Online Information Reviews to Boost Tourism in the B&B Industry to Reveal the Truth and Nexus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Customer Satisfaction with Hotels
2.2. Background of the LSA
2.3. Analysis of the Application of Hotel ORs
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Data Collection
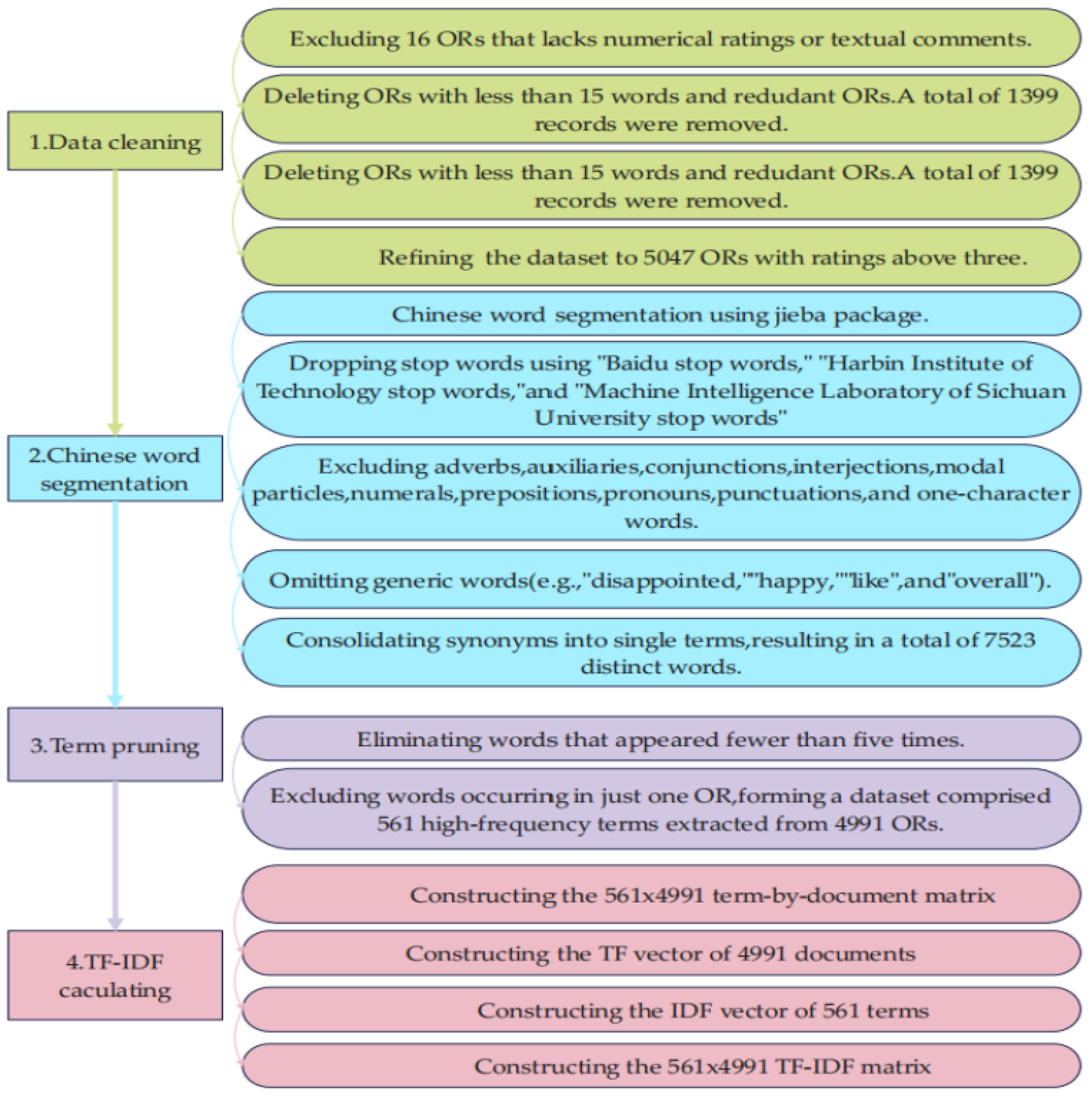
3.3. Data Pre-Processing Stage
3.4. Sentiment Analysis
3.5. TF-IDF Calculation
3.6. Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
3.7. Text Regression
4. Results
4.1. Overview of Analyzed ORs
4.2. RB&B Customer Satisfaction Factors
4.3. Relative Importance of Factors
5. Discussion
5.1. Differences in Customer Satisfaction Factors between RB&Bs and Hotels
5.2. What Factors Should RB&Bs Prioritize in Different Market Segments?
5.3. Implications
6. Conclusions, Limitations, and Future Research
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Phase | Language | Libraries |
|---|---|---|
| Data collection | Python | BeautifulSoup, pymysql, scrapy, selenium |
| Data pre-processing | Python | dbtools, jieba, pandas, pymysql, |
| Sentiment analysis | Python | pandas, SnowNLP |
| TF-IDF calculating | Python | numpy, openpyxl, pandas, sklearn |
| LSA analysis | Python | numpy, pandas, sklearn |
| Text regression | R | stats |
References
- MacCannell, D. Staged authenticity: Arrangements of social space in tourist settings. Am. J. Sociol. 1973, 79, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Guan, J.J. Bed and breakfast lodging development in Mainland China: Who is the potential customer? Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2011, 16, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Wu, M.-Y.; Pearce, P.L. Shaping tourists’ green behavior: The hosts’ efforts at rural Chinese B&Bs. J. Dest. Mark. Manag. 2018, 9, 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-W.; Cheng, J.-S. Exploring driving forces of innovation in the MSEs: The case of the sustainable B&B tourism industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3983. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Mi, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L. Understanding the determinants of consumer satisfaction with B&B hotels: An interpretive structural modeling approach. Int. J. Web Serv. Res. 2019, 16, 21–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Park, Y. An integrated approach to determining rural tourist satisfaction factors using the IPA and conjoint analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, J.T.; Chen, S.L. The relationship between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2001, 13, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, P. A Comparative Study of Customer Perceptions of Urban and Rural Bed and Breakfasts in Beijing: An Analysis of Online Reviews. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M. Feelings and Scenes of Rural Homestay Inns in China: A Perspective of Service Encounter. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 1966335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunkoo, R.; Teeroovengadum, V.; Ringle, C.M.; Sunnassee, V. Service quality and customer satisfaction: The moderating effects of hotel star rating. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 91, 102414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.Z.; Ahmad, N.; Papastathopoulos, A. Measuring service quality and customer satisfaction of the small-and medium-sized hotels (SMSHs) industry: Lessons from United Arab Emirates (UAE). Tour. Rev. 2019, 74, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffin, A.A.M.; Nameghi, E.N.M.; Soon, Y.K. The relationships between national identity, hospitality, and satisfaction among foreign hotel guests. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2015, 32, 778–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Kozak, M. Impact of customer relationship management on customer satisfaction: The case of a budget hotel chain. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2017, 34, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Barnes, S.J.; Jia, Q. Mining meaning from online ratings and reviews: Tourist satisfaction analysis using latent dirichlet allocation. Tour. Manag. 2017, 59, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.A.; Wilson, W.R. Measuring customer satisfaction: Fact and artifact. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1992, 20, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.M.; Lee, S.; Jeong, M. e-Social influence and customers’ behavioral intentions on a bed and breakfast website. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2018, 27, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. Classification of customer satisfaction attributes: An application of online hotel review analysis. In e-Business, e-Services and e-Society; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 238–250. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Schwartz, Z.; Gerdes, J.H., Jr.; Uysal, M. What can big data and text analytics tell us about hotel guest experience and satisfaction? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 44, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeplel, J.A.; Rosenberg, L.J. Consumer satisfaction: Concept and measurement. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1977, 5, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. J. Mark. Res. 1980, 17, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.J.; Neisner, L. Customer satisfaction in a retail setting: The contribution of emotion. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2006, 34, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L.; DeSarbo, W.S. Response determinants in satisfaction judgments. J. Consum. Res. 1988, 14, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, L.O. Satisfaction: A Behavioral Perspective on the Consumer; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhu, A.; Choi, H.; Bujisic, M.; Bilgihan, A. Satisfaction and positive emotions: A comparison of the influence of hotel guests’ beliefs and attitudes on their satisfaction and emotions. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 77, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, Y. The antecedents of customer satisfaction and dissatisfaction toward various types of hotels: A text mining approach. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2016, 55, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, C.-W.; Hu, F. Comprehending customer satisfaction with hotels: Data analysis of consumer-generated reviews. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 1713–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Hussain, K.; Konar, R.; Jeon, H.-M. The effect of technical and functional quality on guests’ perceived hotel service quality and satisfaction: A SEM-PLS analysis. J. Qual. Assur. Hosp. Tour. 2017, 18, 354–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinçer, M.Z.; Alrawadieh, Z. Negative word of mouse in the hotel industry: A content analysis of online reviews on luxury hotels in Jordan. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2017, 26, 785–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Cai, Y.M.; DeFranco, A.; Lee, J. Exploring influential factors affecting guest satisfaction: Big data and business analytics in consumer-generated reviews. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2020, 11, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R. An exploratory study of marketing, physical and people related performance criteria in hotels. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2012, 24, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sann, R.; Lai, P.-C.; Liaw, S.-Y. Online complaining behavior: Does cultural background and hotel class matter? J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2020, 43, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Does traveler satisfaction differ in various travel group compositions? Evidence from online reviews. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 1663–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Chan, J.H.; Qi, X. Why are Chinese and North American guests satisfied or dissatisfied with hotels? An application of big data analysis. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 3249–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelopoulos, N.; Ashton, T.; Winson-Geideman, K.; Roulac, S. Latent semantic analysis and real estate research: Methods and applications. J. Real Estate Lit. 2015, 23, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, M.; Singh, V. Patterns and trends in building information modeling (BIM) research: A latent semantic analysis. Autom. Constr. 2015, 59, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, T.K.; McNamara, D.S.; Dennis, S.; Kintsch, W. Handbook of Latent Semantic Analysis; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sidorova, A.; Evangelopoulos, N.; Valacich, J.S.; Ramakrishnan, T. Uncovering the intellectual core of the information systems discipline. MIS Q. 2008, 32, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilashi, M.; Mardani, A.; Liao, H.; Ahmadi, H.; Manaf, A.A.; Almukadi, W. A hybrid method with TOPSIS and machine learning techniques for sustainable development of green hotels considering online reviews. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.-X.; Tian, Z.-P.; Wang, J.-Q.; Chin, K.S. Hotel selection driven by online textual reviews: Applying a semantic partitioned sentiment dictionary and evidence theory. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 88, 102495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calheiros, A.C.; Moro, S.; Rita, P. Sentiment classification of consumer-generated online reviews using topic modeling. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2017, 26, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hossain, M.A. Adaptive 3D facial action intensity estimation and emotion recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 1446–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, T.K.; Foltz, P.W.; Laham, D. An introduction to latent semantic analysis. Discourse Process. 1998, 25, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Cao, P. Revealing Customer Satisfaction with Hotels Through Multi-Site Online Reviews: A Method Based on the Evidence Theory. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 225226–225239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, S.W.; Goldsmith, R.E.; Pan, B. Electronic word-of-mouth in hospitality and tourism management. Tour. Manag. 2008, 29, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, Q.; Law, R. Determinants of customer satisfaction in the hotel industry: An application of online review analysis. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2013, 18, 784–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakash, A.; Tandon, A.; Aggarwal, A.G. How features embedded in eWOM predict hotel guest satisfaction: An application of artificial neural networks. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2021, 30, 486–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrawadieh, Z.; Law, R. Determinants of hotel guests’ satisfaction from the perspective of online hotel reviewers. Int. J. Cult. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2019, 13, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, R. A fine-grained sentiment analysis of online guest reviews of economy hotels in China. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2021, 30, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I.; Sim, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Byun, J.; Kiatkawsin, K. Topic modeling of online accommodation reviews via latent dirichlet allocation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, B.; Bajwa, I.S.; Jamil, N.; Amin, R.U.; Ramzan, S.; Mirza, F.; Sarwar, N. An intelligent data analysis for recommendation systems using machine learning. Sci. Program 2019, 2019, 5941096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.-K.; Peng, J.-J.; Wang, J.-Q. The differences in hotel selection among various types of travellers: A comparative analysis with a useful bounded rationality behavioural decision support model. Tour. Manag. 2020, 76, 103961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-H.; Hsiao, Y.-T. Online review analytics for hotel quality at macro and micro levels. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2020, 121, 268–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.; Rasoolimanesh, S.M.; Sharif, S.P. Using online travel agent platforms to determine factors influencing hotel guest satisfaction. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. 2020, 11, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, I.K. The 45 Places to Go in 2012. 2012. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2012/01/08/travel/45-places-to-go-in-2012.html (accessed on 8 January 2012).
- Long, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yu, H.; Jiang, H. Development characteristics and evolution mechanism of homestay agglomeration in Mogan Mountain, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Cui, F.; Meng, Y.; Lian, T.; Yu, C. Opinion mining from online travel reviews: A comparative analysis of Chinese major OTAs using semantic association analysis. Tour. Manag. 2019, 74, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Understanding tourist attraction cooperation: An application of network analysis to the case of Shanghai, China. J. Dest. Mark. Manag. 2018, 8, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singha, P.; Sinha, S. Relationship between customer sentiment and online customer ratings for hotels-An empirical analysis. Tour. Manag. 2017, 61, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colladon, A.F.; Guardabascio, B.; Innarella, R. Using social network and semantic analysis to analyze online travel forums and forecast tourism demand. Decis. Support. Syst. 2019, 74, 113075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-N.; Huang, C.-Y. An investigation into online reviewers’ behavior. Eur. J. Mark. 2013, 47, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wen, X.; Yin, C. Conformity feedback in an online review helpfulness evaluation task leads to less negative feedback-related negativity amplitudes and more positive P300 amplitudes. J. Neurosci. Psychol. Econ. 2019, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanwisitkul, P.; Shahgholian, A.; Mehandjiev, N. The reason behind the rating: Text mining of online hotel reviews. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI), Vienna, Austria, 11–13 July 2018; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Gao, M.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, H. Forecasting stock price movements with multiple data sources: Evidence from stock market in China. Phys. A 2020, 542, 123389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgen, E.; Mason, K.J.; Mayer, R. Voice of airline passenger: A text mining approach to understand customer satisfaction. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2019, 77, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, M. Sentiment and guest satisfaction with peer-to-peer accommodation: When are online ratings more trustworthy? Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 86, 102369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, M.; Brooke, J.; Tofiloski, M.; Voll, K.; Stede, M. Lexicon-based methods for sentiment analysis. Comput. Linguist. 2011, 37, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Su, H.; Gui, L.; Cambria, E.; Xu, R. Aspect-based sentiment analysis via affective knowledge enhanced graph convolutional networks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 235, 107643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnowska, K.A.; Ras, Z.W. Sentiment Analysis of Customer Data. In Web Intelligence; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 343–363. [Google Scholar]
- Magnini, V.P.; Crotts, J.C.; Zehrer, A. Understanding customer delight: An application of travel blog analysis. J. Travel Res. 2011, 50, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlington, R. Multiple Tests. In Regression and Linear Models; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 249–276. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, B. ‘Why do kids’ menus always have chicken nuggets? Children’s observations on the provision of food in hotels on family holidays. Hosp. Soc. 2018, 8, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Tang, J. Understanding guest satisfaction with urban hotel location. J. Travel Res. 2018, 57, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanvisitthpon, N. Statistically Validated Component-and Indicator-Level Requirements for Sustainable Thai Homestay Businesses. Sustainability 2021, 13, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.-T. Rural Tourism. In Tourism in Emerging Economies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 103–129. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, A.; Aaltonen, M.; Rantala, K. Social determinants of debt problems in a Nordic welfare state: A Finnish register-based study. J. Consum. Policy 2015, 38, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuckert, M.; Liu, X.; Law, R. Hospitality and tourism online reviews: Recent trends and future directions. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2015, 32, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreón, E.C.A.; España, H.A.M.; Nonaka, H.; Hiraoka, T. Differences in Chinese and Western tourists faced with Japanese hospitality: A natural language processing approach. Inf. Technol. Tour. 2021, 23, 381–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Authors | Methodology | Context | Satisfaction Determinants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ali et al. [27] | PLS-SEM approach based on a survey | hotels in Malaysia | service quality (functional quality defined by tangibility, reliability, responsiveness, confidence, and communications, and technical quality defined by sociability, valence, and waiting time) |
| Dincer and Alrawadieh [28] | content analysis | five-star hotels in Amman | service quality, the efficiency of hotel facilities, and cleanliness and hygiene |
| Guo et al. [14] | LDA and regression analysis | hotels in 16 countries | checking in and out, resort facilities, communication, homeliness, bathroom, room experience, events management, car parking, style and decoration, guest facilities, location in building, breakfast, price and value for money, staff service, room size, apartment, dining, accommodating pets, transport, location, visitor suitability, weather, natural beauty, and nightlife |
| Lee et al. [29] | regression analysis | hotels in New York | Brand type, cleanliness, hotel class, location, room, service, sleep quality, and value |
| Li et al. [26] | regression analysis with dummy variables | hotels in different cities in China | cleanliness, location, room, service, and value |
| Ramanathan [30] | multiple regression analysis | hotels in the United Kingdom | cleanliness, customer service, family friendliness, food quality, room quality, and value for money |
| Sann et al. [31] | manual coding and statistical analysis | hotels in the United Kingdom | cleanliness, location, room, service, sleep quality, and value |
| Sukhu et al. [24] | structural equation modeling approach based on a survey | upscale hotels with at least a four-star rating | social elements, room elements, ambiance elements, public elements, and green elements |
| Xu and Li [25] | LSA | four types of hotels in the 100 largest US cities | location, staff, cleanliness, room, value, restaurant, Wi-Fi, facility, parking, noise, bathroom, and air |
| Xu [32] | LSA and regression analysis | hotels in the 100 largest US cities | basic factors (bed, bathroom, noise, breakfast, and smoking issues), excitement factors (room, staff, location, and access), and performance factors (staff and amenities) |
| Ying et al. [33] | text processing and content analysis | hotels in six famous tourism destinations in China | staff, functionality (room, travel, food, environment, and hotel facility), and price |
| ORs: Number of Different RB&Bs | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Economy RB&Bs | 1394 | 28% |
| Midscale RB&Bs | 1743 | 35% |
| Upscale RB&Bs | 1854 | 37% |
| Ratings | N | % |
| 3.0–3.5 | 58 | 1.2% |
| 3.5–4.0 | 164 | 3.3% |
| 4.0–4.5 | 218 | 4.4% |
| 4.5–5.0 | 4551 | 91.1% |
| Top 10 terms | Frequency | Involving ORs |
| Host | 3784 | 2584 |
| Room | 2212 | 1765 |
| Friendly staff | 1631 | 1489 |
| Breakfast | 1505 | 1404 |
| Cleanness | 1354 | 1217 |
| Tasty food | 1315 | 1156 |
| Environment | 1313 | 1268 |
| Outstanding service | 1254 | 1053 |
| Children | 1217 | 913 |
| Location | 953 | 856 |
| Factor | High-Loading Terms |
|---|---|
| F1 | delicious meal, host, friendliness, food, kind-hearted, cook craft, chef, garden, original taste, delicacy |
| F2 | pets, petting the cat, curtain, photos, funny, shading, mountain forest, archway, projection, pink |
| F3 | price points, discounts, traffic condition, quality, hot water, bathing, furniture, damp, healing, generous |
| F4 | children, swimming pool, brook, swimming, paddling, trampoline, play facilities, parent–child, slide, plants |
| F5 | relax, recover, mountains and streams, rest, away from the hustle and bustle, chowhound, wilderness, birds chirping, swimsuits, respite |
| F6 | good service, caring, steward, take pictures, reservation, take the baggage, help with problems, afternoon tea, look after, Internet celebrities |
| F7 | graceful surroundings, fresh air, ingredients, green trees, snowscape, cool, plum wine, market, open the door |
| F8 | service attitude, humanistic, staff, reception |
| F9 | scenery, balcony, floor-to-ceiling windows, mountains, beauty, terrace, open, coffee, spacious, sight |
| F10 | value for money, facilities, equipment |
| F11 | location, parking, quiet, scenic spots, stroll, self-drive, interchange station, climbing, extra bed, hillside |
| F12 | style, decoration, cleanness, buildings, room, bed linens, design, tidy, public area, scholarly atmosphere |
| F13 | breakfast items, breakfast, supper, taste, hearty, cuisine varieties, nutritious, enough to eat, lunch, Chinese food |
| Factor | Singular Value | Standardized Regression Coefficients | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economy | Midscale | Upscale | ||
| F1 | 7.00 | 0.31 (1) *** | 0.38 (1) *** | 0.29 (1) *** |
| F2 | 4.57 | 0.04 | 0.19 (8) *** | 0.06 (10) * |
| F3 | 4.47 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| F4 | 4.43 | 0.22 (5) *** | 0.23 (5) *** | 0.16 (7) *** |
| F5 | 4.34 | 0.09 (9) ** | 0.09 (10) *** | 0.08 (8) ** |
| F6 | 4.27 | 0.26 (3) *** | 0.26 (3) *** | 0.20 (5) *** |
| F7 | 4.21 | 0.28 (2) *** | 0.32 (2) *** | 0.26 (2) *** |
| F8 | 4.18 | 0.07 (10) * | 0.08 (11) *** | 0.05 (11) * |
| F9 | 4.07 | 0.22 (6) *** | 0.25 (4) *** | 0.22 (3) *** |
| F10 | 4.02 | 0.18 (8) *** | 0.13 (9) *** | 0.07 (9) ** |
| F11 | 3.89 | 0.19 (7) *** | 0.23 (6) *** | 0.17 (6) *** |
| F12 | 3.88 | 0.24 (4) *** | 0.21 (7) *** | 0.21 (4) *** |
| F13 | 3.79 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Factor | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Common factors | F3 (quality and affordability) | Affordability encompasses room and food costs, along with potential discounts. Guest satisfaction levels vary based on their perception of the price paid in relation to the service received [29]. RB&B patrons similarly consider factors, like the price, scrutinizing both affordability and quality elements, such as water temperature and bathing conditions. |
| F4 (family friendly) | Travelers with children have diverse requirements for hotel accommodation, leisure amenities, and catering facilities [71]. The RB&B emerges as an ideal choice for parents seeking quality time with their children, providing an escape from the hustle and bustle of city life for a more enjoyable experience together. Consequently, features tailored for families, such as entertainment activities, child-friendly facilities, and childcare services, play a pivotal role in enhancing customer satisfaction for these specific travelers. | |
| F6 (excellent service) | The paramount importance of service quality in shaping guests’ satisfaction with their lodging experience is underscored by research [13,27,28]. Guests employ diverse criteria that encompass both intangible service elements and tangible physical elements when assessing hotel services [30]. Within the realm of RB&Bs, service quality, inclusive of subdimensions, like contact, reservations, and luggage assistance, emerges as a pivotal factor influencing customer satisfaction. | |
| F7 (natural environment) | The enchanting natural surroundings, embodying the picturesque landscapes and tranquility of a hotel, play a pivotal role in enhancing the overall guest experience [33]. | |
| F8 (friendly staff) | Hotels place a significant emphasis on human resources, recognizing the direct correlation between service quality and the commitment of their staff [28]. Similarly, RB&Bs leave a lasting positive impression on guests when their amicable employees actively engage in service interactions. | |
| F10 (cost-effective amenities) | Customers gauge the perceived value of a product or service by assessing its utility in a comparison between what is given and received [5]. Within RB&Bs, the inclusion of various facilities not only introduces value-added features, but also serves as a key driver in fostering customer satisfaction. | |
| F11(location and convenient amenities) | Attributes, such as a hotel’s accessibility, proximity to attractions, public transportation, and local businesses, have been identified as significant contributors to guest satisfaction [26,29,31,72]. RB&B customers opt for driving, making parking convenience a key motivator. | |
| F13 (diverse culinary offerings) | The satisfaction of hotel guests is intricately tied to factors such as food variety, food quality, and the dining environment [30,33]. RB&Bs distinguish themselves by offering a comprehensive array of food and beverage services, affording guests the convenience of enjoying all three meals within the establishment. Consequently, the culinary aspect assumes a pivotal role in shaping RB&B customer satisfaction. | |
| Unique factors of RB&Bs | F1 (welcoming host with proficient culinary skills) | RB&Bs transcend being mere accommodations; they are immersive tourist destinations. Guests actively seek insights into local cultural characteristics and lifestyles from their hosts, leading to frequent interactions [73]. Additionally, the pivotal role of RB&B hosts extends to preparing meals for their guests, underscoring the importance of a hospitable host with proficient cooking skills in shaping customer satisfaction. |
| F2 (cozy ambiance) | Customer satisfaction in RB&Bs is significantly influenced by the positive emotions evoked through their assessment of the environment and service. Instances like hosts engaging in conversations with guests and the presence of charming pets contribute to fostering warm feelings among customers. | |
| F5 (tranquil escape) | RB&Bs provide an opportunity for urban residents to temporarily escape from the demands of their hectic daily routines, offering a space for rest and relaxation. This respite can contribute to enhancing their overall well-being and satisfaction. | |
| F9 (beautiful landscape) | RB&Bs boast captivating surroundings with picturesque landscapes. The simple act of gazing out of windows or from verandas onto the breathtaking scenery brings joy to guests and significantly contributes to their overall satisfaction. | |
| F12 (aesthetic appeal) | RB&Bs distinguish themselves through unique offerings crafted by architectural designs, interior decor, cleanliness, and bed linens, all of which contribute to customer satisfaction. Tailored architectural structures reflecting local folk customs, as highlighted by Zhang et al. [8], cater to customers’ desires for an immersion into local cultural characteristics. |
| Determinant Type | RB&B Segments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upscale | Midscale | Economy | ||
| hygiene factors | F3 (quality and affordability) F13 (diverse culinary offerings) | F3 (quality and affordability) F13 (diverse culinary offerings) | F3 (quality and affordability) F13 (diverse culinary offerings) | |
| motivation factors | Top 1 | F1 (welcoming host with proficient culinary skills) | F1 (welcoming host with proficient culinary skills) | F1 (welcoming host with proficient culinary skills) |
| Top 2 | F7 (natural environment) | F7 (natural environment) | F7 (natural environment) | |
| Top 3 | F9 (beautiful landscape) | F6 (excellent service) | F6 (excellent service) | |
| Top 4 | F12 (aesthetic appeal) | F9 (beautiful landscape) | F12 (aesthetic appeal) | |
| Top 5 | F6 (excellent service) | F4 (family friendly) | F4 (family friendly) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Gu, Z. Online Information Reviews to Boost Tourism in the B&B Industry to Reveal the Truth and Nexus. Information 2024, 15, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15020103
Wang X, Chen X, Gu Z. Online Information Reviews to Boost Tourism in the B&B Industry to Reveal the Truth and Nexus. Information. 2024; 15(2):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15020103
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoqun, Xihui Chen, and Zhouyi Gu. 2024. "Online Information Reviews to Boost Tourism in the B&B Industry to Reveal the Truth and Nexus" Information 15, no. 2: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15020103
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, X., & Gu, Z. (2024). Online Information Reviews to Boost Tourism in the B&B Industry to Reveal the Truth and Nexus. Information, 15(2), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15020103






