Leveraging Machine Learning Techniques to Investigate Media and Information Literacy Competence in Tackling Disinformation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background, Variables and Research Model
2.1. MIL Against Disinformation
2.2. Associated Variables
2.3. Application of ML Techniques in Educational Perceptions
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design and Study Variables
3.2. Instrument
- Sociodemographic variables: Five items collect information on gender, age, academic year, academic field and prior training in MIL and disinformation.
- Theoretical dimensions of MIL in relation to disinformation: Five items for each theoretical dimension, covering knowledge, skills and attitudes toward disinformation.
- Responsibility toward disinformation: Five items assess the perception of responsibility as future edu-communicators in combating disinformation.
3.3. Participants and Data Collection
3.4. Procedure and Data Preprocessing
4. Experimentation
- Classification of the Knowledge Branch: This task evaluates whether students’ MIL profiles differ systematically between the two academic areas considered: Education and Communication. The purpose is not merely to label students but to identify discipline-specific patterns that may influence the development of MIL competencies. This helps reveal latent relationships in the dataset that are not easily observable through descriptive statistics alone.
- Selection of the Most Relevant Variables: Different feature-selection techniques were applied to determine which variables contribute most to classification performance and to interpret their educational significance in predicting MIL outcomes.
- Regression of the Key Factors: Regression models were trained to estimate the scores students would achieve in each MIL dimension (Knowledge, Skills, Attitudes and Responsibility). This allows the identification of which sociodemographic and academic factors most strongly predict each competence and the extent of their influence.
4.1. Classification of the Knowledge Branch
- Support Vector Machine (SVM): Different configurations were explored by varying the regularization parameter C among {0.1, 1, 10, 100}, the kernel function among {radial basis function (RBF), linear, polynomial} and the parameter , which controls the influence of training samples in defining the decision boundary. Instead of manually selecting , two widely used and theoretically justified heuristics were employed:
- –
- , where is the number of input features and is their variance.
- –
- , which only depends on the number of features.
- Decision Tree (DT): Experiments were conducted by varying the maximum tree depth among {unrestricted, 5, 10, 20} and the minimum number of samples required to split a node among {2, 5, 10, 20}.
- Random Forest (RF): Different numbers of DTs (estimators) were considered, choosing among {10, 50, 100}. Additionally, maximum tree depths {unrestricted, 5, 10, 20} and minimum sample sizes for node splitting {2, 5, 10, 20} were explored.
- Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM): The model was evaluated with different numbers of boosting iterations (estimators) among {50, 100, 200}, maximum depths among {unrestricted, 5, 10} and learning rates among {0.01, 0.1, 0.2}.
- k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN): The number of nearest neighbors was varied among {3, 5, 7, 9}, using two different weighting schemes: uniform (equal weight to all neighbors) and distance-based (closer neighbors have greater influence). Additionally, two distance metrics were considered: Euclidean and Manhattan.
4.2. Selection of the Most Relevant Features for Predicting the Knowledge Branch
- SelectKBest (SKB): This method employs the ANOVA (f_classif) scoring function to evaluate feature importance, selecting the top k features based on their scores. In this case, the selected features were obtained using the dataset transformed by this method.
- Forward Feature Selector (FFS): Using an RF model with specific hyperparameters obtained from the best model configuration for the training data, this method selects features sequentially in a forward manner and optimizes the selection based on the accuracy metric using stratified five-fold cross-validation.
- Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE): Also based on the previously configured RF model, this method recursively eliminates features until the desired number of selected features is reached.
- Feature Importance Based on DT: Using a DT classifier, the importance of each feature was calculated, selecting the most relevant n features according to the generated importance scores (corresponding to the first splits in the tree branches).
4.3. Regression of the Measured Competencies
- Linear Regression (LR): This model captures the linear relationship between predictors and the target variable, estimating how each input feature proportionally influences the predicted competency score. The model was evaluated by considering whether to include an intercept term in the equation. The inclusion of an intercept allows the model to better fit datasets where the dependent variable does not naturally pass through the origin.
- Ridge Regression (RR): RR measures the same linear relationships as LR but adds a regularization term that penalizes large coefficients. Different values for the regularization strength parameter were explored, selecting from {0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10.0}, where higher values impose stronger penalties on large coefficients to prevent overfitting. Additionally, different optimization solvers were tested:
- –
- Singular Value Decomposition (SVD): A matrix factorization method that decomposes the design matrix into singular vectors and singular values.
- –
- Least Squares (LSQR): An iterative method based on the conjugate gradient approach, solving the normal equations for least squares problems.
- –
- SAGA: A stochastic gradient-based method that updates coefficients in small batches, making it efficient for high-dimensional and sparse datasets.
- DT Regressor: This model identifies non-linear, hierarchical relationships by recursively partitioning the feature space, creating threshold-based rules that predict competency scores. The tree-based model was evaluated using different maximum depths among {unrestricted, 5, 10, 20}, where deeper trees can capture more complex patterns but may lead to overfitting. The minimum number of samples required to split a node was varied among {2, 5, 10, 20} to regulate tree complexity. Furthermore, two different criteria for measuring the quality of a split were considered:
- –
- Squared Error: Minimizes the variance within each node, leading to mean-squared-error minimization.
- –
- Absolute Error: Focuses on minimizing the mean absolute deviation, which is more robust to outliers.
- RF Regressor: The RF model extends the DT approach by combining multiple trees to capture more complex patterns and reduce variance. This ensemble learning method was tested with different numbers of trees (estimators) among {10, 50, 100}, balancing computational cost and predictive performance. The features for each of the trees within the forest and the split criteria are the same as those considered for the DT Regressor.
5. Results
5.1. Preliminary Results: Validation and Reliability of the Questionnaire
- Factor 1: Knowledge about disinformation. This dimension includes five items reflecting conceptual understanding of disinformation, i.e., its definition, characteristics and differences from related terms such as fake news or hoaxes. It also encompasses awareness of the mechanisms that facilitate the spread of false content and the risks it poses to informed citizenship.
- Factor 2: Skills and behaviors against disinformation. Comprising six items, this factor captures the ability to verify information accuracy by consulting multiple and credible sources, such as established media outlets, fact-checking organizations and official online platforms. It also reflects students’ discernment in evaluating information from social networks or close contacts.
- Factor 3: Attitudes of commitment and responsibility towards disinformation. This factor, composed of nine items, emphasizes ethical and civic engagement in countering disinformation. It involves recognizing the role of responsible communication in safeguarding freedom of expression and democratic participation, as well as acknowledging the professional duty, particularly among future educators and communicators, to disseminate truthful information in an ethical and reflective manner.
5.2. Classification Results for the Knowledge Branch
5.3. Feature Selection Results for Knowledge-Branch Prediction
5.4. Regression Results for Measured Competencies
6. Discussion and Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marcos-Vílchez, J.M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.; Muñiz-Velázquez, J.A. Effectiveness of training actions aimed at improving critical thinking in the face of disinformation: A systematic review protocol. Think. Skills Creat. 2024, 51, 101474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Ciudadanía Alfabetizada en Medios e Información: Pensar Críticamente, Hacer Clic Sabiamente. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000385119 (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Mateus De Oro, C.; Jabba, D.; Erazo-Coronado, A.M.; Aguaded, I.; Campis Carrillo, R. Educommunication and ICT: From a corpus to a model of educational intervention for critical attitude. Technol. Pedagog. Educ. 2024, 33, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Rodríguez, L.M.; Contreras-Pulido, P.; Pérez-Rodríguez, M.A. Media competencies of university professors and students. Comparison of levels in Spain, Portugal, Brazil and Venezuela. Cult. Educ. 2019, 31, 326–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea-Díaz, G.; Reig, R.; Mancinas-Chávez, R. UNESCO’s Media and Information Literacy curriculum for teachers from the perspective of Structural Considerations of Information. Comunicar 2020, 28, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Beijing Consensus on Artificial Intelligence and Education. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000368303 (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- OECD. Pushing the Frontiers with Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain and Robots; OECD Digital Education Outlook; OECD: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X. Practices and Theories: How Can Machine Learning Assist in Innovative Assessment Practices in Science Education. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2021, 30, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aïmeur, E.; Amri, S.; Brassard, G. Fake news, disinformation and misinformation in social media: A review. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2023, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanaullah, A.R.; Das, A.; Das, A.; Kabir, M.; Shu, K. Applications of machine learning for COVID-19 misinformation: A systematic review. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2022, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, C.; Correia, A.P. A review of research on machine learning in educational technology. Educ. Media Int. 2019, 56, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastrez, P.; Landry, N. Media Literacy and Media Education Research Methods: A Handbook; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, T. Technology criticism and data literacy: The case for an augmented understanding of media literacy. J. Media Lit. Educ. 2020, 12, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.C.; Balaban, D.C. The Effectiveness of an Educational Intervention on Countering Disinformation Moderated by Intellectual Humility. Media Commun. 2025, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Jia, W.; Yu, W. Media Literacy Interventions Improve Resilience to Misinformation: A Meta-Analytic Investigation of Overall Effect and Moderating Factors; Communication Research; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, T. Calling out ‘alternative facts’: Curriculum to develop students’ capacity to engage critically with contradictory sources. Teach. High. Educ. 2019, 24, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguaded, I.; Marin-Gutierrez, I.; Diaz-Parejo, E. Media literacy between primary and secondary students in Andalusia (Spain). Ried-Rev. Iberoam. Educ. Distancia 2015, 18, 275–298. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, R.; Moen, M.; Tang, R.; Steager, P. Measuring the implementation of media literacy statewide: A validation study. Educ. Media Int. 2022, 59, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, N.; Caneva, C. Defining media education policies: Building blocks, scope, and characteristics. In The Handbook of Media Education Research; Frau-Meigs, D., Kotilainen, S., Pathak-Shelat, M., Hoechsmann, M., Poyntz, S.R., Eds.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 289–308. [Google Scholar]
- Aguaded, I.; Delgado-Ponce, A. Educommunication. In The International Encyclopedia of Media Literacy; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna-Acedo, S.; Frau-Meigs, D.; Marta-Lazo, C. Educación mediática y formación del profesorado. Educomunicación más allá de la alfabetización digital. Rev. Interuniv. Form. Profr. 2018, 32, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Golob, T.; Makarovič, M.; Rek, M. Meta-reflexivity for resilience against disinformation. Comunicar 2021, 29, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Diz, P.; Conde-Jiménez, J.; Tapia-Frade, A.; Varona-Aramburu, D. The credibility of online news: An evaluation of the information by university students/La credibilidad de las noticias en Internet: Una evaluación de la información por estudiantes universitarios. Cult. Educ. 2019, 31, 407–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almenar, E.; Aran-Ramspott, S.; Suau, J.; Masip, P. Gender Differences in Tackling Fake News: Different Degrees of Concern, but Same Problems. Media Commun. 2021, 9, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, A.; Tahat, K.; Tahat, D.; Habes, M.; Salloum, S.; Mesbah, H.; Elareshi, M. Gender as a moderating variable in online misinformation acceptance during COVID-19. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouleimen, A.; Luceri, L.; Cardoso, F.; Botturi, L.; Hermida, M.; Addimando, L.; Beretta, C.; Galloni, M.; Giordano, S. Online search is more likely to lead youth to validate true news than to refute false ones. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennycook, G.; Rand, D.G. Who falls for fake news? The roles of bullshit receptivity, overclaiming, familiarity, and analytic thinking. J. Personal. 2020, 88, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avello-Martínez, R.; Villalba-Condori, K.O.; Arias-Chávez, D. Algunos mitos más difundidos sobre las TUC en la educación. Rev. Mendive 2021, 19, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero-Curiel, E.; González-Aldea, P. Impacto de las fake news en estudiantes de periodismo y comunicación audiovisual de la Universidad Carlos III de Madrid. Vivat Academia. Rev. Comun. 2022, 155, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherner, T.S.; Curry, K. Preparing Pre-Service Teachers to Teach Media Literacy: A Response to “Fake News”. J. Media Lit. Educ. 2019, 11, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kahne, J.; Bowyer, B. Education for democracy in a partisan age: Confronting the challenges of motivated reasoning and misinformation. Am. Educ. Res. J. 2017, 54, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, I.; Villalta, E.; Salmerón, L. Are really digital natives so good? Relationship between digital skills and digital reading. Ann. Psychol. 2015, 32, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjin-Tettey, T.D. Combating fake news, disinformation, and misinformation: Experimental evidence for media literacy education. Cogent Arts Humanit. 2022, 9, 2037229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Zou, D.; Hwang, G.J. Application and theory gaps during the rise of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2020, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbert, S.; Coors, S.; Kraus, E.; Bischl, B.; Lindl, A.; Frei, M.; Wild, J.; Krauss, S.; Goretzko, D.; Stachl, C. Machine learning for the educational sciences. Rev. Educ. 2021, 9, e3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersozlu, Z.; Taheri, S.; Koch, I. A review of machine learning methods used for educational data. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 22125–22145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.C.; Ifenthaler, D. Preparing the next generation of education researchers for big data in higher education. In Big Data and Learning Analytics in Higher Education; Daniel, B.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, H.; Vogel, B.; Jacobsson, A. Artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches in digital education: A systematic revision. Information 2022, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Tsai, C.C. A review of using machine learning approaches for precision education. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2021, 24, 250–266. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Jin, H.Y.; Cutumisu, M. The applications of machine learning in computational thinking assessments: A scoping review. Comput. Sci. Educ. 2023, 34, 193–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Vázquez, G.; Ramírez-Montoya, M.S.; Terashima, H. Gender prediction based on university students’ complex thinking competency: An analysis from machine learning approaches. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 2721–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Molina, O.; Mena, J.; López-Padrón, A. The Use of Deep Learning in Open Learning: A Systematic Review (2019 to 2023). Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2024, 25, 370–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero-Corba, W.; Negre Bennasar, F. Diseño y simulación de un modelo de predicción para la evaluación de la competencia digital docente usando técnicas de Machine Learning. Edutec. Rev. Electrón. Tecnol. Educ. 2024, 89, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, A.B.I.; Cordel, M.O.I.I.; Ricardo, J.G.E.; Galanza, M.A.M.C.; Almonte-Acosta, S. Global Citizenship Competencies of Filipino Students: Using Machine Learning to Explore the Structure of Cognitive, Affective, and Behavioral Competencies in the 2019 Southeast Asia Primary Learning Metrics. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Nadaf, A.; Zhou, Z. Machine learning evidence from PISA 2018 data to integrate global competence intervention in UAE K–12 public schools. Int. Rev. Educ. 2023, 69, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Sharma, B. Predicting Media Literacy Level of Secondary School Students in Fiji. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Computer Science and Data Engineering (CSDE), Melbourne, Australia, 9–11 December 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wusylko, C.; Weisberg, L.; Opoku, R.A.; Abramowitz, B.; Williams, J.; Xing, W.; Vu, T.; Vu, M. Using machine learning techniques to investigate learner engagement with TikTok media literacy campaigns. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2024, 56, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nadzir, M.; Abu Bakar, J. A digital literacy predictive model in the context of distance education. J. ICT Educ. 2023, 10, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. La Definición y Selección de Competencias Clave; Resumen Ejecutivo; OECD: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Catalina-García, B.; Sousa, J.P.; Silva Sousa, L.C. Consumo de noticias y percepción de fake news entre estudiantes de Comunicación de Brasil, España y Portugal. Rev. Comun. 2019, 18, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, J.; Santos, S. Percepción de las noticias falsas en universitarios de Portugal: Análisis de su consumo y actitudes. Prof. Inf. 2019, 28, e280315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín Suelves, D.; García Tort, E.; Gabarda Méndez, V. La elección de los grados de Maestro/a: Análisis de tendencias e incidencia del género y la titulación. Educ. Siglo XXI 2021, 39, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Ke, G.; Soukhavong, D.; Lamb, J.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; et al. LightGBM: Light Gradient Boosting Machine, R Package Version 4.6.0.99; CRAN: Windhoek, Namibia, 2025.
| Id | Item | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | I know what misinformation means. | 0.706 | ||
| K2 | I can identify the characteristics of | |||
| misinformation in a fake headline. | 0.757 | |||
| K3 | I differentiate the concept of misinformation | |||
| from similar terms such as “fake news”, | ||||
| “rumors” and “false news”. | 0.665 | |||
| K4 | I understand why misinformation spreads. | 0.694 | ||
| K5 | I can identify the risks of misinformation. | 0.679 | ||
| S1 | I differentiate true information from false | |||
| information based on the author or media outlet. | 0.569 | |||
| S2 | I verify the truthfulness of information with | |||
| different resources (news outlets, fact-checking | ||||
| websites, social media, etc.). | 0.472 | |||
| S3 | I use various reliable sources of information | |||
| such as reputable newspapers, official websites, | ||||
| and institutional pages to search for information | ||||
| on topics that interest me. | 0.430 | |||
| S4 | I share information with my contacts without | |||
| verifying its truthfulness. | 0.704 | |||
| S5 | I report false information when I detect it on any | |||
| channel or platform. | 0.316 | |||
| A1 | I positively value the fight against misinformation | |||
| to guarantee freedom of expression. | 0.684 | |||
| A2 | I am aware that misinformation goes against | |||
| the formation of a free and democratic citizenry. | 0.633 | |||
| A3 | I trust the information I receive through social media. | 0.628 | ||
| A4 | I believe that the media is trustworthy. | 0.786 | ||
| A5 | I give more credibility to information received from | |||
| a close contact (family, friends, etc.) than from | ||||
| other sources. | 0.595 | |||
| R1 | I am aware that misinformation can affect the | |||
| exercise of my future professional practice. | 0.724 | |||
| R2 | I perceive that the fight against misinformation | |||
| falls on professionals in my field. | 0.639 | |||
| R3 | I recognize that misinformation is a necessary topic | |||
| in my education for the practice of my profession. | 0.644 | |||
| R4 | I believe it is each person’s responsibility to fight | |||
| against misinformation. | 0.545 | |||
| R5 | I have the ethical and moral responsibility as a future | |||
| edu-communicator to transmit truthful information. | 0.602 |
| Model | Train (CV) | Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | ||||
| Algorithm | Best Parameters | F1 | F1 | Acc | Acc | F1 | Acc |
| {’C’: 1, ’gamma’: ’scale’, | |||||||
| SVM | ’kernel’: ’rbf’} | 0.734 | 0.032 | 0.782 | 0.033 | 0.815 | 0.814 |
| {’criterion’: ’gini’, | |||||||
| ’max_depth’: 5, | |||||||
| DT Classifier | ’min_samples_split’: 10} | 0.662 | 0.041 | 0.704 | 0.040 | 0.679 | 0.676 |
| {’criterion’: ’entropy’, | |||||||
| ’max_depth’: 5, | |||||||
| ’min_samples_split’: 2, | |||||||
| RF Classifier | ’n_estimators’: 10} | 0.705 | 0.061 | 0.773 | 0.037 | 0.744 | 0.745 |
| {’learning_rate’: 0.1, | |||||||
| ’max_depth’: 5, | |||||||
| LightGBM | ’n_estimators’: 50} | 0.683 | 0.058 | 0.765 | 0.043 | 0.792 | 0.793 |
| {’metric’: ’euclidean’, | |||||||
| ’n_neighbors’: 5, | |||||||
| KNN | ’weights’: ’uniform’} | 0.658 | 0.034 | 0.747 | 0.020 | 0.779 | 0.779 |
| Selector | Train (CV) | Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Best Features | Mean F1 | Std F1 | Mean Acc | Std Acc | F1 | Acc |
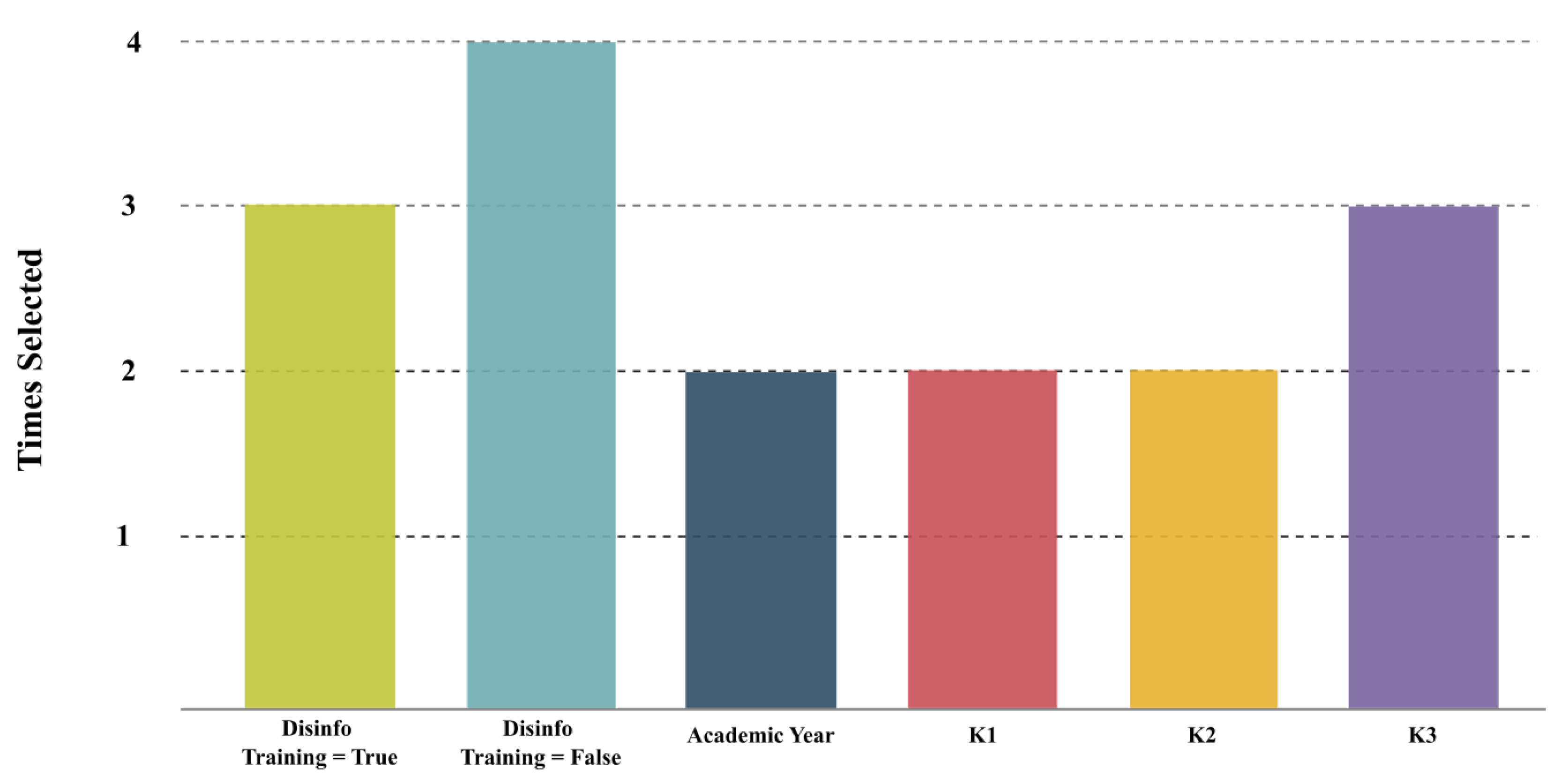
| SKB | K1, K2, K3, | ||||||
| Disinfo Training = False, | |||||||
| Disinfo Training = True | 0.682 | 0.030 | 0.763 | 0.019 | 0.751 | 0.752 | |
| FFS | K3, A3, R5, | ||||||
| Disinfo Training = False, | |||||||
| Disinfo Training = True | 0.665 | 0.039 | 0.760 | 0.021 | 0.756 | 0.759 | |
| RFE | Academic Year, K1, K2, | ||||||
| Disinfo Training = False, | |||||||
| Disinfo Training = True | 0.691 | 0.027 | 0.756 | 0.017 | 0.752 | 0.752 | |
| DT | Academic Year, K3, A4, S5, | ||||||
| Disinfo Training = False | 0.705 | 0.057 | 0.761 | 0.045 | 0.738 | 0.738 | |
| Regression Target and Selected Model | Train (CV) | Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Objective Variable | Best Model | Mean RMSE | Std MSE | Test RMSE |
| Knowledge | LR {’fit_intercept’: True} | 2.201 | 0.311 | 2.287 |
| RF {’criterion’: ’squared_error’, | ||||
| ’max_depth’: 5, | ||||
| ’min_samples_split’: 20, | ||||
| Skills | ’n_estimators’: 100} | 1.759 | 0.455 | 1.835 |
| Attitudes | RR {’alpha’: 10.0} | 1.686 | 0.354 | 1.598 |
| RF {’criterion’: ’squared_error’, | ||||
| ’max_depth’: 5, | ||||
| ’min_samples_split’: 2, | ||||
| Responsibility | ’n_estimators’: 100} | 2.088 | 0.715 | 2.064 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alcalde-Llergo, J.M.; Fernández, M.B.; George-Reyes, C.E.; Zingoni, A.; Yeguas-Bolívar, E. Leveraging Machine Learning Techniques to Investigate Media and Information Literacy Competence in Tackling Disinformation. Information 2025, 16, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110929
Alcalde-Llergo JM, Fernández MB, George-Reyes CE, Zingoni A, Yeguas-Bolívar E. Leveraging Machine Learning Techniques to Investigate Media and Information Literacy Competence in Tackling Disinformation. Information. 2025; 16(11):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110929
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlcalde-Llergo, José Manuel, Mariana Buenestado Fernández, Carlos Enrique George-Reyes, Andrea Zingoni, and Enrique Yeguas-Bolívar. 2025. "Leveraging Machine Learning Techniques to Investigate Media and Information Literacy Competence in Tackling Disinformation" Information 16, no. 11: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110929
APA StyleAlcalde-Llergo, J. M., Fernández, M. B., George-Reyes, C. E., Zingoni, A., & Yeguas-Bolívar, E. (2025). Leveraging Machine Learning Techniques to Investigate Media and Information Literacy Competence in Tackling Disinformation. Information, 16(11), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110929







