MDFA-AconvNet: A Novel Multiscale Dilated Fusion Attention All-Convolution Network for SAR Target Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
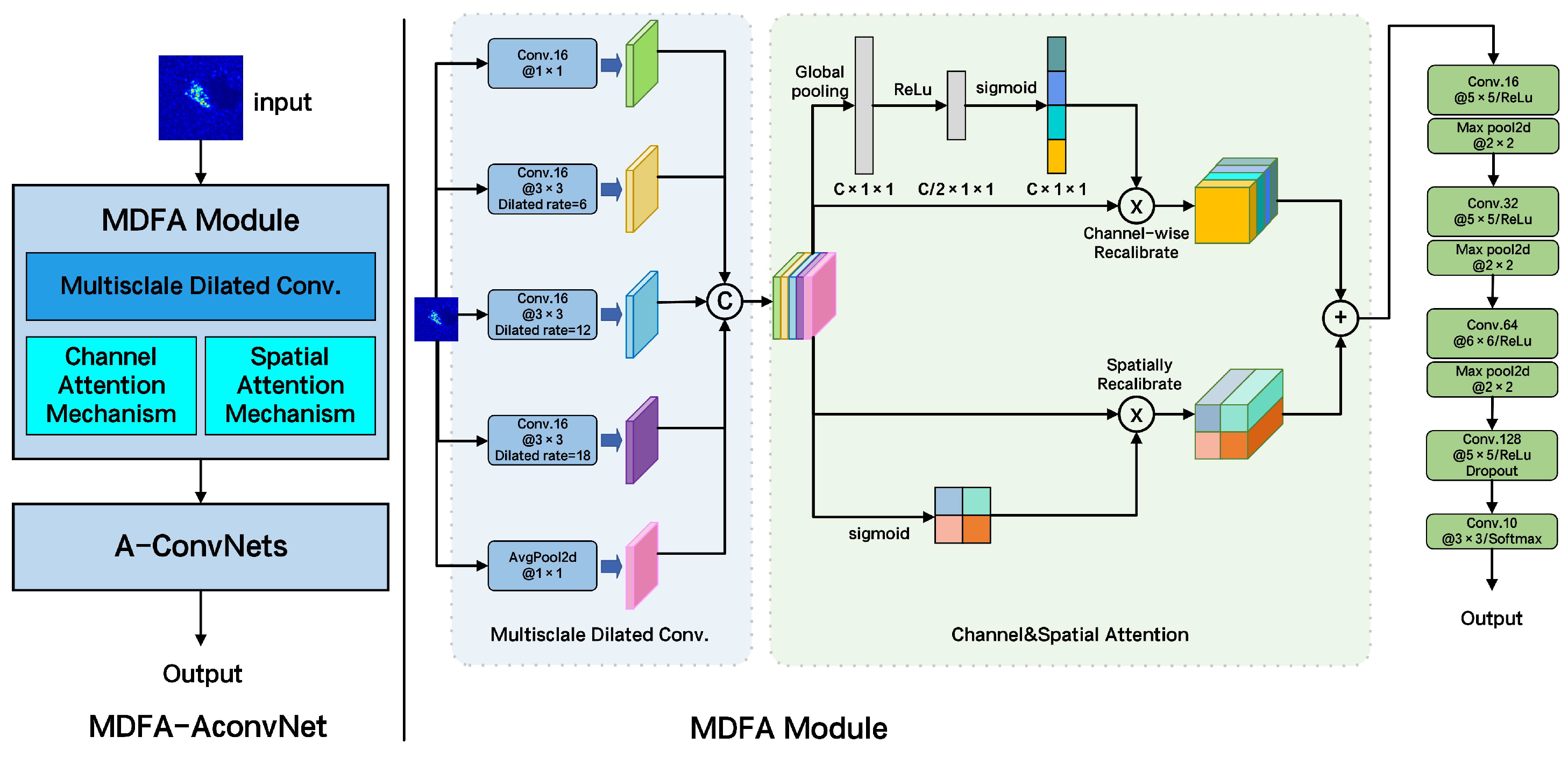
- We introduce MDFA-AconvNet, a new architecture that integrates multiscale dilated convolution and dual attention mechanisms to enhance the representation and discriminability of SAR target features by fusing multiscale receptive fields and adaptively emphasizing informative content.
- The MDFA module extracts features at multiple scales using five parallel convolutional branches with varied dilation rates and incorporates spatial and channel attention to strengthen both global and local features while reducing background clutter and redundancy.
- The use of an all-convolutional structure eliminates fully connected layers, reducing model parameters to only 310,000 and the model size to 1.19 MB, thereby maintaining high classification accuracy while significantly lowering computational and storage demands and mitigating overfitting under limited-data conditions.
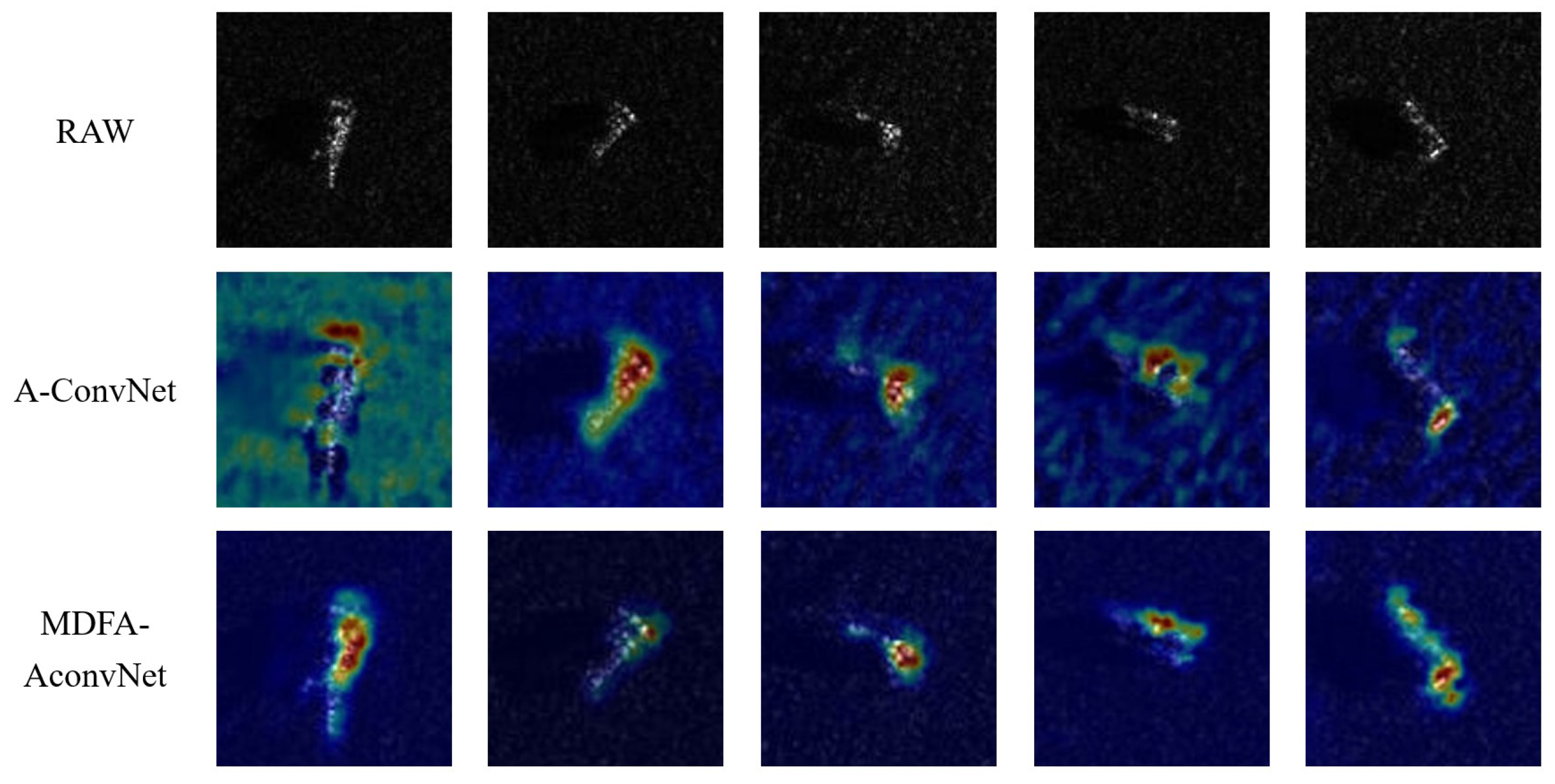
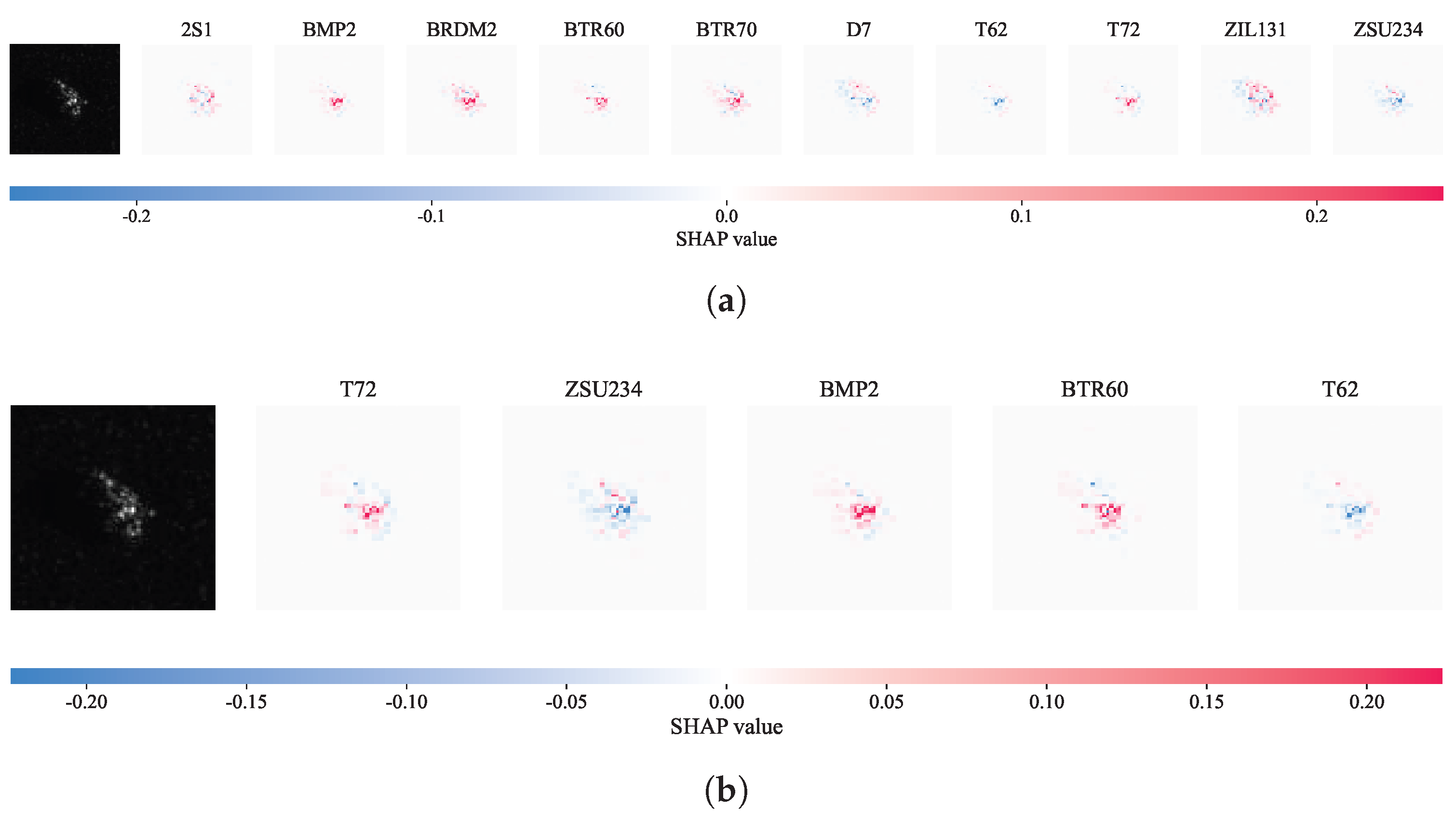
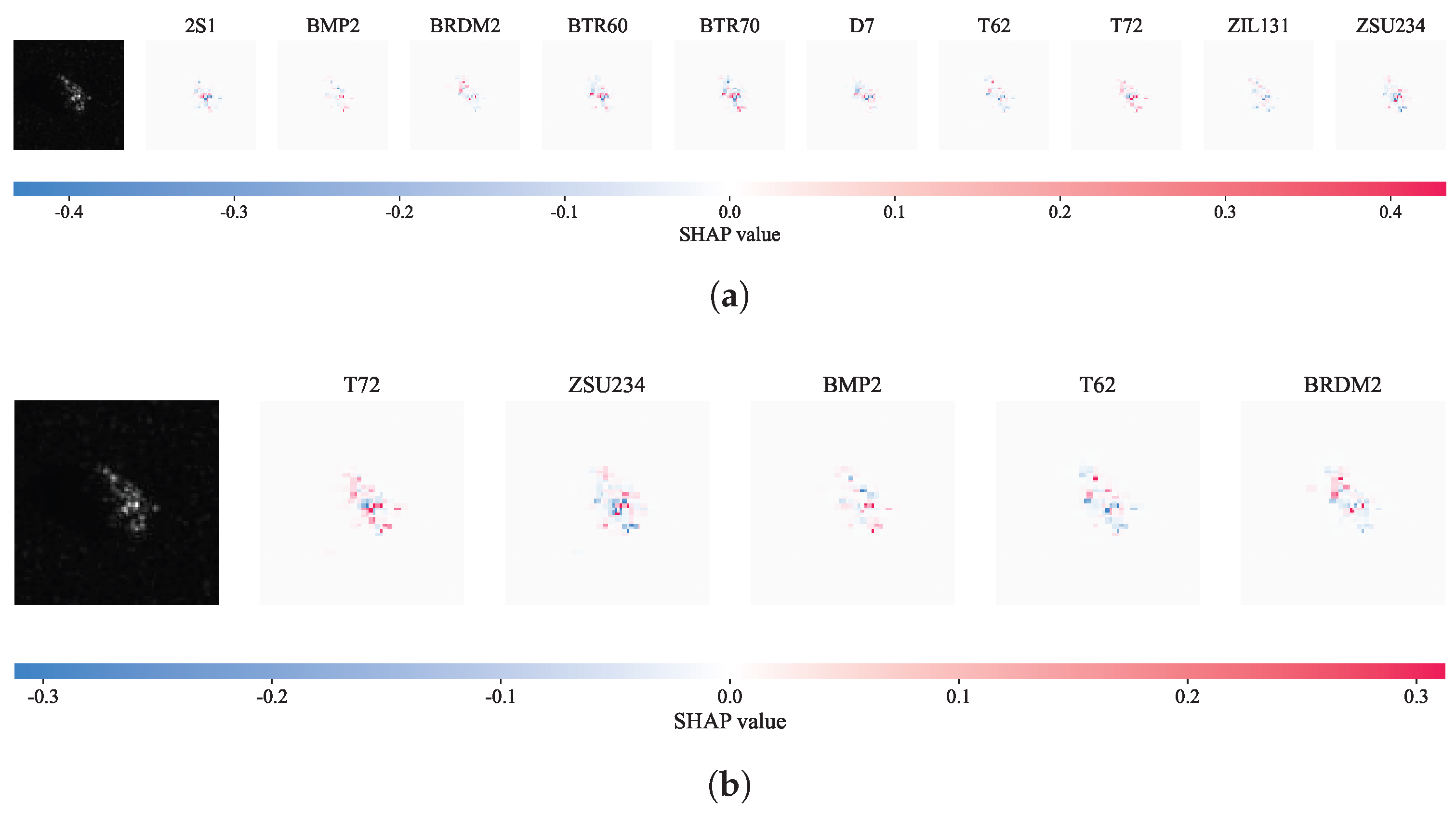
- We employ Grad-CAM and SHAP interpretability techniques to visually validate the model’s ability to accurately extract scattering center features and global structural information, offering physical insight into the model’s decision-making process.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multiscale Receptive Fields for Target Feature Extraction
2.2. Attention Mechanism
3. Method
3.1. Architecture of MDFA-AconvNet
3.2. Multiscale Dilated Fusion Attention Module
3.3. All Convolutional Network Module
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Dataset
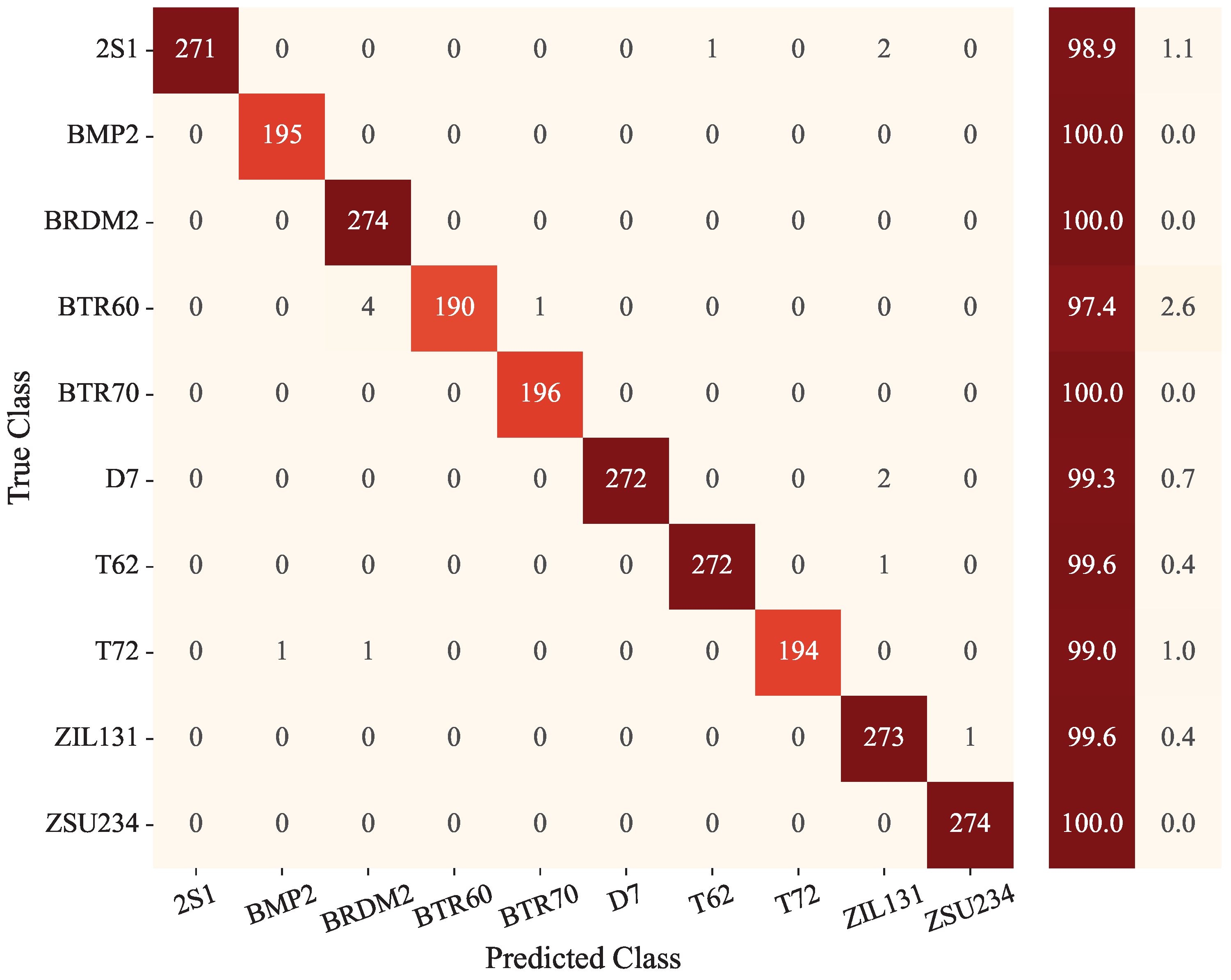
4.2. Results and Analysis Under SOC
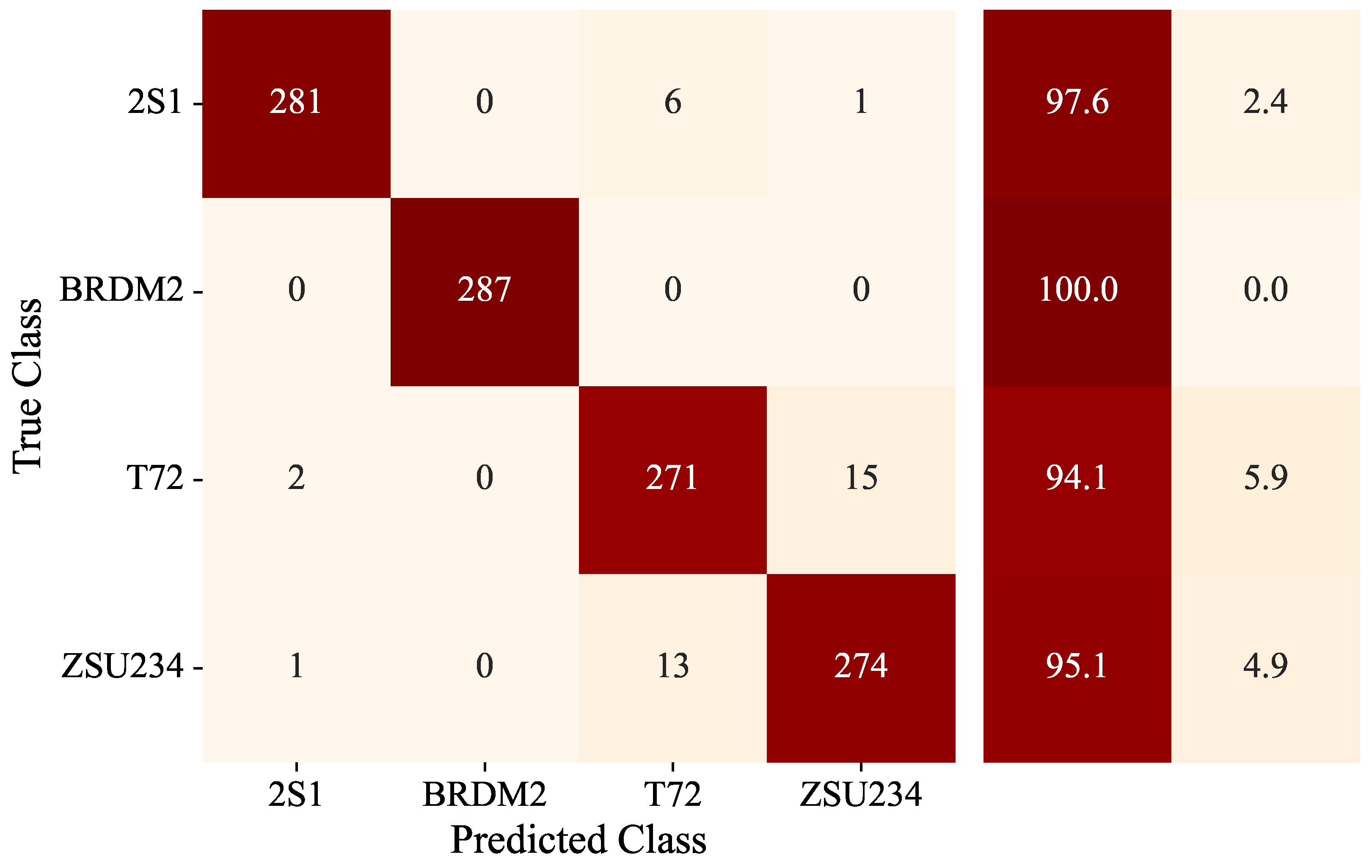
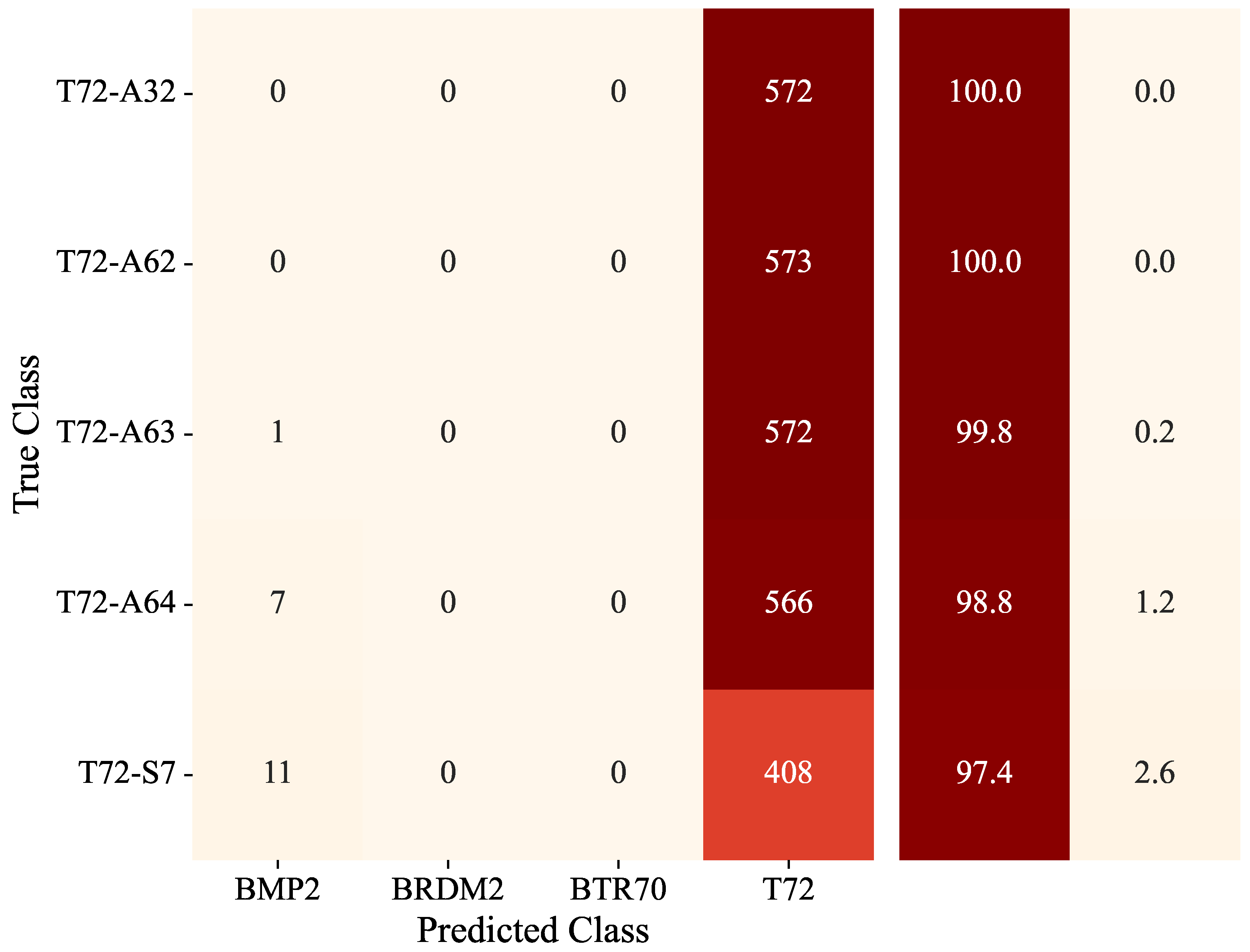
4.3. Results and Analysis Under EOC
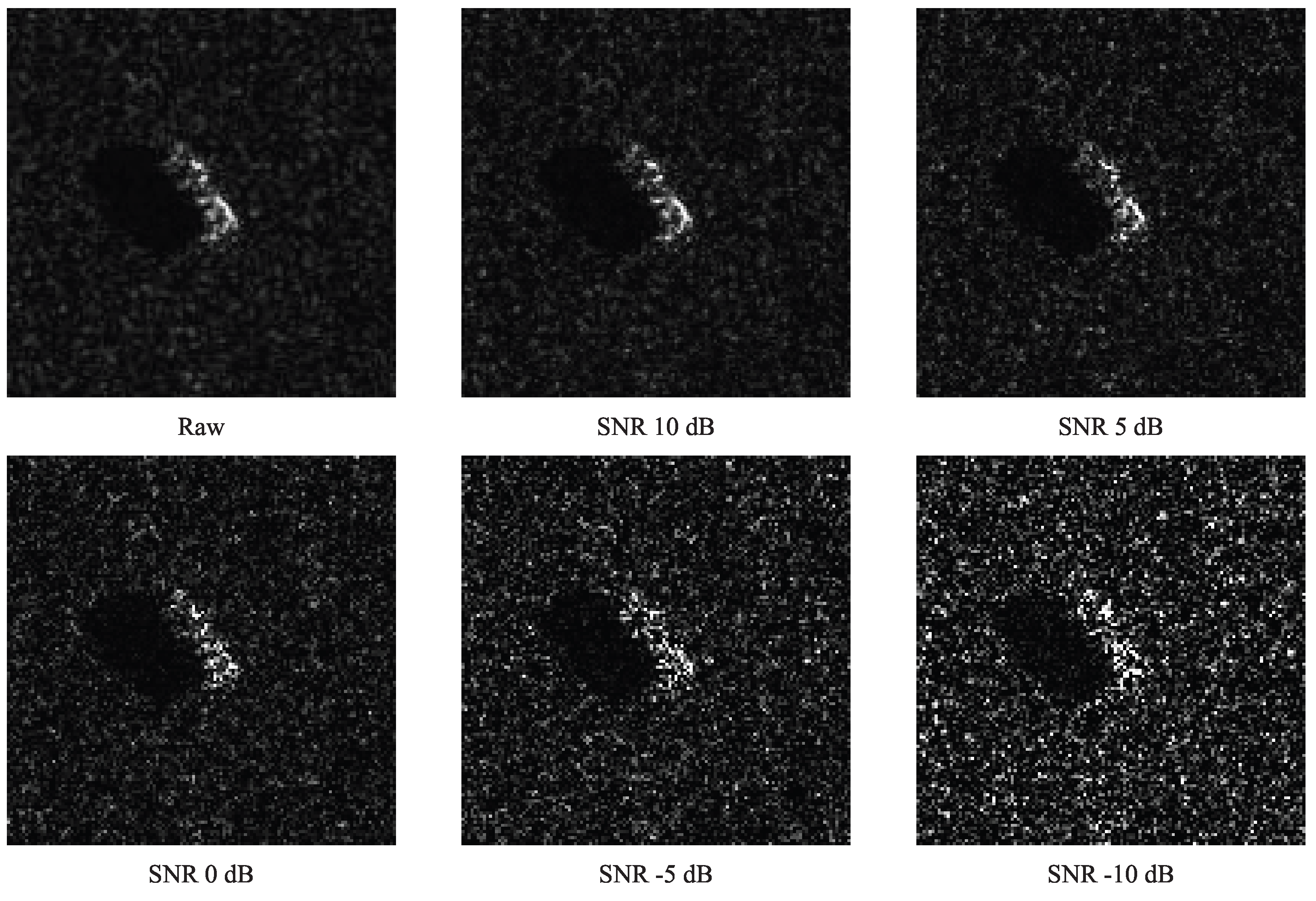
4.4. Noise Robustness Evaluation
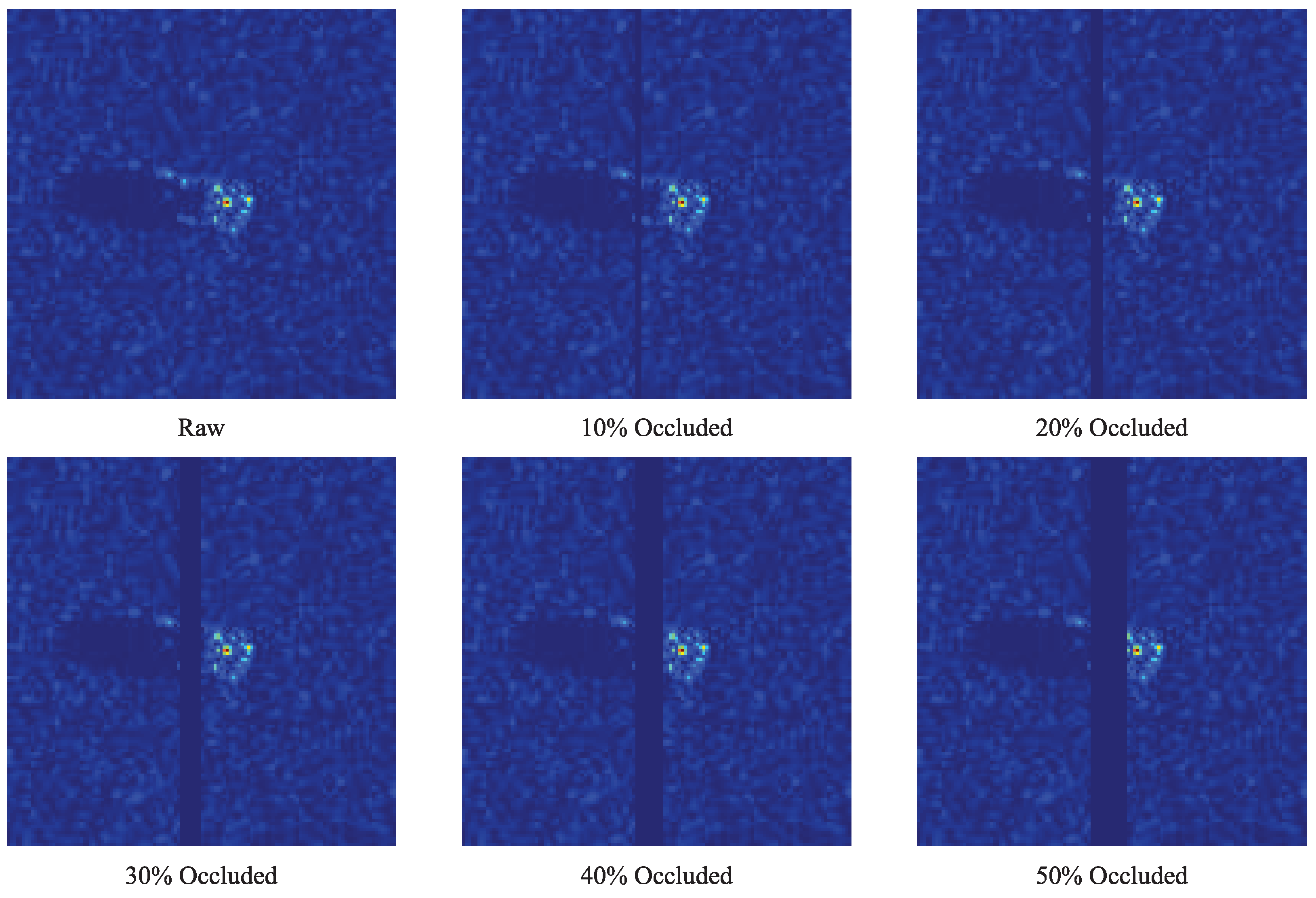
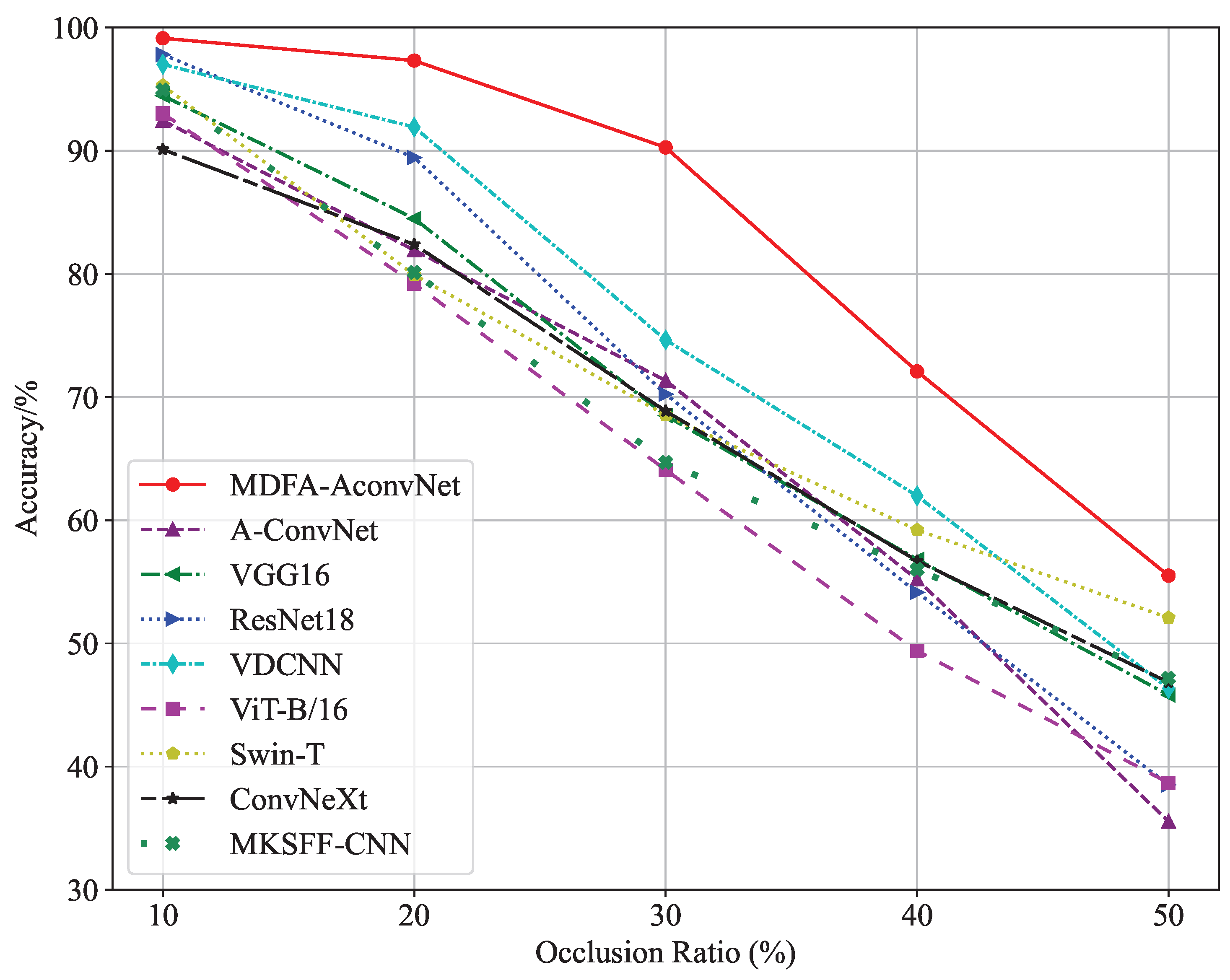
4.5. Occlusion Robustness Evaluation
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Explainability Analysis Based on Grad-CAM and SHAP
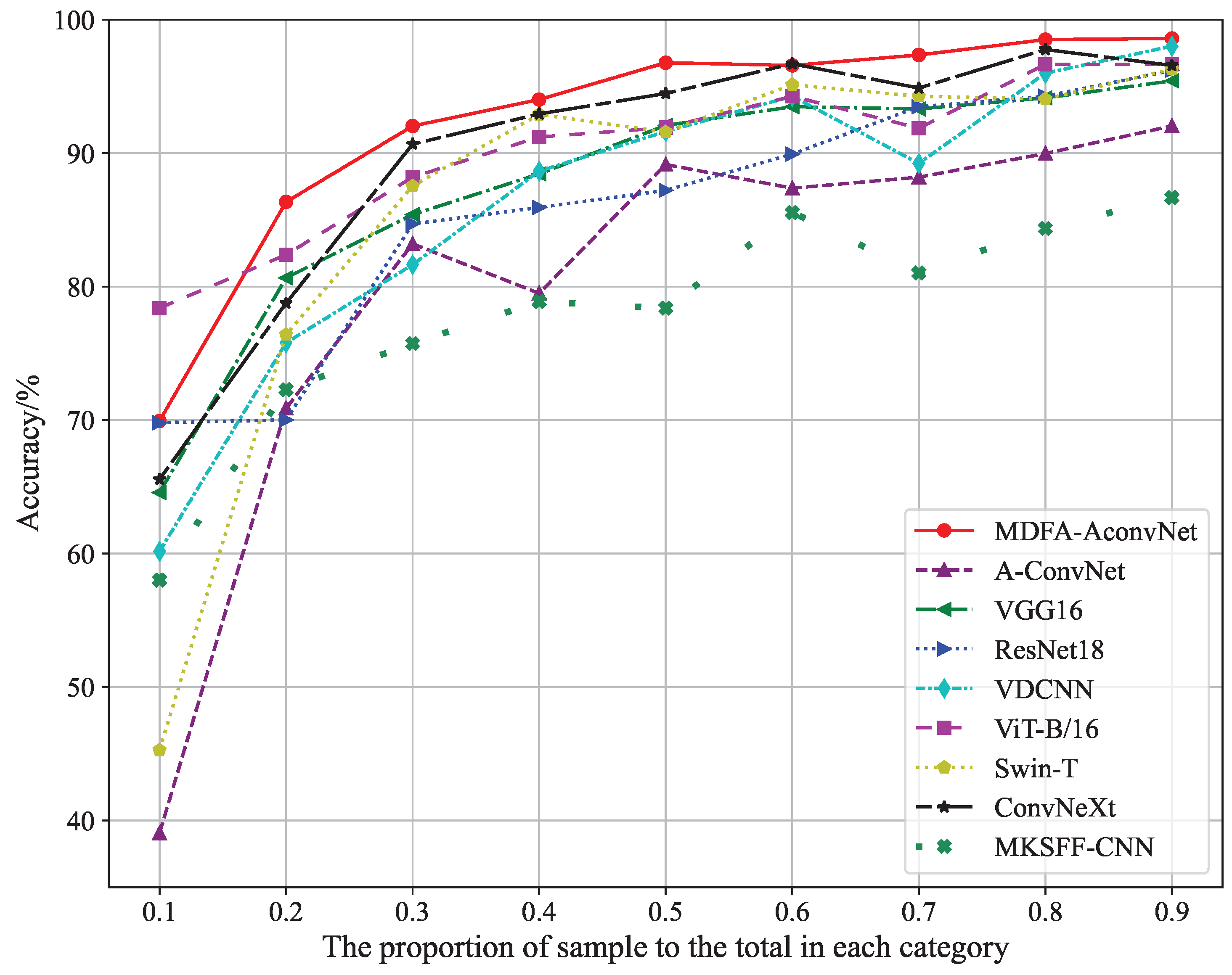
4.8. Classification Accuracy Evaluation Under Small-Size Training Datasets
4.9. Model Size and Computational Efficiency Evaluation
4.10. Ablation Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xing, M.; Yu, H.; Liang, B.; Peng, J.; Sun, G.C. Motion compensation/autofocus in airborne synthetic aperture radar: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 10, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.M.; Easley, G.R.; Healy, D.M.; Chellappa, R. Compressed synthetic aperture radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2010, 4, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.C. Simulation for SAR Feature Image of Planar Structures. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1042, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.E.; Lacoss, R.T. An Overview ofAutomatic Target Recognition. Linc. Lab. J. 1993, 6, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, L.M.; Owirka, G.J.; Brower, W.S.; Weaver, A.L. The automatic target-recognition system in SAIP. Linc. Lab. J. 1997, 10, 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeuchi, K.; Wheeler, M.D.; Yamazaki, T.; Shakunaga, T. Model-based SAR ATR system. In Proceedings of the Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1996; Volume 2757, pp. 376–387. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Lei, P.; Bai, X. Ground target classification in noisy SAR images using convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4180–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Huang, M. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Du, L.; Li, C.; Ding, J.; Liu, H. SAR automatic target recognition based on Euclidean distance restricted autoencoder. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3323–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Jin, Y. Deep Learning as Applied in SAR Target Recognition and Terrain Classification. J. Radars 2017, 6, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Hui, Y. SAR ATR of ground vehicles based on LM-BN-CNN. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 7282–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bai, X.; Zhou, F. SAR ATR of ground vehicles based on ESENet. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; An, J.; Yang, L.D.; Wu, L.; Lu, X.Q. Convolutional neural network with attention mechanism for SAR automatic target recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 4004205. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ren, H.; Li, L. Multi-view classification with semi-supervised learning for SAR target recognition. Signal Process. 2021, 183, 108030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Huang, J.; An, D.; Chen, L. SAR target classification based on multiscale attention super-class network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 9004–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ren, M.; Wu, C. Improved YOLOv4 based on attention mechanism for ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 23785–23797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubel, D.H.; Wiesel, T.N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 1962, 160, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik, S.; Schmid, C.; Ponce, J. Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 2, pp. 2169–2178. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Hsu, K.T.; Eyassu, M.; Chitnis, P.V. Dense dilated UNet: Deep learning for 3D photoacoustic tomography image reconstruction. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.03130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Yin, B.; Du, A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, E.; Sun, J. Learning delicate local representations for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Cai, Q.; Zou, F.; Zhu, Y.; Liao, L.; Guo, F. Biga-yolo: A lightweight object detection network based on yolov5 for autonomous driving. Electronics 2023, 12, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Lu, N. A deep learning based assisted analysis approach for Sjogren’s syndrome pathology images. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Boureau, Y.L.; Ponce, J.; LeCun, Y. A theoretical analysis of feature pooling in visual recognition. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML’10, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Complex-Valued Convolutional Neural Network and Its Application in Polarimetric SAR Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 7177–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFRL. The Air Force Moving and Stationary Target Recognition Database. Available online: https://www.sdms.afrl.af.mil/index.php?collection=mstar (accessed on 16 November 2025).
- Pei, J.; Huang, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yeo, T.S. SAR automatic target recognition based on multiview deep learning framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 2196–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, J.; Mao, Y.; Luo, Q.; Jia, L.; Xing, M. SAR target classification using the multikernel-size feature fusion-based convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5214313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wen, G.; Zhong, J.; Ma, C.; Yang, X. A Robust Similarity Measure for Attributed Scattering Center Sets with Application to SAR ATR. Neurocomputing 2017, 219, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wen, G. Exploiting Multi-View SAR Images for Robust Target Recognition. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Todorovic, S.; Li, J. Adaptive boosting for SAR automatic target recognition. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]





| Class | Serials No. | Train | Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | No. Image | Depression | No. Image | ||
| BMP2 | 9563 | 17° | 233 | 15° | 196 |
| BTR70 | c71 | 17° | 233 | 15° | 196 |
| T-72 | 132 | 17° | 232 | 15° | 196 |
| BTR60 | k10yt7532 | 17° | 256 | 15° | 195 |
| 2S1 | b01 | 17° | 299 | 15° | 274 |
| BRDM2 | E-71 | 17° | 298 | 15° | 274 |
| D7 | 92v13015 | 17° | 299 | 15° | 274 |
| T-62 | A51 | 17° | 299 | 15° | 273 |
| ZIL131 | E12 | 17° | 299 | 15° | 274 |
| ZSU234 | d08 | 17° | 299 | 15° | 274 |
| Class | Serials No. | Train | Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | No. Image | Depression | No. Image | ||
| T-72 | A64 | 17° | 299 | 30° | 196 |
| 2S1 | b01 | 17° | 299 | 30° | 274 |
| BRDM2 | E-71 | 17° | 298 | 30° | 274 |
| ZSU234 | d08 | 17° | 299 | 30° | 274 |
| Class | Serials No. | Train | Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | No. Image | Depression | No. Image | ||
| BMP2 | 9563 | 17° | 233 | - | - |
| BRDM2 | E-71 | 17° | 298 | - | - |
| BTR70 | c71 | 17° | 233 | - | - |
| T-72 | 132 | 17° | 232 | - | - |
| T-72 | S7 | - | - | 15° 17° | 419 |
| T-72 | A32 | - | - | 15° 17° | 572 |
| T-72 | A62 | - | - | 15° 17° | 573 |
| T-72 | A63 | - | - | 15° 17° | 573 |
| T-72 | A64 | - | - | 15° 17° | 573 |
| Class | Serials No. | Train | Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | No. Image | Depression | No. Image | ||
| BMP2 | 9563 | 17° | 233 | - | - |
| BRDM2 | E-71 | 17° | 298 | - | - |
| BTR70 | c71 | 17° | 233 | - | - |
| T-72 | 132 | 17° | 232 | - | - |
| BMP2 | 9566 | - | - | 15° 17° | 428 |
| BMP2 | c21 | - | - | 15° 17° | 429 |
| T-72 | 812 | - | - | 15° 17° | 426 |
| T-72 | A04 | - | - | 15° 17° | 573 |
| T-72 | A05 | - | - | 15° 17° | 573 |
| T-72 | A07 | - | - | 15° 17° | 573 |
| T-72 | A10 | - | - | 15° 17° | 567 |
| Method | 2S1 | BMP2 | BRDM2 | BTR60 | BTR70 | D7 | T-62 | T-72 | ZIL131 | ZSU234 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 92.7 | 92.8 | 95.3 | 93.3 | 93.9 | 94.2 | 94.1 | 95.9 | 96 | 98.2 | 94.64 |
| ResNet18 | 94.9 | 97.4 | 99.3 | 95.4 | 96.9 | 97.4 | 97.1 | 96.9 | 99.6 | 98.9 | 97.38 |
| A-ConvNet | 78.5 | 92.3 | 98.2 | 87.7 | 92.3 | 93.1 | 95.2 | 94.9 | 92.3 | 97.8 | 92.23 |
| VDCNN | 98.9 | 92.3 | 98.5 | 93.8 | 96.9 | 99.3 | 98.9 | 99 | 97.1 | 100 | 97.47 |
| ViT-B/16 | 94.9 | 99 | 99.6 | 97.9 | 100 | 98.9 | 100 | 100 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 98.93 |
| Swin-T | 98.5 | 96.9 | 99.3 | 93.8 | 98 | 97.4 | 99.6 | 90.8 | 99.3 | 98.2 | 97.18 |
| ConvNeXt | 98.2 | 81 | 97.8 | 85.1 | 90.3 | 96.4 | 99.3 | 93.9 | 96.7 | 96 | 93.47 |
| MKSFF-CNN | 97.4 | 84.1 | 97.1 | 87.2 | 92.3 | 98.9 | 98.9 | 99.5 | 100 | 98.9 | 95.43 |
| MDFA-AconvNet | 98.9 | 100 | 100 | 97.4 | 100 | 99.3 | 99.6 | 99 | 99.6 | 100 | 99.38 |
| Method | 2S1 | BRDM2 | T-72 | ZSU234 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 99.0 | 99.7 | 79.9 | 91.0 | 92.40 |
| ResNet18 | 100 | 99.0 | 72.2 | 87.2 | 89.60 |
| A-ConvNet | 100 | 100 | 81.2 | 89.9 | 92.78 |
| VDCNN | 100 | 100 | 97.9 | 78.1 | 94.00 |
| ViT-B/16 | 100 | 98.6 | 80.2 | 91.0 | 92.45 |
| Swin-T | 99.7 | 99.3 | 85.8 | 97.6 | 95.60 |
| ConvNeXt | 97.2 | 96.2 | 84.0 | 67.0 | 86.10 |
| MKSFF-CNN | 100 | 99.3 | 95.1 | 80.9 | 93.83 |
| MDFA-AconvNet | 97.6 | 100 | 94.1 | 95.1 | 96.70 |
| Method | T-72-A32 | T-72-A62 | T-72-A63 | T-72-A64 | T-72-S7 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 96.7 | 95.8 | 93.5 | 92.7 | 95.2 | 94.78 |
| ResNet18 | 99.3 | 97.4 | 97.6 | 93.5 | 98.3 | 97.22 |
| A-ConvNet | 95.3 | 94.2 | 94.6 | 88.7 | 94.5 | 93.46 |
| VDCNN | 96.0 | 94.9 | 94.8 | 90.2 | 96.2 | 94.42 |
| ViT-B/16 | 95.5 | 96.3 | 97.4 | 95.3 | 92.6 | 95.42 |
| Swin-T | 98.6 | 95.5 | 96.0 | 92.3 | 96.9 | 95.86 |
| ConvNeXt | 96.2 | 93.2 | 89.5 | 88.3 | 92.8 | 92.00 |
| MKSFF-CNN | 99.5 | 97.4 | 98.4 | 99.0 | 92.6 | 97.38 |
| MDFA-AconvNet | 100 | 100 | 99.8 | 98.8 | 97.4 | 99.20 |
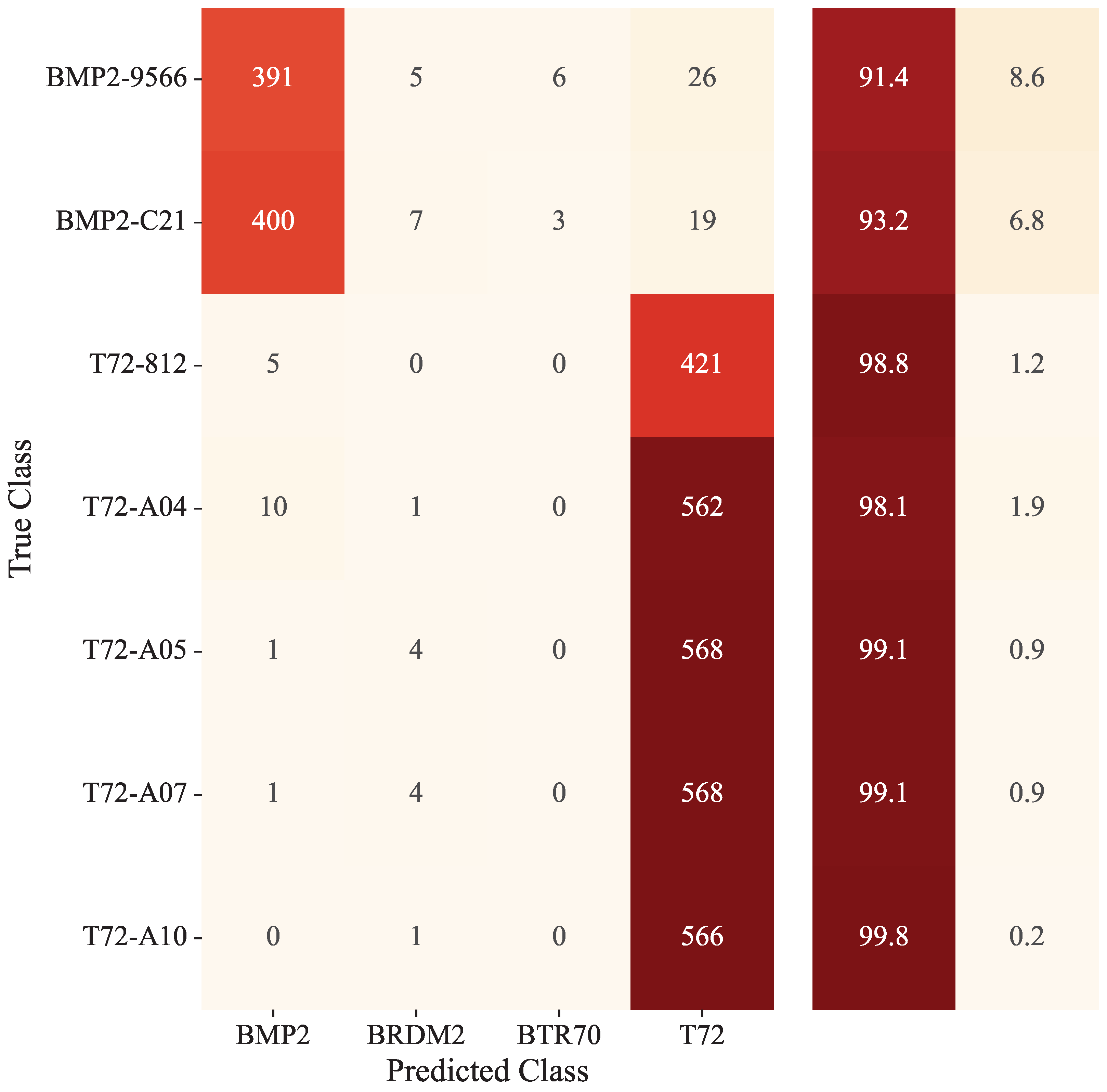
| Method | BMP2-9566 | BMP2-c21 | T-72-812 | T-72-A04 | T-72-A05 | T-72-A07 | T-72- A10 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 81.5 | 87.6 | 96.0 | 96.9 | 97.2 | 97.0 | 99.3 | 93.64 |
| ResNet18 | 95.1 | 93.7 | 89 | 93.5 | 92.7 | 96.5 | 89.4 | 92.84 |
| A-ConvNet | 81.8 | 84.1 | 94.1 | 98.3 | 99.0 | 99.3 | 99.8 | 93.77 |
| VDCNN | 91.1 | 92.8 | 94.6 | 87.6 | 95.6 | 90.9 | 98.4 | 93.00 |
| ViT-B/16 | 70.8 | 81.8 | 95.3 | 96.0 | 96.0 | 99.5 | 86.6 | 89.43 |
| Swin-T | 95.6 | 96.7 | 99.8 | 97.2 | 96.5 | 99.7 | 90.8 | 96.61 |
| ConvNeXt | 73.8 | 79.3 | 90.8 | 80.3 | 85.5 | 84.1 | 92.1 | 83.70 |
| MKSFF-CNN | 86.9 | 81.6 | 89.7 | 95.1 | 97.7 | 95.1 | 99.1 | 92.17 |
| MDFA-AconvNet | 91.4 | 93.2 | 98.8 | 98.1 | 99.1 | 99.1 | 99.8 | 97.07 |
| Class | MDFA-AconvNet Acc (%) | A-ConvNet Acc (%) | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2S1 | 98.91 ± 0.63 | 91.35 ± 2.70 | 9.175 | <0.0001 *** |
| BMP2 | 98.51 ± 0.93 | 88.26 ± 3.21 | 10.230 | <0.0001 *** |
| BRDM2 | 99.53 ± 0.43 | 97.12 ± 1.03 | 6.736 | 0.0001 *** |
| BTR60 | 96.46 ± 0.96 | 90.41 ± 2.56 | 7.143 | 0.0001 *** |
| BTR70 | 99.74 ± 0.26 | 96.28 ± 1.51 | 6.937 | 0.0001 *** |
| D7 | 99.09 ± 0.24 | 96.82 ± 1.89 | 3.708 | 0.0049 ** |
| T62 | 99.56 ± 0.43 | 96.52 ± 0.82 | 11.597 | <0.0001 *** |
| T72 | 99.39 ± 0.38 | 94.80 ± 2.64 | 4.881 | 0.0009 *** |
| ZIL131 | 99.42 ± 0.44 | 95.26 ± 2.02 | 6.119 | 0.0002 *** |
| ZSU234 | 99.78 ± 0.44 | 97.96 ± 1.14 | 4.009 | 0.0031 ** |
| Method | Number of Parameters/ | Model Size/MB | Computation Time per Batch/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 129.03 | 512.32 | 0.0264 |
| ResNet18 | 11.18 | 42.67 | 0.0055 |
| A-ConvNet | 0.30 | 1.16 | 0.0008 |
| VDCNN | 4.42 | 16.88 | 0.0035 |
| ViT-B/16 | 85.41 | 325.83 | 0.4306 |
| Swin-T | 27.52 | 105.22 | 0.0387 |
| ConvNeXt | 87.91 | 335.34 | 0.0720 |
| MKSFF-CNN | 83.33 | 317.89 | 0.0094 |
| MDFA-AconvNet | 0.31 | 1.19 | 0.0012 |
| Multiscale Dilated Conv. | Channel Attention Mechanism | Spatial Attention Mechanism | Accuracy (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 92.23 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 95.75 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 96.00 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 95.13 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 97.62 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 97.28 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 97.03 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 99.38 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Q.; Yang, X.; Du, S.; Bai, X. MDFA-AconvNet: A Novel Multiscale Dilated Fusion Attention All-Convolution Network for SAR Target Classification. Information 2025, 16, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16111007
Wang J, Liu J, Zhang P, Jia Q, Yang X, Du S, Bai X. MDFA-AconvNet: A Novel Multiscale Dilated Fusion Attention All-Convolution Network for SAR Target Classification. Information. 2025; 16(11):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16111007
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiajia, Jun Liu, Pin Zhang, Qi Jia, Xin Yang, Shenyu Du, and Xueyu Bai. 2025. "MDFA-AconvNet: A Novel Multiscale Dilated Fusion Attention All-Convolution Network for SAR Target Classification" Information 16, no. 11: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16111007
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, J., Zhang, P., Jia, Q., Yang, X., Du, S., & Bai, X. (2025). MDFA-AconvNet: A Novel Multiscale Dilated Fusion Attention All-Convolution Network for SAR Target Classification. Information, 16(11), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16111007







