Spanish Workers’ Judgement of Telecommuting during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mixed-Method Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
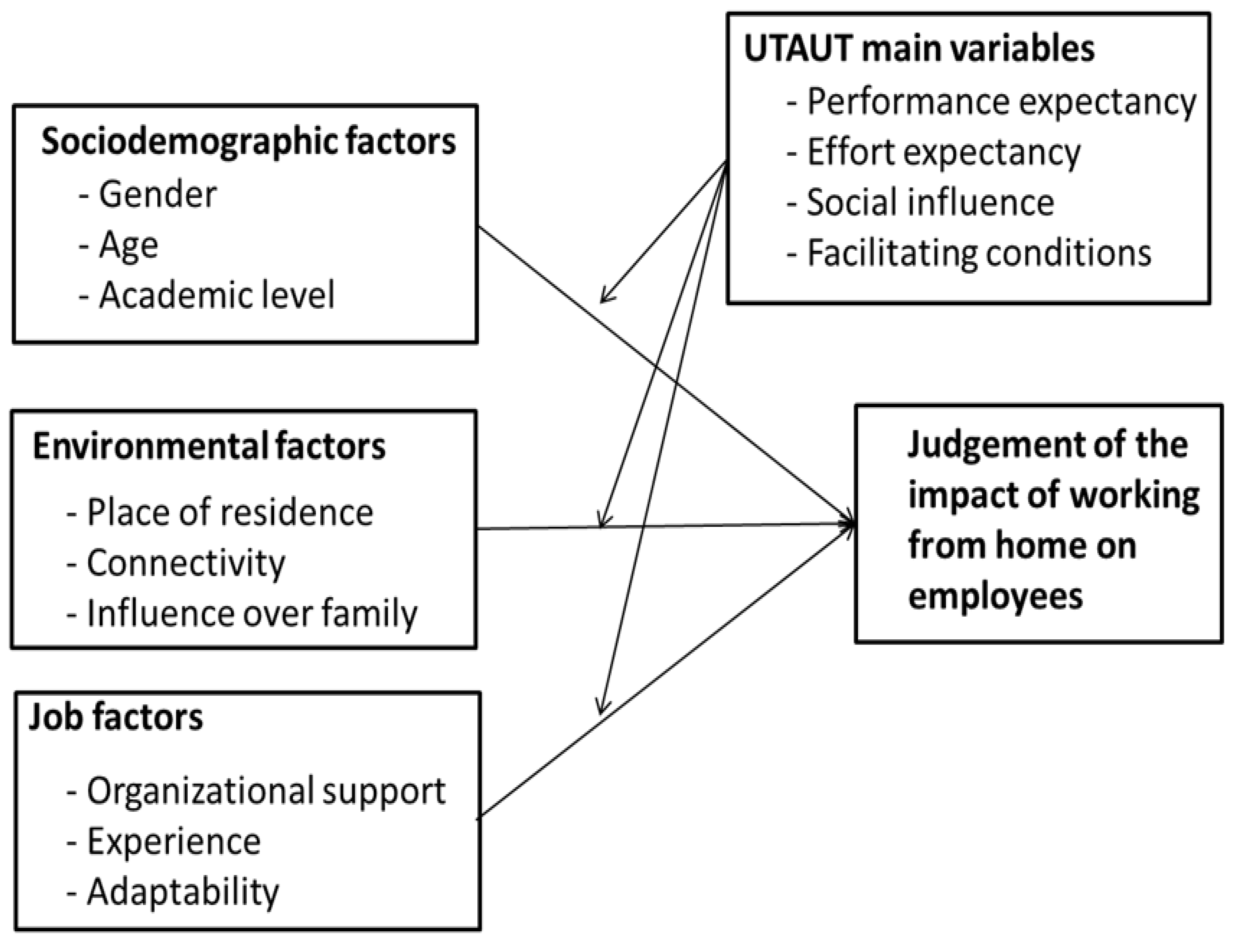
2. Theoretical Ground
2.1. Initial Considerations
2.2. Sociodemographic Variables
2.3. Environmental Factors
2.4. Organizational and Job Factors
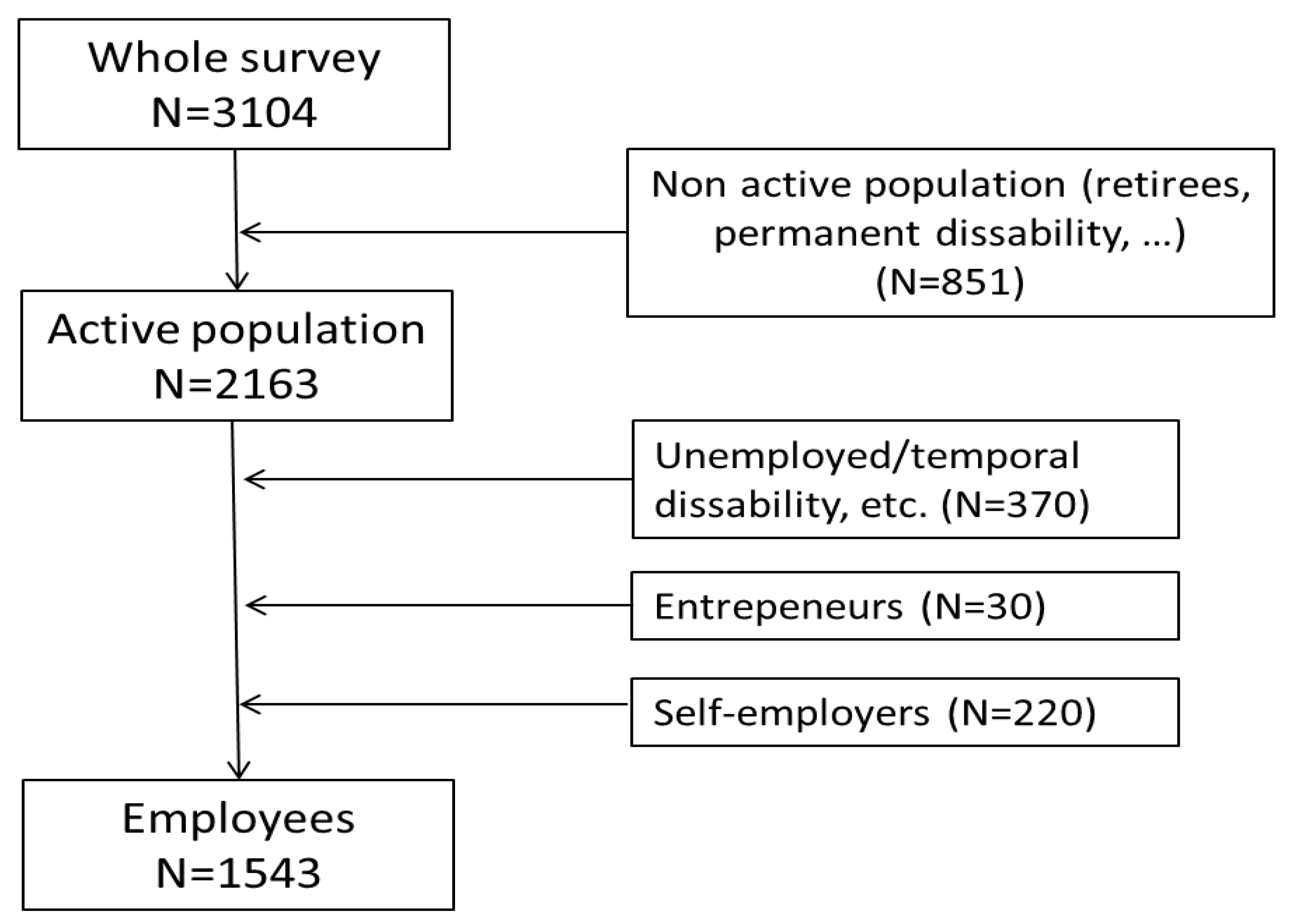
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Definition of the Variables and Membership Functions Used in the Study
3.3. Data Analysis
EXPERIENCE, ADAPTABILITY)
EXPERIENCE, ADAPTABILITY)
4. Results
4.1. Regression Analysis
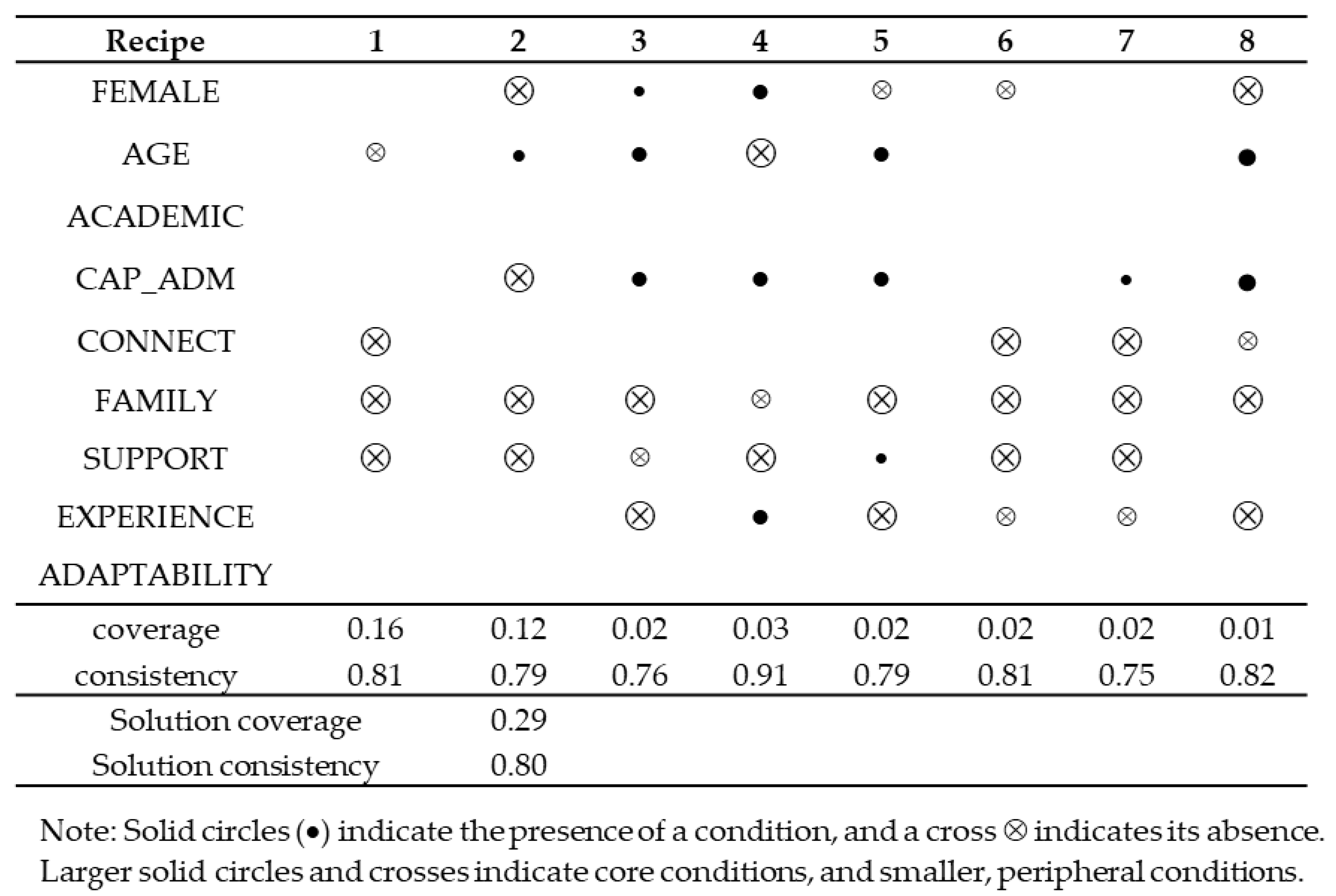
4.2. Fuzzy-Set Qualitative Comparative Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. General Considerations
5.2. Theoretical Implications of This Paper
5.3. Practical Implications of This Paper
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baruch, Y. The status of research on teleworking and an agenda for future research. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2001, 3, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauregard, T.A.; Basile, K.A.; Canónico, E. Telework: Outcomes and facilitators for employees. In The Cambridge Handbook of Technology and Employee Behavior; Landers, R.N., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 511–543. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, D.E.; Kurland, N.B. A review of telework research: Findings, new directions, and lessons for the study of modern work. J. Organ. Behav. 2002, 23, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illegems, V.; Verbeke, A.; S’Jegers, R. The organizational context of teleworking implementation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2001, 68, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fana, M.; Milasi, S.; Napierala, J.; Fernández-Macías, E.; Vázquez, I.G. Telework, Work Organization and Job Quality during the COVID-19 Crisis: A Qualitative Study (No. 2020/11). In JRC Working Papers Series on Labour 2020, Education and Technology; European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC), Seville. Available online: https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/231343/1/jrc-wplet202011.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Gschwind, L.; Vargas, O. Telework and its effects in Europe. In Telework in the 21st Century; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elldér, E. Who is eligible for telework? Exploring the fast-growing acceptance of and ability to telework in Sweden, 2005–2006 to 2011–2014. Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, A.; Isusi, I. Impact of the COVID-19 Confinement Measures on Telework in Spain. European Commission, JRC122651. 2020. Available online: https://joint-research-entre.ec.europa.eu/publications/impact-covid-19-confinement-measures-telework-spain-qualitative-survey_en. (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Herrera, J.; De las Heras-Rosas, C.; Rodríguez-Fernández, M.; Ciruela-Lorenzo, A.M. Teleworking: The Link between Worker, Family and Company. Systems 2022, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres-Sanchez, J.; Belzunegui-Eraso, A.; Souto-Romero, M. Perception of the Effects of Working from Home on Isolation and Stress by Spanish Workers during COVID-19 Pandemic. Soc. Sci. 2023, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarchuk, O.; Gabriele, R.; Neglia, G. Teleworking during the COVID-19 Crisis in Italy: Evidence and Tentative Interpretations. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zoonen, W.; Sivunen, A.E. The impact of remote work and mediated communication frequency on isolation and psychological distress. Eur. J. Work. Organ. Psychol. 2022, 31, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahut, J.M.; Lissillour, R. The adoption of remote work platforms after the COVID-19 lockdown: New approach, new evidence. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 154, 113345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Peláez, A.; Erro-Garcés, A.; Pinilla García, F.J.; Kiriakou, D. Working in the 21st Century. The coronavirus crisis: A driver of digitalisation, teleworking, and innovation, with unintended social consequences. Information 2021, 12, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragin, C.C. Using qualitative comparative analysis to study causal complexity. Health. Serv. Res. 1999, 34, 1225–1239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ragin, C.C. Redesigning Social Inquiry: Fuzzy Sets and Beyond; Chicago University Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, I.O.; Woodside, A.G. Fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (fsQCA): Guidelines for research practice in Information Systems and marketing. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 58, 102310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodside, A.G. Embrace perform model: Complexity theory, contrarian case analysis, and multiple realities. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Rosenberger, P.J.; Fitzgerald, M.; Houlcroft, L. Factors affecting smart working: Evidence from Australia. Int. J. Manpow. 2016, 37, 1042–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H. Factors influencing home-based telework in Hanoi (Vietnam) during and after the COVID-19 era. Transportation 2021, 48, 3207–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raišienė, A.G.; Rapuano, V.; Varkulevičiūtė, K.; Stachová, K. Working from Home—Who Is Happy? A Survey of Lithuania’s Employees during the COVID-19 Quarantine Period. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillo, K.; Cachat-Rosset, G.; Marsan, J.; Saba, T.; Klarsfeld, A. Adjusting to epidemic-induced telework: Empirical insights from teleworkers in France. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2021, 30, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Sánchez, J. A configurational evaluation of Spanish teleworkers’ perception and nonperception of stress during the COVID-19 pandemic. Societies 2023, 3, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Sánchez, J.; Belzunegui-Eraso, A.; Erro-Garcés, A. Perception of home teleworking during covid-19 crisis in Spain: Significant factors and asymmetrical influence on acceptance and resistance. Int. J. Manpow. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, D.; Arendsen, K.; De Bruyn, M.; Severens, V.; Van Hagen, M.; Van Oort, N.; Duives, D. Teleworking during COVID-19 in the Netherlands: Understanding behaviour, attitudes, and future intentions of train travellers. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2022, 159, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, E.; Lippens, L.; Sterkens, P.; Weytjens, J.; Stijn, B. The COVID-19 crisis and telework: A research survey on experiences, expectations and hopes. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2022, 23, 729–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruch, Y.; Nicholson, N. Home, sweet work: Requirements for effective home working. J. Gen. Manag. 1997, 23, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Davis, F.D. A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Manag. Sci. 2000, 46, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Thong, J.Y.L.; Xu, X. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: Extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Q 2012, 36, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Pérez, M.; Martínez Sánchez, A.; de Luis Carnicer, P.; José Vela Jiménez, M. A technology acceptance model of innovation adoption: The case of teleworking. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2004, 7, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.A.; Montoya, R.I.A.; Valencia, A.J.A. The attitude of managers toward telework, why is it so difficult to adopt it in organizations? Technol. Soc. 2019, 59, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, S.; Viola, G.; Toscano, F.; Zappalà, S. Not All Remote Workers Are Similar: Technology Acceptance, Remote Work Beliefs, and Wellbeing of RemoteWorkers during the Second Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ollo-López, A.; Goñi-Legaz, S.; Erro-Garcés, A. Home-based telework: Usefulness and facilitators. Int. J. Manpow. 2021, 42, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosratzadeh, H.; Edrisi, A. An assessment of tendencies toward teleworking using TAMs: Lessons from COVID-19 era for post-pandemic days. Int. J. Workplace Health Manag. 2023, 16, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubelet-Fagoaga, I.; Arnoso-Martinez, M.; Elgorriaga-Astondoa, E.; Martínez-Moreno, E. Telework and Face-to-Face Work during COVID-19 Confinement: The Predictive Factors of Work-Related Stress from a Holistic Point of View. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataki-Bittó, F.; Kun, Á. Exploring differences in the subjective well-being of teleworkers prior to and during the pandemic. Int. J. Workplace Health Manag. 2022, 15, 320–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutarto, A.P.; Wardaningsih, S.; Putri, W.H. Work from home: Indonesian employees’ mental well-being and productivity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Workplace Health Manag. 2021, 14, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckel, J.L.O.; Fisher, G.G. Telework and Worker Health and Well-Being: A Review and Recommendations for Research and Practice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Gao, J. Does telework stress employees out? A study on working at home and subjective well-being for wage/salary workers. J. Happiness Stud. 2020, 21, 2649–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, I.; Coelho, F.; Ferrajão, P.; Abreu, A.M. Telework and Mental Health during COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macciotta, A.; Farinella, D.; Dell’Aversana, G.; Fornili, M.; Petri, D.; Baglietto, L.; Baccini, M.; Berrocal Montiel, C.; Fiorentino, G.; Severi, G.; et al. RemoteWorking and Home Learning: How the Italian Academic Population Dealt with Changes Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, L.R.T.; Sequeira, C.; Ferré-Grau, C.; Araújo, O. Impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on the difficulties and burden experienced by family caregivers of older dependent persons. J. Ment. Health Train. Educ. Pract. 2022, 17, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Kang, S.K.; Kaplan, S. We need to make sure telecommuting does not exacerbate gender disparity. Lancet 2022, 400, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Küll, S.; Niederländer, U.; Stabauer, M. The new normal? Motivators for and hindrances to telework. In International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnier-Watanabe, R.; Benton, C.; Orsini, P.; Uchida, T.; Magnier-Watanabe, K. COVID-19 and mandatory teleworking from home in Japan: Taking stock to improve satisfaction and job performance. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 2022. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakrošienė, A.; Bučiūnienė, I.; Goštautaitė, B. Working from home: Characteristics and outcomes of telework. Int. J. Manpow. 2019, 40, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Kayser, I. The Role of Self-Efficacy, Work-Related Autonomy and Work-Family Conflict on Employee’s Stress Level during Home-Based Remote Work in Germany. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.; Bajpai, A. Living in today’s world: Reflections on the interactions between technology and human relational patterns. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçayir, M.; Dündar, H.; Akçayir, G. What makes you a digital native? Is it enough to be born after 1980? Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 60, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, D.N. How can teleworking be pro-poor? J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2011, 24, 8–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, H.; Gupta, R.; Jin, X. Impacts of COVID-19 on Future Preferences Toward Telework. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022, 2667, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottholmseder, G.; Nowotny, K.; Pruckner, G.J.; Theurl, E. Stress perception and commuting. Health Econ. 2019, 18, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Borger, B.; Proost, S. COVID-19 and optimal urban transport policy. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2022, 163, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.; Frank, R.; Crevenna, R. The impact of lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic on work-related accidents in Austria in 2020. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2022, 134, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillot, A.-S.; Meyer, T.; Prunier-Poulmaire, S.; Vayre, E.A. Qualitative and Longitudinal Study on the Impact of Telework in Times of COVID-19. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Morote, R.; Pontones-Rosa, C.; Núnez-Chicharro, M.; Merino-Madrid, E. Determinant factors of individuals’ decision to emigrate in rural Spain: The role of ICT-based public policies. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, N.; Papagiannidis, S.; Hosany, A.S.; Gentina, E. It’s part of the “new normal”: Does a global pandemic change employees’ perception of teleworking? J. Bus. Res. 2023, 164, 113956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, R.; Kuroda, S.; Okudaira, H.; Owan, H. Working from home and productivity under the COVID-19 pandemic: Using survey data of four manufacturing firms. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, H.M.; Digutsch, J.; Kleinsorge, T.; Fan, Y. Having to work from home: Basic needs, well-being, and motivation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Bala, H. Technology acceptance model 3 and a research agenda on interventions. Decis. Sci. 2008, 39, 273–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, B.; Pansini, M.; De Vincenzi, C.; Buonomo, I.; Benevene, P. Investigating the Role of Remote Working on Employees’ Performance and Well-Being: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayre, É.; Morin-Messabel, C.; Cros, F.; Maillot, A.S.; Odin, N. Benefits and Risks of Teleworking from Home: The Teleworkers’ Point of View. Information 2022, 13, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzunegui-Eraso, A.; Erro-Garcés, A. Teleworking in the Context of the COVID-19 Crisis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Modroño, P. Working conditions and work engagement by gender and digital work intensity. Information 2022, 13, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiden, M.; Widar, L.; Wiitavaara, B.; Boman, E. Telework in academia: Associations with health and well-being among staff. High. Educ. 2021, 81, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Nagata, T.; Fukutani, N.; Tezuka, M.; Shimoura, K.; Nagai-Tanima, M.; Aoyama, T. Health effects of immediate telework introduction during the COVID-19 era in Japan: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinert, C.; Maier, C.; Laumer, S. Why are teleworkers stressed? An empirical analysis of the causes of telework-enabled stress. Wirtsch. Proc. 2015, 2015, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Deschênes, A.A. Professional isolation and pandemic teleworkers’ satisfaction and commitment: The role of perceived organizational and supervisor support. Eur. Rev. Appl. Psychol. 2023, 73, 100823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danker, T.N.; Yap, H.L.; Zalzuli, A.D.; Ho, H.F.; Ang, J. Surviving Work from Home: Observations from Singapore. J. Police Crim. Psychol. 2022, 37, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebuhr, F.; Borle, P.; Börner-Zobel, F.; Voelter-Mahlknecht, S. Healthy and Happy Working from Home? Effects of Working from Home on Employee Health and Job Satisfaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centro de Investigaciones Sociológicas (CIS). Tendencies in the Digital Society during COVID-19 Pandemic. 2021. Available online: http://datos.cis.es/pdf/Es3316marMT_A.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2023). (In Spanish).
- Conroy, R.M. The RCSI Sample Size Handbook. A Rough Guide. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324571619_The_RCSI_Sample_size_handbook (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Ministerio del Trabajo y Economía Social. State Labor Market Report. 2020. Available online: https://www.sepe.es/dctm/informes:09019ae381a473a5/SU5GT1JNRVM=/3583-1.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Press Note of Year 2021. 2021. Available online: https://www.ine.es/prensa/eess_2021_d.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2023). (In Spanish).
- Ragin, C. User’s Guide to Fuzzy-Set/Qualitative Comparative Analysis 3; Department of Sociology, University of California: Irvine, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thiem, A. Set-Relational Fit and the Formulation of Transformational Rules in fsQCA. Compasss Wp Ser. 2010 2010-61. 2010. Available online: http://www.compasss.org/wpseries/Thiem2010 (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Fonner, K.L.; Roloff, M.E. Testing the Connectivity Paradox: Linking Teleworkers’ Communication Media Use to Social Presence, Stress from Interruptions, and Organizational Identification. Commun. Monogr. 2012, 79, 205–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Encuesta Sobre la Población Activa. 2020. Available online: https://www.ine.es/index.htm (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Velasco, L. El Teletrabajo en España Antes, Durante y Después de la Pandemia. Ministerio de Asuntos Económicos y Transformación Digital. 2021. Available online: https://www.ontsi.es/sites/ontsi/files/2022-06/teletrabajoenespana.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2023). (In Spanish).

| IQ1: Sex | IQ2: Age | IQ3: Academic Level |
| Female (49.45%) Male (50.55%) | ≤35 years (18.47%) >35 and ≤45 years (25.08%) >45 and ≤55 years (25.02%) >55 years (31.43%) Mean = 49.69 years. SD = 16.76 years. | Graduate and upper graduate (57.16%) Secondary/vocational training (9.46%) Primary school (20.16%) Others: (13.22%) |
| IQ4: Place of residence | IQ5: Connectivity | |
| Capital of region (65.39%) Cap. of prov. (10.69%) Others (23.91%) |
| |
| IQ6: Consequences of working from home on family | ||
Positive issues
| ||
| IQ7: Organization support | IQ8: Experience | |
Positive issues
| Teleworking before March 2020 was:
| |
| IQ9: Adaptability | ||
| ||
| Output Question: Judgment of the Impact of WFH on Employees |
|---|
Positive arguments
|
| CONNECT | FAMILY | SUPPORT | ADAPTABILITY | JUDGEMENT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −4 | −1 | 0 | −4 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| 5 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 3 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marg. Effect | p-Value | Marg. Effect | p-Value | Marg. Effect | p-Value | |
| Sociodemographic variables | ||||||
| SEX | −0.058 * | 0.0349 | −0.001 | 0.9788 | 0.005 | 0.8140 |
| AGE | −0.081 * | 0.0205 | −0.002 | 0.9498 | −0.002 | 0.9571 |
| ACADEMIC | 0.125 ** | 0.0033 | 0.010 | 0.7986 | −0.008 | 0.8522 |
| Environmental factors | ||||||
| CAP_ADM | --- | --- | −0.062 * | 0.0122 | −0.066 * | 0.0116 |
| CONNECT | --- | --- | 0.123 ** | 0.0010 | 0.100 ** | 0.0095 |
| FAMILY | --- | --- | 0.882 *** | <0.0001 | 0.870 *** | <0.0001 |
| Job/organizational factors | ||||||
| SUPPORT | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.123 ** | 0.0038 |
| EXPERIENCE | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.059 | 0.1167 |
| ADAPTABILITY | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.082 * | 0.0425 |
| Measure | Measure | Δ | Measure | Δ | ||
| AIC | 2624.02 | 2017.28 | −606.74 | 2007.30 | −9.98 | |
| BIC | 2650.73 | 2060.01 | −590.72 | 2066.05 | 6.04 | |
| HQIC | 2633.95 | 2033.17 | −600.78 | 2029.15 | −4.02 | |
| Likelihood ratio | 29.427 *** | 658.73 *** | 675.868 *** | |||
| Hypothesized Sign | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEMALE | Null effect | Not supported | Supported | Supported |
| AGE | Null effect | Not supported | Supported | Supported |
| ACADEMIC | Positive | Supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| CAP_ADM | Negative | Supported | Supported | |
| CONNECT | Positive | --- | Supported | Supported |
| FAMILY | Positive | --- | Supported | Supported |
| SUPPORT | Positive | --- | --- | Supported |
| EXPERIENCE | Positive | --- | --- | Not supported |
| ADAPTABILITY | Positive | --- | --- | Supported |
| JUDGEMENT (Y) | ~JUDGEMENT (~Y) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition (X) | Consistency of X⇒Y | Consistency of ~X⇒Y | Consistency of X⇒~Y | Consistency of ~X⇒~Y |
| FEMALE | 0.63 | 0.67 | 0.37 | 0.37 |
| AGE | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.42 | 0.37 |
| ACADEMIC | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.37 | 0.51 |
| CAP_ADM | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.39 | 0.35 |
| CONNECT | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.36 | 0.49 |
| FAMILY | 0.85 | 0.63 | 0.34 | 0.73 |
| SUPPORT | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.46 | 0.55 |
| EXPERIENCE | 0.64 | 0.69 | 0.37 | 0.34 |
| ADAPTABILITY | 0.75 | 0.63 | 0.33 | 0.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Andrés-Sánchez, J.; Belzunegui-Eraso, Á. Spanish Workers’ Judgement of Telecommuting during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mixed-Method Evaluation. Information 2023, 14, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14090488
de Andrés-Sánchez J, Belzunegui-Eraso Á. Spanish Workers’ Judgement of Telecommuting during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mixed-Method Evaluation. Information. 2023; 14(9):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14090488
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Andrés-Sánchez, Jorge, and Ángel Belzunegui-Eraso. 2023. "Spanish Workers’ Judgement of Telecommuting during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mixed-Method Evaluation" Information 14, no. 9: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14090488
APA Stylede Andrés-Sánchez, J., & Belzunegui-Eraso, Á. (2023). Spanish Workers’ Judgement of Telecommuting during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Mixed-Method Evaluation. Information, 14(9), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14090488









