions are context-sensitive in an explicit, explainable way.
Another aspect is bias mitigation. Bias in automated decisions often creeps in through improper factors (e.g., treating two cases differently due to a factor like the owner’s background which should not matter). In DIKWP, one can more easily enforce fairness constraints by monitoring the purpose and wisdom layers. If “justice” and “equal treatment” are in the wisdom layer, any mapping of an improper factor would not find a legitimate purpose to align with and could be flagged. For instance, if a system for many cases started giving harsher outcomes consistently to a certain group, one would examine the semantic graphs to see what node could be causing that. If no legitimate DIKWP difference exists, then it is a bias—and because outcomes tie to purpose, one could argue the bias yields a misalignment with the declared purposes (hence the decision is unjustified in the model). This is somewhat speculative, but the point is the structure allows scrutiny for fairness at a high level: decisions must be justified by purpose and wisdom; anything else stands out as an unexplained factor.
5.4. Generality and Scalability
While it is theoretically possible—and perhaps ideal—to encode the entire body of relevant law within a comprehensive ontology or legal knowledge graph, our current implementation strategy focuses specifically on encoding those portions of the law directly pertinent to the case at hand. Specifically, legal norms, rules, definitions, and applicable guidelines cited explicitly in case documentation are formalized as nodes within the DIKWP (Content) knowledge layer. Broader or supplementary legal knowledge (e.g., principles, related regulations, or ontological relationships) is represented as needed to support reasoning about the case but is not exhaustively encoded unless directly relevant. In practice, an existing legal ontology could serve as a foundational reference structure, allowing our system to draw upon standardized legal concepts and relationships as needed.
While our evaluation has focused on a single scenario in depth, a question remains: how general is this approach? The DIKWP framework is domain-agnostic in theory (it has been applied to medical disputes, finance compliance, etc.), and here we applied it to administrative law. We believe it generalizes to other legal domains:
- Criminal law: DIKWP could model evidence (data), legal elements of crimes (knowledge), mitigating/aggravating factors (wisdom), and the purposes of sentencing (purpose). The bidirectional mapping would ensure a defendant’s story is considered alongside the legal requirements. This could yield similar benefits in fairness (e.g., accounting for personal circumstances in sentencing while ensuring public safety).
- Civil litigation: Issues of liability and damages similarly involve facts, legal standards, and principles (like reasonableness, equity, deterrence vs. compensation goals). DIKWP can capture the policy purpose of tort law (compensation and deterrence) and ensure, say, that an award is in line with those and with the plaintiff’s harm (and not punishing beyond purpose).
- Contract or commercial cases: Here purpose might be party intentions or business norms, which DIKWP could incorporate to interpret the contract beyond literal text, aligning with doctrines like good faith (wisdom principle) and purpose of the contract.
Scalability is more of an engineering question: can we realistically build DIKWP graphs for complex cases? We foresee using a combination of expert input and AI tools to populate these graphs. The manual case study was manageable. For larger cases (imagine multi-issue litigation), the graph might become big, but still modular by issue. Each legal issue or claim could be its own DIKWP subgraph. We could scale by focusing on one issue at a time (judges often break decisions into issues too). The mapping algorithm complexity is polynomial, which is fine given that in practice the number of nodes per issue is not huge (maybe dozens). Also, many legal cases revolve around a few key points (which our model would highlight as either conflicts or alignments).
Comparison to baselines: We compare the results qualitatively to two baselines:
- A rule-based expert system (1980s-style): It would have given a single recommendation (revoke) because conditions matched a rule, and it would not incorporate the additional semantic nuance we did. Thus, it would have failed to identify the fair solution. It also would explain minimally (“rule triggered”).
- A modern machine learning model (like a black box that learned from data): It might give some prediction (maybe it sees the pattern of not many revocations for such cases and predicts “no revoke”). But it would not explain why, nor ensure alignment with legal principles—which is dangerous (it might be right for the wrong reasons). Our approach provides an explicit rationale and can be audited, which a black box cannot.
- An argumentation model (like reason with pro/con arguments): This is closest in spirit; it would list arguments: “For revocation: repeated violations, risk to public. Against: corrections made, no harm, harsh outcome.” That is good, but argumentation frameworks often leave choosing the outcome to a meta-level preference ordering (like which argument wins). DIKWP provides ordering via purpose—it tells us which concerns are primary. So it is like argumentation with a built-in value analysis. In this case, purpose nodes (public health vs. fairness/economic survival) had to be balanced; our model achieved that balancing explicitly by finding a solution that satisfied the primary purpose without sacrificing the secondary more than necessary. An argumentation model would require the designer to input that one value outweighs another or find a compromise outside the formalism.
In terms of reliability validation, we have conducted preliminary assessments by consulting legal experts who provided targeted feedback on the semantic graphs and reasoning outputs of the administrative law case. These experts, drawn from academia and professional legal practice, evaluated the completeness of the graph representations, logical accuracy of rule applications, and clarity of the semantic explanations provided by the framework. While recognizing that the sample of experts involved at this stage was relatively small, their qualitative feedback consistently affirmed that the semantic reasoning steps produced by our framework align well with standard judicial reasoning practices. To strengthen future validation and generality, we have designed a structured expert evaluation approach incorporating explicit scoring metrics, such as completeness, correctness, and transparency scales. Future work will systematically involve a broader expert panel to quantitatively validate these aspects across multiple case scenarios, thereby providing robust evidence for the framework’s reliability, scalability, and acceptability within the expert legal community.
Moreover, to rigorously validate our symbolic inference method, we formally demonstrate its reasoning capability using the previously presented administrative law scenario. Given the documented factual condition—three confirmed violations within one year ()—the logical structure of Regulation 5.4 can be represented symbolically as follows: If violations reach or exceed three, the conditions of Regulation 5.4 () are triggered, formally stated as . Subsequently, Regulation 5.4 explicitly mandates the revocation decision (). By applying formal logic (modus ponens), we explicitly demonstrate the inference chain:
This formal symbolic deduction transparently verifies the correctness and reliability of the reasoning mechanism embedded within the DIKWP framework, clearly aligning outcomes with explicit legal rules and verified case facts.
5.5. Limitations
No evaluation is complete without addressing limitations:
- Knowledge Engineering Effort: Our method requires constructing and maintaining DIKWP graphs. This is knowledge-intensive. If performed manually for each case, it could be time-consuming. However, we envision partial automation using NLP for fact extraction and established legal ontologies (such as LKIF or LegalRuleML) as the knowledge base for laws. Such ontologies standardize the representation of legal rules, concepts, and relationships, which can be integrated with DIKWP graphs through semantic mapping. Over time, domain-specific DIKWP graphs could reuse these ontology-based representations, significantly reducing the manual effort for modeling new scenarios.
- Quality of Mapping: The benefits rely on a correct and thorough mapping between content and stakeholder semantics. If a stakeholder raises an issue that the system fails to map (perhaps because it is not in its ontology or it is an implicit cultural concern), the risk is the system might still ignore something. Our framework mitigates by design (looking for any unmatched nodes), but it is only as good as the ability to identify those nodes from inputs. Advanced NLP or structured input forms might be needed to capture stakeholder perspectives fully. In a practical setting, one might have the user explicitly input their points in a structured way to help the system map them.
- Resolution of Value Conflicts: In some cases, purposes will conflict with no obvious compromise (e.g., a stakeholder’s goal directly negates the law’s goal). In such cases, the model will basically show that conflict and the decision will favor one side (usually the law’s purpose, since that is the mandate). While the model will be transparent about it, the stakeholder might still feel unfairly treated if their purpose was totally unachievable. Our framework does not magically resolve all conflicts; it just clarifies them. However, even then, explanation helps (procedural justice).
- Judicial Acceptance: If this were used in a court or agency, would decision-makers accept the DIKWP model’s suggestions? This is more a social question. Many judges reason intuitively, not in a structured graph manner. Our approach might at first seem overkill or foreign. But perhaps as a decision-support tool, it could prompt judges to consider things they might otherwise overlook. The acceptance would grow if it demonstrably leads to fewer appeals or higher satisfaction. We cannot fully evaluate that without deployment, but our case study hints that including more semantics likely leads to decisions less likely to be overturned (because they pre-emptively address equity which appeals courts often impose if the first instance did not consider it).
5.6. Summary of Evaluation
The DIKWP semantic judicial reasoning framework shows strong promise in producing decisions that are well-founded, transparent, and fair. The case study illustrates how the framework handles complex reasoning tasks that traditional models struggle with: integrating policy goals and individual context. The evaluation highlighted the following:
- The framework is conceptually robust, encoding all relevant aspects of reasoning and allowing formal inference.
- Explanations derived from the framework are richer and aligned with what human stakeholders expect, likely improving trust in AI-assisted judgments.
- The framework actively engages with fairness by mapping stakeholder viewpoints and balancing them with legal requirements, rather than operating on law alone.
- While the overhead in building semantic models is significant, particularly given the known limitations of symbolic AI (such as brittleness and high knowledge maintenance costs), we envision mitigating this through partial automation using NLP, integration with standardized legal ontologies (e.g., LKIF or LegalRuleML), and modular reuse of knowledge structures. These measures aim to make implementation robust, scalable, and maintainable, thereby justifying the initial investment for critical, high-stakes judicial decisions.
Ultimately, the true test of such a system would be deploying it on real case data (perhaps past cases) and seeing if it reaches similar outcomes as judges and if its explanations align with written opinions. That could be a future empirical evaluation: we could take a set of appellate decisions that corrected lower court decisions for being unfair or not considering something, and see if our model would have flagged those considerations at first instance. Our expectation is that because DIKWP encourages broad consideration of purposes and context, it would catch many of those issues, thus hypothetically reducing the rate of unfair outcomes. Such an evaluation is left for future work but the groundwork laid here strongly suggests the approach is a step in the right direction for “semantic justice” in AI and law.
6. Discussion
The development of a semantic judicial reasoning framework using the DIKWP model has broad implications for the field of AI and law and raises several points of discussion. We consider the impact on explainability and fairness (expanding on the evaluation), the feasibility of implementing such a system in practice (including integration with current technology like large language models), and the steps needed to move toward a general framework for semantic justice in legal AI. We also reflect on limitations and how future work can address them.
6.1. Enhancing Explainability and Transparency in Legal AI
Modern legal systems demand not only that justice be served, but that it be seen to be served. AI systems, if they are to assist or make legal decisions, must therefore provide explanations that meet the standards of legal justification. Our DIKWP-based approach offers a structured transparency: every decision is accompanied by a graph-based trace of how that decision aligns with data, law, and purpose.
One key advantage of this structured semantic approach is in dealing with the complexity of legal justifications. Legal reasoning often involves multiple justifications at different levels—factual reasoning (“what happened”), legal reasoning (“what rule applies”), and purposive reasoning (“why does the rule exist/what outcome serves the policy”). Traditional AI systems tend to focus on one level (e.g., a neural network might focus on factual patterns, an expert system on rule application). DIKWP by design handles multiple layers and thus can produce multi-layered explanations. For instance, a judgment could include the following:
- A factual narrative (data→information explanation);
- A legal rule application explanation (knowledge layer: citing statutes and conditions);
- A policy/principle explanation (wisdom layer: why that statute leads us to that result in view of principles);
- A teleological explanation (purpose layer: how the outcome serves justice or policy goals).This corresponds well to how human judges write opinions (often, there is a section on facts, a section on law, and sometimes a section on the broader implications or purposes, especially in higher courts). An AI that can work similarly would be more readily accepted in legal contexts.
Moreover, this transparency can aid in legal education and decision auditing. If an AI judge provides a DIKWP explanation, a losing party or an appellate court can pinpoint if/where they disagree. For example, if the explanation emphasizes a purpose that the losing party thinks is irrelevant, they can challenge it: “The agency’s purpose of deterrence should not override the individual fairness in this context.” The appellate body can then explicitly weigh those, and since our model externalizes those value choices, it could even allow something like a slider or preference toggle in a simulation: “what if fairness were given priority here, how would the outcome change?”—the system could then show that scenario. This ability to simulate alternate reasoning by toggling wisdom/purpose priorities could be a powerful tool for exploring what-if in jurisprudence, increasing understanding of how outcomes depend on certain value judgments.
6.2. Fairness, Bias, and “Semantic Justice”
We coined “semantic justice” to describe decisions reached by aligning the semantic content of law with the lived semantics of the people involved. This approach inherently promotes fairness, particularly substantive fairness. The case study illustrated substantive fairness by calibrating the outcome to the nuances of the case (not all violations are equal; not all offenders are the same).
One interesting discussion point is how our framework might handle cases of systemic bias or unfair rules. Suppose the law’s purpose itself is arguably unfair (for instance, a law that is outdated or biased). Our DIKWP model would still follow that purpose, because it is encoded as the law’s purpose. However, because we also model stakeholder purposes, if a law truly offends widely held principles (say it conflicts with constitutional principles or fundamental fairness), that tension would show up as a stark conflict in the graphs (the stakeholder or judge’s own higher-level purposes vs. the statute’s purpose). In a human court, that might lead to a declaration that the law is unjust or unconstitutional. An AI system could at least flag it: “there is an irreconcilable purpose conflict—to decide this case I must favor the law’s purpose but doing so undermines another purpose (e.g., equality) that is generally held.” This is speculative, but it suggests DIKWP could be used to monitor justice at a meta level: if too many decisions show a certain purpose (value) consistently being trampled by another, maybe that is a sign of an imbalance in the legal framework that needs addressing. In this sense, our model could inform law reform by aggregating semantics from many cases.
Another fairness aspect is individualization vs. consistency. There is a tension: fairness demands treating like cases alike (consistency) but also treating each case according to its circumstances (individualization). Our semantic approach tries to do both—it individualizes by incorporating case-specific context in the graphs, but it also references general purposes and principles which ensure a baseline consistency. Because purposes and wisdom nodes are often domain-general (not case-specific), they act as the glue that makes sure the reasoning is not idiosyncratic to one case. For example, in every health license case, “protect public health” will be a purpose node. So even if facts differ, all cases are being decided with that common metric in mind. This should help avoid arbitrary decisions. In traditional systems, a risk is a judge might sometimes subconsciously give more weight to fairness in one case and more to strict enforcement in another similar case; if they used a DIKWP tool, it would remind them of the same purposes each time, hopefully leading to more consistent balancing.
Bias mitigation: Although not a cure-all, having an explicit semantic model means any factor influencing the decision must be represented. This can make it easier to detect biases. For example, if an AI was penalizing restaurants owned by a certain group more harshly, one would look for what differs in the semantic graph for those cases. If everything (violations, compliance) was the same except some hidden node (like maybe, in data, the owner’s name or location correlated), then the model should not ideally have that in its reasoning graph—if it is not there, the AI should not discriminate; if it somehow crept in, an audit could find “why did these cases end differently? The graphs show same data, same knowledge, but the outcome node differs—something outside the semantic model influenced it,” which implies a bug or bias in the implementation. Traditional black-box models would have no graph to inspect at all.
6.3. Integration with AI Technologies
Implementing this framework can leverage current AI technologies:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Laws and case files can be processed with NLP to populate the data and knowledge layers. There is ongoing work on converting legal texts to knowledge graphs. Our approach could plug into that: use an NLP pipeline to identify relevant statutes and facts and fill the initial DIKWP (Content) graph. Similarly, stakeholder statements (perhaps given in a hearing or written appeal) can be NLP-analyzed to extract their key arguments (we might use argument mining techniques to identify “claims” and “evidence” in their narrative).
- Large Language Models (LLMs): An LLM (like GPT-based models) could be used as a component to suggest semantic alignments. For example, if a stakeholder says “I think this punishment is too harsh,” an LLM could interpret that and find related concepts like “proportionality” or “leniency policy” in the context. It could effectively translate plain language into the formal nodes we have (a kind of semantic parsing). LLMs have vast knowledge, including likely knowledge of common law principles and even specific case precedents; they might assist in populating wisdom nodes (“Based on the context, principles of X might apply”). We have to be careful—LLMs sometimes hallucinate or err in legal specifics—but within a controlled system, they could be used to propose elements which a human or a smaller rule-checker can verify.
- Knowledge Graph Databases: Storing and querying DIKWP graphs would require a robust graph database. We might use RDF triple stores or property graph DBs (like Neo4j) to represent nodes and edges. This would allow querying like “find all knowledge nodes connected to this purpose” which is useful in reasoning (like finding laws that serve a given purpose).
- Automated Reasoning Engines: Some parts of the graph (especially the knowledge layer with rules) could be fed into a logical reasoner (like a Prolog engine or a description logic reasoner) to derive conclusions. Meanwhile, optimization or decision analysis techniques could be applied at the wisdom/purpose level (e.g., multi-objective decision-making to find an outcome that maximizes purpose satisfaction). This multi-paradigm approach (logic + optimization) could operationalize the reasoning. Our pseudocode was high-level; an implementation might break it into a logical inference step and a value balancing step.
If judges or lawyers are to use this, a user-friendly interface is needed, perhaps a system where they input case facts (or upload documents) and obtain a visual of the DIKWP graph. They could toggle seeing just the legal rule layer or expand to see the principle layer. In a decision-support mode, the system might highlight, “there’s a conflict between applying rule X strictly and the fairness principle; here are some options to resolve: Option1 (strictly enforce, outcome A) vs. Option2 (lenient enforcement, outcome B).” The judge can then decide, but the system ensures they see the implications. This is somewhat akin to how some legal tech tools now highlight risks or inconsistencies in contracts—here it is highlighting moral/legal value conflicts.
6.4. Toward a General Framework for Semantic Judicial AI
Our work is a step towards a general framework for what we call semantic judicial AI. The ultimate vision is an AI that can handle any case by building a semantic representation and reasoning through it similarly to a human judge, complete with transparent justifications. Achieving this generality requires the following:
- Extensive Knowledge Base: A wide coverage of laws and regulations in DIKWP form, possibly a global legal knowledge graph with integrated purpose tags. This is challenging due to the volume of law, but starting domain by domain (like building one for administrative law, one for criminal, etc.) is feasible. Prior work on ontology and knowledge graphs in law is a foundation.
- Standardization: Perhaps a standardized schema for DIKWP in legal context, so that tools and researchers can share models.
- Validation on Real Cases: To generalize, we need to test on many cases. By encoding past landmark cases in DIKWP, we can check if the outcomes align and where the model might have predicted differently. If differences arise, that can show either a gap in the model or perhaps an inconsistency in jurisprudence itself.
- Evolution and Learning: AI systems improve by learning. We might eventually allow the system to learn from decisions. For example, if judges in practice always favor a certain purpose over another in certain contexts, the system could adjust weighting of principles accordingly (learned wisdom priorities). This could be performed via machine learning on a set of resolved DIKWP graphs (cases). However, it is critical that any learned component still yields explainable rules (no black box here.
Finally, a general framework must consider differences in legal systems (common law vs. civil law). DIKWP is flexible enough: common law precedents become knowledge nodes (with possibly high authority weight, akin to purpose if a precedent embodies a policy). In civil law, abstract principles might be explicitly coded in legislation (so they appear as knowledge or wisdom nodes directly from codes).
One might ask, do we envision AI replacing judges using this? Our view is more that it is a collaborative tool for the foreseeable future. Semantic justice does not mean machines alone decide, but that machines contribute to decisions that are semantically informed and justified. Judges could use it to double-check their reasoning, lawyers to prepare arguments (they could input their argument and see how it maps to the court’s likely DIKWP perspective, maybe identifying weak points or missed points). It could also be used after a decision to generate a draft opinion, which the judge can edit.
6.5. Future Work and Extensions
- Empirical Testing: As noted, applying this to a corpus of cases is future work. We might start with a narrow domain and attempt to encode say 50 past cases and see how our system’s recommended outcomes and explanations compare to actual. This would be a strong test of validity.
- User Studies: It would be valuable to conduct experiments with legal professionals using semantic explanations vs. traditional ones, to measure differences in understanding and perceived legitimacy. For example, give two sets of readers two versions of an AI-generated decision (one DIKWP-rich, one minimal) and survey their reactions.
- Refinement of Formalism: We gave definitions, but there is room to formalize further, perhaps in a logical language. For instance, one could formalize mapping constraints (e.g., every knowledge node in content should either find a supporting purpose or be labeled as dormant if the purpose is not present—ensuring no rule is applied without rationale). Formal verification tools might then check the consistency of a DIKWP decision.
- Integration with LegalTech systems: The framework could be integrated with e-discovery or case management systems. For example, as evidence is gathered, it could automatically populate parts of the graph and highlight needed evidence for certain claims (like “to prove this purpose or principle, you need data of type X; none is present!” which could alert attorneys to gather more evidence on, say, harm or compliance efforts).
- Ethical and Legal Considerations: As we move toward AI in judiciary, questions of accountability and acceptance arise. An interesting aspect of our approach is that by making AI reasoning closer to human reasoning, it might be easier to fit into existing legal procedures. For instance, if an AI provides a DIKWP rationale, a higher court can review it similarly to how they review a human’s rationale (because it is in a familiar structure). We might need to ensure the AI does not introduce its own values beyond what law and inputs provide—basically keep it constrained. Our approach tries to do that by grounding purposes in either the law or explicit stakeholder input, not inventing new ones.
6.6. Conclusion of Discussion
Our DIKWP semantic model approach sits at the intersection of legal theory, knowledge representation, and AI, pushing toward a more intelligent and just legal AI. The discussion highlights that while challenges remain, the potential payoff is significant: decisions that are not only technically correct but substantively resonant with human values. This aligns well with the modern drive for trustworthy AI, which emphasizes transparency, fairness, and human oversight. In the sensitive domain of law, these attributes are non-negotiable, and our framework provides a concrete path to realize them.
We have essentially outlined how a future “AI Judge” might think—by simultaneously being a rule-applier, a moral reasoner, and a policy analyst, all within a transparent semantic scaffolding. Achieving semantic justice is an ambitious goal, but it is one that arguably echoes what good judges have always striven for; our contribution is showing how we can imbue AI systems with a semblance of that holistic reasoning ability, formally and computationally.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented a comprehensive framework for semantic judicial reasoning using the DIKWP model, with the aim of advancing AI systems toward delivering “semantic justice”. We assumed the dual perspectives of legal content and stakeholders, modeling each in a rich semantic graph spanning data, information, knowledge, wisdom, and purpose layers. By establishing a bidirectional mapping between these layers, our methodology enables a legal reasoning process that is cognizant of both the letter of the law and the contextual meaning of the situation at hand.
Our framework represents a significant shift from traditional rule-based or purely statistical legal AI models. Instead of operating solely in a formal conceptual space, the DIKWP approach operates in a semantic space where legal rules, facts, principles, and goals are explicitly connected and can be traversed in reasoning. This allowed us to demonstrate how an AI system (or human decision-maker aided by such a system) can transform a legal judgment process: starting from raw data (case facts), moving through normative assessments (violations and their significance), applying rules in context (knowledge of law tempered by guidelines and discretion), and evaluating outcomes against purposes (like public welfare and fairness). Each step is both human-intelligible and machine-computable, fulfilling a dual requirement for formal rigor and explanatory power.
The administrative law case study illustrated the practicality and benefits of our approach. Faced with an agency’s decision to revoke a license and an individual’s plea for leniency, the DIKWP-based reasoning process was able to semantically enrich the problem, revealing that a strictly conceptual application of the rule would have overlooked material semantic nuances—notably the purpose behind the regulation and the stakeholder’s efforts to comply. By mapping content and stakeholder graphs, the system identified a solution that aligned the regulation’s public health purpose with the stakeholder’s goal to continue business safely, thus achieving a form of justice that is both legally sound and contextually fair. The resulting decision was not only a balanced outcome, but one accompanied by a transparent explanation tracing all relevant considerations from data to purpose. This level of explanation addresses the oft-cited “black box” problem in AI and law, offering instead what we might call a “glass box” model, where one can see the inner workings of the decision logic.
The implications of this work are multi-fold:
- For AI researchers and developers: It provides a blueprint for building AI systems that require high degrees of explainability and fairness. The formal definitions, pseudocode, and pipeline we provided can inform the architecture of next-generation legal expert systems or decision-support tools. We demonstrated that it is feasible to embed ethical and purposive reasoning into a formal model without sacrificing computational tractability.
- For the legal community: Our approach offers a way to leverage AI while preserving the nuance of legal reasoning. Rather than replacing human judgment, a DIKWP-based system can serve as an augmentation tool—ensuring that judges and lawyers consider all dimensions of a case and providing second opinions that are backed by semantically rich justifications. This can enhance consistency and reduce oversight, as well as increase trust in AI recommendations because the reasoning is laid bare.
- For interdisciplinary understanding: By marrying concepts from knowledge representation, cognitive science (the idea of conceptual vs. semantic spaces), and legal theory (jurisprudential principles and teleological interpretation), we created a holistic model that could serve as a common language for computer scientists, cognitive scientists, and legal scholars to discuss how decisions are made and justified. This kind of interdisciplinary semantic framework can also aid in education and communication: for instance, teaching law students or AI systems about legal reasoning in terms of DIKWP layers may clarify why certain arguments win or lose (because they fail at a purpose level, because the data does not support the claimed information, etc.).
There are several avenues for future work and improvements. One immediate next step is to test our framework on diverse real-world cases, encoding those cases into DIKWP graphs and seeing if the outcomes derived align with the actual outcomes and rationales. Such validation studies would help refine the mapping rules and identify any patterns of reasoning the model might initially miss (for example, perhaps introducing new wisdom nodes like “judicial economy” or “public sentiment” if those appear in reasoning). We also intend to explore partial automation of graph construction using NLP and knowledge graph techniques, which will be crucial for scalability in practical settings. On the theoretical side, integrating a mechanism for dynamically balancing conflicting purposes (perhaps using weightings or utility functions) could formalize the way the model chooses between two valid but competing principles—essentially adding a decision-theoretic layer on top of the qualitative graphs.
In conclusion, the DIKWP-based semantic reasoning framework we have presented is a step toward AI systems that do not merely apply law but understand it in a way similar to human jurists—contextually, conceptually, and teleologically. By transforming legal judgment processes into DIKWP semantics, we aim to ensure that when AI participates in judicial decision-making, it does so as a principled, transparent, and fair-minded entity. This is the essence of “semantic justice”: a state where the outcomes of algorithmic reasoning can be trusted not just for their accuracy, but for their alignment with the deeper semantic fabric of law and morality. We believe this work lays down a foundation for achieving that vision, and we invite further research and collaboration at this fertile intersection of artificial intelligence, law, and semantic modeling.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.M. and Y.D.; methodology, Y.M. and Y.D.; formal analysis, Y.M.; writing—original draft, Y.M.; writing—review and editing, Y.D.; supervision, Y.D.; validation, Y.M.; visualization, Y.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research project was supported in part by the Hainan Province Health Science and Technology Innovation Joint Program (WSJK2024QN025), in part by the Hainan Province Key R&D Program (ZDYF2022GXJS007, ZDYF2022GXJS010), and in part by the Hainan Province Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disaster Prevention and Mitigation in the South China Sea, Open Fund Project (SCSF202210).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lai, J.; Gan, W.; Wu, J.; Qi, Z.; Yu, P.S. Large language models in law: A survey. AI Open 2024, 5, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattnig, M.; Angerschmid, A.; Reichel, T.; Kern, R. Assessing trustworthy AI: Technical and legal perspectives of fairness in AI. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2024, 55, 106053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, S.; Ning, P.; Chen, M. On the Robustness of Belief-Rule-Based Expert Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 6043–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, A.E.; Göhlich, D. Automated requirement contradiction detection through formal logic and LLMs. Autom. Softw. Eng. 2024, 31, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, A.P. Rule-Based Expert Systems for Automated Legal Reasoning and Contract Analysis: A Case Study in Knowledge Representation. Adv. Comput. Syst. Algorithms Emerg. Technol. 2022, 7, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, J.; Chen, Y.; Zulkernine, F.; Dahan, S. Legal Text Analytics for Reasonable Notice Period Prediction. J. Comput. Cogn. Eng. 2025, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, A.; Lee-Stronach, C. Proceed with Caution. Can. J. Philos. 2022, 52, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, M.; Faldu, K.; Sheth, A. Semantics of the Black-Box: Can Knowledge Graphs Help Make Deep Learning Systems More Interpretable and Explainable? IEEE Internet Comput. 2021, 25, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parycek, P.; Schmid, V.; Novak, A.S. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation in Administrative Procedures: Potentials, Limitations, and Framework Conditions. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 15, 8390–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.E.; Naja, H.; Abdulrab, H.; Khalil, M. CriMOnto: A generalized domain-specific ontology for modeling procedural norms of the Lebanese criminal law. Data Knowl. Eng. 2025, 158, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constant, A. A Bayesian model of legal syllogistic reasoning. Artif. Intell. Law 2024, 32, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Sun, X.; Che, H.; Cao, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. Modeling data, information and knowledge for security protection of hybrid IoT and edge resources. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 99161–99176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Duan, Y. The DIKWP (Data, Information, Knowledge, Wisdom, Purpose) Revolution: A New Horizon in Medical Dispute Resolution. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Duan, Y.; Yu, L.; Che, H. Purpose Driven Biological Lawsuit Modeling and Analysis Based on DIKWP. In Proceedings of the 18th EAI International Conference on Collaborative Computing: Networking, Applications and Worksharing, Hangzhou, China, 1–15 December 2022; pp. 250–267. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Duan, Y.; Spulber, A.B. Physical artificial intelligence (PAI): The next-generation artificial intelligence. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2023, 24, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dai, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; He, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, Q. Mechanism of attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control influence the green development behavior of construction enterprises. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, D.; Yang, F.; Kwon, H.; Dong, W.; Yilmaz, L.; Liu, B. TDM: Trustworthy Decision-Making Via Interpretability Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2022, 6, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, I. Artificial Intelligence, Values, and Alignment. Minds Mach. 2020, 30, 411–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchunov, D.E. Logical Methods for Modeling Reasoning, Concepts and Representations Based on the Partial Model Theory. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Multi-Conference on Engineering, Computer and Information Sciences (SIBIRCON), Novosibirsk, Russia, 9–11 September 2024; pp. 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Garzo, G.; Palumbo, A. Human-in-the-Loop: Legal Knowledge Formalization in Attempto Controlled English. In Proceedings of the 2025 13th International Symposium on Digital Forensics and Security (ISDFS), Boston, MA, USA, 24–25 April 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sarabi, S.; Han, Q.; Vries, B.; Romme, A.G.L.; Almassy, D. The Nature-Based Solutions Case-Based System: A hybrid expert system. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Blaxter, M. TaxMan: A taxonomic database manager. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajollahi, M.; Baradaran, V. Expert System Application in law: A review of research and applications. Int. J. Nonlinear Anal. Appl. 2024, 15, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ashley, K.D. Reasoning with cases and hypotheticals in HYPO. Int. J. Man Mach. Stud. 1991, 34, 753–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruninghaus, S.; Ashley, K.D. Predicting outcomes of case based legal arguments. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Law (ICAIL ’03), Edinburgh, UK, 24–28 June 2003; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, M.; Magesh, V.; Suzgun, M.; Ho, D.E. Large Legal Fictions: Profiling Legal Hallucinations in Large Language Models. J. Leg. Anal. 2024, 16, 64–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi Nejad, S.; Carey, J.P.; McMurtry, M.S.; Hahn, J. Model-based cardiovascular disease diagnosis: A preliminary in-silico study. Biomech. Model Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabitza, F.; Fogli, D.; Lanzilotti, R.; Piccinno, A. Rule-based tools for the configuration of ambient intelligence systems: A comparative user study. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 5221–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulot, E.; Sterlin, J. Steps Towards a Legal Ontological Turn: Proposals for Law’s Place beyond the Human. Transnatl. Environ. Law 2022, 11, 13–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Kumar, Y.J.; Sing, G.O.; Song, F.; Wang, J. A Comprehensive Survey of Graph Neural Networks for Knowledge Graphs. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 75729–75741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, M. Apprehending AI moral purpose in practical wisdom. AI Soc. 2024, 39, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenstein, S. Preserving the rule of law in the era of artificial intelligence (AI). Artif. Intell. Law 2022, 30, 291–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosov, P.; Kadhi, N.E. Cecilia Zanni-Merk, Latafat Gardashova, Advancing XAI: New properties to broaden semantic-based explanations of black-box learning models. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 246, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahrn-Andersen, R. Concrete Concepts in Basic Cognition. Philosophia 2022, 50, 1093–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achaa-Amankwaa, P.; Kushnereva, E.; Miksch, H.; Stumme, J.; Heim, S.; Ebersbach, M. Multilingualism is associated with small task-specific advantages in cognitive performance of older adults. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Pan, Y. Multiple knowledge representation for big data artificial intelligence: Framework, applications, and case studies. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2021, 22, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratianu, C.; Bejinaru, R. From Knowledge to Wisdom: Looking beyond the Knowledge Hierarchy. Knowledge 2023, 3, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, C.; Fereshtehnejad, S.M.; Berg, D.; Bohnen, N.I.; Dujardin, K.; Erro, R.; Espay, A.J.; Halliday, G.; Van Hilten, J.J.; Hu, M.T.; et al. Transitioning from Subtyping to Precision Medicine in Parkinson’s Disease: A Purpose-Driven Approach. Mov. Disord. 2024, 39, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medianovskyi, K.; Pietarinen, A.-V. On Explainable AI and Abductive Inference. Philosophies 2022, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, A.; Bex, F. A Basic Framework for Explanations in Argumentation. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leben, D. Explainable AI as evidence of fair decisions. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1069426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).