Chinese–Vietnamese Pseudo-Parallel Sentences Extraction Based on Image Information Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A pseudo-parallel sentence extraction model based on the adaptive fusion of visual and text features is proposed. The performance of text parallel sentence pair extraction is improved by adaptive fusion of candidate image information.
- A multimodal fusion method based on text selective gating is proposed. Based on multimodal gating, the effective fusion of text and candidate sentences is realized, and the representation ability of text sentence pairs is improved.
- The experimental results based on multimodal data sets show the effectiveness of the proposed method. By fusing the information of image modality, the ability of extracting parallel sentence pairs is effectively improved.
2. Related Work
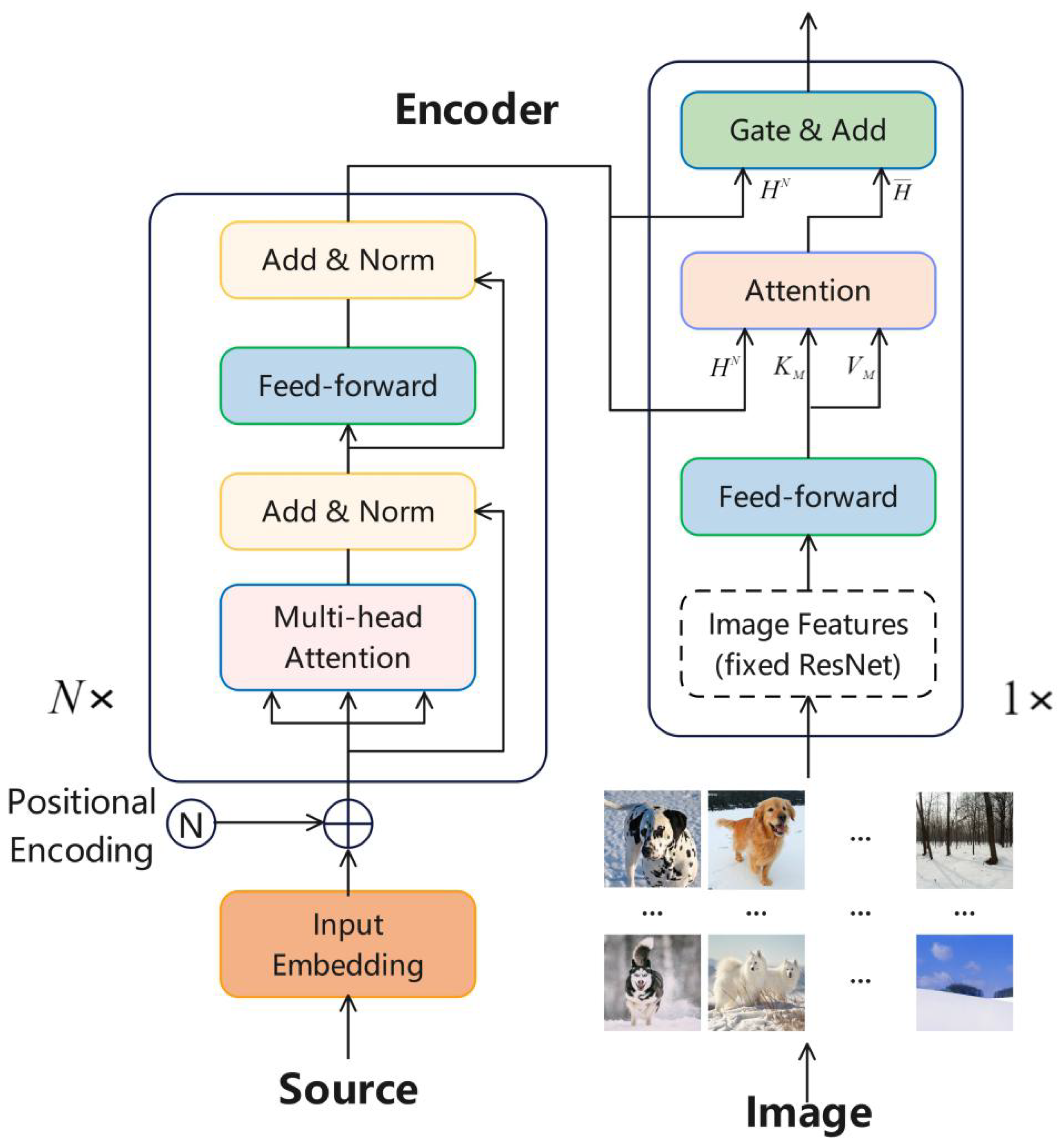
3. Method
3.1. Image Retrieval
3.2. Sentence Information Representation
3.3. Fusion of Text and Image Representation
3.4. Prediction Module
4. Experimental Setting
4.1. Dataset
4.1.1. Pseudo-Parallel Sentences
4.1.2. Text–Image Aligned Corpus
4.1.3. Monolingual Corpus
4.2. Experiment Setup
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Classifier Accuracy
5.2. Machine Translation Quality
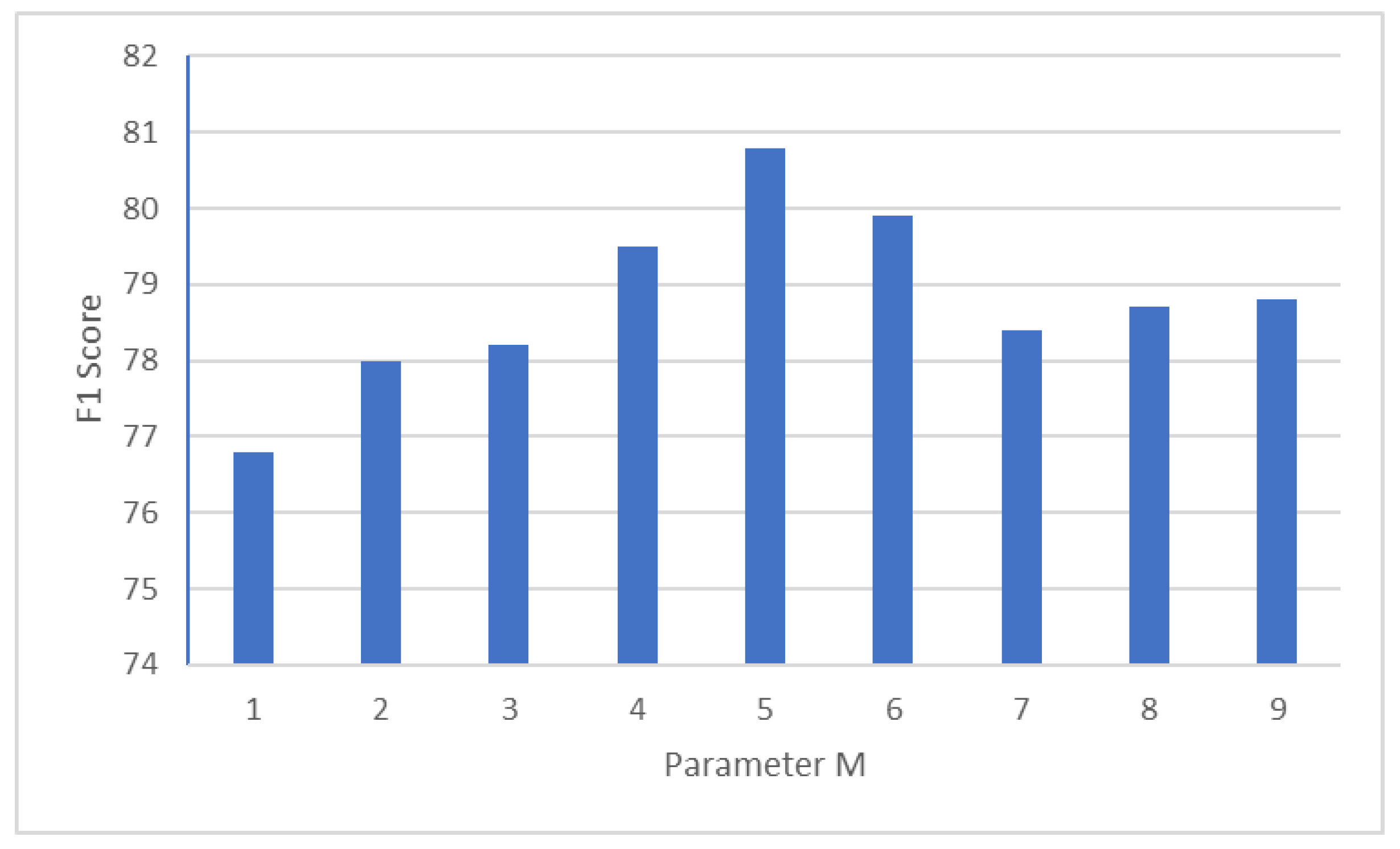
5.3. Parameter M
5.4. Case Study
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koehn, P.; Knowles, R. Six Challenges for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Neural Machine Translation, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20 July–4 August 2017; Association for Computational Linguistics: Toronto, ON, Canada; pp. 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Grégoire, F.; Langlais, P. Extracting Parallel Sentences with Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks to Improve Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; pp. 1442–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, P.; Thien, N.; Dinh, H.V.; Huu-Anh, T.; Bay, V. A Method of Chinese-Vietnamese Bilingual Corpus Construction for Machine Translation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 78928–78938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; Quirk, C.; Toutanova, K. Extracting parallel sentences from comparable corpora using document level alignment. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics on Human Language Technologies, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2–4 June 2010; pp. 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, A.; Ansari, E.; Bigham, B.S. Extracting an English-Persian parallel corpus from comparable corpora. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018; pp. 3477–3482. [Google Scholar]
- Marie, B.; Fujita, A. Efficient Extraction of Pseudo-Parallel Sentences from Raw Monolingual Data Using Word Embeddings. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2): Short Papers, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20 July–4 August 2017; pp. 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- España-Bonet, C.; Varga, C.; Barrón-Cedeño, A.; Genabith, V. An Empirical Analysis of NMT-Derived Interlingual Embeddings and Their Use in Parallel Sentence Identification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangya, V.; Braune, F.; Kalasouskaya, Y. Unsupervised Parallel Sentence Extraction from Comparable Corpora. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 1224–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Xiayang, S.; Ping, Y.; Xinyi, L.; Chun, X.; Lin, X. Obtaining Parallel Sentences in Low-Resource Language Pairs with Minimal Supervision. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 5296946. [Google Scholar]
- Shaolin, Z.; Chenggang, M.; Tianqi, L.; Yang, Y.; Chun, X. Unsupervised Parallel Sentences of Machine Translation for Asian Language Pairs. ACM Trans. Asian Low Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2023, 22, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yifan, F.; Mi, C. Parallel sentences mining with transfer learning in an unsupervised setting. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL’2021), Mexico City, Mexico, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kvapilíková, I.; Artetxe, M.; Labaka, G.; Agirre, E.; Bojar, O. Unsupervised Multilingual Sentence Embeddings for Parallel Corpus Mining. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL’2020), Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, C.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Gu, J. Cross-lingual retrieval for iterative self-supervised training. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Ahuja, C.; Morency, L. Multimodal Machine Learning: A Survey and Taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 41, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Wan, X. Multimodal Transformer for Multimodal Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL’2020), Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 4346–4350. [Google Scholar]
- Caglayan, O.; Kuyu, M.; Amac, M.S.; Madhyastha, P.; Erdem, E.; Erdem, A.; Lucia, S. Cross-lingual Visual Pre-training for Multimodal Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Main Volume, Online, 19–23 April 2021; pp. 1317–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, R.; Utiyama, M.; Sumita, E.; Zhao, T. Neural machine translation with sentence-level topic context. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 1970–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS'17), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Red Hook: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models from Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’2021), Online, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Conneau, A.; Khandelwal, K.; Goyal, N.; Chaudhary, V.; Wenzek, G.; Guzmán, F.; Grave, E.; Ott, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 18 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the 3th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
| Image | Description of Image Content | |
|---|---|---|
 | Chinese | 小狗在雪地里玩耍。 (The dog is playing in the snow.) |
| Vietnamese | Nó đang chơi trong tuyết. | |
| Model | P(%) | R(%) | F1(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bi-RNN | 82.62 | 70.80 | 76.26 |
| Bi-LSTM | 85.25 | 73.64 | 79.04 |
| Transformer | 87.54 | 75.01 | 80.79 |
| Pseudo-Parallel Sentences | Extraction Model | BLEU |
|---|---|---|
| 200 k | Grégoire et al. [2] | 18.04 |
| Tran et al. [13] | 16.34 | |
| Our method | 18.91 | |
| 300 k | Grégoire et al. [2] | 19.02 |
| Tran et al. [13] | 17.02 | |
| Our method | 19.85 |
| Chinese | 根据统计局的预测,今年上半年国内经济增长迅速。(According to the forecast of the Bureau of Statistics, the domestic economy grew rapidly in the first half of this year.) |
| Vietnamese | Theo báo cáo của tổng thống, nền kinh tế đang phát triển nhanh chóng. (According to the report, the economy is growing rapidly.) |
| Chinese | 在这段时间里经常下雨。 (It rains frequently during this time.) |
| Vietnamese | Thời gian này sẽ mở ra một vòng mưa. (There will be a round of rain during this time.) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, Z.; Yu, Z. Chinese–Vietnamese Pseudo-Parallel Sentences Extraction Based on Image Information Fusion. Information 2023, 14, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14050298
Wen Y, Guo J, Yu Z, Yu Z. Chinese–Vietnamese Pseudo-Parallel Sentences Extraction Based on Image Information Fusion. Information. 2023; 14(5):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14050298
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Yonghua, Junjun Guo, Zhiqiang Yu, and Zhengtao Yu. 2023. "Chinese–Vietnamese Pseudo-Parallel Sentences Extraction Based on Image Information Fusion" Information 14, no. 5: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14050298
APA StyleWen, Y., Guo, J., Yu, Z., & Yu, Z. (2023). Chinese–Vietnamese Pseudo-Parallel Sentences Extraction Based on Image Information Fusion. Information, 14(5), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14050298






