Abstract
Accurate tremor classification is crucial for effective patient management and treatment. However, clinical diagnoses are often hindered by misdiagnoses, necessitating the development of robust technical methods. Here, we present a two-stage convolutional neural network (CNN)-based system for classifying physiological tremor, essential tremor (ET), and Parkinson’s disease (PD) tremor. Employing acceleration signals from the hands of 408 patients, our system utilizes both medically motivated signal features and (nearly) raw data (by means of spectrograms) as system inputs. Our model employs a hybrid approach of data-based and feature-based methods to leverage the strengths of both while mitigating their weaknesses. By incorporating various data augmentation techniques for model training, we achieved an overall accuracy of 88.12%. This promising approach demonstrates improved accuracy in discriminating between the three tremor types, paving the way for more precise tremor diagnosis and enhanced patient care.
1. Introduction
Tremors, involuntary oscillatory movements of one or more body parts, can be either physiological or pathological [1]. A physiological tremor is a small amplitude oscillation present in healthy subjects, while pathological tremors have a more evident amplitude, are a symptom of underlying diseases, and can negatively affect daily activities. A pathological tremor can either arise as a single symptom, as in essential tremors (ETs), or as a symptom of a more complex movement disorder, such as Parkinson’s disease (PD). ET is the most prevalent form of tremor without additional symptoms, impacting approximately 1% of the global population [2]. It can cause involuntary shaking of the hands, head, voice, and other body parts. PD is a neurodegenerative disorder that affected an estimated 6.1 million people worldwide as of 2016 [3]. The prevalence in the population is increasing more rapidly than for other neurological disorders. PD tremor is a combined tremor syndrome with other symptoms, such as bradykinesia, rigidity, or gait problems.
The Movement Disorder Society has developed two consensus statements that detail the classification of tremors in clinical settings [1], including tremor due to diseases not addressed in this study. The classification of tremors primarily relies on clinical criteria, with only a limited number of supplementary tests available to enhance diagnosis. These tests include quantitative analysis of tremor movement and electromyographic activity. Despite the availability of tests, the diagnosis of tremor remains challenging due to overlapping characteristics of different tremor types and the difficulty in establishing objective criteria [1,4]. Consequently, misdiagnoses can occur.
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence that employs statistical techniques to enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. Various machine learning algorithms are utilized in diverse medical fields, such as cancer classification [5] or epileptic seizure detection [6]. A feature-based approach to train such a model involves extracting features from data that are relevant for the task. These features are then used to train a machine learning model, such as a support vector machine (SVM) or a neural network. A data-based approach to train models involves training models directly on raw data or representations of raw data, such as time-frequency analyses. In this second approach, the network autonomously extracts relevant features, which is particularly useful when the specific features for classification are unknown. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), for instance, are particularly adept at image classification and can consequently be used to classify raw data represented as spectrograms. These networks have also proven effective in various medical classification applications and therefore also provide a promising approach for tremor classification. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to identify patterns in data that are not obvious to the human eye. This could help to improve the accuracy of tremor classification and reduce the risk of misdiagnoses.
The primary aim of this research is to develop a classification model that can accurately and objectively differentiate between various tremor types. With further development, this model has the potential to serve as a valuable clinical tool to support clinical diagnosis, potentially reducing misdiagnoses. The model is designed to classify three types of tremor (ET, tremor of PD, and physiological tremor) based on the one hand on features identified in our preliminary work [7] and on the other hand on additional features extracted automatically from raw data in the form of spectrograms by a CNN. The aim is to achieve the highest possible overall classification accuracy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Method Overview
The overall system of classifying tremors is shown in Figure 1. The acceleration signals used are preprocessed in two different ways. First, various features are determined from the time signals and spectra, as described in a previous paper [7]. Second, spectrograms are determined. To feed the two CNNs, their input is a composite representation generated by superimposing the spectrograms of the patient’s left and right hand. In the lower half, the spectrogram of the signal of the more-affected hand with the stronger tremor is depicted and in the upper half, the spectrogram of the less-affected hand with the weaker tremor is displayed. The input signals are fed into two trained CNNs. The first one classifies between physiologic and pathologic tremor. In the second network, the two pathologic tremor types used in this study are distinguished. The procedure for the entire system is described in more detail in the following.
2.2. Data Acquisition
For this study, we examined 408 individuals over a period of nine years at the Department of Neurology, University Hospital Schleswig–Holstein, Kiel University, Germany. This dataset is used for the evaluation of the classification models and to compare the results with previous attempts [7]. Based on standardized diagnostic criteria [4], neurologists diagnosed the patients. The dataset consists of
- 130 Parkinsonian patients;
- 209 patients with essential tremor;
- and 54 healthy controls.
The remaining 15 recordings are discarded due to poor signal quality so that a total of 393 recordings can be used for this study. Data were anonymized. The local ethics committee approved this study.
The standardized electrophysiological examination consists of three parts [7]. Each part lasts 30 s, and a sufficiently long rest period was inserted between the partial examinations to avoid overexertion. For the first measurement, the patient sits on a chair and rests their forearms on the armrest. The hands are allowed to hang freely and comfortably, approximating a natural resting posture. Then, for the second position, the patient stretches out their hands so that they are parallel to the floor. For the third part of the measurement, in addition to the second position, a 1 kg weight is attached to the back of the hand.
For data acquisition we used a commercial system (Nicolet EDX EMG System, Natus Medical Incorporated) and an uniaxial accelerometer with a provided sensitivity of 1 milligravity/div up to 20 gravities/div. This sensor was attached to the distal metacarpal phalanx of the patient’s hand. The signals of both hands are sampled synchronously with 800 Hz.
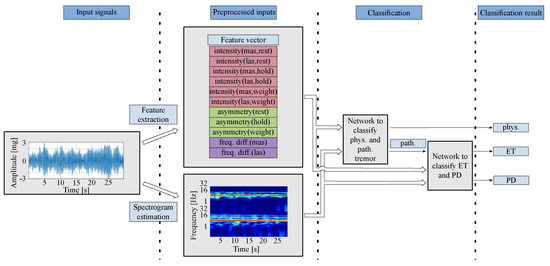
Figure 1.
Overall procedures in tremor classification based on a two-stage 2D-CNN. The acceleration signals are first preprocessed to extract features and calculate spectrograms. Features and spectrograms are calculated each from the hand of the more-affected side (mas) and the less-affected side (las). These two representations serve as input to two different CNNs. The first CNN distinguishes between physiological and pathological tremor. If the result is a pathological tremor, a second CNN with the same inputs is used to differentiate between ET and PD.
2.3. Preprocessing
The preprocessing of the data is implemented in Kiel Real-time Application Toolkit (KiRAT) [8], which is a framework for real-time signal processing. This framework is developed in the group of Digital Signal Processing and System Theory [9] at Kiel University and is used, among other applications, for the classification of tremor patients. The data from the dataset of this study are preprocessed file-based and are later used to train the CNN. Afterwards, the trained model is used in KiRAT to evaluate the model and to classify and diagnose future patients directly during an examination.
Time–frequency analyses are executed based on the raw data from the acceleration sensors used. The time signals consist of 24,000 samples ( 800 Hz · 30 s = 24,000 samples). In the first step, these are divided into short frames of 1024 samples in size. For each of these frames, a fast Fourier transform (FFT) is calculated, whereby the frequency resolution is increased by zero padding to an FFT order of 2048. The spectrogram, which is used as the input for the CNN, has a resulting frequency resolution of 0.39 Hz. By an overlap of 50%, 512 samples are re-examined each time, which corresponds to a time of 0.64 s. Thus, fine changes in frequency as well as in time can be represented.
The amplitudes of the spectrograms are normalized to a range of zero and one for efficient processing. For this purpose, we have determined the maximum value of all estimated spectrograms and selected the normalization factor with 100 mg to the nearest power of 10.
2.3.1. Logarithmic Frequency Axis
Due to the sample rate of 800 Hz, a frequency range of 400 Hz can be mapped for the spectrograms. Since tremors typically oscillate with frequencies smaller than 15 Hz [4], the range is limited manually to 30 Hz. In this range, harmonics can still be displayed without mapping an irrelevant frequency range for tremors.
Furthermore, a logarithmic frequency axis is used. On the one hand, this results in smaller frequencies covering a larger proportion of the spectrogram and, on the other hand, harmonics having a uniform spacing regardless of the fundamental frequency and thus being easier for the kernels of a CNN to be recognized as patterns. For this study, the frequency axis is displayed with the logarithm based on the value two. The comparison of two spectrograms, one with linear and one with a logarithmic frequency axis, are shown in Figure 2.
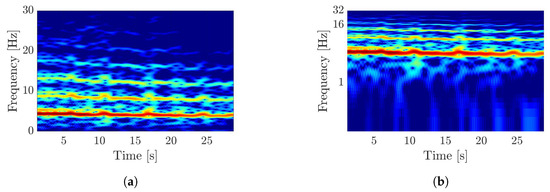
Figure 2.
Visualization of the difference by a logarithmic frequency axis in spectrograms. (a) Spectrogram of an acceleration-tremor signal with linear frequency axis. (b) Spectrogram of an acceleration-tremor signal with logarithmic frequency axis.
2.3.2. Arrangement of Multiple Inputs
A spectrogram is a two-dimensional matrix whose numerical values correspond to the magnitude values of the spectrum per frame. In this study, we use two different spectrograms, one for the more-severely and one for the less-severely affected hand of the patient. The more-affected side is the hand whose tremor has a higher amplitude. To combine these two images, we generate a new image that is composed of the both individual spectrograms with the spectrogram of the more-affected side at the bottom and the other at the top of the image. This creates a two-dimensional matrix as input, whose time axis remains the same and whose frequency axis is doubled. The arrangement of the spectrograms is shown in Figure 1 as the second input to both networks.
This arrangement emerged from several attempts to minimize the dimension of the input images and features to ensure that the limited training data is sufficient to adequately train the model’s free parameters. We also explored alternative input data combinations, such as incorporating electromyography (EMG) data or using data from all of the three distinct recording positions. However, comprehensive testing revealed that the combination of signals and spectrogram arrangement employed here provides the optimal performance for our application, considering the above-mentioned scarcity of training data.
2.4. Feature Extraction
In addition to the spectrograms, features that are typical for the different tremor types are extracted [4]. These will be used in combination with the spectrograms as input for the CNN and thus are expected to lead to a better classification accuracy.
Our previous research [7] examined a diverse range of features from both the time and frequency domains, considering clinical significance and prior literature, to assess their ability to differentiate between the three tremor types. In the time domain, we analyzed first the amplitude of the time series. This enabled us to calculate the amplitude asymmetry between the patient’s two hands and the amplitude ratio relative to the resting position. Additionally, regularity [10] was analyzed to determine whether the amplitude varied over time or remained constant. The spectral domain evaluation began with identifying the maximum of the spectrum and the corresponding frequency. To assess the prominence of the maximum, we calculated the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the bandwidth. Subsequently, we compared the tremor frequencies measured with and without weight to observe any discrepancies.
To achieve the highest possible overall accuracy, we have carefully selected a subset of three feature types that are calculated across all recorded positions of the patients:
- Intensity, to represent the amplitude (six values: three positions and two hands);
- Asymmetry (three values: one value per position);
- Frequency difference (two values: one value per hand).
Choosing all features would necessitate a larger network architecture with more adjustable parameters, which could not be adequately trained due to the limited amount of training data. Therefore, we prioritized features that are also considered in clinical tremor descriptions. The calculated features are summarized in a vector as shown in Figure 1. The more-affected side (mas) is the side whose hand shows a tremor with a higher amplitude compared to the less-affected side (las).
The intensity describes the amplitude of tremor. In contrast to the two pathological tremors, the amplitude of the physiological tremor is not visible to the human eye [4]. The root mean square (RMS) is used for the calculation [7] of the amplitude for both hands in all examined positions.
A Parkinsonian tremor usually occurs asymmetrically [1]. The asymmetry feature describes this and is calculated as the ratio of the intensities of both sides.
Since the frequency of the physiological tremor arises due to the mechanical properties of the hand and the arm, this frequency decreases when the hand is loaded with an additional weight [4,11]. A larger difference between the dominant frequencies in the holding positions without and with weight is indicative of the presence of a physiological tremor.
2.5. Convolutional Neural Network
After estimating the spectrograms and extracting the features, the CNN model is trained with Keras [12] in Python. In total, 60% of the data is used for the training (235 subjects), 20% is used for validation during the training process (79 subjects), and afterwards 20% for testing the trained model (79 subjects). The evaluation of the model is conducted within the so-called KiRAT framework, a frame-based signal processing toolkit, in order to achieve a self-contained environment that will ultimately allow real-time diagnosis during the examination using the trained model.
2.5.1. Model Design
CNNs are a type of artificial neural network (ANN) that are particularly well-suited for image processing. They can be used to classify images, recognize objects, or even generate new images [13,14].
Such models work by passing an image through a series of different layers. Each layer has a specific task, such as extracting features from the image, reducing the size, or classifying the image. The structure of the networks used in this study is shown in Figure 3.
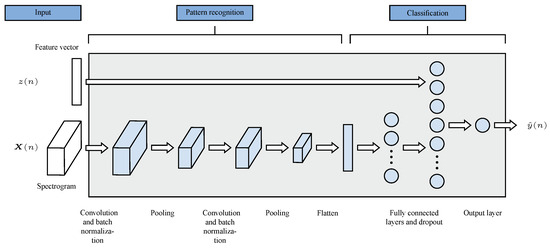
Figure 3.
Architecture of both CNN models.
The first layer of a CNN is typically a convolutional layer. Convolutional layers extract features from the image by sliding small filters called kernels across the image. Each kernel is specialized to detect a particular feature, such as edges, corners, or specific colors. A discrete convolution
of the input image V and the kernel K, which is taken as an M × N matrix, is calculated to obtain the resulting image S. The indices i and j correspond to the indices of the convolution and define the dimension I × J of the resulting image. This is processed with an element-wise activation function. The individual neurons fire when the kernel recognizes certain structures.
To reduce overfitting and improve the accuracy of the model we used batch normalization layers after each convolutional layer. The inputs of each layer are normalized so that they have a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one.
Pooling layers are key components of CNNs and are used for reducing the spatial dimensions of feature maps. This reduces the number of parameters for the following layers and speeds up the computation time. An image is processed section by section using a symmetrical matrix defined by the pooling size. There are two common pooling methods:
- Max-pooling: The pooling layer finds the maximum value in each matrix and transfers it to the downsampled output.
- Average-pooling: The pooling layer calculates the average of each matrix and transfers it to the downsampled output.
The patterns found are divided by the flatten layer in such way that they can be used as an input for fully connected layers. As illustrated in Figure 3, this layer serves as the interface between the pattern recognition and classification components. It transforms the output from the pattern recognition stage into a format suitable for classification tasks.
Fully connected layers are used to classify the patterns recognized from the input image by convolutional and pooling layers. This type of layer is also the basis for previously known ANN and consequently facilitate the processing of the additional feature vector. Any number of fully connected layers with different numbers of neurons can be used with different activation functions in a CNN for classification. The output layer is also a fully connected layer with only one neuron. In our model, a sigmoid activation function is used to produce a value between zero and one, which represents the probability of the input belonging to one of two classes.
To prevent overfitting, dropout layers are used. In this case, a defined number of neurons are randomly set to zero, and thus not considered further. This leads to a generalization of the model for future data. We used one dropout layer after the second fully connected layer.
To find the best parameters of both models, hyperparameter tuning was performed using the hyperband tuner from Keras [15]. The best parameters are summarized in Table 1. The following results were obtained with models trained with these parameters.

Table 1.
Used parameters for both models.
2.5.2. Data Augmentation
Data augmentation is a technique used to increase the amount of training data available for machine learning models by generating new examples from existing data. Data augmentation plays a crucial role in medical applications, particularly in the absence of a substantial collection of labeled data [14,16,17]. The aim is to improve the performance and robustness of the model by exposing it to a broader range of variation and by compensating strong imbalance in the available groups [18,19]. We have used this method to equalize the amount of training data per tremor type. Since many features are newly generated by data augmentation, especially for the control group, we have decided to use three different methods that are frequently used in the literature for time series [20] and also for the application of wearable sensors or inertial measurement units for classification of PD [16,17]:
- A white noise with a low amplitude of −30 dB is added to the time signal.
- The time signals are reversed in time. Here, it is assumed that it is irrelevant for the tremor classification whether the signal is viewed forwards or backwards.
- The individual frames of the time signal are reshuffled in the spectrogram. For this method, the most important assumption is that the time resolution of 0.64 s sufficiently represents short-term changes of the tremor and thus the resorting does not have a negative influence.
For each patient diagnosis, the data imbalance between the diagnosis being evaluated and the diagnosis with the most data is assessed. Up to three synthetic feature sets are generated for each patient. In each case, the synthetic features are subjected to all three types of data augmentation. If the data imbalance persists even after generating synthetic features, the model is trained with this.
We trained the first model using 331 data points, with 96 of them augmented. This creates a dataset of 203 pathological and 128 physiological subjects. For validation, we leverage 112 subjects, including 33 augmented examples. This translates to a validation set of 68 pathological and 44 physiological subjects. The second model was trained on 245 data points, with 42 of them being augmented. This results in a balanced dataset of 123 ET and 122 PD. For validation, we used a set of 80 data points, including 12 augmented versions. This process again yielded a balanced set: 40 subjects from patients with ET and 40 from patients with PD.
2.6. Statistical Methods
To assess the performance of various models, we employ the relative accuracy metric [7]. To ensure independence from the class distribution of the subjects, the correctly classified cases are normalized to the total number of cases belonging to that class. As a result, the relative accuracy measure remains unaffected by the class distribution of the subjects under consideration.
Moreover, we perform pairwise comparisons between different models trained under different conditions. To quantify the improvement, we employ the relative improvement metric. This metric measures the reduction in the remaining difference between the relative accuracy achieved by a model and the ideal accuracy of 100%. The relative improvement is expressed as a percentage and accordingly indicates the relative reduction of the remaining difference to the perfect accuracy.
We evaluate the overall accuracy of the classification model using relative accuracy. This measure indicates the proportion of correctly classified instances, considering all three classes (physiological, ET, PD). To further assess the performance of the model, we calculate specificity and sensitivity [21] with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using the exact Clopper–Pearson method [22]. These measures provide insights into the models ability to correctly identify true-negative and true-positive instances. Since our classification task involves three classes, we use an extension of the measures to a confusion matrix with three classes [23]. The sensitivity and specificity are thus calculated for one class each as a basis.
3. Results
To classify the results, we trained different models and compared them in terms of relative accuracy. For this purpose, we used 54 physiological tremors, 209 recordings from ET, and 130 from PD patients. The corresponding demographic data of these patients are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Demographic data of the patients.
We examined the models in respect to the influence of the methods of data augmentation and the use of the proposed additional features by calculating the relative improvement in comparison to a reference value resulting from models without the respective additions.
3.1. Influence of Data Augmentation on Classification Accuracy
For the training of the models we applied the above-mentioned three variants of data augmentation for the relevant features. In the first step a model was trained only on the basis of the available data without using additional synthetic data. Next, models were trained for which only one method of data augmentation was used in each case and additionally we trained models with different combinations of all three variants. For each method of data augmentation, we compared the relative improvement in mean relative accuracy resulting from ten different splits of training, validation, and test data. The mean value obtained without data augmentation was used as the baseline value in each case. The results are summarized in Table A1 (classifying physiological and pathological tremor) and in Table A2 (classifying ET and PD) in the Appendix A.
The clear advantage of data augmentation is evident when examining the overall accuracy achieved by both individual models in classifying all three classes. Utilizing solely the existing data for model training result in a relative accuracy of 76.88% for all three classes. However, when synthetic data are incorporated using all three methods of data augmentation described, the overall accuracy soars to 88.12%, representing a remarkable relative improvement of 51.38% in comparison to the accuracy of the model trained without data augmentation (76.88%).
3.2. Influence of Additional Features on Classification Accuracy
To investigate the effect of adding additional features for the classification of tremor, we evaluated the performance of two sets of models: one utilizing solely time-frequency analyses as the CNN image input and another incorporating additional features. To quantify the relative improvement in accuracy attributable to these features, we trained the CNN component individually and then a second model with additional features, calculating the corresponding accuracies. The results are summarized in Table 3 (classification of physiological and pathological tremor) and Table 4 (classification of ET and PD).

Table 3.
Influence of combining features and time–frequency analyses for the classification of physiological and pathological tremor.

Table 4.
Influence of combining features and time–frequency analyses for the classification of ET and PD.
A relative improvement of 67.62% to a mean relative accuracy of 95.94% can be achieved for the classification between physiological and pathological tremor (Table 3). Within the 10 tested splits, a maximum relative accuracy of 97.79% is obtained.
The mean relative accuracy for the classification between PD and ET (Table 4) with additional features is significantly lower (69.83%). Nevertheless, a substantial relative improvement of 38.91% is also evident for the network with using additional features. Since the accuracy for the network without additional features is on average about 50% for two classes, we assume that a classification for the two pathological tremors is not possible with the help of a pure CNN based on the time-frequency analyses. An accuracy of approximately 50% indicates a purely random classification. Therefore, we assume that the relative improvement of the network with the features is mainly based on these. For this reason, we trained a pure ANN for this case, which has the following architecture after hyperparameter tuning:
- Input layer.
- Dense layer: 512 neurons, activation function: Hyperbolic tangent.
- Dropout layer: 0.469 dropout rate.
- Dense layer: 256 neurons, activation function: Rectified Linear Unit.
- Dense layer: 128 neurons, activation function: Rectified Linear Unit.
- Output layer: 1 neuron, activation function: Sigmoid.
For this network, this results in an average mean accuracy of 67.73% and thus a relative improvement of 34.66%. A similarly high relative accuracy is achievable compared to that of the CNN-feature combination. However, the latter exhibits a higher mean accuracy by 2.10%, which is why it is considered further in the following.
Considering the overall relative accuracy of both models and the classification of all three classes, we achieve 63.43% without additional features and 88.12% with the CNN-feature combination, corresponding to a relative improvement of 67.51%.
3.3. Evaluation
By combining all three data augmentation methods and using the CNN-feature combination for both partial models of our two-stage approach, we achieved an overall accuracy of 88.12%. The corresponding accuracy and loss curves are shown in Figure 4. Figure 4a,b depict the performance for classifying physiological and pathological tremor, while Figure 4c,d show the results for ET and PD classification. In each subfigure, the mean values are presented with a confidence interval indicating the standard deviation.
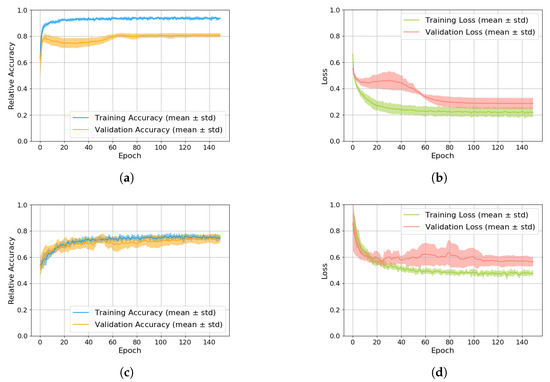
Figure 4.
Accuracy and loss curves of the training processes. (a) Accuracy of training and validation for the model classifying physiological and pathological tremor. (b) Loss of training and validation for the model classifying physiological and pathological tremor. (c) Accuracy of training and validation for the model classifying ET and PD. (d) Loss of training and validation for the model classifying ET and PD.
The upper subfigures (Figure 4a,b) reveal high accuracy and low loss for physiological and pathological tremor classification, with a hint of overfitting. However, the high test accuracy (97.06%) justifies the use of this model despite the overfitting. In contrast, the lower subfigures (Figure 4c,d) for ET and PD classification show significantly lower accuracy and higher loss, suggesting greater difficulty in distinguishing these tremor types. These accuracy and loss curves show no signs of overfitting.
The resulting confusion matrix with absolute values is shown in Figure 5. The confusion matrix shows the number of subjects that were correctly and incorrectly classified for each tremor type. The difference in the number of subjects per diagnosis becomes clear. Therefore, we have normalized the values per class for the calculation of the overall accuracy and thus calculated a relative accuracy.
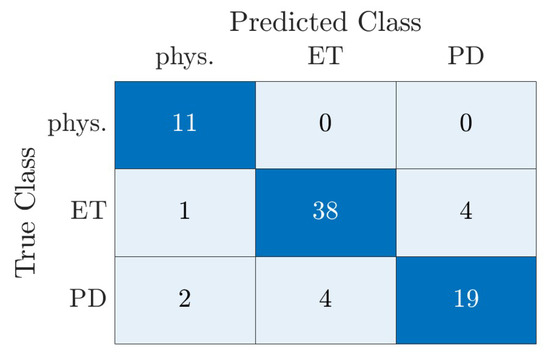
Figure 5.
Confusion matrix of the classification of all three classes by the two-stage model using real test data of the dataset. There was no data augmentation used for the results shown in this figure.
The values of sensitivity and specificity for the overall classification model are summarized in Table 5. The classification model demonstrates excellent performance in distinguishing between physiological and pathological tremor, achieving a specificity of 95.59% (95%-CI: 87.64% to 99.08%) and a sensitivity of 100 % (95%-CI: 71.51% to 100%). This indicates that the model accurately identifies 100% of physiological tremor cases and 95.59 % of pathological tremor cases.

Table 5.
Values of sensitivity and specificity for the overall classification model.
The model also performs well in distinguishing between ET and the other two tremor types with a sensitivity of 88.37% and a specificity of 88.89 %. This suggests that the model correctly identified 88.37% of ET cases. The remaining 11.63% are classified incorrectly. The lowest classification accuracy is observed for PD. In this case, only 76% of the cases are correctly classified. This is also evident in the low sensitivity of 76.0% for PD to physiological tremor and ET.
4. Discussion
In this study, we have investigated the discriminative value of various trained models in distinguishing between distinct tremor types. To achieve this, we analyzed various data augmentation techniques and network architectures, incorporating additional features selected from a clinical perspective. Both data augmentation and the enhanced architecture results in improved accuracy. Notably, the separation of physiological and pathological tremor appears to be possible.
4.1. Influence of Data Augmentation on Classification Accuracy
To explore the impact of data augmentation on the performance of various networks, we first examined the extent to which the three data augmentation techniques enhance performance in comparison to training without data augmentation. We used data augmentation techniques that have been shown to be effective for time series data [20] and classification of PD [16,17]. Other data augmentation methods that are commonly used for CNNs and image processing, such as rotation or scaling [24], are not applicable to spectrograms. As a second step, we evaluated the performance of the trained networks on both real and synthetic data. We tested the trained networks on both the real test dataset and synthetic data generated using the same data augmentation techniques that were used to train the models.
For the classification of physiological and pathological tremor, depending on the type of data augmentation, there is a relative improvement of 62.52% to 86.69% possible. All three types individually bring a big improvement, but the combination of all three methods is best with an average accuracy of 95.94%. For this case of classification, there is a particularly high improvement because previously the ratio of subjects with physiological and pathological tremor in the dataset is very unbalanced. Overall, the dataset contains 54 subjects with physiological and 339 with pathological tremor. Compensating for this difference using synthetic data leads to the high relative improvement.
For the classification of ET and PD there is a significantly worse relative improvement of 3.89% to 12.84%. The classification between the two pathological ones is generally more difficult, as evidenced by the low accuracy, since the features of ET and PD overlap [4,7]. The ratio of PD to ET patients in the dataset is with 40% subjects with PD to 60% with ET significantly more balanced than before for physiological to pathological tremor. Adding synthetic data results in a small relative improvement due to balancing the dataset. However, these small changes in the features are not enough to generalize the model more and thus achieve significant better accuracy.
4.2. Influence of Additional Features on Classification Accuracy
We decided to train models that process a combination of spectrograms and individually extracted features as inputs. For this purpose, we employed relevant features that are crucial for clinical diagnosis. An absent amplitude, reflected in lower intensity, indicates a physiological tremor [4]. An asymmetrical tremor is characteristic of PD [1]. Based on the model of a physiological tremor, a frequency difference between the peak frequency in the holding position with and without additional weight indicates a physiological tremor [11,25]. We did not use more clinical features because we are limited in the number of trainable parameters due to the small amount of data.
Combining spectrograms and individually extracted features enhances the performance of both partial models of the two-stage overall model. For the classification between physiological and pathological tremor, this approach achieved a relative improvement of approximately 70% compared to a CNN trained only with spectrograms. Utilizing these clinically relevant features results in a significant improvement in the accuracy of classification.
The relative accuracy is substantially enhanced by combining the CNN with additional features for the classification between ET and PD. A CNN trained solely on spectrograms demonstrates an average accuracy approximately 50%, rendering it ineffective for classifying two classes. However, incorporating the features increases the accuracy to 69.83%, demonstrating the crucial role of these 11 features. To assess the impact of the features alone, we trained an ANN using only these features as input and achieved comparable accuracy with 67.73%. Minor variations may arise due to data partition into three subsets or random initialization of network parameters. Given the higher overall accuracy of the CNN-feature combination, we have opted to utilize this network for further analysis. Nevertheless, the classification based solely on features has proven to be effective.
4.3. Evaluation of the Overall Accuracy
Employing the trained models and the two-stage approach, we attained an overall accuracy of 88.12% for the classification of the three tremor types. Notably, physiological tremor exhibits exceptional classification accuracy, with 100% correctly identified. ET, the most prevalent tremor type in the dataset, achieves a classification accuracy of 88.37%. PD, while exhibiting the lowest classification accuracy of 76%, still demonstrates a satisfactory performance. It is important to consider how pathological cases that are falsely classified as physiological by the first model in the first stage are handled in the second model. These false negatives from the first stage are excluded from the second classification between ET and PD. Fortunately, the high accuracy of the first model in classifying physiological and pathological cases means that the number of false negatives is very low. For the test data used in our study, this exclusion did not affect the classification of any patient. However, it is important to consider when applying the model to new data.
Future research should delve into the underlying reasons behind misclassification cases. The distinction between physiological and pathological tremor is achieved with remarkable accuracy. Investigating why certain pathological tremors are misclassified as physiological is a crucial area of future research. Determining whether these misclassifications represent borderline cases or inaccuracies in clinical diagnoses is essential.
It is possible to distinguish between physiological and pathological tremor with single features only. Our preliminary studies utilizing frequency difference demonstrated superior differentiation of physiological tremors, achieving an accuracy of 98.8% [7]. Examining individual features yields a high level of accuracy in differentiating between physiological and pathological tremor. However, machine learning algorithms empowers us to further enhance the distinction of physiological and pathological cases, achieving an accuracy of almost 100%.
Previous studies utilizing machine learning approaches have achieved an accuracy of 87.5% [26] or 85.7% [27] in distinguishing ET from PD, even with a substantially smaller dataset. Employing a significantly larger dataset, we attain a comparable level of accuracy. While a larger dataset enhances model training, it also introduces the challenge of identifying and handling more complex or more difficult-to-diagnose cases.
We should also consider if the demographic characteristics of this larger dataset, particularly age and sex distribution, are similar across the diagnostic groups in our study. Table 2 reveals a significantly younger age group for physiological tremor subjects compared to other diagnoses. Additionally, there are more females with physiological tremor compared to ET and PD. Large-cohort data show minor amplitude and frequency variations between various cohorts, including those differentiated by gender and age [28] but these are minor when compared with pathological data such as essential or Parkinsonian tremor. Therefore, comparisons of normal and patient data are usually not controlled for age or sex.
Our preliminary work demonstrated the effectiveness of combining a decision tree with a neural network, achieving an accuracy of 85.76% [7]. The two-stage CNN-feature combination approach yielded a relative improvement of 16.75%. Maintaining our prior achievement of 100% accuracy in classifying physiological cases, the approach specifically enhanced the distinction between ET and PD.
Different studies have shown that clinical diagnoses of PD are not always accurate, with only about 76% of cases being correctly diagnosed in the 1990s [29]. A study in 2001 found that the accuracy rate had improved to 90% [30], and a review in 2016 found that the misdiagnosis rate for PD had not changed significantly between 1988 and 2014 [31]. In our study, we found that 76% of the PD cases were classified correctly. However, our focus was not only on the classification of PD but also on achieving the best possible overall accuracy in the classification of all three types of tremor. The overall accuracy of our model was 88.12%, which is close to the 90% accuracy reported in the 2001 study. It is important to note that our models were trained based on a certain number of misdiagnoses, and we cannot currently compare the results of our study with the real diagnoses that only can be verified after the patient’s death.
The results of this study suggest that this model can be used to classify the three tremor types mentioned with high accuracy. However, this study has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. One limitation is that the study was only conducted on a small dataset of subjects with a limited range of tremor types for the requirements of machine learning training. The small dataset limits the ability to train deep learning models with many parameters. However, our dataset is large compared to other tremor or general medical applications. Future studies should be conducted with larger datasets of subjects with a wider range of tremor types, including those associated with different diseases. Another limitation is that the study only used acceleration data from one axis. This limits the ability to capture the full complexity of tremor. Future studies should investigate the use of acceleration data from multiple axes, as well as data from other sensors, such as electromyography (EMG). EMG data could potentially provide additional information that could be used to improve classification accuracy. Finally, we did not test the results on an independent dataset. This could have introduced bias into the results. To validate the generalizability of the results, future studies should evaluate the model’s performance on an independent dataset. This will help ensure that the high classification accuracy observed in the current study is not solely due to overfitting. Addressing these limitations could lead to the development of machine learning-based tremor-classification systems that are more accurate, reliable, and generalizable.
5. Conclusions and Outlook
This study investigated the effectiveness of a two-stage model in distinguishing between different tremor types. Utilizing various data augmentation techniques, a CNN–feature combination with selected clinical features, the study demonstrated the ability to differentiate between physiological, ET, and PD tremor with a high degree of relative diagnostic accuracy. These findings suggest that appropriate classification methods can effectively reduce misdiagnoses among different tremor types.
The proposed approach has exhibited promising outcomes in improving the accuracy of tremor diagnosis. However, there remains substantial scope for further development. Future research should investigate the potential for extending and modifying network architectures. Therefore, the consistent augmentation of data resources is crucial to enable the training of networks with more adjustable parameters, resulting in even higher classification results.
To not only supplement clinical diagnosis with the output of a trained model but also to cultivate a deeper understanding of the underlying decision-making process, explainable AI techniques can be employed [32]. This type of analysis provides insights into the features that influenced a trained network’s decision, empowering clinicians to better interpret the model’s recommendations and potentially identify patterns that may not be readily apparent from conventional diagnostic methods.
By pursing these avenues of research, the integration of deep learning into clinical practice can be further refined, leading to more accurate and data-driven diagnostic decisions, potentially improving patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.W., G.K., G.D. and G.S.; methodology, P.W. and P.D.S.; software, P.W. and P.D.S.; formal analysis, P.W. and P.D.S.; resources, G.K. and G.D.; writing—original draft preparation, P.W.; writing—review and editing, G.K., G.D. and G.S.; visualization, P.W.; supervision, G.K., G.D. and G.S.; project administration, G.K., G.D. and G.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The research related to human use has complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies, and in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the author’s Institutional Review Board or equivalent committee (Ethikkommission der Medizinischen Fakultät der Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| ET | Essential tremor |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| KiRAT | Kiel Real-time Application Toolkit |
| las | Less-affected side |
| mas | More-affected side |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| Relu | Rectified linear unit |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| Tanh | Hyperbolic tangent |
Appendix A. Influence of Data Augmentation on Classification Accuracy
The mean relative accuracy without data augmentation for the classification between physiological and pathological tremor is 69.50% (Table A1). Combining all three data augmentation methods improves the mean relative accuracy from 69.50% to 95.94% (a relative improvement of 86.69%). Each individual method improves the relative accuracy by between 62.52% and 71.21%, but inverting the time axis of the spectrogram achieves an accuracy that is almost identical to the accuracy of the model that was trained with all three methods. The combination of reversing and mixing results in a relative improvement of 72.82% and thus just the highest relative accuracy with 91.71% apart from the combination of all three methods.

Table A1.
Influence of data augmentation on the classification of physiological and pathological tremor.
Table A1.
Influence of data augmentation on the classification of physiological and pathological tremor.
| Training Conditions | Mean Accuracy (10 Splits) | Relative Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| No data augmentation | 69.50% | Reference value |
| Reverse time signals in time | 91.22% | 71.21% |
| Mix individual frames | 88.57% | 62.52% |
| Add noise | 89.93% | 66.98% |
| Combine reverse and mix | 91.71% | 72.82% |
| Combine all data augmentation methods | 95.94% | 86.69% |
The reference value for the classification between ET and PD (Table A2) is with 68.61% lower than for the classification between physiological and pathological tremor. Combining all three data augmentation methods only improves the mean relative accuracy to 69.83% with a relative improvement of 3.89%. Randomly mixing the frames of the signal achieves the best mean accuracy (72.64%) of the three individually analyzed data augmentation methods, with a relative improvement of 12.84%. Adding noise actually reduces the mean accuracy by 8.79%. If we combine reversion and mixing, we get an accuracy of 71.29% that is almost as high as if we use all three methods of data augmentation.

Table A2.
Influence of data augmentation on the classification of ET and PD.
Table A2.
Influence of data augmentation on the classification of ET and PD.
| Training Conditions | Mean Accuracy (10 Splits) | Relative Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| No data augmentation | 68.61% | Reference value |
| Reverse time signals in time | 70.86% | 7.17% |
| Mix individual frames | 72.64% | 12.84% |
| Add noise | 65.84% | −8.79% |
| Combine reverse and mix | 71.29% | 8.54% |
| Combine all data augmentation methods | 69.83% | 3.89% |
Combining all three data augmentation methods to train a model for classifying physiological and pathological tremor (Table A3) resulted in a 1.39% lower accuracy for synthetic data compared to the original data. The differences were even smaller for the methods of reversed time signals and mixed frames. Only the added noise exhibited a substantial difference between the test data types, with a reduction of 12.4%. The trained model achieved a significantly lower accuracy of just 77.53% for synthetic data generated with added noise. Since the absolute difference for the added noise is the highest by far, we also tested the combination of reversing and mixing. These two methods combined resulted in the highest test accuracy and the difference of 0.16% is negligibly small.

Table A3.
Test of the trained model for physiological and pathological tremor with real and synthetic data.
Table A3.
Test of the trained model for physiological and pathological tremor with real and synthetic data.
| Training Conditions | Mean Accuracy Real Test Data | Mean Accuracy Synthetic Data | Absolute Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse time signals in time | 91.22% | 90.92% | −0.30% |
| Mix individual frames | 88.57% | 89.33% | 0.76% |
| Add noise | 89.93% | 77.53% | −12.40% |
| Combine reverse and mix | 91.71% | 91.87% | 0.16% |
| Combine all data augmentation methods | 95.94% | 94.55% | −1.39% |
We also achieved similar results for the classification of ET and PD (Table A4). The added noise generates a difference in the achieved accuracies of −8.53%. The difference for the other two variants, viewed individually, is very small and the difference for all three methods with a difference of −1.07% is also lower. Also for the classification of ET and PD, the difference achieved between real and synthetic test data is highest for the added noise. When we combine the other two methods, there is a small difference of 0.18%.

Table A4.
Test of the trained model for ET and PD with real and synthetic data.
Table A4.
Test of the trained model for ET and PD with real and synthetic data.
| Training Conditions | Mean Accuracy Real Test Data | Mean Accuracy Synthetic Data | Absolute Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse time signals in time | 70.86% | 70.86% | 0% |
| Mix individual frames | 72.64% | 72.37% | −0.27% |
| Add noise | 65.84% | 57.31% | −8.53% |
| Combine reverse and mix | 71.29% | 71.47% | 0.18% |
| Combine all data augmentation methods | 69.83% | 68.76% | −1.07% |
References
- Bhatia, K.P.; Bain, P.; Bajaj, N.; Elble, R.J.; Hallett, M.; Louis, E.D.; Raethjen, J.; Stamelou, M.; Testa, C.M.; Deuschl, G.; et al. Consensus Statement on the classification of tremors. from the task force on tremor of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2018, 33, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubenberger, D.; Hallett, M. Essential tremor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuschl, G.; Bain, P.; Brin, M. Consensus statement of the Movement Disorder Society on tremor: Ad Hoc Scientific Committee. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 1998, 13, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakoor, R.; Ladhak, F.; Nazi, A.; Huber, M. Using deep learning to enhance cancer diagnosis and classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–19 June; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 28, pp. 3937–3949. [Google Scholar]
- Shoeb, A.H. Application of Machine Learning to Epileptic Seizure Onset Detection and Treatment. Doctoral Thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Piepjohn, P.; Bald, C.; Kuhlenbäumer, G.; Becktepe, J.S.; Deuschl, G.; Schmidt, G. Real-time classification of movement patterns of tremor patients. Biomed. Tech. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 67, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real-Time Framework. Available online: https://www.dss-kiel.de/index.php/research/realtime-framework (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Digital Signal Processing and System Theory. Available online: https://www.dss-kiel.de/ (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Daneault, J.-F.; Carignan, B.; Codère, C.É.; Sadikot, A.F.; Duval, C. Using a Smart Phone as a Standalone Platform for Detection and Monitoring of Pathological Tremors. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, M. Overview of Human Tremor Physiology. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 1998, 13, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keras. Available online: https://keras.io/ (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.06576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.I.; Santella, A.; Bao, Z. Cellular structure image classification with small targeted training samples. IEEE Access Pract. Innov. Open Solut. 2019, 7, 148967–148974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyperband Tuner. Available online: https://keras.io/api/keras_tuner/tuners/hyperband/ (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Um, T.T.; Pfister, F.M.J.; Pichler, D.; Endo, S.; Lang, M.; Hirche, S.; Fietzek, U.; Kulić, D. Data Augmentation of Wearable Sensor Data for Parkinson’s Disease Monitoring using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (ICMI ’17), Glasgow, UK, 13–17 November 2017; pp. 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Uchitomi, H.; Ming, X.; Zhao, C.; Ogata, T.; Miyake, Y. Classification of mild Parkinson’s disease: Data augmentation of time-series gait data obtained via inertial measurement units. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, M.; Kaufhold, M.-A.; Reuter, C. A Survey on Data Augmentation for Text Classification. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.; Song, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, H. Time Series Data Augmentation for Deep Learning: A Survey. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–26 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Trevethan, R. Sensitivity, Specificity, and Predictive Values: Foundations, Pliabilities, and Pitfalls in Research and Practice. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 2296–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clopper, C.J.; Pearson, E.S. The Use of Confidence or Fiducial Limits Illustrated in the Case of the Binomial. Biometrika 1934, 26, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy Amin, M. Confusion Matrix in Three-class Classification Problems: A Step-by-Step Tutorial. J. Eng. Res. 2023, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharana, K.; Mondal, S.; Nemade, B. A review: Data pre-processing and data augmentation techniques. Glob. Transit. Proc. 2022, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elble, R.J.; Randall, J.E. Mechanistic components of normal hand tremor. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1978, 44, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, A. A neural network approach for feature extraction and discrimination between Parkinsonian tremor and essential tremor. Technol. Health Care Off. J. Eur. Soc. Eng. Med. 2013, 21, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, P.M.; Serackis, A.; Griskevicius, J. Support vector machine classification of Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor and healthy control subjects based on upper extremity motion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Biotechnology, Macau, China, 28–30 May 2012; pp. 900–904. [Google Scholar]
- Elble, R.J. Characteristics of physiologic tremor in young and elderly adults. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurgery Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Lees, A.J. Improved accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Lewy body Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 2001, 57, 1497–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, G.; Copetti, M.; Arcuti, S.; Martino, D.; Fontana, A.; Logroscino, G. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2016, 86, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, D.; Aha, D. DARPA’s Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) Program. AI Mag. 2019, 40, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).