Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Based on Attention-Driven Feature Refinement and Spatial Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
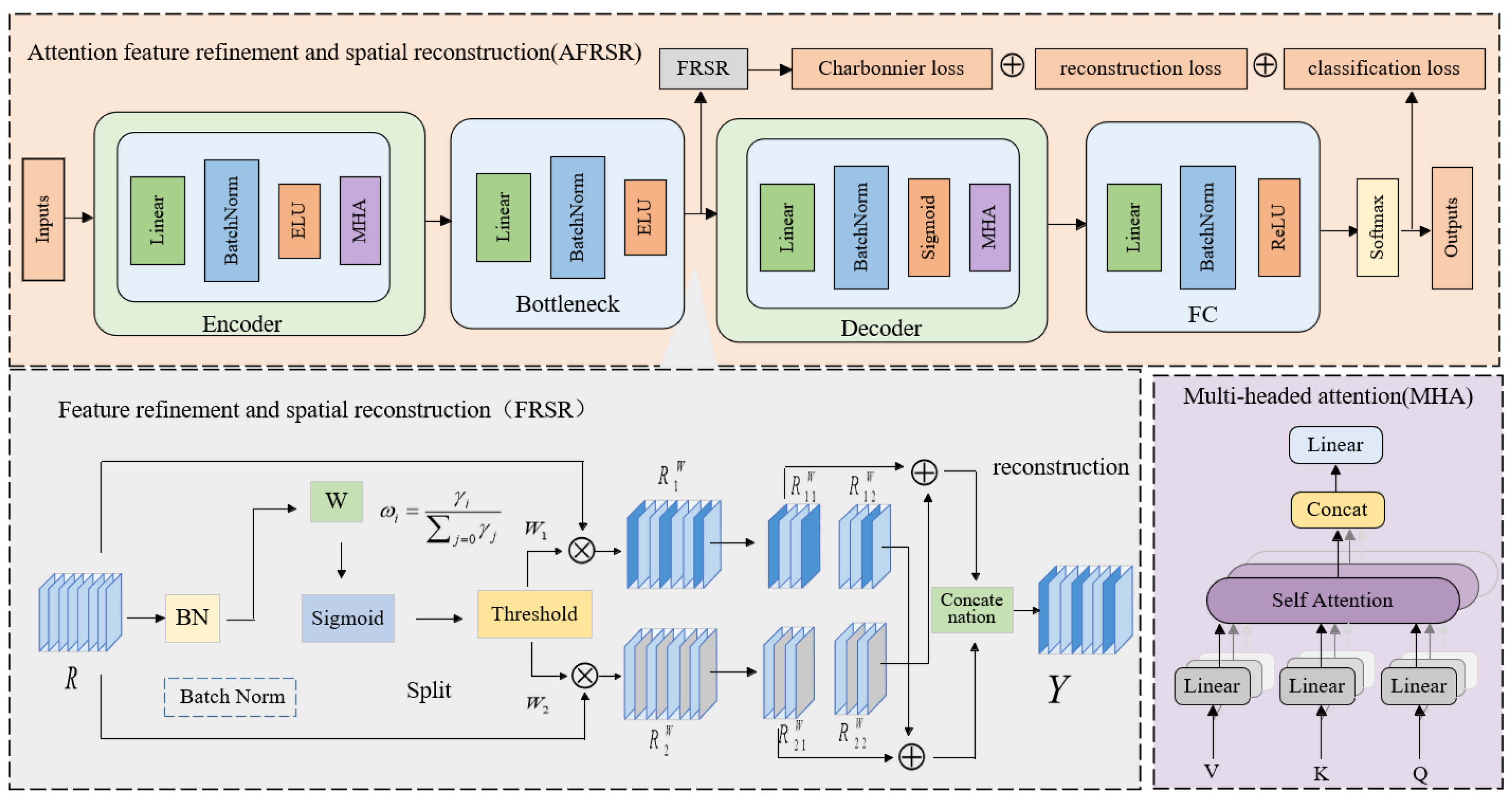
2.1. Framework of Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Model Based on Attention-Driven Feature Refinement and Spatial Reconstruction
2.2. Feature Processing and Normalization
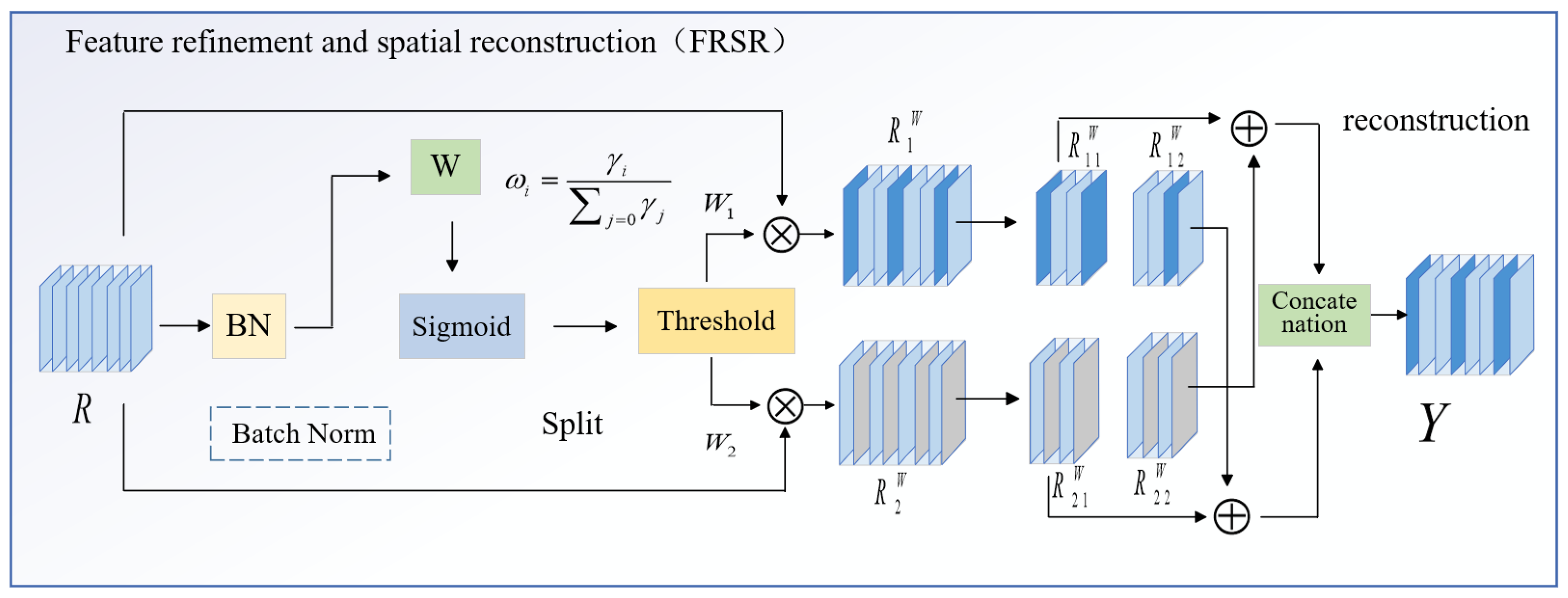
2.3. Attention-Driven Feature Refinement and Spatial Reconstruction
2.4. Loss and Joint Optimization
3. Experiment
3.1. Speech Emotion Corpus
3.2. Experimental Setup and Selection of Evaluation Metrics
4. Results Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Feature Sets
4.2. Comparative Experiments
4.3. Ablation Experiments
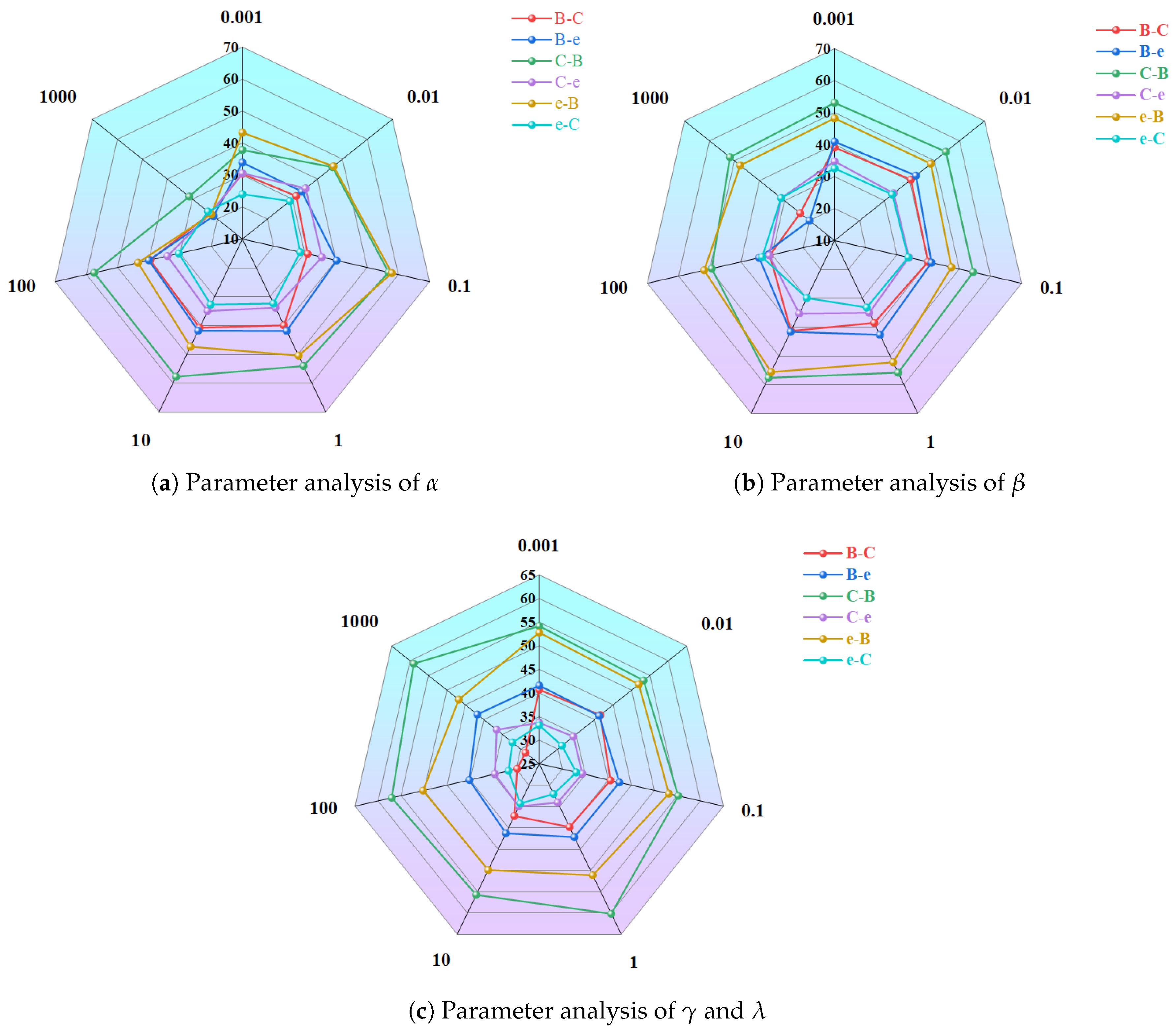
4.4. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
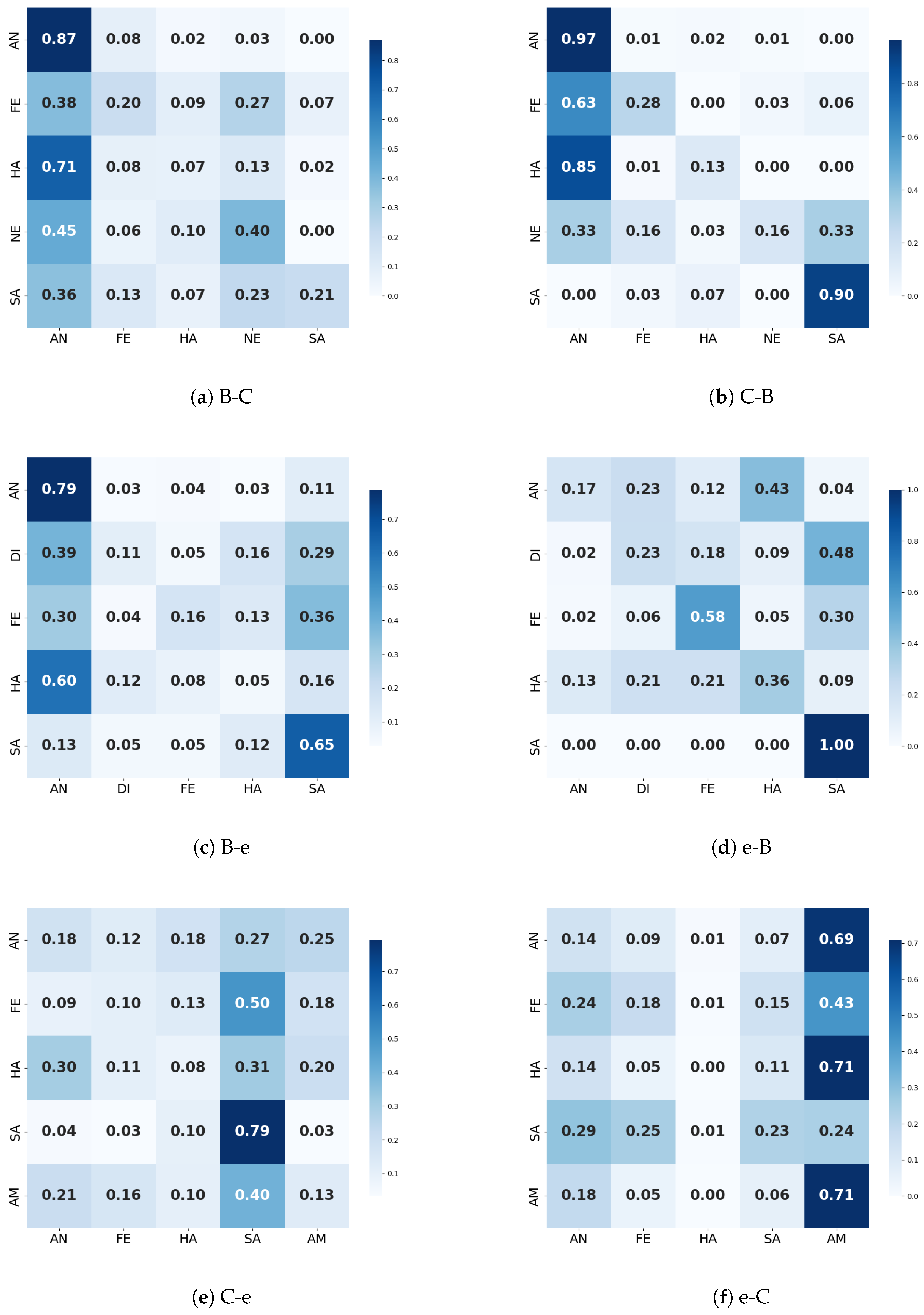
4.5. Confusion Matrix
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Liu, R.; Tao, X.; Zhao, X. Deep Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Front. Neurorobot. 2021, 15, 784514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Saheer, L.B.; Faust, O. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Attention Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, S.; Rana, R.; Khalifa, S.; Jurdak, R.; Schuller, B. Self-Supervised Adversarial Domain Adaptation for Cross-Corpus and Cross-Language Speech Emotion Recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.08625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, M.; Fu, H.L.; Zhu, C.H.; Xie, Y. A Semi-Supervised High-Quality Pseudo Labels Algorithm Based on Multi-Constraint Optimization for Speech Deception Detection. Comput. Speech Lang. 2024, 85, 101586. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Jia, M.; Ru, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Using Subspace Learning and Domain Adaptation. J. Audio Speech Music Process. 2022, 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, K.; Xia, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H. Single- and Cross-Lingual Speech Emotion Recognition Based on WavLM Domain Emotion Embedding. Electronics 2024, 13, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, M.A.; Ribas, D.; Ortega, A.; Miguel, A.; Lleida, E. Cross-Corpus Training Strategy for Speech Emotion Recognition Using Self-Supervised Representations. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeeni, N.; Nasersharif, B. Feature and Classifier-Level Domain Adaptation in DistilHuBERT for Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 194, 110510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi, N.; Nasersharif, B. Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Using Transfer Learning and Attention-Based Fusion of Wav2Vec2 and Prosody Features. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 277, 110814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Xu, X.; Tao, H.; Zhao, L.; Zou, C. Convolutional-Recurrent Neural Networks with Multiple Attention Mechanisms for Speech Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2021, 14, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Meng, J.; Fan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Q. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Dual-Stream Representation and Cross-Attention Fusion. Electronics 2024, 13, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuller, B.; Steidl, S.; Batliner, A.; Burkhardt, F.; Devillers, L.; Müller, C.; Narayanan, S.S. The Interspeech 2010 paralinguistic challenge. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2010, Makuhari, Japan, 26–30 September 2010; pp. 2794–2797. [Google Scholar]
- Eyben, F.; Wollmer, M.; Schuller, B. Opensmile: The munich versatile and fast open-source audio feature extractor. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Firenze, Italy, 25–29 October 2010; pp. 1459–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.; Steidl, S.; Batliner, A. The Interspeech 2009 Emotion Challenge. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH 2009, 10th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Brighton, UK, 6–10 September 2009; pp. 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuller, B.; Steidl, S.; Batliner, A.; Schiel, F.; Krajewski, J. The Interspeech 2011 Speaker State Challenge. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Florence, Italy, 27–31 August 2011; pp. 3201–3204. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.; Steidl, S.; Batliner, A.; Nöth, E.; Vinciarelli, A.; Burkhardt, F.; van Son, R.; Weninger, F.; Eyben, F.; Bocklet, T.; et al. The Interspeech 2012 Speaker Trait Challenge. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Portland, OR, USA, 9–13 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.; Steidl, S.; Batliner, A.; Vinciarelli, A.; Scherer, K.; Ringeval, F.; Chetouani, M.; Weninger, F.; Eyben, F.; Marchi, E.; et al. The Interspeech 2013 Computational Paralinguistics Challenge: Social Signal, Conflict, Emotion, Autism. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Lyon, France, 25–29 August 2013; pp. 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Eyben, F.; Scherer, K.R.; Schuller, B.W.; Sundberg, J.; André, E.; Busso, C.; Devillers, L.Y.; Epps, J.; Laukka, P.; Narayanan, S.S.; et al. The Geneva Minimalistic Acoustic Parameter Set (GeMAPS) for Voice Research and Affective Computing. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 7, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkan, O.; Tsiris, D. Deep Synthesizer Parameter Estimation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 3887–3891. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, B.; Nie, F. Supervised Feature Selection with Orthogonal Regression and Feature Weighting. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.03787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; He, L. SCConv: Spatial and Channel Reconstruction Convolution for Feature Redundancy. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 6153–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, M.; Li, L.; Wang, M. The Detection of Maize Leaf Disease Based on an Improved Real-Time Detection Transformer Model. Symmetry 2025, 17, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, F.; Paeschke, A.; Rolfes, M.; Sendlmeier, W.; Weiss, B. A Database of German Emotional Speech. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2005-Eurospeech, 9th European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology, Lisbon, Portugal, 4–8 September 2005; Volume 5, pp. 1517–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, O.; Kotsia, I.; Macq, B.; Pitas, I. The eNTERFACE’05 Audiovisual Emotion Database. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW’06), Washington, DC, USA, 3–7 April 2006; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Jia, H. Design of Speech Corpus for Mandarin Text-to-Speech. In Proceedings of the Blizzard Challenge 2008 Workshop, Brisbane, Australia, 21 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Song, P. Transfer Sparse Discriminant Subspace Learning for Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 28, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Zong, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, L. Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Using Joint Distribution Adaptive Regression. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 3790–3794. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.H.; Fu, H.L.; Tao, H.W. Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Based on Deep Autoencoder Subdomain Adaptation. J. Comput. Appl. Res. (J. Comput. Appl.) 2021, 38, 3279–3282+3348. [Google Scholar]
- Ganin, Y.; Ustinova, E.; Ajakan, H.; Germain, P.; Larochelle, H.; Laviolette, F.; Marchand, M.; Lempitsky, V. Domain-Adversarial Training of Neural Networks. In Advances in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 189–209. [Google Scholar]

| No | Speech Features | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Loudness | 42 |
| 2 | MFCC | 630 |
| 3 | Log Mel bands | 336 |
| 4 | LSP frequencies | 336 |
| 5 | F0 envelope | 42 |
| 6 | Voiced frequency distribution | 42 |
| 7 | F0 fundamental frequency | 38 |
| 8 | Local jitter | 38 |
| 9 | Consecutive jitter frame pairs | 38 |
| 10 | Local shimmer | 38 |
| 11 | F0 onset time | 1 |
| 12 | Duration | 1 |
| Year | Feature Set Name | Global Feature Dimensionality | Temporal Feature Dimensionality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | INTERSPEECH 2009 Emotion Challenge Feature Set | 384 | 32 |
| 2010 | INTERSPEECH 2010 Paralinguistic Challenge Feature Set | 1582 | 76 |
| 2011 | INTERSPEECH 2011 Speaker State Challenge Feature Set | 4368 | 120 |
| 2012 | INTERSPEECH 2012 Speaker Trait Challenge Feature Set | 5757 | 120 |
| 2013 | Interspeech 2013 ComParE Emotion Sub-Challenge | 6373 | 130 |
| 2022 | eGeMAPS Feature Set | 88 | 25 |
| No | Speech Emotion Corpus | Language | Number of Speeches | Emotion Categories |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Berlin | German | 535 | 7 |
| 2 | eNTERFACE | English | 1287 | 6 |
| 3 | CASIA | Chinese | 1200 | 6 |
| Source Domain | Target Domain | Shared Emotion Types |
|---|---|---|
| eNTERFACE(e) | Berlin(B) | Anger, disgust, fear, joy, sadness |
| Berlin(B) | eNTERFACE(e) | |
| Berlin(B) | CASIA(C) | Anger, fear, joy, neutral, sadness |
| CASIA(C) | Berlin(B) | |
| eNTERFACE(e) | CASIA(C) | Anger, fear, joy, sadness, surprise |
| CASIA(C) | eNTERFACE(e) |
| Feature Set | B-C | B-e | C-e | C-B | e-B | e-C | UAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS09 | 37.33 | 35.78 | 29.28 | 41.01 | 55.11 | 34.28 | 38.80 |
| IS10 | 44.96 | 44.31 | 36.84 | 62.91 | 58.48 | 35.10 | 47.10 |
| IS11 | 33.51 | 38.09 | 32.39 | 24.17 | 52.17 | 32.03 | 35.39 |
| IS12 | 31.63 | 39.93 | 33.75 | 24.34 | 55.34 | 35.69 | 37.10 |
| IS13 | 41.95 | 38.98 | 34.95 | 58.00 | 55.44 | 37.97 | 44.55 |
| eGeMAPS | 42.86 | 36.34 | 36.90 | 55.24 | 48.81 | 39.93 | 43.35 |
| Algorithm | B-C | B-e | C-e | C-B | e-B | e-C | UAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 37.80 | 32.47 | 25.69 | 44.12 | 32.00 | 27.40 | 33.25 |
| TCA | 37.70 | 31.23 | 26.02 | 39.50 | 33.68 | 26.40 | 32.42 |
| TSDSL | 37.40 | 35.44 | 33.25 | 56.74 | 47.41 | 32.50 | 40.46 |
| JDAR | 38.60 | 38.14 | 28.43 | 49.58 | 48.74 | 30.30 | 38.97 |
| DANN | 42.89 | 36.53 | 29.17 | 57.64 | 52.67 | 36.60 | 42.58 |
| DASA | 41.40 | 40.11 | 32.09 | 51.47 | 52.35 | 36.10 | 42.25 |
| AFSR | 44.96 | 44.31 | 36.84 | 62.91 | 58.48 | 35.10 | 47.10 |
| Cross-Corpus Setting | Macro-Precision | Macro-Recall | Macro-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| B → C | 0.4304 | 0.4343 | 0.4266 |
| B → e | 0.3886 | 0.4028 | 0.3850 |
| C → B | 0.6004 | 0.5710 | 0.5753 |
| C → e | 0.3266 | 0.3249 | 0.3250 |
| e → B | 0.5487 | 0.5690 | 0.5519 |
| e → C | 0.3825 | 0.3754 | 0.3664 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Z. Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Based on Attention-Driven Feature Refinement and Spatial Reconstruction. Information 2025, 16, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110945
Tao H, Jiang Y, Li Q, Zhao L, Yang Z. Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Based on Attention-Driven Feature Refinement and Spatial Reconstruction. Information. 2025; 16(11):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110945
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Huawei, Yixing Jiang, Qianqian Li, Li Zhao, and Zhizhe Yang. 2025. "Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Based on Attention-Driven Feature Refinement and Spatial Reconstruction" Information 16, no. 11: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110945
APA StyleTao, H., Jiang, Y., Li, Q., Zhao, L., & Yang, Z. (2025). Cross-Corpus Speech Emotion Recognition Based on Attention-Driven Feature Refinement and Spatial Reconstruction. Information, 16(11), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110945








