SybilEye: Observer-Assisted Privacy-Preserving Sybil Attack Detection on Mobile Crowdsensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Studies
2.1. Mobile Crowdsensing
2.2. Sybil Attack
2.3. RSS-Based Localization
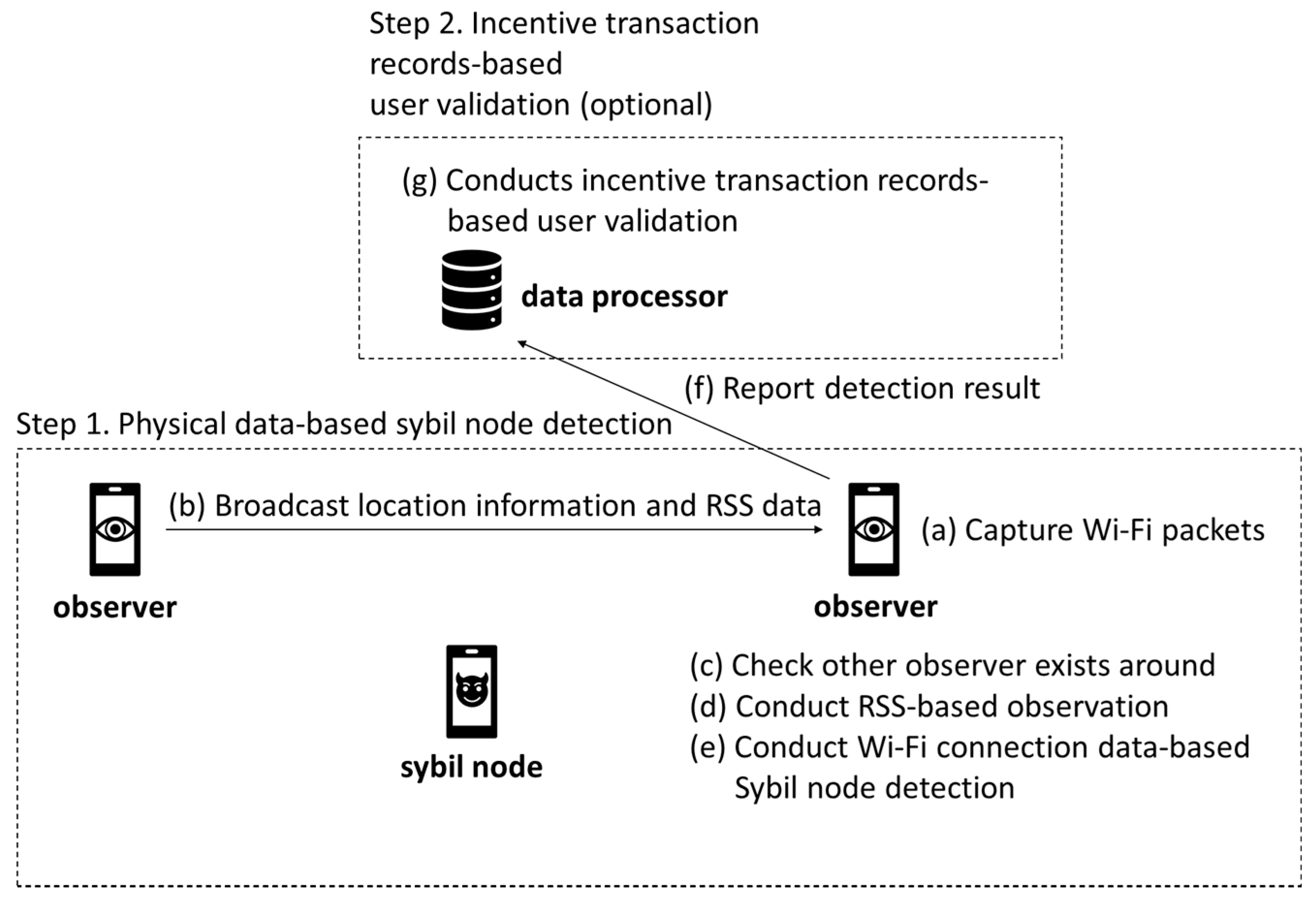
3. Proposed System
3.1. System Structure
3.2. Attack Model
3.3. Sybil Attack Detection
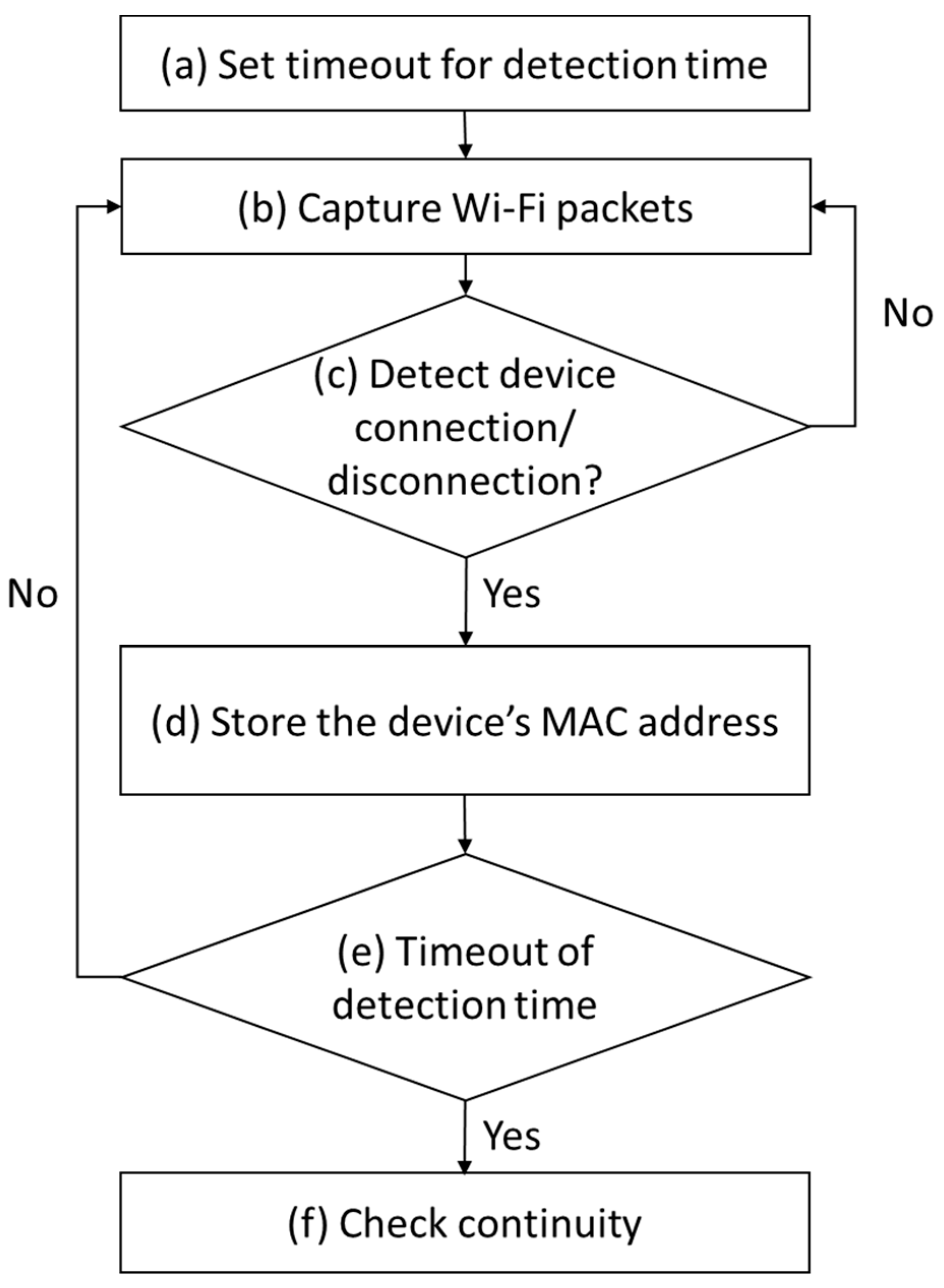
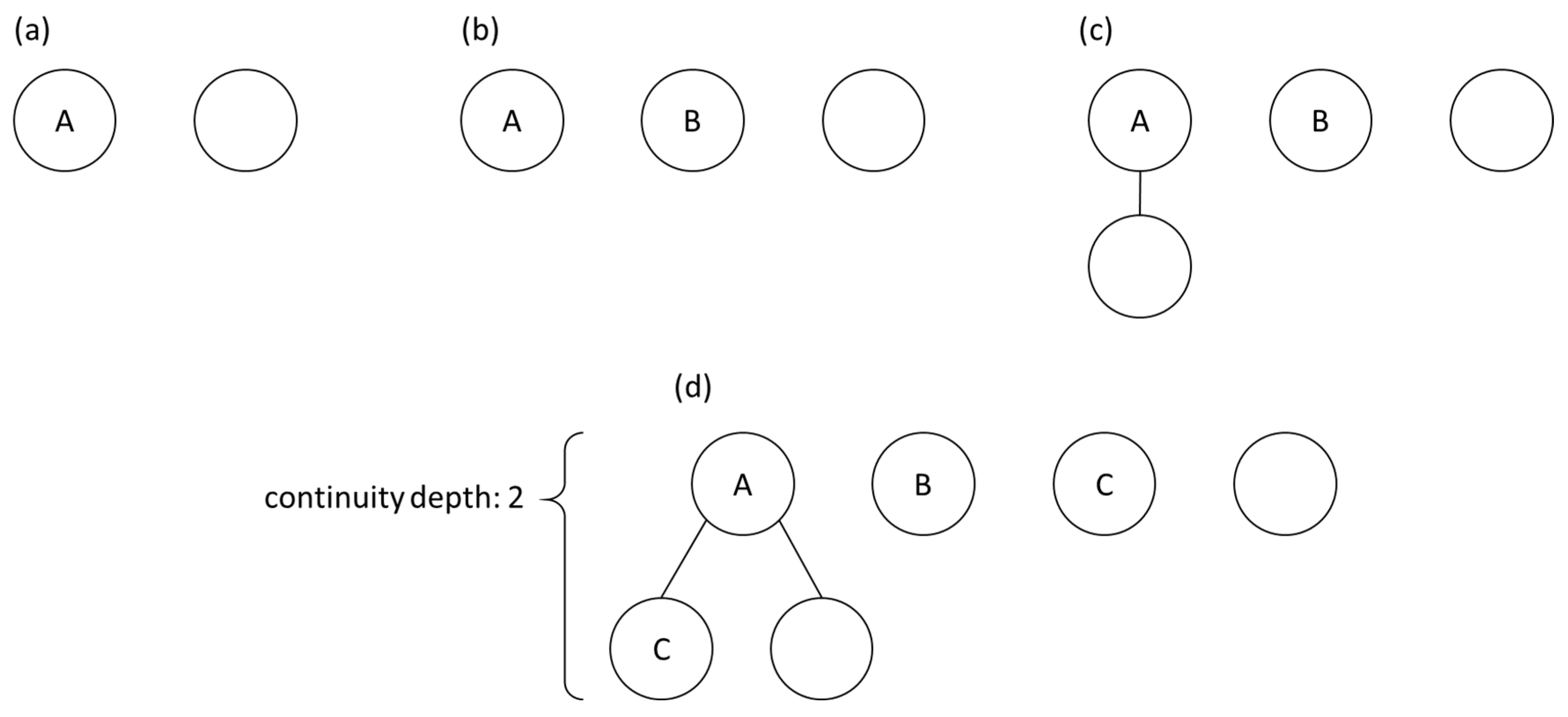
3.3.1. Wi-Fi Connection Data-Based Detection
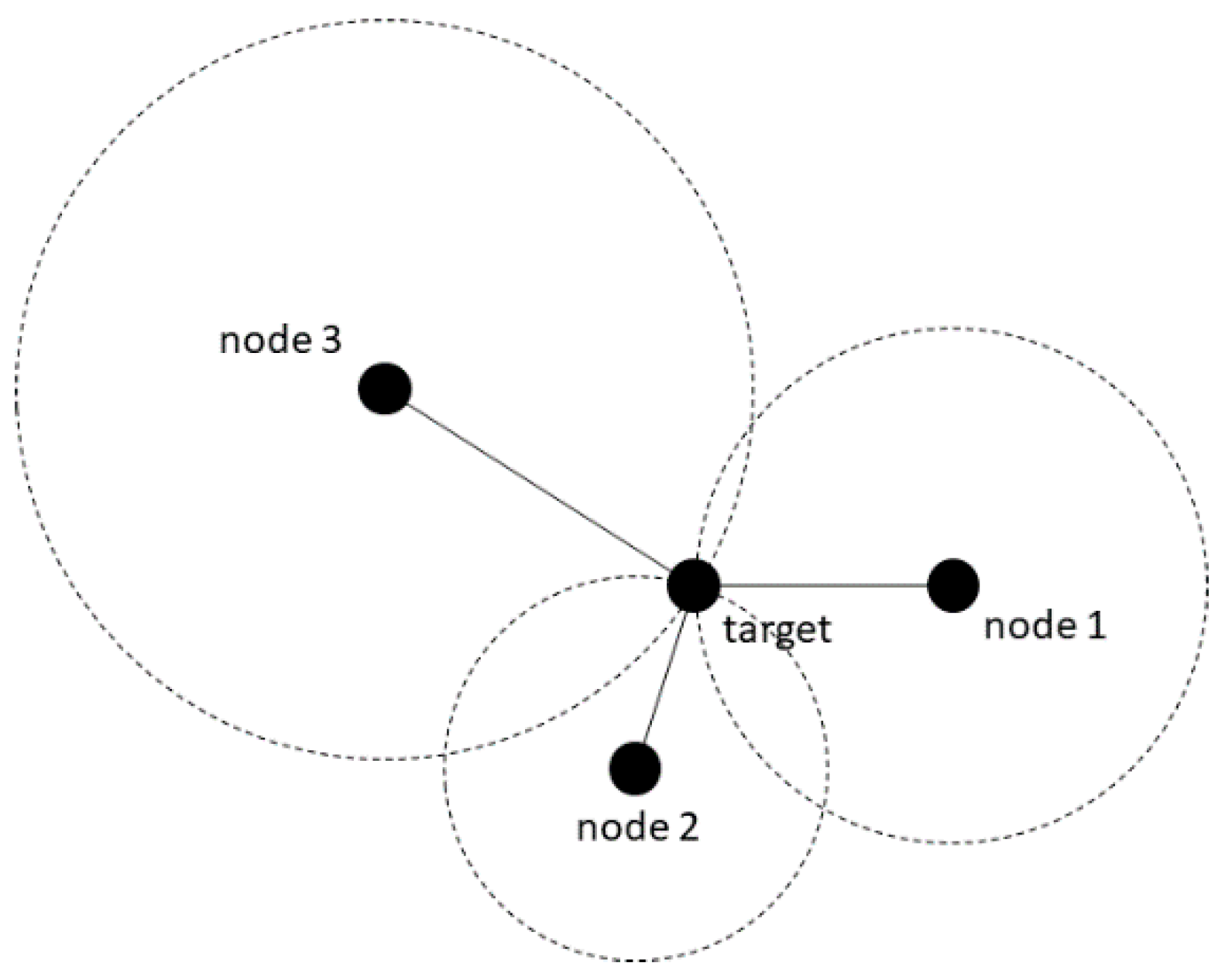
3.3.2. RSS-Based Observation
3.3.3. Incentive Transaction-Record Based User Verification
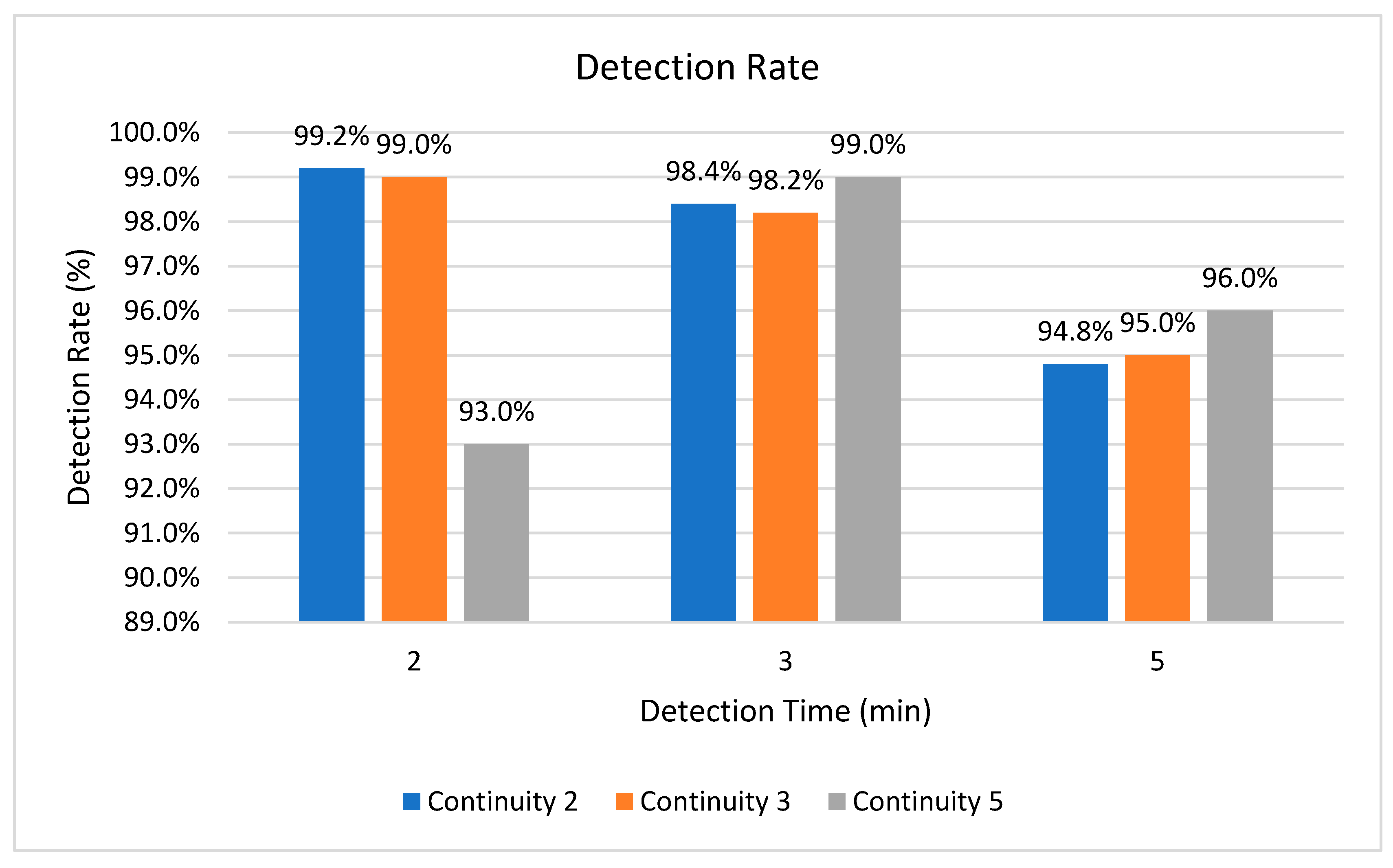
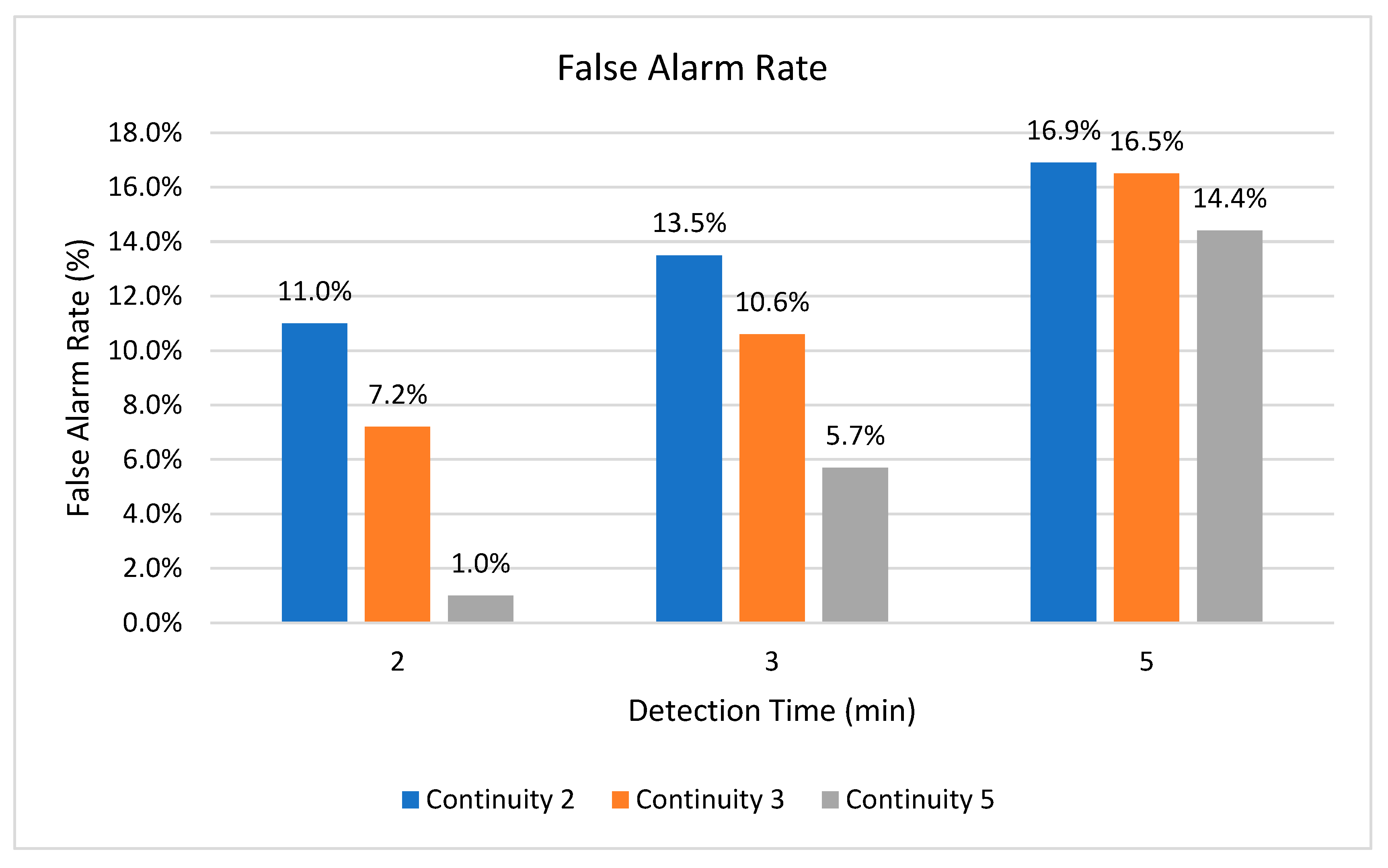
4. Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ganti, R.; Ye, F.; Lei, H. Mobile crowdsensing: Current state and future challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 49, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarazzo, T.J.; Santi, P.; Pakzad, S.N.; Carter, K.; Ratti, C.; Moaveni, B.; Osgood, C.; Jacob, N. Crowdsensing Framework for Monitoring Bridge Vibrations Using Moving Smartphones. Proc. IEEE 2018, 106, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, T.; Reuter, C.; Siebigteroth, T.; Pipek, V. CrowdMonitor: Mobile Crowd Sensing for Assessing Physical and Digital Activities of Citizens during Emergencies. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems—CHI ’15, Seoul, Korea, 18–23 April 2015; pp. 4083–4092. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y.; Tang, S.; Xing, K.; Mao, X. Incentives for Mobile Crowd Sensing: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaims, L.G.; Vergara-Laurens, I.J.; Raji, A. A Survey of Incentive Techniques for Mobile Crowd Sensing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2015, 2, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, J.; Shi, E.; Song, D.; Perrig, A. The Sybil Attack in Sensor Networks: Analysis & Defenses. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Berkeley, CA, USA, 26–27 April 2014; pp. 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D. From Participatory Sensing to Mobile Crowd Sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communication Workshops, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–22 March 2013; pp. 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- Piro, C.; Shields, C.; Levine, B.N. Detecting the Sybil Attack in Mobile Ad hoc Networks. In Proceedings of the 2006 Securecomm and Workshops, Baltimore, MD, USA, 28 August 2006; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.T.; Mistry, N.H. A Review: Sybil Attack Detection Techniques in WSN. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electronics and Communication Systems, Coimbatore, India, 19–20 October 2017; pp. 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, M.A.; Nanda, P.; He, X.; Liu, R.P. A Sybil Attack Detection Scheme for a Forest Wildfire Monitoring Application. FGCS 2016, 80, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douceur, J. The Sybil Attack. In Intl Wkshp on Peer-to-Peer Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Margolin, N.B.; Levine, B.N. Quantifying Resistance to the Sybil Attack. In Proceedings of the Financial Cryptography and Data Security; Tsudik, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Singh, J.; Singh, R. A Novel Sybil Attack Detection Technique for Wireless Sensor Networks. Adv. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 185–202. [Google Scholar]
- Vaghefi, R.M.; Gholami, M.R.; Storm, E.G. RSS-based sensor localization with unknown transmit power. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Pargue, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 2480–2483. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE 802.11-2016 Specification. Available online: https://standards.ieee.org/content/ieee-standards/en/standard/802_11-2016.html (accessed on 23 October 2019).
- IEEE 802.15.1-2005 Specification. Available online: https://standards.ieee.org/standard/802_15_1-2005.html (accessed on 23 October 2019).
- CYW43455 Datasheet. Available online: https://www.cypress.com/file/358916/download (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- TShark Documentation. Available online: https://www.wireshark.org/docs/man-pages/tshark.html (accessed on 30 October 2019).






| Observation [8,9,10] | Certification [11] | Trusted Device [6] | Fee-Charging [12] | Trustiness Scoring [13] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Privacy Problem | O | O | X | X | X |
| Account Extortion Tolerant | O | X | X | O | X |
| Central Overhead | High | High | Low | Low | High |
| Additional Infrastructure Required | O | X | O | X | O |
| Detection Delay | Low | Low | Low | High | Low |
| No. | Disconnected | Connected |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | aa:aa:aa | |
| 2 | aa:aa:aa | bb:bb:bb |
| 3 | cc:cc:cc | dd:dd:dd |
| 4 | bb:bb:bb | dd:dd:dd |
| 5 | dd:dd:dd | ee:ee:ee |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, J.; Kim, M. SybilEye: Observer-Assisted Privacy-Preserving Sybil Attack Detection on Mobile Crowdsensing. Information 2020, 11, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040198
Yun J, Kim M. SybilEye: Observer-Assisted Privacy-Preserving Sybil Attack Detection on Mobile Crowdsensing. Information. 2020; 11(4):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040198
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Junhyeok, and Mihui Kim. 2020. "SybilEye: Observer-Assisted Privacy-Preserving Sybil Attack Detection on Mobile Crowdsensing" Information 11, no. 4: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040198
APA StyleYun, J., & Kim, M. (2020). SybilEye: Observer-Assisted Privacy-Preserving Sybil Attack Detection on Mobile Crowdsensing. Information, 11(4), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/info11040198





