Decentralized Offloading Strategies Based on Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Access Edge Computing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We discuss some shortages in the existing reinforcement learning-based offloading strategies in MEC. For these shortages, we develop a new framework to improve task offloading by introducing the CTDE mechanism.
- We first introduce the centralized training and decentralized execution mechanism into MEC systems, modeling a more feasible reinforcement learning model for MEC task offloading.
- We conduct several experiments on simulation platforms to compare our framework with several existing methods. The results show that our framework outperforms the baseline methods.
2. Motivation
3. Background
3.1. Task Offloading in MEC
3.2. Centralized Training and Decentralized Execution
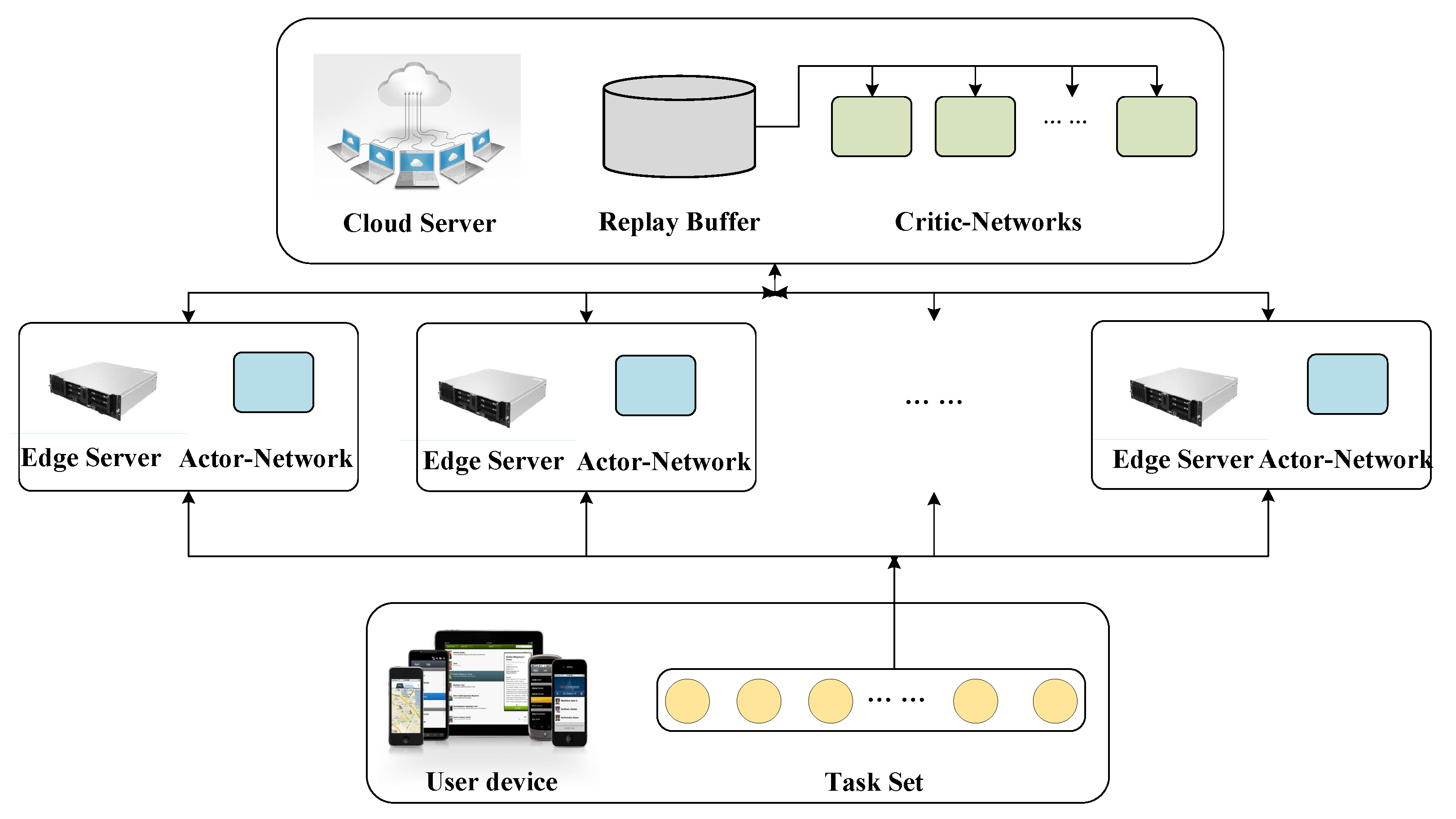
4. The Proposed Method
4.1. Learning Model for MEC
4.2. Update and Training
5. Experiments
5.1. Baseline Methods
5.2. Experiment Setup
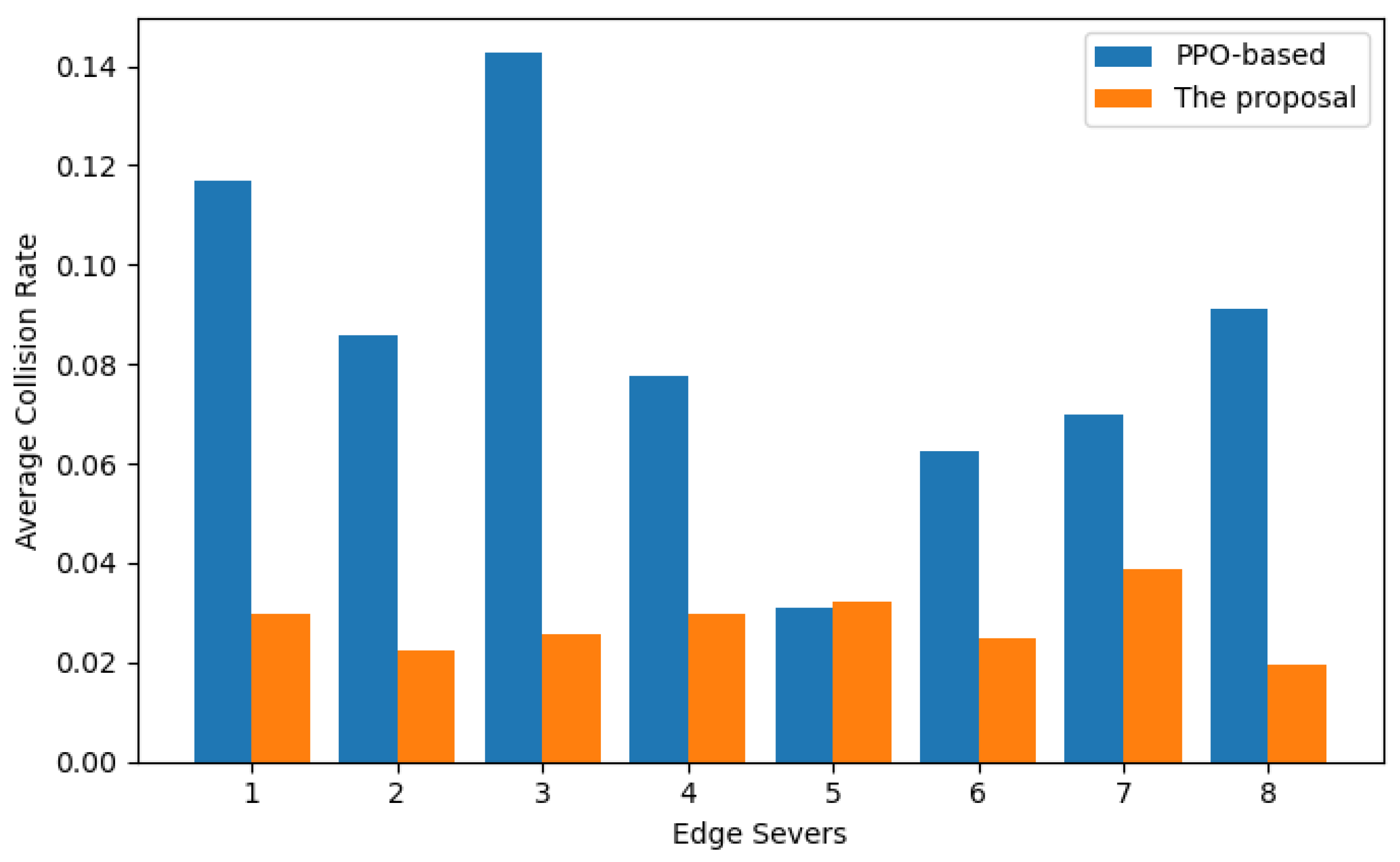
5.3. Result and Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siregar, S.; Syahputra, M.; Rahmat, R. Human face recognition using eigenface in cloud computing environment. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 308, p. 012013. [Google Scholar]
- Badue, C.; Guidolini, R.; Carneiro, R.V.; Azevedo, P.; Cardoso, V.B.; Forechi, A.; Jesus, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixao, T.M.; Mutz, F.; et al. Self-driving cars: A survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 165, 113816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasereddin, H.H.; Omari, A.A.R. Classification techniques for automatic speech recognition (ASR) algorithms used with real time speech translation. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing Conference, London, UK, 18–20 July 2017; pp. 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, B.; Buyya, R. Next generation cloud computing: New trends and research directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 79, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Liang, F.; He, X.; Hatcher, W.G.; Lu, C.; Lin, J.; Yang, X. A survey on the edge computing for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 6900–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Hu, J.; Teng, X.; Wang, B.; Pan, X. Computation offloading strategy in mobile edge computing. Information 2019, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, W.; Fu, Y.; Quek, T.Q.; Zheng, F.C.; Jin, S. Joint uplink/downlink sub-channel, bit and time allocation for multi-access edge computing. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, P.; Islam, R.; Bachman, P.; Pineau, J.; Precup, D.; Meger, D. Deep reinforcement learning that matters. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Gao, G.; Ning, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Approximation Algorithm for the Offloading Problem in Edge Computing. In International Conference on Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference, WASA 2020, Qingdao, China, 13–15 September 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 134–144. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, M.S.; Abedin, S.F.; Tran, N.H.; Hong, C.S. When edge computing meets microgrid: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 7360–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Mao, S.; Ji, Y.; Bennis, M. Performance optimization in mobile-edge computing via deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 88th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Chicago, IL, USA, 27–30 August 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, R.; Wu, Y.; Tamar, A.; Harb, J.; Abbeel, P.; Mordatch, I. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6382–6393. [Google Scholar]
- Alameddine, H.A.; Sharafeddine, S.; Sebbah, S.; Ayoubi, S.; Assi, C. Dynamic task offloading and scheduling for low-latency IoT services in multi-access edge computing. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2019, 37, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porambage, P.; Okwuibe, J.; Liyanage, M.; Ylianttila, M.; Taleb, T. Survey on multi-access edge computing for internet of things realization. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2961–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Huang, W.; Zou, Q.; Yang, X. A dynamic planning framework for qos-based mobile service composition under cloud-edge hybrid environments. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Collaborative Computing: Networking, Applications and Worksharing, London, UK, 19–22 August 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 58–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Q. Genetic algorithm-based optimization of offloading and resource allocation in mobile-edge computing. Information 2020, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, T.X.; Pompili, D. Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-server mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 68, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, K.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. A heuristic algorithm based on resource requirements forecasting for server placement in edge computing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM Symposium on Edge Computing (SEC), Bellevue, WA, USA, 25–27 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 354–355. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, A.; Li, Y.; Esposito, F. Battle of microservices: Towards latency-optimal heuristic scheduling for edge computing. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Network Softwarization (NetSoft), Paris, France, 24–28 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Li, D.; Dai, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, X. A heuristic offloading method for deep learning edge services in 5G networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 67734–67744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Kato, N. Smart resource allocation for mobile edge computing: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qin, Z.; Gao, Y. Resource allocation for edge computing in IoT networks via reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the ICC 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 20–24 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Feng, Z.; Gao, Y. Multi-agent reinforcement learning for resource allocation in IoT networks with edge computing. China Commun. 2020, 17, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Pan, C.; Xu, W.; Aslam, N.; Hanzo, L. Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Trajectory Planning for Multi-UAV Assisted Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2020, 7, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.S.; Abedin, S.F.; Tran, N.H.; Han, Z.; Hong, C.S. A Multi-Agent System toward the Green Edge Computing with Microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Konda, V.R.; Tsitsiklis, J.N. Actor-critic algorithms. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 1008–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Bittencourt, L.F.; Sakellariou, R.; Madeira, E.R. Dag scheduling using a lookahead variant of the heterogeneous earliest finish time algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th Euromicro Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Network-Based Processing, Pisa, Italy, 17–19 February 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, R.V.; Trick, M.A. Round robin scheduling–a survey. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 188, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Che, X. DRL-Based Edge Computing Model to Offload the FIFA World Cup Traffic. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2020, 2020, 8825643. [Google Scholar]
| HEFT | Round-Robin | PPO-Based | DMARL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Episodes | 10 k | 50 k | 100 k | 10 k | 50 k | 100 k | ||
| Waiting Time | 2394 | 5170 | 6132 | 4028 | 3231 | 6547 | 3005 | 1586 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Li, J.; Shi, H.; Ning, B.; Gu, Q. Decentralized Offloading Strategies Based on Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Access Edge Computing. Information 2021, 12, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12090343
Hu C, Li J, Shi H, Ning B, Gu Q. Decentralized Offloading Strategies Based on Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Access Edge Computing. Information. 2021; 12(9):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12090343
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Chunyang, Jingchen Li, Haobin Shi, Bin Ning, and Qiong Gu. 2021. "Decentralized Offloading Strategies Based on Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Access Edge Computing" Information 12, no. 9: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12090343
APA StyleHu, C., Li, J., Shi, H., Ning, B., & Gu, Q. (2021). Decentralized Offloading Strategies Based on Reinforcement Learning for Multi-Access Edge Computing. Information, 12(9), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12090343






