Incorporating an Unsupervised Text Mining Approach into Studying Logistics Risk Management: Insights from Corporate Annual Reports and Topic Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Supply Chain Risks
2.2. Supply Chain Connectivity
- Resilience involves the ability to adapt to disruption events, including finding alternative supplies;
- Redundancy involves increasing product availability through building backup capacity or inventory;
- Robustness is the ability to survive in the face of challenge, which is enhanced by resilient actions and redundant systems;
- Flexibility is attained by being able to sense threats, react, and recover quickly, usually in the form of reallocation of inventory and capacity.
2.3. Bibliometric Analysis of Supply Chain Risk Management
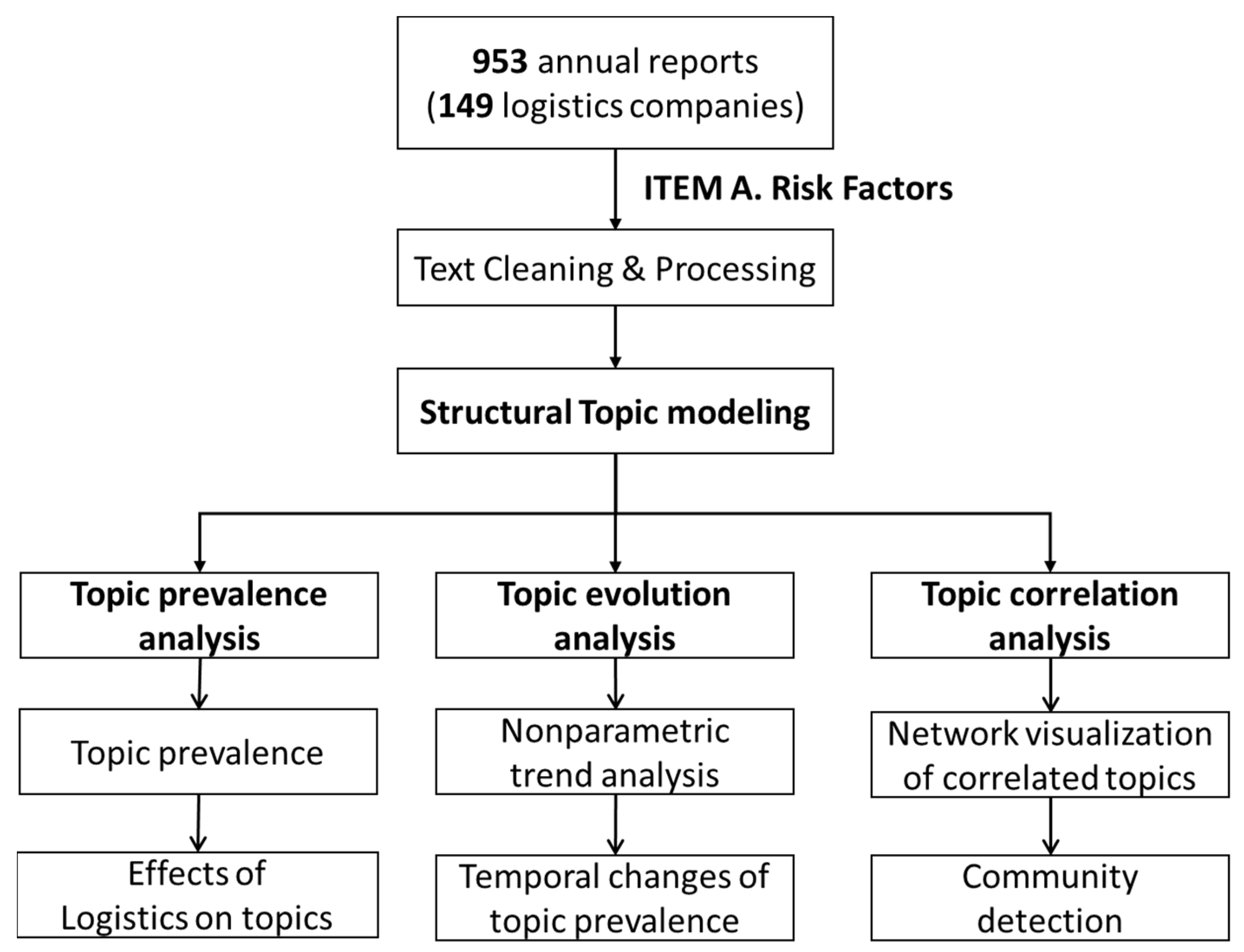
3. Research Methods and Data
3.1. Data
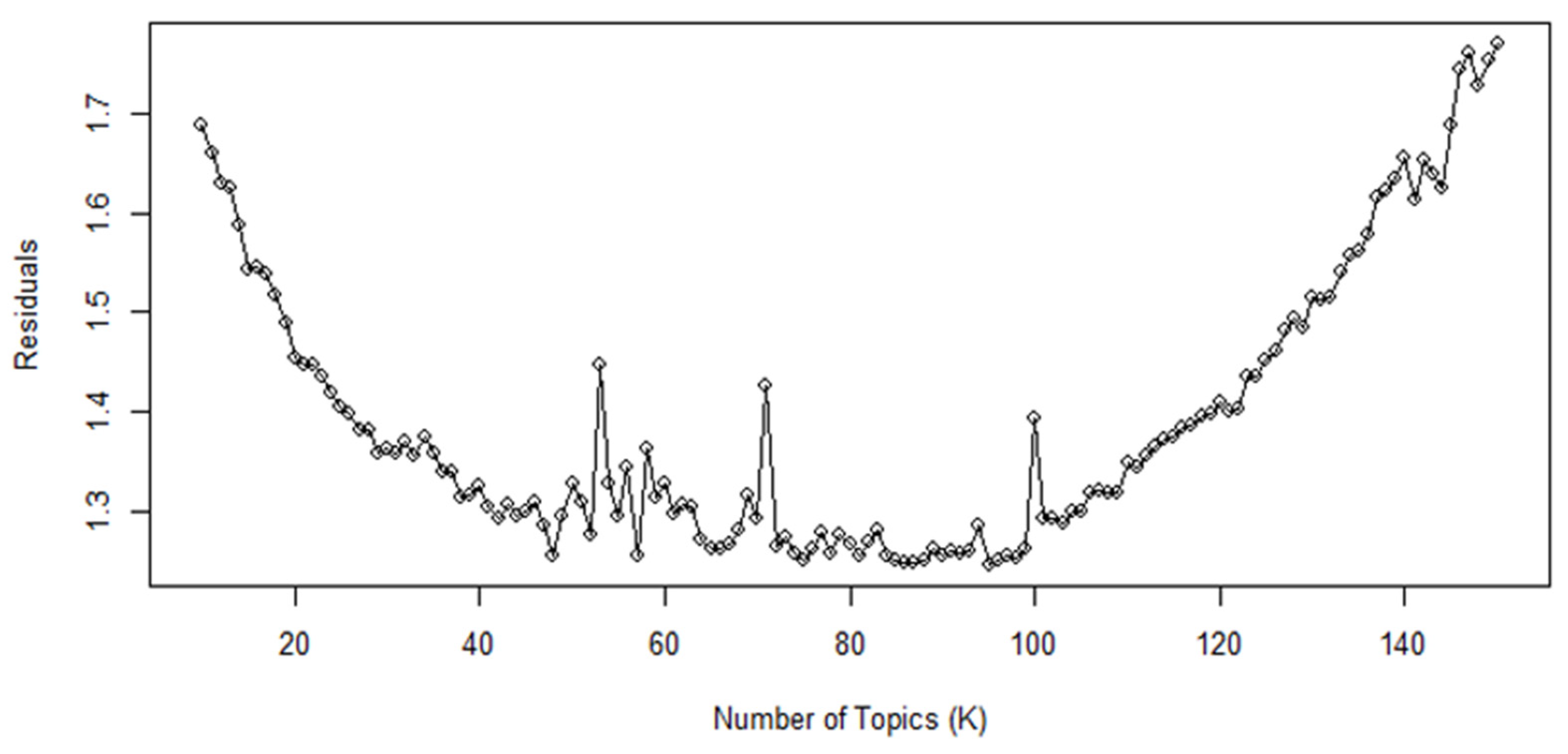
3.2. Structural Topic Modeling (STM)
3.3. Analysis of STM Topic Model
4. Analysis and Results
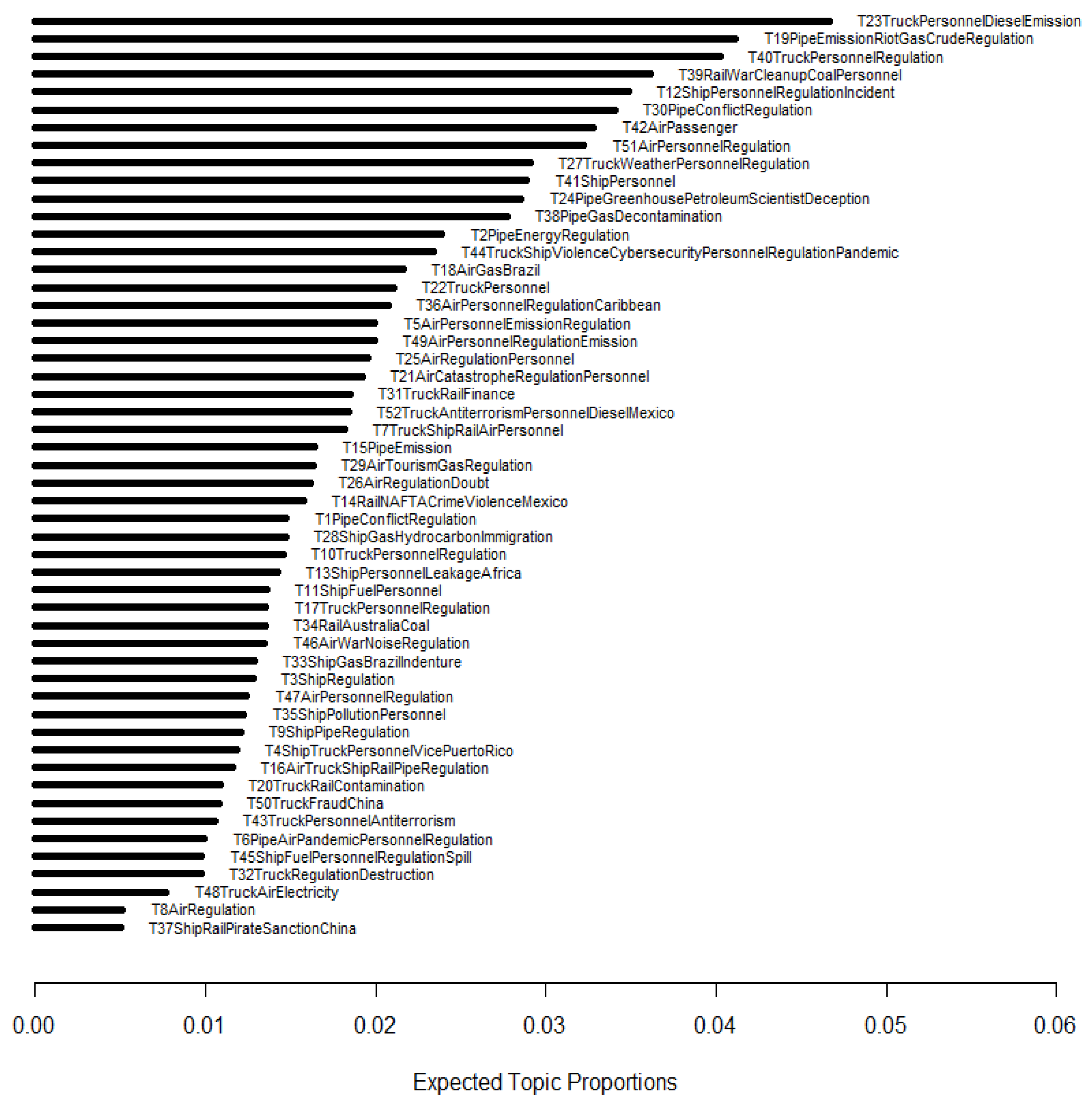
4.1. Topic Prevalence Analysis
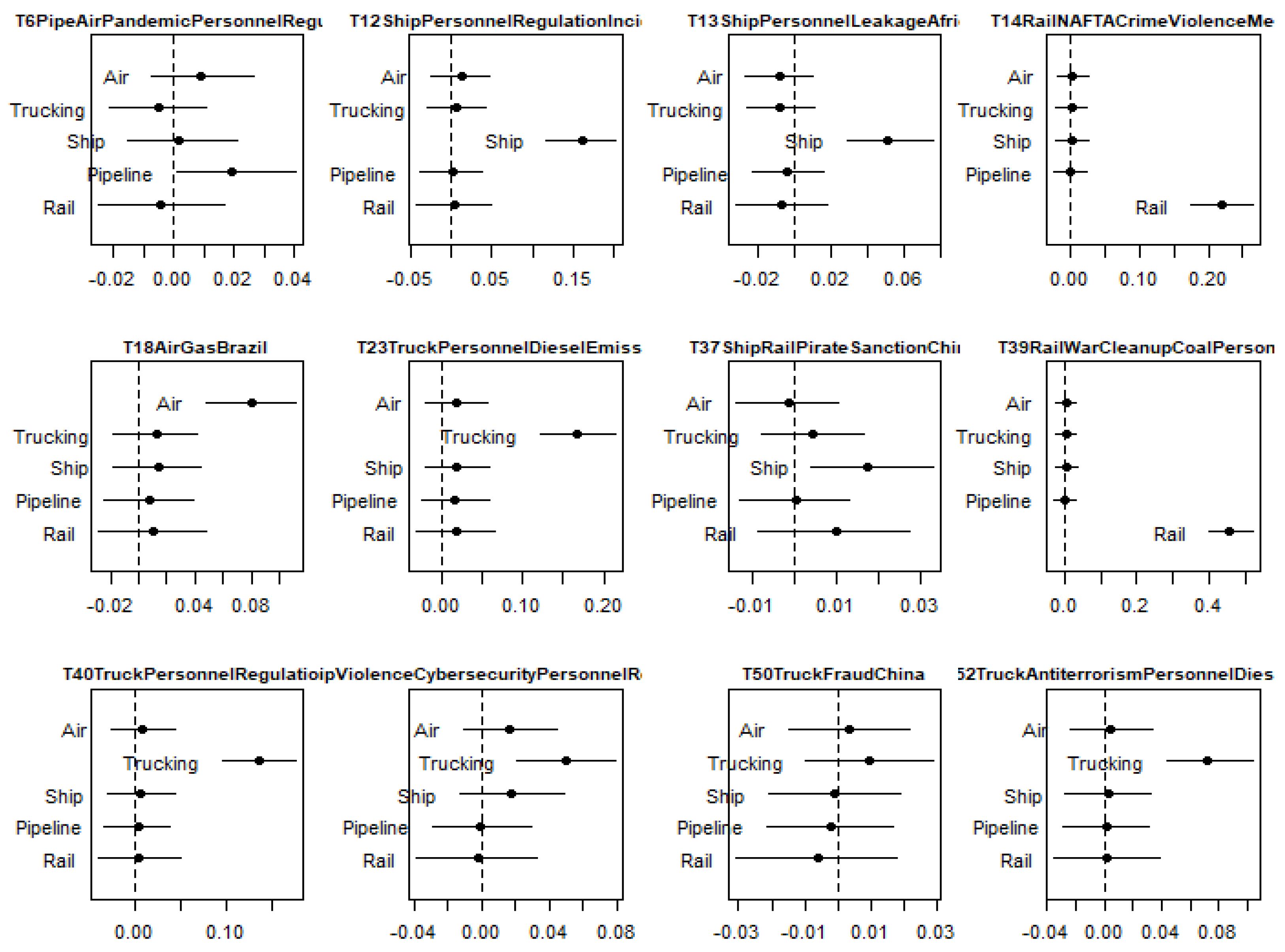
4.2. Topic Evolution Analysis
4.3. Topic Correlation Analysis
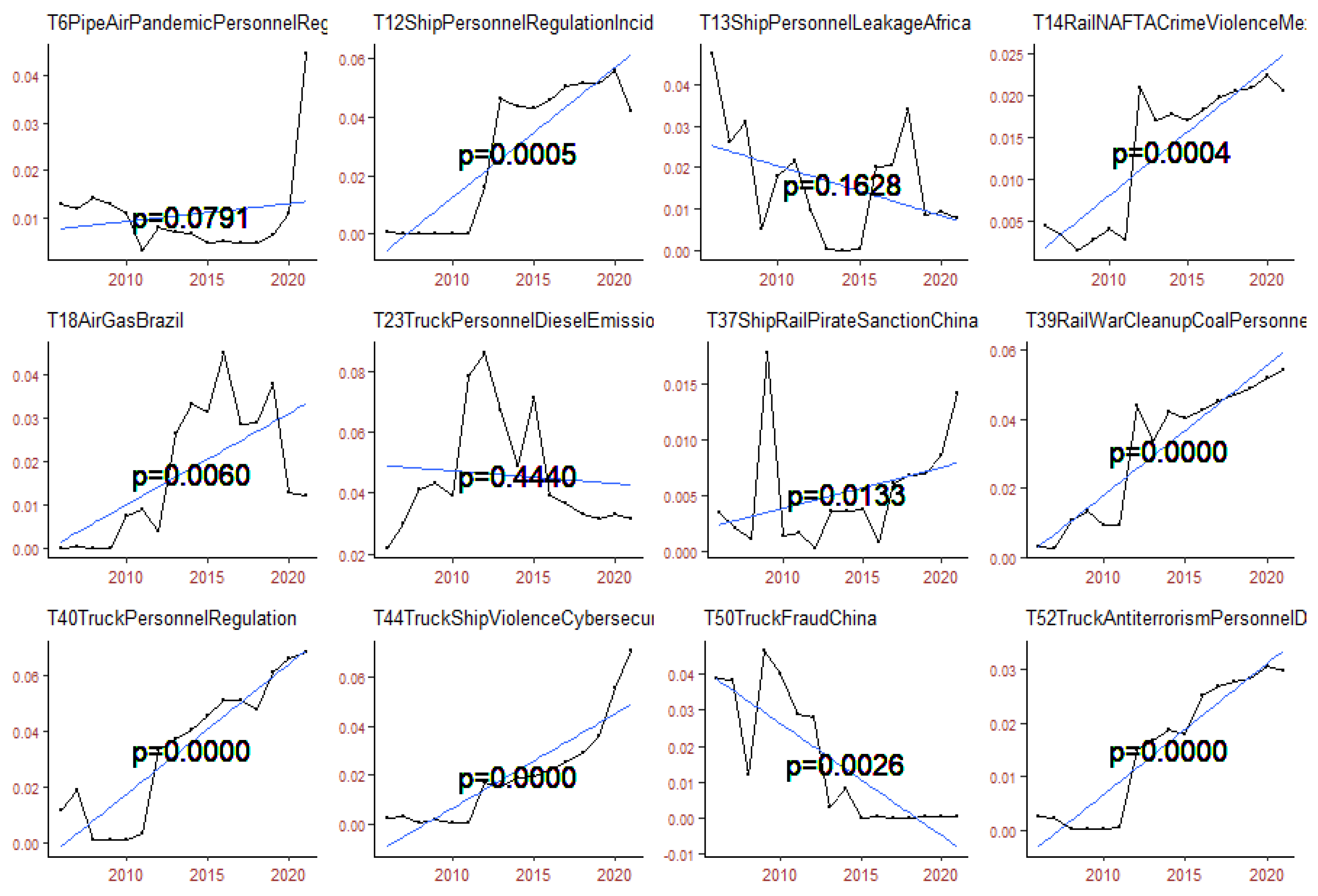
4.4. Logistics Risk Analysis
4.4.1. Personnel and Fuel
4.4.2. Pandemic
4.4.3. International
5. Discussion: Mitigation Strategies
6. Conclusions
6.1. Implications
6.2. Contributions
6.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jüttner, U. Supply chain risk management: Understanding the business requirements from a practitioner perspective. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2005, 16, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, U.; Peck, H.; Christopher, M. Supply chain risk management: Outlining an agenda for future research. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2003, 6, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, M.; Lim, J.Y.; Meng, F. A stochastic model for risk management in global supply chain networks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 182, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thun, J.-H.; Hoenig, D. An empirical analysis of supply chain risk management in the German automotive industry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 131, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedghorban, Z.; Samson, D.; Swink, M. Quo vadis OSCM? An analysis of past and future trends in operations and supply chain management research. Decis. Sci. 2022, 53, 429–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgui, A.; Ivanov, D.; Sokolov, B. Ripple effect in the supply chain: An analysis and recent literature. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrman, A.; Jansson, U. Ericsson’s proactive supply chain risk management approach after a serious sub-supplier accident. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2004, 34, 434–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S. Robust strategies for mitigating supply chain disruptions. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2006, 9, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Zheng, T.; Yildiz, H.; Talluri, S. Supply chain risk management: A literature review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 5031–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.L.; Wu, D.D. Enterprise Risk Management Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, M.; Lau, A.K. A systematic review on supply chain risk management: Using the strategy-structure-process-performance framework. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2020, 23, 443–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M. Probabilistic topic models. Commun. ACM 2012, 55, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Lafferty, J.D. A correlated topic model of science. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2007, 1, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.E.; Stewart, B.M.; Airoldi, E.M. A model of text for experimentation in the social sciences. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2016, 111, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.E.; Stewart, B.M.; Tingley, D. Stm: An R package for structural topic models. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 91, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, O.P.; Ali, R.K.; Maulud, S.Q.; Dhawan, M.; Mohammed, T.A. Will the next spillover pandemic be deadlier than the COVID-19?: A wake-up call. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 97, 106208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Dan, B.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X. Supply chain coordination with information sharing: The informational advantage of GPOs. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 256, 785–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadi, N.; Borbon-Galvez, Y.; Strozzi, F.; Etemadi, T. Supply chain disruption risk management with blockchain: A dynamic literature review. Information 2021, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, F.; Lane, L.; Sáez de Tejada Cuenca, A. Can brands claim ignorance? Unauthorized subcontracting in apparel supply chains. Manag. Sci. 2021, 67, 2010–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lee, Y.M. An investigation of consumers’ perception of food safety in the restaurants. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 73, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Magazine, M.J.; Rao, U. Buyer selection and service pricing in an electric fleet supply chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 295, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghalian, A.; Rezapour, S.; Farahani, R.Z. Robust supply chain network design with service level against disruptions and demand uncertainties: A real-life case. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 227, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Smith, S.A. Optimal inventory management using retail prepacks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 274, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Babai, M.Z.; Boylan, J.E.; Syntetos, A.A. Supply chain forecasting when information is not shared. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 260, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, J.; Guns, T.; Verbeke, W. Using shared sell-through data to forecast wholesaler demand in multi-echelon supply chains. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 288, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.W. Industrial dynamics: A major breakthrough for decision makers. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1958, 36, 37–66. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, N.; Schulze-Schwering, S.; Long, E.; Spinler, S. Risk management of supply chain disruptions: An epidemic modeling approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2023, 304, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuj, I.; Mentzer, J.T. Global supply chain risk management. J. Bus. Logist. 2008, 29, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobanee, H.; Alhajjar, M.; Abushairah, G.; Al Harbi, S. Reputational risk and sustainability: A bibliometric analysis of relevant literature. Risks 2021, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilubi, I. Investigating current paradigms in supply chain risk management—A bibliometric study. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2016, 22, 662–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, M.V.C.; Teles, E.O.; de Melo, S.A.V.; Freires, F.G.M. Decision-making models and support systems for supply chain risk: Literature mapping and future research agenda. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2020, 26, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, M.V.C.; Teles, E.O.; Vieira de Melo, S.A.; Freires, F.G.M. Supply chain risk management modelling: A systematic literature network analysis review. IMA J. Manag. Math. 2020, 31, 387–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senna, P.; da Cunha Reis, A.; Castro, A.; Dias, A.C. Promising research fields in supply chain risk management and supply chain resilience and the gaps concerning human factors: A literature review. Work 2020, 67, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P.; Hassini, E. Evolution of supply chain ripple effect: A bibliometric and meta-analytic view of the constructs. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Tang, C.S.; Davarzani, H.; Sarkis, J. Quantitative models for managing supply chain risks: A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 247, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, H.N.; Hurley, J.; Fahimnia, B.; Reisi, M. The human factor in supply chain forecasting: A systematic review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 274, 574–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournader, M.; Kach, A.; Talluri, S. A review of the existing and emerging topics in the supply chain risk management literature. Decis. Sci. 2020, 51, 867–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksana, A.; Ho, W.; Talluri, S.; Dolgui, A. A decade of progress in supply chain risk management: Risk typology, emerging topics, and research collaborators. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 7155–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, B.; Olson, D. A topical exploration of the intellectual development of decision sciences 1975–2016. Decis. Sci. 2021, 52, 543–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, B.K.; Olson, D. Mapping the Evolution of Social Media Analytics Research in Operations and Supply Chain Management: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Supply Chain Oper. Manag. 2022, 20, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Azmi Shabestari, M.; Moffitt, K.; Sarath, B. Did the banking sector foresee the financial crisis? Evidence from risk factor disclosures. Rev. Quant. Financ. Account. 2020, 55, 647–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janggu, T.; Sawani, Y.; Yusoff, H.; Darus, F.; Mohamed Zain, M. Does social risk management matter? Influencing factors and their link to firms’ financial performances. Manag. Account. Rev. 2017, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wu, K. Corporate risk disclosure and audit fee: A text mining approach. Eur. Account. Rev. 2018, 27, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi Shabestari, M.; Romero, J.A. Textual Analysis and Future Performance: Evidence From Item 1A and Item 7. J. Account. Audit. Financ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, V.; Müßig, A. The effect of business strategy on risk disclosure. Account. Eur. 2022, 19, 190–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T.T.; Kim, J.B.; Wang, Z. Customers’ risk factor disclosures and suppliers’ investment efficiency. Contemp. Account. Res. 2019, 36, 773–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechle, C.; Huang, C.D.; Agarwal, A.; Behara, R.S.; Goo, J. Latent topic ensemble learning for hospital readmission cost optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 281, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk Wheelock, L.; Pachamanova, D.A. Acceptable set topic modeling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2022, 299, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, R.; Singh, L. The evolution of topic modeling. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Ge, R.; Halpern, Y.; Mimno, D.; Moitra, A.; Sontag, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, M. A practical algorithm for topic modeling with provable guarantees. Proc. Int. Conf. Mach. Learn. 2013, 28, 280–288. [Google Scholar]
- Feinerer, I. Introduction to the tm Package Text Mining in R. 2013. Available online: http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/tm/vignettes/tm.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Taddy, M. On estimation and selection for topic models. Proc. Artif. Intell. Stat. 2012, 22, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, T.L.; Steyvers, M. Finding scientific topics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5228–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Cheng, G.; Gong, T. Topics and trends in artificial intelligence assisted human brain research. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.; Hric, D. Community detection in networks: A user guide. Phys. Rep. 2016, 659, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, J.A.; Amburgey, T.L. Organizational ecology. Blackwell Companion Organ. 2017, 304–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L.; Yang, W. Disruption risks in supply chain management: A literature review based on bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 3508–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huchzermeier, A. Operations–finance interface models: A literature review and framework. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 244, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vayansky, I.; Kumar, S.A.P. A review of topic modeling methods. Inf. Syst. 2020, 94, 101582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbalchiero, S.; Eder, M. Topic modeling, long texts and the best number of topics. Some Problems and solutions. Qual. Quant. 2020, 54, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Tang, T.; Li, L.; Zhao, W.X. A survey on long text modeling with transformers. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.14502. [Google Scholar]
- Angelov, D. Top2vec: Distributed representations of topics. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.09470. [Google Scholar]
- Grootendorst, M. BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05794. [Google Scholar]



| Year | Air | Trucking | Rail | Shipping | Pipeline | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 12 | 10 | 2 | 12 | 2 | 38 |
| 2007 | 16 | 12 | 1 | 10 | 4 | 43 |
| 2008 | 13 | 7 | 1 | 10 | 2 | 33 |
| 2009 | 13 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 32 |
| 2010 | 12 | 9 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 36 |
| 2011 | 13 | 9 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 35 |
| 2012 | 11 | 23 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 61 |
| 2013 | 21 | 23 | 5 | 12 | 16 | 77 |
| 2014 | 21 | 22 | 6 | 13 | 20 | 82 |
| 2015 | 22 | 23 | 6 | 15 | 19 | 85 |
| 2016 | 22 | 19 | 6 | 16 | 18 | 81 |
| 2017 | 20 | 17 | 6 | 15 | 17 | 75 |
| 2018 | 19 | 17 | 6 | 15 | 16 | 73 |
| 2019 | 21 | 18 | 6 | 13 | 14 | 72 |
| Topic # | Terms | Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | Loan, pandemic, treasury, restricting, treasury | 0.009958 |
| 12 | Cruise, ship, port, guest, treaty | 0.034844 |
| 13 | Tanker, charter, pool, detention, voyage | 0.014237 |
| 14 | Railroad, concession, Mexico, traffic, crime | 0.015758 |
| 18 | Helicopter, gas, production, exploration, Brazil | 0.021635 |
| 23 | Driver, tractor, diesel, engine, emission | 0.046674 |
| 37 | Sanction, mining, bulk, China, Libor, export | 0.005057 |
| 39 | Rail, railroad, coal, clean-up, concerning | 0.036162 |
| 40 | Driver, contractor, lawsuit, turnover, legislator | 0.040267 |
| 44 | Libor, brand, cybersecurity, pandemic, coronavirus | 0.023404 |
| 50 | Dealer, China, currency, exchange, freight | 0.010799 |
| 52 | Driver, contractor, anti-terrorism, disrupt, closure | 0.018439 |
| # | Topic Clusters |
|---|---|
| 1 | T1PipeConflictRegulation, T13ShipPersonnelLeakageAfrica, T50TruckFraudChina, T4ShipTruckPersonnelVicePuertoRico, T37ShipRailPirateSanctionChina, T17TruckPersonnelRegulation, T20TruckRailContamination, T26AirRegulationDoubt, T34RailAustraliaCoal, T52TruckAntiterrorismPersonnelDieselMexico, T41ShipPersonnel, T45ShipFuelPersonnelRegulationSpill, T46AirWarNoiseRegulation, T48TruckAirElectricity (14 topics) |
| 2 | T15PipeEmission, T6PipeAirPandemicPersonnelRegulation, T19PipeEmissionRiotGasCrudeRegulation, T21AirCatastropheRegulationPersonnel, T24PipeGreenhousePetroleumScientistDeception, T30PipeConflictRegulation, T33ShipGasBrazilIndenture, T36AirPersonnelRegulationCaribbean, T47AirPersonnelRegulation, T51AirPersonnelRegulation (10 topics) |
| 3 | T7TruckShipRailAirPersonnel, T12ShipPersonnelRegulationIncident, T23TruckPersonnelDieselEmission, T10TruckPersonnelRegulation, T16AirTruckShipRailPipeRegulation, T40TruckPersonnelRegulation, T27TruckWeatherPersonnelRegulation, T31TruckRailFinance (eight topics) |
| 4 | T22TruckPersonnel, T44TruckShipViolenceCybersecurityPersonnelRegulationPandemic, T35ShipPollutionPersonnel, T42AirPassenger (four topics) |
| 5 | T18AirGasBrazil, T28ShipGasHydrocarbonImmigration, T29AirTourismGasRegulation (three topics) |
| 6 | T14RailNAFTACrimeViolenceMexico, T39RailWarCleanupCoalPersonnel (two topics) |
| Risk Categories | Trucking | Shipping | Air | Rail | Pipeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personnel | Driver retention, operator, pension, recruitment, unionization | Crew, hire, manning, captain | Pilot, furlough, attendant, dispatcher, union | Injury | Scientist, pension, payroll |
| Fuel | Diesel | Gas, diesel, hydrocarbon | Gas | Coal | Energy, gas, petroleum, crude, distillate |
| Weather | Snow, winter | ||||
| Risks | Terrorism, fraud, underground, emission, destruction | Incident, leakage, immigration, pollution, vice | Catastrophe, war, emission, noise | Crime, clean-up, war, violence | Conflict, emission, riot, greenhouse, deception |
| International | China, Mexico | Africa | Brazil | Mexico, Australia, Canada | |
| Pandemic | Health | Coronavirus | Pandemic | ||
| Regulatory | License, ordinance, hours-of-service, taxation, legislature | Inspection, arrest, treaty, warrant, certificate | FAA, federalization, legislature, auditor, warrant | NAFTA | IRS, shutdown, fracturing, restricting |
| Risk Category | Mitigation (Zhao and Huchzermeier [59]) | Elements (Nakano and Lau [11]) | Robust Strategy (Tang [8]) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply | Multiple suppliers (backup production/suppliers), quantity-flexible contracts, invest in supplier improvement, strategic stock | Redundancy | Strategic stock, economic supply incentives |
| Processing | Production flexibility, modularization, timing of product introduction | Flexibility | Postponement, make-or-buy, transportation flexibility |
| Demand | Shift demand over time, markets, products, customize service | Agility | Influence customer selection, dynamic assortment planning |
| Network | Coordinate decisions (contracts, information sharing) | Collaboration |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olson, D.; Chae, B. Incorporating an Unsupervised Text Mining Approach into Studying Logistics Risk Management: Insights from Corporate Annual Reports and Topic Modeling. Information 2023, 14, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14070395
Olson D, Chae B. Incorporating an Unsupervised Text Mining Approach into Studying Logistics Risk Management: Insights from Corporate Annual Reports and Topic Modeling. Information. 2023; 14(7):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14070395
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlson, David, and Bongsug (Kevin) Chae. 2023. "Incorporating an Unsupervised Text Mining Approach into Studying Logistics Risk Management: Insights from Corporate Annual Reports and Topic Modeling" Information 14, no. 7: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14070395
APA StyleOlson, D., & Chae, B. (2023). Incorporating an Unsupervised Text Mining Approach into Studying Logistics Risk Management: Insights from Corporate Annual Reports and Topic Modeling. Information, 14(7), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14070395





