The Gallery of Memories (GA-ME): A Novel Virtual Navigation Tool for the Study of Spatial Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
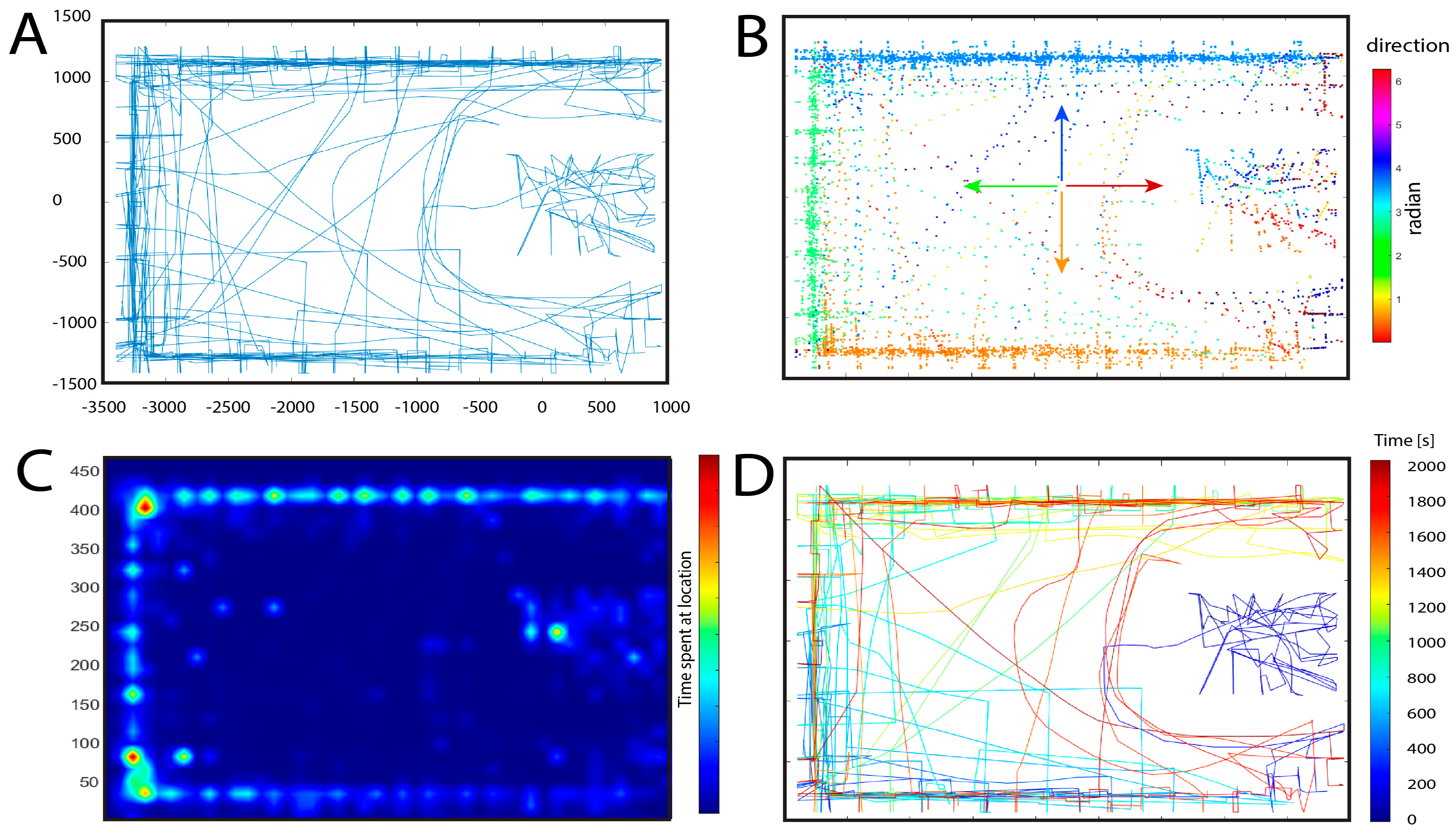
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waller, D.E.; Nadel, L.E. Handbook of Spatial Cognition; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Grieves, R.M.; Jedidi-Ayoub, S.; Mishchanchuk, K.; Liu, A.; Renaudineau, S.; Jeffery, K.J. The place-cell representation of volumetric space in rats. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, C.H. Do ants form practical judgments? Biol. Bull. 1907, 13, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carr, H.; Watson, J.B. Orientation in the white rat. J. Comp. Neurol. Psychol. 1908, 18, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, J.; Dostrovsky, J. The hippocampus as a spatial map: Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res. 1971, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; LaGrow, T.J.; Anumba, N.; Lee, A.; Zhang, X.; Yousefi, B.; Keilholz, S. Functional connectivity of the brain across rodents and humans. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 816331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’keefe, J.; Nadel, L. The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Squire, L.R. Memory and the hippocampus: A synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys, and humans. Psychol. Rev. 1992, 99, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrager, Y.; Bayley, P.J.; Bontempi, B.; Hopkins, R.O.; Squire, L.R. Spatial memory and the human hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2961–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Feo, R.; Giove, F. Towards an efficient segmentation of small rodents brain: A short critical review. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 323, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herculano-Houzel, S. The human brain in numbers: A linearly scaled-up primate brain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadasdy, Z.; Nguyen, T.P.; Török, Á.; Shen, J.Y.; Briggs, D.E.; Modur, P.N.; Buchanan, R.J. Context-dependent spatially periodic activity in the human entorhinal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3516–E3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafting, T.; Fyhn, M.; Molden, S.; Moser, M.B.; Moser, E.I. Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 2005, 436, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolman, E.C.; Ritchie, B.F.; Kalish, D. Studies in spatial learning. I. Orientation and the short-cut. J. Exp. Psychol. 1946, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, C.; Broglio, C.; Durán, E.; Gómez, A.; Rodríguez, F. Spatial Learning in Fish. Learn. Mem. Compr. Ref. 2008, 1, 499–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, E.C. Cognitive maps in rats and men. Psychol. Rev. 1948, 55, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerkes, R.M. The intelligence of earthworms. J. Anim. Behav. 1912, 2, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R.M.; Rawlins, J.N.P. T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Isa, R.; Comi, G.; Leocani, L. Apparatus design and behavioural testing protocol for the evaluation of spatial working memory in mice through the spontaneous alternation T-maze. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olton, D.S.; Samuelson, R.J. Remembrance of places passed: Spatial memory in rats. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 1976, 2, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.A. Memory deficits associated with senescence: A neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1979, 93, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresova, O.; Bures, J. Role of olfactory cues in the radial maze performance of rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1981, 3, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S. How do animals find their way back home? A brief overview of homing behavior with special reference to social Hymenoptera. Insectes Sociaux 2018, 65, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, J.C.; Gillespie, W.T. Individual differences in performance on a largescale, real-world wayfinding task. J. Environ. Psychol. 2001, 21, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingman, V.; Jechura, T.; Kahn, M.C. Behavioral and Neural Mechanisms of Homing and Migration in Birds. Animal Spatial Cognition: Comparative, Neural, and Computational Approaches. 2006. Available online: https://pigeon.psy.tufts.edu/asc/Bingman/Default.htm (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Cagle, F.R. Home Range, Homing Behavior, and Migration in Turtles; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Dittman, A.H.; Quinn, T.P. Homing in Pacific salmon: Mechanisms and ecological basis. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, A.; Nathan, R.; Bartan, Y.; Vyssotski, A.; Dell’Omo, G.; Ulanovsky, N. Large-scale navigational map in a mammal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E718–E724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Topalovic, U.; Barclay, S.; Ling, C.; Alzuhair, A.; Yu, W.; Hokhikyan, V.; Chandrakumar, H.; Rozgic, D.; Jiang, W.; Basir-Kazeruni, S.; et al. A wearable platform for closed-loop stimulation and recording of single-neuron and local field potential activity in freely moving humans. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.A.; Buckwalter, J.G. Virtual reality and cognitive assessment and rehabilitation: The state of the art. Virtual Real. Neuro-Psycho-Physiol. 1997, 44, 123–145. [Google Scholar]
- Cogné, M.; Taillade, M.; N’Kaoua, B.; Tarruella, A.; Klinger, E.; Larrue, F.; Sorita, E. The contribution of virtual reality to the diagnosis of spatial navigation disorders and to the study of the role of navigational aids: A systematic literature review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 60, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, K.; Bohbot, V.D. Spatial navigational strategies correlate with gray matter in the hippocampus of healthy older adults tested in a virtual maze. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 28885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillade, M.; Sauzéon, H.; Dejos, M.; Arvind Pala, P.; Larrue, F.; Wallet, G.; N’Kaoua, B. Executive and memory correlates of age-related differences in wayfinding performances using a virtual reality application. Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2013, 20, 298–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurley, K. Naturalistic neuroscience and virtual reality. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 896251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, M.D. Engaging by design: How engagement strategies in popular computer and video games can inform instructional design. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2005, 53, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutrot, A.; Silva, R.; Manley, E.; de Cothi, W.; Sami, S.; Bohbot, V.D.; Wiener, J.M.; Hölscher, C.; Dalton, R.C.; Hornberger, M.; et al. Global Determinants of Navigation Ability. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2861–2866.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.; Brändle, F.; Botvinick, M.; Fan, J.E.; Gershman, S.J.; Gopnik, A.; Griffiths, T.L.; Hartshorne, J.K.; Hauser, T.U.; Ho, M.K.; et al. Using games to understand the mind. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2024, 8, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.; Crucian, G.; Dalrymple-Alford, J.; Dünser, A. Assessing navigation in real and virtual environments: A validation study. Int. J. Disabil. Hum. Dev. 2011, 10, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutrot, A.; Schmidt, S.; Coutrot, L.; Pittman, J.; Hong, L.; Wiener, J.M.; Spiers, H.J. Virtual navigation tested on a mobile app is predictive of real-world wayfinding navigation performance. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuena, C.; Mancuso, V.; Stramba-Badiale, C.; Pedroli, E.; Stramba-Badiale, M.; Riva, G.; Repetto, C. Egocentric and allocentric spatial memory in mild cognitive impairment with real-world and virtual navigation tasks: A systematic review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 79, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrom, A.D.; Hill, P.F. Spatial navigation and memory: A review of the similarities and differences relevant to brain models and age. Neuron 2023, 111, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejtmanek, L.; Starrett, M.; Ferrer, E.; Ekstrom, A.D. How much of what we learn in virtual reality transfers to real-world navigation? Multisensory Res. 2020, 33, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirgantara, H.B.; Septanto, H. A Prototype of Web-based Picture Cards Matching Video Game for Memory Improvement Training. Int. J. New Media Technol. 2021, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritsen, H.; Heyers, D.; Güntürkün, O. The neural basis of long-distance navigation in birds. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patla, A.E. Understanding the roles of vision in the control of human locomotion. Gait Posture 1997, 5, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrom, A.; Kahana, M.; Caplan, J.B.; Fields, T.A.; Isham, E.A.; Newman, E.L.; Fried, I. Cellular networks underlying human spatial navigation. Nature 2003, 425, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeller, C.; Barry, C.; Burgess, N. Evidence for grid cells in a human memory network. Nature 2010, 463, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Weidemann, C.T.; Miller, J.F.; Solway, A.; Burke, J.F.; Wei, X.X.; Suthana, N.; Sperling, M.R.; Sharan, A.D.; Fried, I.; et al. Direct recordings of grid-like neuronal activity in human spatial navigation. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, S.; Wong, S.; Hodges, J.R.; Irish, M.; Piguet, O.; Hornberger, M. Lost in spatial translation–A novel tool to objectively assess spatial disorientation in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Cortex 2015, 67, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.; Watrous, A.J.; Tsitsiklis, M.; Lee, S.A.; Sheth, S.A.; Schevon, C.A.; Smith, E.H.; Sperling, M.R.; Sharan, A.; Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; et al. Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadasdy, Z.; Howell, D.H.P.; Török, Á.; Nguyen, T.P.; Shen, J.Y.; Briggs, D.E.; Modur, P.N.; Buchanan, R.J. Phase coding of spatial representations in the human entorhinal cortex. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbels, B.; Mertens, G.; Gilles, A.; Moyaert, J.; van de Berg, R.; Fransen, E.; Van de Heyning, P.; Van Rompaey, V. The virtual Morris water task in 64 patients with bilateral vestibulopathy and the impact of hearing status. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Environment | Spatial Memory | Age Scalability | Naturalistic Locomotion | High-Fidelity Rendering | Nested Spaces | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-ME | • | • | • | • | • | 5 |
| Treasure hunt task in a tropical environment [52] | • | ° | • | • | 3.5 | |
| Virtual Morris Water Maze [54] | • | • | 2 | |||
| Bicycle riding game [50] | • | ° | 1.5 | |||
| Backyard, Louvre, Temple of Luxor, Desert [13,53] | • | ° | • | 2.5 | ||
| Circular field surrounded by mountains [49] | • | • | 2 | |||
| Virtual taxi driving game [48] | ° | ° | 1 | |||
| Virtual supermarket [51] | • | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ternei, Z.; Nadasdy, Z. The Gallery of Memories (GA-ME): A Novel Virtual Navigation Tool for the Study of Spatial Memory. Information 2025, 16, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060436
Ternei Z, Nadasdy Z. The Gallery of Memories (GA-ME): A Novel Virtual Navigation Tool for the Study of Spatial Memory. Information. 2025; 16(6):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060436
Chicago/Turabian StyleTernei, Zsolt, and Zoltan Nadasdy. 2025. "The Gallery of Memories (GA-ME): A Novel Virtual Navigation Tool for the Study of Spatial Memory" Information 16, no. 6: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060436
APA StyleTernei, Z., & Nadasdy, Z. (2025). The Gallery of Memories (GA-ME): A Novel Virtual Navigation Tool for the Study of Spatial Memory. Information, 16(6), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060436






