Interactive Segmentation for Medical Images Using Spatial Modeling Mamba
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose ESM-Click, the first interactive medical image segmentation method using the Mamba-based backbone network ESM-Net. Our method reduces the computational cost of the segmentation network while maintaining high-quality segmentation results.
- We design a Spatial Feature Enhancement Convolution (SAC) module to enhance the spatial expression ability of fused features from 2D image information and interaction information, using a gating mechanism to learn dynamic feature selection for each channel and spatial position.
- We construct a multi-scale feature-fusion module as part of the segmentation head, combining the advantages of KAN in nonlinear modeling ability and interpretability to improve the model’s segmentation accuracy.
- Comprehensive evaluations on three medical image datasets demonstrate that our ESM-Click exhibits good robustness, paving the way for Mamba’s application in interactive segmentation.
2. Related Work
2.1. Interactive Image Segmentation
2.2. Visual Applications of Mamba
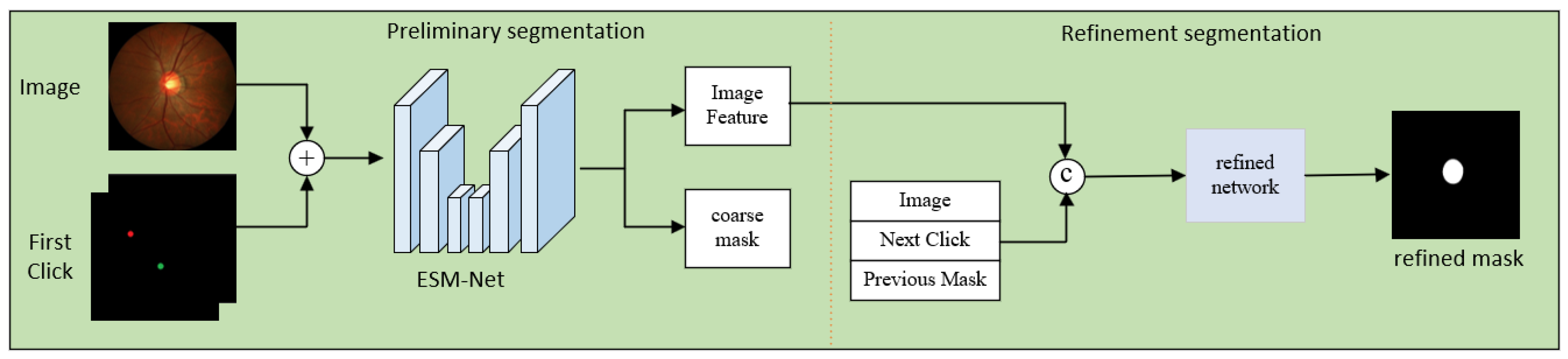
3. Method
3.1. Overview Architecture
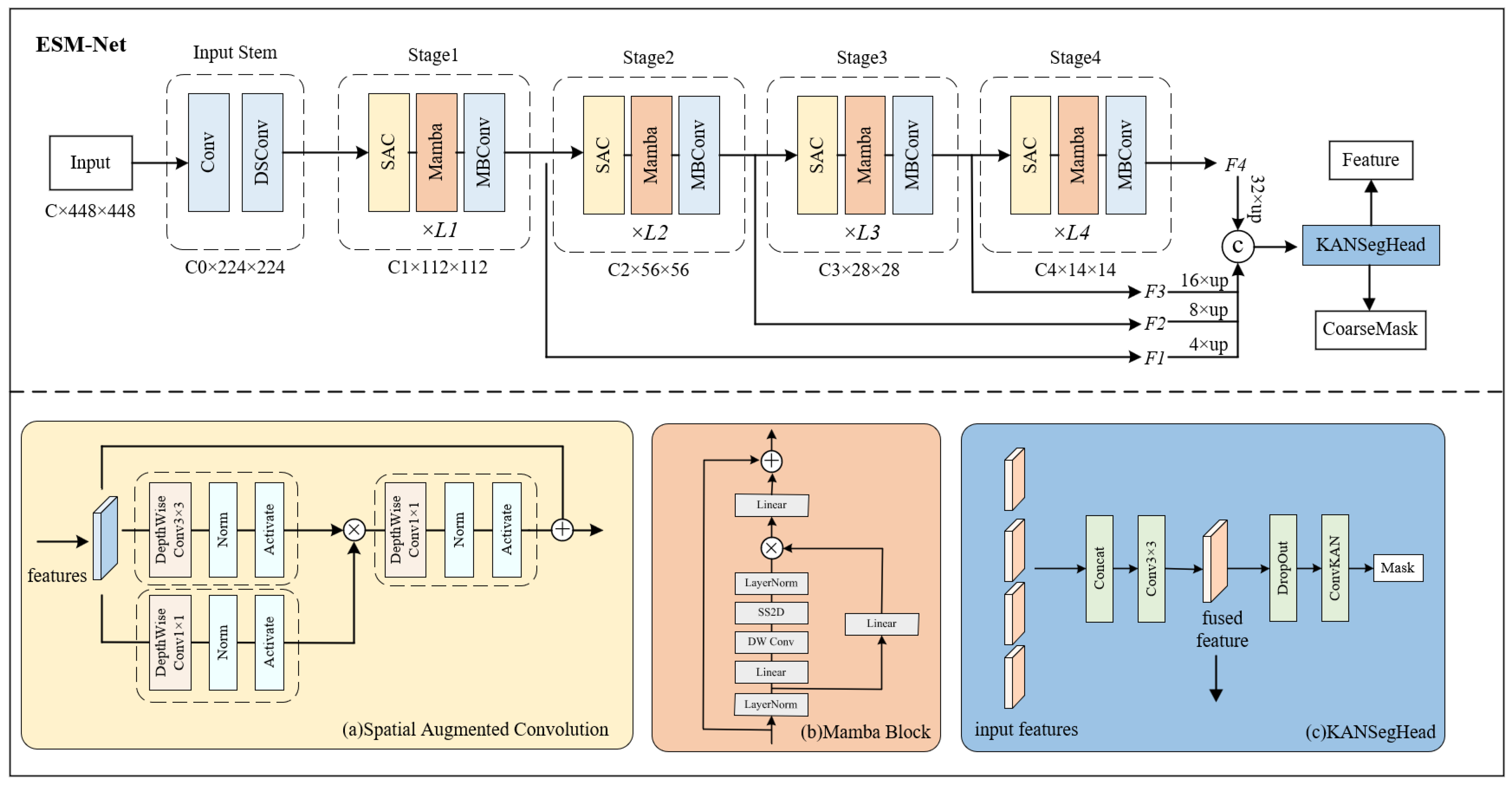
3.2. Proposed ESM-Net
3.2.1. Mamba Block
3.2.2. Spatial Augmented Convolution (SAC) Module
3.2.3. KANSegHead
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
- Kvasir-SEG [45] is a dataset for pixel-level colon polyp segmentation, containing 1000 gastrointestinal polyp images and their corresponding masks, all annotated and verified by experienced gastroenterologists. Following the official dataset split, we selected 800 images for the training set, 100 images for the validation set, and 100 images for the test set.
- CVC-ClinicDB [46] is the official dataset for the MICCAI 2015 sub-challenge on automatic polyp detection in colonoscopy videos, consisting of 612 static images extracted from colonoscopy video sequences from 29 different series. Out of these, 489 images were used for training, 61 images for validation, and 61 images for testing.
- ADAM [47] was introduced at the ISBI 2020 satellite event, aimed at improving diagnostic capabilities for Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD). The primary task of ADAM-Task2 is the detection and segmentation of the optic disc in retinal images. The ADAM dataset includes 381 retinal images and their corresponding masks. Consistent with the splits of the previous datasets, 304 images were used for training, 38 for validation, and 38 for testing.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
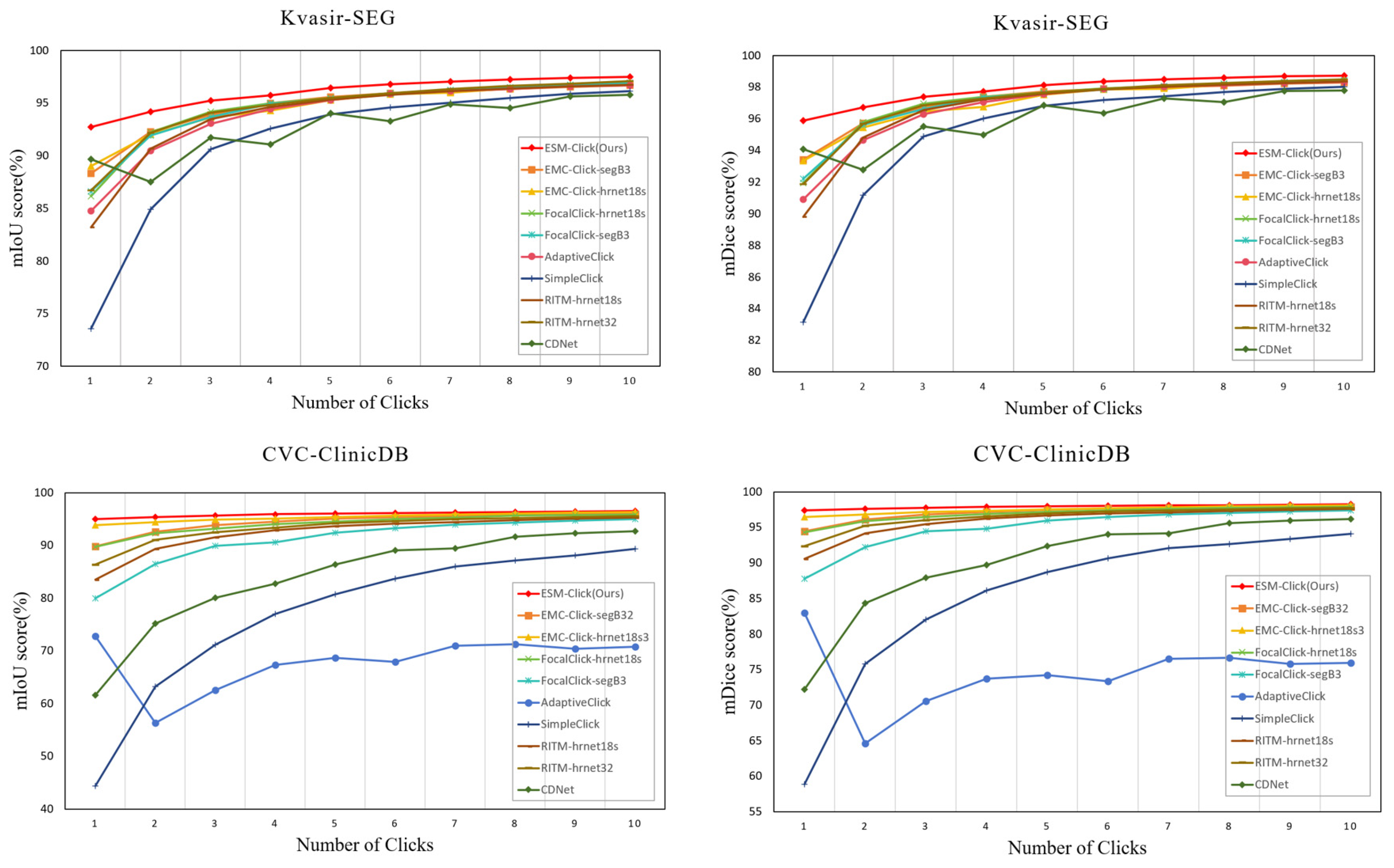
4.4. Comparison with State-of-Art Methods
4.4.1. Computational Analysis
4.4.2. Performance Comparison
- Comparison of the Performance of Different Interactive Segmentation Models
- 2.
- Improvement with a Single Interaction Click
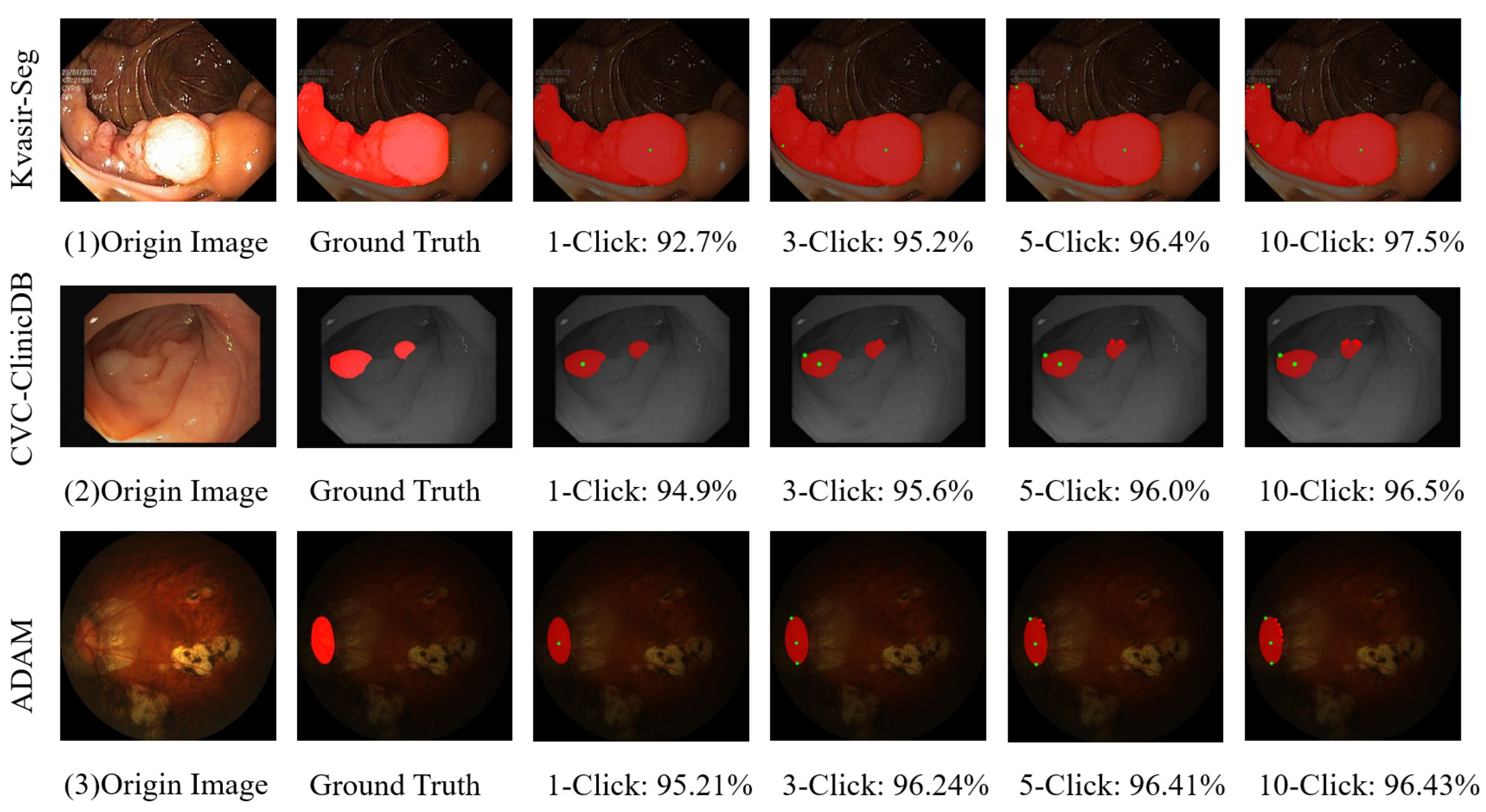
4.5. Qualitative Analysis
4.6. Ablation Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Lei, T.; Cui, R.; Zhang, B.; Meng, H.; Nandi, A.K. Medical image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 1243–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.-I. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Yang, J.; Kumar, S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Sotiras, A. AgileFormer: Spatially Agile Transformer UNet for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, P.; Wang, J.; Zaiane, O.R. Uctransnet: Rethinking the skip connections in u-net from a channel-wise perspective with transformer. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, online, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 2441–2449. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, K.; Matuszewski, B. FCB-SwinV2 transformer for polyp segmentation. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Tomar, N.K.; Sharma, V.; Bagci, U. TransNetR: Transformer-based residual network for polyp segmentation with multi-center out-of-distribution testing. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, Nashville, TN, USA, 10–12 July 2023; pp. 1372–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Price, B.; Cohen, S.; Yang, J.; Huang, T. Deep Interactive Object Selection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Luo, S.; Tu, Z. MILCut: A Sweeping Line Multiple Instance Learning Paradigm for Interactive Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lempitsky, V.; Kohli, P.; Rother, C.; Sharp, T. Image segmentation with a bounding box prior. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rother, C.; Kolmogorov, V.; Blake, A. “GrabCut”: Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. ACM J. 2004, 23, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Wu, X. Error-Tolerant Scribbles Based Interactive Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Grady, L. Random Walks for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 1768–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Tang, C.-K.; Shum, H.-Y. Lazy snapping. ACM J. 2004, 23, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.-D.; Kim, C.-S. Interactive Image Segmentation via Backpropagating Refinement Scheme. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.-Z.; Cheng, M.-M.; Lu, S.-P. Interactive Image Segmentation With First Click Attention. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sofiiuk, K.; Petrov, I.; Barinova, O.; Konushin, A. f-BRS: Rethinking Backpropagating Refinement for Interactive Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sofiiuk, K.; Petrov, I.A.; Konushin, A. Reviving Iterative Training with Mask Guidance for Interactive Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Duan, Z.-P.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, C.-L.; Cheng, M.-M. Focuscut: Diving into a focus view in interactive segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2637–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q. iSegFormer: Interactive Segmentation via Transformers with Application to 3D Knee MR Images. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Bertasius, G.; Niethammer, M. Simpleclick: Interactive image segmentation with simple vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 22290–22300. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, M.; Qi, D.; Zhao, H. FocalClick: Towards Practical Interactive Image Segmentation. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zheng, M.; Planche, B.; Karanam, S.; Chen, T.; Niethammer, M.; Wu, Z. PseudoClick: Interactive Image Segmentation with Click Imitation. arXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F. Efficient mask correction for click-based interactive image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22773–22782. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-Time Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. March 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Vision mamba: Efficient visual representation learning with bidirectional state space model. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liu, Y.J.A. VMamba: Visual State Space Model. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Nath, V.; Tang, Y.; Yang, D.; Roth, H.R.; Xu, D. Swin unetr: Swin transformers for semantic segmentation of brain tumors in mri images. In Proceedings of the International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Online, 27 September 2021; pp. 272–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Li, F.; Wang, B. U-Mamba: Enhancing Long-range Dependency for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Ye, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhu, L. Segmamba: Long-range sequential modeling mamba for 3d medical image segmentation. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boykov, Y.Y.; Jolly, M.-P. Interactive graph cuts for optimal boundary & region segmentation of objects in N-D images. In Proceedings of the Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gulshan, V.; Rother, C.; Criminisi, A.; Blake, A.; Zisserman, A. Geodesic star convexity for interactive image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan, S.; Voigtlaender, P.; Leibe, B. Iteratively Trained Interactive Segmentation. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Vosselman, G.; Yang, M.Y. Interactive image segmentation with cross-modality vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 762–772. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, W.; Tao, X.; Xiong, Z.; Tai, Y.-W.; Pei, W. Feature decoupling-recycling network for fast interactive segmentation. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 6665–6675. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, R.; Wu, F. ClickAttention: Click Region Similarity Guided Interactive Segmentation. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Luo, J. MST: Adaptive Multi-Scale Tokens Guided Interactive Segmentation. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Meng, D.; Zheng, Y. Interactive Segmentation as Gaussian Process Classification. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. EfficientNetV2: Smaller Models and Faster Training. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Vaidya, S.; Ruehle, F.; Halverson, J.; Soljačić, M.; Hou, T.Y.; Tegmark, M. Kan: Kolmogorov-arnold networks. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Long short-term memory. In Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sofiiuk, K.; Barinova, O.; Konushin, A. AdaptIS: Adaptive Instance Selection Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; De Lange, T.; Johansen, D.; Johansen, H.D. Kvasir-seg: A segmented polyp dataset. In Proceedings of the MultiMedia Modeling: 26th International Conference, MMM 2020, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 5–8 January 2020; Part II 26; pp. 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Bernal, J.; Sánchez, F.J.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.; Gil, D.; Rodríguez, C.; Vilariño, F. WM-DOVA maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: Validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2015, 43, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, F.; Fu, H.; Sun, X.; Cao, X.; Lin, F.; Son, J.; Kim, S.; Quellec, G.; Matta, S. Adam challenge: Detecting age-related macular degeneration from fundus images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 2828–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, M. Conditional diffusion for interactive segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 7345–7354. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, K.; Roitberg, A.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Li, S. AdaptiveClick: Click-Aware Transformer with Adaptive Focal Loss for Interactive Image Segmentation. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
| Backbone | FLOPs (G) | Params (M) | SPC/ms |
|---|---|---|---|
| hr18s+ocr | 8.2 | 4.21 | 95 |
| hr32+ocr | 39.27 | 30.94 | 146 |
| Segformer-B3 | 28.9 | 45.66 | 119 |
| ViT-Base448 | 67.17 | 87.02 | 127 |
| ESM-Net | 4.51 | 2.46 | 87 |
| Model | Backbone | Kvasir-SEG | CVC-ClinicDB | ADAM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NoC@85 | NoC@90 | NoC@85 | NoC@90 | NoC@85 | NoC@90 | ||
| CDNet [49] | Resnet34 | 1.4 | 2.05 | 3.7 | 4.93 | 1.24 | 1.95 |
| RITM [17] | HRNet18s | 1.59 | 2.12 | 1.69 | 2.75 | 1.03 | 1.42 |
| HRNet32 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 1.67 | 2.28 | 1.8 | 1.26 | |
| SimpleClick [20] | ViT-B | 2.26 | 3.16 | 6.97 | 9.69 | 6.18 | 7.26 |
| AdaptiveClick [50] | ViT-B | 1.57 | 2.13 | 5.93 | 8.66 | 1.21 | 2.82 |
| FocalClick [21] | HRNet18s-S2 | 1.49 | 1.84 | 1.34 | 2.07 | 1.82 | 2.74 |
| SegformerB3-S2 | 1.46 | 1.87 | 2.08 | 3.15 | 2 | 2.55 | |
| EMC-Click [23] | SegformerB3-S2 | 1.41 | 1.81 | 1.33 | 1.85 | 1.21 | 1.95 |
| HRNet18s-S2 | 1.42 | 1.83 | 1.3 | 1.59 | 1.05 | 1.08 | |
| ESM-Click (Ours) | ESM-Net | 1.17 | 1.43 | 1.15 | 1.57 | 1.03 | 1.03 |
| Model | Backbone | Kvasir-SEG | CVC-ClinicDB | ADAM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU (%) | Dice (%) | IoU (%) | Dice (%) | IoU (%) | Dice (%) | ||
| FocalClick [21] | HRNet18s-S2 | 86.17 | 91.93 | 89.7 | 94.3 | 93.41 | 96.54 |
| SegformerB3-S2 | 86.6 | 92.19 | 79.96 | 87.8 | 93.64 | 96.68 | |
| EMC-Click [23] | SegformerB3-S2 | 88.31 | 93.42 | 89.77 | 94.45 | 88.61 | 93.89 |
| HRNet18s-S2 | 89.01 | 93.33 | 93.83 | 96.46 | 94.37 | 97.09 | |
| ESM-Click (Ours) | ESM-Net | 92.7 | 95.87 | 94.96 | 97.36 | 95.21 | 97.84 |
| Model | Kvasir-SEG | CVC-ClinicDB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NoC@85 | NoC@90 | IoU(%) | Dice (%) | NoC@85 | NoC@90 | IoU (%) | Dice (%) | |
| MBConv | 1.96 | 2.59 | 89.49 | 93.99 | 1.36 | 1.97 | 88.55 | 93.69 |
| mamba*1 | 1.66 | 2.22 | 91.01 | 94.85 | 1.33 | 1.82 | 89.47 | 94.25 |
| mamba*depth-4 | 1.2 | 1.58 | 91.81 | 95.31 | 1.2 | 1.67 | 91.36 | 95.38 |
| Mamba*depth-4+SAC | 1.21 | 1.44 | 92.24 | 95.62 | 1.16 | 1.74 | 92.62 | 96.1 |
| Mamba+SAC+KANSegHead | 1.17 | 1.43 | 92.7 | 95.87 | 1.15 | 1.57 | 94.96 | 97.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhang, X. Interactive Segmentation for Medical Images Using Spatial Modeling Mamba. Information 2024, 15, 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15100633
Tang Y, Li Y, Zou H, Zhang X. Interactive Segmentation for Medical Images Using Spatial Modeling Mamba. Information. 2024; 15(10):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15100633
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yuxin, Yu Li, Hua Zou, and Xuedong Zhang. 2024. "Interactive Segmentation for Medical Images Using Spatial Modeling Mamba" Information 15, no. 10: 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15100633
APA StyleTang, Y., Li, Y., Zou, H., & Zhang, X. (2024). Interactive Segmentation for Medical Images Using Spatial Modeling Mamba. Information, 15(10), 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15100633







