Abstract
Mental reconstruction (MRC) and Free Recall (FR) have been recognized for enhancing the quality of witness statements. However, the mechanisms underlying this association remain insufficiently understood. This study explores how the time allocated to MRC and FR and variations in educational level influence the quality of eyewitness testimonies. Testimony quality is evaluated based on manually annotated content information provided by experts in testimony assessment, which measures adherence to the events. This is further complemented by fine-grained linguistic features, automatically extracted using linguistic analysis tools, to capture stylistic aspects. As a proof of concept, the analysis is performed on a corpus of 96 testimonies in Spanish describing two robbery cases. The results suggest that both mental reconstruction and narration times positively impact the accuracy of testimonies, as inaccuracies predominantly involve peripheral details. Furthermore, while the study confirms that educational level affects testimony quality, no significant differences were observed in the frequency of erroneous reports. This study contributes to the understanding of the relationship between cognitive strategies and the accuracy of witness statements, proposing an analysis approach applicable to forensic psychology for witness assessment.
1. Introduction
Memory is a complex cognitive process that involves different phases, such as the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information [1]. These phases do not operate in isolation but interact with and are influenced by other cognitive processes, such as language, attention, and interpretation [2,3]. As a result, studying the interplay between memory and language is particularly relevant in forensic psychology, where it supports the evaluation of testimony quality.
The quality of a testimony is evaluated mainly in terms of its accuracy, which reflects the degree to which a testimony aligns with reality [2,4]. The alignment between testimony and what was recorded in memory can be influenced by various factors, including those related to the event, the witness, and the methods used to elicit the testimony [5,6]. In terms of witness-related variables, research suggests that emotional state [7,8], substance use [9], or the impact of beliefs [3,10] may influence memory performance, while neither gender nor age (within the developmental range of young to middle adulthood) has a significant impact [11]. Regarding the environment in which the statement is obtained, Mugno et al. (2017) highlight that the quality of witness statements is shaped by an interplay of cognitive, social, and communicative processes, with cognitive processes emerging as critical to the effectiveness of Mental Reinstatement of Context (MRC) [12].
MRC is a process in which witnesses engage in mental immersion in the context of the event before recounting it. This practice is grounded in the principle of specific encoding, which suggests that contextual information is stored in memory alongside the event itself [13]. Similarly, Free Recall (FR), a technique encouraging witnesses to report everything they remember, including seemingly irrelevant details, relies on active witness participation as a social dynamic and the use of detailed-response elicitation as a communicative strategy. Based on the literature, these cognitive, social, and communicative strategies may collectively improve the accuracy of witness testimony [14,15].
Sociodemographic variables are widely recognized for their influence on witness testimony [16]. While variables such as age or gender have often been prioritized in related research [17,18], the role of education on testimony quality has sometimes been overlooked despite its impact on verbal and memory skills [19]. Based on the current literature, it is unclear whether education directly improves cognitive skills, if individuals with better cognitive performance are more likely to have access to advanced education, or if a third variable mediates this process [20]. One hypothesis that addresses the first possibility is the concept of cognitive reserve, which refers to the ability to maintain or optimize cognitive performance despite increased task demands, applicable to both healthy individuals and those with brain damage [21]. Furthermore, the effect of education appears to vary depending on factors such as specific cognitive abilities, years of training [22], and the complexity of the tasks involved [23].
Despite extensive research, there remains a significant gap in understanding the relationship between testimony accuracy, cognitive strategies, and individual differences [1,6,24,25]. This study aims to explore the extent to which the accuracy of testimonies is influenced by two specific cognitive strategies: the time spent on mental reconstruction of context and Free Recall (RQ1). Additionally, the study examines the impact of the witnesses’ educational levels on testimony accuracy (RQ2). To achieve these goals, we propose combining information acquired from manual annotation of testimony content with linguistic information, capturing the narrative style, acquired using tools for automated linguistic analysis. While content information is commonly considered by forensic psychologists when evaluating testimony accuracy (see, for instance, the principles underlying the CBCA model [26,27] discussed in Section 2.4), the use of stylometric features to capture narration style for testimony assessment is relatively more recent. This approach is based on the premise that, since testimonies are conveyed through narratives, linguistic cues can be effectively leveraged to detect deception [28,29,30,31]. This principle was applied to various types of potentially deceptive texts, such as online reviews [32], news articles [33], tweets [34], and court hearings [35]. Among the earliest tools used in testimony analysis was the Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC) software [36], which helped identify linguistic patterns associated with deception [31,35,37]. More recently, large language models have also been explored for this purpose [38].
By analyzing the relationship between testimony accuracy, narration style, and content information, this work is aimed at testing two main hypotheses. We hypothesize that a longer duration in the reconstruction and narration processes would result in an improvement in the quality of testimony, as measured by linguistic, lexical, and content indicators (HP1). Additionally, we predict a positive relationship between higher education levels and MRC and FR times and testimony quality (HP2). We test our hypotheses and analytical approach on a corpus of 96 testimonies describing two robbery cases, collected as part of a research study. While modest in size, the corpus holds value for our purposes, as it was carefully developed under the supervision of forensic psychologists and manually annotated by experts in testimony assessment for a set of fine-grained content information. This unique and high-quality dataset serves as an ideal proof of concept for our method and it is suitable to provide preliminary evidence to verify our hypotheses.
This research has broad relevance in psychology, particularly in the legal field, where testimonies often constitute primary evidence. Specifically, this study offers the following contributions: (i) a mixed-method approach to analyze testimony quality; (ii) a preliminary investigation into the relationship between MRC and FR times, testimony accuracy, and narration style; and (iii) initial evidence on the impact of a witness’s educational level on the quality of details in testimonies.
2. Materials: The Corpus of Testimony
2.1. Research Study Participants
To ensure a diverse sample, a call for participation was disseminated through social networks between March and May 2022, allowing interested candidates to contact the researchers directly. The university overseeing the study, along with its code of ethics, was explicitly mentioned in the announcement. This strategy facilitated the inclusion of the general population, providing an accessible and wide-reaching recruitment method.
The inclusion criteria required participants to be native Spanish speakers without any known linguistic, memory, or attention-related impairments. Additionally, participants had to be between the ages of 18 and 65, in accordance with the age range criterion established by [5].
A group of 48 volunteers took part in the research study carried out to collect testimonies. The selection of participants aimed to achieve an equitable distribution across key sociodemographic factors, resulting in a balanced sample. The sample is balanced in terms of gender (24 males, 24 females) and age, with participants ranging from 18 to 63 years old (AVG = 38.87; SD = ±12.7).
The study was conducted entirely in Spanish within the Valencian Community, where both Castilian Spanish and Valencian hold official language status. Consequently, all participants reported fluency in both languages, with 20.83% identifying Valencian as their mother tongue, 12.5% identifying Castilian Spanish as their mother tongue, and 66.67% indicating equal proficiency in both.
Education Level. Education was classified into four levels, following the Spanish education system. The most basic level, compulsory schooling, is typically completed by the age of 16 and includes primary and secondary education, both of which are mandatory in Spain. Non-Compulsory Preparations encompass the Spanish Baccalaureate (two optional years of high school required for university admission) or vocational training aimed at acquiring professional skills. higher education refers to completing a bachelor’s or master’s degree at a university, while the final level, post-university, includes obtaining a doctorate or a post-university master’s program.
Participants were grouped into these categories according to the highest level of education they had achieved at the time of the interview. The sample was distributed as follows: 25% completed compulsory schooling, 31.25% Non-Compulsory Preparations, 20.83% higher education, and 22.91% post-university education.
2.2. Corpus Creation Procedure
The study consisted of two sessions supervised by a team of forensic psychologists, with the initial session focused on gathering sociodemographic information, verifying inclusion criteria, and having participants read and sign ethical documentation. In the second phase, an interview lasting about 30 min was conducted fully in Spanish and audio-recorded.
The interview consisted of reading two crime stories adapted from Tucker (2019) [39], which are grounded in the research conducted by Helm et al. (2016) [40], and narrating them following the recommendations of the Cognitive Interview to improve recall. The stories, originally written in English, report a robbery and consist of about 140 words. The stories were translated into Spanish and adapted to a Valencian context to enhance participants’ identification with the events by incorporating culturally and contextually familiar scenarios. As participants had no prior exposure to the original English versions, any potential misalignments in translation did not influence their responses. Both stories were complemented by 4 images portraying the key characters: a robber, a victim, and two intervening individuals who come to help the victim. The two stories differ in the character’s physical attributes, the spatiotemporal context, and the modus operandi of the robbery. These narratives were previously used in a study that successfully examined deception detection based on linguistic variations in trial testimonies [41].
After reading each of the two stories, participants were instructed to engage in Mental Reinstatement of Context (MRC) by mentally reconstructing the narrative, immersing themselves in the event, and reflecting on its emotional and contextual aspects. They were encouraged to proceed at their own pace, with the option of closing their eyes to increase concentration. Participants indicated verbally to the interviewer when they felt they had completed the task and the experimenter measured the time allocated to MRC.
Following the MRC task, participants narrated the story as if testifying as witnesses in a crime trial. They were explicitly instructed to recount the events with maximum accuracy. The time each participant spent narrating the events was documented as Free Recall (FR) time. Both the MRC and FR times were recorded as independent variables for the study.
The experimenter also manually transcribed the 96 testimonies, obtaining the study corpus. Natural punctuation [42] (i.e., periods and commas) were added according to speech pauses and intonations to identify major utterance boundaries, roughly corresponding to sentences.
2.3. Ethical Considerations
The research was conducted with human participants and adhered to ethical review, obtaining approval from the UCV/2021-2022/060 ethics committee. The approval endorses compliance with the guidelines established in the Helsinki Declaration. Several documents were included, such as the Participant Information Sheet, which details the study and highlights the absence of financial compensation, Personal Data Protection, informed consent, and the Consent Withdrawal Form.
Note that personal data from voluntary participants were securely stored and accessible only to the researchers involved in the data collection phase. Furthermore, the participants’ identities were anonymized using alphanumeric codes linked to their data.
2.4. Corpus Annotation
The corpus of testimonies was annotated at two complementary levels. The first level regards the linguistic properties of the text, i.e., syntax and morphosyntax. Several studies have highlighted how linguistic style features, such as the use of pronouns, negative adverbs, prepositions, and conjunctions, can be linked to behavioral and emotional outcomes [31]. Building on this premise, prior research has shown that verbal cues are often correlated with deception and truth-telling (see, among others, refs. [28,35,41,43,44,45]). Most of these studies have focused on English-language statements, revealing that deceptive sentences tend to be syntactically simpler. This reduced complexity likely reflects an effort to minimize the cognitive load associated with fabricating a credible false narrative and to facilitate recalling lies [35,46]. Additionally, deceptive texts often contain a higher frequency of verbs and personal pronouns, while truthful texts typically feature more nouns, adjectives, and prepositions [44]. Research in other languages supports these findings, while also uncovering language-specific patterns. For instance, in Spanish, ref. [47] identified that false reports are often characterized by the absence of reflexive pronouns, negations, and common nouns, as well as by generally shorter sentences. Similarly, ref. [48] found that truthful accounts frequently include a higher occurrence of first-person verbs in past and future tenses, sensory-perceptual terms, insight words (e.g., “think”), tentative expressions (e.g., “maybe”), and exclusive words (e.g., “but”). In contrast, deceptive texts exhibited shorter responses in second- and third-person forms and included words associated with negative emotions. These patterns suggest that deceptive statements, regardless of the language, tend to adopt a more impersonal tone, creating emotional and psychological distance from the events being described. Furthermore, they reveal the importance of considering fine-grained linguistic traits when assessing the quality of testimonies.
To acquire the linguistic properties relevant to testimony quality assessment, we account for morpho-syntactic properties automatically extracted from the testimonies using Profiling-UD [49]. The tool first parses the plain texts to automatically acquire their underlying morpho-syntactic structure. Parsing is carried out by the tool relying on UDPipe [50], a pipeline which carries out basic pre-processing steps, i.e., sentence splitting and tokenization, POS tagging, lemmatization, and dependency parsing, with an accuracy in Spanish of around 92%. Then, the Profiling-UD tool automatically extracts approximately 150 features, either at the sentence or document level, derived from raw, morpho-syntactic, and syntactic levels of linguistic representation. The exact number of features extracted from a given text or sentence can vary slightly based on the specific content. In this instance, for example, the tool yielded 125 features extracted from the corpus of testimonies at the document level. The features acquired using the tool are detailed in Table 1. These linguistic characteristics help define language variation within and across texts, reflecting the stylometric properties of testimonies [49,51,52], which, as we discussed above, are highly predictive of testimony quality.

Table 1.
Linguistic indicators at document (testimony) level aggregated by group.
The further level of annotation delved into the content of the testimonies. This annotation was carried out by experts in forensic psychology using a novel set of XML-style tags rooted in [27,53] revisions of the Criteria-Based Content Analysis (CBCA) model. CBCA considers qualitative features of testimonies to assess their credibility, including the structure of the account, references to time and places, presence of details, reported dialogues, and emotional involvement. The model assumes that truthful testimonies are more likely to contain these elements due to the genuine cognitive and emotional processes involved in recalling real events. Table 2 reports the overview of the annotation schema, which encompasses three main groups: cognitive and motivational factors, and memory errors. The selection of these specific criteria was made based on their broad acceptance within the field of psychology in the context of testimony, as well as their suitability for achieving the study’s objectives.

Table 2.
Content indicators aggregated by group.
Regarding cognitive processes, script-deviant information involves the annotation of superfluous details, unnecessary for understanding the main event, such as the taste of the witness’s ice cream. The annotation of episodic autobiographical memory, as per the original schema by [53], encompassed spatial–temporal coordinates of the events and sensory perception details (e.g., I noticed a movement). This study expanded this category to include information about the characters’ physical appearance, acknowledging its relevance in robbery testimonies. Additionally, explicit references to the witnesses’ thoughts, emotions, and attributions related to the perpetrator’s mental state were incorporated into this category, consolidating the “Emotions and Feelings”, “Own Thoughts”, and “Attribution of Perpetrator’s Mental State” classes from the schema of [53].
Motivational criteria, on the other hand, encompass cases of strategic self-presentation. These include cases where witnesses express uncertainty or admit a lack of knowledge (e.g., “I don’t remember her hair color”) and instances of spontaneous self-corrections during narration.
The final category of annotated information focuses on comparisons between testimonies and the original narrative. This comparison enables an assessment of testimony accuracy by calculating the ratio of correct information to total reported information [25]. Memory errors are broadly categorized into two main types, distortions and commissions, following the classification proposed in previous research [24,54,55]. Distortion errors occur when the witness reports modifications or alterations to existing story elements. Commission errors capture cases where entirely new elements, not part of the original story, are introduced, whether they are relevant or marginal details. The memory error annotations were conducted by two experts, achieving an agreement rate of approximately 94%, demonstrating the reliability of the annotations.
3. Results
3.1. Mental Reinstatement and Free Recall
In this section, we present the results of quantitative and qualitative analyses conducted to evaluate the quality of testimonies. The analyses are focused on two dimensions: MRC, namely the time dedicated by participants in the study to the mental reconstruction of their stories; and FR, i.e., the time spent narrating them. We aim to understand how the time-related aspects of these processes influence the accuracy of the testimonies. To carry this out, we illustrate how stylometric and content-related indicators within the testimonies can be monitored to evaluate testimony quality and present the results of our proposed methodology on the testimony corpus presented in Section 2.
Figure 1 displays the seconds employed by each participant for the MRC and FR tasks during the research study. Concerning MRC, on average, participants required 13.5 s to mentally reconstruct the events. In general, the majority of participants (54.64%) performed MRC in 10 s or less. Conversely, only a small minority (16%) took more than 20 s, and none exceeded the 50 s mark in this regard. Concerning FR times, Figure 1 displays that narration times are consistently higher than MRC times. On average, participants spent 46.56 s on the narration process. Notably, a substantial majority of participants (81%) were able to convey the entire story within a minute. These times align with the average reading time of the stories, which is 49.37 s.
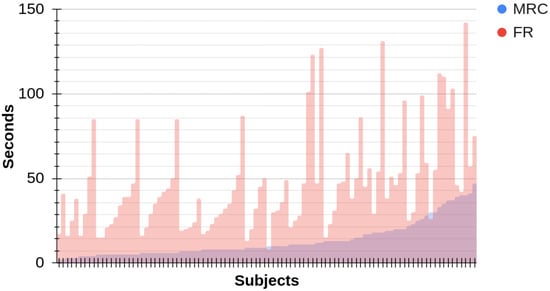
Figure 1.
Time employed during the Mental Reinstatement of Context (blue) and Free Recall (red) processes by each participant in the study.
The graph in Figure 1 indicates a potential relationship between the two temporal variables, which we recommend to further explore through statistical measures such as Spearman correlation analysis () between MRC and FR. The analysis performed on our corpus reveals a statistically significant, in terms of p-value (p), moderate correlation (, ) between these temporal variables. However, some participants exhibited extended FR times despite relatively shorter MRC durations. This observation provides insight into why the correlation is classified as medium rather than strong.
3.1.1. Impact on Narration Style
Correlation analysis can be used to examine whether the duration of mental reinstatement and narration influences the linguistic properties of testimonies. Specifically, Spearman’s rank correlation is used as it is well suited to assessing monotonic relationships between variables. This method enables one to determine whether higher values of the temporal variable correspond to higher (positive correlation) or lower (negative correlation) values of the linguistic features under consideration.
The results of this analysis on the corpus of testimonies are reported in full in Appendix A. Our findings reveal that only a subset of linguistic features demonstrates a significant correlation with the temporal variables: 38.26% of the features correlate with Free Recall, while 26.95% correlate with Mental Reinstatement of Context. Among these features, those related to the length of the testimonies emerge as the most strongly correlated with both temporal metrics. Specifically, MRC times correlate with the number of tokens in the testimonies and with the number of sentences (both ). Notably, the correlation results are even more robust when examining narration times: with the number of words in the narrative and with the number of sentences. Additionally, a significant positive correlation ( with MRC and with FR, for both) is observed with lexical variety, assessed as the ratio of different words to the total number of words in a text (type-token ratio metric, TTR).
Delving into features capturing deeper morpho-syntactic properties, time significantly impacts the overall structure of the dependency tree. Features such as the length of dependency links and the number of prepositional chains within sentences exhibit a moderate yet significant correlation with MRC and FR (see Appendix A). The higher linguistic complexity of narratives with longer narration times may arise from the increased use of coordinated structures and modifiers, particularly adjectives. Content analysis of the manually annotated elements will determine whether this complexity aligns with a greater density of informational content.
Remarkably, the linear order of core sentence elements (subjects and objects) in relation to the dependent verb remains unaffected by FR and MRC times. Conversely, an interesting observation emerges regarding the inflection of verbs and auxiliaries. While MRC does not seem to impact verb inflection, FR time does, particularly concerning the use of the present tense and the person of the verb. This suggests that higher FR times may be associated with more instances where the participant interjects themselves into the narration using expressions like “I don’t remember”, “I think”, or “I believe”.
3.1.2. Cognitive and Motivational Criteria Analysis
The analysis of manual annotation enables one to measure the impact of MRC and FR times on the content information reported in the retellings.
As a proof of concept, we analyzed the retellings of our corpus and their manual annotation. We counted 1078 tags in the corpus, namely 1041 cognitive and 37 motivational criteria tags. This analysis highlights a large disparity between the two categories, with cognitive criteria vastly outnumbering motivational criteria. As shown in Figure 2, this difference underscores the dominant presence of cognitive elements within the testimonies, reflecting their central role in the narrative structure and content of the participants’ accounts. This is not surprising considering that cognitive criteria encompass tags related to the typical information found in eyewitness testimonies, such as actions, spatial and temporal information, the emotions of the witness, and the appearance of the people involved in the events. Among the content criteria, the most frequently occurring tags refer to the spatiotemporal coordinates of the events and the physical appearance of the people involved in the robbery. Notably, information identified by experts as superfluous to the dynamics of the crime was frequently reported in the retellings. The remaining content criteria tags, referring to the participants’ feelings and perceptions, cover a marginal distribution of 2.13%. Among the motivational criteria, tags capturing expressions of forgetfulness emerge as the most frequent, although their overall distribution remains relatively low.
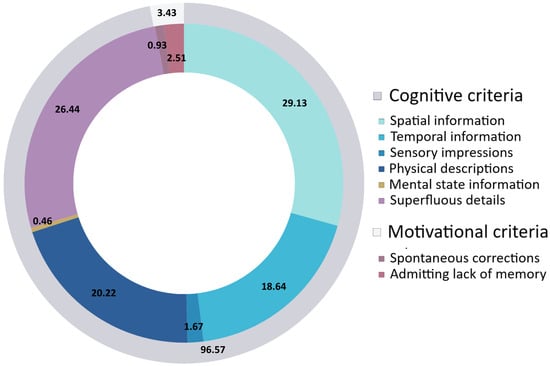
Figure 2.
Frequency distribution as a percentage of tags used to annotate the retellings, grouped by category.
To complement the quantitative findings and provide a deeper understanding of the linguistic and content dimensions of the annotation, we conducted a lexical analysis of the expressions marked with tags. This involves examining the frequency of the words and phrases annotated by the experts and analyzing their distribution across the retellings in the corpus. By identifying patterns and variations in the annotated lexical items, this analysis aims to uncover insights into how specific linguistic elements contribute to the overall narrative structure and testimony quality.
The results align with the tag distribution analysis. Specifically, expressions tied to spatial and temporal aspects, such as “calle” (street), “detrás” (behind), and “de repente” (suddenly), were most frequently identified. Similarly, physical descriptions were notably frequent in the annotations. The descriptions of individuals involved in the events suggested a clear intention of witnesses to characterize the perpetrators of the crime. Specifically, the terms found in the retellings indicated a focus on details related to hair, ethnic features, and physical build, emphasizing the witnesses’ emphasis on portraying key aspects of the individuals. Regarding superfluous details, the most frequently appearing words were “friend” and “ice cream”, associated with the witness’s plans with her friend and their activity during the incident.
A further stage of content analysis delved into the relationship between MRC and FR times and the annotated tags. The outcomes of this correlation analysis on our corpus, outlined in Table 3, reveal several significant patterns. Primarily, a substantial and positive correlation was evident between cognitive and motivational tags and both time variables (, for MRC; , for FR). However, upon closer inspection, it appears that, for MRC, these results are predominantly influenced by cognitive criteria, as motivational criteria exhibit a significant correlation exclusively with FR times. Notably, the correlations are more robust when considering Free Recall times for almost all tags, indicating that, as narrative time increases, cognitive and motivational details tend to rise, with a more pronounced impact on cognitive details compared to motivational ones.

Table 3.
Spearman correlation scores () and p-values (p) between tags and MRC and FR durations. The table also reports the average number of tags present in each retelling of the corpus with standard deviation (column ‘Avg/narr (SD)’).
3.1.3. Memory Error Analysis
Memory errors refer to discrepancies between reported testimonies and actual events. When the facts are definitively known, such as through a reliable external testimony or, as in our corpus, when the events originate from predefined stories, a comparative analysis can be conducted between the original stories and participants’ retellings. This analysis specifically targets tags annotated as episodic autobiographical memories (see Table 2). A testimony’s accuracy is determined as the ratio of correct information encoded within these tags to the total amount of information (including relevant as well as superfluous details) marked as both correct and incorrect [25,54]. By systematically examining the content of each participant’s retelling and comparing it with the original details, this approach enables the identification of discrepancies, such as omissions, distortions, or commissions, and quantifying the extent and nature of memory errors. Through this analysis, we aim to deepen the understanding of the accuracy and reliability of participants’ episodic memory recall, shedding light on the mechanisms underlying memory reconstruction.
When performing the analysis on our corpus, we noticed that participants’ narratives exhibit a high level of accuracy, with correct information reported in 93% of cases. Specifically, we identified 77 instances of tags where the information did not align with the content of the original story. Among these, experts identified 53 cases as distortion errors (i.e., proper mistakes), with the remaining classified as commission errors (namely, instances of made-up information). Notably, these errors were predominantly associated with non-essential details, such as superfluous information in the narrative, rather than critical elements like temporal or spatial information.
3.2. Education-Level Impact
While testimonies from witnesses with higher education levels are often involved in trials as they provide legally relevant knowledge to the court based on their area of expertise [56], the specific ways in which the education level influences the quality and style of a testimony remain underexplored. Conducting a correlation analysis between this sociodemographic variable and the linguistic traits of testimonies can offer valuable insights into how education level impacts narrative style. Furthermore, correlating education level with manually annotated tags can provide a deeper understanding of its influence on the overall quality of the testimony.
We conducted the analysis on our corpus relying on the Kruskal–Wallis non-parametric test (). We chose this test because it is suitable to compute correlations on multiple groups, as in this study we grouped participants on the four levels of education described in Section 2.1: compulsory schooling (B), Non-Compulsory Preparation (HP), higher education (U) and post-university (PU).
For both reconstruction and narration times, the test indicated that there is a significant difference between the four groups (FR time: = 18.19, ; MRC time: = 12.59, ). The post hoc Dunn’s test using a Bonferroni-corrected alpha of 0.0083 indicated that the mean ranks are significantly different between the PU and the B and HP groups concerning FR, and between the PU and the HP group for MRC times. Upon examining the average MRC and FR times for each group, we observed a trend where both times tend to increase with higher levels of education. Consider Figure 3, which illustrates a proportional increase in FR time corresponding to higher education levels. In particular, participants with post-university education are the group dedicating more time to narrating and mentally reconstructing stories compared to those with lower levels of education. Notably, MRC times follow a similar trend to FR times, albeit with a less pronounced tendency. In fact, except for the post-university group, the other groups tend to dedicate a comparable amount of time to MRC.
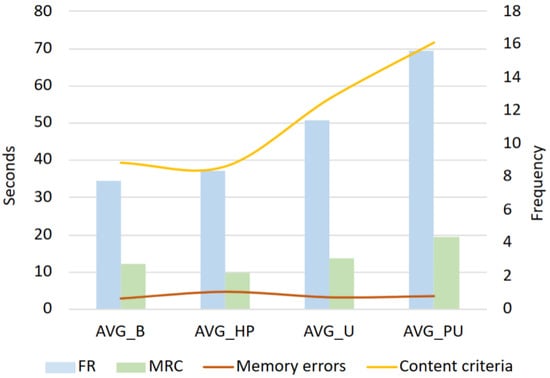
Figure 3.
Average time spent by each education-level group on Free Recall (FR) and Mental Reinstatement of Context (MRC), along with the average number of content tags and memory errors annotated in the narratives of each group.
The Kruskal–Wallis test, conducted on linguistic features across different education-level groups, enables the exploration of the stylistic variations in the narratives of participants based on their education level. The detailed results are available in Appendix B. Upon conducting the analysis, notable differences emerged across various dimensions among the four groups. Particularly prominent is the observed increase in the number of tokens in retellings by participants with higher levels of formal education. Group B (compulsory schooling), on average, produced narratives with 57.98 words, while the post-university group presented narrations with double the word count (106.02), accompanied by longer sentences (18.07 words per sentence on average in B, 20.56 in PU). This discrepancy extends its influence to various linguistic traits. The higher the education level, the higher the lexical variety the retellings exhibit, as well as an increased syntactic complexity. This complexity manifests on multiple levels, including a larger use of subordinate clauses and modifiers, the employment of verbs and auxiliaries in the subjunctive mood, and an elevated use of post-verbal participants, a less standard construction in Spanish.
In terms of content analysis, the results revealed a positive trend in the number of details as the level of education increased. However, it is relevant to note that the educational background of the witness does not seem to affect the frequency of memory errors.
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
The aim of this study was to investigate the interplay between the temporal aspects of the testimonial process and the education level of witnesses, as well as their influence on linguistic expression and the accuracy of eyewitness testimonies. Leveraging a mixed-method approach, we delved into both quantitative and qualitative dimensions, exploring linguistic expressions and the semantic content of testimonies in relation to time and a sociodemographic variable.
The outcomes of the analyses contribute to addressing the two research questions posed in this study. In exploring our first research question, regarding the influence of cognitive strategies on testimonial quality, our findings unveil the profound impact of cognitive processes on both the content and linguistic expression of testimonies. In particular, we found significant correlations between temporal engagement and linguistic style. Regarding the second question investigated in this study, our analysis of the linguistic features of testimonies showed that as education level increases, retellings become more lexically varied and syntactically complex. Finally, errors usually appear as changes to the original events rather than the creation of new information. Below, we address each finding in more depth.
4.2. Impact of Cognitive Strategies
Regarding RQ1, concerned with variations in testimony quality induced by cognitive processes, it was hypothesized that lengthier MRC and FR times would enhance the accuracy of testimony, measured through linguistic and content indicators (HP1). As a first result, we observed a positive correlation between these two variables, noting that individuals who reinstated the context for a longer period also dedicated more time to the testimonial narration, possibly introducing a higher amount of relevant information.
Our analysis then moved to exploring the impact of MRC and FR durations on the linguistic style of testimonies. The correlation between the linguistic properties of the text and reconstruction and narration durations reveals that the time individuals spend mentally reconstructing events exerts a substantial influence on linguistic style. Specifically, longer duration in the reconstruction and narration processes results in higher linguistic complexity of the testimony, as captured by a more diverse vocabulary, a higher number of words and sentences, and greater use of coordinated constructions and modifiers. These results appear to confirm HP1, namely that longer reconstruction and narration durations result in an improvement in the quality of testimonies, as measured by linguistic and lexical indicators. This result is also in line with the related literature, which found that truthful statements tend to be syntactically more complex than deceptive ones (see Section 2.4).
While the variations in linguistic phenomena with narration time were anticipated, as longer stories inherently contain a greater richness of linguistic elements, the correlation with reconstruction times presents a more unexpected and compelling result.
Additionally, our findings point to a positive correlation between the duration of the FR and MRC processes and the overall presence of content cues in the statements. This result is consistent with previous research, which suggests that a combination of both techniques is effective in improving recall, compared to the use of the other components of Cognitive Interview [15]. In particular, the results derived from lexical analysis identified spatiotemporal and superfluous details as the most commonly mentioned in the retellings. The prevalence of spatiotemporal details aligns with established theories on human memory, which posit that our memory system is inherently designed to link information about events to the spatiotemporal context in which the information was encountered [57]. As for the physical descriptions, the witnesses concentrated mainly on hair, ethnicity, and complexion when describing the individuals who participated in the robbery. Regarding motivational content, several factors may explain the limited presence of these tags in the testimonies. Firstly, performing FR and MRC techniques may reduce memory gaps and spontaneous corrections in the retellings, potentially diminishing the need for motivational elements to fill in missing details. Secondly, the annotation process specifically focused on a subset of motivational criteria from the CBCA model, inherently narrowing the scope and providing a partial view of the broader phenomenon.
The enhanced quality of testimony attributed to the use of the MRC technique in the process of retelling events is supported by cognitive theories of memory, particularly the encoding specificity hypothesis [13]. This hypothesis asserts that information retrieval is most effective when the retrieval context closely mirrors the context in which the information was encoded. The MRC technique relies on this principle by reinstating the original context, thereby enhancing the overlap between encoding and retrieval cues, which facilitates access to stored memories [58,59]. This mechanism has also been explored at the neural level, supporting the hypothesis of cortical reactivation, wherein the cortical patterns active during the encoding phase are reactivated during memory retrieval [60,61]. Moreover, the observed relationship between MRC performance and testimony quality may be mediated by cognitive abilities, such as the capacity to mentally travel back in time or vividly re-experience past events [6]. These findings highlight the multifaceted benefits of the MRC technique in improving the quality and richness of testimonies.
Upon reviewing the accuracy rate, our results align with previous works such as [25,62]. Furthermore, we noted a higher frequency of distortion errors than commission errors. This result indicates that individuals tended to modify the details of the original story, rather than introducing completely new, invented details. It was observed in past research that distortions and commissions potentially involve distinct psychological phenomena [63]. Continuing in this vein, reference [64] suggested that most falsehoods, whether intentional or unintentional, tend to take the form that requires the least effort, i.e., is closest to the truth. Our results appear to be aligned with these observations, indicating that distortions occur more frequently due to their higher cognitive efficiency with respect to commissions. It should be noted that distortions, in our data, typically concern marginal aspects of the narrative. This finding aligns with previous research indicating that central details tend to be more accurately recalled compared to peripheral ones, although this may be contingent upon the emphasis placed on the details during the encoding or retrieval phase [65,66].
4.3. Impact of Individual Differences
Concerning RQ2, referring to the impact of sociodemographic differences on testimony quality, we addressed this issue by focusing on the education level of the participants. The results obtained seem to support the hypothesis related to educational level, suggesting that a higher level of education is associated with a longer duration of MRC and FR processes. However, while individuals with higher education levels are inclined to provide more comprehensive testimonies, they are equally prone to committing memory errors as those with lower levels of education. This relationship could be explained by the positive influence of education on cognitive skills such as memory language and attention [67]. During education, individuals encounter tasks that demand the development of cognitive abilities related to memory, but also to language, thus acquiring a larger vocabulary and a greater ability to manipulate syntax. Accordingly, the study’s findings suggest that people with a higher level of education have greater linguistic ability to communicate events. Additionally, this continuous training could lead to an increased cognitive reserve that would allow these individuals to maintain optimal cognitive performance in response to increased demand [22,68]. Consequently, the educational level could act as a protective factor [69]. However, reference [23] suggests that this effect only occurs when sufficient external information is available regarding the more efficient mnemonic strategy.
4.4. Limitations and Further Research
While our study provides results that enrich the understanding of the role of cognitive factors in the accuracy of testimony, it is not without limitations. The modest size of our corpus calls for caution in generalizing findings, and future research with larger samples is warranted to enhance the robustness and applicability of our conclusions. In addition, all participants in the study are Spanish speakers, and the analysis focuses exclusively on two cases of robbery. While these factors limit the generalizability of the findings to different linguistic or cultural contexts and other types of criminal events, conducting a monolingual study provides the advantage of eliminating potential linguistic variability. This allows for more precise conclusions about the linguistic and cognitive processes at play within the specific context of Spanish-language testimonies. Moreover, focusing solely on two robbery cases was a necessary choice, as the study relied on a specialized corpus with manually annotated tags. This ensured a high level of detail and accuracy in the analysis, which would not have been feasible with other, possibly larger, corpora lacking annotation.
The study’s correlational nature limits the ability to establish definitive causal relationships, yet it still provides valuable insights into potential associations that can guide future research. Additionally, while the design does not include direct measures to confirm whether participants successfully reinstated the context as instructed, this approach maintains a more naturalistic and ecologically valid setting for data collection by excluding the use of devices to collect physiological data. Future research could address this by incorporating physiological or behavioral measures to confirm the effectiveness of context reinstatement, thereby strengthening the understanding of its role in enhancing testimony accuracy.
In addition, it is important to recognize that the laboratory context offers significant advantages, such as the ability to standardize conditions and control variables [48]. However, it is essential to interpret the results considering the differences between a simulated environment and reality. For example, the emotional impact and time spent on the statement may vary in real contexts due to the greater personal involvement in the event. Therefore, while this study focused on educational levels and specific cognitive techniques, it is essential to consider other factors that may influence eyewitness testimony, such as personality or emotional state. Further research exploring the interaction between variables in the environment in which the crime occurred, the witness, and the context in which the statement was obtained would be beneficial. In this regard, it would also be interesting to add omissions to the study of memory errors. These would enrich our understanding of the complex psychology of eyewitness testimony and help to better contextualize the findings obtained in controlled settings such as the present study.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the relationships between cognitive and sociodemographic factors, linguistic features, and memory accuracy in witness testimonies. By leveraging a corpus of retellings, annotated for content information under the supervision of forensic psychology experts and for narrative style using an NLP tool, we were able to investigate the interplay of these variables.
Our findings highlight several key aspects. The analysis confirmed the significant influence of MRC and FR durations on the linguistic complexity and information density of testimonies, aligning with cognitive theories, such as the encoding specificity hypothesis, which suggests that recalling the story context facilitates more accurate memory retrieval. Concerning narrative style, the correlation analysis between linguistic features revealed that only a subset of features are significantly associated with MRC and FR durations. This suggests that certain linguistic traits may serve as indicators of memory accuracy and testimony quality. Similarly, this study reveals that the educational background of witnesses has a significant impact on both the style and content of testimonies. Higher education levels were associated with greater linguistic complexity, suggesting that education may influence cognitive skills such as language processing and recall organization.
The use of manual annotation for fine-grained content information proved essential for this research. In this sense, the corpus, while small and monolingual, represented an essential enabling element of this research since such annotations are rarely available in existing corpora. This approach enabled us to identify nuanced patterns in testimony quality and memory errors, underscoring the importance of curated datasets in forensic research.
Overall, this study demonstrates the utility of an integrative approach combining linguistic analysis, sociodemographic factors, and cognitive theories to better understand eyewitness testimonies. Future research should aim to validate these results on larger, more diverse datasets and explore additional factors influencing testimony quality, such as stress, context, and cultural variables. Additionally, integrating physiological measures or automated tools for context monitoring could further enhance the reliability of findings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S.-S., C.A., C.M.-T. and F.D.; Methodology, S.S.-S., C.A., C.M.-T. and F.D.; Software, C.A. and F.D.; Validation, S.S.-S., C.A. and C.M.-T.; Formal analysis, S.S.-S. and C.A.; Investigation, S.S.-S., C.A., C.M.-T. and F.D.; Resources, S.S.-S. and C.M.-T.; Data curation, S.S.-S.; Writing—original draft, S.S.-S. and C.A.; Writing—review & editing, S.S.-S., C.A., C.M.-T. and F.D.; Visualization, S.S.-S.; Supervision, C.M.-T. and F.D.; Project administration, S.S.-S., C.A., C.M.-T. and F.D.; Funding acquisition, S.S.-S. and C.M.-T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the “Conselleria de Innovación, Universidades, Ciencia y Sociedad Digital”, proyecto emergente number: CIGE/2021/051, as well as Becas para la realización de estancias en el extranjero by the Universidad Católica de Valencia San Vicente Mártir, 2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Universidad Católica de Valencia San Vicente Mártir (Protocol Code UCV/2021-2022/060 and date of approval: 10 January 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Correlation Analysis Between Linguistic Features and Mental Reinstatement of Content (MRC) and Free Recall (FR)
Spearman correlation scores () and p-values (p) were computed between linguistic feature values and Free Recall (FR) and Mental Reinstatement of Context (MRC) times. The table includes average values (with standard deviation) for each feature in the testimony corpus.
| Group | Feature | FR (p) | MRC (p) | Feature AVG (SD) |
| RawText | Characters per token | 0.11 (0.30) | 0.12 (0.25) | 4.15 (±0.22) |
| n. sentences | 0.76 (<0.001) | 0.44 (<0.001) | 4.75 (±2.05) | |
| n. tokens | 0.83 (<0.001) | 0.61 (<0.001) | 94.18 (±47.85) | |
| Tokens per sentence | 0.26 (0.01) | 0.37 (<0.001) | 19.95 (±5.34) | |
| Lexical Variety | TTR form | 0.69 (<0.001) | 0.51 (<0.001) | 0.19 (±0.31) |
| TTR lemma | 0.71 (<0.001) | 0.51 (<0.001) | 0.16 (±0.26) | |
| POS | Lexical Density | 0.17 (0.10) | −0.15 (0.13) | 0.46 (±0.03) |
| Adjectives | 0.51 (<0.001) | 0.32 (0.002) | 2.23 (±2) | |
| Adpositions | −0.09 (0.37) | 0.12 (0.26) | 12.45 (±2.66) | |
| Adverbs | 0.09 (0.38) | −0.15 (0.15) | 5.21 (±2.1) | |
| Auxiliaries | 0.17 (0.11) | 0.21 (0.04) | 3.42 (±2.16) | |
| Coordinating conj. | −0.22 (0.03) | −0.18 (0.08) | 6.58 (±2) | |
| Determiners | −0.17 (0.09) | −0.02 (0.82) | 12.41 (±2.24) | |
| Interjections | 0.12 (0.23) | −0.09 (0.38) | 0.01 (±0.06) | |
| Nouns | 0.05 (0.63) | 0.04 (0.71) | 16.28 (±2.3) | |
| Numerals | −0.44 (<0.001) | −0.35 (<0.001) | 1.68 (±0.91) | |
| Pronouns | −0.16 (0.12) | 0 (0.99) | 8.39 (±2.64) | |
| Proper nouns | 0.12 (0.25) | 0.09 (0.36) | 1.76 (±1.23) | |
| Subordinating conj. | 0.2 (0.05) | 0.15 (0.15) | 3.02 (±2.08) | |
| Verbs | −0.4 (<0.001) | −0.27 (0.007) | 15.27 (±3.06) | |
| X | 0.08 (0.47) | 0.13 (0.20) | 0.03 (±0.17) | |
| Syntactic Dep | Adnominal clauses | 0.06 (0.58) | 0.1 (0.32) | 0.24 (±0.59) |
| Relative clauses | −0.02 (0.86) | 0.02 (0.83) | 1.71 (±1.42) | |
| Adverbial clauses | −0.33 (<0.001) | 0.02 (0.86) | 2.96 (±1.87) | |
| Adverbial modifiers | 0.2 (0.05) | −0.16 (0.12) | 4.53 (±2.02) | |
| Adjectival modifiers | 0.44 (<0.001) | 0.26 (0.01) | 1.7 (±1.53) | |
| Appositions | 0.16 (0.13) | 0.24 (0.02) | 0.72 (±1.04) | |
| Auxiliaries | −0.01 (0.89) | 0.13 (0.21) | 2.23 (±1.77) | |
| Auxiliary passes | 0.1 (0.33) | 0.05 (0.65) | 0.21 (±0.53) | |
| Case markers | 0.02 (0.83) | 0.14 (0.18) | 11.11 (±2.85) | |
| Coordinating conj. | −0.2 (0.05) | −0.11 (0.27) | 6.47 (±1.94) | |
| Clausal complements | 0.4 (<0.001) | 0.15 (0.15) | 0.71 (±0.89) | |
| Conjunctions | 0.04 (0.70) | 0.01 (0.95) | 5.22 (±1.85) | |
| Copula | 0.34 (<0.001) | 0.21 (0.04) | 0.94 (±1.27) | |
| Clausal subjects | 0.29 (0.004) | 0.14 (0.18) | 0.05 (±0.23) | |
| Determiners | −0.17 (0.10) | −0.02 (0.88) | 12.42 (±2.23) | |
| Fixed mwe | −0.18 (0.08) | −0.05 (0.64) | 1.04 (±1.21) | |
| Flat mwe | 0.15 (0.15) | 0.13 (0.20) | 0.01 (±0.06) | |
| Indirect objects | −0.29 (0.004) | −0.26 (0.009) | 3.74 (±2.05) | |
| Markers | 0.1 (0.34) | 0.12 (0.25) | 4.06 (±2.47) | |
| Nominal modifiers | 0.33 (<0.001) | 0.28 (0.006) | 3.15 (±2.27) | |
| Nominal subjects | −0.02 (0.83) | −0.08 (0.45) | 3.53 (±1.89) | |
| Nominal subject passes | −0.12 (0.23) | −0.01 (0.91) | 0.06 (±0.33) | |
| Numeral modifiers | −0.45 (<0.001) | −0.29 (0.004) | 1.6 (±0.91) | |
| Direct objects | −0.34 (<0.001) | −0.3 (0.003) | 7.03 (±2.3) | |
| Oblique complements | −0.12 (0.26) | 0.07 (0.51) | 5.95 (±2.14) | |
| Parataxis | 0.38 (<0.001) | 0.16 (0.12) | 0.71 (±0.99) | |
| Roots | −0.26 (0.01) | −0.37 (<0.001) | 5.33 (±1.28) | |
| Open clausal compl. | 0.1 (0.32) | −0.08 (0.43) | 1.31 (±1.3) | |
| Tree Structure | Link length (avg) | 0.32 (0.002) | 0.17 (0.11) | 2.54 (±0.3) |
| Tree depth (avg max) | 0.13 (0.19) | 0.3 (0.003) | 4.3 (±0.95) | |
| Link length (avg max) | 0.33 (0.001) | 0.36 (<0.001) | 9.39 (±3.19) | |
| Prep. chain length (avg) | 0.46 (<0.001) | 0.49 (<0.001) | 0.96 (±0.48) | |
| Tokens per clause (avg) | 0.34 (<0.001) | 0.25 (0.01) | 6.39 (±1.16) | |
| Link length (max) | 0.53 (<0.001) | 0.39 (<0.001) | 16.04 (±7.86) | |
| n. prepositional chains | 0.58 (<0.001) | 0.42 (<0.001) | 2.73 (±2.52) | |
| Prepositional distr. (1) | −0.1 (0.33) | 0 (0.98) | 72.4 (±38.71) | |
| Prepositional distr. (2) | 0.44 (<0.001) | 0.38 (<0.001) | 9.64 (±20.98) | |
| Prepositional distr. (3) | 0.15 (0.13) | 0.28 (0.006) | 1.3 (±4.87) | |
| Order | Object post-verbal | 0.12 (0.24) | 0.12 (0.25) | 63.86 (±17.36) |
| Object pre-verbal | −0.12 (0.24) | −0.12 (0.25) | 36.14 (±17.36) | |
| Subject post-verbal | 0.13 (0.2) | 0.16 (0.12) | 14.43 (±23.68) | |
| Subject pre-verbal | −0.05 (0.65) | −0.06 (0.54) | 80.36 (±30.13) | |
| Verb Inflection | Aux form:fin | 0.12 (0.23) | 0.06 (0.59) | 86.83 (±31.89) |
| Aux form:ger | 0.17 (0.10) | 0.12 (0.23) | 0.41 (±2.93) | |
| Aux form:inf | 0.11 (0.29) | 0.14 (0.16) | 1.21 (±4.83) | |
| Aux form:part | 0.01 (0.89) | 0.17 (0.10) | 0.09 (±0.85) | |
| Aux mood:cnd | 0.09 (0.39) | 0.11 (0.27) | 0.15 (±1.46) | |
| Aux mood:ind | 0.1 (0.33) | 0.1 (0.33) | 87.36 (±32.03) | |
| Aux mood:sub | 0.26 (0.01) | 0.18 (0.08) | 1.03 (±5.15) | |
| Aux num,pers:plur,1 | 0.25 (0.02) | 0.03 (0.74) | 3.42 (±9.78) | |
| Aux num,pers:plur,3 | −0.01 (0.89) | 0.1 (0.32) | 19.02 (±26.47) | |
| Aux num,pers:sing,1 | 0.12 (0.26) | 0.14 (0.16) | 1.44 (±6.84) | |
| Aux num,pers:sing,3 | 0.24 (0.02) | 0.18 (0.08) | 64.65 (±35.58) | |
| Aux tense:imp | 0.3 (0.003) | 0.15 (0.14) | 51 (±36.98) | |
| Aux tense:past | −0.1 (0.33) | 0.05 (0.64) | 23.54 (±31.6) | |
| Aux tense:pres | 0.21 (0.04) | 0.11 (0.28) | 14 (±27.62) | |
| Verb form:fin | 0.08 (0.45) | −0.19 (0.07) | 60.8 (±15.4) | |
| Verb form:ger | −0.07 (0.47) | 0.1 (0.35) | 16.94 (±8.64) | |
| Verb form:inf | −0.07 (0.51) | 0.05 (0.61) | 19.74 (±11.88) | |
| Verb form:part | 0.36 (<0.001) | 0.35 (<0.001) | 2.53 (±6.95) | |
| Verb mood:cnd | 0.31 (0.002) | 0.06 (0.56) | 1.06 (±3.2) | |
| Verb mood:imp | 0.09 (0.36) | 0.09 (0.36) | 0.08 (±0.79) | |
| Verb mood:ind | −0.35 (<0.001) | −0.11 (0.29) | 98.03 (±4.83) | |
| Verb mood:sub | 0.16 (0.11) | 0.09 (0.39) | 0.83 (±3.66) | |
| Verb num,pers:plur | 0.13 (0.2) | 0.08 (0.45) | 0.07 (±0.73) | |
| Verb num,pers:plur,1 | −0.22 (0.03) | 0.02 (0.86) | 13.5 (±15.35) | |
| Verb num,pers:plur,3 | −0.24 (0.02) | −0.25 (0.02) | 22.09 (±15.21) | |
| Verb num,pers:sing | 0.24 (0.02) | −0.02 (0.82) | 0.72 (±2.68) | |
| Verb num,pers:sing,1 | 0.52 (<0.001) | 0.25 (0.01) | 6.31 (±9.84) | |
| Verb num,pers:sing,2 | 0.09 (0.36) | 0.09 (0.36) | 0.08 (±0.79) | |
| Verb num,pers:sing,3 | 0.1 (0.31) | 0.12 (0.25) | 56.61 (±16.3) | |
| Verb tense:fut | 0.15 (0.14) | 0.13 (0.20) | 0.57 (±2.77) | |
| Verb tense:imp | 0.33 (<0.001) | 0.07 (0.50) | 24.38 (±16.58) | |
| Verb tense:past | −0.36 (<0.001) | −0.07 (0.52) | 53.24 (±26.35) | |
| Verb tense:pres | 0.23 (0.02) | 0.12 (0.26) | 21.82 (±27.42) | |
| Verb Predicate | Verbal root (%) | −0.2 (0.05) | −0.07 (0.53) | 93.16 (±11.12) |
| Verb edges (avg) | −0.09 (0.38) | −0.02 (0.87) | 2.63 (±0.33) | |
| Verb edges (0) | 0.02 (0.86) | 0.16 (0.12) | 3.34 (±4.85) | |
| Verb edges (1) | 0.01 (0.9) | −0.03 (0.76) | 14.55 (±10.41) | |
| Verb edges (2) | 0.13 (0.2) | 0.05 (0.65) | 29.03 (±11.92) | |
| Verb edges (3) | −0.11 (0.29) | −0.04 (0.66) | 29 (±12.97) | |
| Verb edges (4) | −0.08 (0.42) | −0.11 (0.28) | 17.92 (±11.94) | |
| Verb edges (5) | 0.27 (0.007) | 0.31 (0.002) | 4.8 (±5.8) | |
| Verb edges (6) | −0.05 (0.61) | −0.07 (0.48) | 1.37 (±3.19) | |
| Verbal heads per sent | 0.05 (0.6) | 0.14 (0.17) | 3.21 (±1) | |
| Subord | subord. chain len. (avg) | 0.08 (0.42) | 0.25 (0.01) | 1.22 (±0.26) |
| principal prop. distr. | −0.08 (0.41) | −0.16 (0.11) | 43.03 (±14.33) | |
| subordinate distr. (1) | −0.05 (0.6) | −0.22 (0.03) | 81.19 (±19.63) | |
| subordinate distr. (2) | 0.1 (0.32) | 0.21 (0.04) | 16.01 (±17.75) | |
| subordinate distr. (3) | 0.07 (0.5) | 0.12 (0.24) | 2.45 (±8.38) | |
| subordinate distr. (4) | 0.09 (0.4) | 0.12 (0.26) | 0.36 (±2.1) | |
| subordinate post | −0.18 (0.09) | −0.17 (0.10) | 89.05 (±23.03) | |
| subordinate pre | 0.18 (0.09) | 0.17 (0.10) | 10.95 (±23.03) | |
| subordinate prop. distr. | 0.08 (0.41) | 0.16 (0.11) | 56.97 (±14.33) |
Appendix B. Correlation Analysis between Linguistic Features and Participants’ Education Level
The following shows Kruskal–Wallis test scores () comparing linguistic features that vary significantly among all four participant groups based on education level (B: basic level; HP: higher preparation; U: university; PU: post-university). The table includes average values (with standard deviation) for each feature in each group. Significance levels:
| Average Values (SD) | ||||||
| Group | Feature | (p) | B | HP | U | PU |
| RawText | Characters per token | 26.88 (<0.001) | 4.11 (±0.27) | 4.11 (±0.26) | 4.27 (±0.25) | 4.22 (±0.22) |
| n. sentences | 55.95 (<0.001) | 3.29 (±1.6) | 3.11 (±1.36) | 3.75 (±1.71) | 5.2 (±2.44) | |
| n. tokens | 70.3 (<0.001) | 57.98 (±31.58) | 59.63 (±29.12) | 77.76 (±40.84) | 106.02 (±53.9) | |
| Tokens per sentence | 17.55 (<0.001) | 18.07 (±5.46) | 20.18 (±7.3) | 21.15 (±6.23) | 20.56 (±4.77) | |
| Lexical Variety | TTR form | 35.7 (<0.001) | 0.04 (±0.16) | 0.05 (±0.18) | 0.15 (±0.28) | 0.23 (±0.33) |
| TTR lemma | 35.31 (<0.001) | 0.03 (±0.13) | 0.05 (±0.16) | 0.13 (±0.24) | 0.2 (±0.27) | |
| POS | Adjectives | 15.94 (0.001) | 3.04 (±2.83) | 2.51 (±2.66) | 3.81 (±2.38) | 3.22 (±2.67) |
| Adpositions | 2.04 (0.56) | 12.29 (±3.52) | 12.49 (±3.26) | 12.35 (±2.77) | 11.81 (±2.88) | |
| Adverbs | 20.24 (<0.001) | 3.41 (±2.31) | 3.89 (±2.68) | 4.52 (±2.36) | 4.97 (±2.56) | |
| Auxiliaries | 10.27 (0.02) | 3.98 (±2.63) | 3.8 (±2.65) | 4.03 (±2.56) | 4.93 (±2.36) | |
| Coordinating conj. | 14.86 (0.002) | 6.91 (±2.64) | 5.81 (±3) | 5.63 (±2.38) | 5.87 (±2.16) | |
| Determiners | 25.78 (<0.001) | 13.77 (±2.89) | 13.88 (±2.57) | 13.57 (±2.58) | 12.27 (±2.3) | |
| Interjections | 0.95 (0.81) | 0.05 (±0.43) | 0.02 (±0.19) | 0.03 (±0.17) | 0.04 (±0.23) | |
| Lexical density | 3.61 (0.31) | 0.45 (±0.04) | 0.45 (±0.04) | 0.46 (±0.03) | 0.45 (±0.03) | |
| Nouns | 31.03 (<0.001) | 17.64 (±3.21) | 18.32 (±3.02) | 17.58 (±2.83) | 15.9 (±2.48) | |
| Numerals | 12.51 (0.006) | 2.26 (±1.72) | 1.98 (±1.33) | 1.86 (±1.28) | 1.58 (±0.87) | |
| Pronouns | 5.85 (0.12) | 7.57 (±2.73) | 7.75 (±3.16) | 6.92 (±3.2) | 8.08 (±2.37) | |
| Proper nouns | 12.96 (0.005) | 1.57 (±1.77) | 1.58 (±1.65) | 1.33 (±1.3) | 2.06 (±1.38) | |
| Subordinating conj. | 26.16 (<0.001) | 2.49 (±2.32) | 3.89 (±2.4) | 3.7 (±2.4) | 4.12 (±2.39) | |
| Verbs | 4.67 (0.2) | 14.74 (±3.64) | 14.63 (±3.04) | 13.96 (±3.96) | 13.97 (±2.88) | |
| X | 15.85 (0.001) | 0.02 (±0.17) | 0.03 (±0.22) | 0.01 (±0.06) | 0.11 (±0.35) | |
| Verb Inflection | Aux form:fin | 0.54 (0.91) | 84.59 (±35.34) | 82.58 (±36.7) | 86.43 (±32.15) | 95.03 (±13.75) |
| Aux form:ger | 9.43 (0.02) | 0 (±0) | 0.22 (±2.36) | 1.25 (±11.18) | 1 (±4.11) | |
| Aux form:inf | 4.43 (0.22) | 0.43 (±3.05) | 0.98 (±4.19) | 1.64 (±11.31) | 1.83 (±6.9) | |
| Aux form:part | 7.87 (0.05) | 0.39 (±2.38) | 0.15 (±1.57) | 1.93 (±8.43) | 1.01 (±3.93) | |
| Aux mood:cnd | 6.83 (0.08) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0.18 (±1.6) | 0.55 (±3.18) | |
| Aux mood:ind | 1.58 (0.66) | 85.42 (±35.48) | 83.75 (±36.86) | 87.73 (±31.8) | 96.75 (±12.32) | |
| Aux mood:sub | 12.49 (0.006) | 0 (±0) | 0.18 (±1.89) | 0.85 (±4.58) | 1.56 (±5.89) | |
| Aux num,pers:plur,1 | 5.93 (0.12) | 7.14 (±21.78) | 3.2 (±12.81) | 2.39 (±8.29) | 5.24 (±14.75) | |
| Aux num,pers:plur,3 | 10.44 (0.02) | 21.69 (±32.24) | 11.93 (±24.77) | 17.16 (±25.05) | 16.83 (±23.92) | |
| Aux num,pers:sing,1 | 12.3 (0.006) | 1.42 (±5.49) | 0.74 (±5.65) | 0.42 (±3.73) | 3.2 (±10.76) | |
| Aux num,pers:sing,3 | 10.81 (0.01) | 55.16 (±39.77) | 68.06 (±39.71) | 68.78 (±35.06) | 73.15 (±28.39) | |
| Aux tense:imp | 3.19 (0.36) | 53.74 (±41.46) | 60.95 (±42.32) | 62.74 (±37.66) | 65.79 (±32.84) | |
| Aux tense:past | 6.94 (0.07) | 21.76 (±34.61) | 11.56 (±24.65) | 18.02 (±26.63) | 13.48 (±21.22) | |
| Aux tense:pres | 17.64 (<0.001) | 9.91 (±23.61) | 11.41 (±28.24) | 7.99 (±21.99) | 19.6 (±30.28) | |
| Verb form:fin | 2.74 (0.43) | 56.57 (±20.34) | 57.09 (±20.77) | 56.09 (±14.56) | 53.25 (±16.51) | |
| Verb form:ger | 3.02 (0.39) | 16.47 (±12.83) | 18.15 (±13.24) | 19.5 (±11.76) | 18.29 (±10.02) | |
| Verb form:inf | 1.01 (0.8) | 15.52 (±12.68) | 16.26 (±14.69) | 14.97 (±11.51) | 16.9 (±10.79) | |
| Verb form:part | 8.94 (0.03) | 11.44 (±16.34) | 8.51 (±13.36) | 9.45 (±11.96) | 11.55 (±12.8) | |
| Verb mood:cnd | 10.91 (0.01) | 2.94 (±9.9) | 2.19 (±10.92) | 5.15 (±11.1) | 3.52 (±9.32) | |
| Verb mood:imp | 4.73 (0.19) | 0 (±0) | 0.14 (±1.07) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | |
| Verb mood:ind | 13.95 (0.003) | 95.61 (±14.08) | 96.59 (±14.39) | 93.73 (±11.59) | 94.9 (±10.45) | |
| Verb mood:sub | 6.83 (0.08) | 0.4 (±2.35) | 0.19 (±1.5) | 1.12 (±4.78) | 1.58 (±5.79) | |
| Verb num,pers:plur | 2.92 (0.4) | 0.07 (±0.73) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | |
| Verb num,pers:plur,1 | 5.78 (0.12) | 15.13 (±21.8) | 11.49 (±19.9) | 16.08 (±19.81) | 14.38 (±18.13) | |
| Verb num,pers:plur,3 | 8.09 (0.04) | 24.47 (±24.18) | 31.19 (±28.8) | 21.5 (±23.29) | 20.45 (±15.69) | |
| Verb num,pers:sing | 4.93 (0.18) | 1.61 (±6.74) | 0.51 (±2.61) | 0.09 (±0.8) | 1.11 (±4.07) | |
| Verb num,pers:sing,1 | 23.37 (<0.001) | 2.12 (±7.39) | 6.43 (±13.76) | 4.02 (±10.43) | 7.02 (±10.13) | |
| Verb num,pers:sing,2 | 2.36 (0.5) | 0 (±0) | 0.07 (±0.73) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | |
| Verb num,pers:sing,3 | 7.32 (0.06) | 55.46 (±27.48) | 48.59 (±27.88) | 57.88 (±26.82) | 56.89 (±16.98) | |
| Verb tense:fut | 4.67 (0.2) | 0 (±0) | 0.87 (±4.64) | 0.32 (±2.11) | 0.36 (±1.75) | |
| Verb tense:imp | 7.19 (0.07) | 26.55 (±21.42) | 24.49 (±25.07) | 30.5 (±18.76) | 27.39 (±16.12) | |
| Verb tense:past | 14.75 (0.002) | 63.29 (±23.89) | 53.46 (±32.66) | 55.88 (±21.67) | 48.31 (±24.72) | |
| Verb tense:pres | 22.24 (<0.001) | 10.15 (±16.81) | 21.19 (±30.08) | 13.3 (±19.71) | 23.94 (±24.93) | |
| Verb Predicate | Verb edges (avg) | 4.58 (0.21) | 3.86 (±6.94) | 2.43 (±5.61) | 3.5 (±6.14) | 2.39 (±3.86) |
| Verb edges (0) | 3.33 (0.34) | 14.54 (±13.49) | 12.62 (±12.31) | 14.42 (±10.74) | 14.91 (±10.04) | |
| Verb edges (1) | 2.46 (0.48) | 27.56 (±16.35) | 27.79 (±15.94) | 29.27 (±16.02) | 30.6 (±12.44) | |
| Verb edges (2) | 2.67 (0.45) | 31.55 (±18.06) | 32.06 (±16.85) | 29.83 (±16.43) | 29.05 (±13.26) | |
| Verb edges (3) | 0.37 (0.95) | 17.38 (±13.65) | 18.02 (±15.46) | 16.76 (±15.56) | 16.76 (±10.41) | |
| Verb edges (4) | 3.81 (0.28) | 4.28 (±7.57) | 5.96 (±9.73) | 4.54 (±6.95) | 4.99 (±6.08) | |
| Verb edges (5) | 4.23 (0.24) | 0.83 (±2.74) | 1.12 (±3.15) | 1.67 (±3.7) | 1.31 (±3.16) | |
| Verb edges (6) | 7.79 (0.05) | 2.6 (±0.43) | 2.72 (±0.42) | 2.61 (±0.38) | 2.62 (±0.33) | |
| Verbal heads per sent | 9.65 (0.02) | 2.77 (±1) | 3.07 (±1.16) | 3.14 (±1.16) | 3.14 (±0.96) | |
| Verbal root (%) | 8.6 (0.04) | 90.65 (±18.66) | 94.54 (±12.67) | 91.45 (±13.91) | 90.57 (±13.74) | |
| Tree Structure | Link length (avg) | 16.34 (<0.001) | 7.96 (±3.34) | 9.14 (±4.17) | 9.83 (±4.57) | 9.63 (±3.37) |
| Tree depth (avg max) | 10.15 (0.02) | 2.4 (±0.35) | 2.44 (±0.35) | 2.55 (±0.42) | 2.54 (±0.37) | |
| Link length (avg max) | 25.52 (<0.001) | 11.77 (±5.22) | 13.08 (±6.84) | 15.9 (±8.71) | 16.89 (±8.03) | |
| Prep. chain length (avg) | 34.42 (<0.001) | 1.74 (±1.83) | 1.62 (±1.26) | 2.64 (±2.59) | 3.35 (±2.59) | |
| Tokens per clause (avg) | 6.94 (0.07) | 0.83 (±0.48) | 0.92 (±0.49) | 0.93 (±0.44) | 0.98 (±0.42) | |
| Link length (max) | 1.15 (0.77) | 71.1 (±41.88) | 73.75 (±42.15) | 76.22 (±36.74) | 78.62 (±34.43) | |
| n. prepositional chains | 2.51 (0.47) | 5.98 (±15.68) | 9.14 (±25.85) | 6.24 (±14.26) | 7.4 (±16.26) | |
| Prepositional distr. (1) | 14.6 (0.002) | 0 (±0) | 0.15 (±1.57) | 1.29 (±5.55) | 1.49 (±4.86) | |
| Prepositional distr. (2) | 1.54 (0.67) | 6.8 (±1.55) | 6.77 (±1.46) | 7.2 (±2.12) | 6.8 (±1.26) | |
| Prepositional distr. (3) | 15.37 (0.002) | 4.05 (±1.05) | 4.46 (±1.44) | 4.55 (±1.11) | 4.49 (±1.03) | |
| Order | Object post-verbal | 5.47 (0.14) | 66.32 (±18.4) | 66.03 (±18.89) | 71.33 (±20.4) | 64.69 (±16) |
| Object pre-verbal | 5.47 (0.14) | 33.68 (±18.4) | 33.97 (±18.89) | 28.67 (±20.4) | 35.31 (±16) | |
| Subject post-verbal | 20.82 (<0.001) | 6.23 (±16.52) | 10.23 (±20.21) | 16.88 (±26.63) | 15.98 (±22.28) | |
| Subject pre-verbal | 11.34 (0.01) | 85.44 (±30.66) | 86.2 (±26.12) | 76.87 (±32.99) | 82.88 (±23.95) | |
| Syntactic Dep | Adnominal clauses | 18.33 (<0.001) | 2 (±1.93) | 1.97 (±2.25) | 2.94 (±1.93) | 2.25 (±1.88) |
| Relative clauses | 15.77 (0.001) | 0.19 (±0.63) | 0.23 (±0.7) | 0.31 (±0.71) | 0.37 (±0.64) | |
| Adverbial clauses | 0.86 (0.83) | 2.91 (±2.36) | 3.02 (±2.17) | 2.87 (±2.03) | 3.03 (±1.7) | |
| Adverbial modifiers | 16.63 (<0.001) | 3.05 (±2.14) | 3.35 (±2.53) | 3.98 (±2.11) | 4.27 (±2.19) | |
| Adjectival modifiers | 4.73 (0.19) | 0.69 (±1.19) | 0.75 (±1.1) | 0.58 (±0.9) | 0.85 (±1.1) | |
| Appositions | 3.7 (0.3) | 2.91 (±2.49) | 2.92 (±2.31) | 2.73 (±2.23) | 3.31 (±2.13) | |
| Auxiliaries | 9.5 (0.02) | 0.18 (±0.58) | 0.07 (±0.35) | 0.2 (±0.56) | 0.19 (±0.47) | |
| Auxiliary passes | 1.42 (0.7) | 11.38 (±3.53) | 11.21 (±3.37) | 11.5 (±2.75) | 10.86 (±2.75) | |
| Case markers | 4.66 (0.2) | 0.38 (±0.86) | 0.53 (±1.01) | 0.44 (±0.78) | 0.51 (±0.73) | |
| Coordinating conj. | 15.24 (0.002) | 0.05 (±0.31) | 0.03 (±0.24) | 0.1 (±0.38) | 0.14 (±0.39) | |
| Clausal complements | 17.32 (<0.001) | 5.69 (±2.84) | 4.2 (±3.13) | 4.67 (±2.7) | 4.7 (±2.29) | |
| Conjunctions | 12.16 (0.007) | 6.76 (±2.69) | 5.72 (±2.97) | 5.57 (±2.35) | 5.84 (±2.18) | |
| Copula | 19.33 (<0.001) | 0.75 (±1.28) | 0.79 (±1.25) | 1.02 (±1.2) | 1.31 (±1.23) | |
| Clausal subjects | 23.18 (<0.001) | 13.63 (±2.97) | 13.97 (±2.58) | 13.52 (±2.48) | 12.34 (±2.32) | |
| Determiners | 20.49 (<0.001) | 6.97 (±2.73) | 7.43 (±2.58) | 6.41 (±2.39) | 5.94 (±1.99) | |
| Fixed mwe | 2.12 (0.55) | 0.74 (±1.17) | 0.95 (±1.3) | 0.88 (±1.16) | 0.76 (±0.99) | |
| Flat mwe | 9.87 (0.02) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0 (±0) | 0.03 (±0.15) | |
| Indirect objects | 12.95 (0.005) | 3.99 (±2.47) | 3.97 (±2.66) | 2.88 (±2.16) | 3.24 (±1.78) | |
| Markers | 23.79 (<0.001) | 3.33 (±2.42) | 4.84 (±2.64) | 4.4 (±2.82) | 4.88 (±2.49) | |
| Nominal modifiers | 4.52 (0.21) | 3.12 (±2.54) | 3.06 (±2.07) | 3.37 (±2.3) | 3.64 (±2.23) | |
| Nominal subjects | 4.65 (0.2) | 4.3 (±2.44) | 4.52 (±2.39) | 3.88 (±2.39) | 3.9 (±1.79) | |
| Nominal subject passes | 4.06 (0.26) | 0.06 (±0.35) | 0.01 (±0.08) | 0.07 (±0.35) | 0.06 (±0.23) | |
| Numeral modifiers | 11.79 (0.008) | 2.06 (±1.67) | 1.94 (±1.36) | 1.69 (±1.25) | 1.44 (±0.89) | |
| Direct objects | 3.51 (0.32) | 5.48 (±2.63) | 5.77 (±3.05) | 6.07 (±2.52) | 5.71 (±2.05) | |
| Oblique complements | 4.83 (0.18) | 1.03 (±1.33) | 0.88 (±1.22) | 1.15 (±1.42) | 1.14 (±1.21) | |
| Parataxis | 18.52 (<0.001) | 0.56 (±1.01) | 0.52 (±0.89) | 0.61 (±0.95) | 0.98 (±1.02) | |
| Roots | 11.11 (0.01) | 1.54 (±1.67) | 2.39 (±2) | 2.28 (±2.27) | 2.09 (±1.77) | |
| Open clausal compl. | 17.55 (<0.001) | 6 (±1.67) | 5.53 (±1.73) | 5.14 (±1.51) | 5.13 (±1.24) | |
| Subord | principal prop. distr. | 16.8 (<0.001) | 48.88 (±17.55) | 44.64 (±17.79) | 42 (±17.46) | 40.8 (±12.83) |
| subord. chain len. (avg) | 17.68 (<0.001) | 1.13 (±0.31) | 1.17 (±0.32) | 1.2 (±0.4) | 1.25 (±0.22) | |
| subordinate distr. (1) | 12.31 (0.006) | 84.01 (±26.52) | 80.23 (±25.64) | 76 (±28.2) | 79.33 (±15.84) | |
| subordinate distr. (2) | 10.6 (0.01) | 12.66 (±22.5) | 15.13 (±20.88) | 16.53 (±21.99) | 16.73 (±14.01) | |
| subordinate distr. (3) | 10.32 (0.02) | 0.99 (±4.79) | 1.66 (±6.66) | 3.72 (±14.31) | 3.75 (±9.13) | |
| subordinate distr. (4) | 1.88 (0.6) | 0.26 (±2.55) | 0.3 (±2.22) | 0 (±0) | 0.2 (±1.31) | |
| subordinate post | 2.04 (0.56) | 88.53 (±25.78) | 90.53 (±23.23) | 90.12 (±23.36) | 92.33 (±13.04) | |
| subordinate pre | 4.57 (0.21) | 9.39 (±22.32) | 6.79 (±17.7) | 6.13 (±15.05) | 7.67 (±13.04) | |
| subordinate prop. distr. | 16.8 (<0.001) | 51.12 (±17.55) | 55.36 (±17.79) | 58 (±17.46) | 59.2 (±12.83) | |
References
- Smith, H.M.J.; Ryder, H.; Flowe, H.D. Eyewitness evidence. In Forensic Psychology: Crime, Justice, Law, Interventions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Baddeley, A. Qué es la memoria. In Memória, 2nd ed.; Alianza Editorial: Madrid, Spain, 2018; pp. 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoni, G. Psicología del Testimonio; Trotta: Roma, Italy, 2019; pp. 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ayala, R. Witness testimonial credibility in criminal proceedings. Rev. Bras. Direito Process. Penal 2020, 6, 453–480. [Google Scholar]
- Manzanero, A. Memoria de Testigos: Obtención y Valoración de la Prueba Testifical; Pirámide: Madrid, Spain, 2010; pp. 23–62. [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Spark, J.H.; Bartimus, J.; Wilcock, R. Mental time travel ability and the Mental Reinstatement of Context for crime witnesses. Conscious. Cogn. 2017, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glomb, K. How to improve eyewitness testimony research: Theoretical and methodological concerns about experiments on the impact of emotions on memory performance. Psychol. Res. 2022, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, C.; Otgaar, H.; Sauerland, M.; Quaedflieg, C.; Hope, L. The effects of stress on eyewitness memory: A survey of memory experts and laypeople. Mem. Cogn. 2021, 49, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowe, H.D.; Colloff, M.F.; Kloft, L.; Jores, T.; Stevens, L.M. Impact of alcohol and other drugs on eyewitness memory. In The Routledge International Handbook of Legal and Investigative Psychology; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2019; pp. 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, G.; Loftus, E.; Grady, R.; Levine, L.; Greene, C. False memories for fake news during Ireland’s abortion referendum. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 30, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanero, A.L. Memoria de testigos. In La Memoria Humana: Aportaciones Desde la Neurociencia Cognitiva; Ediciones Pirámide: Madrid, Spain, 2015; pp. 310–336. [Google Scholar]
- Mugno, A.P.; Malloy, L.C.; La Rooy, D. Interviewing Witnesses. In Forensic Psychology: Crime, Justice, Law, Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 201–223. [Google Scholar]
- Tulving, E.; Thomson, D.M. Encoding specificity and retrieval processes in episodic memory. Psychol. Rev. 1973, 80, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, R.; Bull, R. Back to basics: A componential analysis of the original cognitive interview mnemonics with three age groups. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2002, 16, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.; Meissner, C. The Cognitive Interview: A Meta-Analytic Review and Study Space Analysis of the Past 25 Years. Psychol. Public Policy Law 2010, 16, 340–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, M. The perceived effect of a witness security program on willingness to testify. Int. Crim. Justice Rev. 2018, 28, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxon, P.; Valentine, T. The effects of the age of eyewitnesses on the accuracy and suggestibility of their testimony. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. Off. J. Soc. Appl. Res. Mem. Cogn. 1997, 11, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areh, I. Gender-related differences in eyewitness testimony. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2011, 50, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilar, D.R.; Jaeger, A.; Gomes, C.F.; Stein, L.M. Passwords usage and human memory limitations: A survey across age and educational background. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Loftus, E.F.; Levidow, B.; Duensing, S. Who remembers best? Individual differences in memory for events that occurred in a science museum. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 1992, 6, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, Y. What is cognitive reserve? Theory and research application of the reserve concept. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2002, 8, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrosky-Solís, F.; Esther Gómez-Pérez, M.; Matute, E.; Rosselli, M.; Ardila, A.; Pineda, D. Neuropsi attention and memory: A neuropsychological test battery in Spanish with norms by age and educational level. Appl. Neuropsychol. 2007, 14, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, A.; Wright, H.; Fay, S.; Vanneste, S.; Angel, L.; Bouazzaoui, B.; Taconnat, L. The protective efect of educational level varies as a function of the difculty of the memory task in ageing. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2022, 19, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Bangs, K.; Smith-Spark, J. Mental Reinstatement of Context: Do individual differences in mental time travel and eyewitness occupation influence eyewitness performance over different delay intervals? J. Investig. Psychol. Offender Profiling 2019, 17, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, P.; Nielsen, N.P.; Berntsen, D. Effects of mental context reinstatement on accuracy and recollective experience. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2023, 37, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steller, M.; Köhnken, G. Criteria-Based Content Analysis. In Psychological Methods in Criminal Investigation and Evidence; Raskin, D.C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 217–245. [Google Scholar]
- Volbert, R.; Steller, M. Is this testimony truthful, fabricated, or based on false memory? Credibility assessment 25 years after S teller and Köhnken (1989). Eur. Psychol. 2014, 19, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juola, P. Detecting stylistic deception. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Computational Approaches to Deception Detection, Avignon, France, 23–27 April 2012; pp. 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Galasinski, D. The Language of Deception: A Discourse Analytical Study; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jakupov, A.; Longhi, J.; Zeddini, B. The Language of Deception: Applying Findings on Opinion Spam to Legal and Forensic Discourses. Languages 2023, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.L.; Pennebaker, J.W.; Berry, D.S.; Richards, J.M. Lying words: Predicting deception from linguistic styles. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2003, 29, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, M.; Cardie, C.; Hancock, J.T. Negative deceptive opinion spam. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–14 June 2013; pp. 497–501. [Google Scholar]
- Potthast, M.; Kiesel, J.; Reinartz, K.; Bevendorff, J.; Stein, B. A Stylometric Inquiry into Hyperpartisan and Fake News. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; Gurevych, I., Miyao, Y., Eds.; 2018; pp. 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Zee, S.; Poppe, R.; Havrileck, A.; Baillon, A. A personal model of trumpery: Linguistic deception detection in a real-world high-stakes setting. Psychol. Sci. 2022, 33, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornaciari, T.; Poesio, M. Automatic deception detection in Italian court cases. Artif. Intell. Law 2013, 21, 303–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennebaker, J.W.; Francis, M.E.; Booth, R.J. Linguistic inquiry and word count: LIWC 2001. Mahway Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc. 2001, 71, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vrij, A.; Mann, S.; Kristen, S.; Fisher, R.P. Cues to deception and ability to detect lies as a function of police interview styles. Law Hum. Behav. 2007, 31, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazra, S.; Majumder, B.P. To Tell The Truth: Language of Deception and Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers), Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; pp. 8498–8512. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, T.A. Implicit Bias and the Corresponding Effects on False Memories. Ph.D Thesis, Middle Tennessee State University, Murfreesboro, TN, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Helm, R.K.; Ceci, S.J.; Burd, K.A. Can implicit associations distinguish true and false eyewitness memory? Development and preliminary testing of the IATe. Behav. Sci. Law 2016, 34, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solà-Sales, S.; Alzetta, C.; Moret-Tatay, C.; Dell’Orletta, F. Analysing Deception in Witness Memory through Linguistic Styles in Spontaneous Language. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.R. Transcription Techniques for the Spoken Word; Rowman Altamira: Lanham, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vogler, N.; Pearl, L. Using linguistically defined specific details to detect deception across domains. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2019, 26, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Banerjee, R.; Choi, Y. Syntactic stylometry for deception detection. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 8–14 July 2012; pp. 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalcea, R.; Strapparava, C. The lie detector: Explorations in the automatic recognition of deceptive language. In Proceedings of the ACL-IJCNLP 2009 Conference Short Papers, Suntec, Singapore, 4 August 2009; pp. 309–312. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rosas, V.; Abouelenien, M.; Mihalcea, R.; Burzo, M. Deception detection using real-life trial data. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Seattle, WA, USA, 9–13 November 2015; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Quijano-Sánchez, L.; Liberatore, F.; Camacho-Collados, J.; Camacho-Collados, M. Applying automatic text-based detection of deceptive language to police reports: Extracting behavioral patterns from a multi-step classification model to understand how we lie to the police. Knowl. Based Syst. 2018, 149, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almela, Á. A Corpus-Based Study of Linguistic Deception in Spanish. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunato, D.; Cimino, A.; Dell’Orletta, F.; Venturi, G.; Montemagni, S. Profiling-UD: A Tool for Linguistic Profiling of Texts. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of The 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 7147–7153. [Google Scholar]
- Straka, M.; Hajic, J.; Straková, J. UDPipe: Trainable pipeline for processing CoNLL-U files performing tokenization, morphological analysis, pos tagging and parsing. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portoroz, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 4290–4297. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, T.; Jasbi, M.; Shieber, S. Linguistic Features for Readability Assessment. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications, Seattle, WA, USA, 10 July 2020; Burstein, J., Kochmar, E., Leacock, C., Madnani, N., Pilán, I., Yannakoudakis, H., Zesch, T., Eds.; 2020; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Halteren, H. The Detection of Inconsistency in Manually Tagged Text. In Proceedings of the COLING—2000 Workshop on Linguistically Interpreted Corpora, Centre Universitaire, Luxembourg, 6 August 2000; Abeille, A., Brants, T., Uszkoreit, H., Eds.; 2000; pp. 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, B.; Niehaus, S.; Wacholz, S.; Volbert, R. The Strategic Meaning of CBCA Criteria From the Perspective of Deceivers. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theunissen, T.; Meyer, T.; Memon, A.; Weinsheimer, C. Adult Eyewitness Memory for Single Versus Repeated Traumatic Events. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2017, 31, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oorsouw, K.; Broers, N.; Sauerland, M. Alcohol intoxication impairs eyewitness memory and increases suggestibility: Two field studies. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2019, 33, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, H.J.; Kehn, A.; Wise, R.A.; Cramer, R.J. Attorney beliefs concerning scientific evidence and expert witness credibility. Int. J. Law Psychiatry 2015, 41, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghetti, S.; Bunge, S.A. Neural changes underlying the development of episodic memory during middle childhood. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2012, 2, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiselman, R.; Fisher, R.; MacKinnon, D.; Holland, H. Enhancement of Eyewitness Memory with the Cognitive Interview. Am. J. Psychol. 1986, 99, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcock, R.A.; Bull, R.; Vrij, A. Are old witnesses always poorer witnesses? Identification accuracy, context reinstatement, own-age bias. Psychol. Crime Law 2007, 13, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, S.; Jehee, J.; Fernández, G.; Doeller, C. Reinstatement of Associative Memories in Early Visual Cortex Is Signaled by the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 7493–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, E.; Maureen, R.; Cabeza, R. Reinstatement of individual past events revealed by the similarity of distributed activation patterns during encoding and retrieval. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2015, 27, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wixted, J.T. Time to exonerate eyewitness memory. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 292, e13–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudjonsson, G.; Clare, I. The relationship between confabulation and intellectual ability, memory, interrogative suggestibility and acquiescence. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1995, 19, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCornack, S.; Morrison, K.; Paik, J.; Wisner, A.; Zhu, X. Information Manipulation Theory 2: A Propositional Theory of Deceptive Discourse Production. J. Lang. Soc. Psychol. 2014, 33, 348–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciano, T.; Curci, A. Memory for emotional events: The accuracy of central and peripheral details. Eur. J. Psychol. 2011, 7, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubi-Kelm, S.; Schmidt, A. Interrogator intonation and memory encoding performance. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Sastoque, L.; Bouazzaoui, B.; Burger, L.; Taconnat, L. Effet du niveau d’études sur les performances en mémoire épisodique chez des adultes âgés: Rôle médiateur de la métamémoire. Psychol. Française 2021, 66, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, Y. How Can Cognitive Reserve Promote Cognitive and Neurobehavioral Health? Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2021, 36, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövdén, M.; Fratiglion, L.; Glymour, M.; Lindenberger, U.; Tucker-Drob, E. Education and cognitive functioning across the life span. Psychol. Sci. Public Int. J. Am. Psychol. Soc. 2020, 21, 6–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).