Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Method for Ultra-Wide Band Based on Dual-Branch Feature Fusion Transformer
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A dual-branch feature fusion Transformer (DBFF-Transformer) NLOS identification method is proposed to overcome the limitations of existing approaches that rely solely on original CIR sequences. By making full use of Transformer to process the original CIR sequence, the global feature relationship in the data sequence is learned and the time-domain features extracted from the CIR are combined.
- Based on the channel features of the CIR sequence, the sequence feature network and the time feature network were designed. In the sequence feature network, the multi-head attention mechanism of the Transformer effectively identifies key patterns within NLOS multipath effects. In the time feature network, four time-domain features—FPER, RDS, kurtosis and phase difference—are extracted, which effectively distinguish between LOS and NLOS. The fusion of these two types of modal feature data solves the problem of insufficient accuracy and robustness in NLOS identification.
- Through a series of ablation studies and comparative experiments, the advantages of DBFF-Transformer over other models have been validated. DBFF-Transformer can effectively identify NLOS accurately in typical indoor scenarios, providing a new solution to solve the NLOS problem in UWB indoor positioning.
2. Related Work
2.1. NLOS Identification Method Based on Statistics
2.2. NLOS Identification Method Based on Machine Learning
2.3. Attention Mechanisms and Transformer
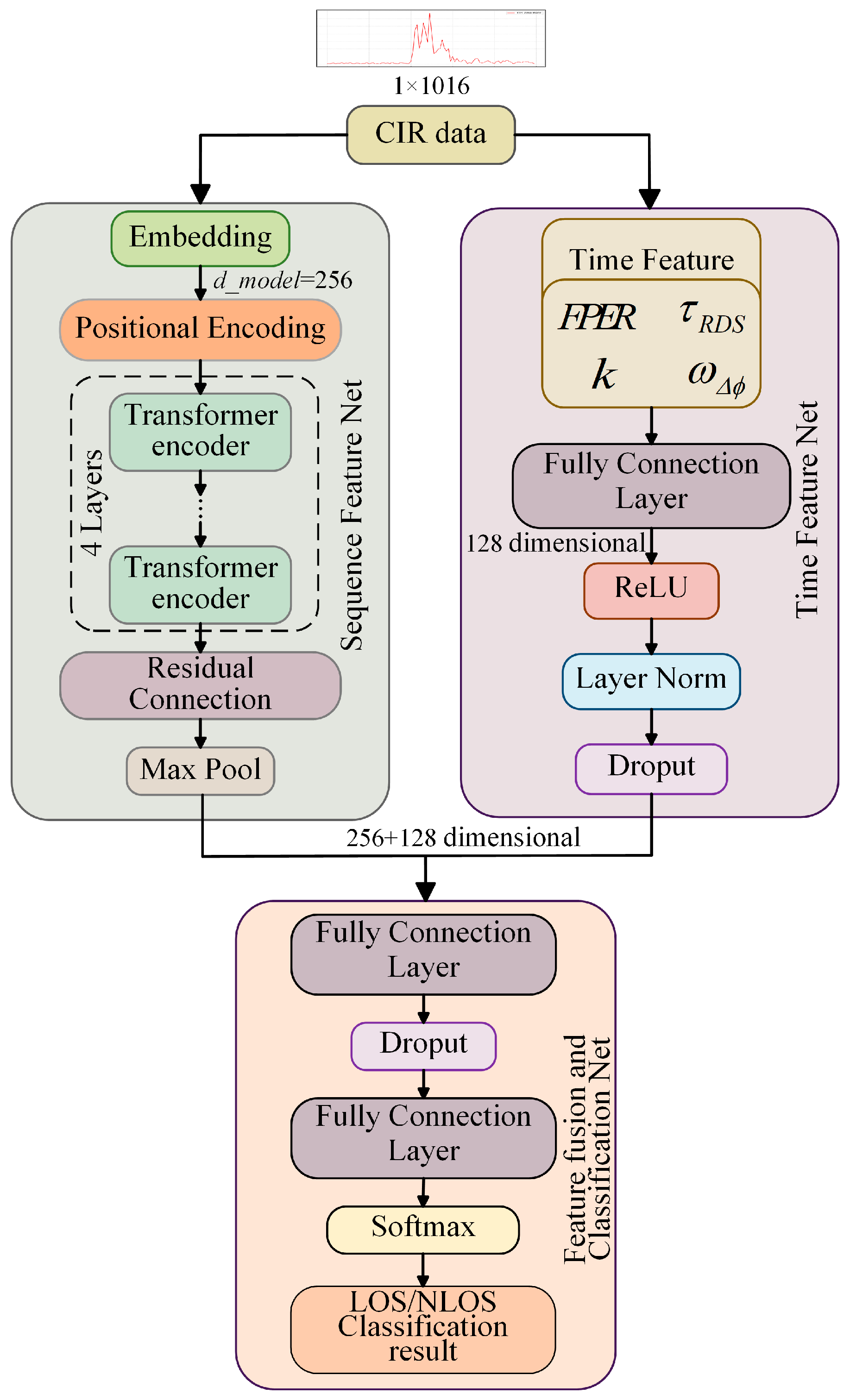
3. The DBFF-Transformer
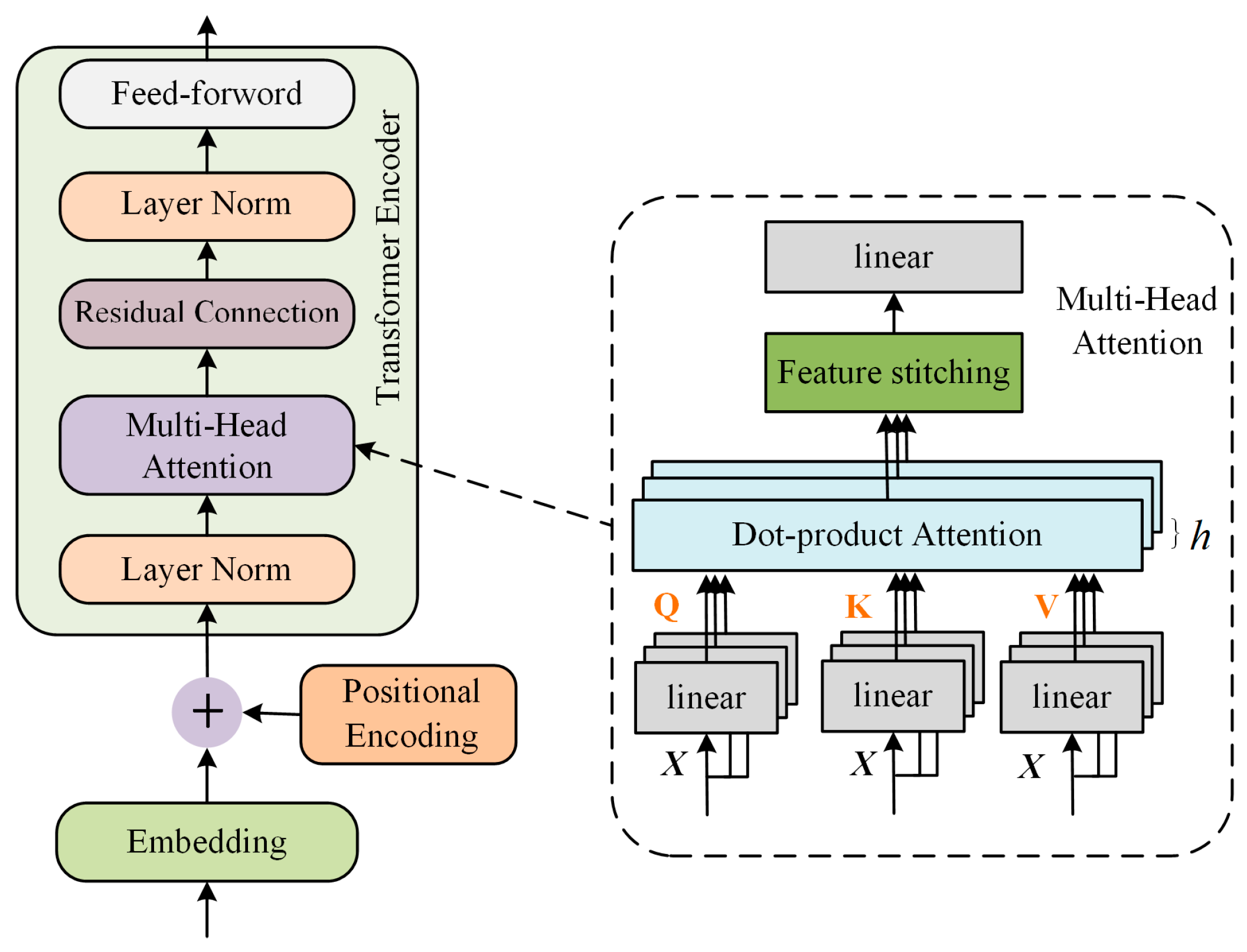
3.1. Sequence Feature Network
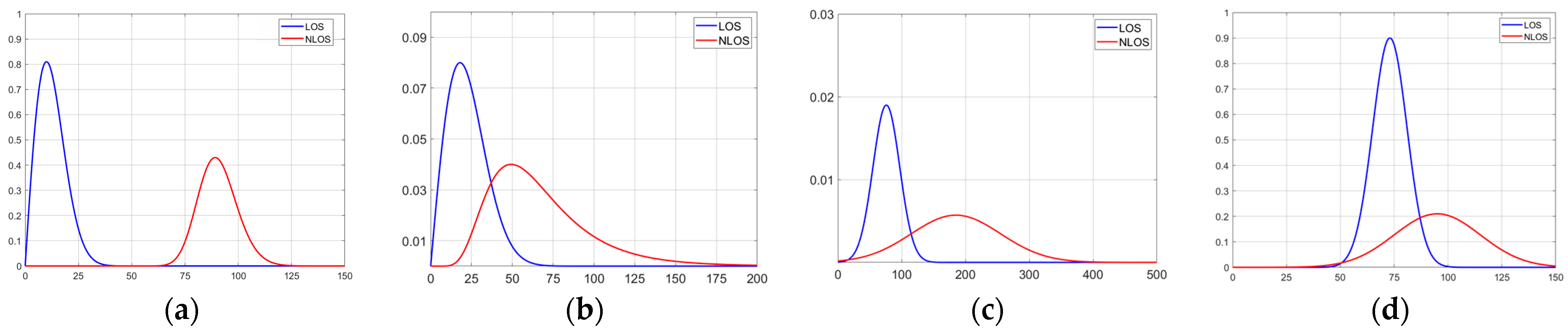
3.2. Time-Domain Feature Network
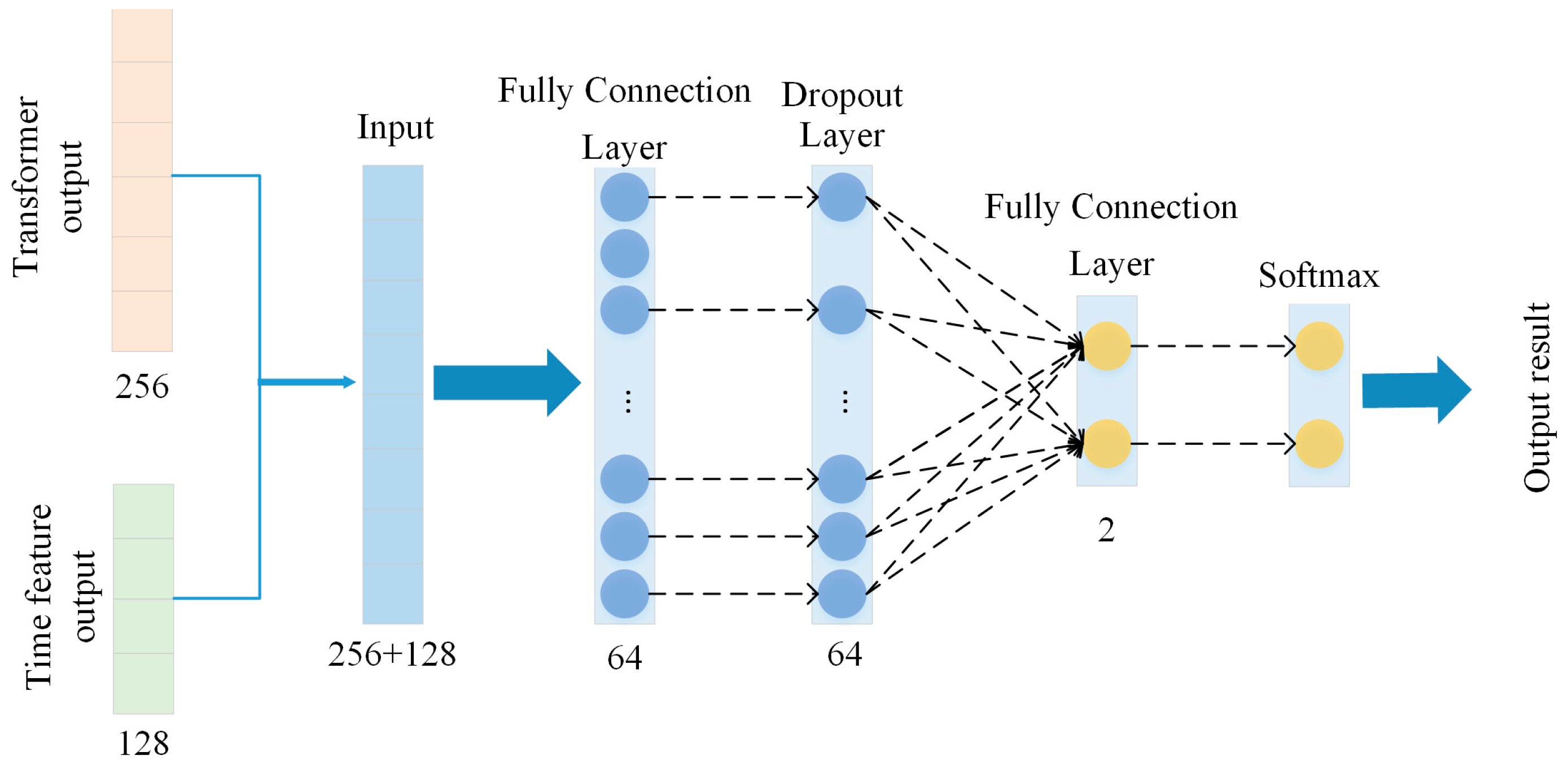
3.3. Feature Fusion and Classification Network
4. Experiment and Analysis of Results
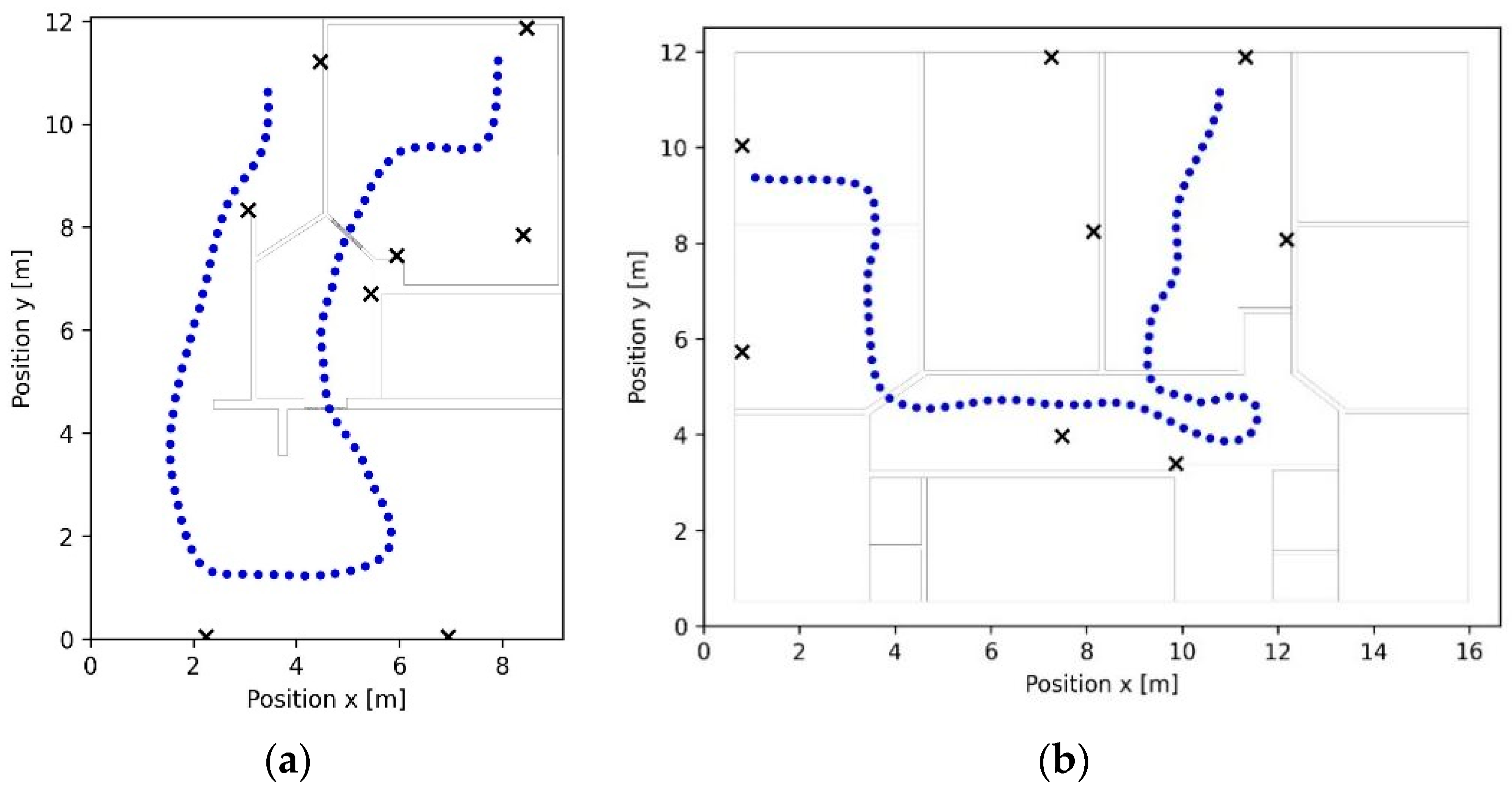
4.1. Experimental Design
4.2. Evaluation Indicators
- The true LOS CIR sample data are classified as LOS data (TP);
- The true LOS CIR sample data are classified as NLOS data (FN);
- The true NLOS CIR sample data are classified as NLOS data (TN);
- The true NLOS CIR sample data are classified as LOS data (FP).
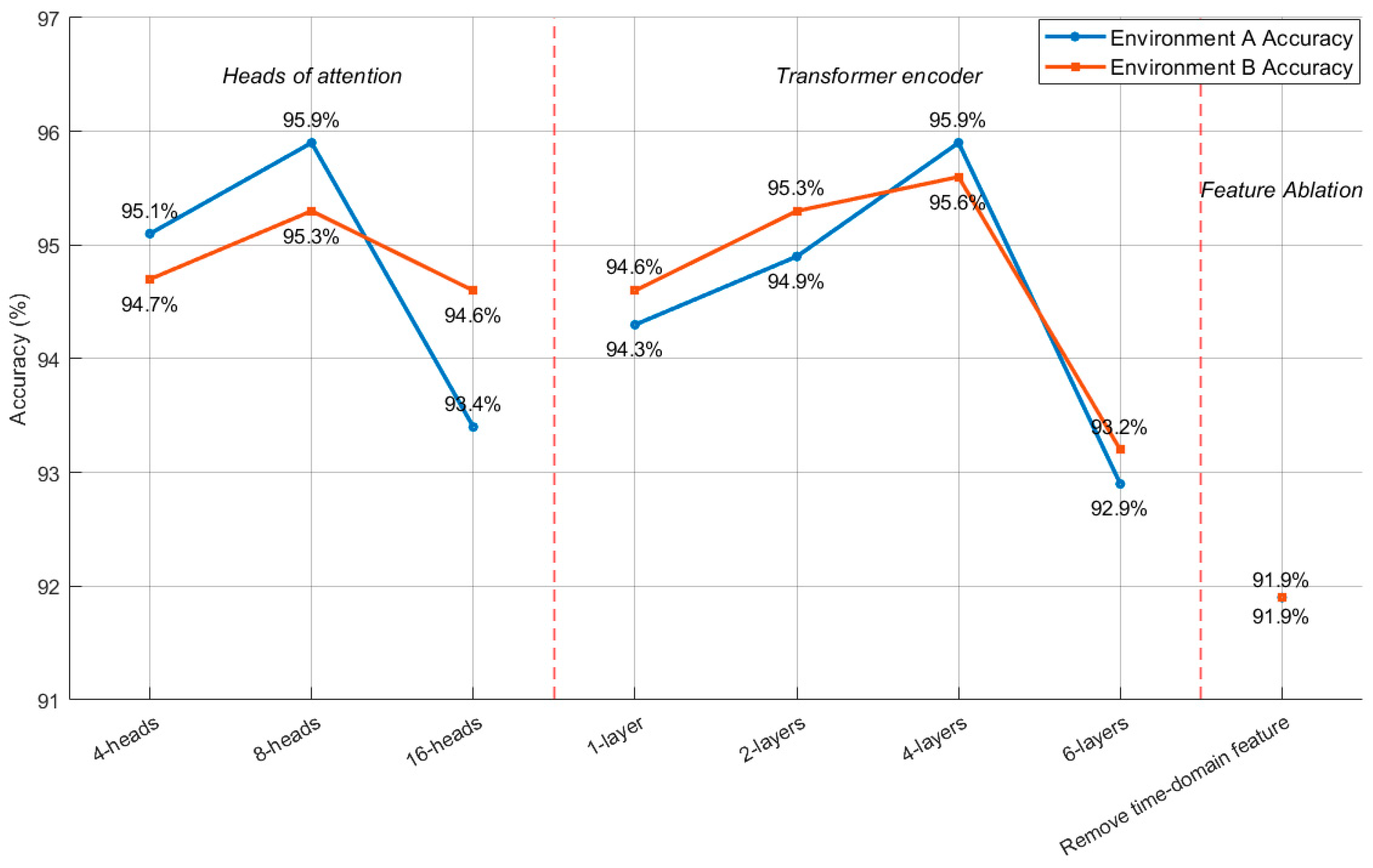
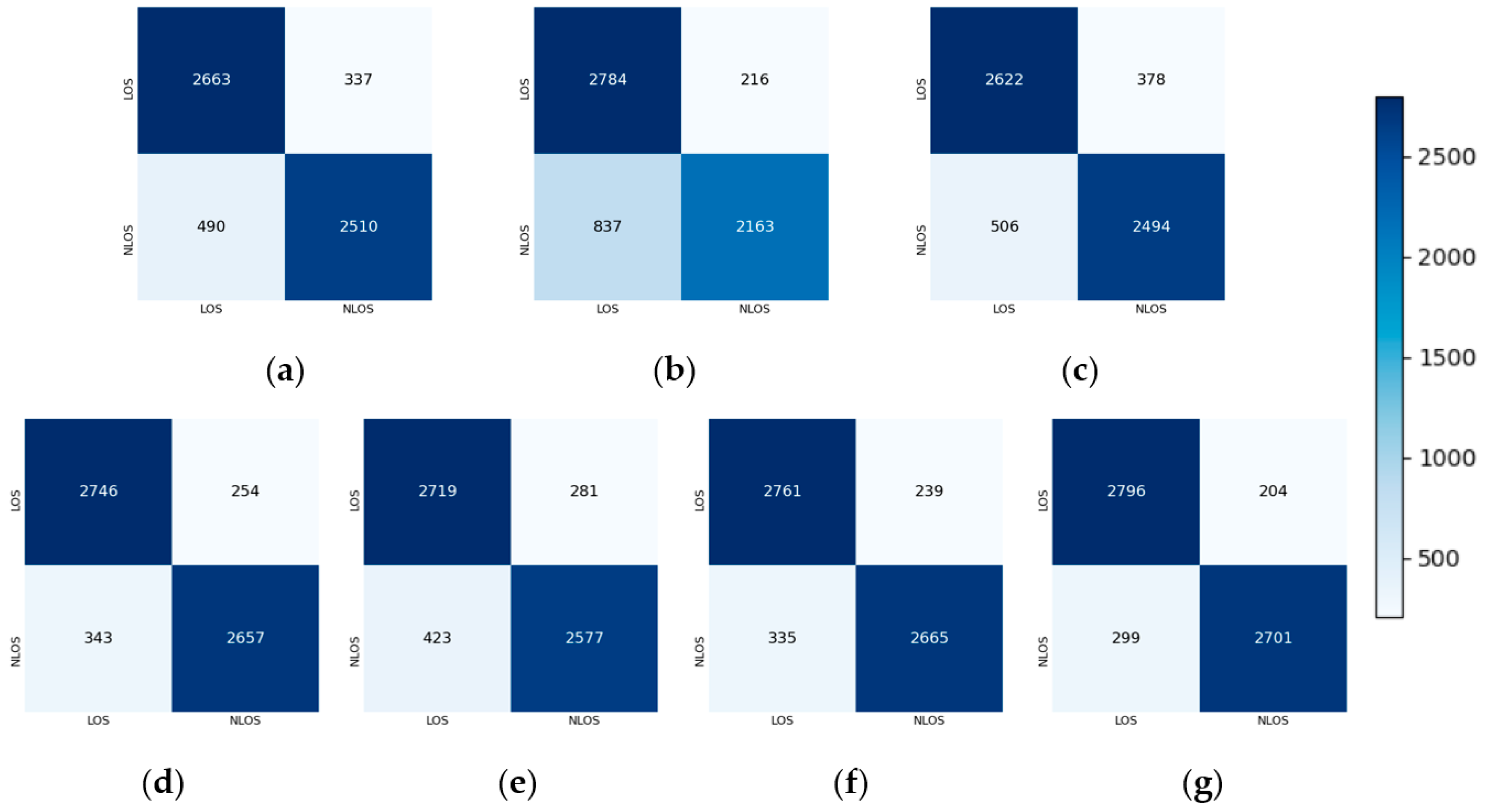
4.3. Ablation Experiment
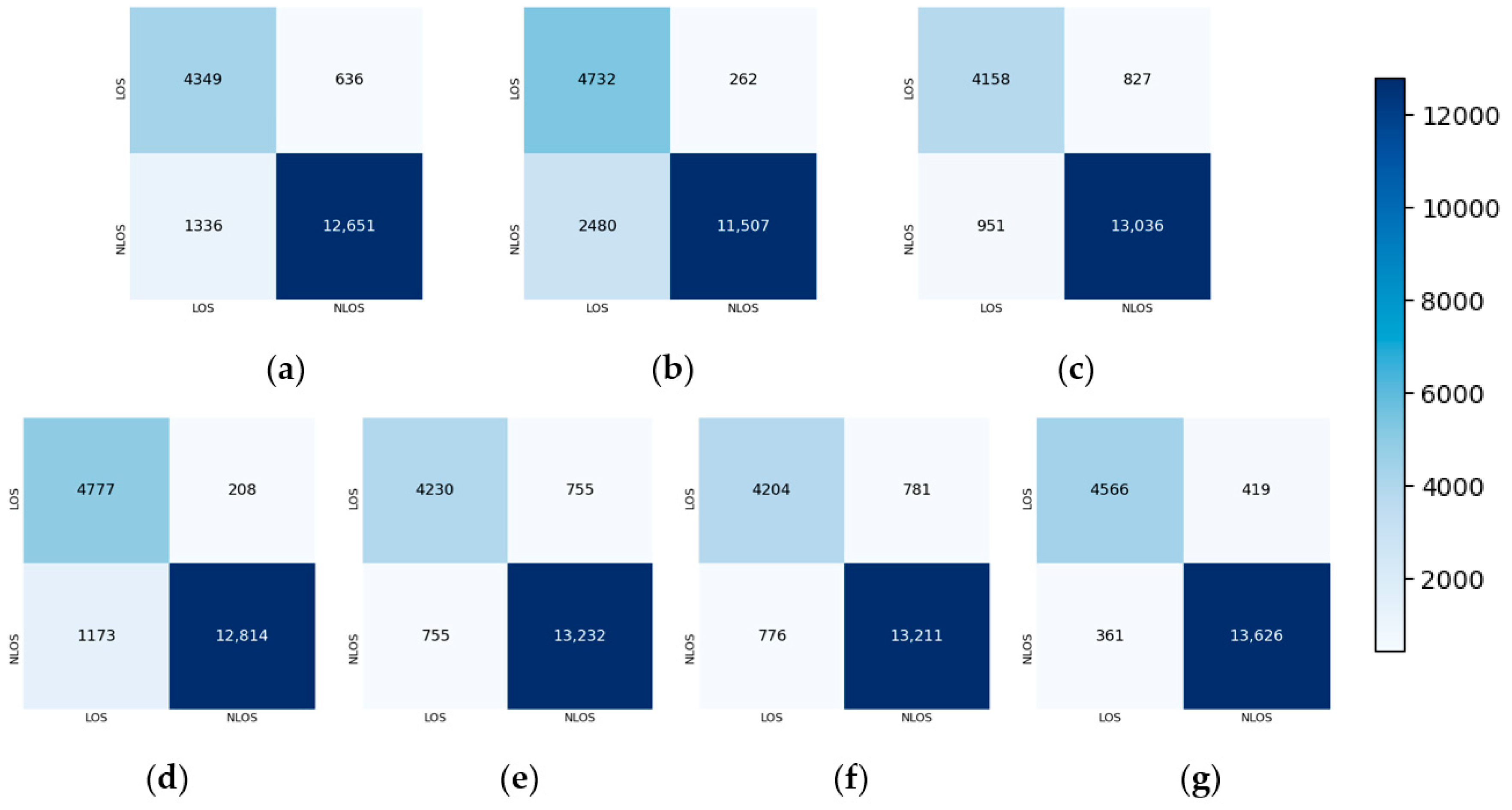
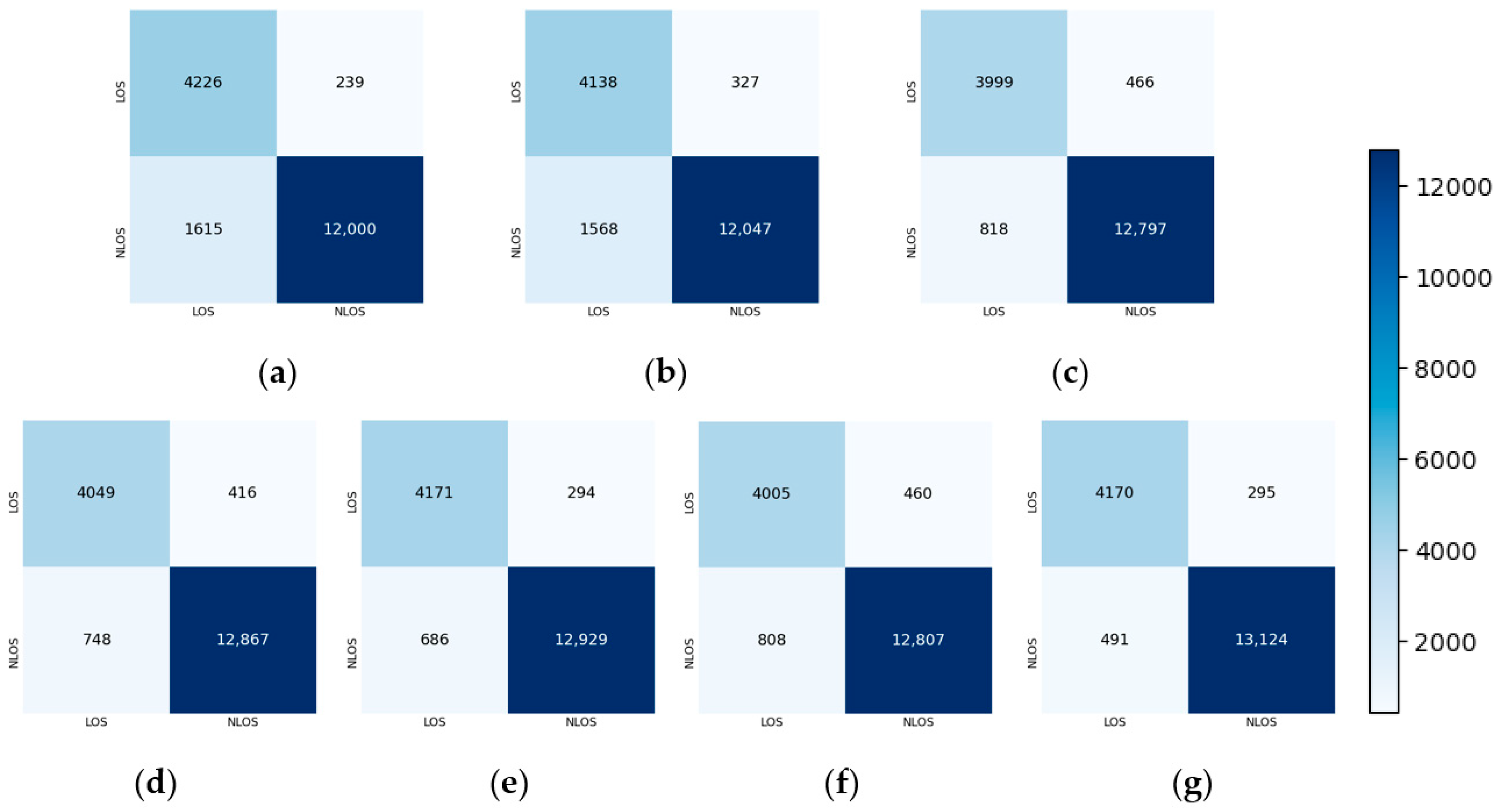
4.4. Comparison Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, F.; Ma, J. Indoor location technology with high accuracy using simple visual tags. Sensors 2023, 23, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syazwani, N.C.J.; Wahab, N.; Sunar, N.; Ariffin, S.; Wong, K.; Aun, Y. Indoor positioning system: A review. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2022, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Chen, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, H. RSSI-based location fingerprint method for RFID indoor positioning: A review. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2024, 39, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Yun, X.; Funeng, W. Improved Pedestrian Location Method for the Indoor Environment Based on MIMU and sEMG Sensors. J. Sens. 2024, 2024, 2205513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, R.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, B.; Yang, L. An improved BPNN method based on probability density for indoor location. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2023, 106, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; You, C.; Park, H. Integrated indoor positioning methods to optimize computations and prediction accuracy enhancement. Comput. Intell. 2024, 40, e12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianhua, L.; Baoshan, Z.; Songnian, L.; Zlatanova, S.; Zhijie, Y.; Mingchen, B.; Bing, Y.; Danqi, W. MLA-MFL: A Smartphone Indoor Localization Method for Fusing Multi-source Sensors under Multiple Scene Conditions. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 26320–26333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tošić, A.; Hrovatin, N.; Vičič, J. A WSN framework for privacy aware indoor location. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Bi, J.; Jia, H.; Seow, C. Ultra-wideband ranging error mitigation with novel channel impulse response feature parameters and two-step non-line-of-sight identification. Sensors 2024, 24, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Zhang, J.; Quan, Z.; Ding, Y. UWB indoor localization method based on neural network multi-classification for NLOS distance correction. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 379, 115904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraha, A.T.; Wang, B. A Survey on Scalable Wireless Indoor Localization: Techniques, Approaches and Directions. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2024, 136, 1455–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalihan, M.; Cao, Z.; Pongsirijinda, K.; Kiat Ng, B.K.; Lau, B.P.L.; Liu, R.; Yuen, C.; Tan, U.X. Localization through mitigating and compensating UWB NLOS ranging error with neural network. Digit. Signal Process. 2025, 166, 105397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Brambilla, M.; Trabattoni, A.; Mervic, S.; Nicoli, M. UWB localization in a smart factory: Augmentation methods and experimental assessment. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2508218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkrow, R.E.; Silva, B.; Boshoff, D.; Hancke, G.; Gidlund, M.; Abu-Mahfouz, A. NLOS Identification and Mitigation for Time-based Indoor Localization Systems: Survey and Future Research Directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, W.; Xiong, M.; Mai, W.; Qin, S. A robust TDOA localization method for researching upper bound on NLOS ranging error. Signal Process. 2025, 235, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathalizadeh, A.; Moghtadaiee, V.; Alishahi, M. A survey and future outlook on indoor location fingerprinting privacy preservation. Comput. Netw. 2025, 262, 111199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Gao, Y.; Hu, J.; Tian, S.; Cheng, J. LOS/NLOS identification for indoor UWB positioning based on Morlet wavelet transform and convolutional neural networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 25, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, J. Exploiting Anchor Links for NLOS Combating in UWB Localization. ACM Trans. Sen. Netw. 2024, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, M. The LOS/NLOS classification method based on deep learning for the UWB localization system in coal mines. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolsi, M.A.; Almutairi, A.F.; Kourah, M.A. LOS/NLOS channel identification for improved localization in wireless ultra-wideband networks. Telecommun. Syst. 2019, 72, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wu, Z. WDMA-UWB Indoor Positioning Through Channel Classification-Based NLOS Mitigation Approach. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 28995–29005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Shi, M.; Li, J.; Gu, X. LOS/NLOS classification using causal backtracking and ResNet in UWB sensing. Phys. Commun. 2025, 72, 102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shehada, I.M.; AlMuallim, A.F.; AlFaqeh, A.K.; Muqaibel, A.H.; Park, K.-H.; Alouini, M.-S. Accurate indoor visible light positioning using a modified pathloss model with sparse fingerprints. J. Light Technol. 2021, 39, 6487–6497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiru Buhari, M.; Bagus Susilo, T.; Khan, I.; Olaniyi Sadiq, B. Statistical LOS/NLOS Classification for UWB Channels. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.07726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K. Hyperbolic Localization Algorithm in Mixed LOS-NLOS Environments. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Power, Intelligent Computing and Systems (ICPICS), Shenyang, China, 28–30 July 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 847–850. [Google Scholar]
- Minango, J.; Paredes-Parada, W.; Zambrano, M. Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms for LOS/NLOS Classification in Ultra-Wide-Band Wireless Channel. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovation and Research, Sangolquí, Ecuador, 1–3 September 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 555–565. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Ahmad, N.S. Improved UWB-based indoor positioning system via NLOS classification and error mitigation. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2025, 63, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tang, H.; Chen, J. Survey on NLOS identification and error mitigation for UWB indoor positioning. Electronics 2023, 12, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregar, K.; Mohorčič, M. Improving Indoor Localization Using Convolutional Neural Networks on Computationally Restricted Devices. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 17429–17441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.; Kim, H.; Jung, J.-I. Accurate indoor positioning for UWB-based personal devices using deep learning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 20095–20113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, K.; Yan, X.; Zhang, C. 1D-CLANet: A Novel Network for NLoS Classification in UWB Indoor Positioning System. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, H.; Su, S.; Tang, Y.; Guo, X.; Sun, X. NLOS identification using parallel deep learning model and time-frequency information in UWB-based positioning system. Measurement 2022, 195, 111191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, Y.; Chen, R.; Li, D.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, X. FCN-Attention: A deep learning UWB NLOS/LOS classification algorithm using fully convolution neural network with self-attention mechanism. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 27, 1162–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Seow, C.K.; Sun, M.; Joseph, W.; Plets, D. A novel credibility evaluation and mitigation for ranging measurement in UWB localization. Measurement 2025, 256, 117721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y. A transformer-based signal denoising network for AoA estimation in NLoS environments. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 2336–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lian, Z.; Núñez-Andrés, M.A.; Yue, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, P.; Wang, M. The application of gated recurrent unit algorithm with fused attention mechanism in UWB indoor localization. Measurement 2024, 234, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregar, K. Indoor UWB positioning and position tracking data set. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lian, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Yue, Z.; Chai, H. Application of a long short-term memory neural network algorithm fused with Kalman filter in UWB indoor positioning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Seow, C.K.; Sun, M.; Coene, S.; Huang, L.; Joseph, W.; Plets, D. Fuzzy Transformer Machine Learning for UWB NLOS Identification and Ranging Mitigation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 8503817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Transformer | 256 | |
| FFN dimension | 512 | |
| Dropout | 0.1 | |
| Activation | ReLU | |
| Optimization | Optimizer | AdamW |
| Learning rate | 1 × 10−3 | |
| Initial cycle length | 10 | |
| Cycle doubling factor | 2 | |
| Weight decay | 0.01 | |
| Dropout | 0.1 | |
| Batch size | 31 | |
| Epoch | 200 |
| Structure Configuration | Number of Layers or Heads | Accuracy: Environment A | Accuracy: Environment B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heads of attention | 4 | 95.1% | 94.7% |
| 8 | 95.9% | 95.3% | |
| 16 | 93.4% | 94.6% | |
| Transformer encoder | 1 | 94.3% | 94.6% |
| 2 | 94.9% | 95.2% | |
| 4 | 95.9% | 95.6% | |
| 6 | 92.9% | 93.2% | |
| Remove feature fusion | 8 + 4 | 91.9% | 91.9% |
| Algorithm | ACC | F1 Score | Recall | AUC-ROC | T-Test (ACC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 89.6% ± 0.14% | 92.8% ± 0.18% | 90.5% ± 0.20% | 95.1% ± 0.11% | −41.9 |
| LSTM | 85.6% ± 0.22% | 89.4% ± 0.24% | 82.3% ± 0.19% | 95.0% ± 0.15% | −67.9 |
| CNN-LSTM | 90.6% ± 0.17% | 93.6% ± 0.21% | 93.2% ± 0.23% | 96.2% ± 0.19% | −30.2 |
| GRU | 92.7% ± 0.20% | 94.9% ± 0.16% | 91.6% ± 0.18% | 97.7% ± 0.16% | −19.2 |
| FCN-Attention | 92.0% ± 0.19% | 94.6% ± 0.13% | 94.6% ± 0.12% | 97.3% ± 0.13% | −22.8 |
| BERT | 91.8% ± 0.12% | 94.4% ± 0.15% | 94.5% ± 0.22% | 97.5% ± 0.10% | −29.6 |
| DBFF-Transformer | 95.9% ± 0.12% | 97.2% ± 0.16% | 97.4% ± 0.15% | 99.1% ± 0.07% |
| Algorithm | ACC | F1 Score | Recall | AUC-ROC | T-Test (ACC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 89.7% ± 0.14% | 92.8% ± 0.17% | 88.2% ± 0.23% | 97.5% ± 0.14% | −82.3 |
| LSTM | 89.5% ± 0.16% | 92.7% ± 0.21% | 88.5% ± 0.19% | 97.0% ± 0.16% | −61.5 |
| CNN-LSTM | 92.9% ± 0.20% | 95.2% ± 0.19% | 94.0% ± 0.21% | 97.7% ± 0.17% | −21.9 |
| GRU | 93.6% ± 0.16% | 95.7% ± 0.15% | 94.1% ± 0.19% | 98.2% ± 0.14% | −22.2 |
| FCN-Attention | 94.6% ± 0.17% | 96.3% ± 0.16% | 95.0% ± 0.14% | 98.7% ± 0.11% | −12.6 |
| BERT | 93.0% ± 0.12% | 95.3% ± 0.14% | 94.1% ± 0.13% | 98.1% ± 0.09% | −33.1 |
| DBFF-Transformer | 95.7% ± 0.13% | 97.1% ± 0.10% | 96.4% ± 0.18% | 99.0% ± 0.06% |
| Algorithm | ACC | F1 Score | Recall | AUC-ROC | T-Test (ACC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 86.2% ± 0.23% | 85.6% ± 0.20% | 88.1% ± 0.18% | 90.4% ± 0.11% | −25.33 |
| LSTM | 82.4% ± 0.17% | 80.4% ± 0.21% | 90.9% ± 0.16% | 89.3% ± 0.14% | −80.8 |
| CNN-LSTM | 85.3% ± 0.20% | 85.0% ± 0.19% | 86.8% ± 0.22% | 91.1% ± 0.17% | −68.4 |
| GRU | 90.1% ± 0.18% | 89.9% ± 0.22% | 91.2% ± 0.21% | 92.9% ± 0.15% | −20.0 |
| FCN-Attention | 88.3% ± 0.20% | 88.0% ± 0.17% | 90.2% ± 0.19% | 92.3% ± 0.15% | −30.9 |
| BERT | 90.4% ± 0.13% | 90.3% ± 0.15% | 91.7% ± 0.16% | 93.6% ± 0.11% | −15.2 |
| DBFF-Transformer | 91.6% ± 0.15% | 91.5% ± 0.18% | 92.9% ± 0.14% | 94.5% ± 0.12% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, G.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Zou, D. Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Method for Ultra-Wide Band Based on Dual-Branch Feature Fusion Transformer. Information 2025, 16, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121033
Xi G, Hu S, Wang J, Zou D. Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Method for Ultra-Wide Band Based on Dual-Branch Feature Fusion Transformer. Information. 2025; 16(12):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121033
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Guangyong, Shuaiyang Hu, Jing Wang, and Dongyao Zou. 2025. "Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Method for Ultra-Wide Band Based on Dual-Branch Feature Fusion Transformer" Information 16, no. 12: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121033
APA StyleXi, G., Hu, S., Wang, J., & Zou, D. (2025). Non-Line-of-Sight Identification Method for Ultra-Wide Band Based on Dual-Branch Feature Fusion Transformer. Information, 16(12), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16121033







