Abstract
Information from social networks is currently being widely used in many application domains, although in the music recommendation area, its use is less common because of the limited availability of social data. However, most streaming platforms allow for establishing relationships between users that can be leveraged to address some drawbacks of recommender systems. In this work, we take advantage of the social network structure to improve recommendations for users with unusual preferences and new users, thus dealing with the gray-sheep and cold-start problems, respectively. Since collaborative filtering methods base the recommendations for a given user on the preferences of his/her most similar users, the scarcity of users with similar tastes to the gray-sheep users and the unawareness of the preferences of the new users usually lead to bad recommendations. These general problems of recommender systems are worsened in the music domain, where the popularity bias drawback is also present. In order to address these problems, we propose a user similarity metric based on the network structure as well as on user ratings. This metric significantly improves the recommendation reliability in those scenarios by capturing both homophily effects in implicit communities of users in the network and user similarity in terms of preferences.
1. Introduction
1.1. Context and Objectives of the Work
Recommender systems have become indispensable on streaming music platforms due to the enormous amount of content they make available to users. These systems help users find items that match their preferences, although they often fail due to the numerous problems that the recommendation methods must address. Collaborative Filtering (CF) is the most extended approach due to its simplicity and good performance [1,2]. However, it has some shortcomings, such as the gray sheep that prevents it from providing reliable recommendations to users with uncommon tastes. This is due to the difficulty of finding neighbors who are users similar to them in terms of item preferences since the recommendations for a given user are based on the ratings given to items by his/her neighbors. In neighborhood-based methods, two users are only considered neighbors if they have rated common items similarly, which limits the number of potentially recommendable items, especially in the gray-sheep scenario. This problem is aggravated by the popularity bias present in the music domain due to the power law distribution of the listening frequencies of musical items. In this type of distribution, also known as long tail, there are few items with high listening frequencies, while the vast majority, those located in the long tail, have low listening frequencies. Indeed, the latter are the ones preferred by gray-sheep users. Another major drawback, called cold start, occurs with users who have few ratings. They are generally users who have recently joined the system. The absence or scarcity of ratings also prevents finding similar users; therefore, another problem analogous to gray sheep arises.
The usual way to tackle these problems is to resort to content-based methods [3], which make use of item attributes to recommend items similar to those previously consumed or rated by the user. However, some hybrid approaches have also been proposed in the literature [4,5] since content-based methods provide worse results than collaborative filtering. Music attributes that have been used in content-based or hybrid methods are mainly either low-level audio features [6,7] or metadata associated with artists or songs, such as genre, year, or tags [8].
In recent years, research has been conducted into ways of exploiting social information to improve recommender systems. The value of information obtained from social networks in multiple domains is indisputable. Data about relationships, opinions, events, policies, etc., are used to find patterns related to user behaviors or trends, among others, which are of potential interest in many areas. Some of the most used techniques in this environment are sentiment analysis, as well as the study of the structure of networks, the propagation of information, and temporal dynamics [9].
In the area of recommender systems, social tags, relationships between users, opinions, etc., are being used as feedback to address various problems in these systems and thus increase the reliability of recommendations [10,11,12,13,14]. The main drawback in the music domain is that this information is not always available. However, most streaming platforms allow friendship relationships to be established between users, and this social structure could be used to capture effects such as social influence or homophily, which can be useful for predicting user preferences. There are many graph-based measures that have been used to infer social influence. Some of them can be obtained from undirected graphs, but most of them require directed graphs. This is so in the case of the well-known centrality metrics based on betweenness, page rank, or HITS [15]. Nevertheless, homophily is inferred by structural metrics of undirected graphs. Homophily in the context of social networks is defined as the similarity between users who share tastes and interests. It can be said that these similar users are part of the communities, which are implicit because users are not aware of belonging to such communities. This is different from belonging to groups in social networks since users have joined voluntarily. The detection of implicit communities in social networks has been widely studied due to interest in multiple application domains. In the field of recommender systems, it can be used to find users who share preferences on certain items. Specifically, regarding the objective of this work, it can help to detect users with similar preferences to those of users with unusual tastes, helping to alleviate the gray sheep problem and those of users with few ratings, contributing to mitigating the cold-start problem. Some measures on the social network graph, such as Jaccard’s or structural equivalence, can be used to detect both implicit communities and affinity or homophily between users. Both metrics are based on determining the intersection between users’ neighborhoods.
It is, therefore, an interesting feature to explore in the area of recommender systems since the objective of these systems is to predict user preferences and interests. For this reason, this paper focuses on investigating how to infer and exploit homophily to improve recommendations.
Although information from social relations has recently been widely exploited in recommender systems [16], there are very few papers in the literature that propose recommendation methods using homophily derived from social networks [17,18].
Recent research is moving toward the application of deep learning algorithms and Graph Neural Networks (GNN) [19], which provide good results when the volume of data is very large since they are endowed with a great ability to extract the complex relationships between users and items from large datasets. However, the target scenarios of this work are precisely those in which there is a scarcity of data, such as users with unusual tastes (gray sheep) as well as users with few interactions with the items (cold start). Furthermore, such methods, especially those based on GNN, are more prone to bias and unfairness [20], which is desirable to avoid, as discussed in the next subsection.
In this work, the social network structure is used to derive similarity metrics between users and aims to minimize gray-sheep and cold-start problems. The main contributions of this work are the following:
- The proposal of a graph-based and rating-based user similarity metric derived from the social network structure that captures homophily between users as well as user similarity in terms of preferences.
- The integration of this similarity metric into a user-based collaborative filtering approach that significantly improves the reliability of recommendations in the context of cold-start and gray-sheep problems.
One of the aspects to point out in the proposed method derives from the fact that it does not require much information from social networks but only the relationships between users. This represents an advantage in music recommender systems, where this is usually the only social network information available. As discussed above, it does not require large volumes of data to produce reliable models, especially in the case under study, which is aimed at improving gray-sheep and cold-start problems. Finally, it should be noted that, as it is a method based on distances, the computational complexity is lower than most of the methods proposed in the literature. This point is analyzed in more detail in Section 5.
1.2. Privacy and Ethical Considerations
An important aspect of Artificial Intelligence (AI) models, which has long been overlooked, is to preserve trust and individuals’ rights, particularly in the context of user data and social networks. To this end, it is crucial that they comply with the privacy standards and ethical considerations that are the subject of some international regulations [21].
There are several fronts on which action can be taken to achieve this purpose [22]. One fundamental aspect is implementing robust data anonymization techniques to protect user identities and sensitive information. Additionally, employing differential privacy mechanisms helps prevent the extraction of individual-level insights from aggregated datasets and strikes a balance between data utility and privacy preservation. Transparency and accountability are also paramount in AI systems operating within software applications. Providing users with clear explanations regarding how their data is collected, processed, and utilized fosters transparency and empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their online activities. Vulnerabilities and security risks of AI systems can also lead to unfair and biased decision-making [23] by adversarial attacks that alter AI models or by manipulating training data.
Recommender systems constitute one of the areas likely to be affected by the problems mentioned above due to their extensive incorporation in applications in multiple domains and their great popularization in society, where users usually base their decision-making on the personalized suggestions that these systems offer them [21,24]. This drawback can be aggravated when information from social networks is used in which individuals and their relationships are the kernel. Therefore, it is a key issue in the field of recommender systems, networks, and other social media to implement robust mechanisms to preserve your privacy and other ethical issues [21,23].
The data used in our study are anonymized to protect user privacy while containing valuable user interaction data. By stripping identifying details, user behavior can be analyzed without compromising individual privacy, given that it is highly unlikely to be able to identify individuals based on their listening habits. In addition, the lack of sensitive attributes mitigates potential discrimination against certain protected groups. By omitting variables related to sensitive features such as race, gender, religion, or sexual orientation, it promotes a more equitable and unbiased analysis environment in which preferences are not based on the characteristics of these groups, often in the case of minorities. In this way, we avoid providing them with recommendations that are less reliable than those of the majority groups; rather, they are more generalizable and independent of sensitive characteristics. In addition, proposing a method that improves the recommendations of users with unusual tastes or low ratings is in itself a way to minimize the bias of recommender systems.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. We first discuss the most relevant related work. The proposed approach is presented in Section 3. Datasets and experimental studies are described in Section 4, which also includes the results. Section 5 presents the discussion, and the last section is devoted to the conclusions.
2. Related Work
Addressing the widely known problems of recommender systems to improve recommendations has been the subject of intensive research for quite some time. We have pointed out in the previous section some of the classic ways of dealing with the problems that are the subject of this work and their main drawbacks. More recent works focus on incorporating social information to address a wide variety of issues that affect the quality of recommendations [25] or resort to newer techniques such as GNN-based methods [19,26], which are also not without weaknesses.
In these studies, we can find the use of very different information from social networks [16]. Social relationships are used jointly with user-items interaction in a method based on matrix factorization [27]. A similar approach, using social relations and matrix factorization, is proposed in [28], where the information dissemination method is used to group users into communities. Social information and item features are used in a matrix factorization-based method [25] to build a user-similarity network and an item-similarity network. Other studies make use of other types of social information that are difficult to obtain or not available in most recommendation systems, such as the location of users [29].
Users’ trust in the opinions of others is another class of social information used in a broad set of recommendation methods [30,31]. However, these methods require users to explicitly express both their trust and their opinions about the items. Thus, the approach is totally different from the methods discussed above and the objective of this paper, where only the structure of the social network is taken into account. From such a structure, the homophily feature can be derived and considered in the recommendation methods to improve the results. One of these proposals is presented in [17], where this feature is obtained from the membership of users in social communities, and it is used in conjunction with other factors in a method for recommending tourist attractions. In the context of music recommendation, we can mention a work [18] that analyzes factors influencing music listening homophily, among which are social information and user demographic attributes. In addition, in [12], social influence and homophily are extracted from social networks and used to expand the neighborhood in k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN)-based CF recommendation methods.
Interest in GGN-based methods has grown in recent years. These can simply make use of user-item interactions, although they usually also require attributes of both users and items and some of their social information. Among the latter are hybrid proposals that combine GNN with other techniques, such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) [32] or clustering [33]. Other proposals involve different types of social data with additional information [34], including information from multiple sources [35]. None of the methods described above are specifically aimed at treating cold-start and gray-sheep problems.
The cold-start problem has been extensively discussed in the literature [36], where there are multiple proposals, mostly content-based, although some of them also exploit information from social networks [37]. Social tags are the data used in cross-system user modeling to deal with the cold-start drawback [38]. Social interests, social influence, and user preferences are utilized with the same purpose in [39]. Trust networks are the base of a method to compute user reputation and generate recommendations for new users in the system [40]. Many studies have resorted to social trust information to solve this problem [41,42,43]. All these proposals require specific information that is not present in most recommender systems, especially music recommender systems.
Fewer papers address the problem of providing reliable recommendations to users with unusual tastes (gray sheep) [44]. Content-based or hybrid methods, together with clustering methods, are the most classical options to address this problem, as well as cold start [45]. In this context, social networks have also been a source of data to identify these types of users and predict their preferences [46], but there are hardly any studies based on this information specifically aimed at treating this case [44].
Our proposal, described in the following section, is specifically focused on both problems that are jointly improved.
3. Materials and Methods
This section presents the proposed recommendation method, which incorporates the hybrid similarity measure based on social network structure and ratings. The purpose of this measure is to jointly capture the effect of homophily between users and their similarity in terms of music listening preferences.
3.1. Rating-Social Hybrid Similarity
Similarity measures in social networks are often used in the detection of implicit communities, i.e., communities formed by users who share interests but whose members are not aware of their membership in that community. Users belonging to the same community can be considered similar because they have common hobbies, preferences, etc. Homophily is based precisely on these shared facets. Similarity of connected users in social networks can be obtained from the network structure or from the user-generated content. Unfortunately, the last information is not usually available in recommender systems, and similarity between users must be computed from the former. Additionally, most of the networks included in the streaming platforms are formed only by friendship relations between users, and therefore, they are represented by undirected graphs. Consequently, the proposed measure must conform to the above restrictions.
Let us consider a graph representing the network, where is the set of vertices corresponding to users and the set of undirected edges corresponding to relationships between users. It is possible to identify in the network implicit communities () of related users.
Identification of implicit communities can be performed using either group-based or member-based algorithms. The first group makes use of the density of interactions among their members, while the second group examines the characteristics of the members. The latter approach is the most appropriate for our work since the objective is to detect affinities between users. Algorithms in this category analyze node characteristics such as degree, accessibility, similarity, etc. For the reason mentioned above, similarity is the most suitable for our purposes.
There are two main similarity metrics between two nodes in a network that can be derived from the structure of connections: structural equivalence and regular equivalence [47]. Users with high similarity according to these metrics will belong to the same implicit community and thereby share interests.
Let be the set of vertex of the network representing users, and the adjacency matrix where if there is a direct connection between vertex and vertex , and otherwise.
Structural equivalence (SE) between two vertices and is defined in terms of their respective neighbors and , where is the set of vertices directly linked to vertex . Therefore, Equation (2) can be used as an absolute measure of structural equivalence:
There are some relative measures that consider the size of both neighborhoods besides their shared vertices. Jaccard is one of these metrics that provide similarity values in the range [0, 1]. It is defined by Equation (3).
Since the similarity measures extracted from the social network structure are to be used as measures of similarity between users in collaborative filtering methods, it may be important not only to measure the size of the intersection of neighborhoods but also the similarity between those neighborhoods. For this, we resort to regular equivalence [48], defined by Equation (4).
In the context of recommender systems, it would be more convenient to measure the similarity between neighborhoods based on the ratings given to the items by the users rather than on the structure of the network. Therefore, we propose to replace the term in Equation (4) with a similarity measure based on ratings. In this way, the metric is no longer recursive. In other application domains, similarity based on ratings can be replaced by another measure of similarity relative to the domain. The new Hybrid Regular Equivalence (HRE) metric based on ratings is defined as follows.
where is the similarity between users that is computed from the ratings they give to items by means of any similarity metric. In this equation, α has been eliminated since similarity values will only be used comparatively, as we will see in the next subsection.
Among the variety of metrics used to compute similarity between users from ratings, cosine is the most extended. For two given users, and , it can be computed by using Equation (6), where and are the vectors containing the ratings given to items by users and , respectively.
Structural equivalence and hybrid regular equivalence based on ratings are combined in a hybrid measure of user similarity that we call rating-social hybrid similarity (RSH_sim), which will be incorporated into the CF recommendation method. Equation (7) is used to compute it.
This hybrid metric encloses both user similarity based on preferences and user homophily induced by the social network structure.
3.2. RSH-Based User k-NN Collaborative Filtering Approach
Collaborative filtering methods base the recommendations on the similarity between users regarding their preferences. Our approach also considers homophily in social networks since this effect occurs when users share interests. It is therefore expected that homophily will be useful, in addition to the ratings, to find users with similar preferences. This is particularly important in two recommendation scenarios: black sheep and cold start. In the first case, it is difficult to find users similar to gray-sheep users because they have unusual tastes, and in the second case, it is because new users have very few ratings on items. In these scenarios, we use the social network structure to identify similar users on which to base recommendations.
The set of m users represented by the vertices of the social network graph have rated a subset of the set of n items . The user receiving the recommendation, called the active user , can receive suggestions for items that he/she has not rated.
The prediction of the rate that the active user would give to an item is based on the ratings that the users most similar to (the nearest neighbors) give to item according to the Equation (8). The rating-social hybrid similarity (RSH_sim) defined in the previous subsection is used to determine the nearest neighbors and to compute . This involves the same time ratings and homophily derived from the social network structure.
where is the ratings of user for item , and and are the average ratings of user and user , respectively.
The items with the highest values will be recommended to the active user. Using the hybrid similarity in Equation (8) instead of rating-based similarity is expected to improve the reliability of the recommendations for gray-sheep users and for those who are new to the system and suffer from the cold-start problem.
3.3. Gray-Sheep and Cold-Start Scenarios
As mentioned above, the proposed approach is mainly focused on the music application domain, where the problems discussed above are aggravated by the power law distribution of the music listening frequency, also known as long tail. This happens because there are few songs or artists that are very frequently listened to, while there are many songs or artists with a low frequency of listening. An additional drawback in this area comes from the fact that explicit ratings of music items are usually not available, and implicit feedback is usually obtained from their frequency of plays. There are several frequency functions that can be used to infer implicit ratings from an matrix of plays that contains the number of times that a given user played an item (artist or song) . We have chosen a linear function of the frequency percentile [49]. The matrix of plays is also used to identify gray-sheep users and those who suffer from the cold-start problem.
In [50], users are characterized according to their degree of gray sheep by defining a user playing coefficient that captures the behavior of users in terms of the popularity of artists or songs they listen to. First, a listening coefficient for the item is defined in order to determine its popularity (Equation (9)).
where is the number of users who play the item , is the average number of users per item and the average number of plays per item of user .
The listening coefficient is normalized as follows:
The normalized coefficient is used to compute the User Playing Coefficient (UPC), which characterizes users based on the popularity of the music items they listen to (Equation (11)).
where is a parameter that takes the value 1 if the item has been played by the user and the value 0 otherwise. is the total number of items played by user . Users with low values of UPC have unusual preferences, so they are gray-sheep users. In the experimental study, we used UPC to validate our proposal with this type of user.
The cold-start scenario occurs mainly with new users who have few ratings or interactions with the items. To test the feasibility of our approach with such users, they were selected based on their number of plays since explicit ratings are not available. Candidates are those with a frequency far below the average play frequency per user, as detailed in the following section.
4. Validation of the Recommendation Approach
This section describes the empirical study conducted to validate the recommendation approach with the types of target users and presents the results obtained.
4.1. Datasets
The dataset Hetrec2011-lastfm [51] for artist recommendation has been used in the study since, as far as we know, it is the only music dataset in which the number of plays per user and artist and social relationships between users are available. Different subsets have been extracted from this dataset to validate the method in the scenarios for which it has been proposed.
Using the UPC coefficient, we created three subsets for different gray-sheep scenarios. We selected the records of the 5%, 10%, and 15% users with the lowest UPC values, respectively. That way, we can test the performance of the method for different degrees of this problem. The fourth subset was used to validate the method with new users in order to test its behavior against the cold-start problem. Users with a number of plays lower than 2000 were selected, which represents around 5% of the average number of plays per user in the dataset.
4.2. Experimental Study
The proposal was validated for both rating prediction and top-N recommendations. In the former, predicted ratings are compared to actual ratings, and error rates such as NMAE (Normalized Mean Absolute Error) and NRMSE (Normalized Root-Mean-Square Error) are computed. In the second, the top-N list of items is evaluated by means of the MAP (Mean Average Precision) and NDCG (Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain) metrics for N = 5. In all experiments, 5-fold cross-validation was applied.
The objective of the study was to verify that the use of the rating-social hybrid similarity in CF methods improves the results of the recommendations in the previously described gray-sheep (5%, 10%, and 15%) and cold-start scenarios with respect to traditional approaches based only on ratings. Therefore, we tested our RSH-based k-NN approach against the most extended CF methods, Matrix Factorization, item-based k-NN and user-based k-NN. In addition, our proposal was compared to other methods described in [12] that exploit social information. These baseline methods are the following: An approach in which CF is constrained to the user social context (SCC), one that combines social similarities and rating-based similarities (SSW), and another that makes use of Social Structure Metrics (SSM).
The value of k in all k-NN methods was set to 20 because smaller values produce worse results, and above 20, they stabilize. The Jaccard metrics were used to compute structural equivalence, and the cosine metric to compute the rating-based user similarity.
The results of all methods in the four scenarios are presented in Table 1, where the best value of each metric is highlighted in bold. We can see that the highest performance is achieved by the proposed RSH-based user k-NN method. It gives the lowest error rates (NMAE and NRMSE metrics) when evaluating rating prediction and the highest values of list quality metrics (MAP and NDCG) when evaluating top-N recommendations in almost all cases. This occurs with the three subsets of gray-sheep users and with the subset of users suffering from cold start. Only the method of SSM presents lower values of NRMSE in two of the gray-sheep scenarios (5% and 10%), but for the rest of the metrics, this method presents a worse performance than our proposal.

Table 1.
Results of the tested CF methods for rating prediction (NMAE and NRMSE) and top-N recommendations (MAP and NDCG) in the gray-sheep and cold-start scenarios.
This behavior can be better appreciated in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 for the gray-sheep scenarios and Figure 4 for the cold start. On the one hand, regarding the studied scenarios, the largest differences between the RSH-based k-NN method and the other methods are in the subset of data with the 5% of gray-sheep users with the lowest UPC values, which are those users with the least similar tastes to other users. These differences are also significant in the case of the cold-start problem. On the other hand, regarding the recommendation methods, the largest differences in the assessment of recommendation reliability occur with methods that do not use social information compared to those that do. Therefore, we can conclude that the exploitation of information from social networks improves the prediction of preferences for those groups of users who have unusual tastes or who have few interactions with the system and who generally receive poor recommendations that do not match their interests.
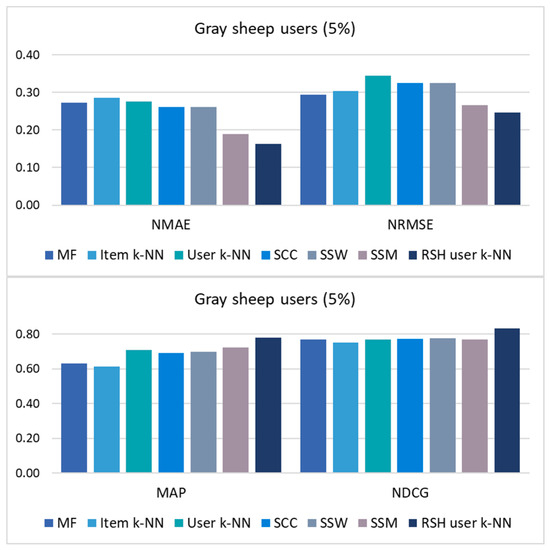
Figure 1.
Results of the error metrics (NMAE and NRMSE) and top-N list metrics (MAP and NDCG) in the gray-sheep scenario (5% of users with the most unusual preferences, which have the lowest values of UPC-User Playing Coefficient).
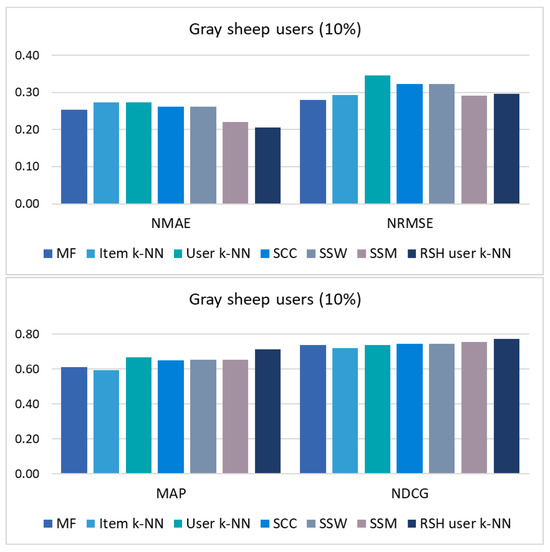
Figure 2.
Results of the error metrics (NMAE and NRMSE) and top-N list metrics (MAP and NDCG) in the gray-sheep scenario (10% of users with the most unusual preferences, which have the lowest values of UPC-User Playing Coefficient).
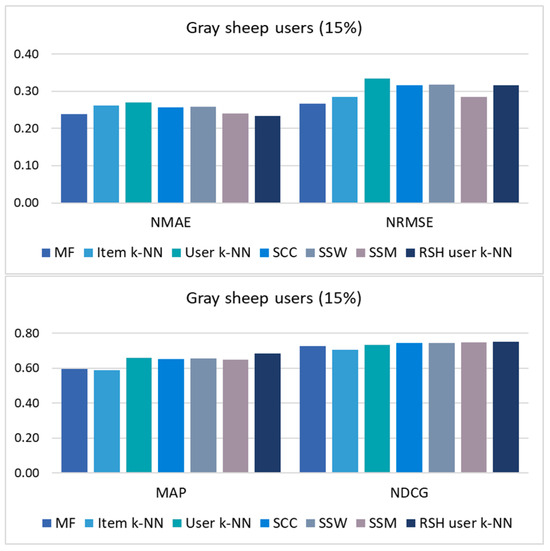
Figure 3.
Results of the error metrics (NMAE and NRMSE) and top-N list metrics (MAP and NDCG) in the gray-sheep scenario (15% of users with the most unusual preferences, which have the lowest values of UPC-User Playing Coefficient).
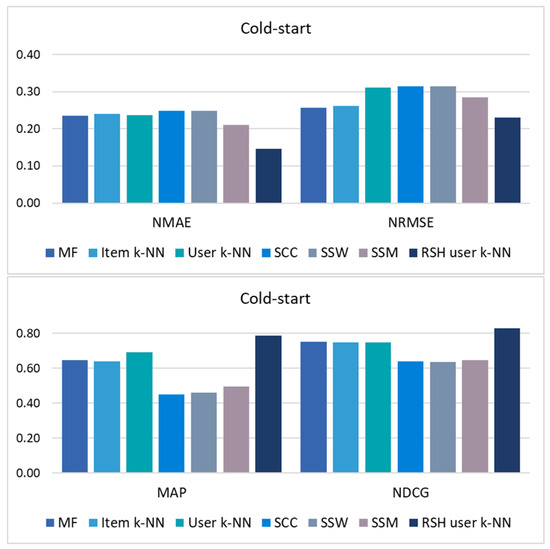
Figure 4.
Results of the error metrics (NMAE and NRMSE) and top-N list metrics (MAP and NDCG) in the cold-start scenario (users with less than 2000 plays).
In addition, other experiments were performed by modifying the cross-validation process. In this case, the same test sets were created as in the previous experiments, but the training sets were created from the complete dataset instead of using the subsets created for each scenario, excluding the examples present in the test set. The results of this study with all methods were much worse than those obtained from the subsets, and although the proposed method produced better results than the rest of the methods, the differences were not as significant. This behavior is consistent with the work reported in the literature since in most of the studies addressing the problems at hand, clusters are created with the types of users, and CF methods are applied to the different clusters separately.
5. Discussion
In view of the results shown in the preceding section, we can state that the use of graphical properties of social networks in combination with user preferences in CF recommendation methods leads to an improvement over traditional approaches that only make use of the latter. To our knowledge, no other work has used the social network structure to address the gray-sheep problem. The cold-start scenario has been studied in previous work [12], where a proposal using social network metrics is presented to address neighborhood bias, but it is not specifically oriented to deal with this drawback. This method and others that use social information were introduced in the study as baselines, in addition to other methods that do not use it. The advantage of our proposal over other content-based or hybrid approaches is that it only requires information available on streaming music platforms, that is, music played by users and social relationships between them.
Other studies in the literature use information from the structure of social networks but are not aimed at solving the problems discussed above. Among them is the proposal of a matrix factorization method presented in [27], where social relationships are used in addition to user-items interactions in order to address the sparsity data problem. Dealing with sparsity is also the objective of another method based on matrix factorization that uses the structure of social networks to group users into communities [28]. In [12], social network structure is used to derive social influence and homophily and is aimed at expanding the neighborhood in k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN)-based CF recommendation methods. There are also proposals that combine information from social networks with additional information such as item features [25] and other characteristics such as the location of users [29] or trust and opinions explicitly expressed by users [30,31], but, as mentioned above, this information is not usually available on streaming platforms.
The results show that the proposed approach (RSH-based user k-NN) is the best-performing method in both item prediction and top-N list recommendation. This behavior is especially evident in the cold-start scenario as well as in the group of users whose preferences are more different from those of the other users (gray sheep 5%). Both scenarios are the main focus of this work. The lowest error rates in rating prediction, measured by NMAE and NMRSE, are achieved with this proposal in the studied scenarios, except for NRMSE in the two weakest gray-sheep scenarios. This implies that the predictions of our method are better, although some larger errors may have occurred in some predictions that are potentiated by NMRSE. Regarding top-N recommendations, our proposal gives the highest values of MAP and NDCG metrics. The fact that these metrics are significantly better indicates that the errors in the predictions mainly occur in the lower-rated items. Since these items are not recommended, this explains the higher quality of the top-N recommendation list containing the items with the highest predicted ratings.
Table 2 shows the percentages of improvement achieved by the method proposed in this work compared to the baselines. As stated above, the largest differences are presented with 5% gray-sheep and cold-start scenarios. By examining this table, it can be seen that the percentage improvement in the error rates given by NMAE is similar for all the methods tested in comparison with RSH-based user k-NN. However, in the MAP and NDCG metrics, the smallest differences with the results of our proposal are found in the methods that use social information. We consider the last metrics more important in recommender systems than the previous ones because they evaluate the quality of the lists of items that are recommended to the user. Their values indicate that social network data, available on most streaming platforms, can be very useful in addressing two of the most important problems of recommender systems, namely gray sheep and cold start.

Table 2.
Improvement in NMAE, MAP, and NDCG achieved by RSH-based user k-NN against baselines.
In the field of music recommender systems, the presence of both drawbacks is unquestionable because the number of plays per song or artist presents a power law distribution, also known as long tail. The fact that there is a very low proportion of songs or artists with a large number of plays and a high proportion of songs or artists with few plays is indicative that there are users, the gray sheep, with tastes different from the majority who listen to those less played songs or artists that are in the long tail. On streaming platforms, there is also evidence of the existence of another group of users who have few plays and, therefore, suffer from the cold start problem. Both types of users tend to receive worse recommendations than other users and may benefit from the application of specific recommendation methods for them. Even though the proposal is directed to the music application domain where the indicated problems are very evident, the method can be extended to many other application domains that also suffer from them, with the only requirement of having some kind of relationship between its users that allows extracting that additional information required by the recommendation algorithm. This is the case for many e-commerce systems, digital libraries, online video games, etc., as well as content and product recommendation systems in the social networks themselves.
In order to provide solid evidence that corroborates these findings, statistical significance tests were performed. For each evaluation metric, a dedicated Critical Difference (CD) diagram was constructed to discern pairwise significance among the recommendation methods (Figure 5). CD diagrams show the result of applying the Wilcoxon signed rank test between each pair of algorithms and Holm to reject the null hypothesis. The thick horizontal line linking some algorithms indicates that the differences between them are not significant. The figure shows that the algorithm RSH-based user k-NN, proposed in this work, is the best performing among all the methods tested for the NMAE, MAP, and NDCG metrics since it is at the extremes of the respective diagrams. Likewise, this algorithm shows a significant difference with respect to the others for these metrics because it is not linked to the others by a horizontal line. The only exception is for NRMSE, for which RSH-based user k-NN ranks among the three best algorithms but with no significant differences between them. However, it presents significant differences with the three worst algorithms. Both NRMSE and NMAE are used in the prediction of ratings, and the former greatly enhances large deviations, even if few of them occur. The fact that the metrics for the evaluation of top-N lists, MAP, and NDCG, give significantly better results for the method RSH-based user k-NN compared to the others indicates that the errors in prediction occur in the lower rated items, which are the least important since they are not recommended to the user. These tests confirm that the proposed method outperforms alternative strategies across various performance indicators.
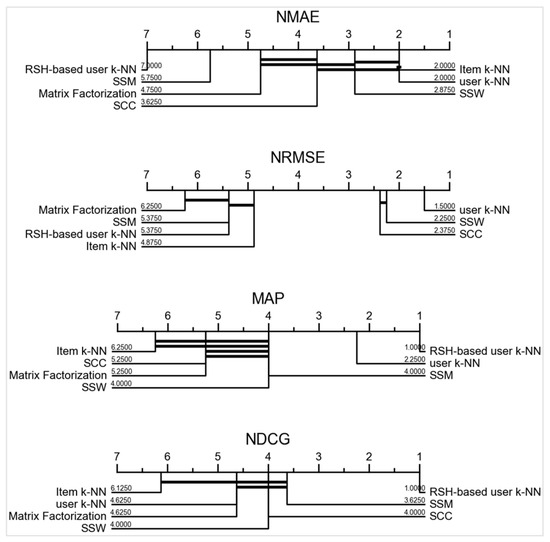
Figure 5.
Critical difference diagrams according to the Wilcoxon-Holm post hoc test for all evaluation metrics used in the study.
The metrics applied over the network structure capture homophily effects, which are useful for dealing with the gray sheep problem by detecting users with preferences similar to those of the gray sheep, who are users with unusual tastes. In addition, they are also useful to compensate for the absence of ratings of some users and alleviate the cold-start problem.
Another aspect that may be subject to discussion is the scalability of recommender systems as the number of users and the number of items increase, which may be affected by the computational complexity of the recommender algorithms. This is especially important when memory-based methods are used since the computations are performed at the recommendation time and may influence the response time to the user. However, when model-based methods are used, the time required for model induction does not affect response time. The only drawback would occur when it is necessary to update the models frequently since the time taken for each update would depend on the recommendation algorithm. Our proposal, although being a k-NN approach, is applied as a method based on models induced prior to the time of recommendation. All the algorithms checked in this study are used to induce recommendation models, so the time required for this process has no impact on the response time to the user.
The time complexity of user k-NN-based recommendation methods is while the time complexity of item k-NN-based methods is , where is the number of users and the number of items. The former may suffer from scalability problems if the number of users and items is very high. However, efficient indexing can reduce the time complexity to or even lower, making them more scalable. In the case of matrix factorization methods, the complexity depends on more factors, mainly the number of users, items, latent factors, and iterations, as well as the optimization algorithm. Other recommendation methods, such as those using deep learning techniques or those based on GNN, present a complexity that depends on their structure but generally requires significant computational resources and has the disadvantage of being more prone to biases. In addition, these methods are usually used when user and item attributes are available. Taking into account the above considerations, we may determine that both the proposal and the baselines are adequate in the context of this work, in which such attributes are not available and the models are created for specific groups.
6. Conclusions
In this work, a user similarity metric, which captures affinities between users in terms of both preferences and homophily, is presented. To this end, it integrates the implicit ratings-based similarity into measures related to the users’ social network graph. The ultimate goal is to use this hybrid metric in a CF method to address two very common problems in this type of recommendation method. In particular, the gray-sheep and cold-start problems have been extensively studied in the literature, although in the domain of music recommendation, the work performed is much scarcer. The usual way to deal with these drawbacks is to resort to content-based or hybrid methods, which usually provide worse results than the CF approaches and require information about items or users that, in many cases, is difficult to obtain. Our proposal, although it can be extended to other domains, is especially aimed at the music domain and makes exclusive use of the information stored by the streaming platforms. This is why the method uses implicit ratings inferred from the music played by users and the structural properties of the social network on the platform itself.
The proposal has been validated in four different scenarios associated with the mentioned problems, resulting in all of them having a significant improvement over other methods based on k-NN and matrix factorization, as well as over approaches using social network information. In the future, we intend to explore further the structural properties of the social network and take advantage of them to address these and other drawbacks of recommender systems, such as the multiple biases they may present.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.S.-M. and M.N.M.-G.; methodology, D.S.-M., V.F.L.B., Á.L.S.L. and M.D.M.V.; software, D.S.-M.; validation, D.S.-M., M.D.M.V. and Á.L.S.L.; formal analysis, D.S.-M. and M.N.M.-G.; investigation, D.S.-M., M.N.M.-G., V.F.L.B., M.D.M.V. and Á.L.S.L.; data curation, D.S.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, D.S.-M.; writing—review and editing, M.N.M.-G.; supervision, M.N.M.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in the study was obtained from Hetrec2011-lastfm, https://files.grouplens.org/datasets/hetrec2011/hetrec2011-lastfm-2k.zip (accessed on 5 February 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Breese, J.S.; Heckerman, D.; Kadie, C. Empirical analysis of predictive algorithms for collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Madison, WI, USA, 24–26 July 1998; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Recommender Systems. In The Testbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Schrauwen, B. Deep content-based music recommendation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26, 2643–2651. [Google Scholar]
- Claypool, M.; Gokhale, A.; Mir, T.; Murnikov, P.; Netes, D.; Sartin, M. Combining content-based and collaborative filters in an online newspaper. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGIR Workshop on Recommender Systems, Berkeley, CA, USA, 19 September 1999; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii, K.; Goto, M.; Komatani, K.; Ogata, T.; Okuno, H.G. Hybrid collaborative and content-based music recommendation using probabilistic model with latent user preferences. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Music Information Retrieval, Victoria, BC, Canada, 8–12 October 2006; University of Victoria: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2006; pp. 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, F.F.; Shan, M.K. A personalized music filtering system based on melody style classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Maebashi City, Japan, 9–12 December 2002; pp. 649–652. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-C.; Chen, A.L.P. A music recommendation system based on music and user grouping. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2005, 24, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantador, I.; Bellogín, A.; Castells, P. A multilayer ontology-based hybrid recommendation model. AI Commun. 2008, 21, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, H.; Komendantova, N.; Rovenskaya, E.; Yeganegi, M.R. Social Intelligence Mining: Unlocking Insights from X. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgikh, D. Graph-based music recommendation approach using social network analysis and community detection method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Hu, L.; Sun, R.; Hu, J.; Zhao, K. SRMCS: A semantic aware recommendation framework for mobile crowd sensing. Inf. Sci. 2018, 433–434, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Moreno, D.; López, V.F.; Muñoz, M.D.; Sánchez, A.L.; Moreno, M.N. Exploiting the user social context to address neighborhood bias in collaborative filtering music recommender systems. Information 2020, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ying, P.; Zou, M. Improving music recommendation by incorporating social influence. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 2667–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, B.; Jacobson, K.; Rhodes, C.; Inverno, M.; Sanler, M.; Casey, M. Analysis and exploitation of musician social networks for recommendation and discovery. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2011, 13, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, C.; Bichler, M. Identification of influencers—Measuring influence in customer networks. Decis. Support Syst. 2008, 46, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Pang, K.; Huang, M.; Liang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, J.; Kong, X. A Survey on Recommendation Methods Based on Social Relationships. Electronics 2023, 12, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, L.; Mardani, S.; Golpayegani, S.-A.H.; Madar, Z.Z. A novel tourism recommender system in the context of social commerce. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 149, 113301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, K.; Zhao, J. Homophily of music listening in online social networks of China. Soc. Netw. 2018, 55, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Qian, H. A Graph Neural Network Social Recommendation Algorithm Integrating the Multi-Head Attention Mechanism. Electronics 2023, 12, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizari, N.; Shoeibi, N.; Moreno-García, M.N. A Comparative Analysis of Bias Amplification in Graph Neural Network Approaches for Recommender Systems. Electronics 2022, 11, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Noia, T.; Tintarev, N.; Fatourou, P.; Schedl, M. Recommender systems under European AI regulations. Commun. ACM 2022, 65, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; García-Ortiz, J. Toward a Comprehensive Framework for Ensuring Security and Privacy in Artificial Intelligence. Electronics 2023, 12, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.C.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, H.H.; Chuang, Y.H. Social Media Privacy Management Strategies: A SEM Analysis of User Privacy Behaviors. Comput. Commun. 2021, 174, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Leyer, M. Me or information technology? Adoption of artificial intelligence in the delegation of personal strategic decisions. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2019, 40, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Liu, P.; Chen, W. Improved Matrix Factorization Algorithm Using Social Information for Recommendation. Comput. Eng. 2021, 47, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Chizari, N.; Tajfar, K.; Moreno-García, M.N. Bias Assessment Approaches for Addressing User-Centered Fairness in GNN-Based Recommender Systems. Information 2023, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, H.; Lyu, M.R.; King, I. SoRec: Social recommendation using probabilistic matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the CIKM08: Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Napa Valley, CA, USA, 26–30 October 2008; pp. 931–940. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, S.; Sun, G. Collaborative Filtering Recommendation Algorithm Based on Multi-relationship Social Network. Comput. Sci. 2019, 46, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, C.; Guan, J.; Zhang, H. SEM-PPA. A semantical pattern and preference-aware service mining method for personalized point of interest recommendation. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 82, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Zhang, J.; Yorke-Smith, N. TrustSVD: Collaborative Filtering with Both the Explicit and Implicit Influence of User Trust and of Item Ratings. In Proceedings of the AAAI’15: Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015; pp. 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Lei, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W. Social Collaborative Filtering by Trust. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1633–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Z.; Jing, L.; Shan, M.; Dou, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, X. Hierarchical Social Recommendation Model Based on a Graph Neural Network. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 9107718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Gao, C.; Zheng, Y.; Hui, Y.; Niu, Y.; Song, Y.; Jin, D.; Li, Y. Sequential Recommendation with Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the SIGIR’21: The 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Virtual Event, 11–15 July 2021; pp. 378–387. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. A Social Movie Recommendation Model Based on Graph Neural Network and Tag Overlapping Community. Inf. Stud. Theory Appl. 2021, 44, 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Du, J. Research on Recommendation Algorithm Based on Heterogeneous Graph neural Network. J. Hunan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2021, 48, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, D.K.; Ray, S. Approaches and algorithms to mitigate cold start problems in recommender systems: A systematic literature review. J Intell. Inf. Syst. 2022, 59, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.A.G.; Alves-Souza, S.N. Social network data to alleviate cold-start in recommender system: A systematic review. Inf. Process. Manag. 2018, 54, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, F.; Herder, E.; Houben, G.J.; Henze, N.; Krause, D. Cross-system user modeling and personalization on the social web. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. 2013, 23, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.C.; Zhang, Z.K.; Dong, Q.; Sun, C.; Fu, Y. Information filtering via biased random walk on coupled social network. Sci. World J. 2014, 829137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, S.; Afsharchi, M.; Meghdadi, M. An effective social recommendation method based on user reputation model and rating profile enhancement. J. Inf. Sci. 2019, 45, 607–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Wan, Y.H.; Chung, M.C.; Sun, Y.C. An effective recommendation method for cold start new users using trust and distrust networks. Inf. Sci. 2013, 224, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Zhang, J.; Thalmann, D. Merging trust in collaborative filtering to alleviate data sparsity and cold start. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 57, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavipour, M.; Meybodi, M.R. Stochastic trust network enriched by similarity relations to enhance trust-aware recommendations. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Bala, P.K.; Kumar, B. New perspectives on gray sheep behavior in E-commerce recommendations. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2020, 53, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfar, M.A.; Prügel-Bennett, A. Leveraging clustering approaches to solve the gray-sheep users problem in recommender systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 3261–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Im, I. Resolving the ‘gray sheep’ problem using social network analysis (SNA) in collaborative filtering (CF) recommender systems. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2014, 20, 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Leicht, E.A.; Holme, P.; Newman, M.E.J. Vertex similarity in networks. Phys. Rev. 2006, E 73, 026120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, M.G.; Borgatti, S.P. Two algorithms for computing regular equivalence. Soc. Netw. 1993, 15, 361–376. [Google Scholar]
- Pacula, M. A Matrix Factorization Algorithm for Music Recommendation Using Implicit User Feedback. Available online: http://www.mpacula.com/publications/lastfm.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Sánchez-Moreno, D.; Muñoz, M.D.; López, V.F.; Gil, A.B.; Moreno-García, M.N. A session-based song recommendation approach involving user characterization along the play power-law distribution. Complexity 2020, 7309453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantador, I.; Brusilovsky, P.; Kuflik, T. 2nd Hetrec workshop. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, RecSys, New York, NY, USA, 23–27 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).