Abstract
For the vast majority of spatial navigation research, experimental tasks are implemented in real-world environments. In recent decades, there has been an increasing trend toward virtual environments, which offer several benefits compared to their real-world counterparts while also having certain limitations. With these properties in mind, we have developed the Gallery of Memories (GA-ME), a customizable virtual-navigation task that is equipped for the assessment of both spatial navigation and memory within a highly controlled three-dimensional environment. The GA-ME provides a 3D position and head direction (pitch and yaw) sampling rate that is significantly higher compared to alternatives, enabling users to reconstruct a participant’s movement in the environment with remarkable spatiotemporal precision while its design, including nested spaces, makes it optimal for the study of place and grid cells in humans. These properties imbue the GA-ME with the potential to be widely utilized in both research and clinical settings for the in-depth study of spatial navigation and memory, with the possibility of conducting human intra- and extra-cranial electrophysiology, imaging, and eye-tracking measurements relevant to these faculties.
1. Introduction
Spatial navigation constitutes one of the most fundamental, yet intricate challenges faced by biological entities. Beneath the surface of this cognitive feat resides an interwoven substrate of mental processes, including perception, attention, categorization, memory, problem-solving, and even language [1]. Grasping the essence of spatial navigation is important not only for deciphering its mechanism but also because it might provide the basis for other cognitive processes [2].
It has been the subject of modern scientific inquiry since the early 20th century, starting with the investigation of homing behavior in ants [3] and rat behavior in mazes [4]. In fact, some of the most important discoveries regarding the neural underpinnings of spatial navigation, such as place and grid cells, were made using rodents [5]. While clearly dissimilar compared to humans at first glance, rats share several fundamental neurological structures with humans [6], including the hippocampal formation, a part of the mammalian brain that is essential for navigation, thus enabling the cross-species interpretation of results [7,8,9]. Rodent brains are also very well mapped [10,11] and relatively simpler compared to human brains [12], making it easier to study specific brain functions and changes. However, rodent results may not generalize across species and are certainly not an adequate model for the cellular computation underlying human grid cell activity, since human grid cell firing scales with environments [13] while rodent grid cell firing does not [14].
Most spatial navigation research has been conducted in mazes, owing to their versatility and ease of adaptation to different species, including rodents and fish [15,16]. The most famous designs include the sunburst pattern maze, used for the study of cognitive maps [15,17]; the T-Maze [18,19], optimal for the study of spatial working memory [20]; the Radial Arm Maze for memory and problem-solving [21]; and the Barnes Maze [22] and Morris Water Maze [23] for allocentric navigation. While mazes offer great environmental control, they scarcely reflect the natural environments in which animals would normally navigate and require extensive maintenance for the elimination of hidden variables, such as olfactory cues in the case of rodents [24].
In contrast to the well-defined and constrained environment of mazes, naturalistic tasks have been developed, aiming to assess spatial navigation in real-life situations. Several designs have been derived to this end, including homing behavior tasks in the case of animals and more complex wayfinding tasks for human participants [25,26]. Homing behavior has been studied across several species, including birds [27], turtles [28], fish [29], insects [25], and Chiroptera [30]. These types of tasks assess the animal’s ability to return to a familiar location after being displaced, providing insights regarding orientational mechanisms, path integration, and allocentric navigation. Various methods for tracking can be utilized, including GPS, radio telemetry, or video recordings [25,27]. Human wayfinding tasks instrumentalize many of the variables seen in homing tasks; however, they can also include the extensive use of tools such as maps, compasses, and GPS devices [26]. While studying human spatial navigation is certainly possible both in mazes and natural environments, it is not necessarily economical, nor is there a high level of control and precision guaranteed. Combining navigation in natural environments with intracranial electrophysiology is almost impractical (but see [31]).
Fortunately, the rapid spread of powerful computing devices has allowed for a new dimension of spatial navigation research to be established in virtual environments (VEs). Their massive potential is evidenced by widespread applications in education, military training, and the study and rehabilitation of cognitive processes as early as the 1990s [32]. Virtual tasks have been widely utilized in both healthy and pathologically affected populations [33]. A literature review conducted by Cogné et al. [33] revealed that a significant number of the studies using VEs were conducted to assess deficits regarding spatial navigation performance or in an attempt to rehabilitate them. An especially diverse set of VEs have been developed for research purposes ranging from classical mazes [34] to entire city districts with detailed environments [35].
VEs are also highly controllable, giving researchers the ability to manipulate the characteristics of environmental factors such as lights, obstacles, sounds, and landmarks with remarkable precision [36]. Another advantage that comes with VEs is the ease of reproducibility. While in the case of physical environments, extensive efforts must be made to recreate the specifics of the experimental task, these difficulties vanish in the case of pre-packaged software, minimizing both the errors that could occur during reproducing experiments and the cost of replication. Recording data is also more streamlined since researchers no longer require separate instruments for videotaping, location tracking, and logging. VEs can also prove to be more engaging, sustaining the attention and motivation of participants [37], and are possible to be deployed for the assessment of participants who may have difficulty with moving in physical space. Utilizing VEs also scales up the deployment of controlled data acquisition via the internet or mobile devices [38], enabling researchers to selectively activate and decipher various cognitive functions [39].
Nevertheless, knowledge transfer between the real and virtual dimensions is essential for the validation of virtual navigation tasks. Several studies have addressed this concern and come up with supportive results. Koenig et al. [40] demonstrated that humans can successfully apply knowledge attained in the real world in VEs. Another study that showed a correlation between spatial navigation performance conducted in VEs and real-world tasks was devised by Coutrot et al. [41]. The study involved a mobile app called “Sea Hero Quest” designed for wayfinding and path integration performance assessment. After completing the virtual tasks, the participants were asked to perform the same tasks, albeit in a different environment in the real world. Coutrot et al. [41] have found that the wayfinding performance of the participants in the VE was significantly correlated with their performance in real-world tasks. In a systematic review of egocentric and allocentric spatial memory performance in individuals with mild cognitive impairment, Tuena et al. [42] also found that real world and virtual tests show a good overlap for the assessment of spatial memory.
However, the testing of egocentric navigation with virtual tools poses one caveat: the lack of proper idiothetic cues. While allocentric navigation is based mostly on visual cues, egocentric navigation relies heavily on vestibular, proprioceptive, somatosensory, and motor efferent signals [43], which are lacking in virtual tasks unless omnidirectional treadmills are also integrated into the procedure [44]. Hejtmanek et al. [44] found that the higher the level of immersion, the greater the rate of learning and transfer of spatial information. An important limitation of immersive VR, however, is the potential for cybersickness and dizziness, which might impact the rate at which participants finish tasks. In this regard, traditional desktop-based navigation tasks can be considered superior [44].
2. Materials and Methods
Building on the trends in spatial navigation research and leveraging technological advancements, we developed a tool that integrates a spatial navigation task with recognition memory. While recognition memory tasks have been previously virtualized for memory improvement [45], at the time of writing, none provide such immersion and spatial extension as the Gallery of Memories (GA-MEs).
The GA-ME consists of two distinct yet nested spaces: a smaller enclosure that also serves as the starting area and a large hall around it (Figure 1A). This design was motivated by a fundamental question in neuroscience concerning the activity of grid cells. Extensive research has demonstrated that neurons in the medial entorhinal cortex of rodents, known as grid cells, encode space through equidistant firing fields (grid fields), forming an internal coordinate system for spatial self-localization [14]. In rodents, the spacing between grid nodes remains consistent and is independent of environmental context. In contrast, human grid cells, although homologous, exhibit context-dependent properties with grid field spacing being scaled according to the size of the environment [13]. For instance, in smaller environments, grid nodes are more densely packed, whereas in larger spaces, the distance between nodes increases. An intriguing question emerges when considering transitions between nested environments. When a person moves from a small enclosure into the larger space encompassing the smaller one, grid fields expand. However, it remains unclear what happens when the person returns to the smaller environment: do the grids contract to their original scale, or do they maintain the expanded spacing, given that the enclosure remains nested within the larger spatial context? The use of nested environments offers a unique opportunity to address this question, especially when combined with cellular electrophysiology recordings in clinical experimental settings.
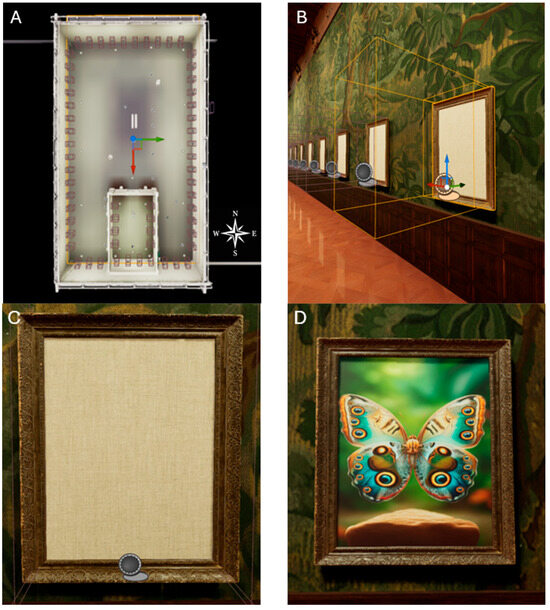

Figure 1.
(A) Bird’s-eye view of the gallery showing the hall with the nested enclosure connected by a door. (B) The larger wireframe cuboid represents the invisible collision box around the painting that the player must cross to see the painting while colliding with the smaller cuboid designates the painting as the currently tracked pair. (C) The painting is blank from a distance and is displayed when the player is inside the collision box (D).
The enclosure is connected to the hall by a door (Figure 2B), and both the enclosure and the hall are populated with two distinct sets of paintings: the first set contains 6 paintings and their identical duplicates (6 pairs = N = 12), which are dispersed randomly but spaced evenly on the walls. The second set, containing 24 different paintings (N = 48), is displayed in the hall in a randomized fashion. The task of the participant is to locate each pair of paintings in the enclosure, then move through the door and continue matching the remaining pairs of paintings. The paintings are hidden from a distance and are visible only when the participant enters their field of view, represented by the collision box, which is otherwise invisible during the trial (32 cm) (Figure 1B–D). The participant increments the score by 1 after visiting a painting and its matching pair consecutively (i.e., by entering the tracking zone of the two paintings without crossing or entering the tracking zone of another painting). When the participant tracks a painting that does not match the previously tracked painting, the latter painting will become the newly found pair. Once the participant’s score reaches 30 by discovering all the painting pairs in both rooms, the task is complete.

Figure 2.
Screenshots of the gallery from the player’s point of view. Panels (A,B) represent views from inside the enclosure when facing the southern wall and the northern wall, respectively. Panels (C,D) show the hall facing the northern wall and the southern wall, respectively.
Owing to its high-fidelity graphics and the vast array of photorealistic assets, our game engine of choice was Unreal Engine version 5.3.2. When designing the interface, interactions, and game logic, we used Blueprints visual programming language.
The main structural components of the gallery are the enclosure, the hall, the walls, and the ceiling (Figure 2). All these components were designed from simple cube actors, molding them into the desired form using the scaling tool found in the level editor. Once the desired setup was reached, we applied individually scaled textures to these surfaces. Following the application of textures, high-quality 3D meshes were imported from Quixel Bridge, which was an official repository maintained by the developer of Unreal Engine. These meshes include everything from railings and modular wooden ceiling elements to decorative beams, vases, and statues (Figure 2).
Light is provided by a Directional Light actor that represents the Sun, which is centered in the sky to reduce shadows and celestial cues that might influence navigation [46]. Additionally, Rectangular Light actors and Reflection Capture Spheres were placed across the Gallery to ensure good visibility. The intensity of the Directional Light was set to 10 lux, with the color of the light being neutral white (B = 255, G = 255, R = 255, A = 255). Rectangular Lights have an intensity of 4 EV and a slight yellow hue (B = 200, G = 255, R = 255, A = 255). An Exponential Height Fog actor was added to provide a more natural look to the Sky actor and the environment. A post-processing volume with infinite extent was added to control the visual fidelity of the level while maintaining a high framerate.
The participant controls the character from a first-person perspective. A head-bob animation and footstep sounds are included but can be turned off at will. The character is surrounded by a Collision Component to ensure appropriate interaction with the environment and paintings. The Character Movement Component handles the movement logic for the associated character. In contrast to the rest of the logic, this element was designed in C++. The starting position is X = 0, Y = 0, Z = 107.8375, facing south, with Z coding for the height of the mid-central point of the character.
The painting actors consist of several parts and are one of the central elements of our software. A default canvas that displays the picture is covered by an empty canvas, the visibility of which changes when the player enters the first collision box (the field of view), which extends in front of the painting (Figure 1B). When the player enters the second collision box (tracking zone), which is closely tied to the body of the painting, the unique Pair ID of the painting is cast to the Game Manager, and the tracking begins. The stimuli consist of 30 animal pictures that were generated by AI (Figure 1D and Figure 3). Care was taken to ensure that the animals did not look feral to facilitate the application of the GA-ME across all age ranges. These pictures can be changed at any time by creating different textures to be displayed on the canvases, allowing the researchers to manipulate the semantics and categories of the paintings displayed. This facet also confers significant age scalability to the GA-ME, as age-appropriate galleries can be created with ease by uploading new images and converting them into textures to be displayed on the canvas. The locations and types of landmarks (vases, statues, benches, and braziers) can also be changed should the need arise, with the option to manually add new ones from online repositories or remove existing ones.
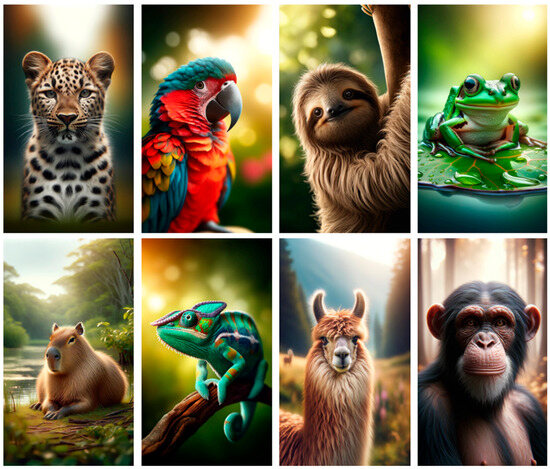

Figure 3.
A sample of eight AI-generated animal images from the 30 total pictures depicting well-recognizable species.
Once the Game Manager has been notified of the interaction, it stores the Pair ID of the painting that was interacted with. Once a second painting is interacted with, the two IDs are compared. If they match, the IsDiscovered variable, which stores Boolean operators, is set to True, the Score variable is incremented by 1, and the Game Manager checks for game completion. This state is reached once the number of discovered pairs is equal to the total number of pairs, which is 30 (60 paintings in total). Once a pair has been discovered, they can no longer be tracked anew. In case the Pair IDs do not match, the Current Pair ID variable is set to the latest painting that was interacted with.
The difficulty of the task can be reduced by allowing the paintings on which the IsDiscovered Boolean is set to True to remain visible from a distance by changing the visibility characteristics of the default canvas actor (Figure 1C) to invisible and, thus, allowing the display of the otherwise hidden painting even when the participant is not colliding with the first collision box. Utilizing this technique significantly reduces difficulty and provides a strong incentive, as the gallery becomes exponentially more beautiful as more pairs are discovered and displayed.
The location tracking logic is handled in the level’s Blueprint. It performs this task by obtaining a reference to the Player Character at the beginning of the trial. Once the Player reference has been obtained, it returns the location coordinates along an X, Y, and Z axis and stores them in an array. The orientation of the Player Character is recorded in radians and stored in the same array as the location coordinates, along with the pitch of gaze. Velocity (0–6 km/h) and time in milliseconds are also stored in the array in question. The key presses are likewise individually recorded, along with the currently tracked painting IDs.
The sampling frequency is tied to the framerate of the game, which is ~60 Hz on a machine equipped with an RTX 3050 (4 GB GDDR6) graphical processing unit. The sampling rate can be increased to the frequency of choice by changing the target framerate in the post-processing volume. It is important to mention that Unreal Engine 5.3.2. does not have a framerate cap, meaning that given powerful enough hardware, the sampling resolution can be increased indefinitely. The sampling rate is not hindered by the capability of the display hardware, as it is dependent on the internal framerate of the engine. For example, researchers can achieve a sampling rate of 240 Hz even with a monitor that has a maximum refresh rate of 60 Hz since the software itself renders 240 frames and, thus, makes 240 calls for positional data, regardless of the display frequency. For the sake of stability in initial testing, we set the target framerate to 60Hz. While small variations occur when the trial is started due to texture streaming, these are far outweighed by the high sampling rate. The recorded data are written live into a CSV file during gameplay, thus avoiding data loss in cases where a crash occurs. Data analysis is conducted in MATLAB Version R2024a.
There are numerous ways to analyze the obtained dataset. As the first step, we visualized the Player Character’s trajectories throughout the session (Figure 4A). This allowed for a qualitative assessment of behavioral strategies—such as how uniformly participants covered space, whether certain areas were prioritized or neglected, and whether the participant adopted a painting-by-painting exploration approach or crossed the room repeatedly. For example, a subject frequently crossing the room or skipping paintings may suggest an active search for remembered pairs, while a subject following the wall may be indicative of systematically pre-screening all the paintings before engaging in pairwise searching. These are distinct exploration strategies that generate discernable patterns.
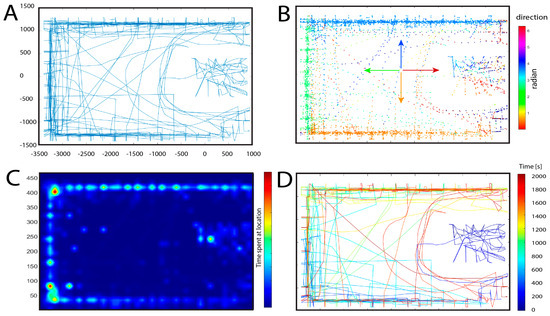
Figure 4.
Examples of data collected from one participant illustrate the capabilities of our software. (A) The raw path taken during navigation. (B) The raw path is supplemented with color coding for head orientation. (C) A heatmap representation of the most frequently visited locations. (D) Illustrates the path taken, imbued with color coding for time.
A second key feature of the data is the relationship between walking direction and head orientation (Figure 4B). Typically, individuals orient their heads in the direction of locomotion to maintain visual focus on a target [47]. Although eye movements are partially independent of head direction, saccadic eye movements are generally aligned with the target. As such, head orientation tends to correspond with the walking direction, which is a pattern confirmed in our pilot data (Figure 4B). However, the GA-ME environment allows for more flexible gaze control: the player can walk forward (in the direction of gaze), backward, or laterally (sideways) using the leftward and rightward keys on the computer keyboard.
A third important dimension of spatial navigation behavior is the distribution of time spent at various locations. This is captured by a 2D probability density map of the avatar’s presence across the environment (Figure 4C). The total area was divided into a 32 × 46 grid of 100 × 100 virtual cm tiles. For each tile, we computed the cumulative duration spent within it and applied Gaussian smoothing to visualize the density. The temporal progression of the session can be visualized through either an animated replay of the avatar’s movement or a static trajectory plot (Figure 4D). The latter represents the avatar’s path with a color gradient ranging from blue (start) to dark red (end), emphasizing the temporal dimension. Compared to Figure 4A, this visualization adds insight into the sequential order of exploration.
While these basic visualizations offer significant insights, more specialized analyses can be developed to address specific scientific questions, for instance, examining memory interference effects across sessions.
3. Results
To demonstrate the capabilities of our software, we present data derived from one participant. Since the participant had no prior experience playing first-person games, a five-minute warm-up period was provided prior to beginning the task in a different environment. We ensured that the participant attained confidence in controlling the Player Character, and following this, we started the trial, which was conducted on a computer screen with a resolution of 1920 × 1080. The trial took a total of 1972.92 s, and the participant managed to discover all the pairs. No signs of cybersickness were reported, and both motivation and attention were successfully maintained across the duration of the task.
The collected data are illustrated in Figure 4. We can observe several trends in the exploratory behavior of the participant. As seen in Figure 4A,D, the movement of the participant showed a greater tendency to cover the central area of the enclosure compared to the hall. This could be due to the smaller size of the enclosure, which enabled the viewing of pictures from a more central position compared to the hall, thus leading to a more uniform coverage of the central area. Plot D (Figure 4) shows that the participant continued to exhibit exploratory behavior by approaching all four walls of the hall one after the other, starting with the portion of the southern wall outside the enclosure, moving on to the western, northern, and eastern walls, and then turning back. We can also see in plot D (Figure 4) a growing tendency to move through the central open area of the hall, which is directly proportional to the passing of time, while in the first portion of the trial, the participant was more likely to move alongside the walls. This could be attributed to the use of shortcuts once the subject better memorized the positions of individual paintings. In plot C, we can see the frequency by which a certain location was visited by the participant. The northwestern and northeastern corners seem to provide an important spatial cue, hence their frequent visitation. Another important allocentric cue is the door connecting the enclosure with the hall (Figure 2C). The southern wall was scarcely visited, which is a result that can be attributed to the smaller number of paintings located in the hall since a large portion of the southern wall is obstructed by the enclosure. Looking at plots C and D, we can see a greater probability of the participant moving near the eastern wall as the experiment neared its end. This behavior can be attributed to the greater difficulty of finding the last few paintings, also prompting the participant to explore larger swaths of space, which indicates a shift in exploratory behavior in the late stages of the trial. In general, we can see a thigmotactic tendency coupled with chaining behavior exhibited at the beginning of the trial, which is a strategy that was gradually abandoned as the participant grew more familiar with the environment.
4. Discussion
Over the past two decades, numerous VEs were developed to investigate various aspects of human spatial behavior, often used in parallel with intracranial recordings and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). For comparative purposes, we selected several VEs that yielded high-impact publications, drawing attention specifically to those designed to probe spatial memory and/or spatial navigation. We evaluated each VE according to five criteria: (1) whether the task requires spatial memory, (2) whether it is scalable across different age groups, (3) whether it simulates naturalistic locomotion, (4) whether it uses high-fidelity rendering, and (5) whether the virtual architecture includes hierarchically nested spaces.
It is important to note that these criteria were defined with a particular scientific question in mind and, therefore, do not represent a consensual or absolute measure of quality. Each VE considered was adequate for the research questions it was originally designed to address at the level of the technology available at the time.
Table 1 summarizes the evaluation of the following VEs: a taxi-driving simulation used in a seminal human place cell study [48]; a circular open field surrounded by mountains developed to elicit signals consistent with grid cell activity in fMRI [49]; a bicycle-riding game in a similar mountain setting for direct grid cell recordings in humans [50]; a virtual supermarket used in the study of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia [51]; a tropical treasure hunt task exploring the lateralization of theta rhythms [52]; four distinct environments (a backyard, the Louvre, the Temple of Luxor, and a desert) developed for a human grid cell study [13,53]; and a virtual Morris Water Maze employed in research on bilateral vestibulopathy [54].

Table 1.
A comparison of VEs developed for spatial memory research, evaluated based on key features relevant to our research objectives. Filled symbols indicate fully implemented features; open symbols indicate partial implementation; empty cells indicate the absence of the feature. Each VE was originally designed to address specific scientific questions, as detailed in the main text.
Although a comprehensive comparison of VE implementations is beyond the scope of this paper, to our knowledge, none of the existing environments—aside from the GA-ME—combine all the desired features: a spatial memory assessment, age scalability, naturalistic locomotion, high-fidelity rendering, and nested spatial structures (the latter being of particular relevance to our experimental aims). As such, the GA-ME stands out as a uniquely comprehensive and promising platform for future research in spatial cognition (see Table 1).
Special attention has been paid to utilizing high-fidelity assets to maximize immersion, which is a characteristic of great importance since the lack of it disrupts spatial learning and memory performance [44].
The high reliability and sampling rate of navigational data also provide a significant advantage over other spatial navigation tasks in either real or virtual environments since (1) there is no risk of malfunctioning GPS devices and (2) the sampling resolution in the current implementation of the GA-ME is magnitudes higher than that found in some other virtual environments, which can have a sampling rate as low as 2 Hz (e.g., Coutrot et al. [41]).
The high sampling rate is critical to attaining reasonable alignment between the intracranial electrophysiology data, sampled between 0.5 and 40.0 kHz, eye tracking data, sampled at 2 kHz–60 Hz, and behavioral data. This enables researchers to recover the path of the participant in the VE with virtual centimeter accuracy, and precise eye tracking data allow for the reconstruction of what the participant was looking at in the VE. With all modalities combined, it is possible to reconstruct the entire course of the trials undertaken by individuals and replay the experience in real time, akin to a game of chess. Although the sampling rate is dependent on the framerate, in which fluctuations might occur due to texture streaming and light bounce computations, the graphical fidelity of the environment can be adjusted to support smooth gameplay and sampling while still retaining vigorously higher levels of fidelity than other virtual environments in spatial navigation research. It is theoretically feasible to increase the sampling rate infinitely, given appropriate hardware.
Our further prospects include the adaptation of the GA-ME to head-mounted VR displays to increase immersion even further, potentially integrating an omnidirectional treadmill, which could aid with idiothetic cues [44] that are lacking due to the traditional desktop environment.
5. Conclusions
We created a virtual reality tool that provides researchers with comprehensive control over the most relevant variables for studying spatial navigation, memory, and executive functions, including the study of grid cell scaling, thanks to the nested spaces approach. This task, presented as a game, is engaging and offers both an immersive and realistic experience for diverse age groups, owing to the high fidelity of the utilized assets, and provides a level of control over the environment that would be challenging to achieve in a real-world task due to external variables. The difficulty of the task can be easily adjusted, and stimuli may be changed at any time should the need arise, providing flexibility and customizability. Due to the possibility of controlling lights, our environment can be utilized for clinical populations with elevated photosensitivity and provides a nonhazardous environment for the assessment of cognitive impairments, which can also be used to monitor changes over time. Since the use of a head-mounted display is not mandatory, it is possible to conduct electrophysiological observations during experiments even in situations where head-mounted displays that integrate Electroencephalography (EEG) are not available.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.N.; Methodology, Z.T.; Software, Z.T.; Validation, Z.T.; Formal analysis, Z.N.; Writing—original draft, Z.T.; Writing—review & editing, Z.T.; Visualization, Z.T. and Z.N.; Supervision, Z.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Eötvös Loránd University Faculty of Education and Psychology (protocol code 2023/314 on the date of 24 May 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Zoltan Nadasdy was employed by the company Zeto, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Waller, D.E.; Nadel, L.E. Handbook of Spatial Cognition; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Grieves, R.M.; Jedidi-Ayoub, S.; Mishchanchuk, K.; Liu, A.; Renaudineau, S.; Jeffery, K.J. The place-cell representation of volumetric space in rats. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, C.H. Do ants form practical judgments? Biol. Bull. 1907, 13, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carr, H.; Watson, J.B. Orientation in the white rat. J. Comp. Neurol. Psychol. 1908, 18, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, J.; Dostrovsky, J. The hippocampus as a spatial map: Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res. 1971, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; LaGrow, T.J.; Anumba, N.; Lee, A.; Zhang, X.; Yousefi, B.; Keilholz, S. Functional connectivity of the brain across rodents and humans. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 816331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’keefe, J.; Nadel, L. The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Squire, L.R. Memory and the hippocampus: A synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys, and humans. Psychol. Rev. 1992, 99, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrager, Y.; Bayley, P.J.; Bontempi, B.; Hopkins, R.O.; Squire, L.R. Spatial memory and the human hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2961–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Feo, R.; Giove, F. Towards an efficient segmentation of small rodents brain: A short critical review. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 323, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herculano-Houzel, S. The human brain in numbers: A linearly scaled-up primate brain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadasdy, Z.; Nguyen, T.P.; Török, Á.; Shen, J.Y.; Briggs, D.E.; Modur, P.N.; Buchanan, R.J. Context-dependent spatially periodic activity in the human entorhinal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3516–E3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafting, T.; Fyhn, M.; Molden, S.; Moser, M.B.; Moser, E.I. Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature 2005, 436, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolman, E.C.; Ritchie, B.F.; Kalish, D. Studies in spatial learning. I. Orientation and the short-cut. J. Exp. Psychol. 1946, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, C.; Broglio, C.; Durán, E.; Gómez, A.; Rodríguez, F. Spatial Learning in Fish. Learn. Mem. Compr. Ref. 2008, 1, 499–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, E.C. Cognitive maps in rats and men. Psychol. Rev. 1948, 55, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerkes, R.M. The intelligence of earthworms. J. Anim. Behav. 1912, 2, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R.M.; Rawlins, J.N.P. T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Isa, R.; Comi, G.; Leocani, L. Apparatus design and behavioural testing protocol for the evaluation of spatial working memory in mice through the spontaneous alternation T-maze. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olton, D.S.; Samuelson, R.J. Remembrance of places passed: Spatial memory in rats. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 1976, 2, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.A. Memory deficits associated with senescence: A neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1979, 93, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R. Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresova, O.; Bures, J. Role of olfactory cues in the radial maze performance of rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1981, 3, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S. How do animals find their way back home? A brief overview of homing behavior with special reference to social Hymenoptera. Insectes Sociaux 2018, 65, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, J.C.; Gillespie, W.T. Individual differences in performance on a largescale, real-world wayfinding task. J. Environ. Psychol. 2001, 21, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingman, V.; Jechura, T.; Kahn, M.C. Behavioral and Neural Mechanisms of Homing and Migration in Birds. Animal Spatial Cognition: Comparative, Neural, and Computational Approaches. 2006. Available online: https://pigeon.psy.tufts.edu/asc/Bingman/Default.htm (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Cagle, F.R. Home Range, Homing Behavior, and Migration in Turtles; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Dittman, A.H.; Quinn, T.P. Homing in Pacific salmon: Mechanisms and ecological basis. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoar, A.; Nathan, R.; Bartan, Y.; Vyssotski, A.; Dell’Omo, G.; Ulanovsky, N. Large-scale navigational map in a mammal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E718–E724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Topalovic, U.; Barclay, S.; Ling, C.; Alzuhair, A.; Yu, W.; Hokhikyan, V.; Chandrakumar, H.; Rozgic, D.; Jiang, W.; Basir-Kazeruni, S.; et al. A wearable platform for closed-loop stimulation and recording of single-neuron and local field potential activity in freely moving humans. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.A.; Buckwalter, J.G. Virtual reality and cognitive assessment and rehabilitation: The state of the art. Virtual Real. Neuro-Psycho-Physiol. 1997, 44, 123–145. [Google Scholar]
- Cogné, M.; Taillade, M.; N’Kaoua, B.; Tarruella, A.; Klinger, E.; Larrue, F.; Sorita, E. The contribution of virtual reality to the diagnosis of spatial navigation disorders and to the study of the role of navigational aids: A systematic literature review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 60, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, K.; Bohbot, V.D. Spatial navigational strategies correlate with gray matter in the hippocampus of healthy older adults tested in a virtual maze. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 28885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillade, M.; Sauzéon, H.; Dejos, M.; Arvind Pala, P.; Larrue, F.; Wallet, G.; N’Kaoua, B. Executive and memory correlates of age-related differences in wayfinding performances using a virtual reality application. Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2013, 20, 298–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurley, K. Naturalistic neuroscience and virtual reality. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 896251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, M.D. Engaging by design: How engagement strategies in popular computer and video games can inform instructional design. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2005, 53, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutrot, A.; Silva, R.; Manley, E.; de Cothi, W.; Sami, S.; Bohbot, V.D.; Wiener, J.M.; Hölscher, C.; Dalton, R.C.; Hornberger, M.; et al. Global Determinants of Navigation Ability. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2861–2866.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.; Brändle, F.; Botvinick, M.; Fan, J.E.; Gershman, S.J.; Gopnik, A.; Griffiths, T.L.; Hartshorne, J.K.; Hauser, T.U.; Ho, M.K.; et al. Using games to understand the mind. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2024, 8, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.; Crucian, G.; Dalrymple-Alford, J.; Dünser, A. Assessing navigation in real and virtual environments: A validation study. Int. J. Disabil. Hum. Dev. 2011, 10, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutrot, A.; Schmidt, S.; Coutrot, L.; Pittman, J.; Hong, L.; Wiener, J.M.; Spiers, H.J. Virtual navigation tested on a mobile app is predictive of real-world wayfinding navigation performance. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuena, C.; Mancuso, V.; Stramba-Badiale, C.; Pedroli, E.; Stramba-Badiale, M.; Riva, G.; Repetto, C. Egocentric and allocentric spatial memory in mild cognitive impairment with real-world and virtual navigation tasks: A systematic review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 79, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrom, A.D.; Hill, P.F. Spatial navigation and memory: A review of the similarities and differences relevant to brain models and age. Neuron 2023, 111, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejtmanek, L.; Starrett, M.; Ferrer, E.; Ekstrom, A.D. How much of what we learn in virtual reality transfers to real-world navigation? Multisensory Res. 2020, 33, 479–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirgantara, H.B.; Septanto, H. A Prototype of Web-based Picture Cards Matching Video Game for Memory Improvement Training. Int. J. New Media Technol. 2021, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritsen, H.; Heyers, D.; Güntürkün, O. The neural basis of long-distance navigation in birds. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patla, A.E. Understanding the roles of vision in the control of human locomotion. Gait Posture 1997, 5, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrom, A.; Kahana, M.; Caplan, J.B.; Fields, T.A.; Isham, E.A.; Newman, E.L.; Fried, I. Cellular networks underlying human spatial navigation. Nature 2003, 425, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeller, C.; Barry, C.; Burgess, N. Evidence for grid cells in a human memory network. Nature 2010, 463, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Weidemann, C.T.; Miller, J.F.; Solway, A.; Burke, J.F.; Wei, X.X.; Suthana, N.; Sperling, M.R.; Sharan, A.D.; Fried, I.; et al. Direct recordings of grid-like neuronal activity in human spatial navigation. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, S.; Wong, S.; Hodges, J.R.; Irish, M.; Piguet, O.; Hornberger, M. Lost in spatial translation–A novel tool to objectively assess spatial disorientation in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Cortex 2015, 67, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.; Watrous, A.J.; Tsitsiklis, M.; Lee, S.A.; Sheth, S.A.; Schevon, C.A.; Smith, E.H.; Sperling, M.R.; Sharan, A.; Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; et al. Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadasdy, Z.; Howell, D.H.P.; Török, Á.; Nguyen, T.P.; Shen, J.Y.; Briggs, D.E.; Modur, P.N.; Buchanan, R.J. Phase coding of spatial representations in the human entorhinal cortex. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbels, B.; Mertens, G.; Gilles, A.; Moyaert, J.; van de Berg, R.; Fransen, E.; Van de Heyning, P.; Van Rompaey, V. The virtual Morris water task in 64 patients with bilateral vestibulopathy and the impact of hearing status. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).