Abstract
Effectively harnessing the power of social media data for disaster management requires sophisticated analysis methods and frameworks. This research focuses on understanding the contextual information present in social media posts during disasters and developing a taxonomy to effectively categorize and classify the diverse range of topics discussed. First, the existing literature on social media analysis in disaster management is explored, highlighting the limitations and gaps in current methodologies. Second, a dataset comprising real-time social media posts related to various disasters is collected and preprocessed to ensure data quality and reliability. Third, three well-established topic modeling techniques, namely Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA), and Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (NMF), are employed to extract and analyze the latent topics and themes present in the social media data. The contributions of this research lie in the development of a taxonomy that effectively categorizes and classifies disaster-related social media data, the identification of key latent topics and themes, and the extraction of valuable insights to support and enhance emergency management efforts. Overall, the findings of this research have the potential to transform the way emergency management and response are conducted by harnessing the power of social media data. By incorporating these insights into decision-making processes, emergency managers can make more informed and strategic choices, resulting in more efficient and effective emergency response strategies. This, in turn, leads to improved outcomes, better utilization of resources, and ultimately, the ability to save lives and mitigate the impacts of disasters.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the world has witnessed a significant increase in the frequency and severity of natural disasters [1]. These events pose significant challenges for emergency management and require timely and accurate information for effective decision-making. Social media has emerged as a valuable data source, providing real-time insights into the impacts of disasters and enabling a better understanding of the evolving situations on the ground [2]. Social media platforms, such as Twitter, have become integral parts of people’s lives, allowing them to share their experiences, thoughts, and concerns during critical events like natural disasters [3,4]. These platforms serve as digital communication channels where affected individuals, eyewitnesses, and volunteers can share valuable information, including photos, videos, and textual updates, in real-time [5]. As a result, social media has transformed into a rich and dynamic data source for researchers and emergency management practitioners seeking to gain deeper insights into the impacts and consequences of disasters. The real-time nature of social media data is particularly valuable during disaster events, as it provides an immediate and unfiltered glimpse into the experiences, needs, and challenges of affected communities [6]. In addition to real-time data analysis, social media data generated during disasters can provide valuable insights that help emergency managers and decision-makers make long-term strategic decisions [7]. Social media data can help identify trends, patterns, and emerging issues that may not be captured through traditional data sources. For example, by monitoring social media conversations, decision-makers can gather information about specific challenges faced by different communities, such as access to resources, infrastructure damage, or gaps in services. These data can inform resource allocation strategies and guide the prioritization of recovery efforts.
The analysis of social media data can be a challenging undertaking due to its complexity [5,8,9,10,11,12]. The complexities associated with analyzing social media data in the context of disasters stem from several factors. First, social media platforms generate an enormous volume of data during disaster events, making it challenging to process and extract meaningful information. The sheer scale of the data requires sophisticated analysis methods that can handle large datasets efficiently. Second, social media data are inherently unstructured, comprising a mix of text, images, videos, and other multimedia content. Traditional analytical techniques are often ill-suited to handle such diverse data types, requiring innovative approaches to extract relevant insights. Textual data, for example, may contain abbreviations, slang, misspellings, and informal language, posing challenges for automated analysis and natural language processing. Third, social media data are characterized by noise. Filtering out the noise and identifying credible sources of information is a crucial step in analyzing social media data effectively.
The objective of this study is to develop a comprehensive framework for analyzing social media data related to disasters and extracting valuable insights to support emergency management efforts. The research focuses on understanding the contextual information present in social media posts during disasters and aims to create a taxonomy that effectively categorizes and classifies the diverse range of topics discussed in these posts. Unlike existing studies, this research specifically tailors the taxonomy to the context of disaster-related social media posts using three topic modeling techniques: Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA), and Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) [13,14,15]. The taxonomy serves as a systematic framework for organizing and interpreting the wealth of information available in social media data [8,16]. It provides a standardized and consistent approach to categorizing social media posts, allowing emergency managers to capture and analyze the needs, concerns, and experiences expressed by affected communities as well as policy makers during disasters. By understanding the specific topics and themes emerging from social media conversations, emergency managers can prioritize response efforts, identify service gaps, and tailor their communication strategies to meet the needs of affected communities better. Moreover, the taxonomy serves as a valuable tool for real-time monitoring of social media data during disasters [8]. By applying the taxonomy to a limited number of related tweets, emergency managers can quickly identify the context and topic of those tweets within the disaster taxonomy framework. This enables a rapid assessment of the key issues and concerns expressed by affected communities, allowing emergency managers to respond promptly and adapt their strategies as the situation evolves.
By developing this taxonomy, this research offers a structured and systematic approach to harnessing the information available in social media data for effective emergency management. The taxonomy not only enhances the understanding of social media conversations during disasters but also informs decision-making processes and resource allocation strategies. It empowers emergency managers to leverage the power of social media as a valuable source of real-time information, enabling them to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to mitigate the impact of disasters on affected communities.
The exposition of this study is as follows. The study begins with a comprehensive literature review, exploring existing research on social media analysis in the context of disaster management and topic modeling techniques. Next, the study outlines the methodology employed to achieve the research objectives. Following the methodology, the study presents the results and analysis section, where the findings from the topic modeling techniques are presented. The significance of the proposed taxonomy is then discussed. Finally, the study concludes by summarizing the key findings, contributions, and potential future research directions.
2. Literature Review
The role of social media in disaster response has been extensively studied by researchers worldwide [4,9,10]. Numerous studies have explored the various ways in which social media platforms are utilized during emergencies, shedding light on their effectiveness, challenges, and implications for disaster response strategies. This literature review aims to synthesize and analyze the findings from a range of studies that have examined social media’s role in disaster response. One common theme in the literature is the use of social media for information dissemination and situational awareness. Researchers have found that social media platforms, such as Twitter and Facebook, play a crucial role in disseminating real-time information during disasters (e.g., [12,17]). These platforms allow affected individuals, emergency responders, and the general public to share updates, photos, videos, and other relevant information, providing immediate insights into the evolving situation on the ground. The rapid flow of information facilitated by social media enables timely decision-making, resource allocation, and coordination of response efforts. Moreover, researchers have explored how social media enhances community engagement and support during disasters (e.g., [4,18]). Social media platforms serve as virtual gathering places where affected individuals can connect, share experiences, seek assistance, and offer support to one another. These platforms foster a sense of community and facilitate the exchange of valuable information, resources, and emotional support. Furthermore, studies have examined the role of social media in volunteer mobilization and the coordination of relief operations [19,20,21]. Platforms such as Twitter and Facebook have been instrumental in facilitating the organization of volunteer groups, disseminating information about donation opportunities, and coordinating rescue and relief operations. Social media has also proven to be an effective tool for rallying support, mobilizing resources, and coordinating the efforts of both formal and informal networks of volunteers. This aspect of social media’s role in disaster response highlights its potential for strengthening community resilience and facilitating grassroots initiatives.
In the context of disasters, social media data analysis is often unstructured, making it challenging to extract useful information and effectively utilize it for emergency response planning [22,23,24]. Without a structured analysis approach, the vast amount of data generated on social media platforms can be overwhelming and difficult to navigate. This unstructured data may contain valuable insights about the needs, concerns, and experiences of affected communities, but without a systematic framework, it becomes challenging to identify and categorize relevant information. However, structured analysis methods, such as the development of a taxonomy or categorization framework, can greatly enhance the understanding and utilization of social media data in emergency response planning.
Text mining can be a valuable tool in developing a taxonomy for social media data analysis in the context of disasters [16]. Text mining techniques allow researchers to extract meaningful information from unstructured text data and uncover patterns, topics, and relationships within the data. By applying text mining methods to the large volume of social media posts, researchers can identify key themes and topics that emerge during and after disasters [25,26,27,28]. One way text mining can contribute to developing a taxonomy is through topic modeling techniques. Topic modeling algorithms can automatically discover latent topics within social media data based on the distribution of words and phrases [29,30,31]. These topics can then be used to form the foundation of the taxonomy, representing the major categories and subcategories of the data. By applying topic modeling, researchers can systematically organize and classify the diverse range of topics discussed in social media posts. Researchers have used these techniques to automatically process and categorize textual data into relevant categories, such as types of disasters, affected regions, and key events [15,32,33,34]. These techniques enable efficient and automated classification of large volumes of text, facilitating the identification of critical information for emergency management and response.
In essence, this research employs sophisticated text mining-based analysis techniques to handle the large volume of data efficiently, utilizes innovative approaches to handle diverse data types, implements techniques for filtering and validating social media content, and incorporates different analysis techniques. By bridging these gaps in the literature, this research contributes to the development of more effective approaches for leveraging social media data in emergency management and response, ultimately enhancing decision-making processes and supporting effective strategies in the face of natural disasters.
3. Methodology
This section delves into four critical aspects that form the foundation of the methodology employed in this study. These aspects encompass the collection and preprocessing of data, the utilization of topic modeling techniques, the establishment of a hierarchical taxonomy, and the implementation of evaluation measures. Through a comprehensive exploration of these issues, this study presents a detailed methodology that serves as a robust framework for conducting the research.
3.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
3.1.1. Data Collection
The dataset utilized in this study was obtained from the CrisisMMD (Multimodal Crisis Dataset), which serves as an extensive collection of data, capturing diverse aspects of disaster events [35,36,37,38]. Specifically designed to support research and analysis in the field of disaster management and emergency response, this dataset encompasses multiple tasks that shed light on various dimensions of disasters. It comprises a substantial volume of tweet data, totaling approximately 14 million tweets, associated with seven distinct global disasters, including Hurricane Irma, Hurricane Harvey, Hurricane Maria, California Wildfires, the Mexico Earthquake, the Iraq–Iran Earthquake, and the Sri Lanka Floods. This comprehensive representation ensures the inclusion of different types of disasters and their geographical locations. Figure 1 illustrates the word clouds of the major contents available in the seven disaster datasets.
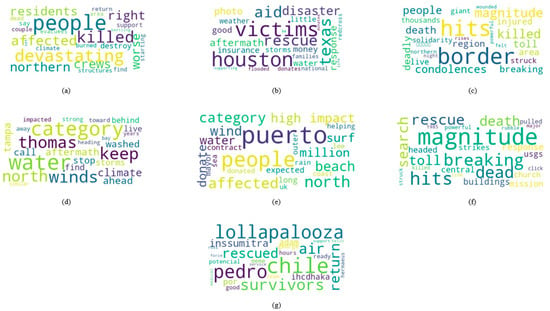
Figure 1.
Word clouds of different disasters: (a) California Wildfire, (b) Hurricane Harvey, (c) Iraq–Iran Earthquake, (d) Hurricane Irma, (e) Hurricane Maria, (f) Mexico Earthquake, and (g) Sri Lanka Flood.
The CrisisMMD dataset encompasses three main tasks that collectively contribute to a holistic understanding of disaster events [37]. Task 1 focuses on distinguishing informative from non-informative tweets, providing insights into the relevance and usefulness of shared information during disasters. Task 2 involves categorizing tweets based on humanitarian aspects, allowing for the identification of key themes and issues relevant to disaster situations. Finally, Task 3 centers around assessing the severity of damage caused by disasters, enabling measurement of their impact and consequences. For the purposes of this research project, Task 2 of the CrisisMMD dataset was selected as the primary data source. It involved categorizing tweets into various humanitarian categories, including Affected Individuals, Infrastructure and Utility Damage, Injured or Dead People, Missing or Found People, Not Humanitarian, Other Relevant Information, Rescue Volunteering or Donation Effort, and Vehicle Damage. These categories encompassed a wide range of aspects related to disaster situations, facilitating a nuanced analysis of the data. Since this study focused on text analysis, only text-based tweets were extracted for further examination.
Note that the data collection period for the CrisisMMD dataset varied in duration depending on the specific disaster. In certain cases, the data collection period aligned with the duration of the disaster itself, while in others, it extended over several months. This diversity in data collection durations highlights the utility of the CrisisMMD dataset as a valuable information source for both short-term and long-term emergency management decision-making. It allows for insights and analysis that can inform immediate response efforts during a crisis as well as support strategic decision-making in the aftermath of a disaster. The comprehensive nature of the dataset enables emergency managers and decision-makers to draw upon a wide range of information to enhance their understanding of various disasters and inform their actions accordingly.
3.1.2. Data Preprocessing
The data preprocessing phase played a crucial role in organizing, cleaning, and preparing the dataset for subsequent topic modeling analyses. The specific steps employed, such as merging, splitting, removing duplicates, and categorizing the data, were driven by the goal of ensuring data integrity, focusing the analysis on specific events and categories, and extracting meaningful insights from the disaster-related tweets. In the data preprocessing phase, the dataset was effectively handled using various packages and libraries in Python programming language, including Pandas, Numpy, and CSV [39]. The dataset was initially categorized in TSV (tab-separated values) format, comprising eight labels: event name, tweet id, image id, tweet text, image, label, label text, and label image. These labels provided essential information about the events, tweets, associated images, and relevant labels. Next, the removal of duplicate entries was performed to maintain data integrity. Duplicates, arising from retweets or reposts, could introduce biases and skew the analysis results. By comparing the unique tweet id of each entry, duplicates were identified. These duplicate entries were then appended to the bottom of the cleaned data CSV file, with appropriate annotations to indicate their duplicate status. This step ensured that the main dataset contained only unique tweets, eliminating redundancy in the subsequent analysis. Following duplicate removal, another split was performed based on the label text column. This categorization facilitated the separation of tweets according to the type of humanitarian category of damage. By creating subsets of data for categories such as Affected Individuals, Infrastructure and Utility Damage, Injured or Dead People, Missing or Found People, Not Humanitarian, Other Relevant Information, Rescue Volunteering or Donation Effort, and Vehicle Damage, the analysis could be focused on specific aspects of the disasters. This categorization provided a more granular understanding of the tweets and enabled deeper insights into the different types of damage, its impacts, and corresponding humanitarian responses.
3.2. Application of Topic Modeling Techniques
After preprocessing and organizing the data, three distinct topic modeling techniques were employed: LDA, LSA, and NMF. The objective of these techniques was to uncover the underlying topics and themes within the tweets related to the disasters. It is important to note that these techniques were simultaneously applied to different subsets of tweet data. For instance, LDA, LSA, and NMF were applied to Infrastructure and Utility Damage data for all seven disaster types, namely Hurricane Irma, Hurricane Harvey, Hurricane Maria, California Wildfires, the Mexico Earthquake, the Iraq–Iran Earthquake, and the Sri Lanka Floods. This resulted in a total of 56 subsets of tweet data across the seven disasters where LDA, LSA, and NMF were concurrently employed. The rationale behind using LDA, LSA, and NMF together lies in the fact that they utilize distinct mechanisms to generate topics. By combining the outputs of these three topic modeling techniques, a comprehensive analysis of the disaster state becomes possible.
During the initial analyses, it was observed that the presence of various unimportant words in the tweets often led to less relevant final sets of topics. To address this, a second set of 56 subsets of tweet data was created, this time with a removal of a set of stop words. The stop words were compiled based on an exhaustive analysis by the research group regarding the tweets’ context. This resulted in a new set of topics and themes, which were then analyzed in conjunction with the previous set of topics and themes where stop words were present in the raw tweets. The combination of output topics both with and without stop words ensured the accumulation of a broad range of final topics and themes. It is worth noting that in finalizing the set of topics and themes, the criteria of being “collectively exhaustive” and “mutually exclusive” were adopted. This means that by utilizing different groupings of raw data (with and without stop words) and employing different types of topic models (LDA, LSA, and NMF), a comprehensive list of final and unique topics and their associated themes was generated. The details about each of the topic modeling techniques are provided below.
3.2.1. Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) assumes that each document is a mixture of various topics, and each topic is characterized by a distribution of words. LDA helps discover the underlying topics and their associated word distributions without any prior knowledge about the topics or the document labels.
Methodology of LDA
The methodology of LDA involves two key steps: the generative process and the inference process. The generative process in LDA represents the hypothetical process by which a collection of documents is created. It assumes that documents are generated according to a probabilistic model. The inference process in LDA aims to estimate the latent topic structure of the given corpus based on the observed documents. The goal is to determine the underlying topic distributions for each document and the word distributions for each topic. The methodology of LDA consists of six steps.
Step 1. Preprocess the text data.
- Tokenize the documents into individual words.
- ○
- Remove stop words, punctuation, and other irrelevant elements.
- ○
- Apply stemming or lemmatization to normalize the words.
Step 2. Create a document-term matrix.
- Construct a matrix where each row represents a document and each column represents a word.
- Count the frequency of each word in each document.
Step 3. Initialize LDA parameters.
- Determine the number of topics to be discovered.
- Initialize the topic proportions for each document and the word distributions for each topic.
Step 4. Conduct iterative training.
- Iterate through each document and each word:
- ○
- For each word, calculate the probability of the topic assignment based on the current topic proportions and word distributions.
- ○
- Sample a new topic assignment for the word based on the calculated probabilities.
- ○
- Update the topic proportions and word distributions based on the new assignments.
Step 5. Repeat Step 4 for a sufficient number of iterations.
Step 6. Analyze the results.
- Examine the estimated topic proportions and word distributions.
- Interpret and label the topics based on the most representative words.
The computational complexity of LDA depends on the number of documents (D), the number of words in the corpus , and the number of topics . The training complexity of LDA is typically expressed as , where is the number of iterations. The inference complexity is . It is important to note that LDA is scalable and can handle large corpora efficiently. Various optimization techniques, such as parallelization and approximate inference algorithms, can be applied to improve the computational efficiency of LDA.
3.2.2. Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA)
Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA), also known as Latent Semantic Indexing, is a statistical method used to extract and represent the underlying semantic structure of a collection of documents. Unlike LDA, which is a generative probabilistic model, LSA is a matrix factorization technique that focuses on capturing the co-occurrence patterns of words within the documents. LSA assumes that words that frequently co-occur in similar contexts are likely to have similar meanings.
Methodology of LSA
The methodology of LSA involves the following key steps.
Step 1. Preprocess the text data.
- Tokenize the documents into individual words.
- Remove stop words, punctuation, and other irrelevant elements.
- Apply stemming or lemmatization to normalize the words.
Step 2. Create a document-term matrix.
- Construct a matrix where each row represents a document and each column represents a term.
- Count the frequency of each term in each document or use TF-IDF to represent the term frequency.
Step 3. Apply Singular Value Decomposition (SVD).
- Perform SVD on the document-term matrix to obtain the and matrices.
- ○
- U represents the left singular vectors and captures the relationships between the documents.
- ○
- Σ is a diagonal matrix representing the singular values, which indicate the importance of each dimension.
- ○
- VT represents the right singular vectors and represents the relationships between the terms.
Step 4. Dimensionality Reduction.
- Retain only the top-k singular values and their corresponding singular vectors.
- By truncating the singular values and vectors, the dimensionality of the matrix is reduced, retaining the most important semantic information.
Step 5. Represent Documents and Terms in the Reduced Space.
- Project the documents and terms onto the reduced-dimensional space using the selected singular vectors.
- The vectors capture the semantic relationships between documents and terms based on their proximity in the reduced space.
Step 6. Compute Semantic Similarities.
- Calculate the cosine similarity between document vectors or term vectors based on their representations in the reduced space.
- Higher cosine similarity values indicate greater semantic similarity.
The computational complexity of LSA primarily depends on the size of the document-term matrix, typically denoted as , where is the number of documents and is the vocabulary size (number of unique terms). The computational complexity of LSA is mainly driven by the SVD step, which is generally the most computationally expensive operation. The time complexity of performing SVD on the document-term matrix is approximately , assuming that the number of documents and vocabulary size are not too disparate. However, in practice, the computational complexity of LSA can be reduced by employing efficient algorithms and techniques for performing SVD. Several optimized algorithms, such as randomized SVD, can be utilized to approximate the singular value decomposition with lower computational costs. These algorithms exploit the structure of the document-term matrix to compute a low-rank approximation, which significantly reduces the time complexity.
3.2.3. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (NMF)
Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) is a dimensionality reduction technique commonly used for topic modeling and feature extraction. NMF differs from LDA and LSA in that it enforces non-negativity constraints on the factor matrices, making it suitable for non-negative data representations. While LDA models the generative process of document creation and LSA captures co-occurrence patterns in a matrix, NMF aims to decompose a non-negative matrix into two non-negative matrices that represent a lower-dimensional approximation of the original data.
Methodology of NMF
The methodology of NMF involves the following key stages: decomposition of a non-negative matrix, dimensionality reduction and feature extraction, and imposing non-negativity constraints. These stages can be differentiated into the following implementation steps.
Step 1. Preprocess the text data.
- Prepare the data by tokenizing the documents into individual words and removing stop words, punctuation, and other noise.
- Represent the data as a document-term matrix, where each row corresponds to a document and each column corresponds to a word, with non-negative values representing the term frequencies.
Step 2. Initialize the factor matrices.
- Given a non-negative matrix , NMF aims to factorize it into two non-negative matrices: and H.
- ○
- W represents the document-topic matrix, where each row corresponds to a document and each column corresponds to a topic.
- ○
- H represents the topic-word matrix, where each row corresponds to a topic and each column corresponds to a word.
- Initialize the document-topic matrix W and the topic-word matrix H with random or predefined non-negative values.
- Typically, the dimensions of W and H are determined by the desired number of topics and the vocabulary size.
Step 3. Update the factor matrices.
- NMF seeks to find a lower-dimensional representation of the original matrix X by minimizing the reconstruction error.
- The matrix multiplication of W and H reconstructs the original matrix X, capturing its salient features and patterns.
- Iterate through an optimization process to update the values of W and H.
- Minimize the reconstruction error between the original matrix X and the product of W and H by using optimization techniques such as gradient descent or multiplicative updates.
- Update the values of W and H based on the optimization algorithm until convergence.
Step 4. Interpret the results.
- Examine the values in the factor matrices W and H to understand the discovered topics and their corresponding word distributions.
- Identify the most important words and their weights in each topic to interpret and label the topics accordingly.
The computational complexity of NMF primarily depends on the size of the input matrix , typically denoted as , where is the number of documents and is the vocabulary size. The time complexity of NMF depends on the number of iterations required for convergence and the dimensionality of the factor matrices and . The most time-consuming step in NMF is the iterative update of the factor matrices. The computational complexity of this step is typically expressed as , where is the number of topics and is the number of iterations required for convergence. This complexity makes NMF computationally efficient for large-scale datasets compared to LDA, which involves a more complex generative process, and LSA, which requires the calculation of SVD. Figure 2 shows a generic pictorial representation of the topic modeling techniques adopted in this study.
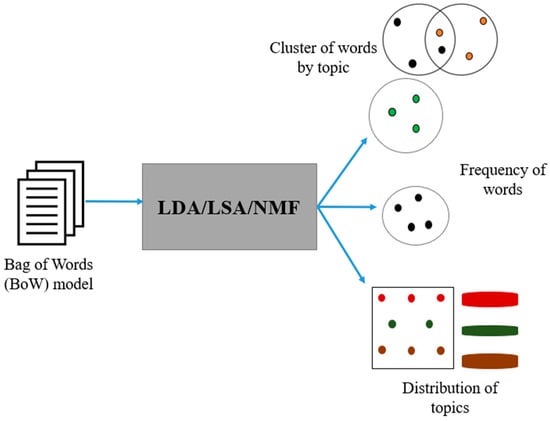
Figure 2.
Generic topic modeling framework using LDA, LSA, and NMF.
3.2.4. Suitability for Analyzing Disaster-Related Tweets
LDA, LSA, and NMF are highly suitable for analyzing disaster-related tweets. LDA, with its ability to identify latent topics within a collection of documents, can uncover the underlying themes and discussions present in disaster-related tweets. By inferring topic distributions for each tweet and word distributions for each topic, LDA enables the automatic identification of critical factors and issues. LSA, on the other hand, analyzes the co-occurrence patterns of words across a document collection to capture the semantic relationships between terms and documents. By reducing the dimensionality of the term-document matrix through SVD, LSA allows for the identification of related topics and the discovery of underlying meaning in disaster-related tweets. NMF, with its non-negativity constraints, is well-suited for analyzing disaster-related tweets due to its ability to generate sparse and interpretable representations. By decomposing the term–document matrix into non-negative factors, NMF enables the identification of key topics and their associated word distributions. All of these approaches are highly valuable for extracting critical factors and issues from the tweet data, allowing emergency response planners and decision-makers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by affected individuals and guide their planning and response strategies accordingly. Figure 3 shows a sample intertopic distance map and relevant topics list from a processed disaster dataset that was generated using LDA.
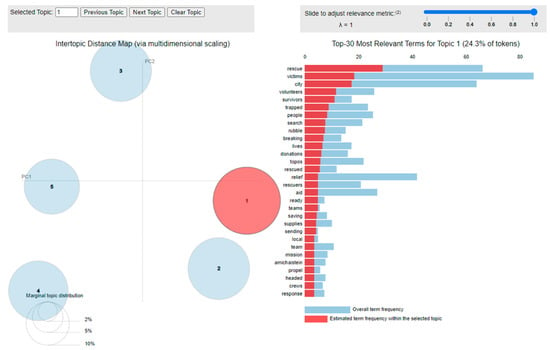
Figure 3.
Sample intertopic distance map and relevant topics using LDA.
3.3. Development of Hierarchical Taxonomy
The taxonomy will be structured into four levels, namely level 0, level 1, level 2, and level 3. Each level represents a different level of granularity in the categorization of topics identified via LDA, LSA, and NMF. The lower levels, specifically level 3, contain the most granular topics within the taxonomy, while the upper levels, such as level 2, represent broader categories that encompass multiple lower-level topics. In the context of disaster-related tweets, level 3 topics are highly specific and provide detailed information about various aspects of disaster management. To build the taxonomy, the lower-level topics (level 3) are grouped together to form the higher-level topics (level 2). This grouping is based on the thematic similarity and commonality among the topics. By organizing the topics into multiple levels, the taxonomy offers a hierarchical structure that facilitates a more systematic and comprehensive analysis of disaster-related tweets. It allows for a multi-dimensional exploration of disaster-related facts. This hierarchical approach provides a flexible and scalable framework that can be applied to different disaster contexts, enabling researchers and practitioners to gain insights into the specific challenges, needs, and progress associated with recovery and reconstruction efforts.
3.4. Evaluation Measures
Evaluation of the quality of the taxonomy is crucial in assessing its effectiveness and utility for analyzing disaster-related tweets. Several criteria were considered to evaluate the taxonomy, including coherence, coverage, and domain-specific relevance. Coherence refers to the logical and meaningful grouping of topics within the taxonomy. It ensures that topics within each level are related and contribute to a clear hierarchical structure. To assess coherence, the relationships between topics within each category were examined by the research team through intra-group discussion. This was done by measuring semantic similarity and evaluating the extent to which the topics shared common keywords or concepts. Coverage and domain-specific relevance assessed the extent to which the taxonomy captured the various dimensions and aspects of disaster-related information. It ensured that the taxonomy encompasses a wide range of relevant topics and adequately represents the diversity of content present in the tweets. To evaluate these two measures, the taxonomy was compared against a comprehensive set of disaster-related topics and concepts identified through a thorough literature review, comparing the taxonomy with established frameworks, and expert knowledge identified via the researchers’ network of collaborators. The aim was to ensure that the taxonomy covered the key factors, issues, and themes relevant to disaster situations. This evaluation step helped validate the domain-specific relevance and applicability of the taxonomy in the context of disaster management.
4. Results and Analysis
A comprehensive analysis of the collected tweets was first conducted to identify common themes, topics, and categories that emerged from the data. Four levels were created that more accurately capture the complexities and interrelationships. Level 0 serves as the overarching category that encompasses all aspects related to managing and responding to disasters. It sets the foundation for the taxonomy and provides a broad framework for understanding and organizing the various elements of disaster management. Level 1 classifies different types of disasters, including hurricanes and earthquakes. This level helps in distinguishing the specific context and characteristics of each type of disaster, facilitating targeted analysis and response strategies. Level 2 expands upon the broader categories of impact resulting from disasters. It recognizes that disasters have multi-dimensional consequences and identifies four key areas of impact: human, economic, environmental, and infrastructure. This level highlights the interconnectedness of these impacts and their significance in disaster management. Level 3 delves deeper into each of the four areas of impact identified in Level 2. It provides a more granular breakdown of the specific aspects and factors within each impact category. For example, under Human Impact, it includes subcategories such as injuries and fatalities, health and medical response, psychosocial support, population displacement and migration, vulnerable groups, disease outbreaks and public health measures, and access to clean water, sanitation, and electricity. Finally, level 4 (within each Level 3 category) further elaborates on the specific topics and issues within each Level 3 subcategory. It allows for a more detailed exploration of the nuances and intricacies of each aspect of disaster impact. For instance, under the subcategory of Injuries and Fatalities (within Human Impact), specific topics may include traumatic injuries, medical emergencies, and fatality rates (see Figure 4 for more details).
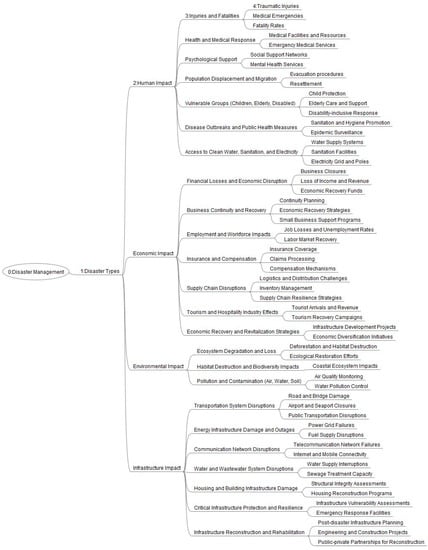
Figure 4.
Developed taxonomy for disaster management using social media data.
The utilization of Levels 3 and 4 in the taxonomy exemplifies the significant value that social media data can offer in the context of disaster management. These levels provide a higher level of granularity, enabling a more focused and targeted response to the challenges presented by disasters. By capturing a wide range of topics and subtopics across various disaster events, Levels 3 and 4 demonstrate the versatility and adaptability of the taxonomy. They facilitate the exploration of crucial areas such as assessing injuries and fatalities, understanding psychosocial support needs, analyzing economic impacts, and examining environmental consequences. This comprehensive framework enables emergency managers to extract valuable insights from social media conversations and make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and develop targeted interventions. The significance of Levels 3 and 4 lies in their ability to capture and characterize specific topics and subtopics within tweets, enabling a deeper understanding of the information shared during disaster periods. The utilization of these levels enhances the capacity to explain and interpret the characterization of particular topics. Due to such significance, Levels 3 and 4 have been used for explaining the taxonomy in this research.
Injuries and Fatalities. During disasters, such as earthquakes, social media platforms served as valuable sources of information for assessing the extent of injuries and fatalities. Numerous tweets shared personal accounts and eyewitness reports of traumatic injuries, medical emergencies, and updates on fatality rates. These firsthand observations offered valuable insights into the types and severity of injuries sustained by individuals affected by the disaster. Additionally, social media provides a platform for individuals to express their urgent need for medical assistance and share information about people trapped under collapsed structures or in need of immediate rescue. The availability of such information on social media platforms allowed researchers, emergency responders, and policymakers to assess the effectiveness of medical response efforts and identify areas where additional resources and support were required. By leveraging this rich source of data, emergency management agencies could gain a more comprehensive understanding of the public health impact of the disaster and make informed decisions to mitigate further casualties and enhance preparedness for future events.
Health and Medical Response. The subcategory of Health and Medical Response focuses on evaluating the healthcare system’s response during disasters, with special attention to the availability and adequacy of medical facilities and resources, as well as the capacity of emergency medical services. Observations of social media users sharing information about the operational status of hospitals, clinics, and healthcare facilities, along with updates on the availability of essential medical supplies, provided valuable insights. The analysis of disaster-related tweets related to health and medical response enhances the understanding of healthcare system challenges, identifies resource and infrastructure gaps, and informs decision-making for emergency managers and healthcare professionals. By leveraging real-time social media data alongside traditional sources, the evaluation of health and medical response can be enhanced, enabling more effective resource allocation to meet the health needs of affected populations in the context of hurricanes.
Psychosocial Support. Within the subcategory of Psychosocial Support, the focus was on addressing the emotional and psychological impact of disasters on individuals and communities. Mental health services played a crucial role in providing support to those affected, with mental health professionals offering counseling and therapy services to help survivors cope with distress and trauma. Social media posts provided insights into the availability and accessibility of mental health services, while social support networks facilitated connections and provided practical and emotional assistance. Analyzing social media data helped identify gaps in services, inform decision-making, and tailor interventions to meet the psychosocial needs of disaster-affected populations. Social media data proved invaluable in understanding and addressing the psychosocial well-being of individuals and communities during the recovery process.
Population Displacement and Migration. The subcategory of Population Displacement and Migration focused on examining the challenges and measures associated with population displacement and migration during a disaster. Special topics within this subcategory were evaluated, including the effectiveness of evacuation procedures and the processes involved in resettlement. Through the analysis of social media data, researchers gained insights into the experiences and needs of displaced populations, such as their evacuation routes, temporary shelter arrangements, and access to basic necessities. These findings provided valuable information for emergency management agencies and humanitarian organizations in improving evacuation protocols, enhancing the efficiency of resettlement processes, and ensuring the safety, well-being, and appropriate support for affected populations.
Vulnerable Groups (Children, Elderly, and Disabled). The subcategory of Vulnerable Groups (Children, Elderly, and Disabled) examined how social media users utilized tweets to highlight the specific vulnerabilities and needs of these groups during a disaster. Through their posts, social media users raised awareness about child protection measures, such as reporting missing children, establishing safe spaces, and ensuring access to essential services. Additionally, they shared information about elderly care and support, including healthcare assistance, shelter arrangements, and initiatives to foster social connections among the elderly population. Social media also played a crucial role in promoting disability-inclusive response strategies, with users discussing accessible communication methods, mobility assistance, and the importance of inclusive emergency shelters. These topics were of significant importance as they helped emergency management agencies and support organizations gain insights into the unique challenges faced by children, elderly individuals, and persons with disabilities during and after a disaster. By leveraging the information shared on social media, policymakers and stakeholders were able to develop targeted interventions and allocate appropriate resources to ensure the protection and resilience of these vulnerable groups.
Disease Outbreaks and Public Health Measures. Social media users were observed to share information on epidemic surveillance, including updates on disease spread due to natural disasters, outbreak hotspots, and preventive measures. They also emphasized the importance of sanitation and hygiene promotion, discussing topics such as access to clean water and proper waste management. These discussions on social media were significant as they provided real-time information and insights into the evolving public health situation during disasters. By analyzing the content shared on social media, public health officials and response agencies could gain valuable insights into the public’s perceptions, concerns, and adherence to recommended health measures. The findings from this research could contribute to a better understanding of the role of social media in disease outbreak response and highlight its potential as a valuable tool for monitoring and disseminating public health information during disasters.
Access to Clean Water, Sanitation, and Electricity. The subcategory of Access to Clean Water, Sanitation, and Electricity observed how social media users utilized tweets to highlight the challenges and concerns related to access to clean water, sanitation, and electricity during and after a disaster. Through their posts, social media users shared information on the status of water supply systems, discussing issues such as disruptions, contamination, or scarcity of clean water sources. They also raised awareness about the condition of sanitation facilities, including the availability of waste management. Additionally, social media users expressed their experiences and concerns regarding the availability and reliability of electricity, highlighting power outages, damage to the electricity grid, and the impact on essential services. These discussions on social media played a significant role in shedding light on the immediate needs and challenges faced by affected communities in accessing these basic amenities. The insights derived from analyzing these tweets could provide valuable information to emergency response teams and relief organizations, enabling them to prioritize resources and support the restoration of clean water, sanitation facilities, and electricity infrastructure. By addressing these critical needs, emergency managers and relief agencies could enhance the overall well-being and quality of life of disaster-affected populations.
Financial Losses and Economic Disruption. The subcategory of Financial Losses and Economic Disruption observed how social media users utilized tweets to highlight the impacts of disasters on financial losses and economic disruption. Through their posts, social media users shared information about business closures, discussing the closure of shops, offices, and other establishments due to the disaster. They also shared their experiences and concerns about the loss of income and revenue, highlighting the economic hardships faced by individuals, families, and communities. Additionally, social media users discussed the availability and utilization of economic recovery funds, highlighting the efforts made by governments, organizations, and communities to support the recovery of local economies. These discussions on social media could play a significant role in raising awareness about the economic consequences of disasters and the challenges faced by businesses and individuals in their recovery process. The insights derived from analyzing these tweets could provide valuable information to policymakers, economists, and business owners, enabling them to assess the economic impact of disasters, allocate resources, and develop strategies for economic recovery. By addressing these financial challenges and supporting economic recovery, stakeholders could facilitate the rebuilding of local economies and improve the livelihoods of affected individuals and communities.
Business Continuity and Recovery. During the examination of Business Continuity and Recovery, social media users were observed to utilize tweets to emphasize the significance of continuity of business planning, economic recovery strategies, and small business support programs in the aftermath of a disaster. Through their posts, social media users shared experiences, information, and resources related to maintaining business operations during and after a crisis. Tweets also highlighted the importance of economic recovery efforts, including government initiatives and financial assistance programs aimed at supporting small businesses affected by the disaster. These social media discussions played a crucial role in disseminating valuable insights and resources to business owners and entrepreneurs, facilitating the exchange of best practices, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders. By utilizing social media as a platform for knowledge sharing and networking, these tweets could contribute to the resilience and recovery of businesses impacted by the disaster.
Employment and Workforce Impacts. Through their posts, social media users shared personal experiences, concerns, and resources related to employment and workforce issues. They discussed the impact of the disaster on businesses, layoffs, and the availability of job opportunities. Tweets also provided updates on the unemployment rates in specific areas affected by the crisis. These discussions on social media platforms played a crucial role in raising awareness about the challenges faced by individuals and communities in finding employment and recovering from the economic impact of the disaster. By sharing information and resources, social media users contributed to the collective understanding of the employment and workforce landscape, facilitating the identification of areas requiring intervention and support. The insights gained from these tweets were valuable for policymakers, government agencies, and organizations involved in labor market recovery efforts.
Insurance and Compensation. Social media users were observed to utilize tweets to shed light on the topics of insurance coverage, claims processing, and compensation mechanisms within the subcategory of Insurance and Compensation. Through their tweets, individuals shared their experiences, frustrations, and successes in dealing with insurance companies, filing claims, and seeking compensation for losses incurred during the disaster. They discussed the complexities of insurance policies, the responsiveness of insurance providers, and the challenges faced in navigating the claims process. Additionally, social media platforms served as a space for individuals to share information about available resources, legal assistance, and advocacy organizations that could aid in obtaining fair compensation. The discussions and insights shared on social media regarding insurance and compensation were significant as they provided a real-time and user-driven perspective on the difficulties and successes individuals encountered when dealing with these matters. Policymakers, insurance companies, and regulatory bodies could leverage these insights to identify areas for improvement in the insurance industry and compensation processes, leading to more streamlined and responsive systems in the future.
Supply Chain Disruptions. During the observation period, social media users actively utilized tweets to draw attention to the topics of logistics and distribution challenges, inventory management, and supply chain resilience strategies within the subcategory of Supply Chain Disruptions. Through their tweets, individuals shared real-time accounts and experiences regarding the obstacles encountered in transporting goods, coordinating distribution networks, and effectively managing inventory levels during and after a disaster. They highlighted the impact of disrupted transportation systems, damaged infrastructure, and limited access to crucial resources on the overall functionality of supply chains. The significance of these user-generated insights is notable as they provided valuable firsthand information, enabling stakeholders to gain a better understanding of the challenges faced by supply chains during disaster events. This information can inform decision-making processes, aid in the development of contingency plans, and foster the implementation of measures to enhance supply chain resilience in the face of future disruptions.
Tourism and Hospitality Industry Effects. Throughout the analyzed period, social media users actively utilized tweets to highlight the topics of tourist arrivals and revenue, as well as tourism recovery campaigns. Through their tweets, individuals shared information and personal experiences related to the impact of disasters on the tourism and hospitality sector. They provided updates on the decline in tourist arrivals, the economic losses suffered by businesses reliant on tourism, and the implementation of recovery initiatives aimed at revitalizing the industry. The significance of these user-generated insights lies in their ability to capture real-time data and perspectives from individuals directly affected by the disruptions. This information can be utilized by industry stakeholders, policymakers, and destination management organizations to assess the scale of the impact, identify areas requiring intervention, and develop targeted strategies for tourism recovery. By leveraging the power of social media, these insights could contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the effects of disasters on the tourism and hospitality industry, enabling informed decision-making and the implementation of effective recovery measures.
Economic Recovery and Revitalization Strategies. During the observation period, social media users actively utilized tweets to highlight the topics of infrastructure development projects and economic diversification initiatives. Through their tweets, individuals discussed ongoing infrastructure development projects, such as the construction of roads, bridges, and public facilities, which were crucial for the recovery and long-term growth of the affected regions. Additionally, they emphasized the significance of economic diversification initiatives, which aimed to reduce dependency on specific industries and promote the growth of new sectors. The insights shared by social media users provided real-time information on the progress, challenges, and impacts of these strategies, offering a unique perspective from those directly affected. Policymakers, local authorities, and economic development agencies could leverage these insights to assess the effectiveness of ongoing initiatives, identify areas requiring further support, and refine strategies for long-term economic sustainability.
Ecosystem Degradation and Loss. During the observation period, social media users actively utilized tweets to draw attention to the topics of deforestation, habitat destruction, and ecological diversification initiatives within the subcategory of Ecosystem Degradation and Loss. Through their tweets, individuals shared information, concerns, and calls for action regarding the detrimental impacts of human activities on natural ecosystems. They highlighted instances of deforestation and the destruction of habitats, emphasizing the need to address these issues for the preservation of biodiversity and the overall health of ecosystems. Furthermore, social media users discussed ecological diversification initiatives aimed at restoring and enhancing ecosystems through measures such as reforestation, habitat restoration, and conservation projects. By amplifying these topics through social media, individuals played a role in influencing public opinion and stimulating discussions on the importance of protecting and restoring ecosystems. Moreover, the collective voices expressed on social media platforms provided valuable feedback and support for ongoing ecological diversification initiatives, encouraging policymakers, environmental organizations, and local communities to prioritize and invest in sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
Habitat Destruction and Biodiversity Impacts. During the observation period, tweets on social media were actively utilized to raise awareness about habitat destruction and its impacts on biodiversity, particularly focusing on coastal ecosystems. Users shared information and personal experiences, expressing concerns about the negative effects of human activities on habitats such as mangroves, coral reefs, and wetlands. They emphasized the importance of these ecosystems in supporting marine life, protecting shorelines, and providing ecological services. The tweets also highlighted the consequences of habitat destruction, such as biodiversity loss and threats to endangered species. This engagement on social media played a significant role in amplifying voices, raising awareness, and mobilizing collective action. The integration of social media data in evaluating habitat destruction provided diverse perspectives and enriched the understanding of the challenges faced by coastal ecosystems. This, in turn, could facilitate the development of informed conservation strategies and policy interventions for preserving these crucial habitats.
Pollution and Contamination (Air, Water, and Soil). During the observation period, social media users played a vital role in raising awareness and addressing the subcategory of Pollution and Contamination, focusing specifically on air, water, and soil pollution. Through their tweets, users shared information, personal experiences, and concerns about the environment’s quality and its impact on human health. They expressed alarm about issues such as industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, wildfires, chemical spills, improper waste disposal, and the use of harmful pesticides. Users played a crucial role in spreading information, mobilizing collective action, and pressuring authorities to address pollution and contamination issues. This information, combined with traditional data sources, contributed to a comprehensive understanding of pollution’s extent and impact in different regions. By harnessing the collective power of social media, policymakers, environmental organizations, and communities were able to drive change, advocate for stricter regulations, and promote sustainable practices to mitigate pollution and protect the environment for future generations.
Transportation System Disruptions. Through their tweets, users shared real-time information, updates, and personal experiences regarding the state of transportation infrastructure and services in disaster-affected areas. They posted information showing the extent of road and bridge damage caused by natural disasters. Additionally, social media users shared information about airport and seaport closures, including flight cancellations, delays, and the impact on trade and travel. They also discussed disruptions to public transportation systems, such as subway closures, bus route changes, and the challenges faced by commuters. Social media platforms provided a means for users to report and share real-time updates on the conditions of roads, bridges, airports, seaports, and public transportation. This information proved invaluable for individuals seeking alternative routes, planning their travel, or staying informed about the status of transportation services. This information not only helped individuals make informed decisions but also aided emergency management authorities in identifying critical areas of concern and coordinating response efforts. By leveraging the power of social media, policymakers, transportation authorities, and emergency management agencies were able to quickly disseminate relevant information, address public concerns, and coordinate efforts to restore and improve transportation infrastructure and services.
Energy Infrastructure Damage and Outages. Through their tweets, users shared real-time information, updates, and personal experiences regarding the state of energy infrastructure in disaster-affected areas. They posted images and videos showing power lines down, damaged substations, and blackouts caused by natural disasters such as storms, earthquakes, or hurricanes. Social media platforms provided a means for users to report and share real-time updates on power outages, energy infrastructure damage, and fuel supply issues. This information proved invaluable for individuals seeking alternative energy sources, planning their activities, or staying informed about the status of energy services. The use of hashtags, geotags, and location-specific tweets facilitated the aggregation of data and the mapping of energy infrastructure disruptions across affected areas. This information not only helped individuals make informed decisions but also aided utility companies and emergency management authorities in identifying critical areas of concern and coordinating response efforts. By leveraging the power of social media, policymakers, utility companies, and emergency management agencies could be able to quickly disseminate relevant information, address public concerns, and coordinate efforts to restore and improve energy infrastructure and services.
Communication Network Disruptions. During the observed period, social media users actively utilized tweets to bring attention to the subcategory of Communication Network Disruptions, specifically focusing on telecommunication network failure and internet and mobile connectivity issues. Through their tweets, users shared firsthand accounts, frustrations, and updates about the breakdown of communication networks during and after disasters. They expressed concerns about the inability to make calls, send messages, or access the internet due to damaged infrastructure or overloaded networks. Social media played a crucial role as an alternative communication tool when traditional channels were compromised. The aggregation of tweets provided valuable insights into the extent and geographical distribution of the disruptions, aiding telecommunication companies and emergency response teams in prioritizing restoration efforts. Social media also facilitated community resilience by enabling affected individuals to seek assistance, connect with loved ones, and explore alternative communication methods. Integrating social media data with traditional networks enhanced situational awareness, helping stakeholders understand the impact of communication disruptions on public safety and emergency response. By harnessing the power of social media, policymakers, and telecommunication providers could address concerns, coordinate response efforts, and work towards enhancing the resilience and reliability of communication networks for future disasters.
Water and Wastewater System Disruptions. During the observed period, social media users actively utilized tweets to raise awareness about the subcategory of Water and Wastewater System Disruptions, specifically focusing on water supply interruptions and sewage treatment capacity. Through their tweets, users shared experiences and concerns regarding the breakdown of these systems during and after disasters, emphasizing issues such as water shortages and contaminated water. They also expressed frustrations over reduced sewage treatment capacity. Social media played a significant role in providing real-time updates and information on the extent and duration of the disruptions. Social media essentially served as a platform for affected individuals to seek assistance, share water conservation tips, and highlight alternative sources of clean water. Integrating social media data with traditional monitoring systems enhanced the understanding of the impact on public health and environmental sustainability. By leveraging social media, authorities addressed concerns, coordinated response efforts, and worked towards restoring water and wastewater services. Insights from social media data contributed to more effective decision-making, resource allocation, and resilience-building strategies for future disasters.
Housing and Building Infrastructure Damage. During the observed period, social media users played a significant role in highlighting the subcategory of Housing and Building Infrastructure Damage through their tweets. They actively shared information about the structural integrity assessments of buildings and the implementation of housing reconstruction programs in the aftermath of disasters. Users expressed their concerns and experiences regarding the extent of damage to residential and commercial structures, including collapsed buildings, structural failures, and compromised safety. The significance of these results lies in the valuable real-time updates and firsthand accounts shared by social media users. Their tweets provided critical insights into the urgent need for structural assessments and the importance of implementing housing reconstruction programs to restore safe and sustainable living conditions. This information was crucial for emergency response teams, government agencies, and NGOs involved in disaster recovery efforts. By analyzing the tweets, stakeholders could assess the scale of the damage, prioritize areas for immediate attention, and allocate resources accordingly. By leveraging social media data, policymakers and organizations could enhance their disaster response and recovery plans, leading to improved housing conditions and the overall well-being of affected communities.
Critical Infrastructure Protection and Resilience. Social media users actively contributed to raising awareness about the subcategory of Critical Infrastructure Protection and Resilience through their tweets. They shared information and expressed concerns about infrastructure vulnerability assessments and the availability of emergency response facilities during and after a disaster. Their tweets provided critical insights into the state of infrastructure, identifying areas that were at risk or had experienced damage. By analyzing the tweets, stakeholders could assess the effectiveness of existing infrastructure protection measures, identify gaps in emergency response capabilities, and plan for future resilience enhancements. The collective efforts of social media users and relevant authorities contributed to the formulation of effective plans and policies to protect and enhance critical infrastructure, ensuring the continuity of essential services and the safety of communities during and after disasters. By leveraging social media data, decision-makers could make informed choices, allocate resources more effectively, and prioritize infrastructure investments based on the identified vulnerabilities and community needs.
Infrastructure Reconstruction and Rehabilitation. Social media users have played a crucial role in highlighting the subcategory of Infrastructure Reconstruction and Rehabilitation through their active participation on platforms. They actively shared information and expressed opinions regarding post-disaster infrastructure planning, engineering, and construction projects and the involvement of public–private partnerships in the reconstruction efforts. By using hashtags and geotags, users created online communities, and discussions focused on infrastructure reconstruction, sharing updates, progress reports, and photographs of ongoing projects. The significance of these results lies in the ability of social media to facilitate transparency, accountability, and public engagement in the infrastructure reconstruction process. Additionally, the active participation of social media users allowed them to contribute their perspectives, suggestions, and feedback on the reconstruction efforts, fostering a sense of ownership and collaboration. By leveraging social media, decision-makers could gather valuable feedback, assess public sentiment, and address the specific needs and aspirations of the affected communities. Ultimately, the active participation of social media users in highlighting infrastructure reconstruction and rehabilitation could contribute to the successful and sustainable rebuilding of critical infrastructure, promoting the overall resilience and well-being of the communities affected by the disaster.
5. Significance of the Proposed Taxonomy
The taxonomy plays a crucial role in enhancing emergency management efforts by providing a structured framework for organizing and understanding the information derived from real-time social media data during disasters. Its significance lies in several ways. First, the taxonomy enables emergency managers to gain a deeper understanding of the context and nature of the information shared on social media during disasters. By categorizing tweets into specific topics and subtopics, the taxonomy helps decision-makers grasp the key issues, challenges, and needs expressed by affected individuals and communities. This contextual understanding allows for more targeted and informed decision-making. Second, the taxonomy facilitates trend analysis of social media data. By analyzing the frequency and distribution of topics within the taxonomy, emergency managers can detect emerging trends and patterns. This analysis provides valuable insights into the evolving situation, helping decision-makers anticipate challenges and allocate resources effectively. Third, the taxonomy guides resource allocation. Decision-makers can map the identified topics to specific response actions or resource needs, enabling them to prioritize and allocate resources based on the identified priorities. This targeted approach ensures that resources are directed to address the most pressing needs.
Moreover, the taxonomy aids in developing targeted messaging and communication strategies. By understanding the topics that resonate with affected individuals, emergency managers can tailor their messaging to address specific concerns and provide relevant information. This targeted approach improves the effectiveness of communication efforts and helps build trust and engagement with the affected population. Furthermore, the taxonomy enhances situational awareness by providing a systematic framework for organizing and analyzing social media data. It allows decision-makers to quickly grasp the overall picture of the disaster, including its impacts, ongoing challenges, and emerging issues. This situational awareness facilitates timely and informed decision-making, leading to a more coordinated and effective response. The taxonomy also serves as a common language and reference point for collaboration and coordination among different stakeholders involved in emergency management. It enables effective sharing and exchange of information, enhancing collaboration, streamlining decision-making processes, and promoting coordinated response efforts. Lastly, the taxonomy facilitates rapid information extraction. By integrating real-time social media data monitoring with the taxonomy, decision-makers can quickly extract valuable information. Through automated or manual processes, they can classify and categorize incoming tweets based on the taxonomy’s predefined topics. This enables them to stay updated on the evolving situation, identify critical issues, and respond promptly to emerging needs.
The taxonomy exhibits a high level of generalizability, allowing for its application across various domains, including the medical or biomedical field. Although the overall methodology and framework can be readily adapted to analyze tweets in different contexts, specific considerations are essential when applying it to the medical or biomedical domain. For example, first, the preprocessing stage of the study would need to consider the unique characteristics of medical or biomedical tweets. This may involve implementing specialized text normalization techniques, entity recognition methods, and domain-specific stop-word lists to ensure accurate and meaningful analysis of the medical content. Second, the topic modeling techniques used in the study, such as LDA, LSA, and NMF, can be employed to extract topics and themes from medical or biomedical tweets. However, it is crucial to train these models using a relevant medical or biomedical corpus to capture the specific concepts and terminology used in the domain. Third, the development of the taxonomy would require consideration of the specific categories and subcategories relevant to the medical or biomedical context. Collaborating with domain experts, such as medical professionals or researchers, would be essential in identifying and defining the relevant topics and concepts to be included in the taxonomy. By adapting the proposed study to the medical or biomedical domain and incorporating domain-specific knowledge and techniques, valuable insights can be derived from analyzing social media data related to healthcare. This can support various applications, including public health monitoring, sentiment analysis, identification of emerging health trends, and understanding patient experiences. However, it is important to tailor the study to the specific requirements and characteristics of the medical domain to ensure its applicability and effectiveness. To extend the study’s applicability to processing biomedical literature in PubMed, several important updates can be implemented. These updates involve customizing the text preprocessing pipeline specifically for PubMed articles, enhancing entity recognition algorithms to accurately identify biomedical entities, adapting topic modeling techniques to cater to the unique characteristics of the biomedical domain, and engaging in collaboration with domain experts to validate and refine the taxonomy. By incorporating these updates, the study becomes equipped to extract valuable insights from PubMed, contributing to biomedical research and facilitating informed healthcare decision-making.
6. Conclusions
This research makes significant contributions to the scientific understanding and practical applications of disaster management and social media analysis. The theoretical contributions lie in the development of a comprehensive hierarchical taxonomy that organizes and categorizes disaster-related topics into multiple levels. This taxonomy provides a structured framework that goes beyond surface-level analysis, allowing for a deeper understanding of the various dimensions and complexities associated with disasters. By categorizing topics at different levels, the taxonomy offers a systematic approach to capturing the diverse aspects of disasters, such as different types of damage, humanitarian categories, and recovery efforts. Moreover, the integration of three popular topic modeling techniques (LDA, LSA, and NMF) into the taxonomy-based analysis contributes to the theoretical understanding of these methods in the context of disaster management. Each technique offers unique insights into the underlying patterns and themes present in large volumes of disaster-related data. The application of these models enhances the understanding of disaster dynamics, enabling researchers and practitioners to uncover hidden relationships, detect emerging trends, and identify relevant information from vast amounts of unstructured social media data.
From a practical perspective, this research has direct implications for emergency management efforts. By leveraging the taxonomy and conducting real-time social media data monitoring during disasters, emergency managers can extract valuable insights from the flood of information shared on social platforms. By feeding the data into the taxonomy, decision-makers can quickly identify and categorize the context of related tweets, allowing for rapid assessment of the situation on the ground. This helps in gaining situational awareness, understanding the needs and concerns of affected populations, and allocating resources effectively to address critical areas. Furthermore, the developed taxonomy and findings can aid emergency managers in various other ways. They can inform the development of targeted communication strategies, allowing for timely and accurate dissemination of information to the public. By understanding the prevalent topics and sentiments expressed on social media, decision-makers can tailor their messages and address specific concerns, ultimately improving public engagement and fostering community resilience. Additionally, the taxonomy can serve as a knowledge repository, facilitating knowledge sharing and collaboration among different stakeholders involved in disaster management.
Note that while the evaluation of coherence, coverage, and domain-specific relevance is essential for validating the taxonomy’s effectiveness, it is crucial to acknowledge and address the inherent limitations and potential biases that may arise in the taxonomy creation process. While the article focuses on the criteria of coherence, coverage, and domain-specific relevance, it is important to acknowledge the inherent limitations and potential biases that can arise in any taxonomy creation process. One such concern is subjectivity, as taxonomies are developed by specific individuals or groups, introducing the possibility of personal biases and perspectives shaping the classification process. Additionally, taxonomies are not static entities but evolve and change over time as new information and understanding emerge. The complexity of the real world and cultural variability pose challenges in capturing all the nuances and variations in disaster-related topics within a hierarchical framework. Furthermore, interactions within hierarchical classifications can lead to overlaps or gaps between categories, potentially affecting the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the taxonomy. To address these concerns and ensure the robustness of the taxonomy, future research could consider conducting the proposed approach (LDA, LSA, and NMF) on alternative corpora, such as texts of different lengths or diverse datasets produced by independent researchers. This would help identify potential distortions or biases in the final taxonomy and validate the methodology across different contexts. Although not included in the present study, such an additional test could strengthen the reliability and generalizability of the taxonomy, providing a more comprehensive understanding of its strengths and limitations. By critically examining these concerns and conducting further validation studies, researchers can enhance the reliability and applicability of the taxonomy, leading to improved decision-making processes, resource allocation, and overall effectiveness of emergency response strategies.
The presented research also offers several other potential research directions for further exploration in the field of disaster management and social media analysis. These include enhancing the developed taxonomy to capture additional dimensions of disaster-related topics, improving topic modeling techniques with advanced algorithms, exploring real-time event detection and situational awareness systems, conducting sentiment analysis and emotion detection, investigating cross-platform analysis, and delving into user profiling and targeted interventions. These research directions aim to advance the field by addressing specific challenges, leveraging emerging techniques, and utilizing social media data to enhance disaster response, recovery, and community support. Pursuing a research direction focused on developing an ontology that incorporates the interrelationship between various concepts, utilizing techniques such as association rule mining and inferential statistical analysis, holds significant potential. Such an ontology would enable a deeper understanding of the connections and dependencies between concepts, offering valuable insights into complex domains. By pursuing these avenues, researchers can contribute to the development of more comprehensive and effective strategies for managing disasters and leveraging social media as a valuable resource in emergency management efforts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C.; methodology, S.C.; software, J.D.; data curation, J.D., Formal Analysis, J.D.; validation, J.D. and S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C. and J.D.; writing—review and editing, S.C. and A.A.; supervision, S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chowdhury, S.; Shahvari, O.; Marufuzzaman, M.; Li, X.; Bian, L. Drone routing and optimization for post-disaster inspection. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 159, 107495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tim, Y.; Pan, S.L.; Ractham, P.; Kaewkitipong, L. Digitally enabled disaster response: The emergence of social media as boundary objects in a flooding disaster. Inf. Syst. J. 2016, 27, 197–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgens, M.; Helsloot, I. The effect of social media on the dynamics of (self) resilience during disasters: A literature review. J. Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2017, 26, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.; Goldberg, A.; Adini, B. Socializing in emergencies—A review of the use of social media in emergency situations. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2015, 35, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaigo, M. Social Media Usage During Disasters and Social Capital: Twitter and the Great East Japan Earthquake; Keio Communication Review; Keio University: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn, J.A.; de Moel, H.; Jongman, B.; de Ruiter, M.C.; Wagemaker, J.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. A global database of historic and real-time flood events based on social media. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, H.; Pérez-Delhoyo, R.; Paredes-Pérez, J.F.; Mollá-Sirvent, R.A. Analysis of Social Networking Service Data for Smart Urban Planning. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Seker, D.Z.; Hameed, S.; Draheim, D. The Rising Role of Big Data Analytics and IoT in Disaster Management: Recent Advances, Taxonomy and Prospects. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54595–54614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Castillo, C.; Diaz, F.; Vieweg, S. Processing Social Media Messages in Mass Emergency: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2014, 47, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Lampert, A.; Cameron, M.; Robinson, B.; Power, R. Using Social Media to Enhance Emergency Situation Awareness. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2012, 27, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Big Data in Natural Disaster Management: A Review. Geosciences 2018, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Rahman, Z. The social role of social media: The case of Chennai rains-2015. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2016, 6, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-T.; Liu, C. A study on topic models using LDA and Word2Vec in travel route recommendation: Focus on convergence travel and tours reviews. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2020, 26, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, J.; Park, Y. Applying LSA text mining technique in envisioning social impacts of emerging technologies: The case of drone technology. Technovation 2017, 60–61, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Alzarrad, A. Applications of Text Mining in the Transportation Infrastructure Sector: A Review. Information 2023, 14, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Zhu, J. Investigation of Critical Factors for Future-Proofed Transportation Infrastructure Planning Using Topic Modeling and Association Rule Mining. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2023, 37, 04022044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, B.; Tandoc, E.C.; Carmichael, C. Communicating on Twitter during a disaster: An analysis of tweets during Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 50, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.E. Social Media in Disaster Risk Reduction and Crisis Management. Sci. Eng. Ethic 2013, 20, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, C.; Ludwig, T.; Kaufhold, M.-A.; Pipek, V. XHELP: Design of a Cross-platform Social-media Application to Support Volunteer Moderators in Disasters. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 18–23 April 2015; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Johnston, E.W. A framework for analyzing digital volunteer contributions in emergent crisis response efforts. New Media Soc. 2017, 19, 1308–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, A.; Moshtari, M. Challenges in disaster relief operations: Evidence from the 2017 Kermanshah earthquake. J. Humanit. Logist. Supply Chain Manag. 2020, 11, 107–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Injadat, M.; Salo, F.; Nassif, A.B. Data mining techniques in social media: A survey. Neurocomputing 2016, 214, 654–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chang, Y.; Liu, H. Mining Social Media with Social Theories: A Survey. ACM Sigkdd Explor. Newsl. 2014, 15, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.; Abdelwahab, A.; Ahdelkader, H. A Proposed Framework for Improving Analysis of Big Unstructured Data in Social Media. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Systems (ICCES), Cairo, Egypt, 17 December 2019; pp. 61–65. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348578774 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Chen, Z.; Huang, K.; Wu, L.; Zhong, Z.; Jiao, Z. Relational Graph Convolutional Network for Text-Mining-Based Accident Causal Classification. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuen, K.F. Sustainability disclosure for container shipping: A text-mining approach. Transp. Policy 2021, 110, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirunagari, S. Data Mining of Causal Relations from Text: Analysing Maritime Accident Investigation Reports. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1507.02447. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.-Y.; Park, K.; Kremer, G.E. A global supply chain risk management framework: An application of text-mining to identify region-specific supply chain risks. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 45, 101053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Jang, H.; Roh, S. A systematic literature review on humanitarian logistics using network analysis and topic modeling. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2022, 38, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Song, B. Exploring Technological Trends in Logistics: Topic Modeling-Based Patent Analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Kwak, D.; Khan, P.; El-Sappagh, S.; Ali, A.; Ullah, S.; Kim, K.H.; Kwak, K.-S. Transportation sentiment analysis using word embedding and ontology-based topic modeling. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2019, 174, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Zhu, J. Future-Proof Transportation Infrastructure through Proactive, Intelligent, and Public-involved Planning and Management; University of Maine: Orono, ME, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hagras, M.; Hassan, G.; Farag, N. Towards Natural Disasters Detection from Twitter Using Topic Modelling. In Proceedings of the 2017 European Conference on Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS), Bern, Switzerland, 17–19 November 2017; pp. 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kireyev, K.; Palen, L.; Anderson, K.M. Applications of Topics Models to Analysis of Disaster-Related Twitter Data. In NIPS Workshop on Applications for Topic Models: Text and Beyond; NIPS Workshop: Whistler, BC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, F.; Ofli, F.; Imran, M.; Alam, T.; Qazi, U. Deep Learning Benchmarks and Datasets for Social Media Image Classification for Disaster Response. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), The Hague, The Netherlands, 7–10 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.; Gan, H.; Huang, Q.; Cai, T.; Cao, K. Disaster Image Classification by Fusing Multimodal Social Media Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Ofli, F.; Imran, M. CrisisMMD: Multimodal Twitter Datasets from Natural Disasters. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 25–28 June 2018; pp. 465–473. Available online: https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/ICWSM/article/view/14983 (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Abavisani, M.; Wu, L.; Hu, S.; Tetreault, J.; Jaimes, A. Multimodal Categorization of Crisis Events in Social Media. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 14679–14689. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9157116 (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Nelli, F. Python Data Analytics: With Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib, 2nd ed.; Apress Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).