PFMNet: Few-Shot Segmentation with Query Feature Enhancement and Multi-Scale Feature Matching
Abstract
:1. Introduction
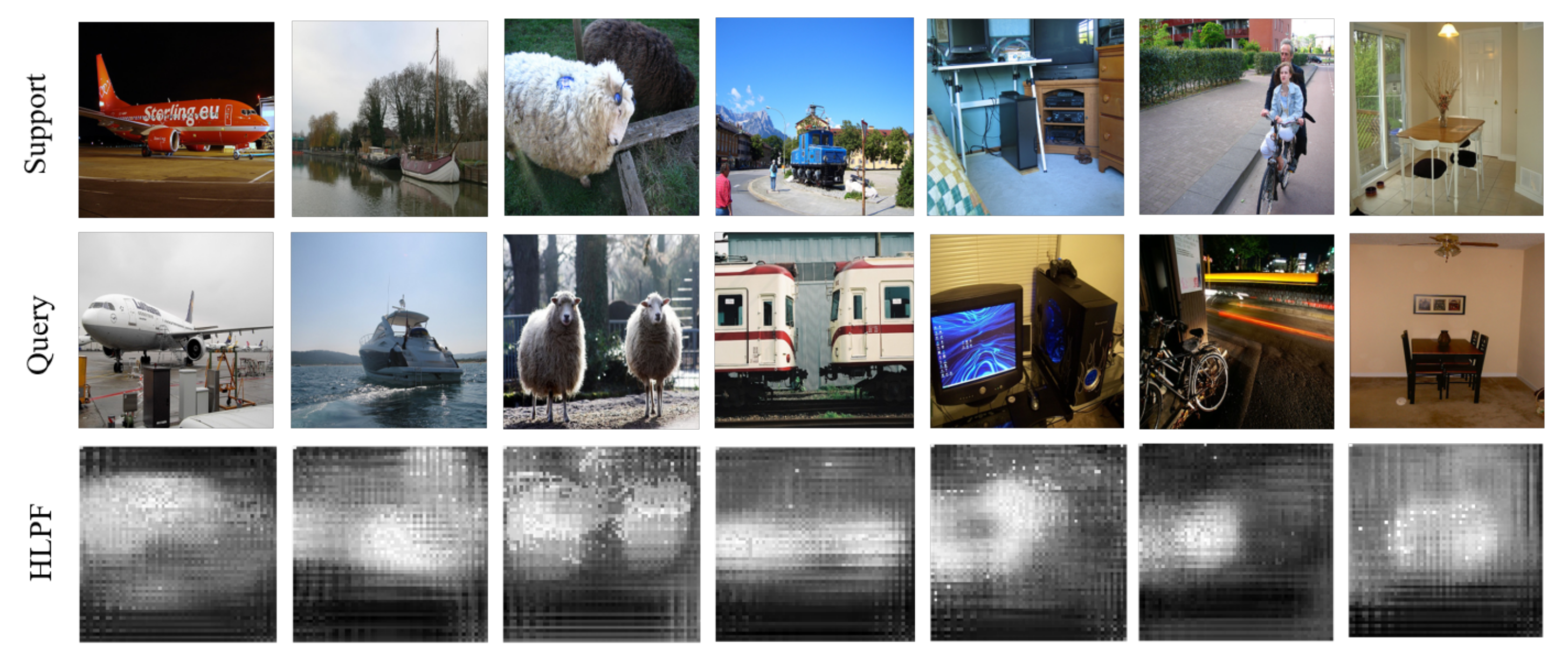
1.1. Inadequate Application of High-Level Features
1.2. Inconsistency of Segmenting Object Scales
- In order to make use of pixel-level search and dynamic pooling methods, we propose a prior feature matching network (PFMNet) for few-shot segmentation. It is well-learned by the model from fewer annotations.
- To apply higher-level features as much as possible, we propose a Query Feature Enhancement Module in order to take full advantage of the high-level semantic information of the support set.
- We adopt a more reasonable feature-matching method, a multi-scale feature matching module to normalize the segmenting objects’ scale to medium-scale and increase the probability of segmenting objects scales matching in multi-scale feature maps.
2. Related Work
2.1. Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Application of High-Level Feature
2.3. Multi-Scale Feature Processing
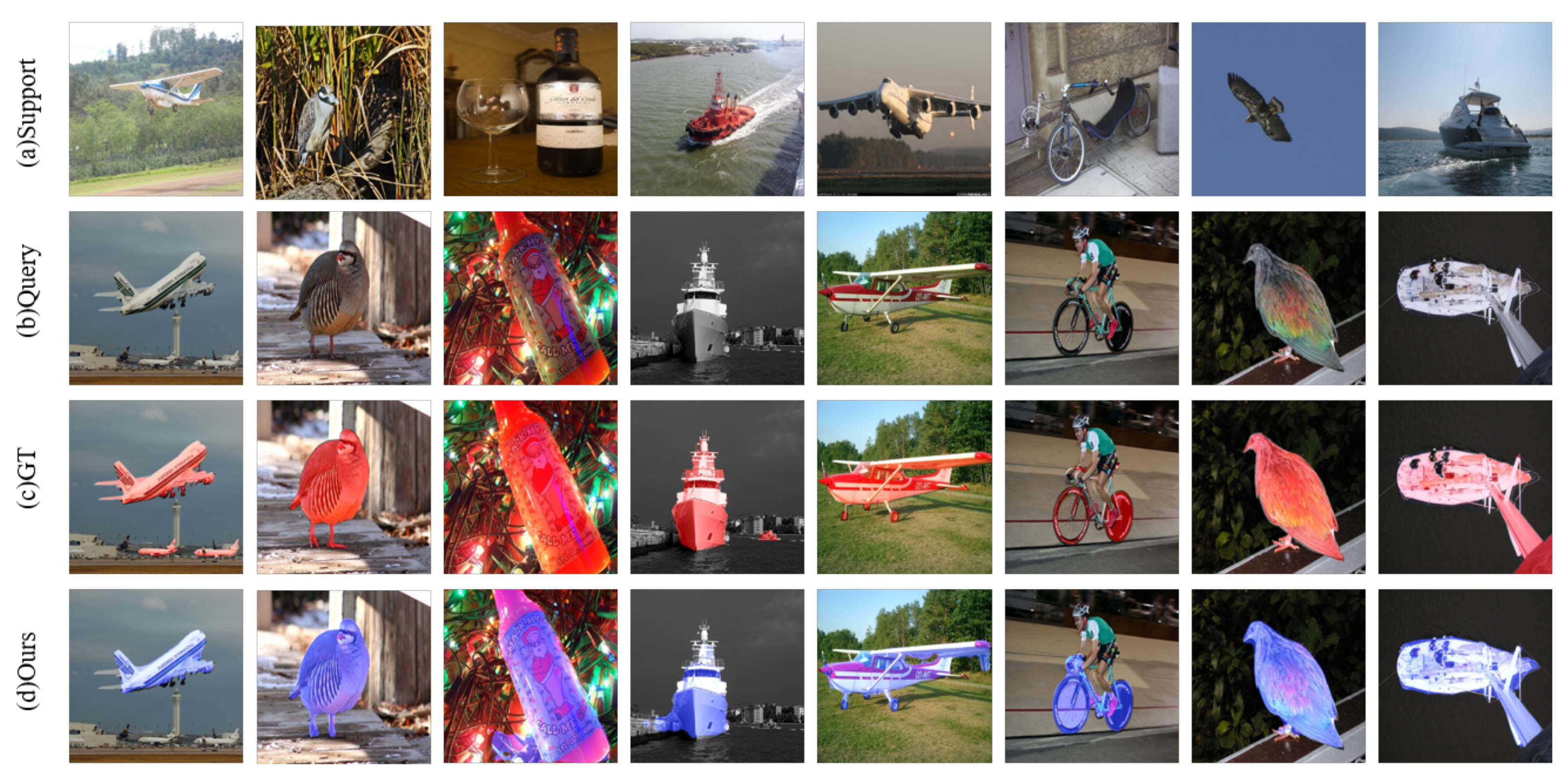
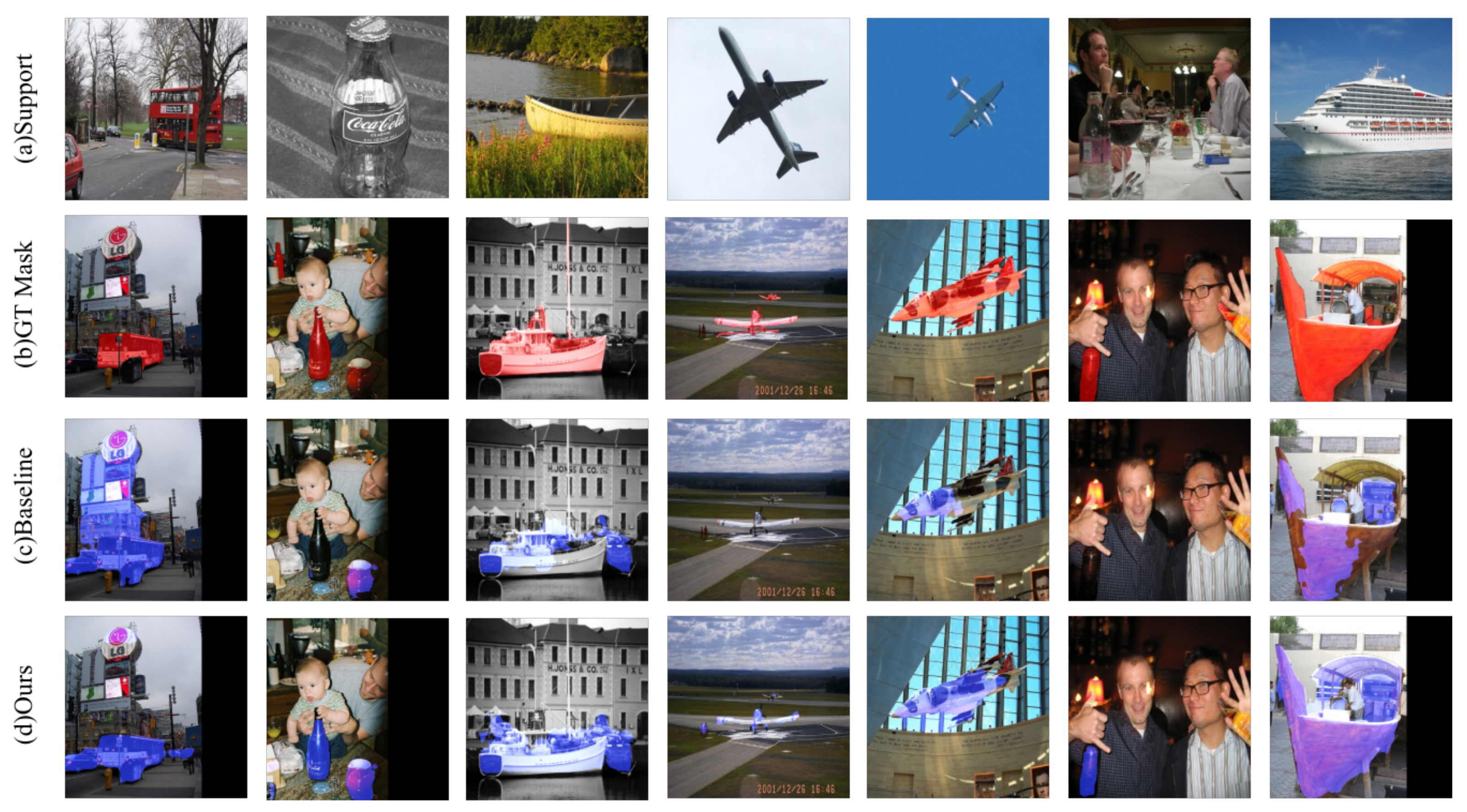
3. Our Method
3.1. Prior Feature Matching Network
3.2. Query Feature Enhancement Module
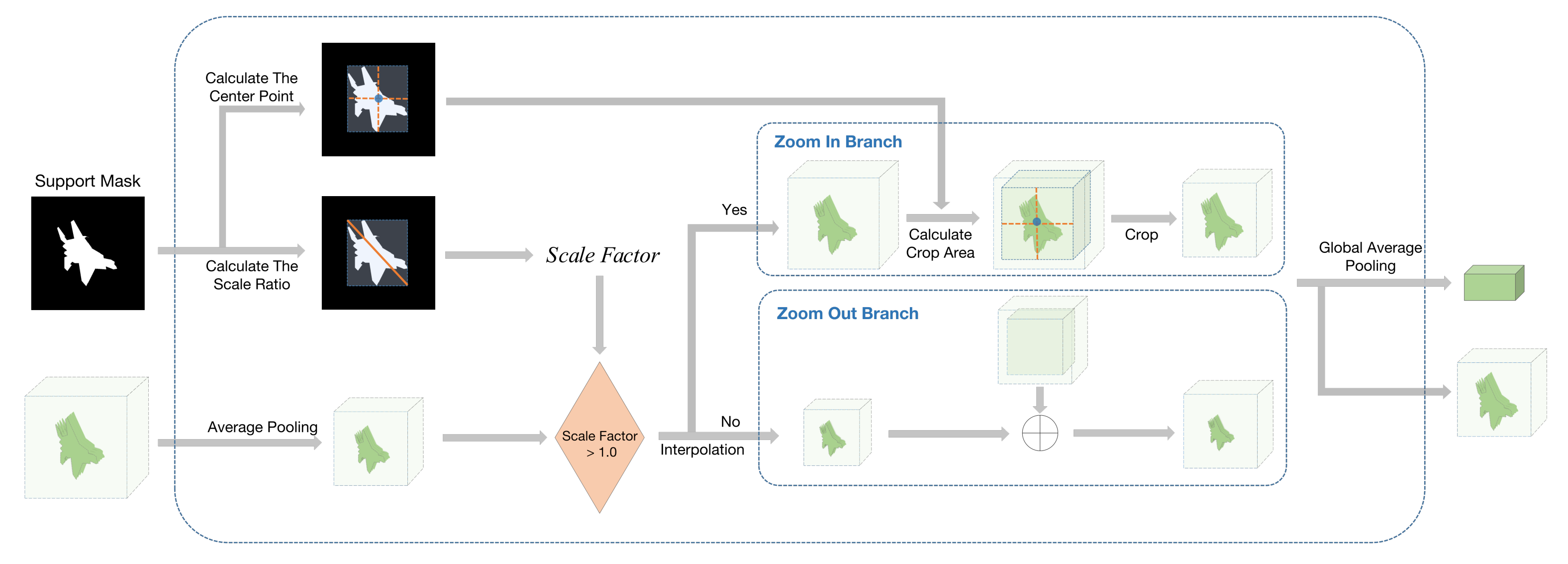
3.3. Multi-Scale Feature Matching Module
| Algorithm 1 Multi-Scale Feature Matching Module |
Require: support feature , feature pyramid sizes , scaling control parameter
|
3.4. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Description of Datasets and Environments
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Ablation Experiments
4.5. Comparative Experiments
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PFMNet | prior feature matching network |
| QFEM | query feature enhancement module |
| MFMM | multi-scale feature matching module |
| HLPF | high-level prior feature |
| ResNet | residual network |
| mIoU | mean intersection over union |
| FB-IoU | foreground-background intersection over union |
References
- Cai, Q.; Pan, Y.; Yao, T.; Yan, C.; Mei, T. Memory matching networks for one-shot image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4080–4088. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, M. Bag of tricks for image classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Mikołajczyk, A.; Grochowski, M. Data augmentation for improving deep learning in image classification problem. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Interdisciplinary PhD Workshop (IIPhDW), Swinoujscie, Poland, 9–12 May 2018; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, L.; Wang, J. The effectiveness of data augmentation in image classification using deep learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.04621. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual attention network for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.J.; Yousaf, A.; Javed, N.; Nadeem, S.; Khurshid, K. Automatic target detection in satellite images using deep learning. J. Space Technol. 2017, 7, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Suhao, L.; Jinzhao, L.; Guoquan, L.; Tong, B.; Huiqian, W.; Yu, P. Vehicle type detection based on deep learning in traffic scene. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 131, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Liao, Q. A study on radar target detection based on deep neural networks. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2019, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Fowlkes, C.C. Laplacian pyramid reconstruction and refinement for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 519–534. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1925–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Siam, M.; Oreshkin, B.N.; Jagersand, M. Amp: Adaptive masked proxies for few-shot segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5249–5258. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Luo, P.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Semantic image segmentation via deep parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1377–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Jayasumana, S.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Vineet, V.; Su, Z.; Du, D.; Huang, C.; Torr, P.H. Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1529–1537. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, H. One-Shot Image Segmentation with U-Net. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1848, 012113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jampani, V.; Sevilla-Lara, L.; Sun, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Adaptive Prototype Learning and Allocation for Few-Shot Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8334–8343. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Liew, J.H.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Panet: Few-shot image semantic segmentation with prototype alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9197–9206. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; He, X. Part-aware prototype network for few-shot semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 142–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, G.; Liu, F.; Yao, R.; Shen, C. Canet: Class-agnostic segmentation networks with iterative refinement and attentive few-shot learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5217–5226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, F.; Li, H.; Ngan, K.N.; Wu, Q. A New Few-shot Segmentation Network Based on Class Representation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Sydney, Australia, 1–4 December 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, R.; Fayjie, A.R.; Kauffman, C.; Ayed, I.B.; Pedersoli, M.; Dolz, J. On the Texture Bias for Few-Shot CNN Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 2674–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Shu, M.; Yang, Z.; Li, R.; Jia, J. Prior guided feature enrichment network for few-shot segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, J.; Swersky, K.; Zemel, R.S. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.05175. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Qin, Y. Prototype refinement network for few-shot segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.03579. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Liu, C.; Li, B.; Jiao, J.; Ye, Q. Prototype mixture models for few-shot semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 763–778. [Google Scholar]
- Shaban, A.; Bansal, S.; Liu, Z.; Essa, I.; Boots, B. One-shot learning for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.03410. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, T.S. Sg-one: Similarity guidance network for one-shot semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 3855–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, K.; Liu, Z.; Zang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C. PGNet: A Part-based Generative Network for 3D object reconstruction. Knowl. Based Syst. 2020, 194, 105574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Lin, G.; Liu, F. Crnet: Cross-reference networks for few-shot segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 4165–4173. [Google Scholar]
- Gairola, S.; Hemani, M.; Chopra, A.; Krishnamurthy, B. Simpropnet: Improved similarity propagation for few-shot image segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.15014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, F.; Li, H.; Wu, Q.; Xu, X.; Chen, S. A new local transformation module for few-shot segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Daejeon, Korea, 5–8 January 2020; pp. 76–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]










| Datasets | Test Classes |
|---|---|
| PASCAL-5 | aeroplane, bicycle, bird, boat, bottle |
| PASCAL-5 | bus, car, cat, chair, cow |
| PASCAL-5 | dining table, dog, horse, motorbike, person |
| PASCAL-5 | potted plant, sheep, train, tv/monitor |
| Shot | Aero | Bike | Bird | Boat | Bottle | Bus | Car | Cat | Chair | Cow |
| 1-Shot | 36.9 | 82.2 | 57.3 | 57.1 | 80.8 | 60.9 | 87.2 | 21.2 | 91.2 | 87.9 |
| 5-Shot | 37.5 | 83.1 | 60.5 | 60.5 | 83.9 | 63.2 | 88.7 | 24.9 | 91.2 | 89.1 |
| Table | Dog | Horse | Mbike | Person | Plant | Sheep | Sofa | Train | Tv | MIoU |
| 84.0 | 87.4 | 82.3 | 8.3 | 19.8 | 90.9 | 54.7 | 79.8 | 30.8 | 24.2 | 61.2 |
| 86.2 | 89.3 | 78.5 | 12.9 | 20.4 | 90.4 | 52.7 | 76.0 | 46.0 | 33.0 | 63.4 |
| Methods | 1-Shot | 5-Shot |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 61.7 | 63.1 |
| Baseline+MFMM | 61.0 | 63.2 |
| Baseline+QFEM | 61.3 | 65.1 |
| Baseline+MFMM+QFEM | 62.9 | 65.1 |
| Methods | 1-Shot | ||||
| Fold-0 | Fold-1 | Fold-2 | Fold-3 | Mean | |
| CANet [25] | 52.5 | 65.9 | 51.3 | 51.9 | 55.4 |
| PGNet [34] | 56.0 | 66.9 | 50.6 | 50.4 | 56.0 |
| CRNet [35] | - | - | - | - | 55.7 |
| SimPropNet [36] | 54.9 | 67.3 | 54.5 | 52.0 | 57.2 |
| LTM [37] | 52.8 | 69.6 | 53.2 | 52.3 | 57.0 |
| RPMM [31] | 55.2 | 66.9 | 52.6 | 50.7 | 56.3 |
| PPNet [24] | 47.8 | 58.8 | 53.8 | 45.6 | 51.5 |
| PFENet [28] | 61.7 | 69.5 | 55.4 | 56.3 | 60.8 |
| Ours | 62.9 | 69.7 | 56.4 | 56.1 | 61.3 |
| Methods | 5-Shot | ||||
| Fold-0 | Fold-1 | Fold-2 | Fold-3 | Mean | |
| CANet [25] | 55.5 | 67.8 | 51.9 | 53.2 | 57.1 |
| PGNet [34] | 54.9 | 67.4 | 51.8 | 53.0 | 56.8 |
| CRNet [35] | - | - | - | - | 58.5 |
| SimPropNet [36] | 57.2 | 68.5 | 58.4 | 56.1 | 60.0 |
| LTM [37] | 57.9 | 69.9 | 56.9 | 57.5 | 60.6 |
| RPMM [31] | 56.3 | 67.3 | 54.5 | 51.0 | 57.3 |
| PPNet [24] | 58.4 | 67.8 | 64.9 | 56.7 | 62.0 |
| PFENet [28] | 63.1 | 70.7 | 55.8 | 57.9 | 61.9 |
| Ours | 65.1 | 71.4 | 57.5 | 59.5 | 63.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Lu, Z. PFMNet: Few-Shot Segmentation with Query Feature Enhancement and Multi-Scale Feature Matching. Information 2021, 12, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12100406
Li J, Cheng L, Zheng Z, Chen J, Zhao G, Lu Z. PFMNet: Few-Shot Segmentation with Query Feature Enhancement and Multi-Scale Feature Matching. Information. 2021; 12(10):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12100406
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jingyao, Lianglun Cheng, Zewen Zheng, Jiahong Chen, Genping Zhao, and Zeng Lu. 2021. "PFMNet: Few-Shot Segmentation with Query Feature Enhancement and Multi-Scale Feature Matching" Information 12, no. 10: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12100406
APA StyleLi, J., Cheng, L., Zheng, Z., Chen, J., Zhao, G., & Lu, Z. (2021). PFMNet: Few-Shot Segmentation with Query Feature Enhancement and Multi-Scale Feature Matching. Information, 12(10), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12100406






