The Effects of Major Selection Motivations on Dropout, Academic Achievement and Major Satisfactions of College Students Majoring in Foodservice and Culinary Arts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Backgrounds
2.1. Motivation for Choosing a Major
2.2. Dropout
2.3. Academic Achievement
2.4. Major Satisfaction Level
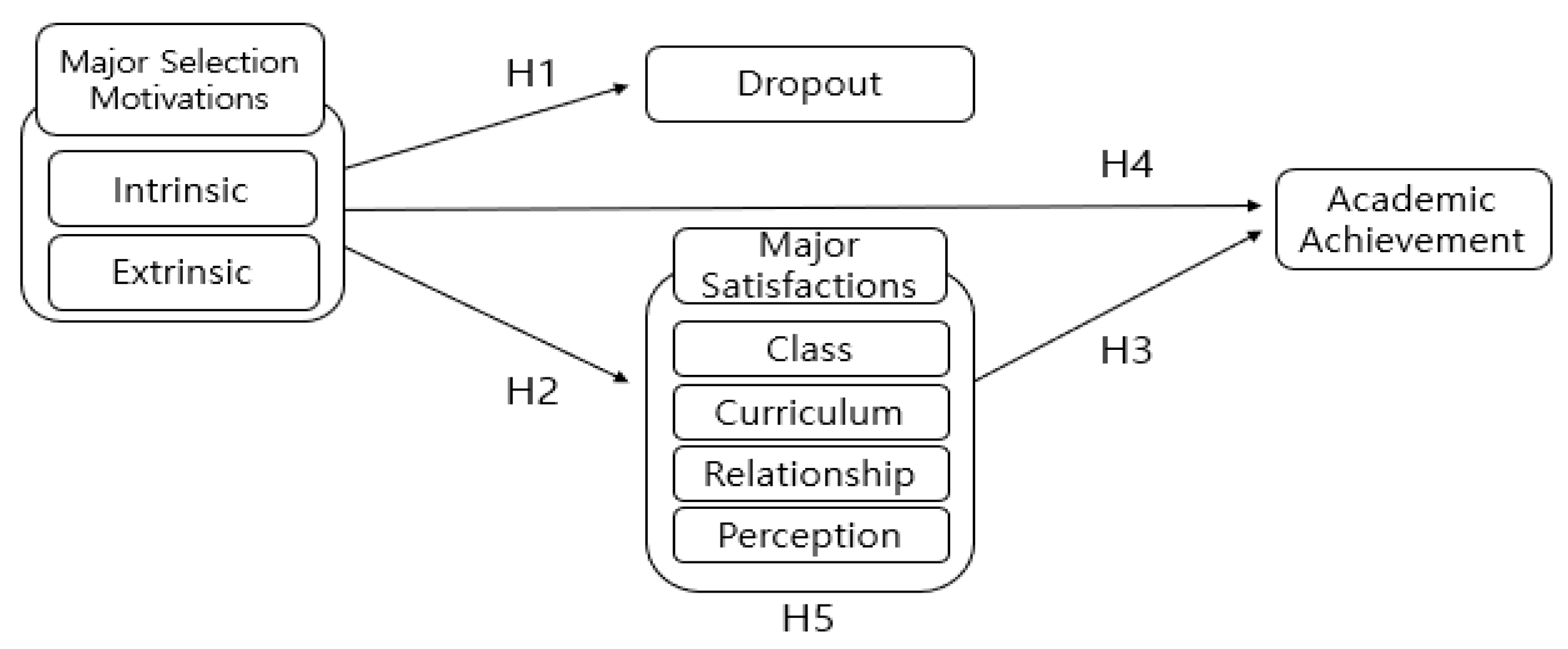
3. Research Model
4. Hypothesis Setting
5. Investigated Subject
6. Questionnaire Composition
- (1)
- Motivation for choosing a major
- (2)
- Major Satisfaction
- (3)
- Academic achievement and dropout
7. Empirical Analysis
7.1. Demographic Status
7.2. Validity and Reliability of Measurement Tools
7.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis
7.4. Structural Equation Model Analysis
7.5. Mediated Effect
8. Conclusions
9. Limitations and Suggestions of Research
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seo, B.W. The Effects of Motivation for major choice of University Students on Vocation Choice Factors. J. Employ. Career 2013, 3, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.H. The effects of major selection motivation on major satisfaction and vocation selection-focused on the college students major in hospitality and tourism. J. Hosp. Tour. Stud. 2015, 17, 323–347. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.J.; Lee, J.H. A Study on Major Satisfaction and Career Maturity according to the Values of College Students—Majoring in Food Management and Culinary Arts. Culin. Sci. Hosp. Res. 2013, 19, 76–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.J.; Lee, E.J. Career adjustment process of college students who decided on their majors based on extrinsic motivation. Korean J. Couns. 2014, 15, 1771–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.S.; Kim, H.K. The effect of motivation for major choice and satisfaction in major on the adaption of university life among university students. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2016, 17, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.J.; Cho, K.K. The Mediating Effect of Major Satisfaction and Professor-Student Interaction on the Relationship Between Intrinsic Motivation and School Life Adjustment. J. Res. Inst. Korean Educ. 2012, 34, 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.W. Relationship between university student’s attributional-style and learning adaptation considered in department selection. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2012, 13, 694–700. [Google Scholar]
- OECD Education Indicators; KDI Economic Information and Education Center: Seoul, Korea, 2019.
- Han, Y.J. The Study on the Relationship Between the Degree of Instruction Participation and Major Satisfaction and the Employment Preparation Behavior by the Major Selection Motive and Their Work Values of University Students. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyungsung University, Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.K.; Woo, L.S. The Study on the Influence of Career Selection Type of University Students Major in Food-service, Class Participation, Career Preparation Behavior. Culin. Sci. Hosp. Res. 2015, 21, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gottfredson, L.S.; Becker, H.J. A challenge to vocational Paychology—How important are aspirations in determining male career development? J. Vocat. Behav. 1981, 18, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, S.; Akkas, O.A. Quality of college life of students in turkey: Students’ life satisfaction and identification. Soc. Indic. Res. 2014, 115, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.H.; Kim, K.H. Compromise process of Korean high school graduates’ decision-making. Korean J. Couns. 2003, 4, 19–36. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y. Research on the Development of Social Adjustment Counseling Policy for Dropout Students; Youth Dialogue Square, Report; The Korea Social Policy Institute: Seoul, Korea, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.H.; Lee, E.K.; Lee, E.T. Trends and Influencing Factors of College Students’ Dropout Intention; Forum for Youth Culture Volume 58; Research Center for Korea Youth Culture: Seoul, Korea, 2019; pp. 5–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H. The Hierarchical Relationship between Individual, College, Social Variable, and Dropout Intention of College Students. J. Vocat. Educ. Res. 2011, 30, 249–266. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, D.W.; Jin, K.H.; Jeong, K.O. An Empirical Study on the Analysis of Chinese Foreign Students’ Academic Achievement and Fallout. J. Inf. Technol. Appl. Manag. 2020, 27, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.J. The Effect of Major Selection Motivation Major Satisfaction and Professor-Student Interaction of University Students on their School Life Adijustment. Ph.D. Thesis, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, H.S. The Effects of Major Selection Motivation on Career Efficacy and Major Satisfaction of College Students majoring in Culinary Art and Food-service Management. Culin. Sci. Hosp. Res. 2017, 23, 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Yoon, H.H. The Influence of Major Satisfaction and Self-Efficacy of University Students Majoring in Culinary Arts on Career Preparation Behavior. Culin. Sci. Hosp. Res. 2020, 26, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.M.; Ko, J.W. Factors Affecting Diversity Experiences of College Students: An Analysis of Institutional Difference. J. Educ. Adm. 2015, 33, 319–342. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, R.C.; Miller, C. Life Satisfaction and Life Demands in College Students. Sch. Behav. Pers. 1998, 26, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A. A Study on Student Satisfaction with Educational Environment, Innovation Configuration, and Intervention Demand of Students in Culinary Practice Education—Focusing on University Students Majoring in Culinary Arts. Culin. Sci. Hosp. Res. 2013, 19, 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, K.H. Impacts of Major Selection Motivation on Person-University Fit, Person-Major Fit, Major Satisfaction and Job Seeking Efficacy in Food & Culinary Arts Students, Focused on Mentoring. Ph.D. Thesis, Sejong University, Seoul, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.R. Promotion of culinary education through the importance and satisfaction surveys for cooking training: A survey of cooking department university student on Busan. Master’s Thesis, Graduate School of Nambu, Gwangju, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuckle, J.L. IBM SPSS Amos 20 User’s Guide; IBM: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 595–620. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Operational Definition | Items | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major Selection Motivations | Intrinsic | The criteria for major selection are intrinsic motivations such as interest, aptitude and values. | 3 | Song (2014) |
| Extrinsic | The criteria for major selection are extrinsic motivations such as major popularity, family recommendation, mass media and employment prospect. | 3 | ||
| Major Satisfactions | Class | Class Progress, Atmosphere, Use of Supplementary Materials | 3 | Yoon (2015) |
| Curriculum | Curriculum Content, Teaching Time, Teaching-Practice Link, Diversity | 4 | ||
| Relationship | Student-Professor Communication, Career Guidance, Teaching Guidance Accessibility | 4 | ||
| Perception | Employment Prospect, External Perception, Major Popularity, Competitiveness | 4 | ||
| Academic Achievement | Problem-Solving Ability, Decision-Making Ability, Grade | 3 | ||
| Dropout | They′re in college, but they want to drop out of school. | 4 | Lee (2006) | |
| General characteristics | Gender, School year | 2 | ||
| General Information | General Information | Frequency (N) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 62 | 28.1 |
| Female | 159 | 71.9 | |
| School year | Freshmen | 52 | 23.5 |
| Sophomore | 63 | 28.5 | |
| Junior | 69 | 31.2 | |
| Senior | 37 | 16.7 | |
| Total | 221 | 100.0 | |
| Factor | Factor Loading | Eigen-Value | Variance (%) | k-m-o | Cronbach′s α | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major Selection Motivations | Extrinsic | 1-1 | 0.904 | 2.363 | 78.755 | 0.732 | 0.865 |
| 1-2 | 0.879 | ||||||
| 1-3 | 0.879 | ||||||
| Intrinsic | 1-4 | 0.755 | 2.087 | 69.573 | 0.657 | 0.781 | |
| 1-5 | 0.855 | ||||||
| 1-6 | 0.887 | ||||||
| Major Satisfactions | Relationship | 3-1 | 0.635 | 2.674 | 66.855 | 0.786 | 0.831 |
| 3-2 | 0.849 | ||||||
| 3-3 | 0.877 | ||||||
| 3-4 | 0.884 | ||||||
| Perception | 3-5 | 0.797 | 2.87 | 71.74 | 0.821 | 0.780 | |
| 3-6 | 0.88 | ||||||
| 3-7 | 0.889 | ||||||
| 3-8 | 0.817 | ||||||
| Class | 3-9 | 0.810 | 2.116 | 70.542 | 0.699 | 0.789 | |
| 3-10 | 0.848 | ||||||
| 3-11 | 0.861 | ||||||
| Curriculum | 3-12 | 0.786 | 2.522 | 63.041 | 0.786 | 0.803 | |
| 3-13 | 0.773 | ||||||
| 3-14 | 0.857 | ||||||
| 3-15 | 0.757 | ||||||
| Dropout | 2-1 | 0.797 | 2.870 | 71.740 | 0.821 | 0.868 | |
| 2-2 | 0.880 | ||||||
| 2-3 | 0.889 | ||||||
| 2-4 | 0.817 | ||||||
| Academic Achievement | 4-1 | 0.727 | 1.996 | 66.544 | 0.647 | 0.747 | |
| 4-2 | 0.868 | ||||||
| 4-3 | 0.845 | ||||||
| Category | Standard Regression Weight | Standard Error | t-Value | Construct Reliability | Average Variance Extracted | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extrinsic | 1-1 | 0.875 | - | - | 0.908 | 0.768 |
| 1-2 | 0.803 | 0.072 | 13.072 | |||
| 1-3 | 0.799 | 0.069 | 13.012 | |||
| Intrinsic | 1-4 | 0.58 | 0.075 | 7.889 | 0.886 | 0.727 |
| 1-5 | 0.757 | 0.093 | 9.458 | |||
| 1-6 | 0.89 | - | - | |||
| Dropout | 2-1 | 0.701 | 0.079 | 10.554 | 0.916 | 0.732 |
| 2-2 | 0.833 | 0.083 | 12.846 | |||
| 2-3 | 0.858 | 0.087 | 13.236 | |||
| 2-4 | 0.773 | - | - | |||
| Relationship | 3-1 | 0.54 | 0.071 | 8.292 | 0.886 | 0.666 |
| 3-2 | 0.767 | 0.067 | 13.069 | |||
| 3-3 | 0.846 | 0.067 | 15 | |||
| 3-4 | 0.856 | - | - | |||
| Perception | 3-5 | 0.659 | 0.144 | 7.733 | 0.849 | 0.585 |
| 3-6 | 0.755 | 0.129 | 8.456 | |||
| 3-7 | 0.735 | 0.129 | 8.323 | |||
| 3-8 | 0.632 | - | - | |||
| Class | 3-9 | 0.714 | 0.104 | 9.462 | 0.813 | 0.592 |
| 3-10 | 0.736 | 0.108 | 9.659 | |||
| 3-11 | 0.795 | - | - | |||
| Curriculum | 3-12 | 0.685 | 0.111 | 8.538 | 0.839 | 0.568 |
| 3-13 | 0.673 | 0.117 | 8.419 | |||
| 3-14 | 0.827 | 0.122 | 9.644 | |||
| 3-15 | 0.669 | - | - | |||
| Academic Achievement | 4-1 | 0.558 | 0.094 | 7.423 | 0.821 | 0.611 |
| 4-2 | 0.842 | 0.113 | 9.535 | |||
| 4-3 | 0.74 | - | - | |||
| Path | B | Beta | S.E. | C.R. | P | Adopt or Reject | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
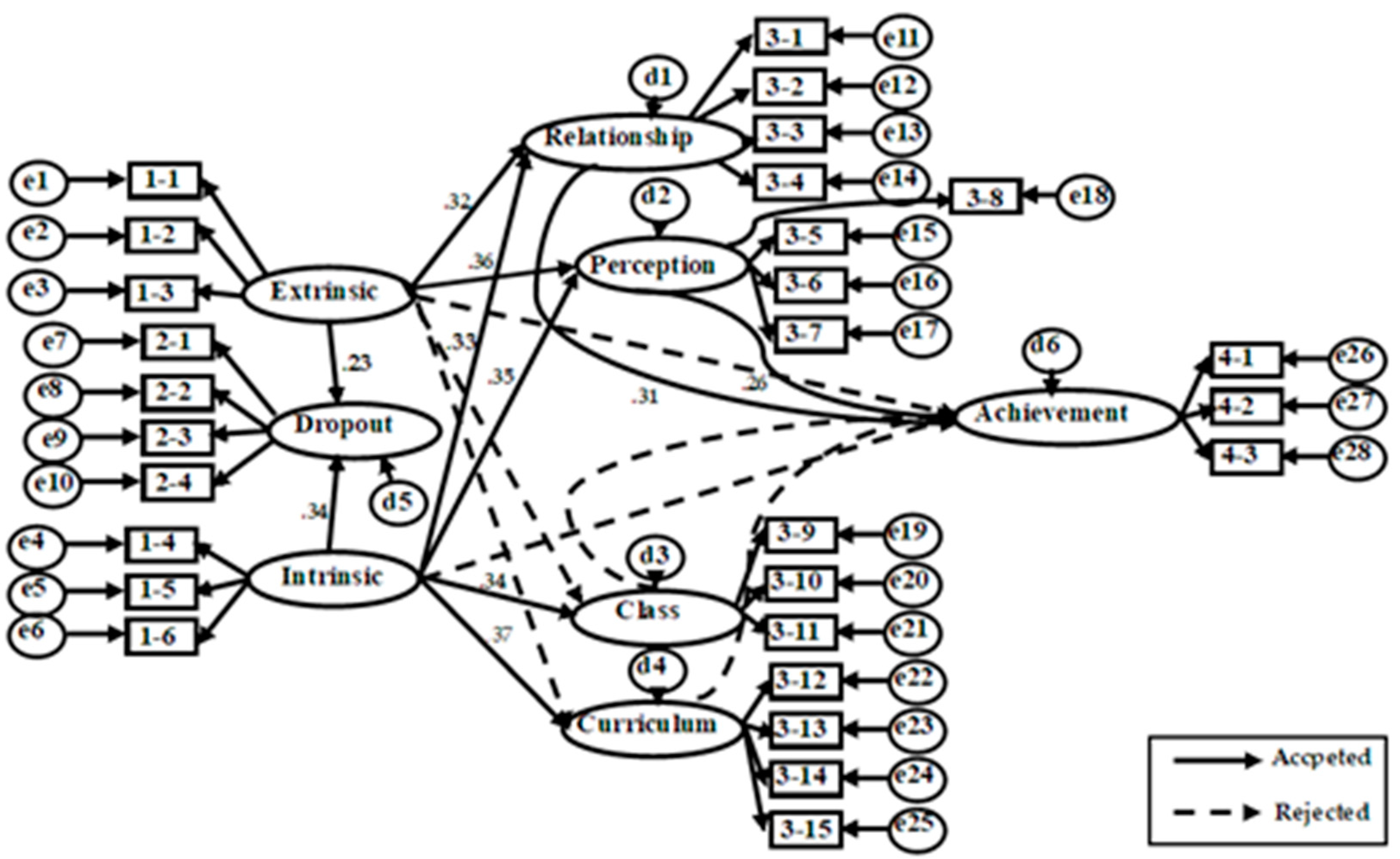
| H1-1 | Intrinsic | → | Dropout | 0.258 | 0.339 | 0.058 | 4.423 | *** | accepted |
| H1-2 | Extrinsic | → | Dropout | 0.229 | 0.268 | 0.066 | 3.475 | *** | accepted |
| H2-1 | Intrinsic | → | Class | 0.321 | 0.34 | 0.079 | 4.088 | *** | accepted |
| H2-2 | Intrinsic | → | Curriculum | 0.322 | 0.374 | 0.071 | 4.556 | *** | accepted |
| H2-3 | Intrinsic | → | Relationship | 0.191 | 0.331 | 0.048 | 3.973 | *** | accepted |
| H2-4 | Intrinsic | → | Perception | 0.28 | 0.348 | 0.066 | 4.261 | *** | accepted |
| H2-5 | Extrinsic | → | Class | 0.098 | 0.093 | 0.085 | 1.165 | 0.244 | rejected |
| H2-6 | Extrinsic | → | Curriculum | 0.112 | 0.116 | 0.075 | 1.492 | 0.136 | rejected |
| H2-7 | Extrinsic | → | Relationship | 0.21 | 0.324 | 0.055 | 3.79 | *** | accepted |
| H2-8 | Extrinsic | → | Perception | 0.328 | 0.364 | 0.077 | 4.256 | *** | accepted |
| H3-1 | Intrinsic | → | Academic Achievement | 0.077 | 0.123 | 0.063 | 1.226 | 0.22 | rejected |
| H3-2 | Extrinsic | → | Academic Achievement | −0.123 | −0.175 | 0.066 | −1.869 | 0.062 | rejected |
| H4-1 | Class | → | Academic Achievement | 0.08 | 0.121 | 0.055 | 1.459 | 0.145 | rejected |
| H4-2 | Curriculum | → | Academic Achievement | 0.105 | 0.145 | 0.061 | 1.711 | 0.087 | rejected |
| H4-3 | Relationship | → | Academic Achievement | 0.339 | 0.313 | 0.107 | 3.154 | 0.002 | accepted |
| H4-4 | Perception | → | Academic Achievement | 0.201 | 0.258 | 0.077 | 2.595 | 0.009 | accepted |
| Category | Path | Total | Direct | Indirect | p | Adopt or Reject | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H5-1 | Intrinsic | → | Major Satisfactions | → | Academic Achievement | 0.412 | 0.123 | 0.289 | 0.005 | accepted |
| H5-2 | Extrinsic | → | 0.048 | −0.175 | 0.223 | 0.019 | accepted | |||
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.S. The Effects of Major Selection Motivations on Dropout, Academic Achievement and Major Satisfactions of College Students Majoring in Foodservice and Culinary Arts. Information 2020, 11, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11090444
Kim JS. The Effects of Major Selection Motivations on Dropout, Academic Achievement and Major Satisfactions of College Students Majoring in Foodservice and Culinary Arts. Information. 2020; 11(9):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11090444
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jung Soo. 2020. "The Effects of Major Selection Motivations on Dropout, Academic Achievement and Major Satisfactions of College Students Majoring in Foodservice and Culinary Arts" Information 11, no. 9: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11090444
APA StyleKim, J. S. (2020). The Effects of Major Selection Motivations on Dropout, Academic Achievement and Major Satisfactions of College Students Majoring in Foodservice and Culinary Arts. Information, 11(9), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11090444




