Abstract
Fire refers to a disaster caused by combustion that is uncontrolled in the temporal and spatial dimensions, occurring in diverse complex scenarios where timely and effective detection is crucial. However, existing fire detection methods are often challenged by the deformation of smoke and flames, resulting in missed detections. It is difficult to accurately extract fire features in complex backgrounds, and there are also significant difficulties in detecting small targets, such as small flames. To address this, this paper proposes a YOLO-Multi-scenario Fire Detector (YOLO-MFD) for multi-scenario fire detection. Firstly, to resolve missed detection caused by deformation of smoke and flames, a Scale Adaptive Perception Module (SAPM) is proposed. Secondly, aiming at the suppression of significant fire features by complex backgrounds, a Feature Adaptive Weighting Module (FAWM) is introduced to enhance the feature representation of fire. Finally, considering the difficulty in detecting small flames, a fine-grained Small Object Feature Extraction Module (SOFEM) is developed. Additionally, given the scarcity of multi-scenario fire datasets, this paper constructs a Multi-scenario Fire Dataset (MFDB). Experimental results on MFDB demonstrate that the proposed YOLO-MFD achieves a good balance between effectiveness and efficiency, achieving good effective fire detection performance across various scenarios.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of society and the accelerated urbanization process, the interaction between humans and nature continues to increase, leading to more diverse scenarios of fire outbreaks. In this context, achieving highly sensitive and precise early fire detection holds significant importance for effectively reducing fire-related losses. However, traditional fire detection methods rely on sensor technologies such as smoke detectors or heat sensors. These conventional fire detection technologies often exhibit notable limitations when applied to complex architectural structures or environments with multiple interference sources, including high rates of missed detections, frequent false alarms, and detection delays. These shortcomings compromise the reliability of fire early warning systems.
In recent years, with the advancement of computer vision, vision-based fire detection has become a research hotspot. By processing image data captured by cameras, the presence of flame or smoke features can be accurately identified to determine whether a fire is occurring and to locate it. Therefore, the study of real-time fire detection algorithms based on visual pixel information from natural scenes is of great significance. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been proven to be effective in automatically learning and extracting effective image features. They have been widely used in areas such as medical imaging, visual search, and autonomous driving, demonstrating outstanding performance. In this context, CNNs have been introduced into fire detection by researchers, promoting the development of feature extraction techniques [1,2,3] for fire. Detection algorithms for smoke and flames have been developed [3], and classic models such as AlexNet, VGG, Inception, and ResNet have been improved by integrating temporal sequence information [4]. Additionally, the deployment of CNN-based methods on mobile platforms such as drones has been explored for forest fire detection tasks [5].
YOLO, as a widely adopted baseline algorithm in object detection, has achieved notable success in applications like vehicle detection, face detection, and mask detection. In recent years, with the introduction of models such as YOLOv5 [6], YOLOv6 [7], YOLOv7 [8], and YOLOv8 [9], detection performance has been continuously improved. Consequently, YOLO has been applied to fire detection and optimized based on the challenges found in fire scenarios [10]. Efforts have also been made to reduce model size for deployment on edge devices [11]. Li et al. [12] proposed an improved YOLOX framework integrated with edge computing, incorporating frequency-domain analysis, wavelet transforms, fuzzy loss functions, and model quantization to reduce false alarms and detection latency in tunnel environments. Zheng et al. [13] combined MobileNetV3 with YOLOv4 to construct a lightweight architecture optimized through feature fusion and quantization, enabling efficient fire detection on embedded devices. Talaat et al. [14] introduced SFDS, a YOLOv8-based system built on a multi-layer IoT architecture, offering scalable and real-time fire detection for smart cities. Li et al. [15] developed Edge-YOLO, a compact infrared detection model employing a ShuffleBlock backbone and attention mechanisms to enhance accuracy and edge deployment efficiency. These research efforts have primarily focused on model lightweighting, attention mechanisms, feature fusion methods, loss function refinements, and integration with edge computing. Furthermore, techniques such as quantization and backbone optimization have enabled efficient deployment on embedded systems. Collectively, these advancements have improved detection accuracy and computational efficiency across diverse application scenarios.
Although these improved YOLO-based fire detection methods address some limitations of traditional approaches, several challenges remain. The irregular shapes and varying scales of smoke and flames make it difficult to extract representative fire features. Moreover, early-stage flames with low visual saliency may lose feature information as the network depth increases, which affects the timeliness of fire warning. The diversity and complexity of background information during fire incidents also hinder the learning and recognition of smoke and flame features. To overcome these issues, existing studies have increased the depth of convolution layers to improve nonlinearity and enhance feature extraction. However, this often results in higher computational cost and slower detection speed.
Based on the review of existing methods and current challenges in fire detection, two main issues have been identified: the lack of large-scale fire image datasets and the complex background and scale variability in fire scenes, including the presence of small objects. To address these issues, this paper presents the following contributions:
- We explore image characteristics and target extraction mechanisms for fires, proposing a lightweight detection algorithm for multi-scenario smoke and flame detection. Additionally, to address the current scarcity of data, we created a new fire image detection dataset named Multi-scenario Fire Dataset (MFDB) to facilitate fire image detection across diverse scenarios.
- To address the missed detection issues caused by deformations in smoke and flames, a Scale Adaptive Perception Module (SAPM) is proposed. By superimposing the spatial-domain branch and frequency-domain branch along the channel dimension, and subsequently fusing spatial- and frequency-domain information through pointwise convolution, the module captures rich feature information to enhance the model’s perception capability.
- To address the issue of low detection accuracy in fire image target detection caused by complex background information suppressing critical fire features, we propose a Feature Adaptive Weighting Module (FAWM) that enhances detection precision without increasing computational overhead.
- To improve the detection of small flames and targets in fire images, a fine-grained Small Object Feature Extraction Module (SOFEM) is introduced. By embedding combinations of convolutional receptive fields within a spatial pyramid sampling structure, a finer multi-scale representation is achieved.
The sections of this paper are organized as follows: Section 2 presents various methods for fire detection. Section 3 elaborates on the overall architecture and key modules of YOLO-MFD. Subsequently, Section 4 focuses on the introduction of datasets, along with experimental analysis and comparisons. Finally, Section 5 summarizes the conclusions and highlights potential directions for future improvements.
2. Related Work
In recent years, numerous detection methods have been proposed for smoke and flames. From the perspective of data acquisition, these methods can be broadly categorized into threshold-based sensor fire detection methods and image-based fire detection methods [16]. The former (sensor-based methods) are more suitable for short-range applications. However, their effectiveness diminishes at large scales and long-distance open spaces, as signals like smoke density and temperature weaken, leading to reduced fire alarm performance. In contrast, image-based fire detection methods leverage pixel-level information to extract flame characteristics such as color and texture patterns for fire identification. The following section further elaborates on these approaches from a methodological perspective, dividing them into three categories: traditional methods based on handcrafted features and classifiers, deep learning-based fire detection methods, and hybrid approaches combining both techniques.
2.1. Traditional Fire Detection Methods
Traditional fire detection methods based on manual features and classifiers mainly implement detection by learning the surface characteristics of fires. In most cases, fire features in images are primarily divided into static and dynamic ones. Static features mainly include the color, shape, and size of flames or smoke, while dynamic features encompass the spread rate, burning direction, and flickering characteristics of the fire. Based on this, Wang et al. [17] utilized static and dynamic features, detected smoke through changes in shape and state, used Gaussian mixture models to extract candidate smoke areas, and established an SVM model for fire detection. Ye et al. [18] analyzed the static and dynamic features of flames and smoke, proposing an algorithm capable of simultaneously detecting smoke and flames in open spaces. Rui et al. [19] extracted significant fire areas by analyzing static features such as the shape of smoke and dynamic features like the flickering intensity of flames in fire images. They proposed a method for fire detection within a close range of 50 m. Han et al. [20] analyzed the dynamic features of flame movement and static features such as color for fire image detecting. Alamgir et al. [21] proposed a method for smoke detection based on static and dynamic features of local and global texture in flame images, using mean algorithms for classification. Gong et al. [22] extracted static features such as color from fire images, integrating frame difference methods and classifiers to determine the category and location of fires. He et al. [23] detected fires by extracting flame brightness and color information. Due to the variability in static and dynamic features, these traditional fire detection methods have difficulty distinguishing fire and smoke from complex backgrounds, and their performance is poor in actual scenes. In addition, feature extraction leads to slow detection speed, which makes it difficult to meet the requirements of real-time detection.
2.2. Fire Detection Based on Deep Learning
Fire detection algorithms based on deep learning are mainly driven by large-scale data to train neural network architectures. Through this process, the feature representations of fire are learned to accomplish fire detection tasks. On this basis, Kim and Lee [24] proposed a recurrent convolutional neural network (RCNN) [25]. The RCNN combines the spatial feature extraction capability of CNNs [26] and the temporal sequence processing ability of an RNN [27], making it suitable for capturing dynamic changes. In fire detection, flames may expand or change shape within a short period, and smoke may tend to spread. These dynamic features can be modeled using an RCNN. By analyzing the temporal dynamics of flame and smoke in consecutive frames, detection accuracy and robustness can be improved.
Different convolutional neural network architectures and their variants were studied by Thomson et al. [28]. Muhammed et al. [29] improved the structure of AlexNet and applied fine-tuning of CNNs for fire detection in indoor and outdoor environments. Muhammad et al. [30] proposed a method based on the SqueezeNet [31] architecture, aiming to balance detection accuracy and efficiency for fire localization and detection. Considering real fire scenarios, it is necessary to predict both class probabilities and object locations. A flame detection method was proposed by Li et al. [32] based on YOLO [33], where flame features were fused and analyzed for fire detection.
Yu et al. [34] introduced an improved method based on Mask R-CNN. In their work, bottom-up feature fusion was realized within the feature pyramid network, effectively enhancing flame localization accuracy. A video-based flame detection method was proposed by Aslan et al. [35], in which temporal slices were used to generate deep convolutional generative adversarial networks (DCGANs). Xu et al. [36] proposed a method for smoke detection in videos using deep saliency networks. Lin et al. [37] developed a joint framework using deep convolutional and 3D convolutional neural networks to solve smoke detection and localization problems. Forest fire images were processed by Wu et al. [38], and the processed images were then used to train a model.
The limitations of single-model learning and perception were addressed by Xu et al. [39], who integrated YOLOv5 [6] and EfficientNet [40] for fire detection and localization. Ghosh et al. [41] introduced a deep learning network combining CNN and RNN for forest fire classification. Later, Gong et al. [42] proposed a novel smoke recognition method based on dark channel prior and hybrid attention mechanisms. Venâncio et al. [43] applied YOLOv5 [6] to fire and smoke detection (FSD) tasks. Their experimental results showed improvements in both smoke and flame detection accuracy.
2.3. Hybrid Fire Detection
Hybrid fire detection methods mainly combine traditional handcrafted feature extraction with deep learning techniques. For example, a color-guided anchoring strategy was explored by Zhang et al. [44], in which flame color features were used to constrain the position of anchor boxes. Wu et al. [45] applied background subtraction through a camera to detect moving objects. Then, a fire detection model was used to identify the frames containing the moving objects and to output fire regions and locations. A region classification model was employed to determine whether the detected objects represented fire. However, in these hybrid methods, feature extraction is often overly complex, which imposes a significant computational burden on the network. In addition, features extracted by traditional methods may mislead the subsequent processing of deep learning models, resulting in biased fire prediction outcomes.
3. Research Method
3.1. Overall Structure
In this paper, a YOLO-MFD object detection algorithm is proposed for complex fire scenarios. The overall architecture is shown in Figure 1. It mainly consists of a backbone network for feature extraction, a fusion network for feature enhancement, and a detection head for generating the final prediction results.
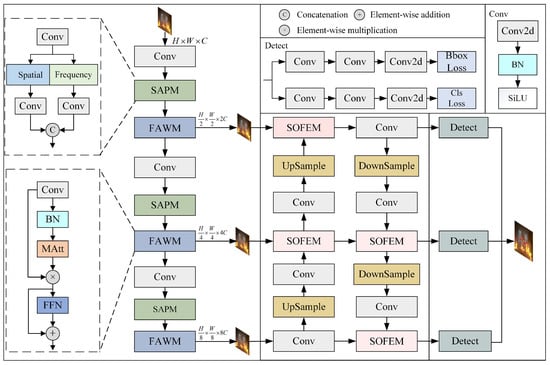
Figure 1.
Overall structure of YOLO-MFD.
Specifically, for an RGB fire image, the backbone feature extraction network is constructed by stacking residual convolutional modules. The input features are first split along the channel dimension and then merged through a cross-stage hierarchical structure. To address severe deformation of fire features and complex backgrounds, the SAPM and FAWM are introduced into the original feature extraction network. These modules are used to effectively perceive scale variation and suppress background information, thereby enhancing the representation and generalization ability of the output feature maps.
Three feature layers of different spatial resolutions can be obtained from the backbone and are used as inputs to the subsequent feature enhancement network. To avoid the loss of small-object information during the top-down and bottom-up fusion processes, the SOFEM is designed to preserve fine-grained features of small fire targets. This provides the detection module with more comprehensive and salient fire-related features.
3.2. SAPM
In deep visual models, attention mechanisms have become a crucial component for enhancing feature representation capabilities. Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) [46] captures global semantic relationships between channels through global pooling and adaptively adjusts feature scales on a per-channel basis. However, it cannot perceive position information. Building upon this, CBAM [47] introduces a spatial attention module, sequentially applying two submodules—channel and spatial attention—which enhances the ability to distinguish key information regions. Despite this, these methods remain primarily limited to local feature interactions. To address this limitation, Non-Local incorporates the concept of self-attention, enabling the capture of long-range dependencies across the entire feature map and significantly improving the perception of global spatial information [48]. Vision Transformer (ViT) [49] fully adopts the self-attention mechanism in the visual domain by dividing the image into patches and calculating multi-head self-attention, thereby capturing a global view in a highly parallelized manner. In response to the diverse characteristics of flames and smoke—such as morphological variations, scale differences, and distribution variability—the SAPM module, inspired by these attention mechanisms, integrates both spatial- and frequency-domain information. This approach preserves local details while ensuring global perception, thereby effectively enhancing the detection capability for flames and smoke in various forms. As shown in Figure 2, this module consists of two branches: a spatial-domain branch and a frequency-domain branch. After being concatenated along the channel dimension, spatial and frequency information is fused using pointwise convolution. Then, a spatio-temporal channel attention mechanism is applied to reduce redundant information and enhance the global perception ability of the model. The spatial- and frequency-domain branches are introduced in detail below.
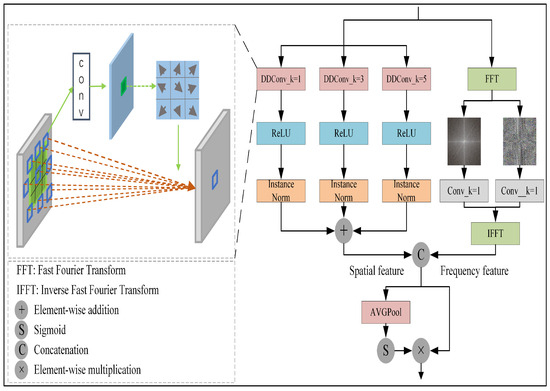
Figure 2.
Scale Adaptive Perception Module (SAPM).
3.2.1. Spatial-Domain Branch
In the spatial-domain branch, a multi-scale deformation perception unit is constructed to accurately capture complex deformation features in fire scenes. In this module, deformable convolution is introduced. Unlike traditional convolution, which performs spatial sampling with a fixed kernel, deformable convolution adapts to the nonlinear geometric transformations commonly present in fire images, such as rotation, scale scaling, and perspective distortion. Traditional convolution can lead to a decrease in fire detection performance due to these transformations.
Specifically, the SAPM utilizes deformable convolution to implement an adaptive sampling mechanism. A learnable offset prediction branch is embedded into the standard convolution kernel. The theoretical sampling coordinates are fused element-wise with the offset to form dynamically adjusted sampling positions. Irregular sampling is then performed within the local neighborhood, allowing for the precise capture of smoke features with diffusive patterns and flame features with complex deformations.
Deformable convolution [50], as the core of this unit, is explained here using the classic convolution kernel to illustrate its working process. First, the two-dimensional regular grid of this convolution kernel can be represented as
For ordinary convolution, we have
For deformable convolution, an offset is defined as , , and the output at each corresponding position is
It can be seen that the position of deformable convolution sampling is irregular and each position is an offset.
The operation of the entire airspace branch can be expressed as
Here, RELU denotes the activation function, denotes batch normalization, is the input of the spatial branch, and is the output of the spatial branch.
3.2.2. Frequency-Domain Branch
We input the feature map into the designed frequency-domain branch, and perform the two-dimensional fast Fourier transform (FFT) as shown in Equation (5).
The amplitude component (denoted as ) and phase component (denoted as ) undergo separate convolutional operations for frequency-domain feature extraction. This dual-path processing achieves two critical advantages: (1) The global receptive field inherent in frequency-domain analysis effectively captures spatiotemporal evolution patterns of fire propagation, which is crucial for fire behavior modeling; (2) the frequency-specific feature extraction mechanism enables precise discrimination of different spectral components in fire images, thereby refining fire intensity estimation and regional segmentation. Finally, an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) is implemented to reconstruct the enhanced features back into the spatial domain.
After obtaining the spatial- and frequency-domain branches, feature stacking is performed along the channel dimension in the fusion path. The fused features are then divided into two parts: one part is used to generate the spatio-temporal channel attention, and the other part is retained as the original fused features. The entire process can be expressed by the following formula.
where and , respectively, represent the outputs of the frequency-domain branch and the spatial-domain branch; denotes the fused feature; and is the output feature of the spatio-temporal evolution module.
3.3. FAWM
In fire scenarios, there is significant scale differences between targets. For instance, smoke often exhibits a large-scale, low-texture distribution, while flames are more localized and characterized by high-frequency edge features. For capturing these multi-scale features, first, a set of convolutions with different sizes is introduced to fuse semantic information from different layers, enhancing the feature completeness of fire scenes. Then, weights are generated from multi-scale features to adaptively weight the significant features in the scene.
Figure 3 illustrates the complete process of the FAWM for processing input fire features. First, the fire feature map undergoes batch normalization, adjusting the input for the subsequent attention layers to a specific distribution. The output of the attention layer is element-wise multiplied with the original input to enhance the expressive power of the input features. Then, the adaptively weighted feature map is passed to the feed-forward network layer to maintain the model’s nonlinearity. Finally, pointwise convolution is used to adjust the channel number of the original feature map, enabling a skip connection with the feature map output from the feed-forward network layer, thus achieving the fusion of high-dimensional features and shallow features to obtain richer feature information. The attention layer, as a key component of the entire FAWM, is based on multi-scale feature fusion, which uses convolution kernels of sizes , , and to jointly fuse features from different scales. The convolution is used to enhance the nonlinear expressive capability between channels while controlling the parameter scale. The convolution is suitable for capturing standard local structural information, whereas the convolution contributes to modeling contextual features of large-scale, blurry targets such as smoke. This combination of multi-scale convolutions improves the FAWM’s sensitivity to and expressive capability for different fire elements, enabling the FAWM to exhibit stronger feature extraction and discriminative abilities in complex scenarios, thereby enhancing the accuracy and robustness of fire detection.
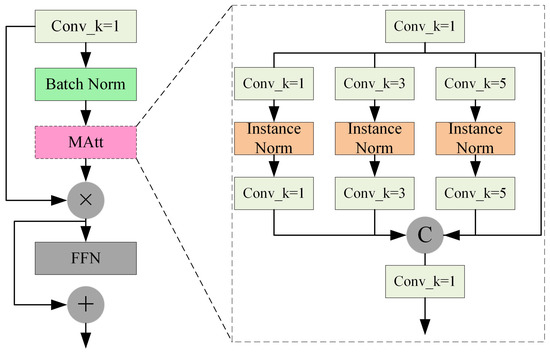
Figure 3.
Feature Adaptive Weighting Module (FAWM).
3.4. SOFEM
In fire images, early flame features are relatively small, and the ability to accurately detect them is crucial for timely fire alerts. To address this, the SOFEM was designed. This module adopts a feature pyramid structure, embedding a combination of convolutions with different receptive fields on top of spatial sampling to construct finer-grained scale layers, enabling the perception of small-object features in fire images.
Figure 4 illustrates the structure of the SOFEM. Based on the three scale feature layers defined by spatial sampling, the module first performs coarse fusion through downsampling and concatenation operations, followed by fine-grained layer enhancement through the Group Fusion Module. In the Group Fusion Module, two parallel branches are included: one branch directly generates features through pointwise convolution, and the other branch stacks a convolution after the pointwise convolution to increase the receptive field. Features with different receptive fields are generated through convolutions with varying scales to equivalently represent the two sub-scale layers. The two sub-scale features are then fused by element-wise addition, generating a more refined scale fusion result. Finally, the fine-grained fused features are sent into the detection head.
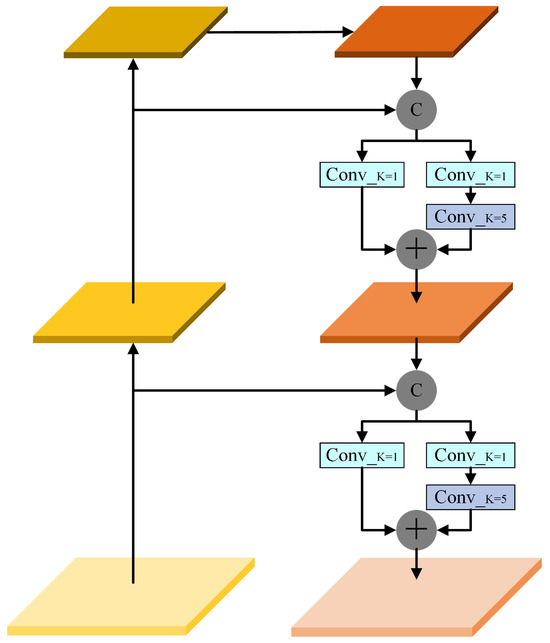
Figure 4.
Small Object Feature Extraction Module (SOFEM).
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Environment
The experimental environment consisted of Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, PyTorch 2.0.0, and a single NVIDIA RTX 3090 24 GB GPU. All models were trained/evaluated under the same experimental conditions. The model used a cosine learning rate to control the loss decay process. Figure 5 illustrates the training process of YOLO-MFD. During training, a freezing training strategy was adopted. The input image size was set to , with 600 training epochs and an initial learning rate of 0.0001. In the first 200 epochs, the backbone of the model was frozen, meaning the feature extraction network remained unchanged, thereby occupying less GPU memory. The freeze batch size was set to 32. After unfreezing, all network parameters were allowed to change, and the batch size was reduced to 16. This strategy not only accelerated the convergence speed of model but also reduced the hyperparameter tuning space. The model employed a cosine learning rate schedule to control the loss decay process. Figure 5 illustrates the training process of YOLO-MFD.
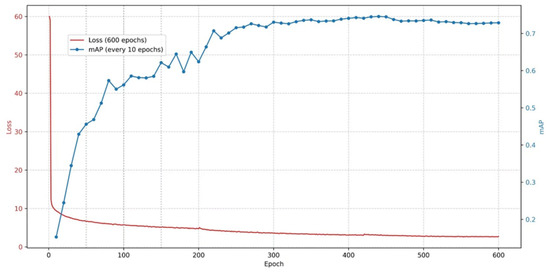
Figure 5.
Model training process.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
Samples are classified into four categories: True positive (TP)—correctly identified fire/smoke instances; false positive (FP)—non-fire/smoke incorrectly labeled as fire/smoke; true negative (TN)—correctly identified non-fire/smoke cases; false negative (FN)—fire/smoke incorrectly identified as non-fire/smoke. These metrics form the basis for calculating precision and recall.
The evaluation metric we use is mAP (mean average precision), a critical indicator for measuring the accuracy and recognition capability of fire target detection models. A higher mAP value indicates more reliable detection performance across diverse fire scenarios and lower false alarm rates. It is defined as
mAP50 [51] is a specific version of mAP, which represents the average accuracy of the model at an IoU threshold of 0.5.
4.3. Dataset
To evaluate the real-time ability and effectiveness of the proposed method for fire detection and early warning, a dataset named MFDB was created through self-collection and self-annotation. This dataset includes data from public datasets as well as from the internet and offline organizations. The dataset covers various real-world fire scenarios, including forests, grasslands, buildings, and roads. It comprises 4000 training images, 400 validation images, 400 full test images, and 300 small-target test images. Figure 6 shows some examples of the dataset.

Figure 6.
Samples of our collected dataset MFDB.
To ensure the consistency of data annotation, our paper introduces the intersection over union (IoU) in the annotation review process, which is used to measure the overlap of bounding boxes for the same target between different annotators. During the cross-checking, all image annotation results are compared using IoU calculations. If the IoU between two bounding boxes for a particular target exceeds the preset threshold of 0.8, the annotations are considered consistent and no adjustment is needed. If the IoU is below this set threshold, the sample is automatically tagged for recheck. The boundary location of the annotation boxes, separation strategies, and the decision to merge annotations are then discussed based on contextual information, image semantics, and visual boundary judgment criteria. As shown in Figure 6, the MFDB encompasses a wide range of image resolutions and covers various fire-scene object categories, including buildings, forests, streets, factories, hotels, and others. R1-C7: The small-object subset is determined by calculating the size of all fire targets in each image after labeling all fire scene. If the size proportion of a target is less than 10% of the entire image, it is classified as a small object. If the number of such small objects exceeds 60% of the total number of fire targets in the image, we categorize the image into the small-object fire data subset.
4.4. Ablation Experiment
4.4.1. Ablation Experiment
In order to verify the effectiveness of this method, we conducted ablation experiments on each module. “✓” means that the module is used, and “-” means that the module is not used. The results of the ablation experiments are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Ablation study of YOLO-MFD.
SAPM: When only the SAPM module is retained, the mAP metric reaches 72.63%, with a smoke class mAP of 66.81% and a fire class mAP of 78.46%. The experimental results demonstrate that by introducing the Feature Adaptive Weighting Module, YOLO-MFD is endowed with deformation-aware capabilities for fire targets. Redundant information in fire images is reduced in both the spatial and frequency domains, and the model’s ability is enhanced. More accurate flame and smoke features are extracted, thereby enabling the subsequent feature fusion to output more expressive fire-related representations.
FAWM: This module is designed to effectively reduce interference from redundant background information during image feature extraction. The experimental results show that the mAP metric reaches 72.42%, with a smoke class mAP of 67.04% and a fire class mAP of 77.80%. The results demonstrate that by employing adaptive weighting, feature information in the image can be captured more precisely, thereby improving the detection accuracy of the model.
SOFEM: After embedding the fine-grained small-target feature extraction module, the mAP metric reaches 72.21%, with the smoke class mAP achieving 67.84% and fire class mAP reaching 76.59%. The results demonstrate that by incorporating combinations of convolutional receptive fields with different sizes into spatial sampling, finer-grained scale hierarchies can be constructed, enabling effective small-target feature perception in fire images.
SAPM and FAWM: Through the combination of the adaptive extraction module and Feature Adaptive Weighting Module, the mAP metric is improved to 73.91%, representing increases of 1.28% and 1.49% compared to using the SAPM or FAWM individually. Building upon the feature adaptive extraction module, the introduction of the Feature Adaptive Weighting Module enhances the model’s detection capability for flames and smoke with varying shapes under complex backgrounds.
SAPM and SOFEM: When combining the SAPM with the SOFEM, the mAP metric is elevated to 73.40%. The experimental results demonstrate that the spatial- and frequency-domain operations can effectively capture deformation information in feature maps during the extraction stage. Through the grouped fusion mechanism for fine-grained small-target features introduced in the feature fusion stage, the loss of small-target information is prevented during both top-down and bottom-up feature fusion processes.
FAWM and SOFEM: Weighting operations applied to feature maps during the feature extraction stage effectively suppress interference from redundant information, producing feature maps with richer semantic content. The fine-grained small-target feature extraction module simultaneously captures multi-scale small-target information. These combined operations yield a 1.37% mAP improvement. The results indicate that employing both attention mechanisms and fine-grained small-target feature extraction enhances overall detection performance. However, due to the lack of deformation-aware capabilities, further improvements could still be made in fire detection performance.
SAPM and FAWM and SOFEM: When all modules are combined, the mAP reaches 75.09%, with the smoke class mAP achieving 70.91% and fire class mAP attaining 79.28%, which verifies the complementary nature of these modules. The results further demonstrate that YOLO-MFD is better suited for fire and smoke detection across diverse scenarios.
4.4.2. An Ablation Experiment on SAPM
In order to verify the rationality of the SAPM, we divide it into the spatial-domain branch and frequency-domain branch according to its module composition, and then carry out the ablation experiment shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Ablation study on SAPM.
The experimental results demonstrate that when spatial- and frequency-domain operations are independently introduced, no significant improvement in detection performance is observed for fire images. However, when both spatial- and frequency-domain branches are simultaneously incorporated and merged along the channel dimension through pointwise convolution for feature fusion, the model achieves superior metrics: an mAP of 75.09%, with the smoke class mAP reaching 70.91% and fire class mAP attaining 79.28%. These results validate that using the dual-branch architecture (combining spatial and frequency domains) during feature extraction not only enhances feature extraction precision but also strengthens the model’s global perception capability.
In order to show the effectiveness and real-time capability of YOLO-MFD for fire detection, we compare it with cutting-edge target detection algorithms. The experimental results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparison of multi-scene fire detection.
4.4.3. Overall Comparison
As shown in the comparison experiment in Table 3, models from different YOLO series demonstrate varying trade-offs between accuracy and speed in multi-scene fire detection tasks. YOLOv5 achieves only 65.05% mAP in fire scenarios. Despite a fast inference speed of 36 FPS, its limited feature extraction capability struggles to effectively handle complex fire features. YOLOX introduces dynamic label assignment and an anchor-free mechanism, improving the overall detection accuracy to 71.95%, while maintaining a 33 FPS inference speed. The flame detection achieves a Fire_mAP50 of 77.67%, outperforming YOLOv5. YOLOv7 strikes a good balance between an mAP of 72.17% and inference speed, achieving strong real-time detection capability through reparameterized convolutions and multi-scale feature fusion. YOLOv8, with its new backbone network and decoupled head, excels in smoke detection but underperforms in flame detection, as indicated by the relatively low Fire_mAP50, demonstrating limited adaptability to flame features. YOLOv10 removes traditional NMS operations and integrates a transformer mechanism, achieving 72.00% mAP accuracy while maintaining an inference speed of 45 FPS. This makes it highly suitable for scenarios with stringent low-latency requirements. YOLOv9-CBM integrates attention mechanisms, reaching a high accuracy of 72.93% in flame detection, yet its smoke detection capability and inference speed remain limited, affecting its overall practical value. YOLO-SF incorporates semantic segmentation to enhance detection boundaries. Although it improves smoke detection accuracy, its high computational cost of segmentation results in a speed of only 15 FPS, and its generalization capability decreases in diverse fire scenarios, yielding an overall mAP of only 70.31%. YOLOv11, as a multi-task executable detection model, excels in extracting detailed information, offering more stable overall performance. YOLOv12 benefits from both the efficient inference of convolutional networks and the strong modeling capabilities of attention mechanisms, yet it struggles to achieve a good trade-off between detection accuracy and speed across various fire scenarios. In contrast, the proposed YOLO-MFD achieves a remarkable 72.44% in flame detection while maintaining a 35 FPS inference speed, demonstrating its superior feature representation and scene adaptability. This makes YOLO-MFD an optimal solution for multi-scene fire detection, striking a balance between accuracy and real-time requirements. R2-C4: It is worth noting that among these methods, the overall performance of smoke detection is generally lower than that of flame detection. This is primarily because smoke typically appears gray and semi-transparent, has low contrast with the background, exhibits blurred and irregular boundaries, and lacks distinctive color and texture features, which collectively make it more difficult to detect accurately in images.
4.4.4. Comparison of Small Targets
To validate the detection capability of YOLO-MFD for small targets, comparative experiments were conducted on a small-target fire dataset, as shown in Table 4. Compared with other YOLO variants, YOLOv8 and YOLOv10 achieve superior mAP scores of 66.38% and 66.15%, respectively. Due to the weak features of early-stage small flames, YOLO-SF fails to achieve effective detection even with segmentation-guided techniques. YOLOv9-CBM enhances fire features through an attention mechanism. Although feature retention is not fully considered, the elimination of redundant features can improve flame feature representation, resulting in a higher mAP. YOLOv11 further optimizes the semantic transmission path of the feature pyramid, enhancing the coherence of small-object modeling while maintaining high detection accuracy. Its mAP reaches 68.21%, with Smoke_mAP50 at 66.85% and Fire_mAP50 at 70.13%. This improves overall performance and surpasses YOLOv10, demonstrating stronger adaptability to complex scenes. YOLOv12, on the other hand, introduces a cross-scale information enhancement module and an improved self-attention mechanism. Smoke_mAP50 and Fire_mAP50 reach 67.72% and 71.18%, respectively, achieving higher accuracy in early flame and smoke detection. The proposed YOLO-MFD, leveraging fine-grained perception, attains an mAP of 67.59%, demonstrating improved performance in early fire warning.

Table 4.
Comparison of small-target flame detection.
4.4.5. Visual Comparison
To more intuitively demonstrate the effectiveness of YOLO-MFD in fire image detection, the detection results of different methods are presented in Figure 7. Regardless of whether the fire images contain deformation features or complex background interference, the proposed model is shown to accurately identify critical fire-related information.

Figure 7.
Visual comparison experiment in wide-area scenarios.
To intuitively compare the detection capabilities of different methods on small-scale flames, we randomly select images from the small-target dataset, and the detection results are shown in Figure 8. It can be seen that YOLOv5, YOLO-SF, and YOLOv9-CBM all exhibit false negatives. In contrast, YOLO-MFD shows no significant false negatives in either complex or single-fire scenarios, and its detection accuracy is higher than that of the comparison methods, indicating better early warning performance for fires.

Figure 8.
Visual comparison experiment in small-flame scenarios.
As shown in the experimental results in Figure 9, to validate the model’s transferability, we tested images obtained from public sources other than the MFDB dataset. The YOLO-MFD fire detection model exhibited exceptional transferability across various scenarios, including occlusion, low light, and heavy fog. In the occlusion scenario, the model maintained stable confidence in detecting fire sources and effectively adapted to morphological changes when the fire was located in the background of the image. Under low-light conditions, the model successfully identified flames, overcoming the interference from feature discontinuity in such environments. In the heavy fog scenario, the flame detection and the analysis of smoke correlation further validated the model’s adaptability to irregular combustion patterns. These transferability tests across different scenarios demonstrate the effectiveness of YOLO-MFD in capturing the essential features of fire.

Figure 9.
Generalization testing experiments: (a) Occlusion scenario, (b) low-light scenario, (c) heavy fog scenario.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed a fire image detection framework, YOLO-MFD, designed to address common challenges in fire image detection, such as object deformation, foreground–background interference, and the difficulty in detecting small-scale targets. The SAPM mitigates the issue of missed detection caused by the morphological changes of smoke and fire in different scenes by modeling spatially adaptive receptive fields. The FAWM focuses on enhancing the separation between foreground and background features, improving the model’s discriminative ability in complex backgrounds, and significantly enhancing detection stability across multiple scales. The SOFEM improves the perception of small fire sources at long distances through a fine-grained semantic enhancement strategy. Although the proposed YOLO-MFD demonstrates a clear advantage in accuracy, the current model structure is relatively complex, and its inference efficiency has yet to fully reflect the lightweight characteristics typical of YOLO models, resulting in certain deployment costs. Future work will focus on model compression and structural reparameterization to further enhance the model’s application efficiency in edge devices and real-world fire monitoring systems. Additionally, the model’s generalization ability under extreme occlusion, nighttime scenarios, and other special conditions still requires further exploration, which will be an important direction for future research.
Author Contributions
Methodology, F.M.; Formal analysis, S.L. and T.S.; Writing—original draft, F.M. and S.L.; Writing—review & editing, F.M., S.W., R.C. and T.S.; Visualization, F.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (62371084), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX1418), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022MD723727), and the Special Support for Chongqing Postdoctoral Research Project (2022CQBSHTB2041).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tao, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P. Smoke detection based on deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Industrial Informatics-Computing Technology, Intelligent Technology, Industrial Information Integration (ICIICII), Wuhan, China, 3–4 December 2016; pp. 150–153. [Google Scholar]
- Filonenko, A.; Kurnianggoro, L.; Jo, K.H. Comparative study of modern convolutional neural networks for smoke detection on image data. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th International Conference on Human System Interactions (HSI), Ulsan, Republic of Korea, 17–19 July 2017; pp. 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Wang, W.; Dou, Z.; Li, Y. Fire recognition based on multi-channel convolutional neural network. Fire Technol. 2018, 54, 531–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namozov, A.; Im Cho, Y. An efficient deep learning algorithm for fire and smoke detection with limited data. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2018, 18, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, P.; Huang, D. Fire smoke detection algorithm based on motion characteristic and convolutional neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 15075–15092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. YOLOv5 by Ultralytics. 2023. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov5/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. YOLOv8 by Ultralytics. 2023. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov8/ (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Ren, J.F.; Xiong, W.H.; Wu, Z.H.; Jiang, M. Fire detection and identification based on improved YOLOv3. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2019, 28, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Research on lightweight forest fire detection algorithm based on YOLOv5s. J. Graph. 2023, 44, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhu, B.; Chen, G.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z. Intelligent Monitoring of Tunnel Fire Smoke Based on Improved YOLOX and Edge Computing. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Duan, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y. Real-time fire detection algorithms running on small embedded devices based on MobileNetV3 and YOLOv4. Fire Ecol. 2023, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, F.M.; ZainEldin, H. An improved fire detection approach based on YOLO-v8 for smart cities. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 20939–20954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, J. Edge-YOLO: Lightweight infrared object detection method deployed on edge devices. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.T.; Qin, Y.Y.; Ji, X.F. Review on video based flame detection algorithm. J. Data Acquis. Process. 2020, 35, 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; He, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, J. Video smoke detection using shape, color and dynamic features. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 33, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Bai, Z.; Chen, H.; Bohush, R.; Ablameyko, S. An effective algorithm to detect both smoke and flame using color and wavelet analysis. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 2017, 27, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.; Lu, Z.M.; Ji, Q.G. Real-time multi-feature based fire flame detection in video. IET Image Process. 2017, 11, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.F.; Jin, J.S.; Wang, M.J.; Jiang, W.; Gao, L.; Xiao, L.-P. Video fire detection based on Gaussian Mixture Model and multi-color features. Signal Image Video Process. 2017, 11, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgir, N.; Nguyen, K.; Chandran, V.; Boles, W. Combining multi-channel color space with local binary co-occurrence feature descriptors for accurate smoke detection from surveillance videos. Fire Saf. J. 2018, 102, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Li, C.; Gong, W.; Li, X.; Yuan, X.; Ma, Y.; Song, T. A Real-Time Fire Detection Method from Video with Multifeature Fusion. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 1939171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Chen, M. Video fire detection based on multi-feature fusion. Softw. Trib. 2020, 19, 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Lee, J. A video-based fire detection using deep learning models. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O. Recurrent neural network regularization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.2329. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, W.; Bhowmik, N.; Breckon, T.P. Efficient and compact convolutional neural network architectures for non-temporal real-time fire detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 19th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Virtual Event, 14–17 December 2020; pp. 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, K.; Ahmad, J.; Baik, S.W. Early fire detection using convolutional neural networks during surveillance for effective disaster management. Neurocomputing 2018, 288, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Ahmad, J.; Lv, Z.; Bellavista, P.; Yang, P.; Baik, S.W. Efficient deep CNN-based fire detection and localization in video surveillance applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 49, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.J.; Zhang, D.S.; Sun, L.L. Light flame detection method based on CNN in complex scene. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2021, 34, 415–422. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Liu, J. Flame image recognition algorithm based on improved Mask R-CNN. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2020, 56, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, S.; Güdükbay, U.; Töreyin, B.U.; Cetin, A.E. Deep convolutional generative adversarial networks based flame detection in video. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.01824. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, G.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, J. Video smoke detection based on deep saliency network. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 105, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Q. Smoke detection on video sequences using 3D convolutional neural networks. Fire Technol. 2019, 55, 1827–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Guo, C.; Yang, J. Using PCAand one-stage detectors for real-time forest fire detection. J. Eng. 2020, 2020, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Lin, H.; Lu, K.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y. A forest fire detection system based on ensemble learning. Forests 2021, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, R.; Kumar, A. A hybrid deep learning model by combining convolutional neural network and recurrent neural network to detect forest fire. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 38643–38660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Hu, H.; Wu, Z.; He, L.; Yang, L.; Li, F. Dark-channel based attention and classifier retraining for smoke detection in foggy environments. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 123, 103454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Venâncio, P.V.A.B.; Campos, R.J.; Rezende, T.M.; Lisboa, A.C.; Barbosa, A.V. A hybrid method for fire detection based on spatial and temporal patterns. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 9349–9361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoxia, C.; Shang, W.; Zhang, F. Information-guided flame detection based on faster R-CNN. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58923–58932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, D.; Zhao, J. An intelligent fire detection approach through cameras based on computer vision methods. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 127, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2018–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, I. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-Local Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Springenberg, J.; Riedmiller, M.; Brox, T. Image Transformer. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, R.; Netto, S.L.; da Silva, E.A. A Comparative Analysis of Object Detection Metrics with a Companion Open-Source Toolkit. Electronics 2020, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Su, Y.; Geng, X.; Wang, Y. YOLO-SF: YOLO for fire segmentation detection. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 111079–111092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Han, X.; Cao, X.; Su, Y.; Shu, D. YOLOV9-CBM: An improved fire detection algorithm based on YOLOV9. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 19612–19623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. Yolov12: Attention-centric real-time object detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).